Remote Sensing Monitoring of Green Tide Disaster Using MODIS and GF-1 Data: A Case Study in the Yellow Sea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
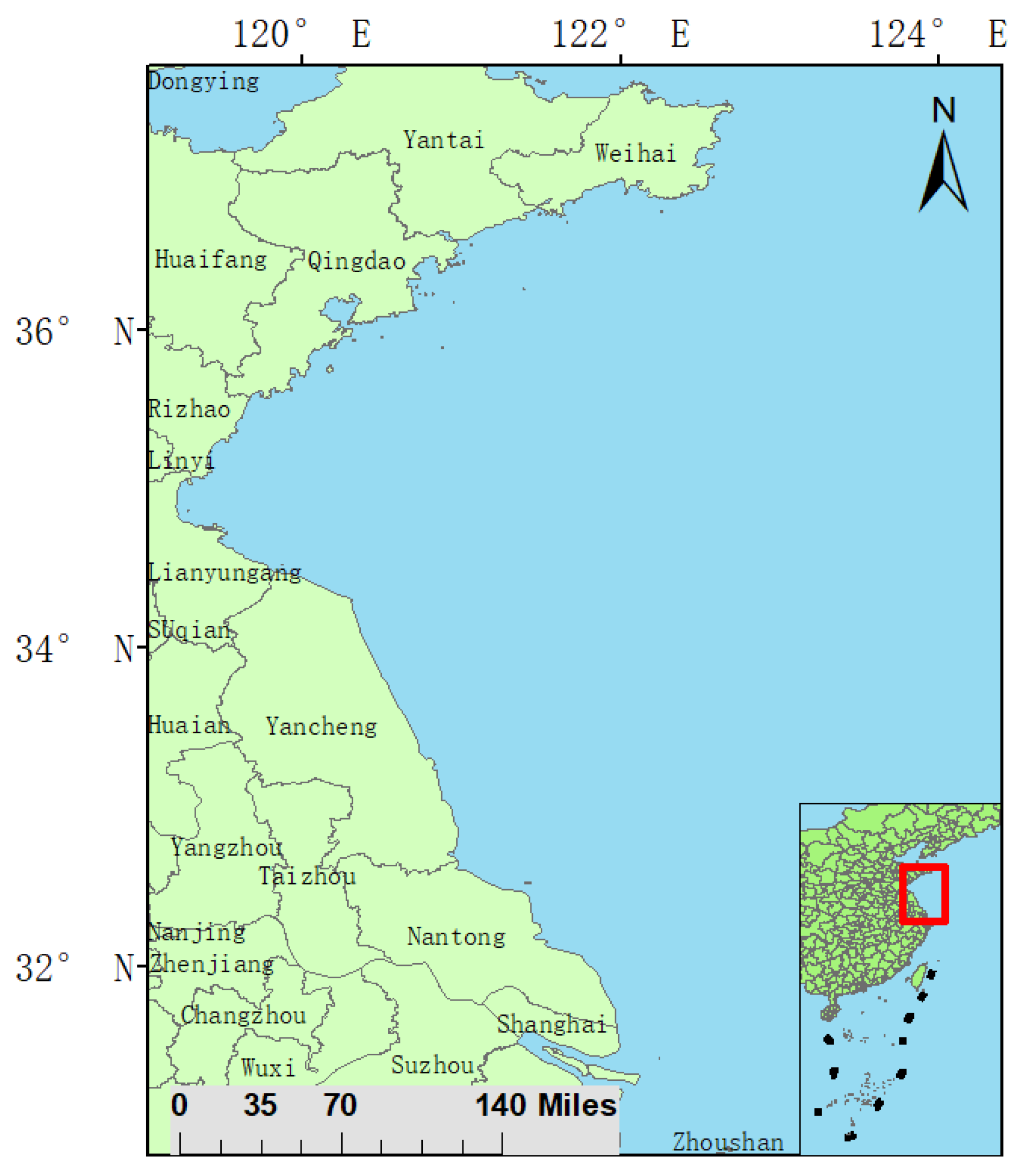
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Dataset
2.3. Data Preprocessing
2.4. Methods
3. Results
3.1. MODIS Green Tide Area Correction
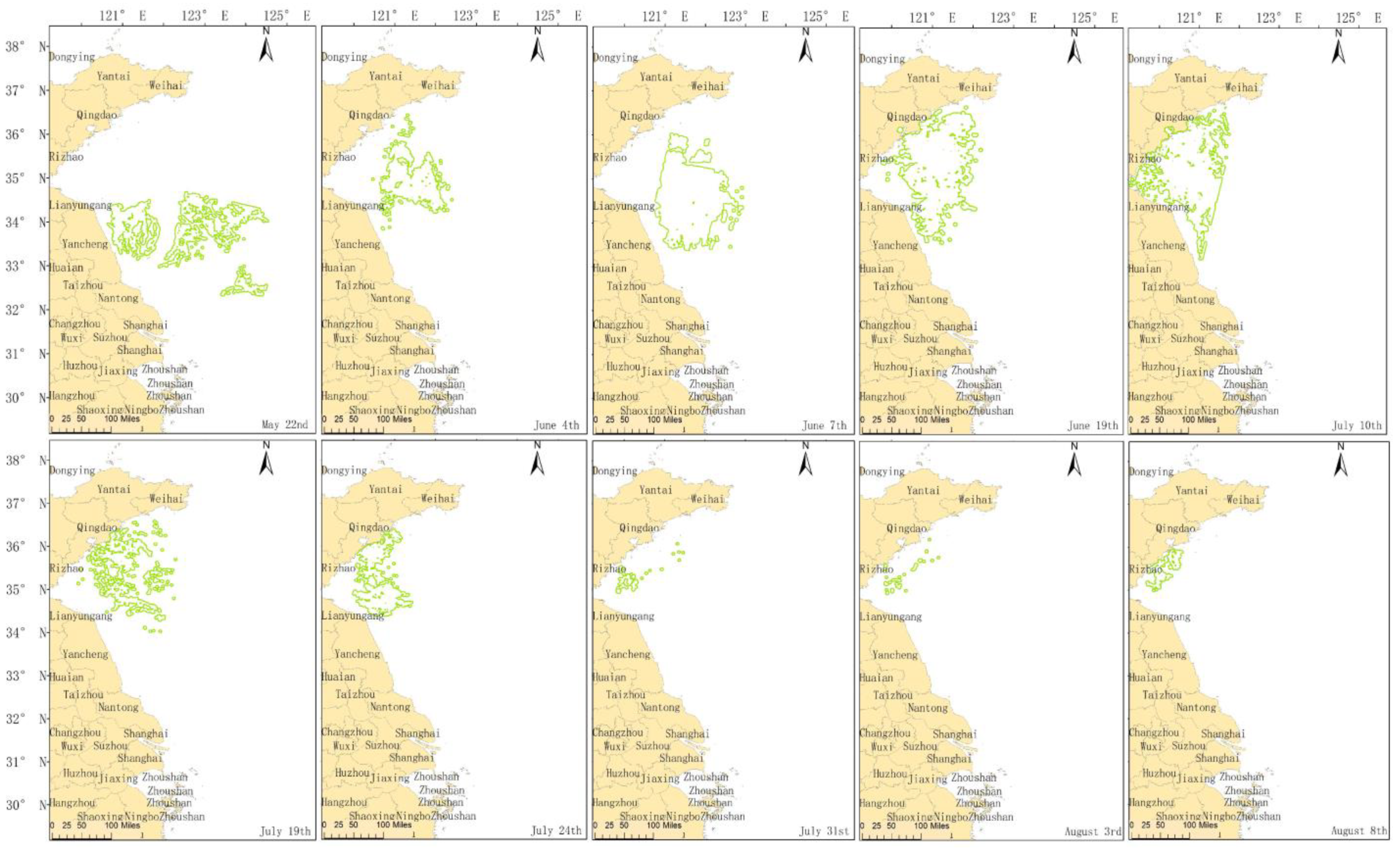
3.2. Analysis of the Green Tide Drift Path and Influencing Factors in 2021
3.3. Causes of Large-Scale Green Tide Outbreaks in 2021
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, M.-J.; Shen, Z.-L.; Yu, R.-C. Responses of a coastal phytoplankton community to increased nutrient input from the Changjiang (Yangtze) River. Cont. Shelf Res. 2008, 28, 1483–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Q.; Hu, C. Mapping macroalgal blooms in the Yellow Sea and East China Sea using HJ-1 and Landsat data: Application of a virtual baseline reflectance height technique. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 178, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Keesing, J.K.; Dong, Z.; Zhen, Y.; Di, B.; Shi, Y.; Fearns, P.; Shi, P. Recurrence of the world’s largest green-tide in 2009 in Yellow Sea, China: Porphyra yezoensis aquaculture rafts confirmed as nursery for macroalgal blooms. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2010, 60, 1423–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Hu, C.; Ming-Xia, H. Remote estimation of biomass of Ulva prolifera macroalgae in the Yellow Sea. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 192, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Zeng, K.; Hu, C.; He, M.-X. On the remote estimation of Ulva prolifera areal coverage and biomass. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 223, 194–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, W.; Gao, Z.; Jiang, X.; Liu, C.; Gao, W. Green Tide Disaster Monitoring System Based on Multi-Source Data; SPIE: Bellingham, DC, USA, 2016; Volume 9975. [Google Scholar]
- Shang, W.; Gao, Z.; Gao, M.; Jiang, X. Monitoring Green Tide in the Yellow Sea Using High-Resolution Imagery and Deep Learning. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, B.; Zhang, H.; Jing, W.; Liu, H.; Cui, J. SRSe-Net: Super-Resolution-Based Semantic Segmentation Network for Green Tide Extraction. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, T.-W.; Zhang, J.; Sun, L.-E.; Jia, Y.-J.; Zhao, W.; Wang, Z.-L.; Meng, J.-M. Satellite monitoring of massive green macroalgae bloom (GMB): Imaging ability comparison of multi-source data and drifting velocity estimation. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 33, 5513–5527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Cui, T. High-precision extraction of nearshore green tides using satellite remote sensing data of the Yellow Sea, China. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 1626–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adjovu, G.E.; Stephen, H.; James, D.; Ahmad, S. Overview of the Application of Remote Sensing in Effective Monitoring of Water Quality Parameters. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemas, V. Remote sensing of algal blooms: An overview with case studies. J. Coast. Res. 2012, 28, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Xu, Q.; Li, G.; Liou, Y.-A.; Wang, B.; Mei, H.; Tong, K. Remotely-Observed Early Spring Warming in the Southwestern Yellow Sea Due to Weakened Winter Monsoon. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Wong, K.; Tsou, J.Y.; Zhang, Y. Investigating spatial distribution of green-tide in the Yellow Sea in 2021 using combined optical and SAR images. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Yuen, K.-V.; Gu, X.; Sun, C.; Gao, L. Influences of environmental factors on the dissipation of green tides in the Yellow Sea, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 189, 114737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; He, P.; Li, H.; Li, G.; Liu, J.; Jiao, F.; Zhang, J.; Huo, Y.; Shi, X.; Su, R. Ulva prolifera green-tide outbreaks and their environmental impact in the Yellow Sea, China. Neurosurgery 2019, 6, 825–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Pang, I.C.; Moon, I.J.; Ryu, J.H. On physical factors that controlled the massive green tide occurrence along the southern coast of the Shandong Peninsula in 2008: A numerical study using a particle-tracking experiment. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2011, 116, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Han, L. Drift path of green tide and the impact of typhoon “Chan-hom” in the Chinese Yellow Sea based on GOCI images in 2015. Ecol. Inform. 2020, 60, 101156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Gao, Z.; Song, D. Analysis of environmental factors affecting the large-scale long-term sequence of green tide outbreaks in the Yellow Sea. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2021, 260, 107504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Gao, Z.; Wang, Z. Analysis of the reasons for the outbreak of Yellow Sea green tide in 2021 based on long-term multi-source data. Mar. Environ. Res. 2022, 178, 105649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Gao, Z.; Xu, F. Research on the dissipation of green tide and its influencing factors in the Yellow Sea based on Google Earth Engine. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 172, 112801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Zheng, X.; Gao, Z.; Song, D.; Chen, M. Multi-resource data-based research on remote sensing monitoring over the green tide in the Yellow Sea. In Proceedings of the Remote Sensing & Modeling of Ecosystems for Sustainability XIV, San Diego, CA, USA, 1 September 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, X.; Gao, Z.; Ning, J.; Xu, F.; Liu, C.; Sun, Z. Remote Sensing Monitoring of Green Tide in the Yellow Sea in 2015 Based on GF-1 WFV Data; SPIE: Bellingham, DC, USA, 2016; Volume 9975. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Gao, Z.; Song, D.; Shang, W.; Jiang, X. Characteristics and influence of green tide drift and dissipation in Shandong Rongcheng coastal water based on remote sensing. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2019, 227, 106335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zheng, X.; Wei, Z.; Zou, J.; Xing, Q. A Spectral-Mixing Model for Estimating Sub-Pixel Coverage of Sea-Surface Floating Macroalgae. Atmos. -Ocean 2018, 56, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Gao, Z.; Ning, J.; Zheng, X.; Liu, C.; Gao, W. Error Analysis on Green Tide monitoring using MODIS Data in the Yellow Sea Based on GF-1 WFV Data; SPIE: Bellingham, DC, USA, 2016; Volume 9975. [Google Scholar]
- Rouse, J.W.; Haas, R.H.; Schell, J.A.; Deering, D.W. Monitoring vegetation systems in the Great Plains with ERTS. NASA Spec. Publ. 1974, 351, 309. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.; Lee, J.-Y.; Lee, W.-K.; Cui, G.; Cho, J.-K.; Wei, G.; Li, L. Application of CASI Hyperspectral Image to Analysis of the Distribution of Hydrogen-Fluoride-Damaged Vegetation in Gumi, Korea. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2017, 45, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keesing, J.K.; Liu, D.; Fearns, P.; García, R. Inter- and intra-annual patterns of Ulva prolifera green tides in the Yellow Sea during 2007-2009, their origin and relationship to the expansion of coastal seaweed aquaculture in China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 1169–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, Q.; Zheng, X.-Y.; Shi, P.; Hao, J.; Yu, D.; Liang, S.; Liu, D.; Zhang, Y.-Z. Monitoring “green tide” in the Yellow Sea and the East China Sea using multi-temporal and multi-source remote sensing images. Guang Pu Xue Yu Guang Pu Fen Xi 2011, 31, 1644–1647. [Google Scholar]
- Sakib, M.H.; Rashid, H.; Yang, C.-S. Comparing performance of inter-sensor NDVI for the detection of floating macroalgal blooms in the Yellow Sea. Indian J. Geo-Mar. Sci. 2021, 50, 613–619. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Fang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Liang, J.; Song, X. Multi-Source Evidence Data Fusion Approach to Detect Daily Distribution and Coverage of Ulva Prolifera in the Yellow Sea, China. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 115214–115228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, T.; Liang, X.; Gong, J.; Tong, C.; Xiao, Y.; Liu, R.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J. Assessing and refining the satellite-derived massive green macro-algal coverage in the Yellow Sea with high resolution images. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 144, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.H.; Huo, Y.Z.; Zhang, Z.L.; Yu, K.F.; He, Q.; Zhang, L.H.; Yang, L.L.; Xu, R.; He, P.M. Variations of morphology and photosynthetic performances of Ulva prolifera during the whole green tide blooming process in the Yellow Sea. Mar. Environ. Res. 2013, 92, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Song, W.; Xiao, J.; Wang, Z.; Fu, M.; Zhu, M.; Li, R.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X. Tempo-spatial distribution and species diversity of green algae micro-propagules in the Yellow Sea during the large-scale green tide development. Harmful Algae 2014, 39, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Ge, J.; Liu, D.; Ding, P.; Chen, C.; Wei, X. The Lagrangian-based floating macroalgal growth and drift model (FMGDM v1. 0): Application to the Yellow Sea green tide. Geosci. Model Dev. 2021, 14, 6049–6070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qingdao Municipal Ocean Development Bureau. Stay True to the Original Aspiration, Take on the Mission Courageously, Anchor the Goal, and Strive Forward. 2021. Available online: https://ocean.qingdao.gov.cn/gzdt/202110/t20211030_23701888.shtml (accessed on 24 February 2023).
- Department of Marine Early Warning and Monitoring. China Marine Disaster Bulletin 2022; Ministry of Natural Resources: Beijing, China, 2021.
- Chen, Z.; Liu, M.; Yang, Y.; Bi, M.; Li, M.; Liu, W. Environmental and economic impacts of different disposal options for ulva prolifera green tide in the yellow Sea, China. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 11483–11492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Hu, C.; Barnes, B.B.; Lapointe, B.E.; Chen, Y.; Xie, Y.; Wang, M. Climate and anthropogenic controls of seaweed expansions in the East China Sea and Yellow Sea. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2022, 49, e2022GL098185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, R.A.; Fong, P. Physiological responses of a bloom-forming green macroalga to short-term change in salinity, nutrients, and light help explain its ecological success. Estuaries 2004, 27, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, A.P.; Wang, C.; Pan, G.H.; Song, L.Y.; Gao, S.; Xie, X.J.; Wang, Z.Y.; Niu, J.F.; Wang, G.C. Diluted seawater promoted the green tide of Ulva prolifera (Chlorophyta, Ulvales). Phycol. Res. 2011, 59, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamboya, F.; Lyimo, T.J.; Landberg, T.; Björk, M. Influence of combined changes in salinity and copper modulation on growth and copper uptake in the tropical green macroalga Ulva reticulata. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2009, 84, 326–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xiao, J.; Fan, S.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, D. Who made the world’s largest green tide in China?—An integrated study on the initiation and early development of the green tide in Yellow Sea. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2015, 60, 1105–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schories, D.; Anibal, J.; Chapman, A.S.; Herre, E.; Isaksson, I.; Lillebø, A.I.; Pihl, L.; Reise, K.; Sprung, M.; Thiel, M. Flagging greens: Hydrobiid snails as substrata for the development of green algal mats (Entero-morpha spp.) on tidal flats of North Atlantic coasts. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2000, 199, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Zhang, J.; Liu, S. Characterization of nutrients in the atmospheric wet and dry deposition observed at the two monitoring sites over Yellow Sea and East China Sea. J. Atmos. Chem. 2007, 57, 41–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, R.; Fletcher, R.; Raven, J. Preliminary studies on the growth of selected ‘green tide’algae in laboratory culture: Effects of irradiance, temperature, salinity and nutrients on growth rate. Bot. Mar. 2001, 44, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Wu, M.; Zhang, A.; Xing, Q.; Zhou, M.; Zhao, D.; Song, X.; Yu, Z. Influence of Sea Surface Temperature on Outbreak of Ulva prolifera in the Southern Yellow Sea, China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2020, 30, 631–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Su, R.; Shi, X.; Zhang, C.; Yin, H.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, G. Role of nutrients in the development of floating green tides in the Southern Yellow Sea, China, in 2017. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 156, 111197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chongrong, Z.; Guangyi, L.; Jingwi, C.; Baoqing, L.; Fan, Y.; Rui, Y. Potential Effects of Some Environmental Factors on a Dinoflagellate Red Tide Caused by Gymnodinium cat-enatum in Shenhu Bay in 2017. Meteorol. Environ. Res. 2019, 10, 30–34. [Google Scholar]
- Van Alstyne, K.L.; Nelson, T.A.; Ridgway, R.L. Environmental Chemistry and Chemical Ecology of “Green Tide” Seaweed Blooms. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2015, 55, 518–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Zhao, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, F.; Zhang, Y. Distribution characteristics of green tides and its impact on environment in the Yellow Sea. Mar. Environ. Res. 2022, 181, 105756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Satellite | Band Order | Wavelength (nm) |
|---|---|---|
| GF-1 WFV | 1 | 450–900 |
| 2 | 450–520 | |
| 3 | 520–590 | |
| 630–690 | ||
| MODIS | 1 | 620–670 |
| 2 | 841–876 |
| Satellite | Time | Pixel Size (m) | Number of Pixels | Area (km2) | MODIS Converted Area (km2) | Error |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GF-1 | 8 June 2019 | 19 × 19 | 1,766,965 | 637.87 | - | - |
| 3 July 2019 | 18 × 18 | 1,795,157 | 581.63 | - | - | |
| 20 June 2021 | 19 × 19 | 2,278,052 | 822.38 | - | - | |
| MODIS | 8 June 2019 | 250 × 250 | 15,952 | 997 | 696.03 | 9.12% |
| 3 July 2019 | 250 × 250 | 15,264 | 954 | 666.015 | 14.51% | |
| 20 June 2021 | 19 × 19 | 3,671,233 | 1325.32 | 925.24 | 12.51% |
| Time | Satellite | Coverage Area (km2) | Coverage Area in Converted MODIS Images (km2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 22 May | GF | 82.29 | \ |
| 4 June | MODIS | 1406.63 | 820.84 |
| 7 June | GF | 1371.89 | \ |
| 19 June | MODIS | 2766.06 | 1776.88 |
| 10 July | GF | 611.35 | \ |
| 19 July | MODIS | 310.56 | 55.64 |
| 24 July | MODIS | 440.06 | 146.05 |
| 31 July | MODIS | 26.25 | \ |
| 3 August | MODIS | 21.00 | \ |
| 8 August | GF | 15.11 | \ |
| Year | The Earliest Discovery Time | Extinction Time | Maximum Distribution Area (km2) | Maximum Coverage Area (km2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2012 | Mid to late May | Late August | 19,610 | 267 |
| 2013 | Mid May | Mid August | 29,733 | 790 |
| 2014 | Mid May | Mid August | 50,000 | 540 |
| 2015 | Mid to late May | Early August | 52,700 | 594 |
| 2016 | Early May | Early August | 57,500 | 554 |
| 2017 | Mid May | Mid to late July | 29,522 | 281 |
| 2018 | Late May | Mid August | 38,046 | 193 |
| 2019 | Mid to late May | Early September | 55,699 | 508 |
| 2020 | Late May | Late July | 18,237 | 192 |
| 2021 | Mid May | Late August | 61,898 | 1746 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Men, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ma, Y.; Wong, K.P.; Tsou, J.Y.; Zhang, Y. Remote Sensing Monitoring of Green Tide Disaster Using MODIS and GF-1 Data: A Case Study in the Yellow Sea. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 2212. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11122212
Men Y, Liu Y, Ma Y, Wong KP, Tsou JY, Zhang Y. Remote Sensing Monitoring of Green Tide Disaster Using MODIS and GF-1 Data: A Case Study in the Yellow Sea. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2023; 11(12):2212. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11122212
Chicago/Turabian StyleMen, Yanzhuo, Yingying Liu, Yufei Ma, Ka Po Wong, Jin Yeu Tsou, and Yuanzhi Zhang. 2023. "Remote Sensing Monitoring of Green Tide Disaster Using MODIS and GF-1 Data: A Case Study in the Yellow Sea" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 11, no. 12: 2212. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11122212
APA StyleMen, Y., Liu, Y., Ma, Y., Wong, K. P., Tsou, J. Y., & Zhang, Y. (2023). Remote Sensing Monitoring of Green Tide Disaster Using MODIS and GF-1 Data: A Case Study in the Yellow Sea. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 11(12), 2212. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11122212








