Benthic Respiration and Heavy Metal Benthic Fluxes in Artificial Shihwa Lake: Approaching In Situ Measurement
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Sampling and Methods
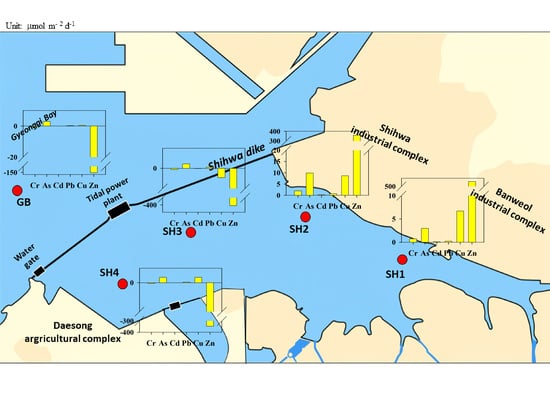
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Field Surveys and Sampling
2.3. In Situ Chamber Experiment
2.4. Sediment Trap
2.5. Laboratory Analysis
2.6. Calculation
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Physicochemical Characteristics of Water and Vertical Fluxes
3.2. Porewater and Solid-Phase Geochemistry
3.3. Sediment Oxygen Demand and Benthic Nutrient Flux
3.4. Heavy Metal Benthic Flux
4. Discussion
4.1. Control Factors for Sediment Oxygen Demand
4.2. Benthic Nutrient Flux and Benthic–Pelagic Coupling
4.3. Control Factors for Heavy Metal Benthic Flux
4.4. Assessing the Contribution and Risk of Heavy Metal Benthic Fluxes in Shihwa Lake
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, S.G. The evolution of coastal wetland policy in developed countries and Korea. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2010, 53, 562–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Lee, B.Y.; Chang, W.K.; Hong, S.; Song, S.J.; Park, J.; Kwon, B.O.; Khim, J.S. Environmental and ecological effects of Lake Shihwa reclamation project in South Korea: A review. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2014, 102, 545–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.-K.; Kim, D.-S.; Cho, K.-J. Dynamics of water environmental factors and phytoplankton before and after inflow of seawater in Shihwa Reservoir. J. Korean Environ. Sci. Soc. 2000, 9, 115–123. [Google Scholar]
- An, S.U.; Mok, J.S.; Kim, S.H.; Choi, J.H.; Hyun, J.H. A large artificial dyke greatly alters partitioning of sulfate and iron reduction and resultant phosphorus dynamics in sediments of the Yeongsan River estuary, Yellow Sea. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 665, 752–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.W.; Park, Y.C. The development of anoxia in the artificial Lake Shihwa, Korea, as a consequence of intertidal reclamation. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1999, 38, 1194–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Park, K.T.; Lim, J.H.; Yoon, J.E.; Kim, I.N. Hypoxia in Korean coastal waters: A case study of the natural Jinhae Bay and artificial Shihwa Bay. Front. Mar. Sci. 2018, 5, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, D.; Wang, X.; Holloway, P. Tidal characteristic adjustment due to dyke and seawall construction in the Mokpo Coastal Zone, Korea. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2004, 59, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Lee, J.S.; Hyun, J.H. Extremely high sulfate reduction, sediment oxygen demand and benthic nutrient flux associated with a large-scale artificial dyke and its implication to benthic-pelagic coupling in the Yeongsan River estuary, Yellow Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 120, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Kim, K.H.; Shim, J.; Han, J.H.; Choi, Y.H.; Khang, B.J. Massive sedimentation of fine sediment with organic matter and enhanced benthic–pelagic coupling by an artificial dyke in semi-enclosed Chonsu Bay, Korea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweerts, J.P.R.; Bär-Gilissen, M.J.; Cornelese, A.A.; Cappenberg, T.E. Oxygen-consuming processes at the profundal and littoral sediment-water interface of a small meso-eutrophic lake (Lake Vechten, The Netherlands). Limnol. Oceanogr. 1991, 36, 1124–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jessen, C.; Bednarz, V.N.; Rix, L.; Teichberg, M.; Wild, C. Marine Eutrophication. In Environmental Indicators; Armon, R., Hänninen, O., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 177–203. [Google Scholar]
- Canfield, D.E.; Kristensen, E.; Thamdrup, B. Aquatic Geomicrobiology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.H.; An, S.U.; Lee, W.C.; Lee, J.S.; Hyun, J.H. Influence of Manila clam aquaculture on rates and partitioning of organic carbon oxidation in sediment of Keunso Bay, Yellow Sea. Aquac. Environ. Interact. 2020, 12, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, K.T.; Kim, S.L.; Yu, O.H.; Lim, D.; Kim, S.H. Low benthic mineralization and nutrient fluxes in the continental shelf sediment of the northern East China Sea. J. Sea Res. 2020, 164, 101934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Pérez, F.; Castro, C.G. Benthic oxygen and nutrient fluxes in a coastal upwelling system (Ria de Vigo, NW Iberian Peninsula): Seasonal trends and regulating factors. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2014, 511, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, D.; Dagg, M.J.; Liu, H.; Cummings, S.R.; Ortner, P.B.; Kelble, C. Wind events and benthic-pelagic coupling in a shallow subtropical bay in Florida. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2004, 266, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahtera, E.; Conley, D.J.; Gustafsson, B.G.; Kuosa, H.; Pitkänen, H.; Savchuk, O.P.; Tamminen, T.; Viitasalo, M.; Voss, M.; Wasmund, N. Internal ecosystem feedbacks enhance nitrogen-fixing cyanobacteria blooms and complicate management in the Baltic Sea. J. Hum. Environ. Stud. 2007, 36, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luoma, S.N. Can we determine the biological availability of sediment-bound trace elements? Hydrobiologia 1989, 176, 379–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cundy, A.B.; Croudace, I.W.; Cearreta, A.; Irabien, M.A.J. Reconstructing historical trends in metal input in heavily-disturbed, contaminated estuaries: Studies from Bilbao, Southampton Water and Sicily. Appl. Geochem. 2003, 18, 311–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigg, L.; Sturm, M.; Kistler, D. Vertical transport of heavy metals by settling particles in Lake Zurich. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1987, 32, 112–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heggie, D.; Kahn, D.; Fischer, K. Trace metals in metalliferous sediments, MANOP Site M: Interfacial pore water profiles. Earth Planet Sci. Lett. 1986, 80, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundby, B.; Anderson, L.G.; Hall, P.O.; Iverfeldt, Å.; van der Loeff, M.M.R.; Westerlund, S.F. The effect of oxygen on release and uptake of cobalt, manganese, iron and phosphate at the sediment-water interface. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1986, 50, 1281–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, M.; Silva Filho, E.; Sarkar, S.; Sella, S.; Bhattacharya, A.; Satpathy, K.; Prasad, M.; Chakraborty, S.; Bhattacharya, B. Distribution and possible source of trace elements in the sediment cores of a tropical macrotidal estuary and their ecotoxicological significance. Environ. Int. 2007, 33, 346–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankhla, M.S.; Kumari, M.; Nandan, M.; Kumar, R.; Agrawal, P. Heavy metals contamination in water and their hazardous effect on human health-a review. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2016, 5, 759–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ra, K.; Bang, J.H.; Lee, J.M.; Kim, K.T.; Kim, E.S. The extent and historical trend of metal pollution recorded in core sediments from the artificial Lake Shihwa, Korea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 1814–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyeonggi Green & Agriculture Foundation. Environmental Management Strategies for the Utilization of Hwaseong Lake, Tando Lake, and Nearby Reclaimed Land; Gyeonggi Green & Agriculture Foundation: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Moon, H.-B.; Choi, M.; Yu, J.; Jung, R.-H.; Choi, H.-G. Contamination and potential sources of polybrominated diphyenyl ethers (PBDEs) in water and sediment from the artificial Lake Shihwa, Korea. Chemospher 2012, 88, 837–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.; Choi, J.Y.; Lee, J.; Ra, K. Investigations of Pb and Cu isotopes to trace contamination sources from the artificial Shihwa Lake in Korea. J. Coast. Res. 2020, 95, 1122–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostkowski, P.; Yamashita, N.; So, I.M.K.; Taniyasu, S.; Lam, P.K.S.; Falandysz, J.; Lee, K.T.; Taniyasu, S.; Kim, S.K.; Khim, J.S.; et al. Perfluorinated compounds in streams of the Shihwa industrial zone and Lake Shihwa, South Korea. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2006, 25, 2374–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, H.; Yamashita, N.; Taniyasu, S.; Lee, K.T.; Jones, P.D.; Newsted, J.L.; Khim, J.S.; Giesy, J.P. Perfluoroalkyl acids in marine organisms from Lake Shihwa, Korea. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2009, 57, 552–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Kim, Y.T.; Shin, K.H.; Hyun, J.H.; Kim, S.Y. Benthic nutrient fluxes at longline sea squirt and oyster aquaculture farms and their role in coastal ecosystems. Aquac. Int. 2011, 19, 931–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; An, S.U.; Park, Y.-G.; Kim, E.; Kim, D.; Kwon, J.N.; Kang, D.J.; Noh, J.-H. Rates of total oxygen uptake of sediments and benthic nutrient fluxes measured using an in situ autonomous benthic chamber in the sediment of the slope off the southwestern part of Ulleung Basin, East Sea. Ocean Sci. J. 2015, 50, 581–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, Y.T.; Hong, S.J.; Han, J.H.; Hyun, J.H.; Shin, K.H. Influence of sea squirt (Halocynthia roretzi) aquaculture on benthic–pelagic coupling in coastal waters: A study of the South Sea in Korea. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2012, 99, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, K.; King, G.M.; Kristensen, E. Impact of the soft-shell clam Mya arenaria on sulfate reduction in an intertidal sediment. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 1996, 10, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, T.R.; Maita, Y.; Lalli, C.M. Determination of Chlorophylls and Total Carotenoids: Spectrophotometric Method, a Manual of Chemical and Biological Methods for Seawater Analysis; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1984; pp. 101–112. [Google Scholar]
- Stookey, L.L. Ferrozine–a new spectrophotometric reagent for iron. Anal. Chem. 1970, 42, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cline, J.D. Spectrophotometric determination of hydrogen sulfide in natural waters 1. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1969, 14, 454–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fossing, H.; Jørgensen, B.B. Measurement of bacterial sulfate reduction in sediments: Evaluation of a single-step chromium reduction method. Biogeochemistry 1989, 8, 205–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhen, X.; Wang, X.; Ren, Y.; Hu, L.; Bai, Y.; Liu, J.; Shi, X. Benthic trace metal fluxes in a heavily contaminated bay in China: Does the sediment become a source of metals to the water column? Environ. Pollut. 2020, 257, 113494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jongman, E.; Jongman, S.R.R. Data Analysis in Community and Landscape Ecology; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.; Choi, M.; Jang, D.; Joe, D.; Park, K.; Lee, H.; Woo, J.; Kim, T.; Park, J. Spatiotemporal distribution of dissolved heavy metals in Gyeonggi Bay, Korea. Ocean Sci. J. 2020, 55, 69–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glud, R.N. Oxygen dynamics of marine sediments. Mar. Biol. Res. 2008, 4, 243–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, B.B.; Wenzhöfer, F.; Egger, M.; Glud, R.N. Sediment oxygen consumption: Role in the global marine carbon cycle. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2022, 228, 103987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Kim, H.C.; Choi, S.H.; Lee, W.C.; Jung, R.H.; Hyun, J.H.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, J.S. Benthic respiration and nutrient release associated with net cage fish and longline oyster aquaculture in the Geoje-Tongyeong coastal waters in Korea. Estuar. Coast. 2020, 43, 589–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrón, S.; Alonso-Pérez, F.; Ortega, T.; Forja, J.M. Benthic respiration on the northeastern shelf of the Gulf of Cádiz (SW Iberian Peninsula). Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2009, 392, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edberg, N.; Hofsten, B.V. Oxygen uptake of bottom sediments studied in situ and in the laboratory. Water Res. 1973, 7, 1285–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmer, M.; Duarte, C.M.; Heilskov, A.; Olesen, B.; Terrados, J. Biogeochemical conditions in sediments enriched by organic matter from net-pen fish farms in the Bolinao area, Philippines. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2003, 46, 1470–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouret, A.; Anschutz, P.; Deflandre, B.; Chaillou, G.; Hyacinthe, C.; Deborde, J.; Etcheber, H.; Jouanneau, J.-M.; Grémare, A.; Lecroart, P. Oxygen and organic carbon fluxes in sediments of the Bay of Biscay. Deep-Sea Res. I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2010, 57, 528–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, N.S.; Lee, K.H.; Jeong, H.J.; Du Yoo, Y.; Seong, K.A.; Potvin, É.; Hwang, Y.J.; Yoon, E.Y. Red tides in Shiwha Bay, western Korea: A huge dike and tidal power plant established in a semi-enclosed embayment system. Harmful Algae 2013, 30, S114–S130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Han, J.H.; An, S.U.; Na, K.T.; Kwon, J.N.; Kim, E.S. Sedimentary organic carbon budget of coastal sediments and the importance of benthic-pelagic coupling off Namhae Island in the South Sea of Korea. Ocean Sci. J. 2014, 49, 433–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, K.T.; Kim, H.C.; Lee, W.C.; Choi, D.; Choi, S.H.; Choi, J.H.; Lee, H.J.; Shin, J.H. Aquaculture Farming Effect on Benthic Respiration and Nutrient Flux in Semi-Enclosed Coastal Waters of Korea. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laursen, A.E.; Seitzinger, S.P. The role of denitrification in nitrogen removal and carbon mineralization in Mid-Atlantic Bight sediments. Cont. Shelf Res. 2002, 22, 1397–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, M.; Archambault, P.; Thouzeau, G.; Desrosiers, G. Summer influence of 1 and 2 yr old mussel cultures on benthic fluxes in Grande-Entrée lagoon, Îles-de-la-Madeleine (Québec, Canada). Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2007, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boynton, W.R.; Kemp, W.M. Nutrient regeneration and oxygen consumption by sediments along an estuarine salinity gradient. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. Oldendorf 1985, 23, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, J.; Dinkel, C.; Friedl, G.; Pimenov, N.; Wijsman, J.; Gomoiu, M.-T.; Cociasu, A.; Popa, L.; Wehrli, B. Benthic nutrient cycling and diagenetic pathways in the north-western Black Sea. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2002, 54, 369–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkinson, C.S., Jr.; Giblin, A.E.; Tucker, J. Benthic metabolism and nutrient regeneration on the continental shelf of Eastern Massachusetts, USA. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2001, 224, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinelli, R.L.; Jahnke, R.A.; Craven, D.B.; Nelson, J.R.; Eckman, J.E. Sediment nutrient dynamics on the South Atlantic Bight continental shelf. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1998, 43, 1305–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratihary, A.; Naqvi, S.; Narvenkar, G.; Kurian, S.; Naik, H.; Naik, R.; Manjunatha, B. Benthic mineralization and nutrient exchange over the inner continental shelf of western India. Biogeosciences 2014, 11, 2771–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, J. Variation of Primary Productivity and Pigment of Phytoplankton According to Operation of Lake Shihwa Tidal Power Plant; Hanyang University: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, J.H.; An, S.U.; Choi, J.H.; Lee, H.J.; Woo, S.B.; Hyun, J.H.; Kim, S.H. Rates and Controls of Organic Matter Mineralization and Benthic Nutrient Release in the Coastal Sediment Near Lake Shihwa. Sea J. Korean Soc. Oceanogr. 2021, 26, 110–123. [Google Scholar]
- MOTIE (Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy). 2023. Available online: http://www.motie.go.kr/www/main.do (accessed on 1 March 2023).
- Ra, K.; Kim, E.S.; Kim, J.K.; Kim, K.T.; Lee, J.M.; Kim, E.Y. Distribution and Pollution Assessment of Trace Metals in Core Sediments from the Artificial Lake Shihwa, Korea. Ocean Polar Res. 2013, 35, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shine, J.P.; Ika, R.; Ford, T.E. Relationship between oxygen consumption and sediment-water fluxes of heavy metals in coastal marine sediments. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1998, 17, 2325–2337. [Google Scholar]
- Turetta, C.; Capodaglio, G.; Cairns, W.; Rabar, S.; Cescon, P. Benthic fluxes of trace metals in the lagoon of Venice. Microchem. J. 2005, 79, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emili, A.; Acquavita, A.; Covelli, S.; Spada, L.; Di Leo, A.; Giandomenico, S.; Cardellicchio, N. Mobility of heavy metals from polluted sediments of a semi-enclosed basin: In situ benthic chamber experiments in Taranto’s Mar Piccolo (Ionian Sea, Southern Italy). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 12582–12595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warnken, K.W.; Gill, G.A.; Griffin, L.L.; Santschi, P.H. Sediment-water exchange of Mn, Fe, Ni and Zn in Galveston Bay, Texas. Mar. Chem. 2001, 73, 215–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellali, M.A.; Zaaboub, N.; Oueslati, W.; Added, A.; Aleya, L. Diagenetic processes and sediment–water exchanges of heavy metals in the Mejerda River Delta (Gulf of Tunis). Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 6665–6679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audry, S.; Blanc, G.; Schäfer, J.; Chaillou, G.; Robert, S. Early diagenesis of trace metals (Cd, Cu, Co, Ni, U, Mo, and V) in the freshwater reaches of a macrotidal estuary. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2006, 70, 2264–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tribovillard, N.; Algeo, T.J.; Lyons, T.; Riboulleau, A. Trace metals as paleoredox and paleoproductivity proxies: An update. Chem. Geol. 2006, 232, 12–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, T.J.; Gieskes, J.M.; Jahnke, R.A. Early diagenesis in differing depositional environments: The response of transition metals in pore water. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1990, 54, 1233–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Jeong, H.R.; Choi, J.Y.; Ra, K. The spatial and Vertical Variations of Metal Pollution in Sediments after Tidal Power Plant Operation in Shihwa Lake. Sea J. Korean Soc. Oceanogr. 2019, 24, 535–547. [Google Scholar]






| Station | Latitude | Longitude |
|---|---|---|
| SH1 | 37°17.961′ N | 126°43.901′ E |
| SH2 | 37°18.656′ N | 126°40.984′ E |
| SH3 | 37°18.319′ N | 126°38.588′ E |
| SH4 | 37°17.643′ N | 126°36.044′ E |
| GB | 37°19.165′ N | 126°33.406′ E |
| Station | Depth | Temperature | Salinity | DO | Chl-a | NH4+ | NO3− | PO43− | Si(OH)4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (m) | (°C) | (%) | (μg L−1) | (μmol L−1) | ||||||
| SH1 | 4.4 | S | 21.2 | 30.67 | 97 | 4.0 (±1.0) | 18.1 (±0.2) | 6.7 (±0.1) | 1.80 (±0.02) | 41.9 (±0.0) |
| B | 19.9 | 31.16 | 94 | 6.6 (±0.7) | 2.0 (±0.1) | 1.4 (±0.1) | 0.76 (±0.00) | 35.8 (±0.1) | ||
| SH2 | 6.1 | S | 20.3 | 31.20 | 113 | 6.2 (±0.0) | 0.6 (±0.1) | 0.3 (±0.1) | 0.28 (±0.00) | 27.3 (±0.7) |
| B | 17.9 | 31.28 | 79 | 7.9 (±0.2) | 1.1 (±0.0) | 0.7 (±0.0) | 0.44 (±0.07) | 28.8 (±3.7) | ||
| SH3 | 7.9 | S | 17.7 | 31.28 | 105 | 5.9 (±0.2) | 2.9 (±0.4) | 2.8 (±0.5) | 0.30 (±0.03) | 6.1 (±0.5) |
| B | 17.0 | 31.26 | 98 | 2.7 (±0.0) | 4.0 (±0.5) | 3.7 (±0.6) | 0.30 (±0.01) | 7.7 (±0.3) | ||
| SH4 | 6.0 | S | 17.7 | 31.23 | 103 | 7.4 (±0.3) | 1.8 (±0.5) | 1.9 (±0.4) | 0.16 (±0.02) | 10.4 (±1.2) |
| B | 17.0 | 31.24 | 97 | 5.0 (±0.6) | 4.0 (±0.4) | 2.6 (±0.4) | 0.37 (±0.08) | 8.3 (±2.0) | ||
| GB | 7.1 | S | 18.1 | 31.17 | 135 | 15.3 (±0.9) | 0.6 (±0.1) | 0.2 (±0.0) | BDL a | 3.3 (±0.0) |
| B | 16.7 | 31.27 | 109 | 3.8 (±0.4) | 2.0 (±0.0) | 1.7 (±0.0) | 0.10 (±0.00) | 4.1 (±0.0) | ||
| Station | TM Flux | δ13C | POC | TN | POC Flux | TN Flux | C/N Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (g m−2 d−1) | (‰) | (%, dry wt.) | (mmol m−2 d−1) | ||||
| SH1 | 100 (±10) | −24.5 (±0.8) | 1.05 (±0.07) | 0.118 (±0.019) | 87 (±9) | 8.4 (±0.8) | 10.4 |
| SH2 | 130 (±12) | −24.2 (±0.1) | 1.00 (±0.04) | 0.117 (±0.005) | 109 (±10) | 10.9 (±1.0) | 10.0 |
| SH3 | 117 (±4) | −23.4 (±0.1) | 1.04 (±0.04) | 0.108 (±0.005) | 101 (±4) | 9.0 (±0.3) | 11.2 |
| SH4 | 142 (±10) | −23.3 (±0.3) | 1.33 (±0.17) | 0.122 (±0.009) | 157 (±11) | 12.4 (±0.9) | 12.7 |
| Station | Porewater | Solid Phase | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (mmol m−2) | (mol m−2) | |||||
| NH4+ | NO3− | PO43− | Si(OH)4 | Fe2+ | TRS | |
| SH1 | 36.38 | 0.106 | 1.72 | 14.25 | 15.45 | 2.54 |
| SH2 | 23.95 | 0.108 | 3.00 | 23.51 | 6.62 | 2.67 |
| SH3 | 12.19 | 0.117 | 0.64 | 13.45 | 9.50 | 2.56 |
| SH4 | 17.90 | 0.078 | 0.46 | 10.98 | 8.19 | 1.43 |
| GB | 17.07 | 0.084 | 0.17 | 14.54 | 12.70 | 1.19 |
| Station | SOD | BNF | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (mmol m−2 d−1) | |||||
| O2 | NH4+ | NO3− | PO43− | Si(OH)4 | |
| SH1 | 30.6 (±0.0) | 7.36 (±2.69) | −1.99 (±0.45) | 0.51 (±0.02) | 3.56 (±0.36) |
| SH2 | 42.8 (±0.1) | 12.50 (±3.72) | 1.31 (±0.17) | 1.11 (±0.17) | 12.68 (±1.92) |
| SH3 | 42.9 (±0.1) | 12.15 (±1.94) | 0.66 (±0.08) | 0.19 (±0.02) | 8.17 (±0.39) |
| SH4 | 83.3 (±0.2) | 11.21 (±0.80) | −0.32 (±0.20) | 0.52 (±0.04) | 24.59 (±1.65) |
| GB | - | 7.59 (±1.18) | 1.11 (±0.28) | 1.18 (±0.12) | 29.00 (±3.71) |
| Station | Mn | Fe | Cr | Co | As | Cd | Pb | Ni | Cu | Zn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| μmol m−2 d−1 | ||||||||||
| SH1 | 573 (±139) | 10 (±4) | 0.72 (±0.18) | 0.9 (±0.1) | 3.0 (±2.0) | 0.09 (±0.05) | 0.24 (±0.15) | 40 (±3) | 6.7 (±2.7) | 546 (±212) |
| SH2 | 3028 (±195) | 28 (±9) | 1.93 (±0.76) | 2.9 (±0.2) | 9.9 (±2.4) | 0.23 (±0.07) | 0.74 (±0.12) | 38 (±3) | 8.7 (±1.7) | 359 (±101) |
| SH3 | 2060 (±169) | 50 (±23) | −0.54 (±0.35) | 1.7 (±0.7) | 2.2 (±2.4) | −0.08 (±0.03) | 0.53 (±0.25) | 27 (±4) | −4.6 (±2.4) | −404 (±86) |
| SH4 | 5488 (±242) | 136 (±8) | −0.41 (±0.28) | 4.8 (±0.3) | 3.7 (±0.6) | −0.08 (±0.04) | 0.35 (±0.09) | 51 (±7) | 3.7 (±1.9) | −346 (±156) |
| GB | 2473 (±95) | 96 (±13) | −0.43 (±0.15) | 1.8 (±0.2) | 2.9 (±0.8) | −0.01 (±0.02) | 0.17 (±0.04) | 9 (±2) | 0.4 (±0.0) | −151 (±92) |
| Location | Environmental Description | Water Depth | Temp | Salinity | SOD | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (m) | (°C) | (psu) | (mmol m−2 d−1) | |||
| Shihwa Lake, South Korea | Enclosed saline lake | 4.4–7.1 (6.3 ± 1.3) | 16.6–19.9 (14.7 ± 7.3) | 31.2–31.3 | 30.6–83.3 (49.9 ± 23.0) | This study |
| Chonsu Bay, South Korea | Enclosed bay | 12–17 | 20–21 | 31.5–31.7 | 25.6–50.4 (37.5 ± 12.4) | [9] |
| Namhae and Geoje Islands, South Korea | Coastal continental shelf | 24–28 | 19.8–20.5 | 33.7–34.5 | 34.9–54.1 (46.3 ± 10.1) | [50] |
| Geoje-Tongyoung coastal, South Korea | Oyster farm | 11 | 15.3–18.8 | - | 60–84 (73 ± 12) | [51] |
| Finfish farm | 19 | 15.9–19.1 | - | 77–157 (117 ± 40) | ||
| Gulf of Cadiz, Iberian Peninsula | Near-shore continental shelf | 8–34 | 12–24 | 35.3–36.7 | 9–27 (18 ± 5) | [45] |
| Northern East China Sea (ECS) | Continental shelf | 83–93 | 13.4–14.1 | 32.0–33.9 | 2.7 and 8.4 (5.6 ± 4.1) | [14] |
| Station | Benthic Nutrient Flux (mmol m−2 d−1) | Contribution of BNF to PP (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DIN | DIP | DIN | DIP | |
| SH1 | 5.37 (±3.14) | 0.51 (±0.02) | 56 | 85 |
| SH2 | 13.82 (±3.90) | 1.11 (±0.17) | 144 | 184 |
| SH3 | 12.82 (±2.02) | 0.19 (±0.02) | 133 | 32 |
| SH4 | 10.90 (±0.99) | 0.52 (±0.04) | 113 | 86 |
| GB | 8.70 (±1.46) | 1.18 (±0.12) | 35 | 75 |
| Location | Shihwa Lake, South Korea | New Bedford Harbor, USA | Lagoon of Venice, Italy | Mar Piccolo, Italy | Galveston Bay, USA | Mejerda River Delta, Tunisia |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mn | 573–5488 (2724 ± 1794) | - | 2.9–4.6 (3.7 ± 1.2) | 4.7–5.0 (4.9 ± 0.2) | 450–2320 (1207 ± 792) | 86–190 (130 ± 35) |
| Fe | 10–136 (64 ± 51) | - | −1.5–0.8 (−1.2 ± −1.5) | 3.9–8.7 (6.3 ± 3.4) | 6.3–34 (18 ± 12) | - |
| Cr | −0.54–1.93 (0.3 ± 1.1) | - | - | −1.2–0.6 (−1.0 ± 0.4) | - | - |
| Co | 0.9–4.8 (2.4 ± 1.5) | 0.001–0.045 (0.02 ± 0.02) | - | - | - | −0.38–1.92 (0.67 ± 0.79) |
| As | 2.2–9.9 (4.3 ± 3.2) | - | −0.04–0.06 (0.01 ± 0.07) | −0.15–0.83 (0.34 ± 0.69) | - | - |
| Cd | −0.08–0.23 (0.03 ± 1.13) | 0.01–0.29 (0.12 ± 0.11) | 0.04–0.05 (0.05 ± 0.01) | −0.04–0.00 (−0.02 ± 0.03) | - | −0.38–0.38 (−0.05 ± 0.32) |
| Pb | 0.1–0.74 (0.41 ± 0.23) | −0.04–0.14 (0.03 ± 0.06) | - | 0.12–0.27 (0.19 ± 0.11) | - | 0.2–0.5 (0.41 ± 0.11) |
| Ni | 9–51 (33 ± 16) | 0.04–1.10 (0.5 ± 0.4) | - | 0.32–0.37 (0.35 ± 0.04) | 0.9–2.7 (1.6 ± 0.6) | - |
| Cu | −4.6–8.7 (3.0 ± 5.3) | 1.3–11.0 (4.8 ± 3.1) | 0.07–0.12 (0.09 ± 0.04) | −0.9–7.0 (3.1 ± 5.6) | - | 0.1–0.4 (0.22 ± 0.09) |
| Zn | −404–546 (1 ± 428) | 4–51 (20 ± 15) | 15–16 (15 ± 1) | −0.4–6.9 (3.3 ± 5.2) | 1.8–3.3 (2.3 ± 0.5) | 27–270 (135 ± 86) |
| Reference | This study | [63] | [64] | [65] | [66] | [67] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cho, Y.-H.; Baek, J.-W.; An, S.-U.; Yoo, H.-J.; Baek, H.-M.; Choi, J.Y.; Kim, T.H.; Kim, K.-T.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, S.-H. Benthic Respiration and Heavy Metal Benthic Fluxes in Artificial Shihwa Lake: Approaching In Situ Measurement. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 2186. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11112186
Cho Y-H, Baek J-W, An S-U, Yoo H-J, Baek H-M, Choi JY, Kim TH, Kim K-T, Lee JS, Kim S-H. Benthic Respiration and Heavy Metal Benthic Fluxes in Artificial Shihwa Lake: Approaching In Situ Measurement. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2023; 11(11):2186. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11112186
Chicago/Turabian StyleCho, Yu-Hyeon, Ju-Wook Baek, Sung-Uk An, Hyun-Ju Yoo, Hyun-Min Baek, Jin Young Choi, Tae Ha Kim, Kyung-Tae Kim, Jae Seong Lee, and Sung-Han Kim. 2023. "Benthic Respiration and Heavy Metal Benthic Fluxes in Artificial Shihwa Lake: Approaching In Situ Measurement" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 11, no. 11: 2186. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11112186
APA StyleCho, Y.-H., Baek, J.-W., An, S.-U., Yoo, H.-J., Baek, H.-M., Choi, J. Y., Kim, T. H., Kim, K.-T., Lee, J. S., & Kim, S.-H. (2023). Benthic Respiration and Heavy Metal Benthic Fluxes in Artificial Shihwa Lake: Approaching In Situ Measurement. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 11(11), 2186. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11112186