Potential Applications of Whisker Sensors in Marine Science and Engineering: A Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Typical Categories of Whisker Sensors
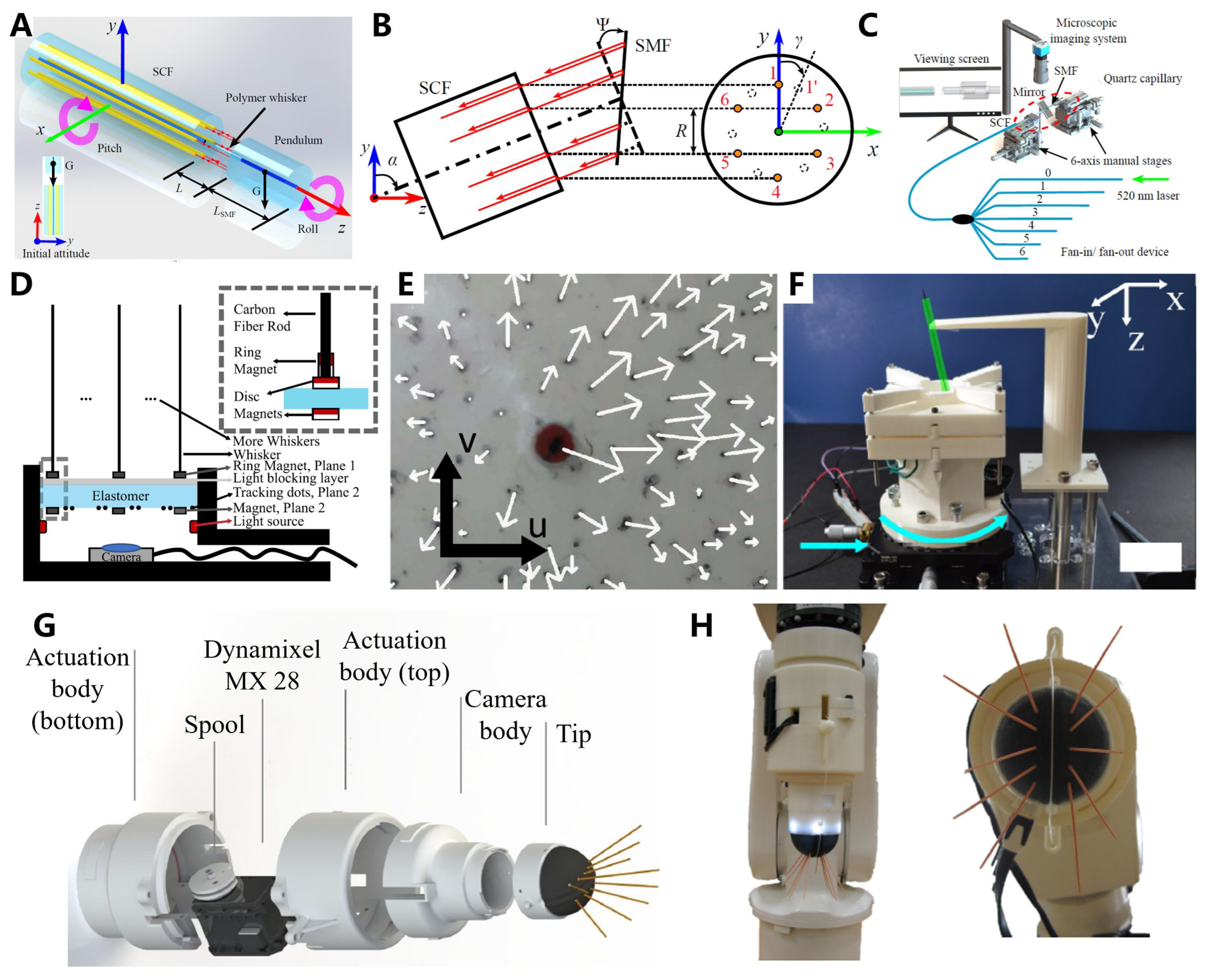
2.1. Optical Whisker Sensors
2.2. Magnetic Whisker Sensors
2.3. Resistive Whisker Sensors
2.4. Capacitive Whisker Sensors
2.5. Piezoelectric Whisker Sensors
2.6. Triboelectric Whisker Sensors
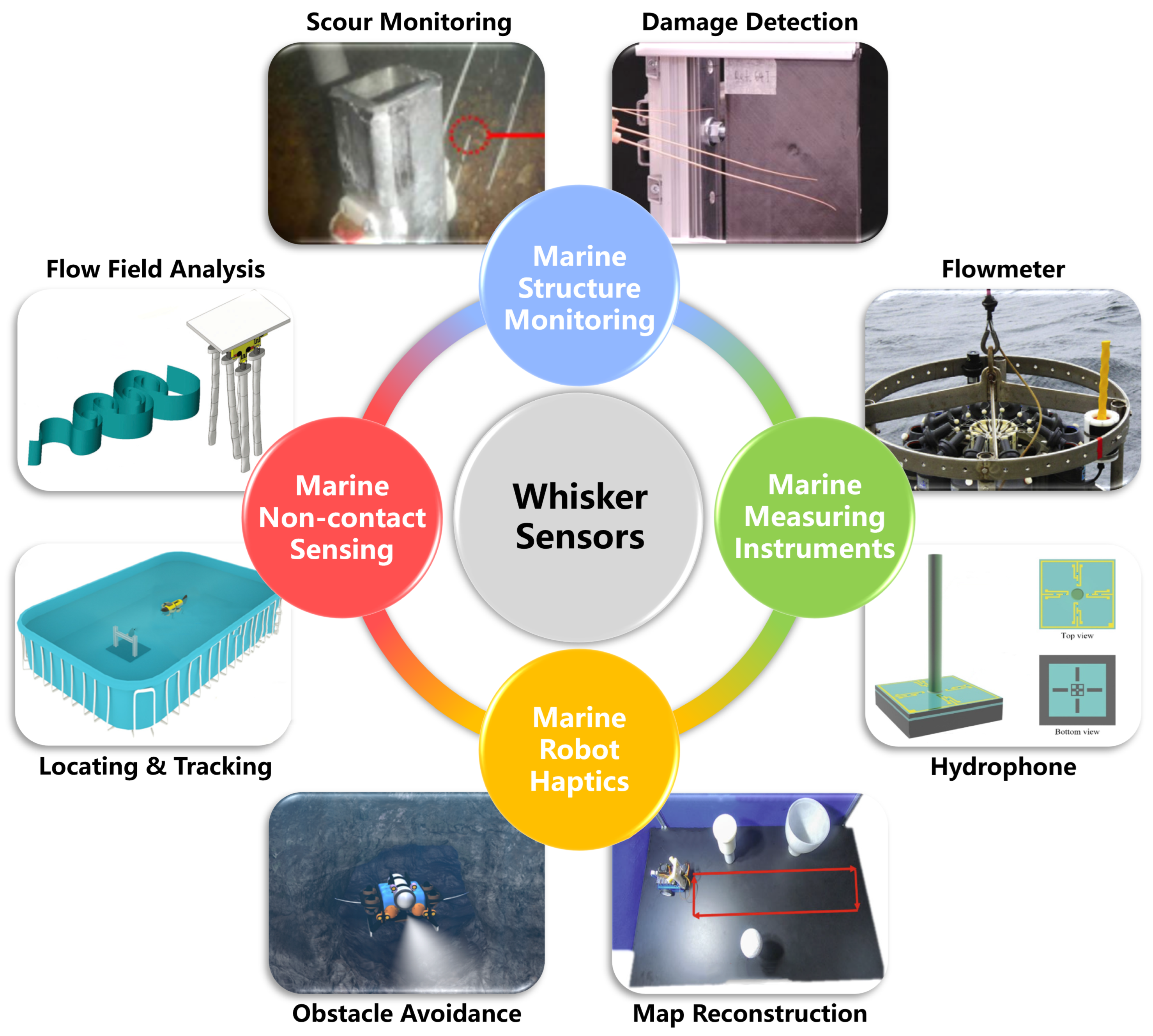
3. Potential Applications of Whisker Sensors in Marine Science and Engineering
3.1. Marine Structure Monitoring
3.2. Marine Measuring Instruments
3.3. Marine Robot Tactile Perception
3.4. Marine Non-Contact Environmental Sensing
4. Challenges and Future Perspectives
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ROV | Remotely Operated Vehicles |
| SCF | Seven-core optical Fiber |
| PDMS | Polydimethylsiloxane |
| PCB | Printed Circuit Board |
| PLA | Polylactic Acid |
| PVDF | Polyvinylidene Difluoride |
| PZT | Lead Zirconium Titanate |
| TENG | Triboelectric Nanogenerator |
| FEP | Fluorinated Ethylene Propylene |
| CPP | Cast Polypropylene |
| BVID | Barely Visible Impact Damage |
| LVI | Low-velocity Impact |
| SVM | Support Vector Machine |
| USDOT | U.S. Department of Transportation |
| VLS | Vapor–liquid–solid method |
| IC | Integrated Circuit |
| SLAM | Simultaneous Localization and Mapping |
| MEMS | Micro-electromechanical Systems |
| AGV | Autonomous Guided Vehicle |
| BWMR | Biomimetic Whisker Mechanoreceptor |
| BWS | Bionic Whisker Sensor |
| VIV | Vortex-induced Vibration |
| WIV | Flow-induced Vibration |
| WIDTS | Wake Information Detection and Tracking System |
| UBWS | Underwater Bionic Whisker Sensor |
| LiDAR | Light Detection And Ranging |
| IoT | Internet of Things |
References
- Spencer, B., Jr.; Ruiz-Sandoval, M.E.; Kurata, N. Smart sensing technology: Opportunities and challenges. Struct. Control Health Monit. 2004, 11, 349–368. [Google Scholar]
- Sladen, A.; Rivet, D.; Ampuero, J.P.; De Barros, L.; Hello, Y.; Calbris, G.; Lamare, P. Distributed sensing of earthquakes and ocean-solid Earth interactions on seafloor telecom cables. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5777. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gao, W.; Emaminejad, S.; Nyein, H.Y.Y.; Challa, S.; Chen, K.; Peck, A.; Fahad, H.M.; Ota, H.; Shiraki, H.; Kiriya, D.; et al. Fully integrated wearable sensor arrays for multiplexed in situ perspiration analysis. Nature 2016, 529, 509–514. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Gui, F. The Application and Research of New Digital Technology in Marine Aquaculture. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 401. [Google Scholar]
- Mohsan, S.A.H.; Li, Y.; Sadiq, M.; Liang, J.; Khan, M.A. Recent Advances, Future Trends, Applications and Challenges of Internet of Underwater Things (IoUT): A Comprehensive Review. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 124. [Google Scholar]
- Campagnaro, F.; Steinmetz, F.; Renner, B.C. Survey on Low-Cost Underwater Sensor Networks: From Niche Applications to Everyday Use. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 125. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, J.S. Sensor Technology Handbook; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Chaste, J.; Eichler, A.; Moser, J.; Ceballos, G.; Rurali, R.; Bachtold, A. A nanomechanical mass sensor with yoctogram resolution. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2012, 7, 301–304. [Google Scholar]
- Bayley, H.; Cremer, P.S. Stochastic sensors inspired by biology. Nature 2001, 413, 226–230. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, D.; Pikhitsa, P.V.; Choi, Y.W.; Lee, C.; Shin, S.S.; Piao, L.; Park, B.; Suh, K.Y.; Kim, T.I.; Choi, M. Ultrasensitive mechanical crack-based sensor inspired by the spider sensory system. Nature 2014, 516, 222–226. [Google Scholar]
- Sabri, N.; Aljunid, S.; Salim, M.; Ahmad, R.B.; Kamaruddin, R. Toward optical sensors: Review and applications. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2013, 423, 012064. [Google Scholar]
- Breazeal, C.; Scassellati, B. Robots that imitate humans. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2002, 6, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kundu, T. Acoustic source localization. Ultrasonics 2014, 54, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akyildiz, I.F.; Pompili, D.; Melodia, T. Underwater acoustic sensor networks: Research challenges. Ad Hoc Netw. 2005, 3, 257–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwana, M.I.; Redmond, S.J.; Lovell, N.H. A review of tactile sensing technologies with applications in biomedical engineering. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2012, 179, 17–31. [Google Scholar]
- Dahiya, R.S.; Metta, G.; Valle, M.; Sandini, G. Tactile sensing—From humans to humanoids. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2009, 26, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Xie, D.; Li, Z.; Zhu, H. Recent advances in wearable tactile sensors: Materials, sensing mechanisms, and device performance. Mater. Sci. Eng. Rep. 2017, 115, 1–37. [Google Scholar]
- Yousef, H.; Boukallel, M.; Althoefer, K. Tactile sensing for dexterous in-hand manipulation in robotics—A review. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2011, 167, 171–187. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, L.A.; Sarter, N.B. Tactile displays: Guidance for their design and application. Hum. Factors 2008, 50, 90–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fettweis, G.P. The tactile internet: Applications and challenges. IEEE Veh. Technol. Mag. 2014, 9, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, P.M.; Ackland, H.M.; Lowery, A.J.; Rosenfeld, J.V. Restoration of vision in blind individuals using bionic devices: A review with a focus on cortical visual prostheses. Brain Res. 2015, 1595, 51–73. [Google Scholar]
- Pearson, M.J.; Mitchinson, B.; Sullivan, J.C.; Pipe, A.G.; Prescott, T.J. Biomimetic vibrissal sensing for robots. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2011, 366, 3085–3096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Pei, Y.; Zhang, C.; Kottapalli, A.G.P. Bioinspired designs and biomimetic applications of triboelectric nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2021, 84, 105865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Song, X.; Li, X.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, C.; Zhou, Q.; Chen, Y. Recent progress in biomimetic additive manufacturing technology: From materials to functional structures. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1706539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayegh, M.A.; Daraghma, H.; Mekid, S.; Bashmal, S. Review of recent bio-inspired design and manufacturing of whisker tactile sensors. Sensors 2022, 22, 2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beem, H.R.; Triantafyllou, M.S. Wake-induced ‘slaloming’ response explains exquisite sensitivity of seal whisker-like sensors. J. Fluid Mech. 2015, 783, 306–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholz, G.R.; Rahn, C.D. Profile sensing with an actuated whisker. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 2004, 20, 124–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijaya, J.A.; Russell, R.A. Object exploration using whisker sensors. In Proceedings of the 2002 Australasian Conference on Robotics and Automation, Auckland, New Zealand, 27–29 November 2002; Australian Robotics and Automation Association (ARAA): Sydney, NSW, Australia, 2002; pp. 180–185. [Google Scholar]
- Grant, R.A.; Mitchinson, B.; Fox, C.W.; Prescott, T.J. Active touch sensing in the rat: Anticipatory and regulatory control of whisker movements during surface exploration. J. Neurophysiol. 2009, 101, 862–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, M.J. Active sensing capabilities of the rat whisker system. Auton. Robot. 2001, 11, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamond, M.E.; Von Heimendahl, M.; Knutsen, P.M.; Kleinfeld, D.; Ahissar, E. ‘Where’ and ‘what’ in the whisker sensorimotor system. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2008, 9, 601–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamond, M.E.; Arabzadeh, E. Whisker sensory system—From receptor to decision. Prog. Neurobiol. 2013, 103, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehnhardt, G.; Mauck, B.; Bleckmann, H. Seal whiskers detect water movements. Nature 1998, 394, 235–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Kamat, A.M.; Cao, M.; Kottapalli, A.G.P. Creating underwater vision through wavy whiskers: A review of the flow-sensing mechanisms and biomimetic potential of seal whiskers. J. R. Soc. Interface 2021, 18, 20210629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirose, S.; Inoue, S.; Yoneda, K. The whisker sensor and the transmission of multiple sensor signals. Adv. Robot. 1989, 4, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prescott, T.J.; Pearson, M.J.; Mitchinson, B.; Sullivan, J.C.W.; Pipe, A.G. Whisking with robots. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 2009, 16, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hires, S.A.; Pammer, L.; Svoboda, K.; Golomb, D. Tapered whiskers are required for active tactile sensation. eLife 2013, 2, e01350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, R.A. Using tactile whiskers to measure surface contours. In Proceedings of the 1992 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Nice, France, 12–14 May 1992; pp. 1295–1296. [Google Scholar]
- Bovet, S.; Fend, M.; Pfeifer, R. Simulating whisker sensors—On the role of material properties for morphology, behavior and evolution. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on the Simulation of Adaptive Behavior; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2004; pp. 122–130. [Google Scholar]
- Prescott, T.J.; Diamond, M.E.; Wing, A.M. Active touch sensing. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2011, 366, 2989–2995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, J.H.; Hartmann, M.J. Artificial whiskers suitable for array implementation: Accounting for lateral slip and surface friction. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2008, 24, 1157–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, S.; Honda, W.; Arie, T.; Akita, S.; Takei, K. Fully printed, highly sensitive multifunctional artificial electronic whisker arrays integrated with strain and temperature sensors. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 3921–3927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Wang, Y.; Sun, C.; Shu, Q.; Hu, T.; Xuan, S.; Gong, X. Three-dimensional structured dual-mode flexible sensors for highly sensitive tactile perception and noncontact sensing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 20955–20964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, K.C.; Sou, K.W.; Chan, W.S.; Yan, J.; Ping, S.; Peng, D.; Ding, W.; Zhang, X.P. WSTac: Interactive Surface Perception based on Whisker-Inspired and Self-Illuminated Vision-Based Tactile Sensor. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2308.13241. [Google Scholar]
- Tuna, C.; Jones, D.L.; Kamalabadi, F. Tactile soft-sparse mean fluid-flow imaging with a robotic whisker array. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2015, 10, 046018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Ai, J.; Ma, Z.; Zhang, X.; Du, Z.; Liu, Z.; Chen, D.; Su, B. Flexible out-of-plane wind sensors with a self-powered feature inspired by fine hairs of the spider. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 44865–44873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwana, M.I.; Tiwana, M.I.; Redmond, S.J.; Lovell, N.H.; Iqbal, J. Bio-inspired PVDF-based, mouse whisker mimicking, tactile sensor. Appl. Sci. 2016, 6, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bebek, O.; Cavusoglu, M.C. Whisker sensor design for three dimensional position measurement in robotic assisted beating heart surgery. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Rome, Italy, 10–14 April 2007; pp. 225–231. [Google Scholar]
- Glick, R.; Muthuramalingam, M.; Brücker, C. Fluid-structure interaction of flexible whisker-type beams and its implications for flow sensing by pair-wise correlation. Fluids 2021, 6, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Shan, X.; Xie, T.; Miao, J.; Du, H.; Song, R. Harbor seal whisker inspired self-powered piezoelectric sensor for detecting the underwater flow angle of attack and velocity. Measurement 2021, 172, 108866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rooney, T.; Pearson, M.; Welsby, J.; Horsfield, I.; Sewell, R.; Dogramadzi, S. Artificial active whiskers for guiding underwater autonomous walking robots. In Proceedings of the CLAWAR 2011, Paris, France, 6–8 September 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Xu, P.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Liu, C.; Song, L.; Xie, G.; Xu, M. Bionic tactile sensor based on triboelectric nanogenerator for motion perception. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 16th International Conference on Nano/Micro Engineered and Molecular Systems (NEMS), Xiamen, China, 25–29 April 2021; pp. 1853–1857. [Google Scholar]
- y Alvarado, P.V.; Bhat, S. Whisker-like sensors with tunable follicle sinus complex for underwater applications. In Proceedings of the Bioinspiration, Biomimetics, and Bioreplication 2014, San Diego, CA, USA, 9–12 March 2014; Volume 9055, pp. 79–88. [Google Scholar]
- Wegiriya, H.; Herzig, N.; Abad, S.A.; Sadati, S.H.; Nanayakkara, T. A stiffness controllable multimodal whisker sensor follicle for texture comparison. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 20, 2320–2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, R.A.; Wijaya, J.A. Object location and recognition using whisker sensors. In Proceedings of the Australasian Conference on Robotics and Automation, Sydney, NSW, Australia, 1–3 December 2003; pp. 761–768. [Google Scholar]
- Fox, C.; Evans, M.; Pearson, M.; Prescott, T. Tactile SLAM with a biomimetic whiskered robot. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Saint Paul, MN, USA, 14–18 May 2012; pp. 4925–4930. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Zuo, S. A Novel Bioinspired Whisker Sensor for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2023, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kent, T.A.; Emnett, H.; Babaei, M.; Hartmann, M.J.; Bergbreiter, S. Identifying Contact Distance Uncertainty in Whisker Sensing with Tapered, Flexible Whiskers. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), London, UK, 29 May–2 June 2023; pp. 607–613. [Google Scholar]
- Toal, D.J.; Flanagan, C.; Lyons, W.B.; Nolan, S.; Lewis, E. Proximal object and hazard detection for autonomous underwater vehicle with optical fibre sensors. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2005, 53, 214–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deer, W.; Pounds, P.E. Lightweight whiskers for contact, pre-contact, and fluid velocity sensing. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2019, 4, 1978–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beem, H.; Hildner, M.; Triantafyllou, M. Calibration and validation of a harbor seal whisker-inspired flow sensor. Smart Mater. Struct. 2012, 22, 014012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, S.; Park, J.; Jones, N.; Werely, N.; Flatau, A. Magnetostrictive whisker sensor application of carbon fiber-alfenol composites. Smart Mater. Struct. 2018, 27, 105010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotouhi, S.; Khayatzadeh, S.; Pui, W.X.; Damghani, M.; Bodaghi, M.; Fotouhi, M. Detection of barely visible impact damage in polymeric laminated composites using a biomimetic tactile whisker. Polymers 2021, 13, 3587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, B.; Ren, Z.; Ding, J.; Xu, W.; Zhang, G.; Liu, J.; Zhang, W.; Xue, C.; Zhang, B.; Wang, R. Cross-supported planar MEMS vector hydrophone for high impact resistance. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2017, 263, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Wang, X.; Wang, S.; Chen, T.; Liu, J.; Zheng, J.; Li, W.; Xu, M.; Tao, J.; Xie, G. A triboelectric-based artificial whisker for reactive obstacle avoidance and local mapping. Research 2021, 2021, 9864967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Xu, P.; Wang, X.; Zheng, J.; Liu, X.; Liu, J.; Chen, T.; Wang, H.; Xie, G.; Tao, J.; et al. Underwater bionic whisker sensor based on triboelectric nanogenerator for passive vortex perception. Nano Energy 2022, 97, 107210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xu, P.; Zheng, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, S.; Guan, T.; Xie, G.; Xu, M. Whisker-inspired and self-powered triboelectric sensor for underwater obstacle detection and collision avoidance. Nano Energy 2022, 101, 107633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Kamat, A.M.; Cao, M.; Kottapalli, A.G.P. Wavy Whiskers in Wakes: Explaining the Trail-Tracking Capabilities of Whisker Arrays on Seal Muzzles. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, 2203062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Wang, S.; Jiang, J.; Li, Z.; Yang, H.; Dai, X.; Liu, T. A Fiber-Optic Extrinsic Fabry–Perot Hydrophone Based on Archimedes Spiral-Type Sensitive Diaphragm. IEEE Sens. J. 2022, 22, 22654–22660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepora, N.F. Biomimetic active touch with fingertips and whiskers. IEEE Trans. Haptics 2016, 9, 170–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Jiang, Q.; Li, Y. A novel biomimetic whisker technology based on fiber Bragg grating and its application. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2017, 28, 095104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yang, X.; Wang, A.; Jiang, H.; Bai, L.; Meng, H.; Li, S.; Geng, T.; Sun, W. Bio-Inspired Fiber Attitude Sensor for Direction-Distinguishable Pitching and Rolling Sensing. J. Light. Technol. 2023, 41, 6844–6851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kent, T.A.; Kim, S.; Kornilowicz, G.; Yuan, W.; Hartmann, M.J.; Bergbreiter, S. WhiskSight: A reconfigurable, vision-based, optical whisker sensing array for simultaneous contact, airflow, and inertia stimulus detection. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2021, 6, 3357–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepora, N.F.; Pearson, M.; Cramphorn, L. TacWhiskers: Biomimetic optical tactile whiskered robots. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Madrid, Spain, 1–5 October 2018; pp. 7628–7634. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.; Velez, C.; Patel, D.K.; Bergbreiter, S. A magnetically transduced whisker for angular displacement and moment sensing. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Macau, China, 3–8 November 2019; pp. 665–671. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, R.; Lu, Q.G.; Cao, Q. Magnetostrictive bioinspired whisker sensor based on galfenol composite cantilever beam realizing bidirectional tactile perception. Appl. Bionics Biomech. 2018, 2018, 4250541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Möller, R. Passive sensing and active sensing of a biomimetic whisker. In Proceedings of the International Conference on the Simulation and Synthesis of Living Systems, Bloomington, IN, USA, 3–6 June 2006; Indiana University Press: Bloomington, IN, USA, 2006; pp. 127–131. [Google Scholar]
- Volkova, T.; Böhm, V.; Naletova, V.; Kaufhold, T.; Becker, F.; Zeidis, I.; Zimmermann, K. A ferrofluid based artificial tactile sensor with magnetic field control. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 431, 277–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Kubicek, R.; Paris, A.; Tagliabue, A.; How, J.P.; Bergbreiter, S. A whisker-inspired fin sensor for multi-directional airflow sensing. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 24 October–24 January 2020; pp. 1330–1337. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Z.; Sadati, S.H.; Perera, S.; Hauser, H.; Childs, P.R.; Nanayakkara, T. Tapered whisker reservoir computing for real-time terrain identification-based navigation. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 5213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, L.; Zhang, S.; Xie, T.; Zhao, C. Contour recognition method of Hall-effect-based whisker sensor. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2022, 33, 065104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yan, S.; Wei, Z.; Chen, X.; Fukuda, T.; Shi, Q. A small-scale, rat-inspired whisker sensor for the perception of a biomimetic robot: Design, fabrication, modeling, and experimental characterization. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 2022, 29, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad Ridzuan, N.A.; Miki, N. Tooth-inspired tactile sensor for detection of multidirectional force. Micromachines 2018, 10, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, R.; Zhu, J.; Wu, H.; Zhang, K.; Zou, B.; Zhang, X.; Liang, J.; Zheng, B.; Li, S.; Zhang, W.; et al. 3D-conductive pathway written on leather for highly sensitive and durable electronic whisker. J. Mater. Chem. C 2020, 8, 9748–9754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.W.; Zhao, Z.; Kim, J.; Huang, J. Pencil drawn strain gauges and chemiresistors on paper. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 3812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakabayashi, S.; Yamaguchi, T.; Arie, T.; Akita, S.; Takei, K. Out-of-plane electric whiskers based on nanocarbon strain sensors for multi-directional detection. Carbon 2020, 158, 698–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Kamat, A.M.; Krushynska, A.O.; Cao, M.; Kottapalli, A.G.P. 3D Printed Graphene Piezoresistive Microelectromechanical System Sensors to Explain the Ultrasensitive Wake Tracking of Wavy Seal Whiskers. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2207274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- y Alvarado, P.V.; Subramaniam, V.; Triantafyllou, M. Design of a bio-inspired whisker sensor for underwater applications. In Proceedings of the SENSORS, 2012 IEEE, Taipei, Taiwan, 28–31 October 2012; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Hua, Q.; Liu, H.; Zhao, J.; Peng, D.; Yang, X.; Gu, L.; Pan, C. Bioinspired Electronic Whisker Arrays by Pencil-Drawn Paper for Adaptive Tactile Sensing. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2016, 2, 1600093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Qi, D.; Leow, W.R.; Yu, J.; Xiloyannnis, M.; Cappello, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, B.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, G.; et al. 3D-structured stretchable strain sensors for out-of-plane force detection. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1707285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takei, K.; Yu, Z.; Zheng, M.; Ota, H.; Takahashi, T.; Javey, A. Highly sensitive electronic whiskers based on patterned carbon nanotube and silver nanoparticle composite films. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 1703–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stocking, J.; Eberhardt, W.; Shakhsheer, Y.; Calhoun, B.; Paulus, J.; Appleby, M. A capacitance-based whisker-like artificial sensor for fluid motion sensing. In Proceedings of the SENSORS, 2010 IEEE, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 1–4 November 2010; pp. 2224–2229. [Google Scholar]
- Assaf, T.; Rossiter, J.; Pearson, M. Contact sensing in a bio-inspired whisker driven by electroactive polymer artificial muscles. In Proceedings of the SENSORS, 2013 IEEE, Baltimore, MD, USA, 3–6 November 2013; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Droogendijk, H.; Bruinink, C.; Sanders, R.G.; Krijnen, G.J. Non-resonant parametric amplification in biomimetic hair flow sensors: Selective gain and tunable filtering. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 99, 213503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberhardt, W.C.; Wakefield, B.F.; Murphy, C.T.; Casey, C.; Shakhsheer, Y.; Calhoun, B.H.; Reichmuth, C. Development of an artificial sensor for hydrodynamic detection inspired by a seal’s whisker array. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2016, 11, 056011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delamare, J.; Sanders, R.; Krijnen, G. 3D printed biomimetic whisker-based sensor with co-planar capacitive sensing. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE SENSORS, Orlando, FL, USA, 30 October–3 November 2016; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Fend, M.; Bovet, S.; Hafner, V. The artificial mouse—A robot with whiskers and vision. In Proceedings of the 35th International Symposium on Robotics (ISR 2004), Paris, France, 23–26 March 2004. International Federation of Robotics 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, Z.; Qin, Y.; Guo, G.; Zheng, Z.; Bian, Y. Design and fabrication of an E-whisker using a PVDF ring. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2021, 16, 036007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bebek, O.; Cavusoglu, M.C. Whisker-like position sensor for measuring physiological motion. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2008, 13, 538–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kottapalli, A.; Asadnia, M.; Miao, J.; Triantafyllou, M. Harbor seal whisker inspired flow sensors to reduce vortex-induced vibrations. In Proceedings of the 2015 28th IEEE International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems (MEMS), Estoril, Portugal, 18–22 January 2015; pp. 889–892. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Guo, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wu, Z.; Shen, H.; Gong, J.; Bian, Y. Design and Fabrication of a Four-Electrodes PVDF Fiber for a Flow Sensor. IEEE Sens. J. 2022, 23, 1982–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, F.; Ling, S.F. Sensing fluid viscosity and density through mechanical impedance measurement using a whisker transducer. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2013, 24, 055105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Li, Y.; Hu, X.; Lu, L.; Xu, P.; Chen, X.; Liu, C.; Wang, L.; Liu, B.; Suo, L.; et al. Electrohydrodynamic jet printed bioinspired piezoelectric hair-like sensor for high-sensitivity air-flow detection. Smart Mater. Struct. 2023, 32, 095020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xu, P.; Ma, Z.; Wang, S.; Xie, G.; Xu, M. A bio-inspired whisker sensor based on triboelectric nanogenerators. In Proceedings of the 2020 35th Youth Academic Annual Conference of Chinese Association of Automation (YAC), Zhanjiang, China, 16–18 October 2020; pp. 105–109. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Xu, P.; Liu, J.; Wang, S.; Chen, T.; Guan, T.; Tao, J.; Xu, M. Semi-flexible bionic whisker sensor based on triboelectric nanogenerators. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Electromechanical Automation (AIEA), Guangzhou, China, 14–16 May 2021; pp. 194–198. [Google Scholar]
- Puneetha, P.; Mallem, S.P.R.; Park, S.C.; Kim, S.; Heo, D.H.; Kim, C.M.; Shim, J.; An, S.J.; Lee, D.Y.; Park, K.I. Ultra-flexible graphene/nylon/PDMS coaxial fiber-shaped multifunctional sensor. Nano Res. 2023, 16, 5541–5547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, A.; Chen, L.; Chen, X.; Zhang, A.; Fan, F.; Zhan, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric sensor as self-powered signal reader for scanning probe surface topography imaging. Nanotechnology 2015, 26, 165501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Guo, Y.; Su, J.; Huang, Q.; Fukuda, T.; Cao, C.; Shi, Q. Bioinspired, Multifunctional, Active Whisker Sensors for Tactile Sensing of Mobile Robots. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2022, 7, 9565–9572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swartz, R.A.; Rajbandari, B.; Winter, B.D. Autonomous Scour Monitoring of Bridges and Embankments Using Bio-Inspired Whisker Flow Sensor Arrays. In Proceedings of the Smart Materials, Adaptive Structures and Intelligent Systems, Newport, RI, USA, 8–10 September 2014; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Raghunath, G.; Flatau, A.B.; Na, S.-M.; Barkley, B. Development of a Bio-Inspired Tactile Magnetostrictive Whisker Sensor Using Alfenol. In Proceedings of the Smart Materials, Adaptive Structures and Intelligent Systems, Newport, RI, USA, 8–10 September 2014; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Ju, F.; Ling, S.F. Bioinspired active whisker sensor for robotic vibrissal tactile sensing. Smart Mater. Struct. 2014, 23, 125003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, J.H.; Hartmann, M.J.Z. Extracting Object Contours with the Sweep of a Robotic Whisker Using Torque Information. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2010, 29, 1233–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeder, J.T.; Kang, T.; Rains, S.; Voit, W. 3D, reconfigurable, multimodal electronic whiskers via directed air assembly. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1706733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Kent, T.A.; Bergbreiter, S. Design of Whisker-Inspired Sensors for Multi-Directional Hydrodynamic Sensing. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2307.09569. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Fu, J.H.; Zhao, H.; Xiang, W.; Zhan, F.; Sun, C.; Tang, S.; Wang, L.; Liu, J. Electronic whiskers for velocity sensing based on the liquid metal hysteresis effect. Soft Matter 2022, 18, 9153–9162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, R.; Routray, P.K.; Subudhi, D.; Manivannan, M. Whiskered Contact-Based Non-Intrusive Vibrometer. In Proceedings of the 2022 10th International Conference on Control, Mechatronics and Automation (ICCMA), Belval, Luxembourg, 9–12 November 2022; pp. 161–167. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Liu, Y.; Bai, B.; Guo, N.; Guo, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, M.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, B.; Xue, C.; et al. Wide-frequency-bandwidth whisker-inspired MEMS vector hydrophone encapsulated with parylene. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2016, 49, 07LT02. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Ding, J.; Xu, W.; Liu, Y.; Wang, R.; Han, J.; Bai, B.; Xue, C.; Liu, J.; Zhang, W. Design and optimization of stress centralized MEMS vector hydrophone with high sensitivity at low frequency. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2018, 104, 607–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Herbert, R.; Yeo, W.H.; Hammond, F.L. Kirigami Skin Based Flexible Whisker Sensor. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Kyoto, Japan, 23–27 October 2022; pp. 10015–10020. [Google Scholar]
- Rooney, T.; Pearson, M.J.; Pipe, T. Measuring the local viscosity and velocity of fluids using a biomimetic tactile whisker. In Proceedings of the Biomimetic and Biohybrid Systems: 4th International Conference, Living Machines 2015, Barcelona, Spain, 28–31 July 2015; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 75–85. [Google Scholar]
- Ikedo, A.; Ishida, M.; Kawano, T. Out-of-plane high-density piezoresistive silicon microwire/p-n diode array for force-and temperature-sensitive artificial whisker sensors. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2011, 21, 035007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.H.; Ho, V.A. Mechanics and Morphological Compensation Strategy for Trimmed Soft Whisker Sensor. Soft Robot. 2022, 9, 135–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, R.A.; Wijaya, J.A. Recognising and manipulating objects using data from a whisker sensor array. Robotica 2005, 23, 653–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, M.J.; Pipe, A.G.; Melhuish, C.; Mitchinson, B.; Prescott, T.J. Whiskerbot: A Robotic Active Touch System Modeled on the Rat Whisker Sensory System. Adapt. Behav. 2007, 15, 223–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salman, M.; Pearson, M.J. Whisker-RatSLAM Applied to 6D Object Identification and Spatial Localisation. In Proceedings of the Biomimetic and Biohybrid Systems; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 403–414. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Z.; Shi, Q.; Li, C.; Yan, S.; Jia, G.; Zeng, Z.; Huang, Q.; Fukuda, T. Development of an MEMS based biomimetic whisker sensor for tactile sensing. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Cyborg and Bionic Systems (CBS), Munich, Germany, 18–20 September 2019; pp. 222–227. [Google Scholar]
- An, J.; Chen, P.; Wang, Z.; Berbille, A.; Pang, H.; Jiang, Y.; Jiang, T.; Wang, Z.L. Biomimetic hairy whiskers for robotic skin tactility. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2101891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.; Bhamitipadi Suresh, D.; Jin, Y. Coupling between vortex flow and whisker sensor in cylinder wakes with time-varying streamwise gaps. Phys. Rev. Fluids 2023, 8, 034701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Jiang, W.; Zheng, X.; Xue, Q. Flow-signal correlation in seal whisker array sensing. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2021, 17, 016004. [Google Scholar]
- Gul, J.Z.; Su, K.Y.; Choi, K.H. Fully 3D Printed Multi-Material Soft Bio-Inspired Whisker Sensor for Underwater-Induced Vortex Detection. Soft Robot. 2018, 5, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Jiang, Y.; Wu, P.; Ma, Z.; Chen, H.; Zhang, D. Artificial Whisker Sensor with Undulated Morphology and Self-Spread Piezoresistors for Diverse Flow Analyses. Soft Robot. 2023, 10, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









| Category | Performance | Potential Applications | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Magnetic | Response time of less than 0.88 s | Surface recognition | [108] |
| Magnetic | Accuracy level of almost 100% | Damage detecting | [63] |
| Magnetic | Scour monitoring at Maryland State Highway bridges | Scour monitoring | [62] |
| Magnetic | Success generally increases as flow rate increases | Scour monitoring | [109] |
| Magnetic | Frequency sensitive | Scour monitoring | [110] |
| Magnetic | Robustly classifying the viscosity of fluids | Viscometer | [120] |
| Magnetic | Root mean squared percentage error less than 3.96% | Flow meter | [114] |
| Magnetic | Force resolution 0.4 mN, spatial resolution 0.04 mm × 0.04 mm | Vibrometer | [116] |
| Resistive | Response time of less than 250 s | Surface recognition | [113] |
| Resistive | Roughly check and estimate the surrounding flow rate | Flow meter | [119] |
| Resistive | Small detection area (∼20 ) and high spatial resolution (∼100 m in pitch) | Thermometer | [121] |
| Resistive | Recognize precision is as low as 0.2 ms within 0.1 s | Flow meter | [115] |
| Resistive | Sensitivities about −204.6 dB@300 Hz (X channel) and −210.2 dB@300 Hz (Y channel) | Hydrophone | [64] |
| Resistive | Resonance frequency of sensor is nearly 1450 Hz | Hydrophone | [117] |
| Resistive | Available bandwidth of sensor ranging from 20 to 500 Hz | Hydrophone | [118] |
| Resistive | Compensation error with only 20.385% | Robot tactile perception | [122] |
| Resistive | Scan the surface profile of touched objects | Robot tactile perception | [123] |
| Resistive | Simultaneous Localization and Mapping | Robot tactile perception | [124] |
| Resistive | Simultaneous Localization and Mapping | Robot tactile perception | [125] |
| Resistive | Trail tracking | Flow field perception | [68] |
| Resistive | Sensitivity of sensor in any direction is detectable and remarkably high (% ∼1180) | Flow field perception | [130] |
| Resistive | Perceive intricate flow details | Flow field perception | [131] |
| Capacitive | Target tracking | Flow field perception | [95] |
| Piezoelectric | Mechanical impedance is correlated with roughness | Surface recognition | [111] |
| Piezoelectric | Measurement uncertainty is less than 0.60% | Viscometer | [102] |
| Piezoelectric | Determine obstacle distance | Robot tactile perception | [126] |
| Triboelectric | Shaded object detection and environment recognition | Robot tactile perception | [127] |
| Triboelectric | Simultaneous Localization and Mapping | Robot tactile perception | [65] |
| Triboelectric | Perceiving underwater environment and avoiding reactive obstacles | Robot tactile perception | [67] |
| Triboelectric | Passive vortex perception | Flow field perception | [66] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, S.; Liu, J.; Liu, B.; Wang, H.; Si, J.; Xu, P.; Xu, M. Potential Applications of Whisker Sensors in Marine Science and Engineering: A Review. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 2108. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11112108
Wang S, Liu J, Liu B, Wang H, Si J, Xu P, Xu M. Potential Applications of Whisker Sensors in Marine Science and Engineering: A Review. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2023; 11(11):2108. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11112108
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Siyuan, Jianhua Liu, Bo Liu, Hao Wang, Jicang Si, Peng Xu, and Minyi Xu. 2023. "Potential Applications of Whisker Sensors in Marine Science and Engineering: A Review" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 11, no. 11: 2108. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11112108
APA StyleWang, S., Liu, J., Liu, B., Wang, H., Si, J., Xu, P., & Xu, M. (2023). Potential Applications of Whisker Sensors in Marine Science and Engineering: A Review. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 11(11), 2108. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11112108









