Nonparametric Identification Model of Coupled Heave–Pitch Motion for Ships by Using the Measured Responses at Sea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Mathematical Model
3. Identification Method
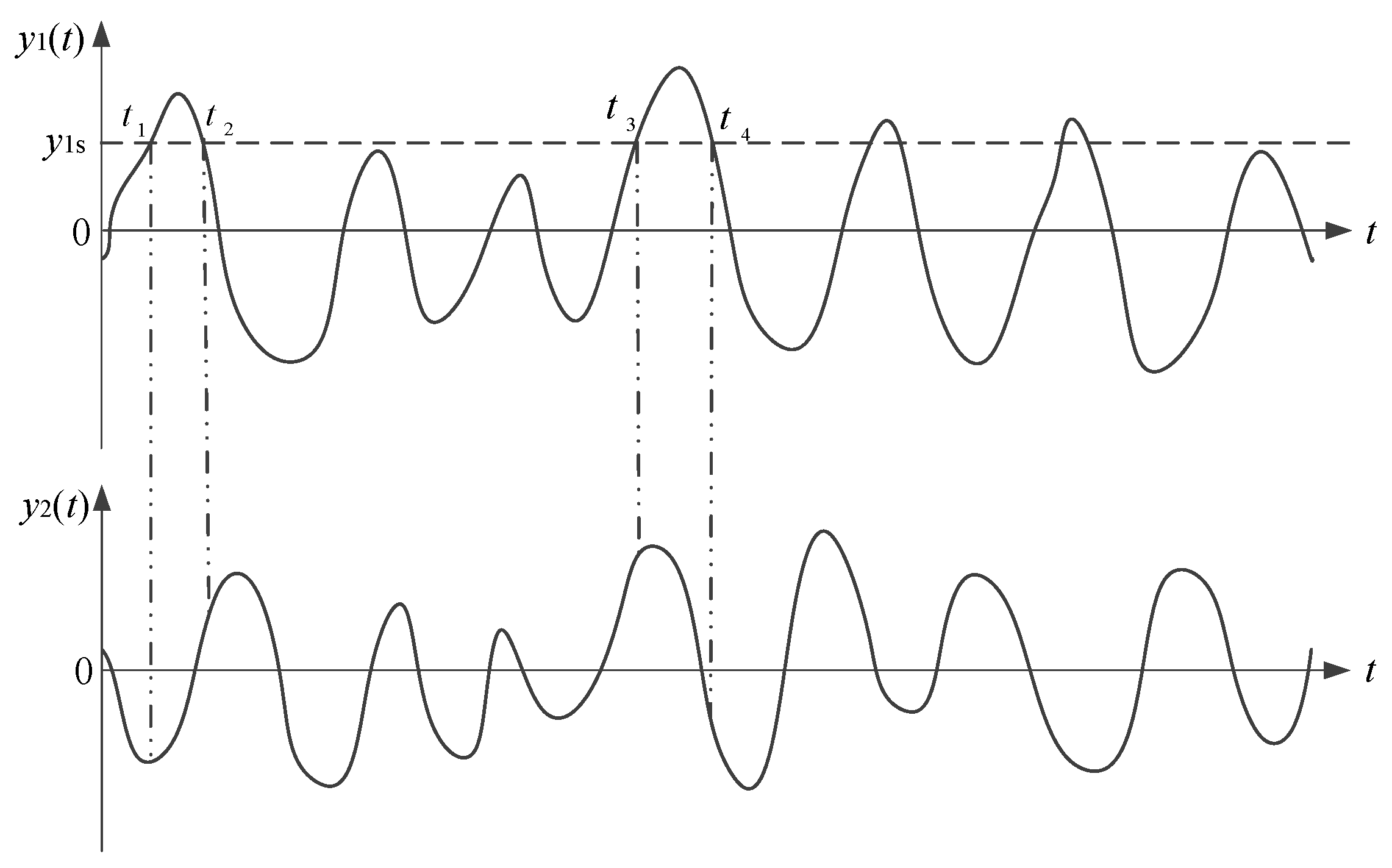
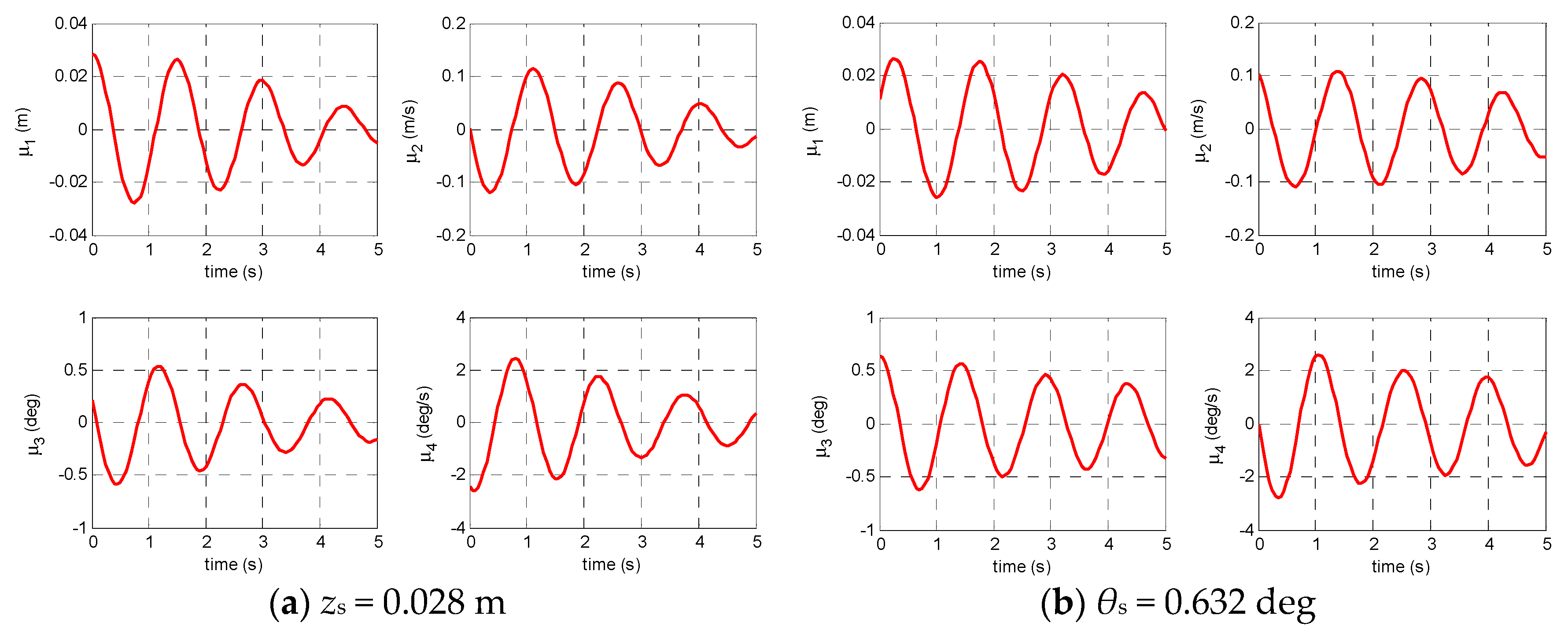
3.1. Random Decrement Technique
3.2. Support Vector Regression
4. Nonparametric Identification
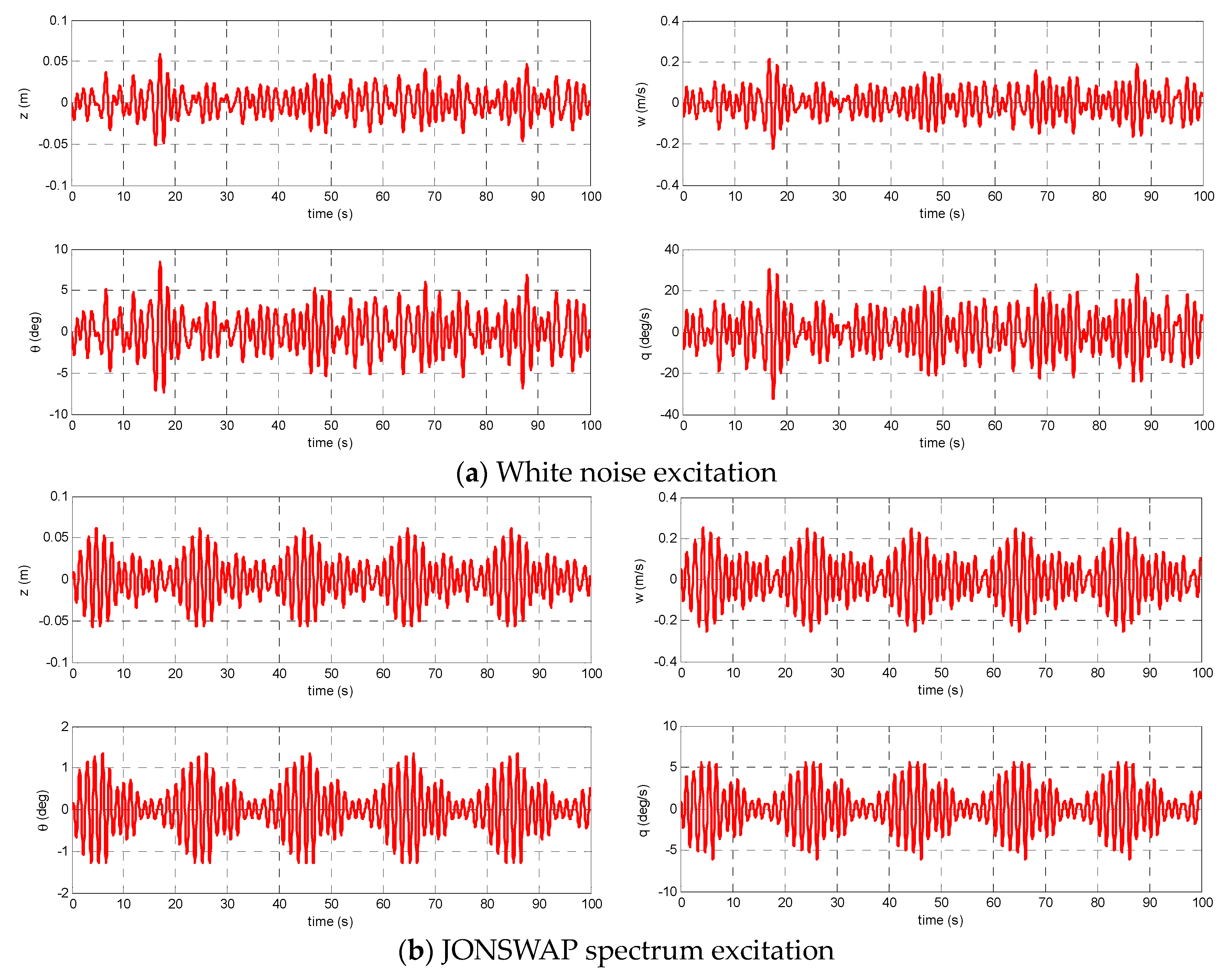
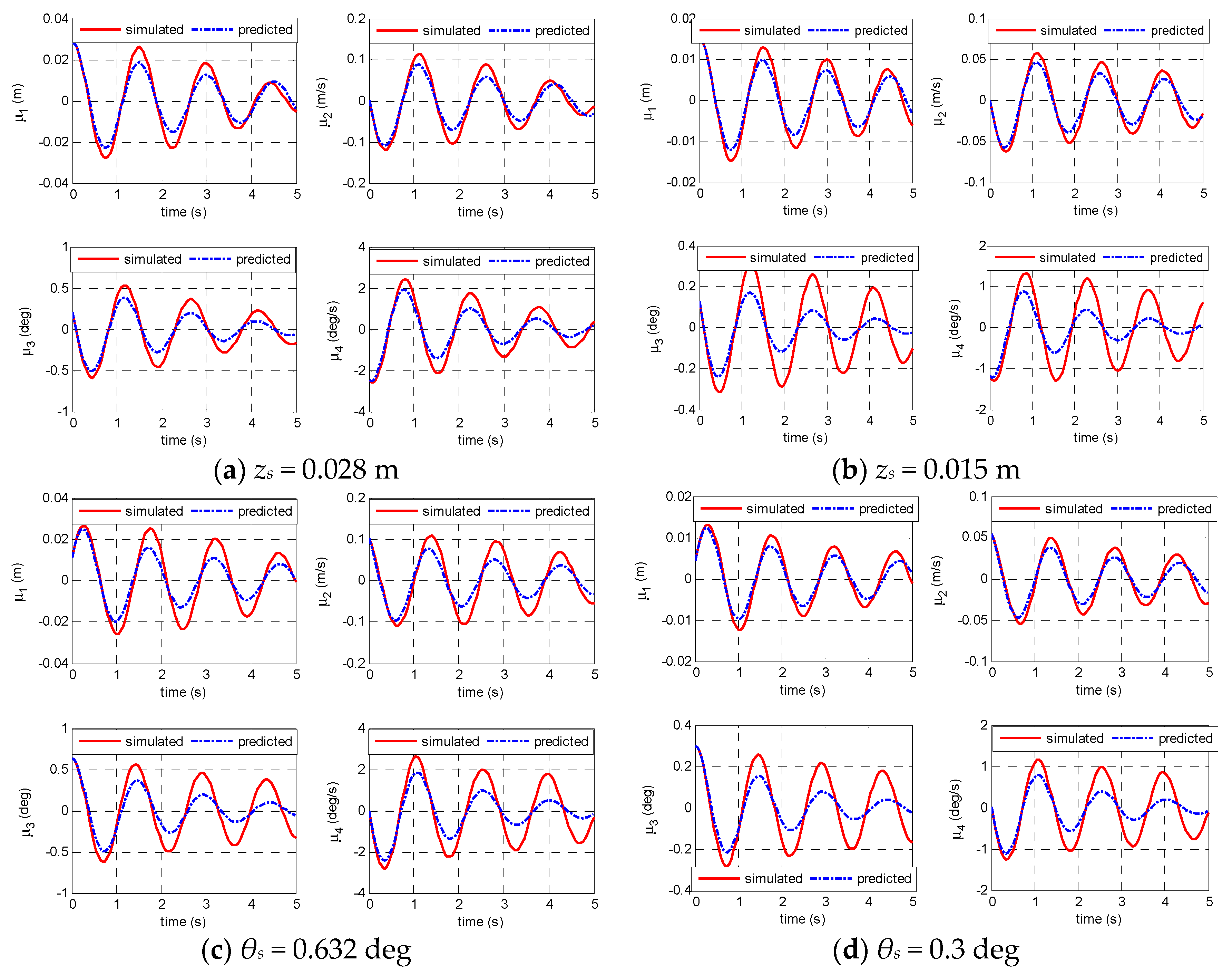
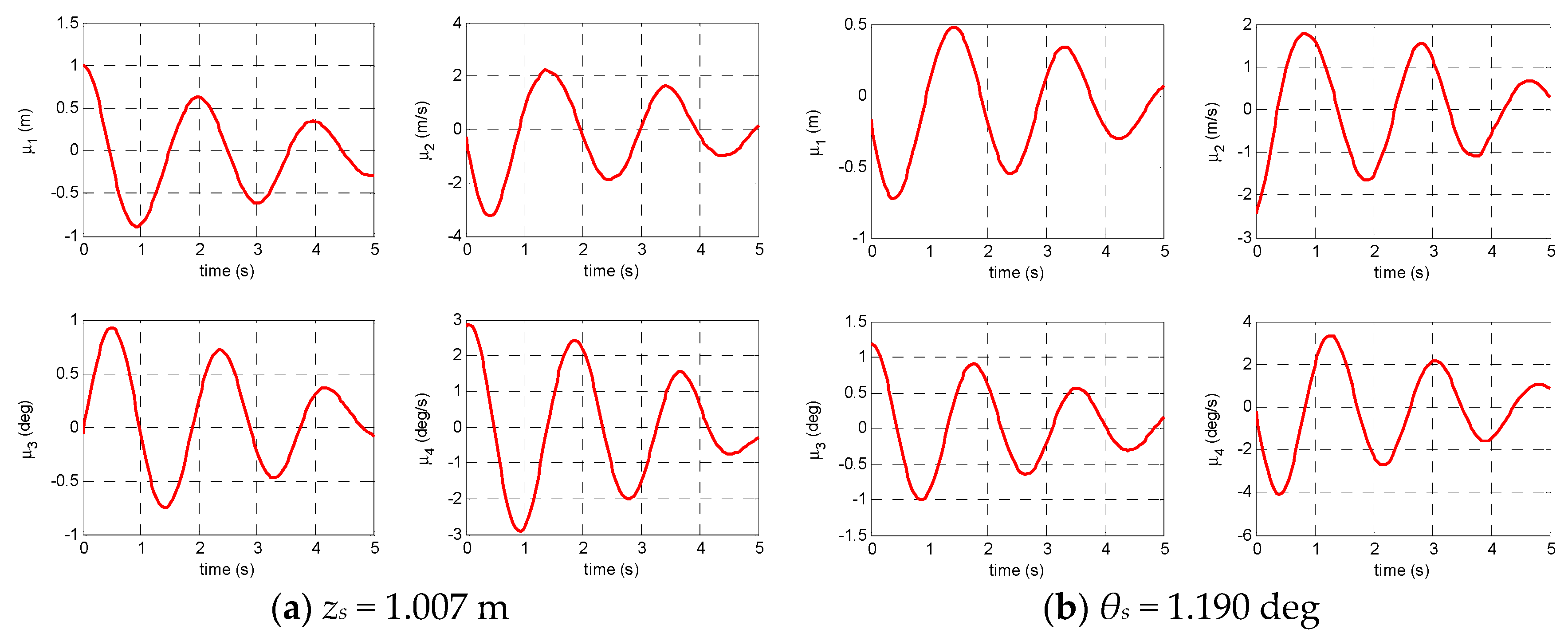
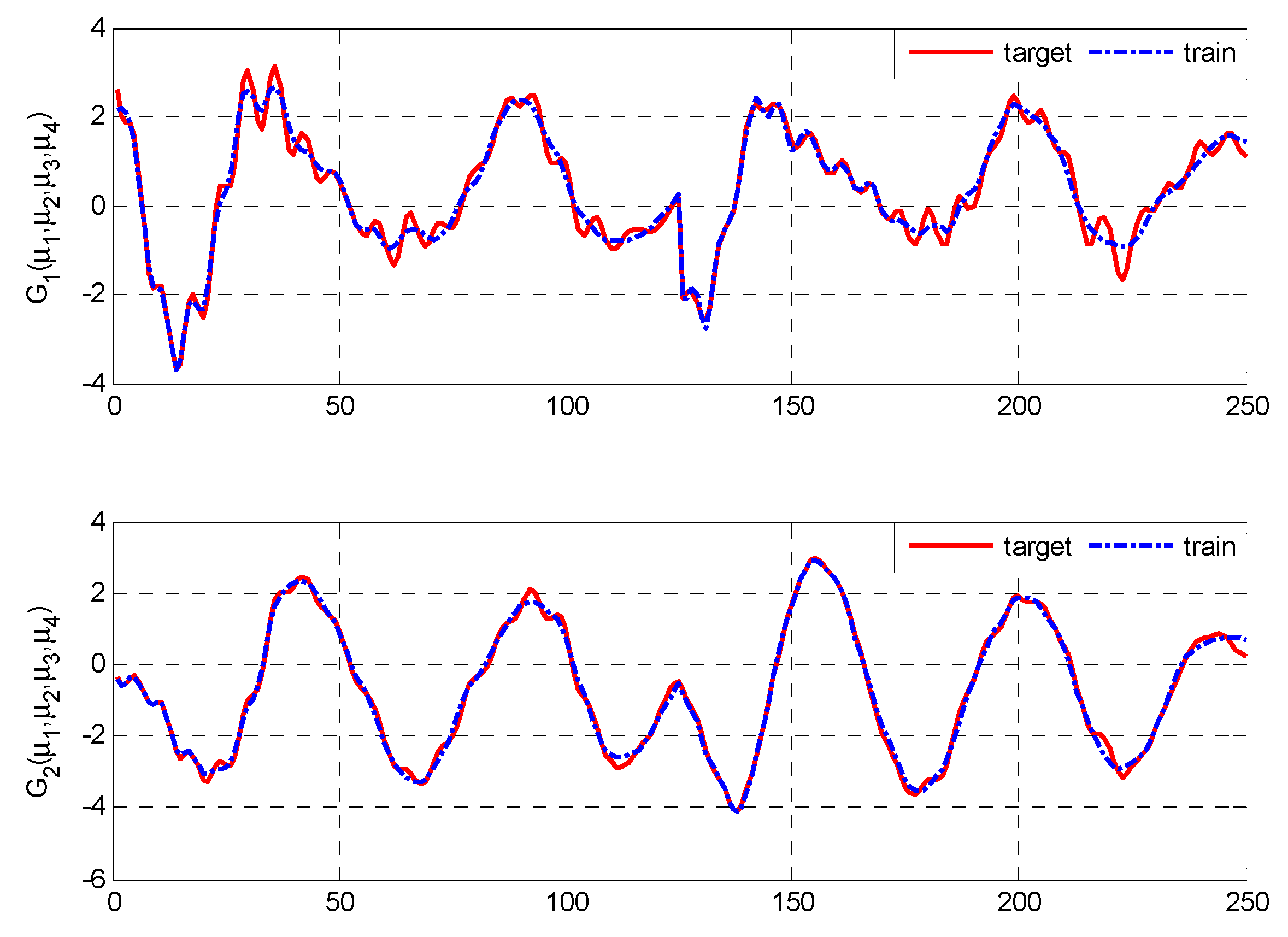
4.1. Identification Example Based on the Simulated Data
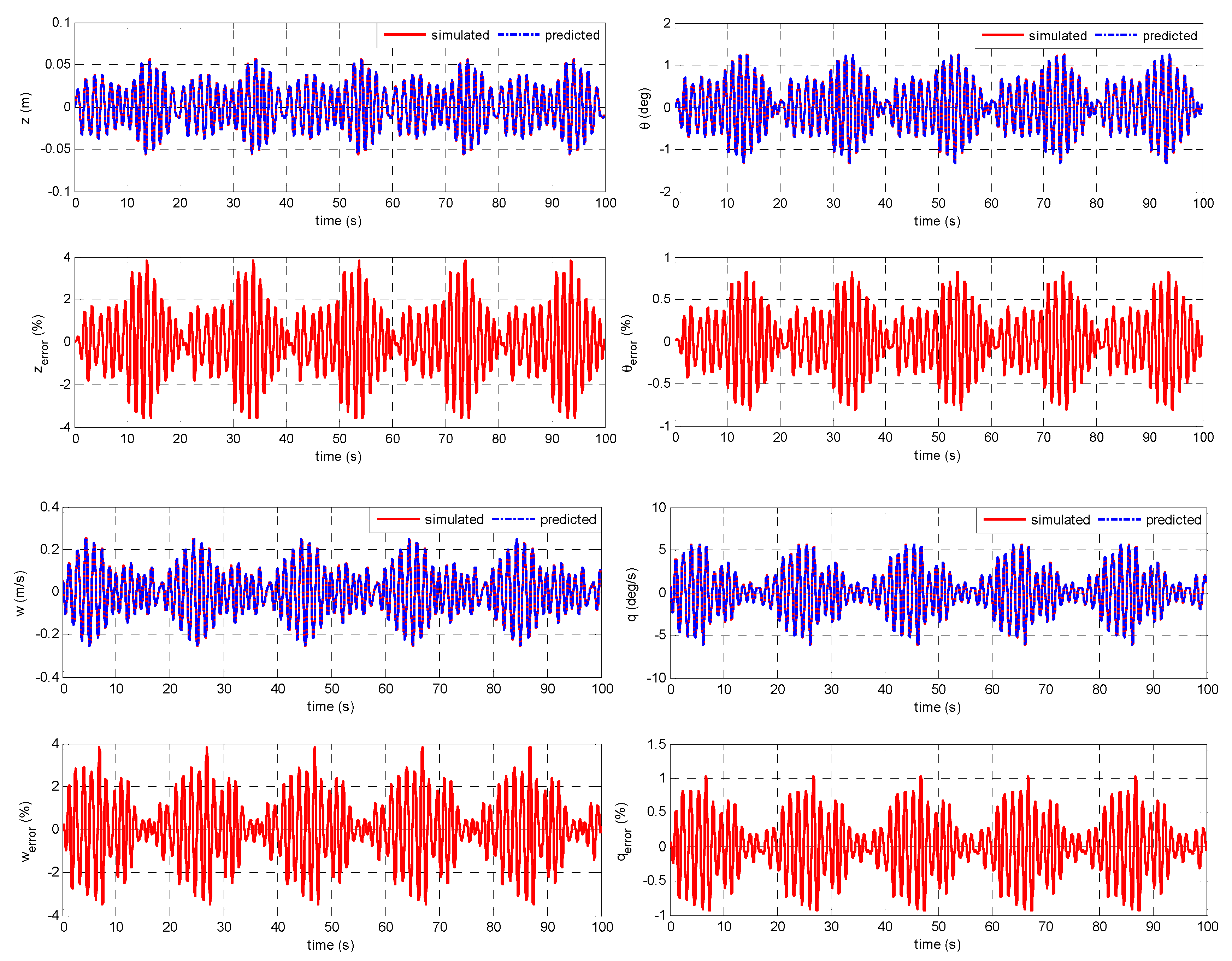
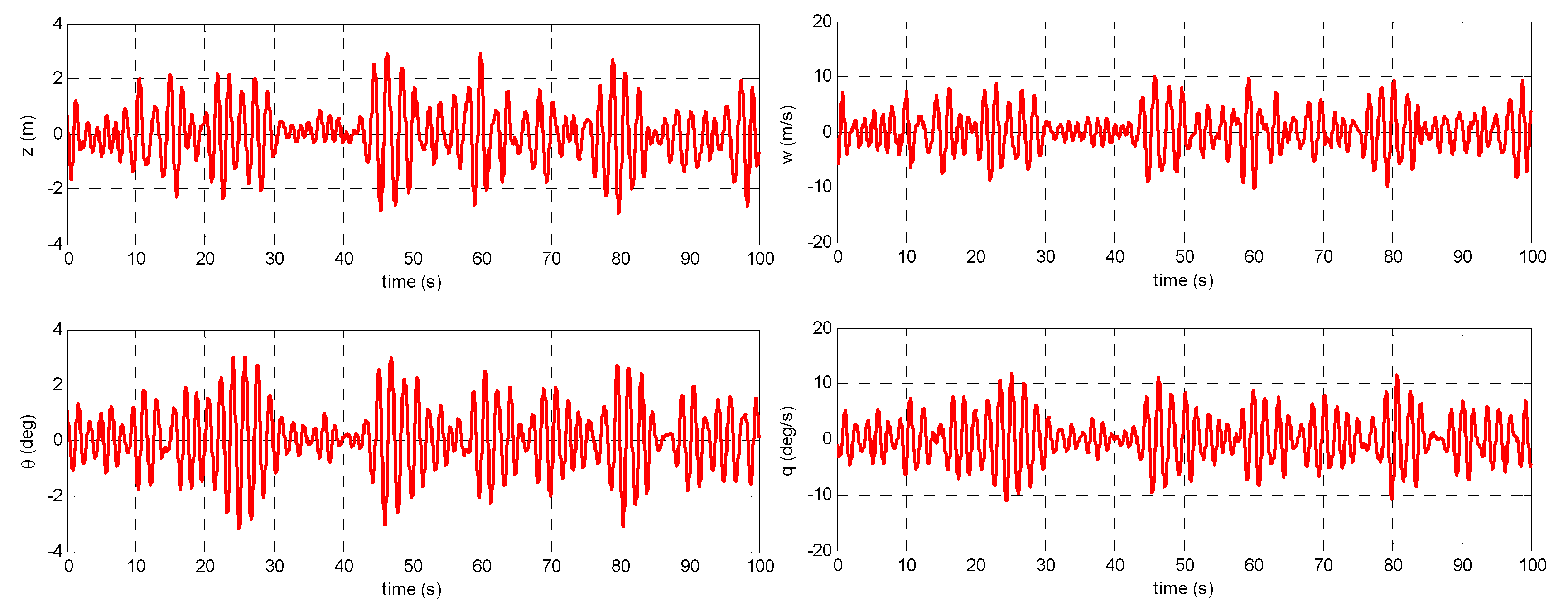
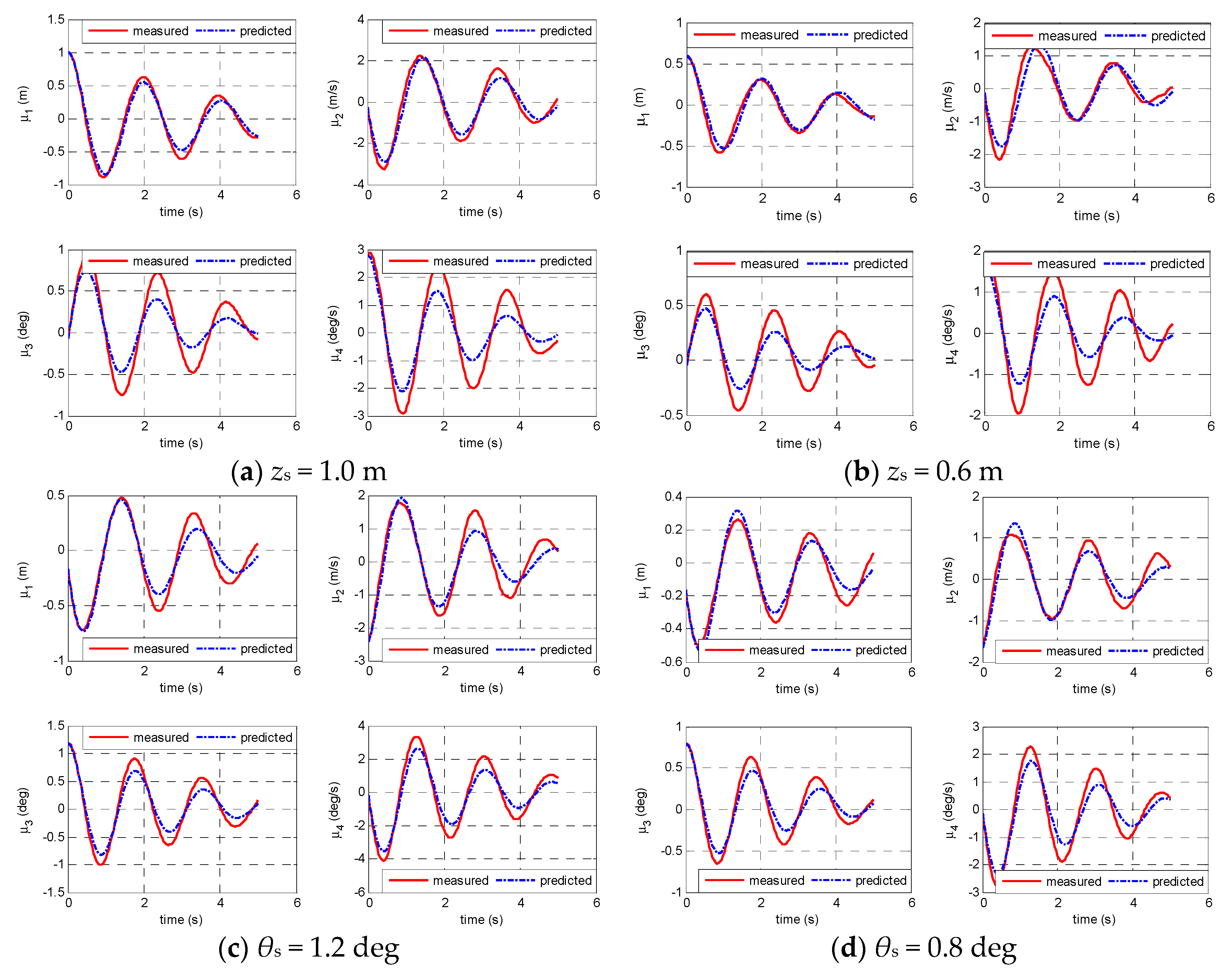
4.2. Validation/Verification Based on the Experimental Data
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Glossary
| Symbol | Description |
| z | heave linear displacement |
| θ | pitch angle |
| M | mass of inertia |
| Iyy | pitch moment of inertia |
| M33 | added mass |
| Jyy | added moment of inertia |
| Dii (i = 3, 5) | damping coefficients |
| Cii (i = 3, 5) | restoring moment coefficients |
| Mij, Dij, Cij (i, j = 3, 5, i ≠ j) | coupled hydrodynamic coefficients |
| F3, M5 | wave exciting force and moment |
| ω3, ω5 | damped frequency |
| E[·] | ensemble average |
| ψ3, ψ5 | variances of the excitation functions |
| δ | Dirac delta function |
| μi, (i = 1, 2, 3, 4) | random decrement signature |
| τ | time length of the random decrement signature |
| zs | selected trigger value of the random decrement signature |
| l | number of training samples |
| mapping function of SVR | |
| weight matrix | |
| bias value | |
| C | penalty factor |
| ξ, ξ* | slack factor vectors |
| 𝜀 | insensitive zone parameter |
| Lagrange multipliers | |
| K | kernel function matrix |
| h | time step size |
| σ | width parameter |
References
- Vakilabadi, K.A.; Khedmati, M.R.; Seif, M.S. Experimental study on heave and pitch motion characteristics of a wave-piercing trimaran. Trans. FAMENA 2014, 38, 13–26. [Google Scholar]
- Mahesh, J.R.; Nallayarasu, S.; Bhattacharyya, S.K. Assessment of nonlinear heave damping model for Spar with heave plate using free decay tests. In Proceedings of the ASME 2016, 35th International Conference on Ocean, Offshore and Arctic Engineering, Busan, Republic of Korea, 19–24 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqui, M.A.; Grecoab, M.; Lugni, C.; Faltinsen, O.M. Experimental studies of a damaged ship section in forced heave motion. Appl. Ocean Res. 2019, 88, 254–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coslovich, F.; Kjellberg, M.; Östberg, M.; Janson, C.E. Added resistance, heave and pitch for the KVLCC2 tanker using a fully nonlinear unsteady potential flow boundary element method. Ocean Eng. 2021, 229, 108935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonsen, C.D.; Otzen, J.F.; Joncquez, S.; Stern, F. EFD and CFD for KCS heaving and pitching in regular head waves. J. Mar. Sci. Technol. 2013, 18, 435–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.S.; Park, D.M.; Kim, Y. Study on nonlinear heave and pitch motions of conventional and tumblehome hulls in head seas. Ocean Eng. 2022, 247, 110671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathyaseelan, D.; Hariharan, G.; Kannan, K. Parameter identification for nonlinear damping coefficient from large-amplitude ship roll motion using wavelets. Beni Suef Univ. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2017, 6, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Cheng, R.; Yao, X.; Liu, L. Hydrodynamic coefficients identification of pitch and heave using multi-objective evolutionary algorithm. Ocean Eng. 2019, 171, 33–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.F.; Liu, Y.J.; Ji, C.; Xue, G. Hydrodynamic parameter identification for ship manoeuvring mathematical models using a Bayesian approach. Ocean Eng. 2020, 195, 106612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.S.; Wang, L.J.; Im, N.; Zhang, W.D.; Li, X.J. Real-time parameter identification of ship maneuvering response model based on nonlinear Gaussian Filter. Ocean Eng. 2022, 247, 110471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.H.; Wu, J.B.; Zeng, C.H.; Huang, Y.X. Identification of hydrodynamic coefficients of a ship manoeuvring model based on PRBS input. Ocean Eng. 2022, 246, 110640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Hou, X.R.; Wang, X.G.; Wang, Z.H.; Yang, Z.L.; Zou, Z.J. Identification modeling and prediction of ship maneuvering motion based on LSTM deep neural network. J. Mar. Sci. Technol. 2022, 27, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, L.Z.; Han, Y.; Shi, C.; Pan, Z.Y. Recurrent neural networks for nonparametric modeling of ship maneuvering motion. Int. J. Nav. Archit. Ocean Eng. 2022, 14, 100436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.F.; Chen, G.; Li, Z.T.; Xue, G.; Wang, W.; Liu, Y.J. Online identification of a ship maneuvering model using a fast noisy input Gaussian process. Ocean Eng. 2022, 250, 110704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.R.; Zou, Z.J. SVR-based identification of nonlinear roll motion equation for FPSOs in regular waves. Ocean Eng. 2015, 109, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.R.; Zou, Z.J. Parameter identification of nonlinear roll motion equation for floating structures in irregular waves. Appl. Ocean Res. 2016, 55, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.R.; Zou, Z.J.; Xu, F. SVR-based parameter identification of coupled heave-pitch motion equations in regular waves. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Sixth International Ocean and Polar Engineering Conference, Rhodes, Greece, 26 June–2 July 2016; pp. 580–585. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.H.; Zou, Z.J.; Guedes Soares, C. Identification of ship manoeuvring motion based on nu-support vector machine. Ocean Eng. 2019, 183, 270–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Zhang, X.F.; Zhu, J.X. Parameter identification of ship motion mathematical model based on full-scale trial data. Int. J. Nav. Archit. Ocean Eng. 2022, 14, 100437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.R.; Zou, Z.J.; Liu, C. Nonparametric identification of nonlinear ship roll motion by using the motion response in irregular waves. Appl. Ocean Res. 2018, 73, 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.T.; Guedes Soares, C. Manoeuvring modelling of a containership in shallow water based on optimal truncated nonlinear kernel-based least square support vector machine and quantum-inspired evolutionary algorithm. Ocean Eng. 2020, 195, 106676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshafey, A.A.; Haddara, M.R.; Marzouk, H. Identification of the excitation and reaction forces on offshore platforms using the random decrement technique. Ocean Eng. 2009, 36, 521–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Park, S.G. Wet damping estimation of the scaled segmented hull model using the random decrement technique. Ocean Eng. 2014, 75, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, N.; Guo, J.; Nishi, T. Global convergence of SMO algorithm for support vector regression. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 2008, 19, 971–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.S. Identification of Ship Coupled Heave and Pitch Motions Using Neural Networks. Master’s Thesis, Memorial University of Newfoundland, Norris Point, NL, Canada, 1997. [Google Scholar]
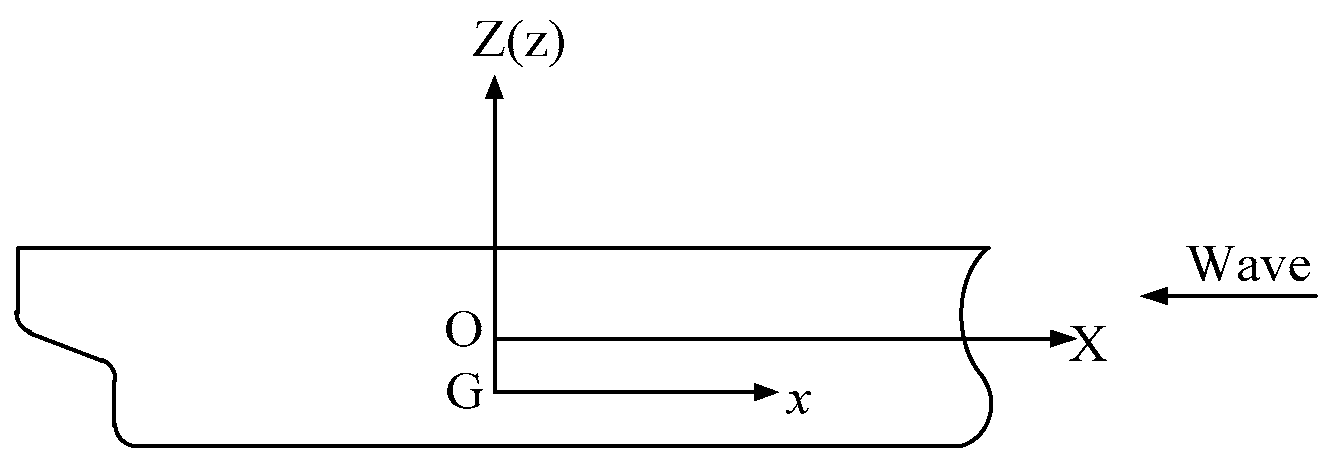





| Item | Symbol | Unit | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Length between perpendiculars | Lpp | m | 2.1985 |
| Length of waterline | Lwl | m | 2.3250 |
| Breadth | B | m | 0.4840 |
| Mean draft | T | m | 0.1735 |
| Displacement volume | m3 | 0.1190 | |
| Wetted surface area | S | m2 | 1.1335 |
| Transverse metacentric radius | Rx | m | 0.122 |
| Longitudinal metacentric radius | Ry | m | 2.4 |
| White Noise Excitation | JONSWAP Spectrum Excitation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency | Known | Identified | Error (%) | Identified | Error (%) |
| ω3 | 4.488 | 4.483 | 0.111 | 4.171 | 7.063 |
| ω5 | 4.597 | 4.533 | 1.392 | 4.379 | 4.742 |
| Item | Symbol | Unit | FPSO | Model |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Length over all | Loa | m | 309.31 | 3.82 |
| Length between perpendiculars | Lpp | m | 300.80 | 3.71 |
| Breadth | B | m | 54.5 | 0.67 |
| Depth | D | m | 25.98 | 0.32 |
| Mean draft | T | m | 12.5 | 0.15 |
| Block coefficient | Cb | - | 0.97 | 0.97 |
| Radius of roll gyration | kx | m | 18.4 | 0.23 |
| Radius of pitch gyration | ky | m | 75 | 0.93 |
| Bilge keel | Lk × Bk | m | 230.4 × 0.64 | 2.85 × 0.01 |
| Frequency | ω3 | ω5 |
|---|---|---|
| Value | 3.037 | 3.649 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hou, X.; Zhou, X. Nonparametric Identification Model of Coupled Heave–Pitch Motion for Ships by Using the Measured Responses at Sea. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 676. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11030676
Hou X, Zhou X. Nonparametric Identification Model of Coupled Heave–Pitch Motion for Ships by Using the Measured Responses at Sea. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2023; 11(3):676. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11030676
Chicago/Turabian StyleHou, Xianrui, and Xingyu Zhou. 2023. "Nonparametric Identification Model of Coupled Heave–Pitch Motion for Ships by Using the Measured Responses at Sea" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 11, no. 3: 676. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11030676
APA StyleHou, X., & Zhou, X. (2023). Nonparametric Identification Model of Coupled Heave–Pitch Motion for Ships by Using the Measured Responses at Sea. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 11(3), 676. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11030676





