Living on the Coast in Harmony with Natural Processes
Abstract
:1. Introduction—Coastal and Ocean Concerns
- Inundation, flood, and storm damage;
- Erosion and sediment deficits;
- Wetland loss (and change);
- Rising water tables/impeded drainage;
- Saltwater intrusion;
- Biological effects.
2. On the Climate Change—Current Status and the Future
- Global warming from fossil fuels.
- Melting ice caps and sea level rise.
- Ocean pollution.
- Ocean acidification.
- Groundwater salinity.
- Biodiversity loss.
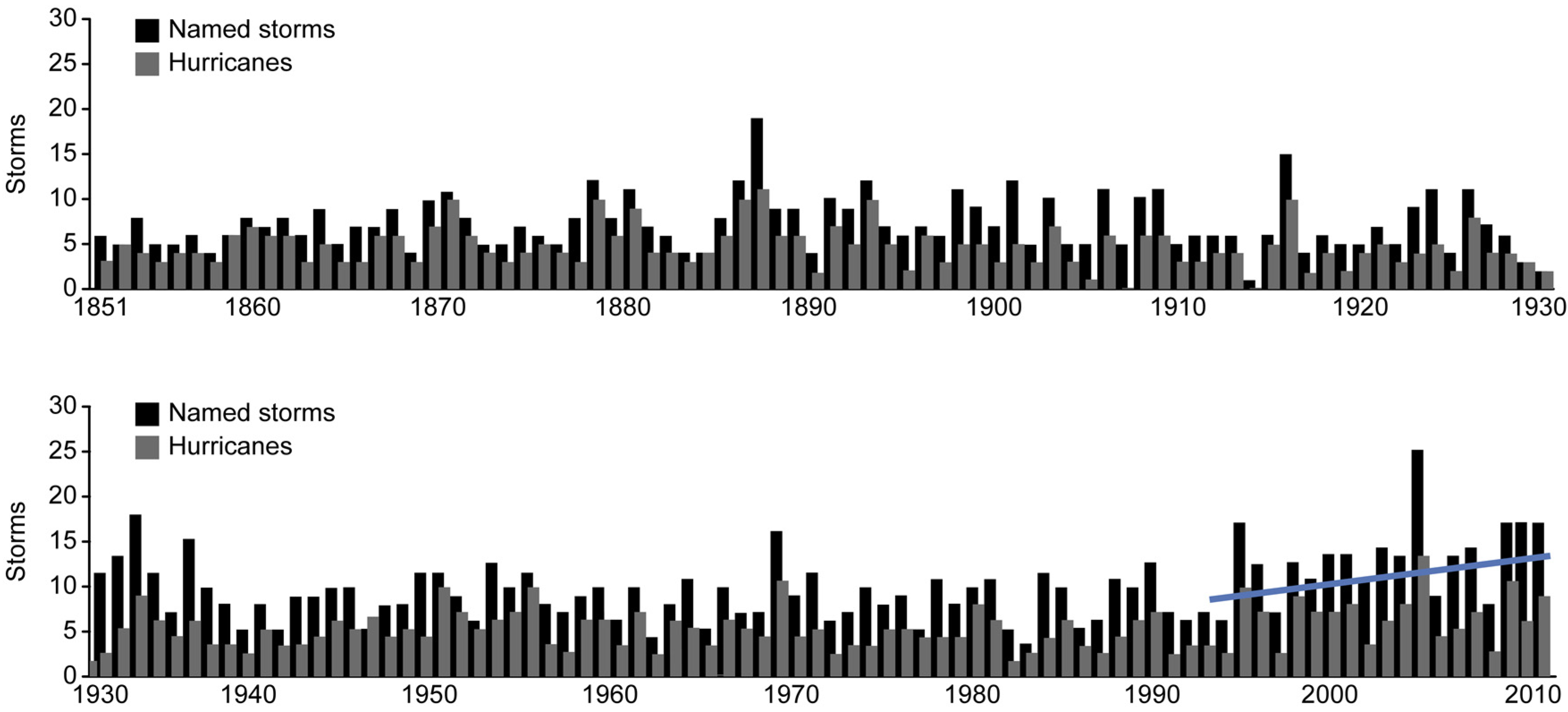
- Severe storms.
- Loss of climate regulation.
- Overfishing.
- Poor governance.
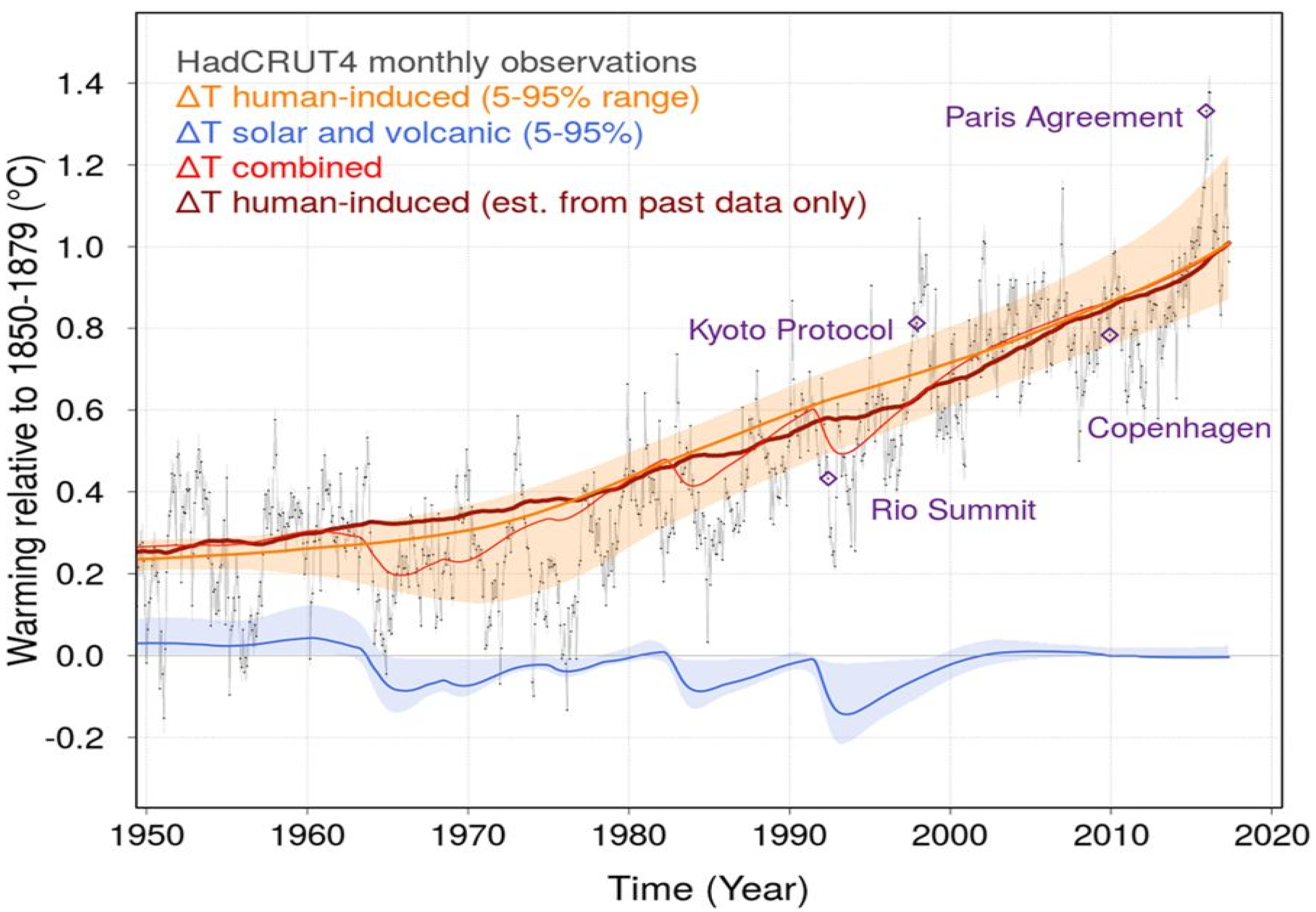
2.1. How Have Climate Issues Been Addressed in Recent Decades?
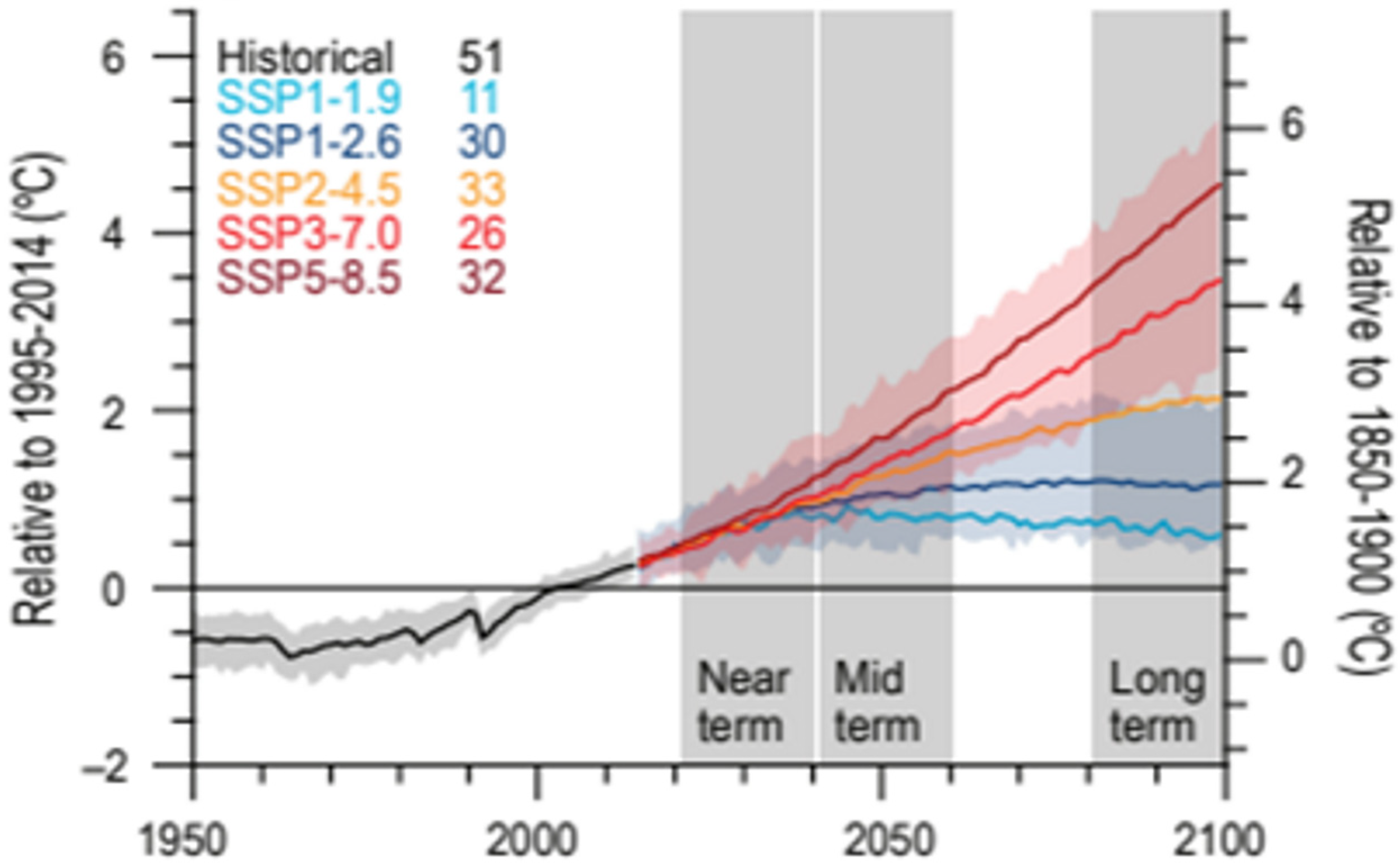
2.2. What Can We Expect from Ongoing Climate Change?
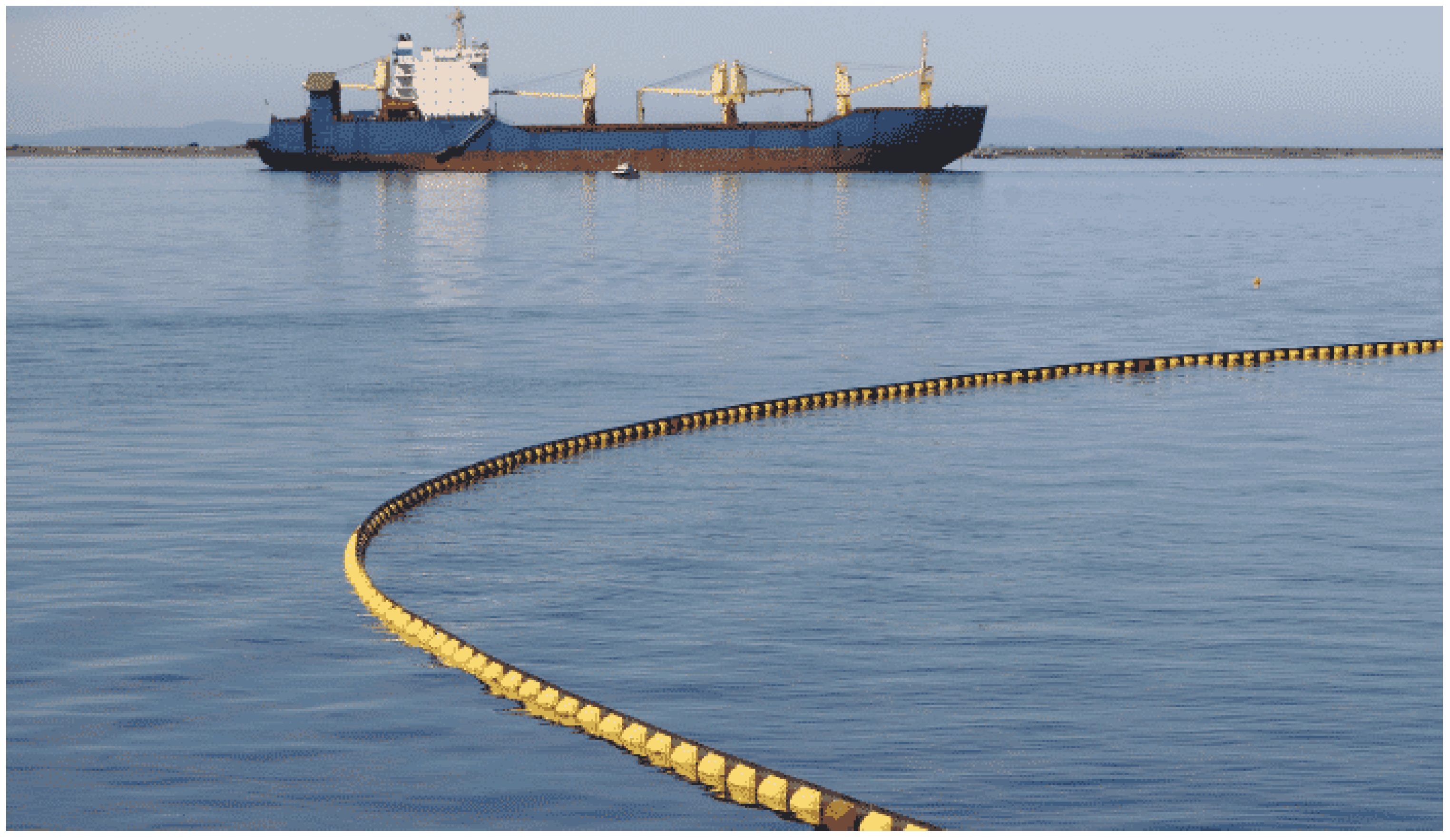
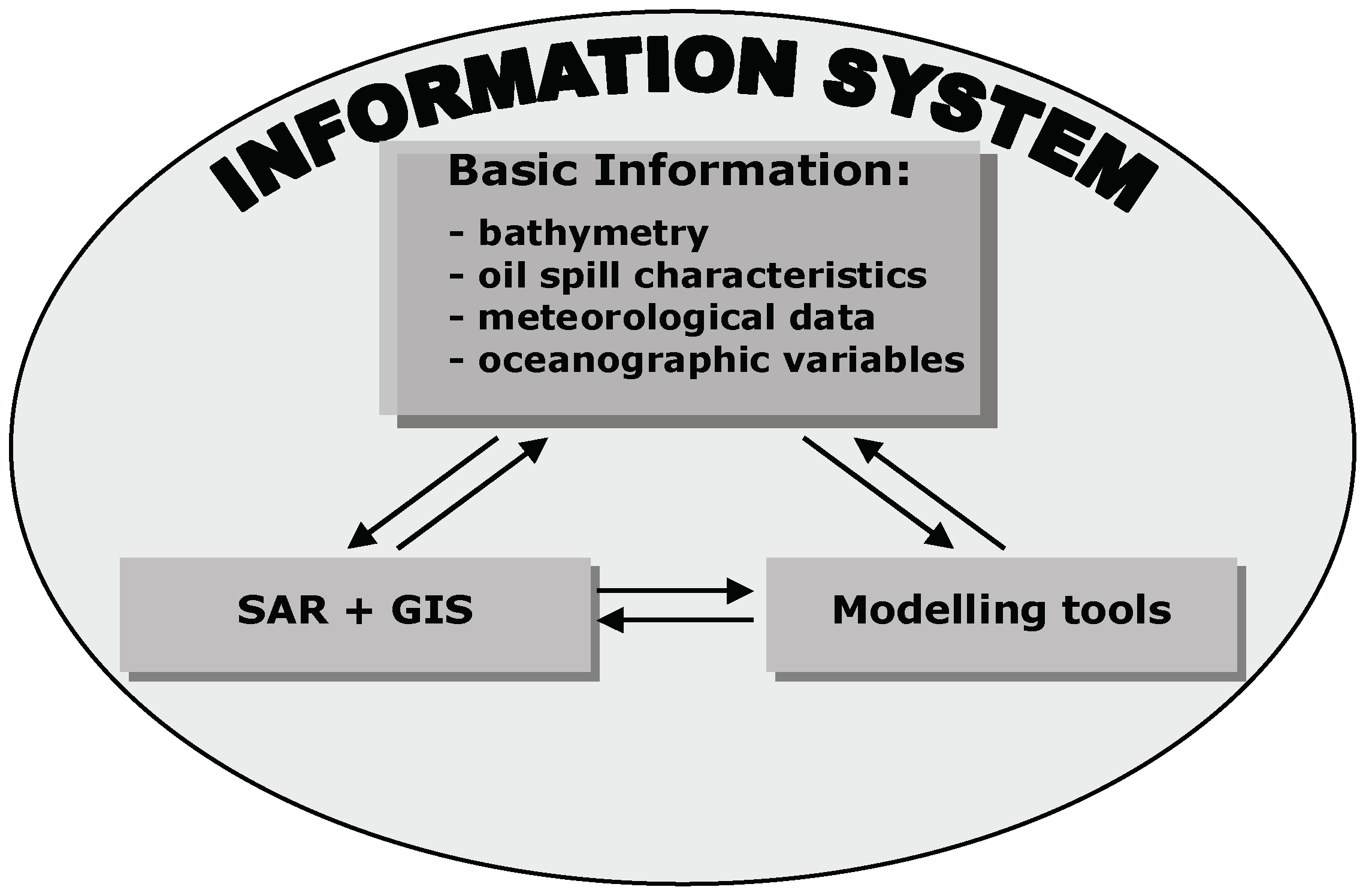
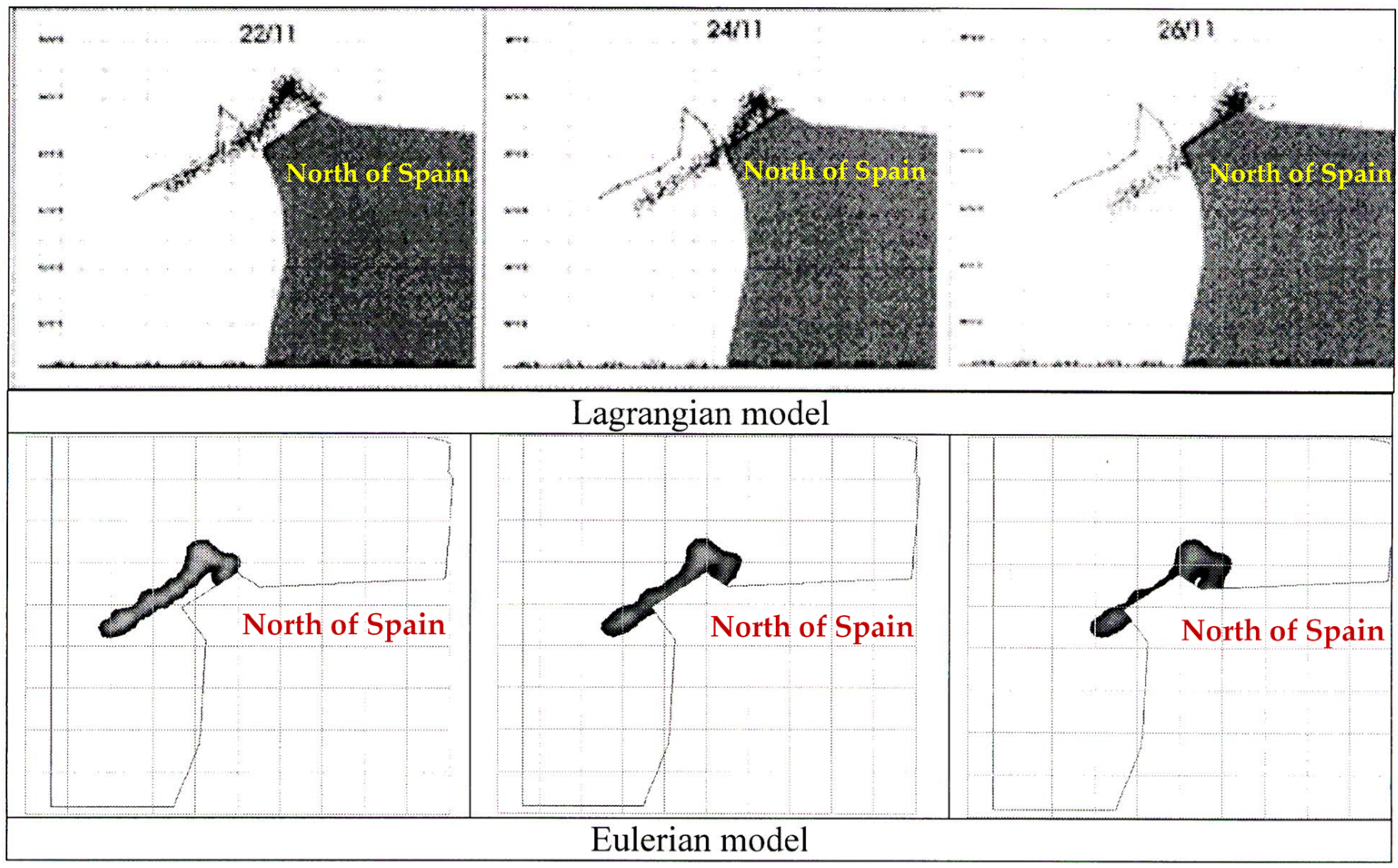
3. On the Ocean Pollution—Detection, Control, and Cleanup
- What is the position of the oil slick?
- Where is it heading?
- What is the state of the product?
4. In the Coastal Zone—Coastal Protection and Adaptation Measures
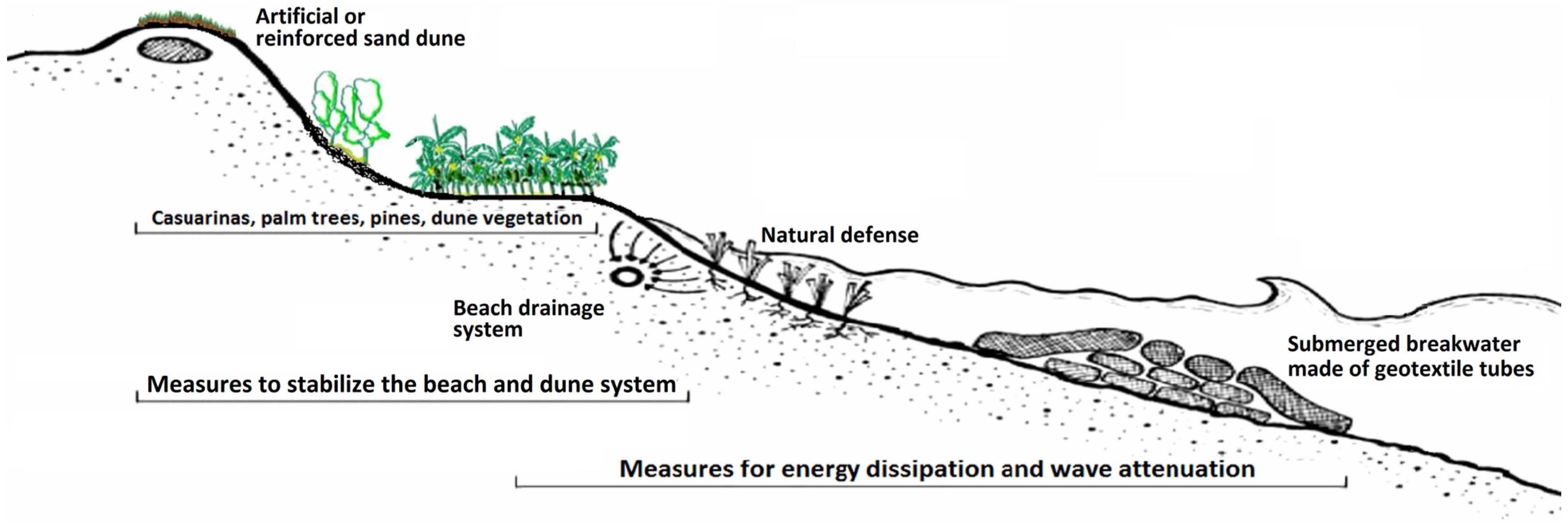
4.1. Coastal Protection—Traditional Approach
4.2. Adaptation Measures—Adaptive Management Process
- Technical effectiveness
- Costs
- Benefits
- Implementation
- Public institutions (local, regional, national);
- Technicians (engineers, geologists, biologists, economists, sociologists, lawyers, etc.);
- Nongovernmental organizations;
- Stakeholders;
- Businesspeople;
- Investors;
- Residents;
- Citizens, etc.
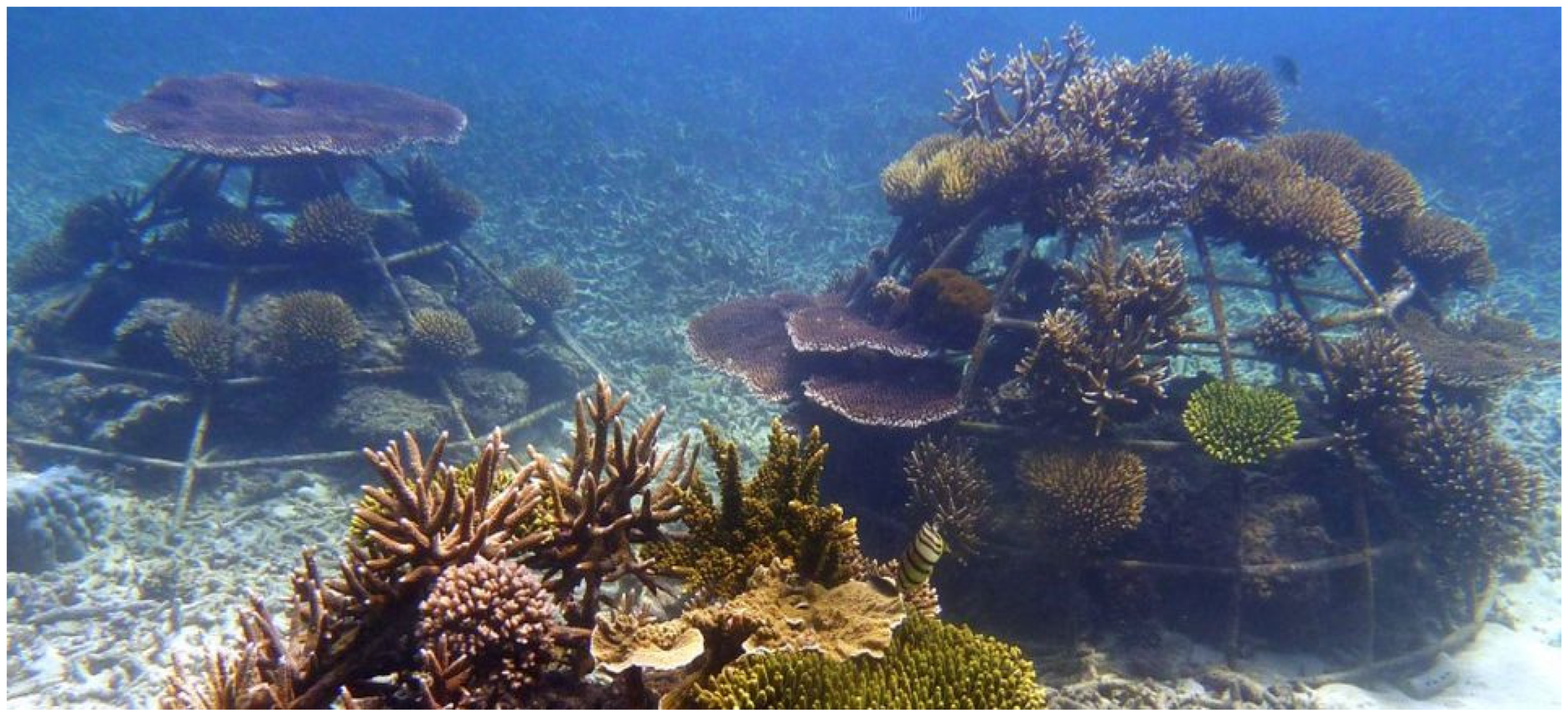
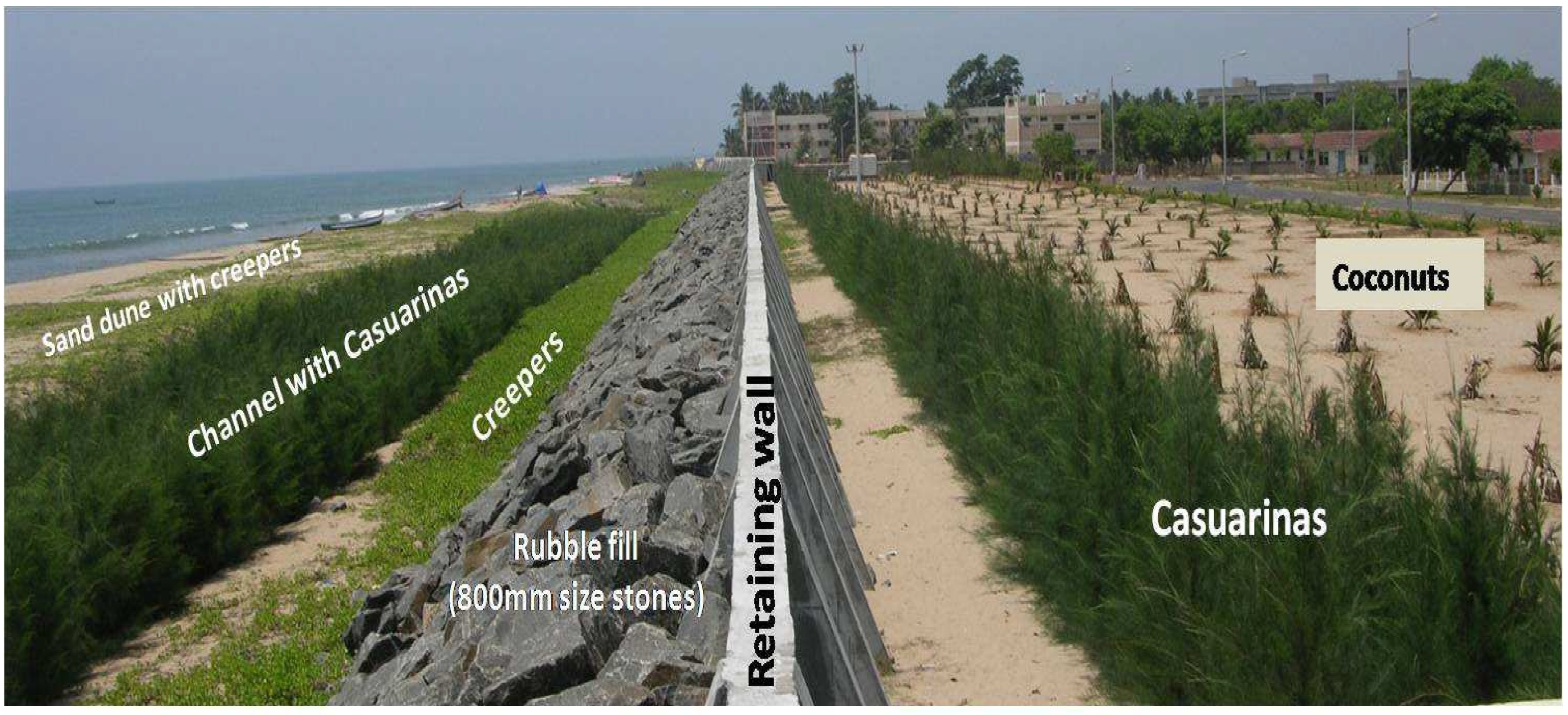
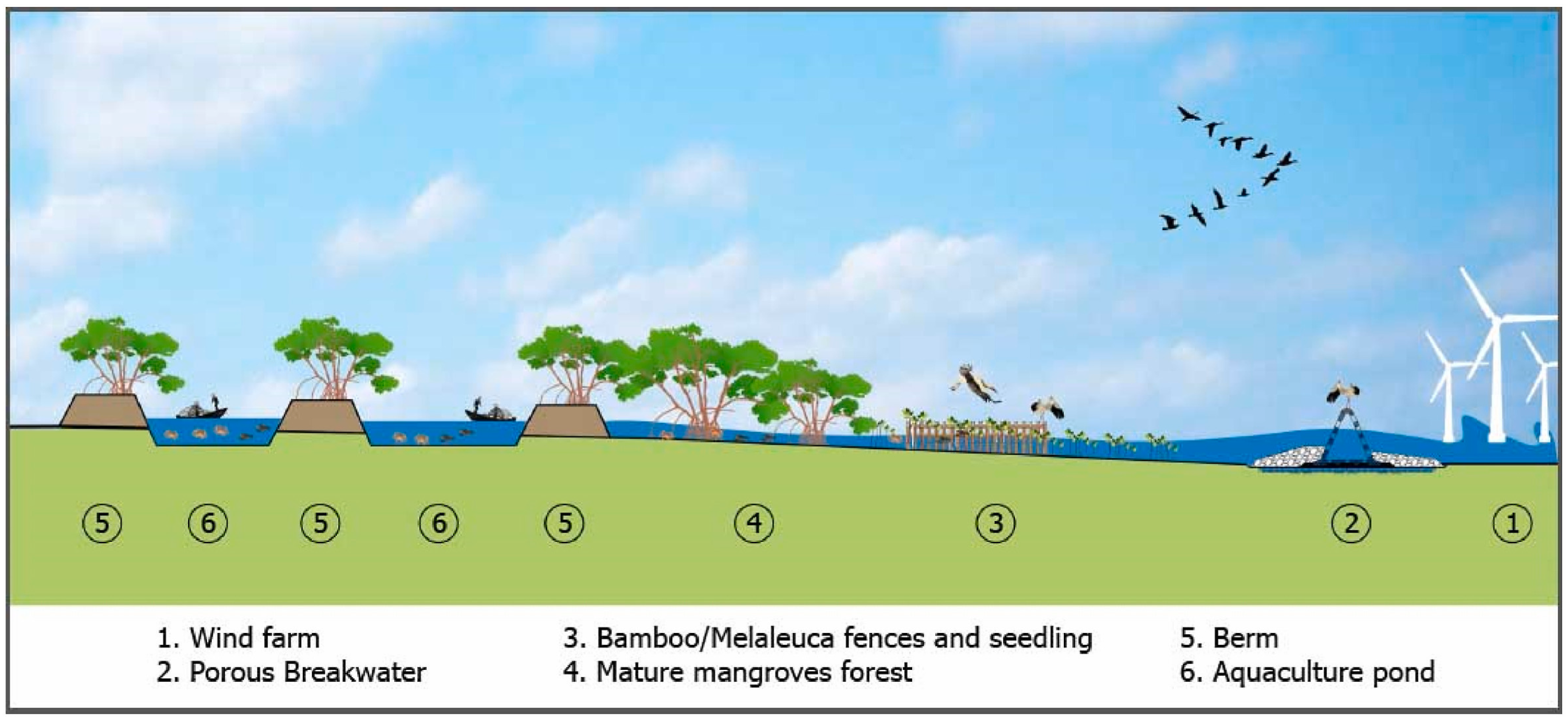
4.3. Adaptation Strategies—Ecofriendly and Balanced Multipurpose Solutions

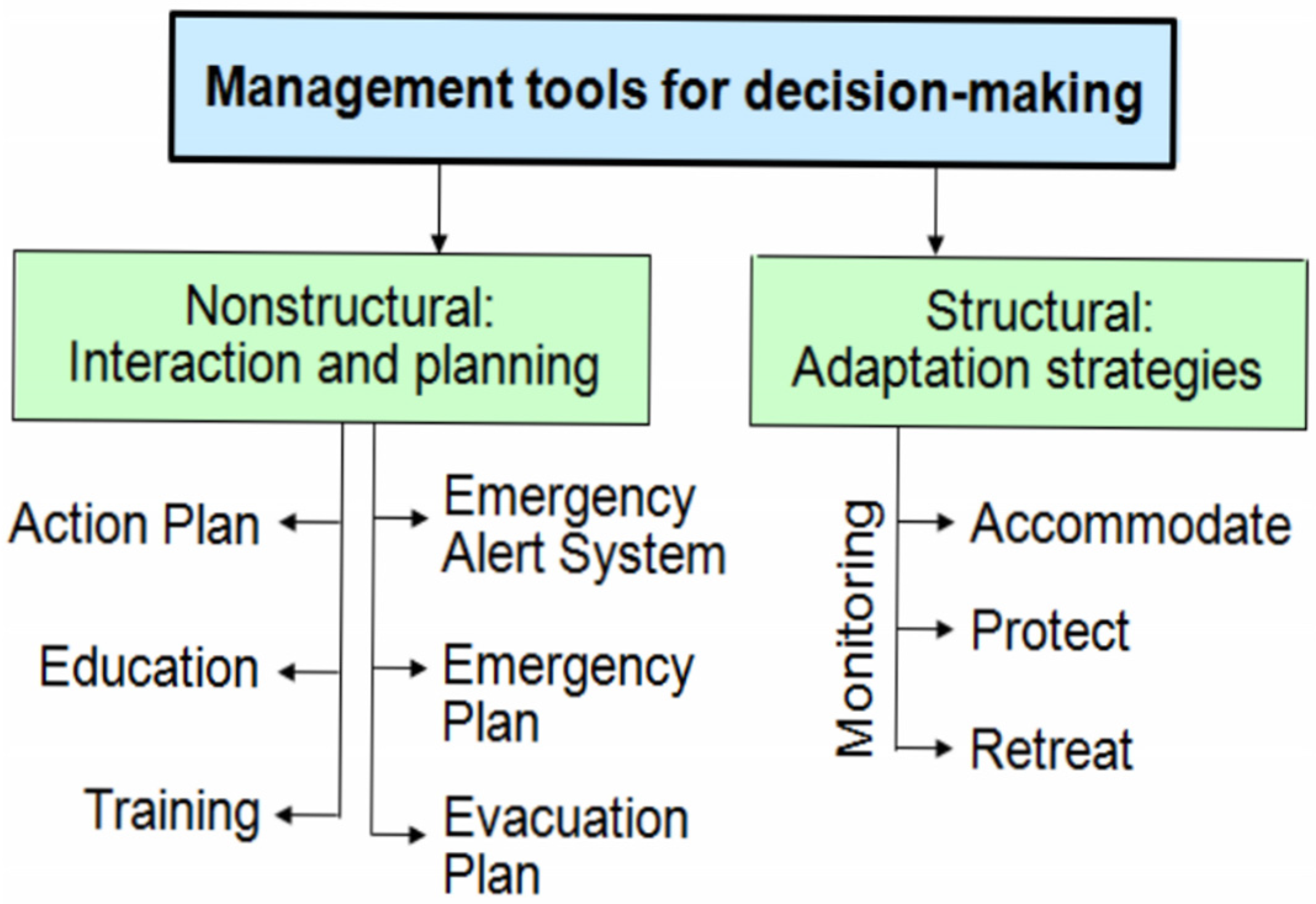
5. Discussion—Suitable Future Management for Decision Making
- Accommodation accepting risk:
- What is the risk?
- Is the risk acceptable?
- Protection at any cost:
- What are the consequences?
- Is soft protection enough?
- How long is it safe?
- Retreat to a safer place:
- How long is it safer?
- Are the costs acceptable and available?
6. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- EPA–United States Environmental Protection Agency. Climate Impacts on Coastal Areas 2017. Available online: https://19january2017snapshot.epa.gov/climate-impacts/climate-impacts-coastal-areas_.html (accessed on 21 August 2023).
- Antunes do Carmo, J.S. The changing paradigm of coastal management: The Portuguese case. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 695, 133807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmo, J.S.A.D. Climate Change, Adaptation Measures, and Integrated Coastal Zone Management: The New Protection Paradigm for the Portuguese Coastal Zone. J. Coast. Res. 2018, 34, 687–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, M.T. Pitfalls in developing coastal climate adaptation responses. Clim. Risk Manag. 2015, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seitz, R.D.; Wennhage, H.; Bergstrom, U.; Lipcius, R.N.; Ysebaert, T. Ecological value of coastal habitats for commercially and ecologically important species. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2014, 71, 648–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saengsupavanich, C.; Ratnayake, A.S.; Yun, L.S.; Ariffin, E.H. Current challenges in coastal erosion management for southern Asian regions: Examples from Thailand, Malaysia, and Sri Lanka. Anthr. Coasts 2023, 6, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, J.; Cardona, F.S.; Bio, A.; Ramos, S. Importance of Protection Service Against Erosion and Storm Events Provided by Coastal Ecosystems Under Climate Change Scenarios. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 726145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perricone, V.; Mutalipassi, M.; Mele, A.; Buono, M.; Vicinanza, D.; Contestabile, P. Nature-based and bioinspired solutions for coastal protection: An overview among key ecosystems and a promising pathway for new functional and sustainable designs. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2023, 80, 1218–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Airoldi, L.; Beck, M.W. Loss, Status and Trends for Coastal Marine Habitats of Europe. Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. Annu. Rev. 2007, 45, 345–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pörtner, H.-O.; Roberts, D.C.; Masson-Delmotte, V.; Zhai, P.; Tignor, M.; Poloczanska, E.; Mintenbeck, K.; Alegría, A.; Nicolai, M.; Okem, A.; et al. (Eds.) IPCC: Summary for Policymakers. In IPCC Special Report on the Ocean and Cryosphere in a Changing Climate; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 3–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manno, G.; Anfuso, G.; Messina, E.; Williams, A.T.; Suffo, M.; Liguori, V. Decadal evolution of coastline armouring along the Mediterranean Andalusia littoral (South of Spain). Ocean Coast. Manag. 2016, 124, 84–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinay, L.; Carter, R.W. Climate Change Adaptation Options for Coastal Communities and Local Governments. Climate 2020, 8, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagariba, C.J.; Song, S.; Baoro, S.K.G.S. Climate Change Adaptation Strategies and Constraints in Northern Ghana: Evidence of Farmers in Sissala West District. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griggs, G.; Reguero, B.G. Coastal Adaptation to Climate Change and Sea-Level Rise. Water 2021, 13, 2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabana, D.; Röfer, L.; Evadzi, P.; Celliers, L. Enabling Climate Change Adaptation in Coastal Systems: A Systematic Literature Review. Earth’s Future 2023, 11, e2023EF003713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cochrane, K.L.; Rakotondrazafy, H.; Aswani, S.; Chaigneau, T.; Downey-Breedt, N. Tools to Enrich Vulnerability Assessment and Adaptation Planning for Coastal Communities in Data-Poor Regions: Application to a Case Study in Madagascar. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 5, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnan, A.K.; Oppenheimer, M.; Garschagen, M.; Buchanan, M.K.; Duvat, V.K.E.; Forbes, D.L.; Ford, J.D.; Lambert, E.; Petzold, J.; Renaud, F.G.; et al. Sea level rise risks and societa adaptation benefts in low-lying coastal areas. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 10677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehvar, S.; Filatova, T.; Dastgheib, A.; van Steveninck, E.R.; Ranasinghe, R. Quantifying Economic Value of Coastal Ecosystem Services: A Review. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2018, 6, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EEA—European Environment Agency. What We Do. Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/en (accessed on 22 August 2023).
- USA TODAY. Available online: https://eu.usatoday.com/story/news/nation/2020/07/30/climate-change-coastal-flooding-cost-14-trillion-worldwide/5545712002/ (accessed on 23 August 2023).
- Gomes, M.P.; Pinho, J.L.; Carmo, J.S.A.D.; Santos, L. Hazard assessment of storm events for The Battery, New York. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2015, 118, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamarin, T.; Kaspi, Y. The poleward shift of storm tracks under global warming: A Lagrangian perspective. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 10666–10674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberato, M.L. The 19 January 2013 windstorm over the North Atlantic: Large-scale dynamics and impacts on Iberia. Weather Clim. Extrem. 2014, 5–6, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masselink, G.; Castelle, B.; Scott, T.; Dodet, G.; Suanez, S.; Jackson, D.; Floc’h, F. Extreme wave activity during 2013/2014 winter and morphological impacts along the Atlantic coast of Europe. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 2135–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebbe, T.B.; Rey-Valette, H.; Chaumillon, E.; Camus, G.; Almar, R. Designing coastal adaptation strategies to tackle sea level rise. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 740602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton-Grier, A.S.; Wowk, K.; Bamford, H. Future of our coasts: The potential for natural and hybrid infrastructure to enhance the resilience of our coastal communities, economies and ecosystems. Environ. Sci. Policy 2015, 51, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.; Baek, S.; Kwon, Y.; Lee, J.; Cha, S.M.; Kwon, S. Improved Coastal Erosion Prevention Using a Hybrid Method with an Artificial Coral Reef: Large-Scale 3D Hydraulic Experiment. Water 2020, 12, 2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palinkas, C.M.; Orton, P.; Hummel, M.A.; Nardin, W.; Sutton-Grier, A.E. Innovations in Coastline Management With Natural and Nature-Based Features (NNBF): Lessons Learned From Three Case Studies. Front. Built. Environ. 2022, 8, 814180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mölter, T.; Schindler, D.; Albrecht, A.T.; Kohnle, U. Review on the Projections of Future Storminess over the North Atlantic European Region. Atmosphere 2016, 7, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC—Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Special Report Emissions Scenarios 2000. Available online: https://www.ipcc.ch/site/assets/uploads/2018/03/sres-en.pdf (accessed on 24 August 2023).
- Lee, J.-Y.; Marotzke, J.; Bala, G.; Cao, L.; Corti, S.; Dunne, J.P.; Engelbrecht, F.; Fischer, E.; Fyfe, J.C.; Jones, C.; et al. Future Global Climate: Scenario-Based Projections and Near-Term Information. In Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Masson-Delmotte, V., Zhai, P., Pirani, A., Connors, S.L., Péan, C., Berger, S., Caud, N., Chen, Y., Goldfarb, L., Gomis, M., et al., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 553–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC—Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Climate Change 2023: Synthesis Report 2023. Summary for Policymakers. Available online: https://biodiv.mnhn.fr/news/2023-ipcc-synthesis-report-summary-policymakers (accessed on 22 August 2023).
- IPCC—Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. AR6 Synthesis Report: Climate Change 2023. Available online: https://www.ipcc.ch/report/ar6/syr/ (accessed on 22 August 2023).
- Simmons, A.J. Trends in the tropospheric general circulation from 1979 to 2022. Weather Clim. Dyn. 2022, 3, 777–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ESA—The European Space Agency. ESA Climate Office. Sea Level. Available online: https://climate.esa.int/en/projects/sea-level/ (accessed on 24 August 2023).
- The Royal Society. Climate Change Evidence & Causes. An Overview from the Royal Society and the US National Academy of Sciences, Update 2020. Available online: https://royalsociety.org/~/media/Royal_Society_Content/policy/projects/climate-evidence-causes/climate-change-evidence-causes.pdf (accessed on 24 August 2023).
- Sterr, H.; Klein, R.; Reese, S. Climate Change and Coastal Zones: An Overview of the State-of-the-Art on Regional and Local Vulnerability Assessment, Nota di Lavoro No. 38. 2000. Fondazione Eni Enrico Mattei (FEEM), Milan. Available online: https://www.econstor.eu/bitstream/10419/155092/1/NDL2000-038.pdf (accessed on 24 August 2023).
- Nicholls, R.J. Case Study on Sea-Level Rise Impacts. OECD Workshop on the Benefits of Climate Policy: Improving Information for Policy Makers 2003. Available online: https://www.oecd.org/env/cc/2483213.pdf (accessed on 25 August 2023).
- Lloyd-Smith, M.; Immig, J. Ocean Pollutants Guide: Toxic Threats to Human Health and Marine Life 2018. IPEN for a Toxics-Free Future. Available online: https://ipen.org/sites/default/files/documents/ipen-ocean-pollutants-v2_1-en-web.pdf (accessed on 25 August 2023).
- UNESCO—United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization. Ocean Plastic Pollution an Overview: Data and Statistics. Available online: https://oceanliteracy.unesco.org/plastic-pollution-ocean/ (accessed on 24 August 2023).
- EIA—U.S. Energy Information and Administration. Trends in U.S. Oil and Natural Gas Upstream Costs. 2016. Available online: https://www.eia.gov/analysis/studies/drilling/pdf/upstream.pdf (accessed on 24 August 2023).
- Amaechi, C.V.; Reda, A.; Butler, H.O.; Ja’e, I.A.; An, C. Review on Fixed and Floating Offshore Structures. Part I: Types of Platforms with Some Applications. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NOAA—National Oceanic Atmospheric Administration. Oil Spills. Available online: https://www.noaa.gov/education/resource-collections/ocean-coasts/oil-spills (accessed on 25 August 2023).
- Antunes do Carmo, J.S.; Pinho, J.S.; Vieira, J.P. Oil spills in coastal zones: Environmental impacts and practical mitigating solutions. In Proceedings of the 12th International Congress of the International Maritime Association of the Mediterranean, IMAM 2005—Maritime Transportation and Exploitation of Ocean and Coastal Resources, Lisboa, Portugal, 26–30 September 2005; Volume 2, pp. 1689–1696. [Google Scholar]
- ITOFT—International Tanker Owners Pollution Federation. Oil Tanker Spill Statistics 2022. Available online: https://www.itopf.org/knowledge-resources/data-statistics/statistics/ (accessed on 25 August 2023).
- NOAA—How Oil Harms Animals and Plants in Marine Environments. Available online: https://response.restoration.noaa.gov/oil-and-chemical-spills/oil-spills/how-oil-harms-animals-and-plants-marine-environments.html (accessed on 25 August 2023).
- Chen, X.; Bi, H.; Yue, R.; Chen, Z.; An, C. Effects of oil characteristics on the performance of shoreline response operations: A review. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 1033909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haustein, K.; Allen, M.R.; Forster, P.M.; Otto, F.E.L.; Mitchell, D.M.; Matthews, H.D.; Frame, D.J. A real-time Global Warming Index. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasselmann, K. Multi-pattern fingerprint method for detection and attribution of climate change. Clim. Dyn. 1997, 13, 601–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CCPI: Climate Change Performance Index. CCPI 2023: Ranking and Results. Available online: https://www.ccpi.org (accessed on 27 August 2023).
- Burck, J.; Uhlich, T.; Bals, C.; Hohne, N.; Nascimento, L.; Tavares, M.; Strietzel, E. Climate Change Performance Index 2023. Available online: https://ccpi.org/download/climate-change-performance-index-2023/ (accessed on 27 August 2023).
- EPA—United States Environmental Protection Agency. Climate Change Science. Future of Climate Change. Available online: https://climatechange.chicago.gov/climate-change-science/future-climate-change#Temperature (accessed on 26 August 2023).
- UCAR—University Corporation for Atmospheric Research. Predictions of Future Global Climate. Available online: https://scied.ucar.edu/learning-zone/climate-change-impacts/predictions-future-global-climate (accessed on 28 August 2023).
- Zhu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Yan, X.; Guan, Q.; Zhong, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, D. Oil Spill Contextual and Boundary-Supervised Detection Network Based on Marine SAR Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5213910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wan, J.; Liu, S.; Chen, Y.; Yasir, M.; Xu, M.; Ren, P. BO-DRNet: An Improved Deep Learning Model for Oil Spill Detection by Polarimetric Features from SAR Images. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Xu, J.; Wu, P.; Kong, P. Oil Spill Detection Based on Deep Convolutional Neural Networks Using Polarimetric Scattering Information From Sentinel-1 SAR Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Li, J.; Li, B.; Jin, Y.; Miao, S. Marine Oil Spill Detection from Low-Quality SAR Remote Sensing Images. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafirakou, A.; Palantzas, G.; Samaras, A.; Koutitas, C. Oil Spill Modeling Aiming at the Protection of Ports and Coastal Areas. Environ. Process. 2015, 2 (Suppl. S1), S41–S53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inan, A. Modeling of Oil Pollution in Derince Harbor. J. Coast. Res. 2011, 64, 894–898. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/26482302 (accessed on 27 August 2023).
- Cho, Y.-S.; Kim, T.-K.; Jeong, W.; Ha, T. Numerical Simulation of Oil Spill in Ocean. J. Appl. Math. 2012, 2012, e681585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-D.; Shen, Y.-M.; Guo, Y.-K.; Tang, J. Three-dimensional numerical simulation for transport of oil spills in seas. Ocean Eng. 2008, 35, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iouzzi, N.; Ben Meftah, M.; Haffane, M.; Mouakkir, L.; Chagdali, M.; Mossa, M. Modeling of the Fate and Behaviors of an Oil Spill in the Azemmour River Estuary in Morocco. Water 2023, 15, 1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WEO—World Energy Outlook Special Report 2018. Available online: https://www.iea.org/reports/offshore-energy-outlook-2018 (accessed on 27 August 2023).
- Marine Insight. Understanding Oil Spill at Sea: Drills, Prevention and Methods of Cleanup. Available online: https://www.marineinsight.com/environment/what-is-an-oil-spill-at-sea/ (accessed on 29 August 2023).
- Kraus, N.C.; Dougal, W.G. The Effects of Seawalls on the Beach: Part I, An Updated Literature Review. J. Coast. Res. 1996, 12, 691–701. [Google Scholar]
- Dean, R.G.; Chen, R.; Browder, A.E. Full scale monitoring study of a submerged breakwater, Palm Beach, Florida, USA. Coast. Eng. 1997, 29, 291–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granja, H.M.; Carvalho, G.S. Is the Coastline "Protection" of Portugal by Hard Engineering Structures Effective? J. Coast. Res. 2009, 11, 1229–1241. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/4298426 (accessed on 27 August 2023).
- Schoonees, T.; Mancheño, A.G.; Scheres, B.; Bouma, T.J.; Silva, R.; Schlurmann, T.; Schüttrumpf, H. Hard Structures for Coastal Protection, Towards Greener Designs. Estuaries Coasts 2019, 42, 1709–1729. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/48703231 (accessed on 27 August 2023). [CrossRef]
- DELOS. Environment Design of Low Crested Defence Structures. EU Fifth Framework Programme 1998–2002. Energy, Environment and Sustainable Development 2004. Available online: www.delos.unibo.it (accessed on 27 August 2023).
- Antunes do Carmo, J.S. Coastal Defenses and Engineering Works. In Encyclopedia of the UN Sustainable Development Goals; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, B.K.; Szaro, R.C.; Shapiro, C.D. Adaptive Management. The U.S. Department of the Interior Technical Guide 2009 Edition. Available online: https://www.doi.gov/sites/doi.gov/files/uploads/TechGuide-WebOptimized-2.pdf (accessed on 29 August 2023).
- Williams, B.K.; Brown, E.D. Double-Loop Learning in Adaptive Management: The Need, the Challenge, and the Opportunity. Environ. Manag. 2018, 62, 995–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Arsdale. Online Textbook, Chapter 10, Coral Reefs 2020. Available online: https://mrvanarsdale.com/marine-science/online-textbook/chapter-10-coral-reefs/ (accessed on 29 August 2023).
- Reguero, B.G.; Storlazzi, C.D.; Gibbs, A.E.; Shope, J.B.; Cole, A.D.; Cumming, K.A.; Beck, M.W. The value of US coral reefs for flood risk reduction. Nat. Sustain. 2021, 4, 688–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- New Heaven. Artificial Reefs: What Works and What Doesn’t. Available online: https://newheavenreefconservation.org/marine-blog/147-artificial-reefs-what-works-and-what-doesn-t (accessed on 29 August 2023).
- Armono, H.D.; Hall, K.R. Wave transmission on submerged breakwaters made of hollow hemispherical shape artificial reefs. In Proceedings of the Annual Conference—Canadian Society for Civil Engineering, Moncton, NB, Canada, 4 June 2003; pp. 313–322. [Google Scholar]
- Buccino, M.; Del Vita, I.; Calabrese, M. Predicting wave transmission past Reef Ball™submerged breakwaters. J. Coast. Res. 2013, 65, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srisuwan, C.; Rattanamanee, P. Modeling of Seadome as artificial reefs for coastal wave attenuation. Ocean Eng. 2015, 103, 198–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Gent, M.R.; Buis, L.; Bos, J.P.V.D.; Wüthrich, D. Wave transmission at submerged coastal structures and artificial reefs. Coast. Eng. 2023, 184, 104344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reguero, B.G.; Beck, M.W.; Agostini, V.N.; Kramer, P.; Hancock, B. Coral reefs for coastal protection: A new methodological approach and engineering case study in Grenada. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 210, 146–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, A.; Pinho, J.L.S.; Valente, T.; do Carmo, J.S.A.; Hegde, A. Performance Assessment of a Semi-Circular Breakwater through CFD Modelling. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, A.; Qin, J.; Rubinato, M.; Sun, T.; Wang, M.; Wang, S.; Wang, L.; Zhu, J.; Zhu, F. An Experimental Investigation of Turbulence Features Induced by Typical Artificial M-Shaped Unit Reefs. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, L.E. Artificial Reefs for Ecosystem Restoration and Coastal Erosion Protection with Aquaculture and Recreational Amenities. Reef J. 2009, 1, 235–246. Available online: https://www.thereefjournal.com/files/18._Harris.pdf (accessed on 30 August 2023).
- Hoegh-Guldberg, O.; Poloczanska, E.S.; Skirving, W.; Dove, S. Coral Reef Ecosystems under Climate Change and Ocean Acidification. Front. Mar. Sci. 2017, 4, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yip, M. An Overview of Artificial Reefs, Advantages and Disadvantages of Artificial Reefs Design, Material and Concepts of Realization around the Globe 1998. Available online: https://biophysics.sbg.ac.at/ar/reef.htm (accessed on 30 August 2023).
- Voorde, M.T.; Carmo, J.S.A.D.; Neves, M.G. Designing a Preliminary Multifunctional Artificial Reef to Protect the Portuguese Coast. J. Coast. Res. 2009, 25, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, I.; Tinoco, H.; Aragonés, L.; García-Barba, J. The multifunctional artificial reef and its role in the defence of the Mediterranean coast. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 550, 910–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendonça, A.; Fortes, C.J.; Capitão, R.; Neves, M.d.G.; Moura, T.; Carmo, J.S.A.D. Wave hydrodynamics around a multi-functional artificial reef at Leirosa. J. Coast. Conserv. 2012, 16, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmo, J.A.D.; Reis, C.S.; Freitas, H. Working with Nature by Protecting Sand Dunes: Lessons Learned. J. Coast. Res. 2010, 26, 1068–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, P.; Gordon, A.; Lord, D.; Mariani, A.; Nielsen, L.; Panayotou, K.; Rogers, M.; Tomlinson, R. Climate change adaptation guidelines in coastal management and planning. In The National Committee on Coastal and Ocean Engineering 2012; Engineers Australia: Crows Nest, Australia; ISBN 9780858259591. (ebook:pdf).
- Le Xuan, T.; Ba, H.T.; Thanh, V.Q.; Wright, D.P.; Tanim, A.H.; Anh, D.T. Evaluation of coastal protection strategies and proposing multiple lines of defense under climate change in the Mekong Delta for sustainable shoreline protection. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2022, 228, 106301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackledge, J.; Coyle, E.; Kearney, E.; McGuirk, D.; Norton, B. Estimation of wave energy from wind velocity. IAENG Eng. Lett. 2013, 4, 158–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abanades, J.; Flor-Blanco, G.; Flor, G.; Iglesias, G. Dual wave farms for energy production and coastal protection. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2018, 160, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Delgado, C.; Bergillos, R.J.; Ortega-Sánchez, M.; Iglesias, G. Wave farm effects on the coast: The alongshore position. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 640–641, 1176–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carmo, J.S.A.D. Living on the Coast in Harmony with Natural Processes. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 2113. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11112113
Carmo JSAD. Living on the Coast in Harmony with Natural Processes. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2023; 11(11):2113. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11112113
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarmo, José Simão Antunes Do. 2023. "Living on the Coast in Harmony with Natural Processes" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 11, no. 11: 2113. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11112113
APA StyleCarmo, J. S. A. D. (2023). Living on the Coast in Harmony with Natural Processes. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 11(11), 2113. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11112113











