Influence of Algal Organic Matter on Algal Removal Efficiency by Flocculation of Modified Clay
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cultivation of Algal Cells
2.2. Extraction of dAOM
2.3. Preparation of MC and Algal Bloom Biological Removal Experiment
2.4. Characterization Methods of Floc Characteristic Parameters
2.5. Methods of Characteristic Analysis of Algal Organic Matter
2.5.1. Determination of DOC and SUVA254
2.5.2. Determination of Molecular Weight
2.6. Determination of Zeta Potential
2.7. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effect of dAOM on the MC Flocculation Process
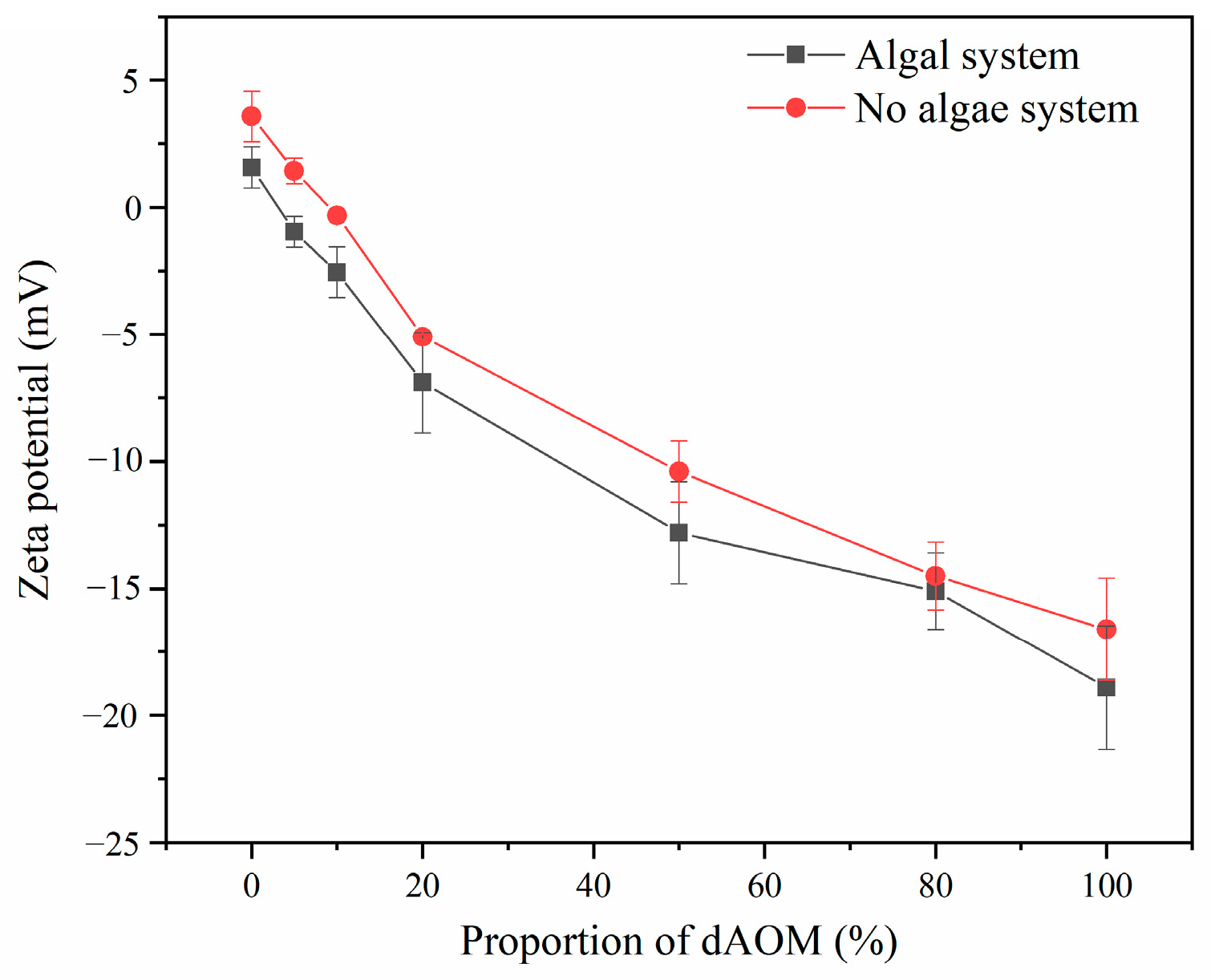
3.1.1. Zeta Potential
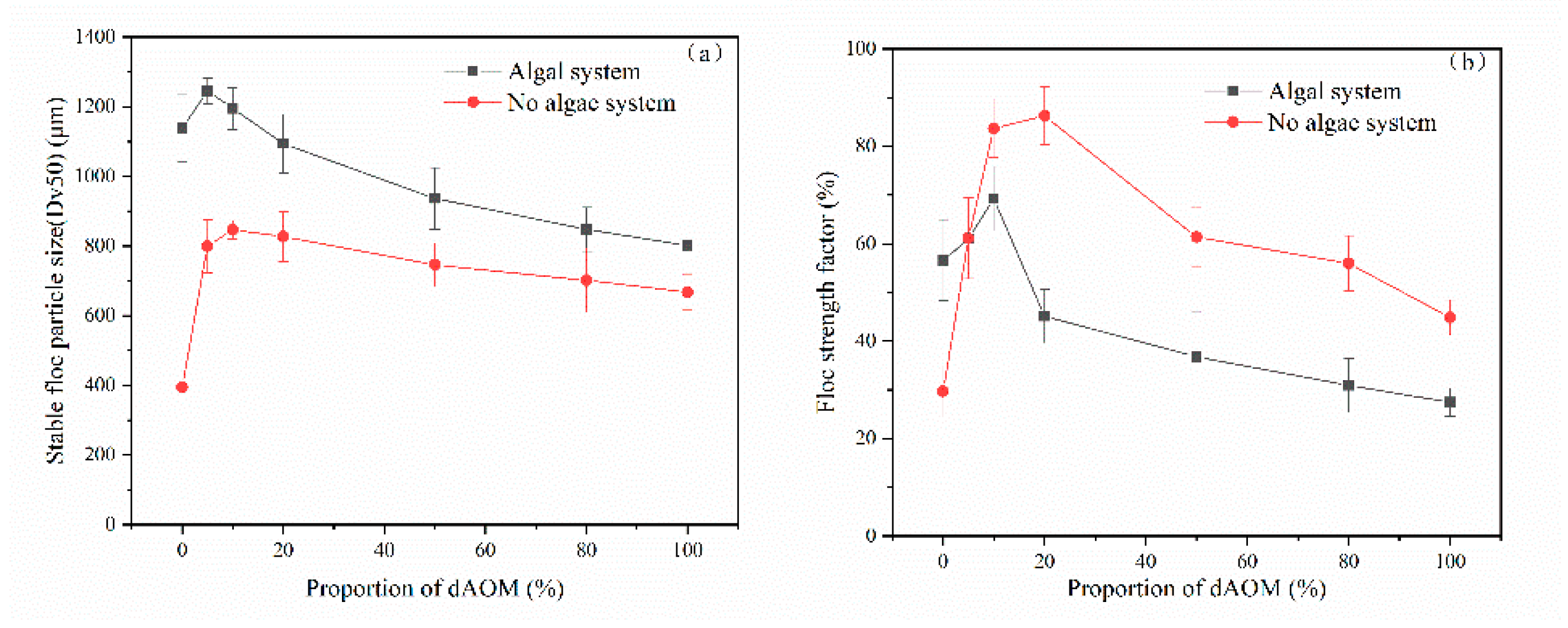
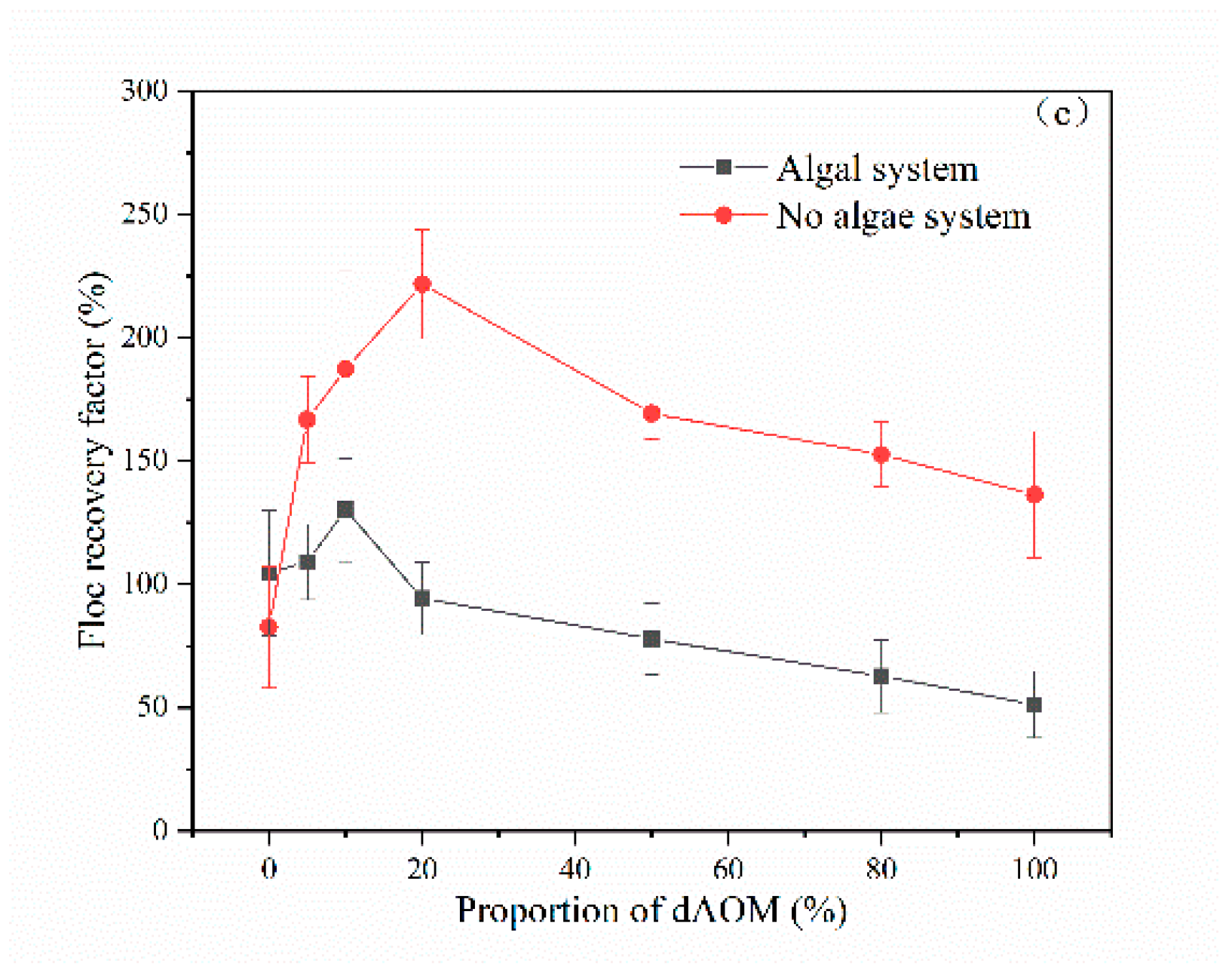
3.1.2. Flocs
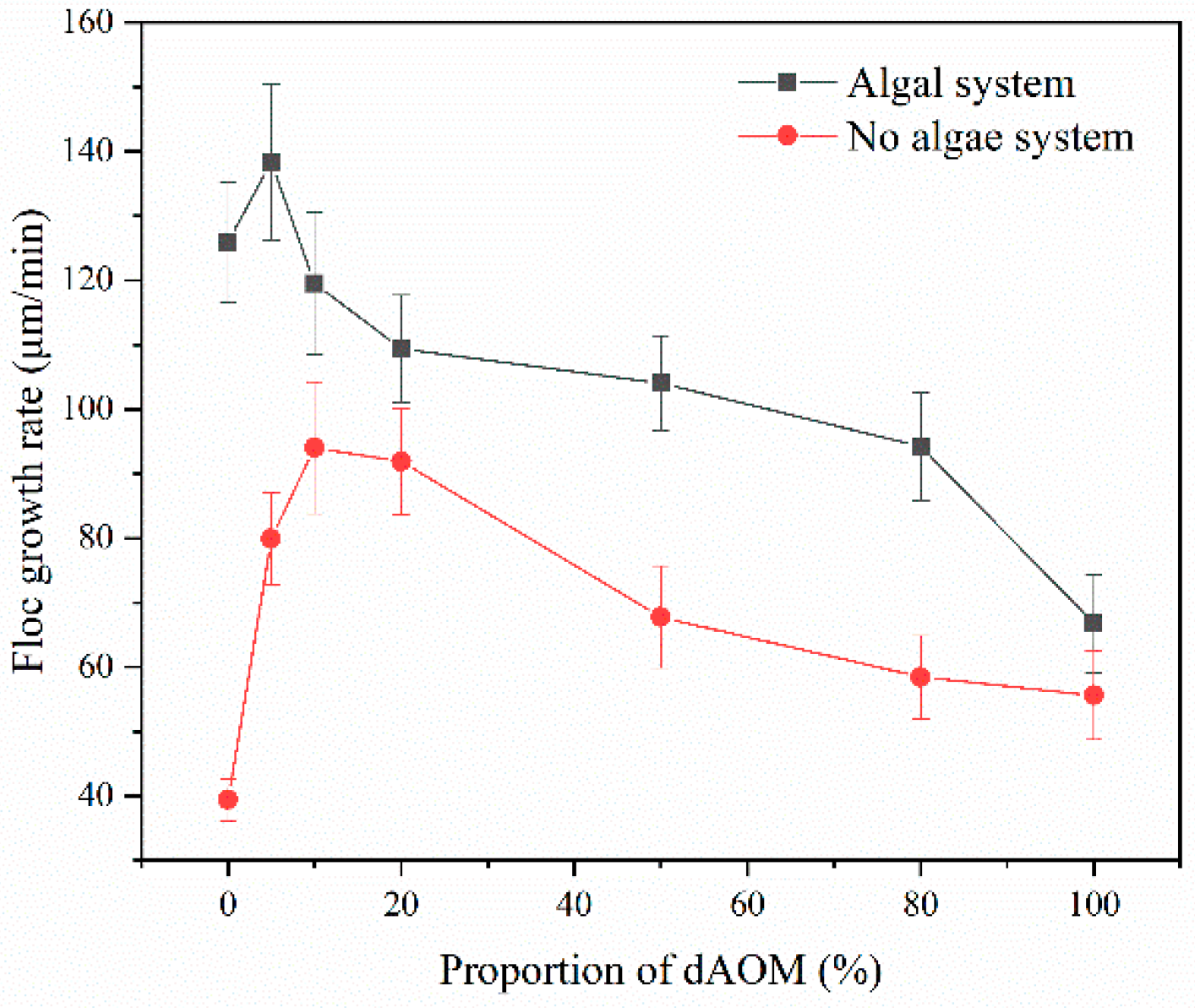
3.1.3. Flocculation Kinetics
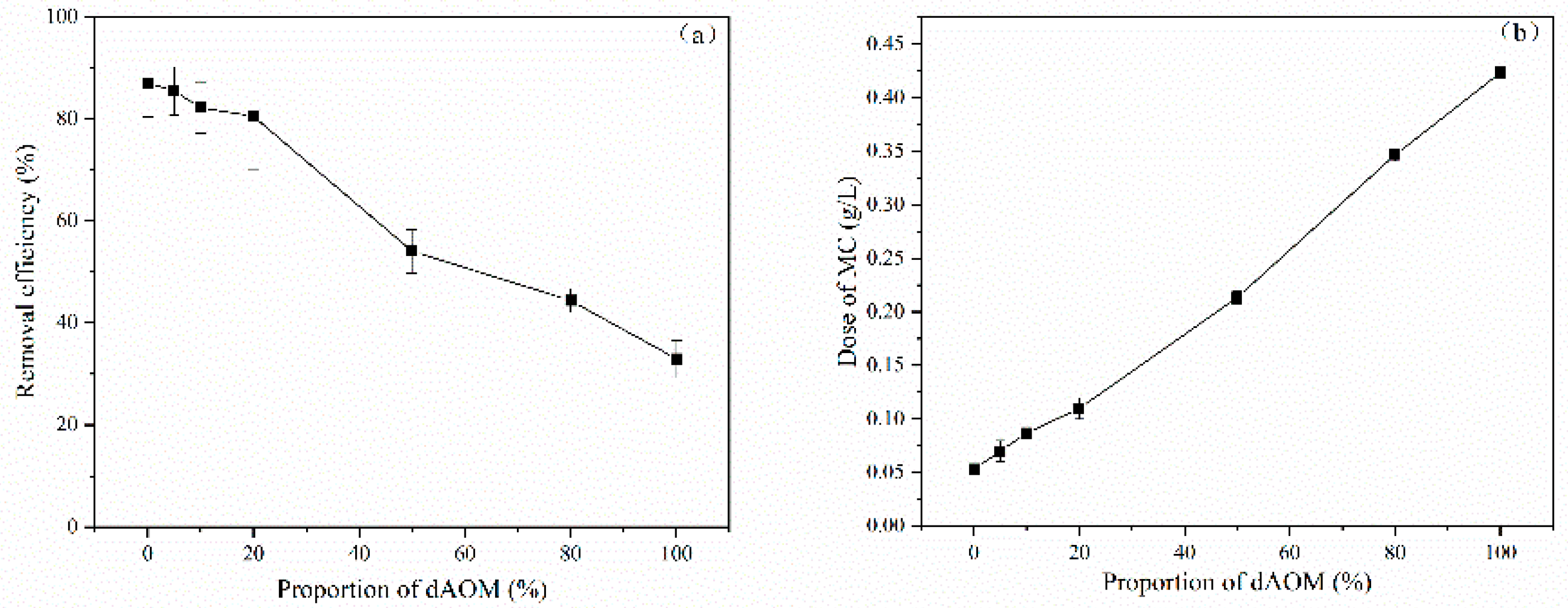
3.2. Effect of dAOM on the Algal Removal Efficiency of MC
3.3. Mechanism of dAOM Affecting Flocculation and Algal Removal Efficiency of MC
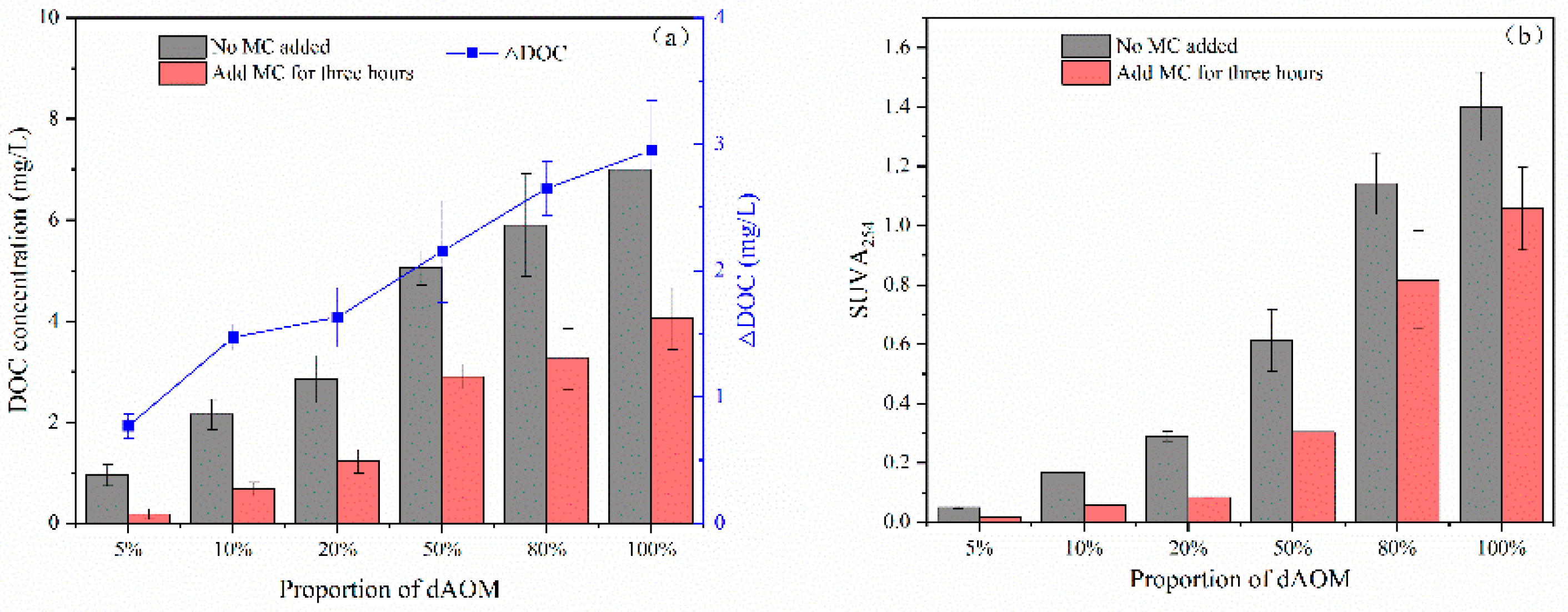
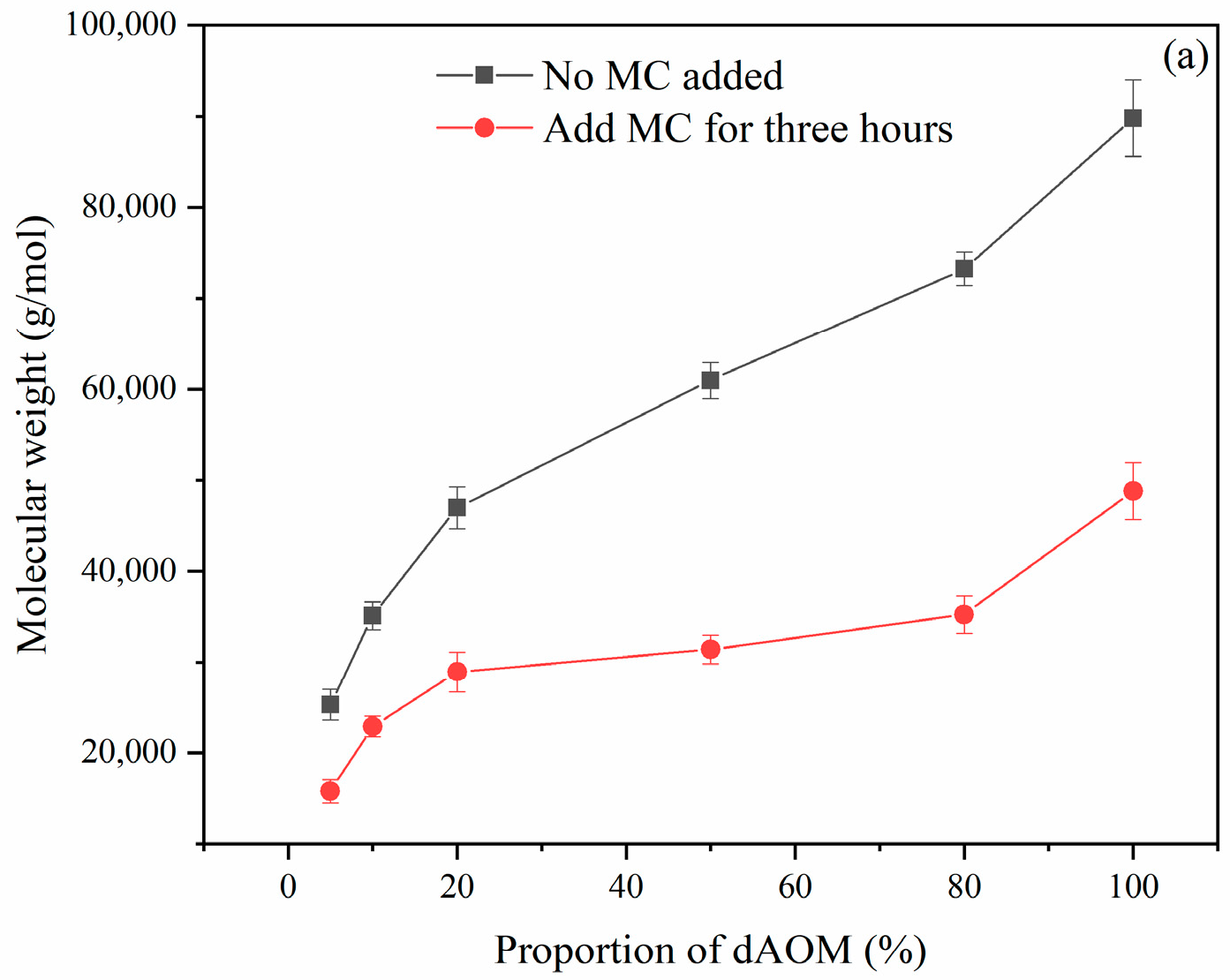
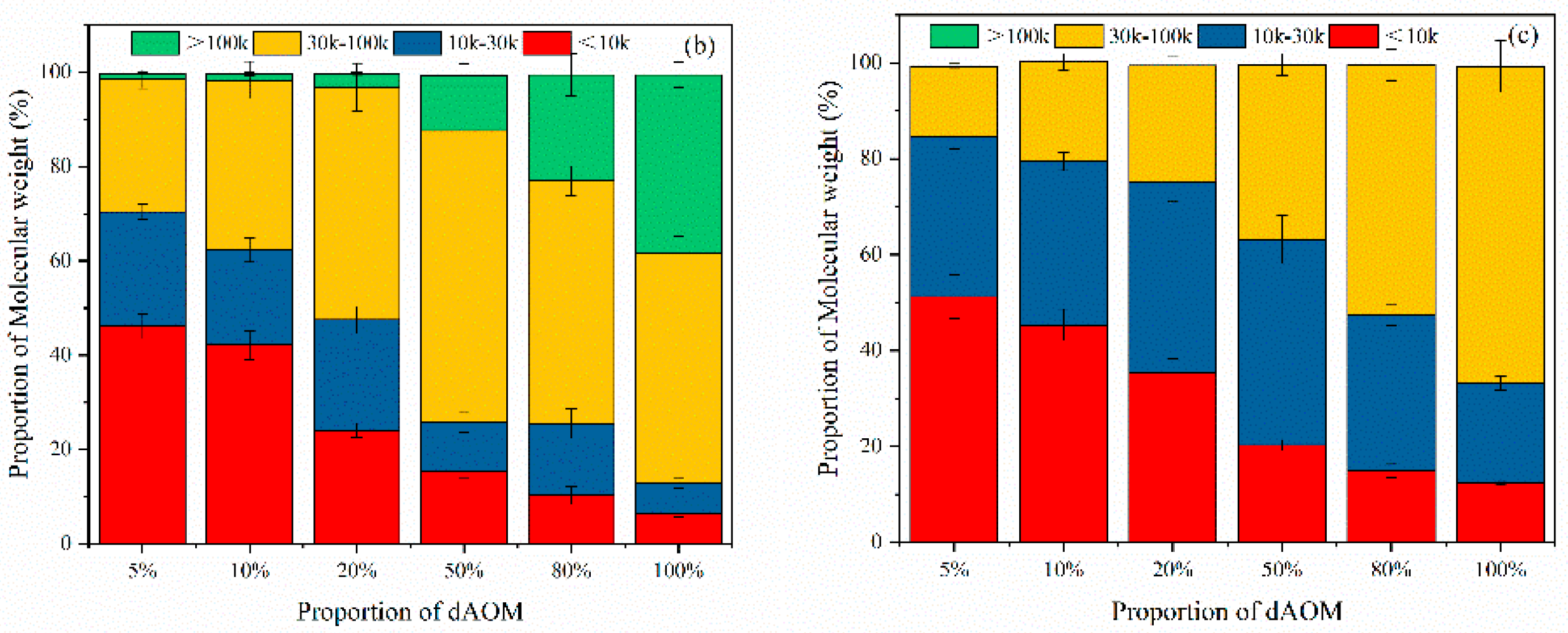
3.3.1. Changes in dAOM Properties
3.3.2. Mechanism of Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yu, Z.; Chen, N. Emerging trends in red tide and major research progresses. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. 2019, 50, 474–486. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, D.M.; Cembella, A.D.; Hallegraeff, G.M. Progress in Understanding Harmful Algal Blooms: Paradigm Shifts and New Technologies for Research, Monitoring, and Management. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2012, 4, 143–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grattan, L.M.; Trainer, V.L. Special Issue: Harmful Algal Blooms and Public Health Preface. Harmful Algal 2016, 57, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, D.M. Turning back the harmful red tide—Commentary. Nature 1997, 388, 513–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.M. Approaches to monitoring, control and management of harmful algal blooms (HABs). Ocean Coast. Manag. 2009, 52, 342–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Zou, J.; Ma, X. A new method to improve the capability of clays for removing red tide organisms. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. 1994, 25, 226–232. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Cao, X.H.; Yu, Z.M.; Song, X.X.; Qiu, L.X. Controlling harmful algae blooms using aluminum-modified clay. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 103, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.M.; Song, X.X.; Cao, X.H.; Liu, Y. Mitigation of harmful algal blooms using modified clays: Theory, mechanisms, and applications. Harmful Algae 2017, 69, 48–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brezinski, K.; Gorczyca, B. An overview of the uses of high performance size exclusion chromatography (HPSEC) in the characterization of natural organic matter (NOM) in potable water, and ion-exchange applications. Chemosphere 2019, 217, 122–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golea, D.M.; Jarvis, P.; Jefferson, B.; Moore, G.; Sutherland, S.; Parsons, S.A.; Judd, S.J. Influence of granular activated carbon media properties on natural organic matter and disinfection by-product precursor removal from drinking water. Water Res. 2020, 174, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alldredge, A.L.; Silver, M.W. Characteristics, dynamics and significance of marine snow. Prog. Oceanogr. 1988, 20, 41–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.B.; Yu, Z.M.; Cao, X.H.; Jiang, K.Q.; Yuan, Y.Q.; Anderson, D.M.; Song, X.X. Effects of soluble organics on the settling rate of modified clay and development of improved clay formulations for harmful algal bloom control. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 289, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, H.N.; Yu, Z.M.; He, L.Y.; Zhu, J.N.; Cao, X.H.; Song, X.X. Programmed cell death induced by modified clay in controlling Prorocentrum donghaiense bloom. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 109, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.X.; Liu, B.M.; Lu, M.F.; Li, Y.P.; Jiang, Y.Y.; Zhao, M.X.; Huang, Z.X.; Pan, Y.; Miao, H.F.; Ruan, W.Q. Characterization of algal organic matter as precursors for carbonaceous and nitrogenous disinfection byproducts formation: Comparison with natural organic matter. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 282, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pivokonsky, M.; Naceradska, J.; Kopecka, I.; Baresova, M.; Jefferson, B.; Li, X.; Henderson, R.K. The impact of algogenic organic matter on water treatment plant operation and water quality: A review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 46, 291–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pivokonsky, M.; Safarikova, J.; Bubakova, P.; Pivokonska, L. Coagulation of peptides and proteins produced by Microcystis aeruginosa: Interaction mechanisms and the effect of Fe-peptide/protein complexes formation. Water Res. 2012, 46, 5583–5590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhardt, H.; Hoyer, O.; Schell, H.; Lüsse, B. Reaction mechanisms involved in the influence of algogenic organic matter on flocculation. Z. Wasser. Abwasser. Forsch 1985, 18, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhardt, H.; Hoyer, O.; Lusse, B.; Schell, H. Influence of Algogenic Organic-Substances on Flocculation and Filtration. Acta Hydrochim. Hydrobiol. 1989, 17, 235–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pivokonsky, M.; Safarikova, J.; Baresova, M.; Pivokonska, L.; Kopecka, I. A comparison of the character of algal extracellular versus cellular organic matter produced by cyanobacterium, diatom and green alga. Water Res. 2014, 51, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvis, P.; Jefferson, B.; Parsons, S.A. Breakage, regrowth, and fractal mature of natural organic matter flocs. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 2307–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weishaar, J.L.; Aiken, G.R.; Bergamaschi, B.A.; Fram, M.S.; Fujii, R.; Mopper, K. Evaluation of specific ultraviolet absorbance as an indicator of the chemical composition and reactivity of dissolved organic carbon. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 4702–4708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, W.Q.; Tan, W.Q.; Wang, L.J.; Pan, G. Removal of Microcystis aeruginosa using cationic starch modified soils. Water Res. 2016, 97, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yukselen, M.A.; Gregory, J. The reversibility of floc breakage. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2004, 73, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pivokonsky, M.; Kloucek, O.; Pivokonska, L. Evaluation of the production, composition and aluminum and iron complexation of algogenic organic matter. Water Res. 2006, 40, 3045–3052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, R.K.; Parsons, S.A.; Jefferson, B. The impact of differing cell and algogenic organic matter (AOM) characteristics on the coagulation and flotation of algae. Water Res. 2010, 44, 3617–3624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, J. The role of colloid interactions in solid-liquid separation. Water Sci. Technol. 1993, 27, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, X.W.; Gao, B.Y.; Peng, N.N.; Wang, Y.; Yue, Q.Y.; Zhao, Y.C. Coagulation performance and floc properties of compound bioflocculant-aluminum sulfate dual-coagulant in treating kaolin-humic acid solution. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 173, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chekli, L.; Eripret, C.; Park, S.H.; Tabatabai, S.A.A.; Vronska, O.; Tamburic, B.; Kim, J.H.; Shon, H.K. Coagulation performance and floc characteristics of polytitanium tetrachloride (PTC) compared with titanium tetrachloride (TiCl4) and ferric chloride (FeCl3) in algal turbid water. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 175, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Wang, F.Y.; Jiang, H.L.; Huang, Q.Y.; Xu, C.H.; Yu, P.; Cong, H.B. Analysis on the flocculation characteristics of algal organic matters. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 302, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chekli, L.; Phuntsho, S.; Roy, M.; Shon, H.K. Characterisation of Fe-oxide nanoparticles coated with humic acid and Suwannee River natural organic matter. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 461, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloux, J.; Chekli, L.; Phuntsho, S.; Tijing, L.D.; Jeong, S.; Zhao, Y.X.; Gao, B.Y.; Park, S.H.; Shon, H.K. Coagulation performance and floc characteristics of polytitanium tetrachloride and titanium tetrachloride compared with ferric chloride for coal mining wastewater treatment. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 152, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.X.; Lian, H.Q.; Tian, C.; Li, H.B.; Xu, W.Y.; Phuntsho, S.; Shih, K.M. Surface water treatment benefits from the presence of algae: Influence of algae on the coagulation behavior of polytitanium chloride. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2021, 15, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pivokonska, L.; Pivokonsky, M.; Tomaskova, H. Optimization of NOM removal during water treatment. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2008, 43, 1687–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pivokonsky, M.; Pivokonska, L.; Baumeltova, J.; Bubakova, P. The effect of cellular organic matter produced by cyanobacteria Microcystis aeruginosa on water purification. J. Hydrol. Hydromech. 2009, 57, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, R.K.; Baker, A.; Parsons, S.A.; Jefferson, B. Characterisation of algogenic organic matter extracted from cyanobacteria, green algae and diatoms. Water Res. 2008, 42, 3435–3445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Q.; Yu, Z.M.; Song, X.X.; Cao, X.H.; Jiang, W.B.; Chu, Y.Y. The synthesis of an acrylamide copolymer and its synergistic effects on clay flocculation of red tide organisms. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 332, 117326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yu, Z.M.; Cao, X.H.; Song, X.X. Chitosan modification and its synergism with clay to mitigate harmful algal blooms. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2023, 29, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Floc Characteristic Parameter | Pearson’s Correlation Coefficient (r) | Significance Level (p) | Number of Samples (n) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Floc size | −0.977 | p < 0.01 | 6 |
| Floc strength factor | −0.877 | p < 0.05 | 6 |
| Floc recovery factor | −0.870 | p < 0.05 | 6 |
| Floc growth rate | −0.961 | p < 0.01 | 6 |
| Floc Characteristic Parameter | Pearson’s Correlation Coefficient (r) | Significance Level (p) | Number of Samples (n) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Floc size | 0.967 | p < 0.01 | 6 |
| Floc strength factor | 0.896 | p < 0.05 | 6 |
| Floc recovery factor | 0.926 | p < 0.01 | 6 |
| Floc growth rate | 0.916 | p < 0.05 | 6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, M.; Zhang, B.; Cao, X.; Li, F.; Song, X.; Yu, Z. Influence of Algal Organic Matter on Algal Removal Efficiency by Flocculation of Modified Clay. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 613. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11030613
Wang M, Zhang B, Cao X, Li F, Song X, Yu Z. Influence of Algal Organic Matter on Algal Removal Efficiency by Flocculation of Modified Clay. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2023; 11(3):613. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11030613
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Mingyong, Bowen Zhang, Xihua Cao, Fang Li, Xiuxian Song, and Zhiming Yu. 2023. "Influence of Algal Organic Matter on Algal Removal Efficiency by Flocculation of Modified Clay" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 11, no. 3: 613. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11030613
APA StyleWang, M., Zhang, B., Cao, X., Li, F., Song, X., & Yu, Z. (2023). Influence of Algal Organic Matter on Algal Removal Efficiency by Flocculation of Modified Clay. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 11(3), 613. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11030613






