Abstract
Improving the availability of new sources of probiotics is essential to continue implementing alternative solutions to improve coral health; one such source is urban corals. However, little is known about urban coral’s health status and whether they can harbor bacteria exhibiting probiotic traits. Here, we explored the status of the urban coral Madracis auretenra and the presence of probiotic traits in its associated culturable bacteria. After assessing ecological attributes, we observed a similar abundance (cover %) when comparing patches of M. auretenra occurring in both an urban site and a marine protected area. The urban patch also exhibited a high abundance of vibrios in coral tissues and signs of ecosystem deterioration. However, this patch showed a “good” health index condition; so, we hypothesized the presence of beneficial bacteria. We isolated 132 bacterial strains from this healthy urban M. auretenra. These bacteria were affiliated with 11 genera, including Vibrio, Shewanella, Bacillus, Exiguobacterium, Priestia, and Niallia, among others. Screenings revealed the predominant presence of potential probiotic traits such as catalase, antiQS, and the production of siderophores activities among the bacterial isolates. We proposed a list of 24 bacterial isolates as probiotic precandidates that jointly exhibited three or more of these traits, among which the Vibrio and Bacilli strains stand out. We provide insights into the health status of this urban coral and its potential as a source of bacteria exhibiting potential probiotic traits.
1. Introduction
Recently, the manipulation of coral-associated microbial communities has received particular attention as an intervention strategy to protect and improve coral health in response to climate change and local anthropogenic disturbances. Rapidly deteriorating environmental conditions can cause coral physiological stress and nutrient limitation, leading to coral bleaching and infectious disease outbreaks [1,2,3,4]. The application of beneficial bacteria, now referred to as coral probiotics, is a promising novel approach to compensate for these impacts [5,6,7,8]. Environmental conditions triggered either naturally or by global or local disturbances act as selective forces that reward the most advantageous phenotypes [9]. These resistant and adapted individuals harbor beneficial bacteria [10,11,12]. The number of these bacteria that naturally occur in the compartments (i.e., mucus, tissues, or skeleton) of these corals often increases, and this gives the coral a genetic potential to adapt rapidly to changes, since these bacteria evolve much more rapidly than the coral host [13,14,15]. By doing so, the probiotic bacteria provide benefits to their coral host that help buffer or exacerbate the effects of disturbance [16].
Given that coral-associated microbial communities often exhibit species-specific patterns, the first step in developing coral probiotics is sourcing corals from locally impacted environments previously exposed to stressful conditions [5,17]. The next step is isolating and selecting putative beneficial bacteria [6,17]. The identification of potentially beneficial probiotic traits is essential to selecting the most appropriate formulation consortia. Some examples of these probiotic traits include (1) the production of compounds such as detoxifying enzymes (e.g., catalases) and sun-protective pigments that might help facilitate an enhanced coral response to thermal and UV-radiation stress [18,19]; (2) the synthesis of antimicrobial and anti-quorum sensing (antiQS) compounds that inhibit or maintain controlled potential opportunistic pathogens [20,21]; and (3) the production of nutrient scavengers such as siderophores that indirectly help the coral host by increasing the availability of essential trace nutrients (metals and vitamins) that algal symbionts require to recover after bleaching events [22]. An effective probiotic must exhibit at least one of these traits [8,23]. Despite this importance, to date, few studies have been conducted to assess the potential of different corals as sources of probiotic bacteria [7,24,25,26,27].
Coral reefs in impacted urban coastlines hold immense probiotic potential. “Urban corals” have adapted to highly variable conditions (i.e., turbidity, eutrophication, pollution, and fishing) due to their robustness, stress tolerance, and relative resistance to bleaching [28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35]. This adaptation is thought to be related to flexible host–bacterial associations that provide a dynamic microbiome that allows corals to respond more rapidly to prevailing conditions [10]. This flexible microbiome and the coral host adaptative mechanisms improve the response and increase survival [31]. This makes urban corals a potential source of beneficial bacteria. Although local stressors along urban coastlines have been identified [36,37,38,39], little is known about the status of urban corals and their associated bacteria, and whether these corals harbor probiotic bacteria needs to be addressed.
In the present study, we explored the status of the urban coral patch of the species Madracis auretenra in Santa Marta, Colombia and characterized its associated culturable bacteria in search of probiotic potential. We assessed coverage, interactions, and deterioration in the benthic community, counted bacterial loads in its mucus and tissue, and compared it to a nonurban coral reef formation of the same species. Since the target coral patch lies in an urban-influenced environment and exhibits an apparent healthy status, we hypothesized that this coral harbors beneficial bacteria with probiotic potential. We taxonomically characterized culturable bacteria associated with the urban M. auretenra and screened for probiotic traits (catalase, pigments, antagonism, antiQS activity, and siderophore production).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Permits
Individual and framework “Permits for the Collection of Specimens of Wild Species of Biological Diversity for Non-Commercial Scientific Research Purposes” were issued for sample collection inside the Tayrona National Natural Park (PNN Tayrona) and outside the jurisdiction of National Natural Parks. Individual permit expedient PIR 007-2021 was issued through Resolution 191 of 16 December 2021. The National Environmental Licensing Authority (ANLA) of Colombia through Resolution 1715 of 30 December 2015, and the modified Instruction Normative No. 00213 of 28 January 2021 issued the framework permits.
2.2. Study Area
The coastal area of Santa Marta, Colombian Caribbean (Figure 1) has a narrow continental shelf with rocky coasts [40] and includes two urban settlements, El Rodadero and the city of Santa Marta, altogether containing 546,979 inhabitants [41] (Figure 1), where the port and tourist activities predominate. This area also includes the Parque Nacional Natural (PNN) Tayrona, a protected area where tourism and fishing are restricted, located 11.7 km2 from the main urban center [42]. The climatic regime is annually bimodal (Figure 1). The dry season (December–April) is characterized by cold waters ranging from 20 °C (min) to 25 °C (max) and salinity > 36; and the rainy season (May–November) is characterized by warmer waters between 27 °C (min) and 29 °C (max) and salinity < 34 [43,44]. The high discharges from the submarine outfall, the local rivers, the overflow of sewers, and the Magdalena River and Cienega Grande de Santa Marta (CGSM) affect the quality of the coastal waters, increasing nutrients, sedimentation, algae biomass, and bacterial load [44,45,46]. This area harbors several coral reef formations (typically patchy). Live coral cover reaches ~62% inside the PNN Tayrona but is much lower (~4 to 22%) near the urban settlements [47]. Here, we describe the status of an urban coral patch of the species M. auretenra and compare it with the same species found in the PNN Tayrona protected area. The nonurban site—CHE—was located at Chengue Bay (11°19′30″ N, 74°07′41.8″ W), whereas the urban site—INC—was at the Inca Inca sector (11°12′58.4″ N, 74°14′6.3″ W).
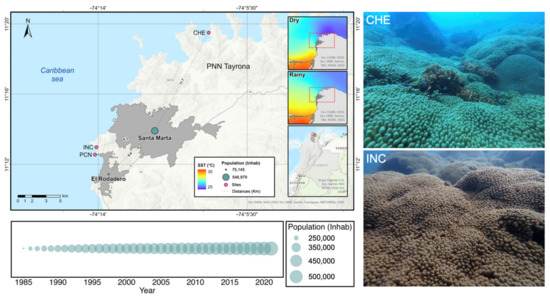
Figure 1.
Map of the study area on the coast of Santa Marta, Colombian Caribbean. Site CHE is located at Chengue Bay inside the PNN Tayrona (11°19′30″ N, 74°07′41.8″ W). Site INC is located at the Inca Inca sector (11°12′58.4″ N, 74°14′6.3″ W) between the two urban settlements of Santa Marta City and El Rodadero. The figure also shows the population increases over the last 35 years (left bottom) and the coral patches of Madracis auretenra in each site (right). SST: sea surface temperature, Inhab: inhabitants.
2.3. Evaluation of Madracis auretenra Reef Patches Status
We performed microbiological (counts of heterotrophic bacteria and vibrios), ecological (cover, interactions, and health status), and environmental surveys in the patches of M. auretenra at each site during the dry season in March 2022 by scuba diving at a depth of ~4 to 9 m.
2.3.1. Sample Collection
Patches of M. auretenra were recognized according to Locke et al. [48]. This species exhibits a branching morphology with strong secondary and tertiary branches and forms plocoid colonies, where patches generally reach 2–5 m in diameter [49]. Healthy colonies were identified by having a bright yellow to golden color with no apparent deterioration (stress signs and/or disease). Specimens were confirmed taxonomically under a stereoscope (Figure 2) [48].
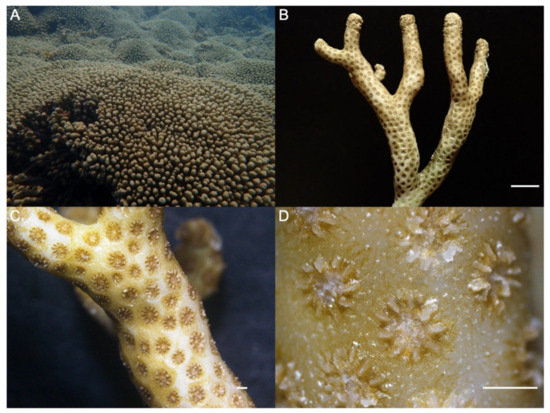
Figure 2.
(A) Madracis auretenra in its natural habitat. (B) Normal branching morphology, strong secondary and short tertiary branches, and dead basal branch portions. (C) Corallite distribution in one branch with differing columella morphology. (D) Round to slightly oval corallites of 1–2 mm in diameter, boundary spines between corallites, and massive and styliform columella. Scale bars = 1 cm, 1 mm, and 1 mm, respectively.
Three to four fragments (~5 cm) were collected manually from each of the three different healthy and diseased (stressed, i.e., bleached, paled, partially dead) colonies. Colonies were randomly picked (individual phenotypes separated by >5 m from each other) along a marked 10 m transect using sterile gloves. Samples were maintained in separated sterile packages at 4 °C during transport (approximately 1 h). At the laboratory facilities of Universidad de Bogota Jorge Tadeo Lozano, samples were processed immediately as described by Cárdenas et al. [50], with modifications. Fragments were cut into 3 cm pieces and slightly washed five times with sterile Phosphate Buffered Saline-PBS (137 mM NaCl, 2.7 mM KCl, 100 mM Na2HPO4, and 2 mM KH2PO4, pH 7.4) with stirring to remove loosely attached bacteria and particles. To confirm sterile conditions, 0.1 mL of the water from the last wash was plated on Marine Agar (Condalab, Spain), and the absence of growth after 48 h indicated that no associated bacteria were removed. Three washed pieces were set in triplicate into flasks containing 60 mL of sterile PBS. Mucus was obtained under stirring (135 rpm × 1 h) at room temperature (28 °C). Then, fragments were macerated in mortar, and tissue slurry was recovered in 60 mL of PBS. Samples from each site, coral compartment (mucus and tissue), and health condition (healthy and diseased) were pooled, respectively, concentrated at 3000× g, and resuspended in 6 mL of sterile PBS for further analysis.
2.3.2. Counts of Total Heterotrophic Bacteria and Vibrios
We estimated the load of heterotrophic bacteria and vibrios in the mucus and tissue of healthy and diseased M. auretenra. Ten-fold dilutions were prepared from 1 mL of four independent replicates from Section 2.3.1, and 0.1 mL of dilutions of 10−3 and 10−4 were spread onto Marine Agar and Thiosulfate–Citrate–Bile–Sucrose Agar (TCBS, Oxoid, UK) plates. Colony-forming units (CFU) were enumerated, and total heterotrophic bacteria were counted from Marine Agar after five days and vibrios from TCBS agar after 24 h of incubation at 28 °C. Data were reported as CFU per mL or g of mucus or dry tissue, respectively.
2.3.3. Benthic Community and Health Status
The composition of the benthic community associated with the patches of M. auretenra was evaluated by estimating the percent cover from 60 photo quadrats (0.25 m2) shot in situ with strobe lighting (Olympus Tg-6), as proposed by Brown et al. [51]. Quadrats were alternately placed left and right along three 10 m2 transect belts every 5 m at a constant depth. Benthic community composition was determined from 10 categories, with the 4 central categories being hard coral, soft coral, macroalgae, and abiotic substrate. The hard coral category was divided into Madracis auretenra and other hard corals. Macroalgae were differentiated as fleshy, filamentous/cyanobacteria, and crustose coralline-CCA. The abiotic substrate category was defined as other nonliving substrates and consisted of sediment and coral rubble. The percentage of each benthic community category was estimated from 30 random points using Photo Quad v1.4 software [52].
The composition of the interactions in the patches of M. auretenra was estimated through the frequencies of contact recorded, as previously described by Barott et al. [53]. Three 10 m2 transects were used at a constant depth, where a 1 m belt of the transect line was examined with a 0.5 × 0.5 m gridded quadrat (25 grids). Any M. auretenra branch physically touching macroalgae, sponges, hard/soft corals, or other invertebrates was documented (area totaling 30 m2). The frequency of interaction of functional groups was determined by counting the number of grids where the contact was occurring over the total grids at each quadrat, and the data were expressed as a percentage.
We also recorded the occurrence of deterioration signs and the health status. The frequency of bleaching (bright white polyps), paleness (loss of bright yellow), overturning, partial mortality, sedimentation, and bites were estimated by the presence–absence of that condition at each quadrat, and the data were expressed as the percentage of occurrence of the deterioration sign. A customized health index was also calculated according to Cuthbert et al. [54], with modifications. The index included the average of three measurements: (i) hard coral cover, (ii) macroalgae cover, and (iii) the proportion of vibrios in coral tissue. On a scale of 5–1, the measurements were scored 5 when coral cover > 40%, macroalgae cover < 1% and the count of vibrios was 0–10 UFC g−1 (see Table S1). An average value of 5.0–4.3 indicates a very healthy status, 4.2–3.5 indicates good health, 3.4–2.7 is a regular condition, and values below 2.6 and 1.8 are bad and critical conditions, respectively.
2.3.4. Physicochemical Analysis
Water samples were taken randomly at a constant depth over transect belts. About 1 L of water was collected in triplicate, stored at 4 °C for less than 24 h, and analyzed for nitrites (NO2−), nitrates (NO3−), ammonia (NH4+), phosphates (PO43−), and suspended total solids (SST) [55,56]. Analysis was performed at the LABCAM unit of the Marine and Coastal Research InstituteInvemar. The “Instituto de Hidrología, Meteorología y Estudios Ambientales-IDEAM” accredited the results under Resolution 0049 of 15 January 2021. Temperature (°C), pH, salinity, and percentage of oxygen saturation were measured in situ. At least three independent replicates were analyzed for each variable.
2.3.5. Statistical Analysis
Data were expressed as mean ± standard error (SE). All data were visualized using the R Studio package. To avoid redundancy, a correlation analysis was performed (r > 0.95, p > 0.05), and one of the variables was excluded. Transformations and resemblances of the set of data were performed before the statistical test. A Log (X + 1) transformation and the Euclidean distance were used for environmental data. The square root and fourth root transformations were used for community composition and microbiological data, and the distances were calculated using Bray–Curtis similarity. Permutational Multivariate Analysis of Variance (PERMANOVA) [57] was performed with the homonymous routines in PRIMER7 [58] to detect significant differences at a confidence level of 95%. PERMANOVA main test was performed using the site as the main factor, allowing unrestricted permutations of the raw data and accounting for type III error, where the fixed effects sum to zero with 999 random permutations. Two additional individual factors, each with two levels, were evaluated for statistical inference of the microbiological data and consisted of (i) compartment (mucus and tissue) and (ii) health condition (healthy and diseased).
A RELATE testing match was conducted with the Spearman rank correlation method to find the relationship between environmental variables and the community composition. Then, a Distance-based Multivariate Multiple Regression test (DistLM; stepwise, adjusted r2) was performed to establish the significance of the most explanatory variables [59]. A Redundancy Analysis (RDA) was conducted using a constrained ordination model to visualize the prediction of the environmental variables over the community composition. The input consisted of cover data that were first transformed using the “decostand()” function in the R package “vegan” with the Hellinger distance method [60]. Non-collinearity of variables was checked, and the most explanatory variables were simplified in the model and visualized in a plot. The significance of the RDA model was tested with the “anova.cca()” function. Differences between sites concerning the frequency of contact were analyzed through the STATGRAPHICS Centurion package 19.4.02 version, and differences were detected using a Chi2 test [61].
2.4. Characterization of Culturable Bacteria and Screening of Probiotic Traits
2.4.1. Coral-Associated Bacterial Isolation
Bacteria were isolated from healthy samples of urban M. auretenra collected at Inca Inca (Figure 1) by scuba diving at a depth of 4 to 7 m. The mean seawater temperature, pH, and salinity for the sampling location in this month were 27.7 ± 0.30 °C, 8.1 ± 0.05, and 33.4 ± 0.28, respectively. Healthy fragments were collected and processed, as previously described in Section 2.3.1. Ten-fold serial dilutions (10−1, 10−2, 10−3, and 10−4) were prepared in PBS from 1 mL of the mucus and tissue samples. Then, 0.1 mL of each dilution was spread in triplicate onto plates of Marine Agar and Tryptone Soy Agar (TSA, Oxoid) with NaCl 1% and were incubated at 28 °C for 24 h to 5 days [25,62,63]. After incubation, bacteria were picked according to the differences in colony morphology (size, margin, color, elevation, texture, and shape). The selected bacterial colonies were systematically purified until they exhibited one unique morphology and were characterized by Gram-staining. All the isolates were stored in a glycerol broth suspension (20%, v/v) at −80° C (for one year), and some copies were maintained at −20 °C (for six months).
2.4.2. Qualitative Functional Screening of Coral Probiotic Traits
Each morphologically different bacterial isolate was screened for coral probiotic traits, as proposed by Peixoto et al. [8]. The screening was focused on the need to mitigate the impacts of climate change on corals, i.e., thermal stress, UV damage, increase in pathogens and opportunists, and iron limitation. These probiotic traits included (i) antioxidant activity, (ii) pigment production, (iii) antagonistic activity, (iv) antiQS activity, and (v) siderophore production and were qualitatively described (see Table S10). For all assays, bacteria were grown in Marine Agar and Marine Broth media at 28 °C when corresponding.
Antioxidant Activity and Pigment Production
The antioxidant activity was detected by catalase test according to Rosado et al. and Reiner [25,64]. A drop (100 µL) of 3% (v/v) hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) was deposited on a microscope slide and mixed with a small amount of fresh inoculum of the test bacteria. The isolate was considered catalase-positive if bubbles appeared, and the activity was systematically classified as + low activity (25% of the surface covered with bubbles), ++ moderate activity (50% of the surface covered with bubbles), +++ high activity (75% of the surface covered with bubbles), or ++++ very high activity (100% of the surface covered with bubbles). Staphylococcus aureus Rosenbach ATCC® 25923™ was used as the positive control. Bacterial isolates exhibiting distinctive coloration (i.e., yellow, pink–red, brown, and orange) were selected and analyzed by spectrophotometry. From 100 mL of 72 h broth cultures, pigments were methanol-extracted (1:1), and the absorbance of the colored extracts was measured in triplicate every 25 nm at a range from 400 to 700 nm in a GENESYS 10 UV spectrophotometer [65]. Curves were drawn to observe potential absorbance peaks.
Antagonistic and antiQS Activities
The antagonistic activity against coral pathogen Vibrio coralliilyticus was tested by the cross-streak method [66]. The test isolate was streaked across the agar plates, and V. coralliilyticus was perpendicularly streaked to the test isolate. After 24 h of incubation, the presence of halos indicated the inhibition of growth [67]. The antiQS activity was tested by the ability of the isolate to inhibit the bioluminescence of the biosensor Photobacterium sp. ICM9 (OL964654). This biosensor was isolated from the mucus of healthy M. auretenra and was selected on the basis that bioluminescence has been reported under the QS mechanism in Vibrio and Photobacterium species [68,69]. A disk diffusion assay was performed to detect antiQS activity according to Ma et al. [21], with modifications. Briefly, the biosensor was streaked continuously in three directions onto agar plates using a sterile loop [70], and sterile filter paper circles (0.5 cm diameter) were placed on the agar surface at regular intervals. The test isolates were cultured overnight in 1.5 mL of broth at a constant shaking (145 rpm), and 10 µL of cultured bacterial suspension (OD600 = 0.4–0.6) was pipetted onto the filter paper. After incubation for 24 h, the plates were visualized in complete darkness, and inhibition of bioluminescence was detected by the appearance of an obscure halo over the biosensor growth around the disk. The assay was performed in three independent replicates and the potential antiQS isolates were confirmed using biosensor Chromobacterium violaceum [21] donated from the Department of Chemistry of the National University of Colombia. Marine broth and Escherichia coli ATCC® 25922™ were used as blank and negative controls, respectively.
Siderophores Production
The ability of the isolates to produce siderophores was tested using the CAS (Chrome Azurol Sulfonate) solid assay, as described by Schwyn and Neilands [71] and modified by Pérez-Miranda et al. [72]. The medium for a liter of overlay was prepared as follows: CAS 60.5 mg, hexadecyl trimethyl ammonium bromide (HDTMA) 72.9 mg, and 1 mM FeCl3·6H2O in 10 mL of 10 mM HCl. The CAS solution and a solution of the gelling agent agarose (0.9%, w/v) were sterilized (121 °C × 15 min) separately, cooled, and mixed. About 10 mL overlays of this mixture were poured over agar plates containing the cultured test isolates. After 4 h of incubation at room temperature, a color change surrounding the bacterial colony indicated a positive result. Color changes occurred from blue to orange (siderophores of the hydroxamate type) and from blue to light yellow (carboxylate type). This assay was repeated at least three times for the sample. Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC® 27853™ was used as a positive control.
2.4.3. DNA Extraction and Identification via 16S rRNA Gene Sequence Analysis
Genomic DNA of all the screened bacterial isolates was extracted via Zymo Research Bacterial/Fungal DNA MicroPrep™ Kit. Overnight cultures of each isolate were prepared and centrifuged at 3000× g. The pellet was washed once with sterile PBS (to remove the culture medium) and resuspended in 0.2 mL of the buffer. The extraction was performed according to the manufacturer’s protocol. DNA samples were evaluated by electrophoresis in 0.8% agarose gels in 0.5 X TBE buffer (45 mM Tris-borate, 45 mM boric acid, 1 mM EDTA, pH 8.2) and via Nanodrop Multiskan™ Go Microplate.
The identification was carried out through 16S rRNA gene amplification and sequencing using bacterial universal primers 27F (5′-AGAGTTTGATCCTGGCTCAG-3′) and 1492R (5′-GGTTACCTTGTTACGACTT-3′) [73]. Up to 50 ng of extracted DNA was used with a master mix containing 1 X of Buffer + Mg2+, 0.5 mM of dNTPs, 0.25 µM of each primer, 2 mM of MgSO4, 0.05 u × μL−1 of Taq Polymerase, and sterile grade water. For 50 µL, the reaction was performed with an initial denaturation at 94 °C × 2 min, followed by 30 cycles of 1 min at 94 °C, 2 min at 55 °C, 2 min at 72 °C, and extension at 72 °C × 5 min. The amplified products were visualized in 2.0% gels, stored at −20 °C, and sequenced through the SANGER dideoxy platform using forward primer. Lower-quality reads were removed using Bioedit V7.2 software [74], and cleaned FASTA sequences were matched against the EzBioCloud database (http://www.ezbiocloud.net, accessed on 30 August 2022), assigning taxa at the genus level when the similarity with the hit reference was >97% and at the species level when >99% [75,76].
2.4.4. Phylogenetic Analysis
We performed a phylogenetic analysis of two datasets. One included all the isolates from this study, and the second included the 16S rRNA sequences of bacterial isolates from scleractinian corals collected from ~52 studies [77]. The sequences from the database (http://isolates.reefgenomics.org/, accessed on 30 November 2022) were filtered based on the information about the collection site (near urban and nonurban sites), compartment or source of isolation (mucus and tissue), and health status (healthy and diseased). All the filtered sequences were verified via NCBI with accession numbers, and sequences with incomplete information were excluded. From the original database, a total of 329 filtered 16S rRNA sequences were used in the analysis, and accession numbers are summarized in Table S11. Multiple sequence alignment was carried out in MUSCLE, and phylogenetic trees were obtained through MEGA X version 11.0.10 [78] with the neighbor-joining method, p-distance model, and a bootstrap value of 1000 replicates to evaluate the topologies of the trees [62]. Thermotoga maritima MSB8 (NR_102775.2) was used as the outgroup. The output files were uploaded to iTOL for tree visualization [79] and then edited using the R Studio package.
2.4.5. Data Analysis
The data were expressed in percentages. A Venn plot was used to observe the number of traits that were shared between the isolates and served as an indicator of the probiotic redundancy in the studied culturable fraction. A Principal Component Analysis (PCA) was used to show the possible association between qualitative variables based on the compartment [80]. The statistical significance of the PCA analysis was evaluated using the R package “PCAtest”.
3. Results
3.1. Environmental and Microbiological Conditions
Environmental conditions are summarized in Table 1. Both patches of M. auretenra occurred at a similar depth (4–9 m). Temperature (~26 °C), salinity (~36), and pH (8.3–8.5) were similar at both sites and corresponded to typical values of the dry season in the Colombian Caribbean. Oxygen saturation (69.90 ± 5.93%) was lower at the urban site (INC), while nitrates and ammonia were higher (21.12 ± 0.53 µg L−1 and 12.27 ± 0.57 µg L−1, respectively). No significant differences (PERMANOVA; Pseudo-F = 4.1; df = 1, 5; p > 0.05) were observed in the physicochemical variables between the two sites.

Table 1.
Environmental conditions in the patches of Madracis auretenra at both sites.
Regarding the microbiological surveys, differences between sites (PERMANOVA; Pseudo-F = 9.7; df = 1, 28; p < 0.05) and compartments (PERMANOVA; Pseudo-F = 34.6; df = 1, 28; p < 0.05) were detected. Heterotrophic bacteria and vibrios were higher at the urban site and in coral tissue (Figure 3). The bacterial counts ranged from 105 to 107 CFU in the urban samples up to almost two orders of magnitude higher compared with the nonurban samples. Likewise, the highest value of heterotrophic bacteria was observed in healthy tissue (1.80 ± 0.46 × 107 CFU g−1), whereas the higher count of vibrios was obtained in diseased tissue (3.28 ± 1.98 × 107 CFU g−1). Although the counts of vibrios and heterotrophic bacteria were generally higher in the diseased samples, this study reported no significant differences between the counts regarding the health condition (PERMANOVA; Pseudo-F = 1.6; df = 1, 28; p > 0.05; see also Table S2).
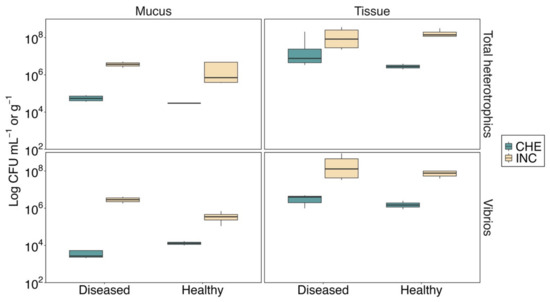
Figure 3.
Count of total heterotrophic bacteria and vibrios in healthy and diseased mucus and tissue of Madracis auretenra. Data are expressed as mean ± SE of CFU per mL of mucus or g of tissue. CFU: colony-forming units. CHE: nonurban site—Chengue. INC: urban site—Inca Inca.
3.2. Benthic Community and Health Status
The patches of M. auretenra were significantly different based on the percentage cover of the benthic categories (PERMANOVA; Pseudo-F = 24.17; df = 1, 119; p < 0.05). However, the cover of M. auretenra was not significantly different when comparing both sites (~72%) (PERMANOVA; Pseudo-F = 0.11; df = 1, 119; p > 0.05; Table S3). The remaining percentage (Figure 4A) was mainly attributed to other hard corals, macroalgae, sponges, soft corals, and abiotic substrate categories, although the soft coral category was only present at the CHE site (cover = 1.78 ± 0.88%). At the urban site, the cover of the macroalgae category was lower (10.94 ± 1.55%), although the CCA subcategory was significantly higher (5.22 ± 0.81%), and particularly, fleshy macroalgae were not present at the time of sampling. Sponges and abiotic substrates were significantly higher (3.11 ± 0.69% and 13.94 ± 1.90%, respectively) compared with the nonurban site. We also found that the variation in the benthic community structure across these coral patches was poorly explained by the environmental variables. The Rho value predicted 33.9% of the relationship, and only the orthophosphates variable had a significant influence over the variables of the community composition (DistLM; Pseudo-F = 4.52; df = 1, 4; p < 0.05; see also Table S4). The RDA showed that soft coral, other hard coral, filamentous/cyanobacteria, and fleshy categories at the CHE site were influenced by the pH. In contrast, at the urban site, CCA, sponges, and abiotic substrate categories were mainly predicted by nutrients (NO2−, NO3−, and PO43−) (Figure 4B). The distribution in the M. auretenra coral patches at both sites is not apparently influenced by any of the environmental variables evaluated at the moment of sampling during the dry season.
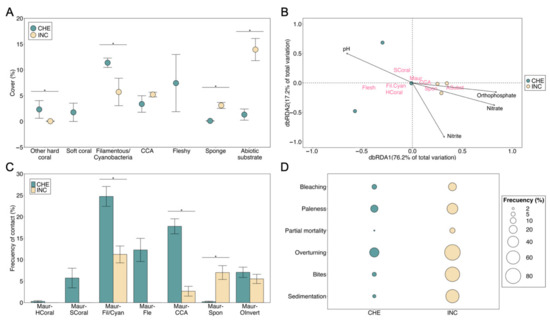
Figure 4.
Biological assessment of the Madracis auretenra patches: (A) The mean composition of the benthic categories (percentage ± SE). (B) Ordination of the benthic community associated with M. auretenra patches and physicochemical variables based on the Redundancy Analysis (RDA) (eigenvalue RDA1 = 0.06865, eigenvalue RDA2 = 0.01504; orthophosphate R2 = 0.50, p = 0.05; nitrite R2 = 0.61, p = 0.16; pH R2 = 0.86, p = 0.05; nitrate R2 = 0.97, p = 0.86). (C) The mean frequency of contact between M. auretenra and other benthic categories (percentage ± SE). (D) Frequency of the signs of deterioration (%). Bars with asterisk indicate significance (p < 0.05). CCA: Crustose Coralline algae. CHE: Chengue. Fil/Cyan: filamentous/cyanobacteria. Fle: fleshy. HCoral: other hard coral. INC: Inca Inca. Maur: M. auretenra. SCoral: soft coral. Spon: sponge. OInvert: other invertebrate.
Figure 4C,D shows the frequency of contact between M. auretenra and other benthic categories and the signs of deterioration. Significant differences in the frequency of contact were detected between sites in almost all pair interactions (Table S5) and were generally higher at the nonurban site. In contrast, the contact between M. auretenra and the sponge category at the urban site (7.00 ± 1.61%) was significantly higher (Chi2; X2 = 7.54; df = 1, 1; p < 0.05). Otherwise, the frequency of signs of deterioration was higher at the urban site. In general, the frequency ranged from 8.33 to 85.00% at the urban site, whereas at the CHE site, it ranged from 3.33 to 28.33%. Overturning (fragmentation) was the most frequent sign in both sites (>80% at the urban site). The bites and the sedimentation were also higher (73.33 and 60%, respectively). The frequency of bleaching and paleness was <40% and lower at the nonurban site (6.67 and 16.67%, respectively). The Reef Health Index indicated both sites harbor patches of M. auretenra in a “good” health condition (3.67 on a scale of 1.0–5.0; see Supplementary Tables).
3.3. M. auretenra-Associated Culturable Bacteria and Phylogenetic Analysis
A total of 132 bacterial isolates were obtained from visually healthy M. auretenra from the urban site (INC). The great majority of the isolates were obtained from mucus (70.45% of the isolates) and most of them corresponded to Gram-negative rod-shaped (short, medium, large, curve, and filamentous) morphotypes (Table S10). One hundred and twenty-five of these isolates were effectively identified (16S rRNA partial gene 97–100% identity). About 5 orders, 5 families, and 11 genera were found to be associated with the culturable fraction of M. auretenra (Figure 5A, Table S10). The most abundant cultured taxon was Vibrionales (class Gammaproteobacteria), which included 93 isolates that were affiliated with Vibrio spp., 16 with Photobacterium spp., and 1 with Grimontia sp. The order Bacillales (class Bacilli) was the second most abundant taxa and included Bacillus spp. (4 isolates), Priestia spp. (2 isolates), Fictibacillus spp. (2 isolates), Niallia sp. (1 isolate), and Exiguobacterium sp. (1 isolate). Other taxa included the order Alteromonadales (class Gammaproteobacteria) represented by the genus Shewanella (three isolates), as well as the genera Nocardiopsis and Cellulosimicrobium (class Actinomycetia), represented by one isolate. The GeneBank accession numbers for these isolates are OL964632-OL964656 and OP339924-OP340023 (see Table S10).
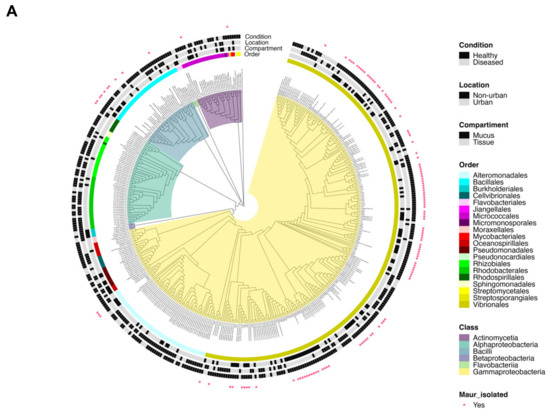
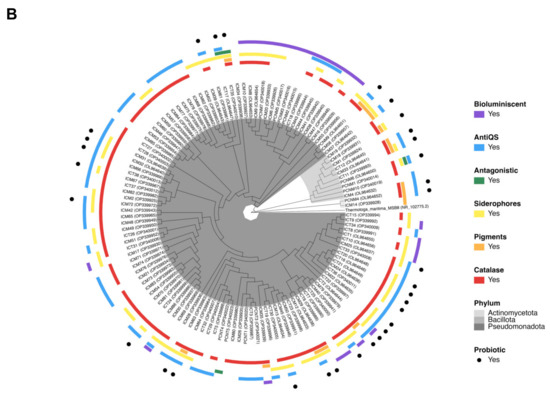
Figure 5.
Phylogenetic trees: (A) Representation of 445 isolated coral-associated bacteria based on 16S rRNA gene sequences. A total of 125 sequences from the present study and 330 filtered sequences from the database http://isolates.reefgenomics.org/ (accessed on 30 November 2022) were used in the analysis. Strains were affiliated with 20 orders and 6 classes. The accession number is color-coded according to classes and the genus/species name is included in parentheses. The external ring is color-coded according to orders. Three external rings are black and white coded according to (from central to outer rings) their “compartment” (mucus and tissue), “location” (nonurban and urban sites), and “condition” (healthy and diseased). The strains from the present study are marked with pink dot symbols. (B) Representation of the phylogenetic relationships between the Madracis auretenra-associated culturable bacteria from the present study and their probiotic potential. The isolate ID is color-coded according to the phylum, and the accession number is included in parentheses. Isolates are distributed along 11 genera and 3 phyla. The external ring is color-coded according to genera. Six external rings are color-coded according to the presence of a probiotic trait (catalase, pigments, antiQS, siderophores, and antagonistic) and an additional observed feature (bioluminescence). The isolates exhibiting three or more probiotic traits are marked with black dots symbols. Both trees were constructed using the neighbor-joining method, p-distance model, and a bootstrap value of 1000 replicates. Thermotoga maritima (NR_102775.2) was used as an out-group.
A total of 455 16S rRNA gene sequences were used in the phylogenetic analysis, including 330 sequences from coral-culturable-associated bacteria collected from Sweet et al. [77] and 125 from the present study. Six taxa were found to represent the culturable fraction of different scleractinian corals (Figure 5A), with the predominance of classes Gammaproteobacteria, Alphaproteobacteria, Bacilli, and Actinomycetia. Most of the sequences have been recovered from the healthy coral tissues collected in nonurban sites. Most of the bacteria from diseased and healthy corals were affiliated with the class Gammaproteobacteria, and many of the isolates from the class Actinomycetia were recovered from urban sites. Close relationships within the location, condition, and coral compartment were observed. Some bacteria isolated from coral tissues were closely related to the bacteria isolated from coral mucus, and some Vibrio species isolated from the healthy M. auretenra were closely related to Vibrio species isolated from diseased corals.
3.4. Probiotic Potential of M. auretenra-Associated Bacteria
All the isolates were screened for potential probiotic traits (Figure 5B, Table S10). A total of 98 isolates (74%) showed detectable high catalase production activity, 71 isolates (54%) were positive for siderophores production, and 70 isolates (53%) inhibited the bioluminescent activity of Photobacterium sp. ICM9, and were confirmed by the inhibition of violacein production in C. violaceum. Only 15 isolates (11%) produced pigments, and 3 (2%) had preliminary antagonistic activity against the coral pathogen V. coralliilyticus. Figure 6A,B represents the antiQS activity and siderophore production of isolate ICT17 as examples of these results. The PCA indicated that the first three axes explained 70% of the variation in activities when comparing coral compartments (Figure 6C), and PC1 was significant (p < 0.005) and accounted for 34.8% of the total variation. This analysis showed a grouping of the data where catalase, antiQS, and pigment production activities are positively related and formed PC1. Here, we proposed probiotic precandidates based on the presence of three or more of the screened probiotic traits. In addition, other features such as rapid growth and nonrelation with pathogenic/opportunistic bacteria to corals (based on phylogenetics) were also considered. Initially, 32 isolates filled the first condition (Figure 5B, Table S10); most of them (69%) were affiliated with Vibrio spp. The isolates that showed a close relationship with pathogenic/opportunistic vibrios (Figure 5A, Table S10) were excluded considering their role in coral diseases [81]. Nocardiopsis sp. PCNM4 was also excluded due to slow growth. Thus, we propose a total of 24 bacterial strains as coral probiotic precandidates (Table 2), most of which were isolated from healthy M. auretenra mucus.
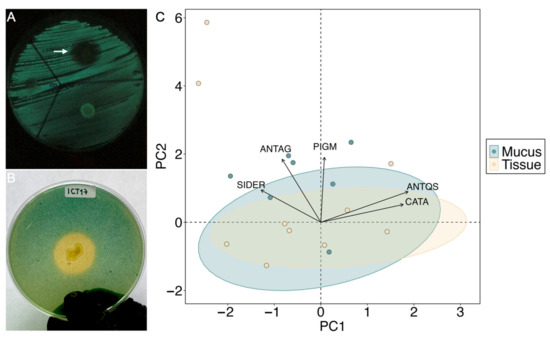
Figure 6.
Screening of some probiotic traits: (A) AntiQS activity. Disruption of the bioluminescence activity that was tested through disk diffusion. The white arrow indicates a positive result where a black halo is formed around the biosensor Photobacterium sp. ICM9 with no growth inhibition. The blank and negative results are also shown (left and right, respectively). (B) Siderophore production detected through chrome azurol sulfonate (CAS) solid assay. A change in color around the colony indicates the release of the dye after the strong ligand siderophore forms a complex with the Fe3+. In this case, the color change occurred from blue to yellow, suggesting the production of carboxylates. (C) Principal Component Analysis (PCA) with data on the probiotic traits. Isolates are color-represented according to the source of isolation (mucus and tissue). PC1: principal component 1. PC2: principal component 2. CATA: catalase. PIGM: pigments. SIDER: siderophores. ANTAG: antagonism. ANTQS: antiQS.

Table 2.
Identity of the coral probiotic precandidates obtained in the present study.
4. Discussion
4.1. Status of Urban Madracis auretenra Coral and Culturable Bacteria
Most coral losses have been ascribed to local habitat destruction, algae overgrowth, pollution, and sedimentation [5]. The urban-influenced M. auretenra patch occurring at Inca Inca, Santa Marta, Colombia is exposed to locally stressful conditions, mainly related to high microbial loads, eutrophication, and algal overgrowth relative to the coral patch of the same species found in the PNN Tayrona. Although nutrients and SST did not significantly differ between sites, and their influence over the benthic categories was weak, higher NO2−, NO3−, and PO43− values seem to predict the shape of the benthic community in the urban site [82,83,84,85]. On the contrary, counts of heterotrophic bacteria and vibrios varied between sites. Urban-influenced coastal environments are exposed to water pollution that introduces allochthonous microorganisms into the marine environment [86,87], and these microorganisms can become opportunistic pathogens to several marine organisms [88,89,90], including corals [91]. The Santa Marta coastal area is an example of this phenomenon, as increases in bacterial loads in seawater surrounding the main discharge sources have been previously documented [92,93,94]. These results suggest that this coral formation dominated by M. auretenra might be experiencing a continuous input of bacterial loads, possibly attributed to anthropogenic activities [95,96].
The high frequency of signs of deterioration such as overturning and sedimentation (Figure 4) might be also associated with anthropogenic activities, since tourism, boat traffic, and coastal development are common on these urban coasts [29,97]. The combination of these stressors promotes increases in the diversity and abundance of microbial groups such as the Vibrionales, often involved in diseases [10,36,38,98,99]. Despite the presence of these local stressors, the urban coral patch exhibits a significantly similar cover and a “good” health index condition compared with the protected M. auretenra occurring at the PNN Tayrona. Considering these findings, we suggest that this coral may be experiencing a site-specific acclimatization/resistance [10,11,12,100]. This could explain why other benthic categories had lower coverage in the urban site, as well as the lack of differences in microbial loads when comparing healthy and diseased corals. These observations are a snapshot of one-time points, and further surveys and monitoring are needed to assess the role of the different factors shaping the benthic distribution of these M. auretenra patches at these sites.
Regarding the M. auretenra-associated cultured bacteria, most isolated strains were Gram-negative bacteria. This is in agreement with other coral–bacteria studies, where Gram-negative bacteria dominate the culturable fraction [101,102,103,104,105]. These bacteria were affiliated with common bacterial groups in coral holobionts, such as Actinomycetota, Bacillota, and Pseudomonadota [16,62,102,106,107,108,109]. We accomplished isolating 11 genera using MA and TSA 1% NaCl, where Vibrio and Photobacterium represented about 74% of the total isolates, compared with other studies which obtained between 9% and 26% bacterial genera [108] and a lower proportion of Vibrio in healthy corals [6,25,50,62,77,110]. As Vibrio species are fast-growing bacteria, it is reasonable that the majority of the isolated strains were affiliated with this genus, as vibrios regularly tend to grow over many other marine bacteria, such as bacteria belonging to Flavobacteriaceae and Oceanospirillaceae [25]. The focus of this study was to culture M. auretenra-associated bacteria (obligate and nonobligate) for probiotic screening; we found MA and TSA 1% NaCl media suitable for this purpose, since these media allow the isolation of different heterotrophic bacterial species, as documented in Sweet et al. [77]. Our results are the first insight into the culturable fraction associated with M. auretenra in the Colombian Caribbean, and preliminary information suggests the existence of a signature in coral-culturable bacteria also observed in microbiome studies [10,107,108,109,111]. We hypothesize the predominance of specific bacterial groups in urban-influenced environments, and we do not dismiss the possibility of Vibrio being proof of this, since the evidence found here showed that vibrio load was significantly higher in urban coral healthy samples, even when other findings suggest this genus is presented at low densities in healthy corals [112,113,114]. Vibrio has been detected as a representative part of the microbial community of other coral species occurring in urban-influenced environments in the Colombian Caribbean [11,50]; however, its dynamics and roles are still subject to future research. This study also reports the presence of Priestia and Niallia genera associated with a scleractinian coral for the first time.
4.2. Presence of Potential Probiotic Traits in M. auretenra-Associated Bacteria
As bacteria are primed to cope with changes in environmental conditions and, by association, so is their coral host, the combination of probiotic traits (Figure 6C and Figure S1) might constitute an intrinsic holobiont defense mechanism [25,115,116]. Since corals are more susceptible to disease when antioxidant activity is low [117], QS signals increase [118], and nutrient starvation occurs [22], enriching corals with bacteria exhibiting combined traits such as “catalase–pigments–antiQS–siderophores” could help the coral to boost health status and fitness. This study provides insight into the functional redundancy capacity of cultured bacteria of urban M. auretenra, as critical criteria for selecting potential probiotics candidates for corals to aim for a synergistic effect. We summarized in Table 3 different studies that have obtained probiotic bacteria (mainly consortia) from several coral species models exhibiting different beneficial traits, and we included the present work. Our work also constitutes the first evaluation of an urban coral as a source of culturable bacteria that jointly exhibit climate-change-mitigation-related beneficial traits.
Here, a broad taxonomic span of taxa constitutes an optimal antioxidant defense. Although the Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) are an inevitable byproduct of homeostatic biological processes [119,120], ROS excess in coral tissues is attributed to the increase in temperature and UV radiation and is the major cause of thermal bleaching [121]. Because bacteria synthesize enzymatic antioxidants, such as catalase, to neutralize and detoxify free ROS [122], increasing the concentration of this enzyme in coral tissues through the application of catalase-positive bacteria could attenuate the impact of oxidative stress when the water warms (Table 3). In this study, the bacterial isolates Vibrio, Shewanella, Exiguobacterium, Priestia, Fictibacillus, and Bacillus, obtained from healthy urban coral, unveil potential as antioxidant candidates. Additionally, some of the isolates exhibited pigment production, which peaks at 400–500 nm, suggesting most are carotenoid-like pigments (see Figure S2) [123,124,125]. Carotenoids can act as a photoprotector, antioxidant, antibiotic, and cytotoxic [115,126,127]. The accumulation of carotenoids has been found as a propitious scenario to counteract the harmful effect of ROS [128], as well as acting as a “sunscreen” to counteract the effect of harmful high UV-radiation exposure [65,129,130].
In the same scenario of climate change, acidification is expected to cause a reduction in bioavailable iron in the environment, making our findings of ubiquitous siderophore production a promising mechanism to exploit to indirectly help corals [25,131,132,133]. Siderophore-producing bacteria could help maintain iron availability, a micronutrient necessary for the growth and multiplication of algal symbionts [134]. Although catecholates are the strongest chelating siderophores [135], here, we report the isolation of hydroxamate- and carboxylate-type siderophores-producing bacteria (see Table S10). Additionally, here, antiQS activity was well represented in cultured bacteria compared with other studies that report from 15% (200 tested isolates against Chromobacterium violaceum) to 24% (120 tested isolates against bioluminescent mutant Escherichia coli) positive isolates obtained from scleractinian corals [21,136,137]. Since we found low antagonism, antiQS activity might act as a competition-related control mechanism that allows the coexistence of the bacterial members in the coral compartments [106]. Destabilized QS communication plays a key role in stressed corals [138], leading to disease outbreaks [118,139,140,141]. However, some studies have shown that the addition of quorum-sensing inhibitors (QSIs) arrests the development of disease in Acropora cervicornis [141,142]. Despite their applicability potential, QSIs have not been widely explored as a probiotic trait tool (Table 3), even when they are by far one of the most important traits in selecting probiotic candidates [143].

Table 3.
Summary of studies that aimed at isolating and characterizing probiotic coral-associated bacteria.
Table 3.
Summary of studies that aimed at isolating and characterizing probiotic coral-associated bacteria.
| Probiotic Candidates (Genera) | Source of Isolation | Compartment and Condition | Location | Exhibited Probiotic Trait(s) | Tested Efficacy | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vibrio and Pseudoalteromonas | Various scleractinian corals | Healthy mucus | Gulf of Eilat, Israel | Anti-QS activity (Quorum sensing disruption of different biosensors) | No | [136] |
| Bacillus, Acinetobacter, Paracoccus, Pseudomonas, Vibrio, and Psychrobacter | Mussismilia harttii | Healthy tissue | Natural Park, Recife de Fora, Porto Seguro, Bahia, Brazil | Degradation of pollutants (oils) | Yes | [24] |
| Cobetia, Halomonas, and Pseudoalteromonas | Aquaria-maintained Pocillopora damicornis | Healthy tissue and surrounding water | Rio de Janeiro, Brazil | Catalase, antagonism against V. coralliilyticus and nifH and nirK | Yes | [25] |
| Bacillus, Pseudomonas, Photobacterium, Acinetobacter, Vibrio, and Enterobacter | Exposed low-tide Porites spp., and Turbinaria | Healthy and diseased mucus | Poshitra Natural Park, GoK, Jamnagar, Gujarat, India | Siderophore production | No | [22] |
| Shewanella, Cobetia, Halomonas, and Pseudoalteromonas | Oil-influenced Siderastrea stellata | Healthy tissue | Armação dos Búzios, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil | Degradation of pollutants (oils) | Yes | [7] |
| Bacillus, Planococcus, Salinivibrio, and Brachybacterium | Thermally resistant Mussismilia hispida | Healthy tissue | Maraú, Bahia, Brazil | Catalase, antagonism against V. coralliilyticus and V. alginolyticus, and nifH and nirK | Yes | [26] |
| Yangia, Roseobacter, Phytobacter, and Salinicola | Various scleractinian corals | Healthy tissue | Gaven Reef, Fiery Cross Reef, Johnson South Reef, South China Sea | Nitrogen-cycling genes nifH | Yes | [27] |
| Vibrio, Shewanella, Exiguobacterium, Bacillus, Fictibacillus, and Priestia | Urban Madracis auretenra | Healthy mucus and tissue | Inca Inca, Santa Marta, Colombia | Catalase, pigment, antagonism and anti-QS, and siderophore production | Not yet | Present study |
After observing the presence of these probiotic traits, we highlight that healthy mucus is a potential source of beneficial bacteria, in agreement with the fact that it is considered the first line of defense and protection of the coral host [144]. Despite Bacillus species being widely tested as probiotics for a broad range of animals [145,146] and Shewanella spp being used to degrade different pollutants, we propose genera Fictibacillus, Exiguobacterium, and Priestia (all Bacilli) as promising novel candidates to be tested in future probiotic-based assays in coral hosts (Table 3). Although Vibrio has been considered commensal, opportunistic, and pathogenic [21,81,116,143], some species have been used as beneficial bacteria for corals (Table 3). The probiotic potential of Vibrio species has not yet been demonstrated, because they are generally excluded due to their pathogenic behavior [7,26]; however, due to these vibrios being isolated from healthy M. auretenra, our findings suggest that some of these may exhibit probiotic traits such as catalase, antiQS, or the production of siderophores activities. We hypothesize that as some Vibrio switch from commensal to opportunistic–pathogenic behavior, others might switch to a beneficial state when control mechanisms (i.e., antiQS activity) are present. This is supported by the fact that Vibrio species play essential roles in coral hosts, as some are nitrogen fixers in mucus and dominate the culturable nitrogen-fixing bacteria of some corals [147,148], and others have exhibited antimicrobial and antiQS activity against other vibrios. This all suggests some vibrios play a role in coral defense [91,136,137]; however, this hypothesis requires further testing and study.
5. Conclusions
We assessed the probiotic potential of culturable bacteria associated with an urban coral in the search for candidates that exhibit traits that may contribute to mitigating the impacts on corals under local anthropogenic disturbances and global climate change. We proposed a list of a variety of taxa that exhibit different probiotic traits, and we highlighted the inclusion of possible beneficial vibrios. We also aimed to identify possible local stressors in urban-influenced environments that may be shaping the structure of benthic communities and their associated bacteria. Coral probiotics are a promising intervention strategy to protect and improve coral health. Further studies are required to target diverse coral species as new potential sources of bacteria exhibiting probiotic traits. A big challenge is to validate the efficacy and feasibility of a probiotic treatment strategy, especially in the Caribbean countries, where there is an urgent need to prioritize the search for solutions to the outbreak of infectious diseases and the rapid loss of coral cover.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/jmse11102006/s1, Figure S1: Venn Diagram of probiotic traits; Figure S2: Curve of absorbance peaks of bacterial pigments. Table S1: Health index scores and calculation. Table S2: PERMANOVA analysis of the microbiological data. Table S3: PERMANOVA analysis of the biological-coverage data. Table S4: DistLM analyses of the RDA model of the environmental and biological data. Table S5: Chi2 analysis of the biological interaction data. Table S6: Environmental conditions in the patches of Madracis auretenra at both sites. S1: Chengue, S2: Inca Inca, T: Temperature, S: Salinity, TSS: Total suspended solids. Table S7: Counts of total vibrios and heterotrophs. S1: Chengue, S2: Inca Inca, S: Healthy, E: Diseased, M: Mucus, T: Tissue. Table S8: Coverage (%) of the benthic categories associated with the Madracis auretenra patches. CCA: Crustose coralline algae. Table S9: Frequency of contact (%) between M. auretenra and other benthic categories. CCA: Crustose coralline algae. Table S10: Raw data from the bacterial isolation. Isolates ID, morphology, and screenings. Database of the bacterial isolates regarding information about collection and molecu-lar identification with NCBI access codes. Matrix for PCA analysis and a summary of the selection of the final probiotic precandidates. Table S11: NCBI access codes of the bacterial strains isolated from scleractinian corals and collected from the database http://isolates.reefgenomics.org/ (accessed on 30 November 2022) and used in the phylogenetic analysis.
Author Contributions
J.S.R.-T., conceptualization, methodology, software, validation, formal analysis, investigation, data curation, writing—original draft preparation, writing—review and editing, visualization, supervision, project administration, and funding acquisition; L.A.Y.-D., methodology, software, validation, investigation, data curation, and visualization; C.H.K., methodology, software, validation, and investigation; I.R.B., methodology, resources, and writing—review and editing; A.S.-M., formal analysis, writing—review and editing, and funding acquisition; M.M., resources, writing—review and editing, supervision, and project administration; A.F.-H., resources, writing—review and editing, supervision, project administration, and funding acquisition. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Corporation Center of Excellence in Marine Sciences-CEMarin, Call No° 21 of 2021 for financial support for postgraduate thesis projects in marine sciences and related areas, and by the Universidad de Bogota Jorge Tadeo Lozano, Call No° 21 of 2021 and resolution No° 007 of 25 May 2022.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was conducted in accordance with the approval of the Ethics Committee of Universidad de Bogota Jorge Tadeo Lozano (8 April 2022). “Not applicable” for studies not involving humans or animals.
Data Availability Statement
The new dataset of partial 16S rRNA sequences obtained in this study can be found in the NCBI database (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ (accessed on 30 November 2021)) and in the original publications. Please refer to Tables S10 and S11 for specific accession numbers.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the personnel from the Universidad de Bogota Jorge Tadeo Lozano, Santa Marta, and the Water Quality Laboratory, as well as the Evolution, Systematics, and Molecular Ecology Laboratory units at Universidad del Magdalena. We thank the LABCAM unit of the Marine and Coastal Research Institute-INVEMAR for the chemical analysis. We especially thank Carlos España and Angel Oviedo for their help in the laboratory, Luis Garzón for his help in drawing the schematic map, and Natalia Comba for her advice and reagent donations. We also thank the Ministerio de Ciencias y Tecnología-MINCIENCIAS for the Bicentennial Doctoral Excellence Grant.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Uthicke, S.; Ebert, T.; Liddy, M.; Johansson, C.; Fabricius, K.E.; Lamare, M. Echinometra Sea Urchins Acclimatized to Elevated PCO2 at Volcanic Vents Outperform Those under Present-Day PCO2 Conditions. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2016, 22, 2451–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenger, A.S.; Williamson, D.H.; da Silva, E.T.; Ceccarelli, D.M.; Browne, N.K.; Petus, C.; Devlin, M.J. Effects of Reduced Water Quality on Coral Reefs in and out of No-Take Marine Reserves. Conserv. Biol. 2016, 30, 142–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, T.P.; Anderson, K.D.; Connolly, S.R.; Heron, S.F.; Kerry, J.T.; Lough, J.M.; Baird, A.H.; Baum, J.K.; Berumen, M.L.; Bridge, T.C.; et al. Spatial and Temporal Patterns of Mass Bleaching of Corals in the Anthropocene. Science 2018, 359, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellis, J.I.; Jamil, T.; Anlauf, H.; Coker, D.J.; Curdia, J.; Hewitt, J.; Jones, B.H.; Krokos, G.; Kürten, B.; Hariprasad, D.; et al. Multiple Stressor Effects on Coral Reef Ecosystems. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2019, 25, 4131–4146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine. A Research Review of Interventions to Increase the Persistence and Resilience of Coral Reefs; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2019; ISBN 978-0-309-48535-7. [Google Scholar]
- Villela, H.D.M.; Vilela, C.L.S.; Assis, J.M.; Varona, N.; Burke, C.; Coil, D.A.; Eisen, J.A.; Peixoto, R.S. Prospecting Microbial Strains for Bioremediation and Probiotics Development for Metaorganism Research and Preservation. J. Vis. Exp. 2019, 152, e60238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, D.P.; Villela, H.D.M.; Santos, H.F.; Duarte, G.A.S.; Ribeiro, J.R.; Ghizelini, A.M.; Vilela, C.L.S.; Rosado, P.M.; Fazolato, C.S.; Santoro, E.P.; et al. Multi-Domain Probiotic Consortium as an Alternative to Chemical Remediation of Oil Spills at Coral Reefs and Adjacent Sites. Microbiome 2021, 9, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peixoto, R.S.; Sweet, M.; Villela, H.D.M.; Cardoso, P.; Thomas, T.; Voolstra, C.R.; Høj, L.; Bourne, D.G. Coral Probiotics: Premise, Promise, Prospects. Annu. Rev. Anim. Biosci. 2021, 9, 265–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reshef, L.; Koren, O.; Loya, Y.; Zilber-Rosenberg, L.; Rosenberg, E. The Coral Probiotic Hypothesis. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 8, 2068–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, M.; Grupstra, C.G.B.; Barreto, M.M.; Eaton, M.; BaOmar, J.; Zubier, K.; Al-Sofyani, A.; Turki, A.J.; Ormond, R.; Voolstra, C.R. Coral Bacterial Community Structure Responds to Environmental Change in a Host-Specific Manner. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roitman, S.; López-Londoño, T.; Pollock, J.F.; Ritchie, K.B.; Galindo-Martínez, C.T.; Gómez-Campo, K.; González-Guerrero, L.A.; Pizarro, V.; López-Victoria, M.; Iglesias-Prieto, R.; et al. Surviving Marginalized Reefs: Assessing the Implications of the Microbiome on Coral Physiology and Survivorship. Coral Reefs 2020, 39, 795–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deignan, L.K.; McDougald, D. Differential Response of the Microbiome of Pocillopora Acuta to Reciprocal Transplantation within Singapore. Microb. Ecol. 2022, 83, 608–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziegler, M.; Seneca, F.O.; Yum, L.K.; Palumbi, S.R.; Voolstra, C.R. Bacterial Community Dynamics Are Linked to Patterns of Coral Heat Tolerance. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savary, R.; Barshis, D.J.; Voolstra, C.R.; Cárdenas, A.; Evensen, N.R.; Banc-Prandi, G.; Fine, M.; Meibom, A. Fast and Pervasive Transcriptomic Resilience and Acclimation of Extremely Heat-Tolerant Coral Holobionts from the Northern Red Sea. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2023298118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maire, J.; van Oppen, M.J.H. A Role for Bacterial Experimental Evolution in Coral Bleaching Mitigation? Trends Microbiol. 2022, 30, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourne, D.G.; Morrow, K.M.; Webster, N.S. Insights into the Coral Microbiome: Underpinning the Health and Resilience of Reef Ecosystems. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 70, 317–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thatcher, C.; Høj, L.; Bourne, D.G. Probiotics for Coral Aquaculture: Challenges and Considerations. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2022, 73, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindran, J.; Kannapiran, E.; Manikandan, B.; Francis, K.; Arora, S.; Karunya, E.; Kumar, A.; Singh, S.K.; Jose, J. UV-Absorbing Bacteria in Coral Mucus and Their Response to Simulated Temperature Elevations. Coral Reefs 2013, 32, 1043–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dungan, A.M.; Bulach, D.; Lin, H.; Van Oppen, M.J.H.; Blackall, L.L. Development of a Free Radical Scavenging Probiotic to Mitigate Coral Bleaching. bioRxiv 2020, 1, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raina, J.B.; Tapiolas, D.; Motti, C.A.; Foret, S.; Seemann, T.; Tebben, J.; Willis, B.L.; Bourne, D.G. Isolation of an Antimicrobial Compound Produced by Bacteria Associated with Reef-Building Corals. PeerJ 2016, 4, e2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.P.; Song, Y.; Cai, Z.H.; Lin, Z.J.; Lin, G.H.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, J. Anti-Quorum Sensing Activities of Selected Coral Symbiotic Bacterial Extracts from the South China Sea. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, N.P.; Shimpi, G.G.; Haldar, S. Evaluation of Heterotrophic Bacteria Associated with Healthy and Bleached Corals of Gulf of Kutch, Gujarat, India for Siderophore Production and Their Response to Climate Change Factors. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 113, 106219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peixoto, R.S.; Rosado, P.M.; Leite, D.C.A.; Rosado, A.S.; Bourne, D.G. Beneficial Microorganisms for Corals (BMC): Proposed Mechanisms for Coral Health and Resilience. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fragoso Ados Santos, H.; Duarte, G.A.S.; Rachid, C.T.D.C.; Chaloub, R.M.; Calderon, E.N.; Marangoni, L.F.D.B.; Bianchini, A.; Nudi, A.H.; Do Carmo, F.L.; Van Elsas, J.D.; et al. Impact of Oil Spills on Coral Reefs Can Be Reduced by Bioremediation Using Probiotic Microbiota. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 18268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosado, P.M.; Leite, D.C.A.; Duarte, G.A.S.; Chaloub, R.M.; Jospin, G.; Nunes da Rocha, U.; Saraiva, J.P.; Dini-Andreote, F.; Eisen, J.A.; Bourne, D.G.; et al. Marine Probiotics: Increasing Coral Resistance to Bleaching through Microbiome Manipulation. ISME J. 2019, 13, 921–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoro, E.P.; Borges, R.M.; Espinoza, J.L.; Freire, M.; Messias, C.S.M.A.; Villela, H.D.M.; Pereira, L.M.; Vilela, C.L.S.; Rosado, J.G.; Cardoso, P.M.; et al. Coral Microbiome Manipulation Elicits Metabolic and Genetic Restructuring to Mitigate Heat Stress and Evade Mortality. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, 3088–3101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, Q.; Ling, J.; Long, L.; Huang, H.; Yin, J.; Wu, M.; Tang, X.; Lin, X.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Shifting the Microbiome of a Coral Holobiont and Improving Host Physiology by Inoculation with a Potentially Beneficial Bacterial Consortium. BMC Microbiol. 2021, 21, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camp, E.F.; Schoepf, V.; Suggett, D.J. How Can “Super Corals” Facilitate Global Coral Reef Survival under Rapid Environmental and Climatic Change? Glob. Change Biol. 2018, 24, 2755–2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heery, E.C.; Hoeksema, B.W.; Browne, N.K.; Reimer, J.D.; Ang, P.O.; Huang, D.; Friess, D.A.; Chou, L.M.; Loke, L.H.L.; Saksena-Taylor, P.; et al. Urban Coral Reefs: Degradation and Resilience of Hard Coral Assemblages in Coastal Cities of East and Southeast Asia. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 135, 654–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wainwright, B.J.; Afiq-Rosli, L.; Zahn, G.L.; Huang, D. Characterisation of Coral-Associated Bacterial Communities in an Urbanised Marine Environment Shows Strong Divergence over Small Geographic Scales. Coral Reefs 2019, 38, 1097–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Röthig, T.; Ochsenkühn, M.A.; Roik, A.; Van Der Merwe, R.; Voolstra, C.R. Long-Term Salinity Tolerance Is Accompanied by Major Restructuring of the Coral Bacterial Microbiome. Mol. Ecol. 2016, 25, 1308–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, K.T.; Bender-Champ, D.; Hoegh-Guldberg, O.; Dove, S. Seasonal Shifts in the Competitive Ability of Macroalgae Influence the Outcomes of Coral-Algal Competition. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2020, 7, 201797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Castillo, V.; Rodríguez-Troncoso, A.P.; Santiago-Valentín, J.D.; Cupul-Magaña, A.L. The Influence of Urban Pressures on Coral Physiology on Marginal Coral Reefs of the Mexican Pacific. Coral Reefs 2020, 39, 625–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, M.O.; Rossi, S.; Gurgel, A.R.; Lucas, C.C.; Tavares, T.C.L.; Diniz, B.; Feitosa, C.V.; Rabelo, E.F.; Pereira, P.H.C.; de Kikuchi, R.K.P.; et al. Impacts of a Changing Environment on Marginal Coral Reefs in the Tropical Southwestern Atlantic. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2021, 210, 105692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burt, J.A.; Camp, E.F.; Enochs, I.C.; Johansen, J.L.; Morgan, K.M.; Riegl, B.; Hoey, A.S. Insights from Extreme Coral Reefs in a Changing World. Coral Reefs 2020, 39, 495–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDevitt-Irwin, J.M.; Baum, J.K.; Garren, M.; Vega Thurber, R.L. Responses of Coral-Associated Bacterial Communities to Local and Global Stressors. Front. Mar. Sci. 2017, 4, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouédraogo, D.Y.; Delaunay, M.; Sordello, R.; Hédouin, L.; Castelin, M.; Perceval, O.; Domart-Coulon, I.; Burga, K.; Ferrier-Pagès, C.; Multon, R.; et al. Evidence on the Impacts of Chemicals Arising from Human Activity on Tropical Reef-Building Corals; a Systematic Map. Environ. Evid. 2021, 10, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, E.I.; Juhmani, A.S.F.; Jacob, J.H.; Telfah, M.A.; Al-Razaq, M.A.A.; Al-Horani, F.A.; Al Zoubi, M.S.; Malkawi, H.I. Effect of Various Local Anthropogenic Impacts on the Diversity of Coral Mucus-Associated Bacterial Communities. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winston, M.; Oliver, T.; Couch, C.; Donovan, M.K.; Asner, G.P.; Conklin, E.; Fuller, K.; Grady, B.W.; Huntington, B.; Kageyama, K.; et al. Coral Taxonomy and Local Stressors Drive Bleaching Prevalence across the Hawaiian Archipelago in 2019. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0269068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Márquez, A. Estudio Sedimentológico y Morfológico de La Plataforma Continental Caribe Entre El Sector de Santa Marta y Punta Morro Hermoso. Boletín Cient. CIOH 1993, 1, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cámara de Comercio de Santa Marta. Informe Económico Anual de La Jurisdicción; Cámara de Comercio de Santa Marta: Magdalena, Colombia, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Parques Nacionales Naturales de Colombia. Unidad Administrativa Especial del Sistema de Parques Naturales; Parques Nacionales Naturales de Colombia: Bogotá, Colombia, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Franco-Herrera, A. Oceanografía de La Ensenada de Gaira; Universidad Jorge Tadeo Lozano: Bogotá, Colombia, 2005; ISBN 958-9029-72-8. [Google Scholar]
- Vega-Sequeda, J.; Polo-Silva, C.J.; Franco-Herrera, A.; Paramo-Granados, J.; Sanjuan-Muñoz, A. Dynamics of Physicochemical Variables of the Northern Colombian Caribbean Coastal Waters. DYNA 2019, 86, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Ortega, L.M.; Vidal, L.A.; Vilardy, S.; Saavedra-Díaz, L. Análisis de La Contaminación Microbiológica (Coliformes Totales y Fecales) En La Bahía de Santa Marta, Caribe Colombiano. Acta Biol. Colomb. 2008, 13, 87–98. [Google Scholar]
- García, F.; Palacio, C.; Garcia, U. Calidad Del Agua En El Área Costera de Santa Marta (Colombia). DYNA 2012, 79, 85–94. [Google Scholar]
- Vega-Sequeda, J.; Rodríguez-Ramírez, A.; Reyes-Nivia, M.C.; Navas-Camacho, R. Formaciones Coralinas Del Área de Santa Marta: Estado y Patrones de Distribución Espacial de La Comunidad Bentónica. Boletín Investig. Mar. Costeras 2008, 37, 87–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locke, J.M.; Weil, E.; Coates, K.A. A Newly Documented Species of Madracis (Scleractinia: Pocilloporidae) from the Caribbean. Proc. Biol. Soc. Wash. 2007, 120, 214–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Invemar (Ed.) Corales Escleractinios de Colombia; No. 14; Invemar Serie de Publicaciones Especiales: Santa Marta, Colombia, 2010; Volume 14, ISBN 978-958-8448-21-3. [Google Scholar]
- Cárdenas, A.; Rodriguez, R.L.M.; Pizarro, V.; Cadavid, L.F.; Arévalo-Ferro, C. Shifts in Bacterial Communities of Two Caribbean Reef-Building Coral Species Affected by White Plague Disease. ISME J. 2012, 6, 502–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, K.T.; Bender-Champ, D.; Bryant, D.E.P.; Dove, S.; Hoegh-Guldberg, O. Human Activities Influence Benthic Community Structure and the Composition of the Coral-Algal Interactions in the Central Maldives. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2017, 497, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trygonis, V.; Sini, M. PhotoQuad: A Dedicated Seabed Image Processing Software, and a Comparative Error Analysis of Four Photoquadrat Methods. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2012, 424, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barott, K.; Smith, J.; Dinsdale, E.; Hatay, M.; Sandin, S.; Rohwer, F. Hyperspectral and Physiological Analyses of Coral-Algal Interactions. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e8043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuthbert, M.W.; Smith, D.W.; Arróliga, O.; Mendoza, J.; Torres, N.; Flores, O. Indice de Salud Arrecifal (ISA) En Los Arrecifes Coralinos de Cayos Miskitos. Rev. Univ. Del. Caribe 2019, 22, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Grimón, R.; Campos, N.H.; Castro, Í.B. Effect of Maritime Traffic on Water Quality Parameters in Santa Marta, Colombia. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strickland, J.D.H.; Parsons, T.R. A Practical Handbook of Seawater Analysis; Fisheries Research Board of Canada: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 1972; Volume 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.J. Permutation Tests for Univariate or Multivariate Analysis of Variance and Regression. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2001, 58, 626–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, K.R.; Gorley, R.N. Getting Started with PRIMER v7. PRIMER-E; Plymouth Marine Laboratory: Plymouth, UK, 2015; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Legendre, P.; Legendre, L. Numerical Ecology; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Oksanen, J.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; O’Hara, B.; Stevens, M.H.H.; Oksanen, M.J.; Suggests, M.A.S.S. The Vegan Package; 2008; Volume 10. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Gavin-Simpson-2/publication/228339454_The_vegan_Package/links/0912f50be86bc29a7f000000/The-vegan-Package.pdf (accessed on 26 September 2023).
- Cooksey, R.W. Illustrating Statistical Procedures: Finding Meaning in Quantitative Data; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; ISBN 978-981-15-2537-7. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Zou, Y.; Yang, J.; Li, Q.; Bourne, D.G.; Sweet, M.; Liu, C.; Guo, A.; Zhang, S. Cultured Bacteria Provide Insight into the Functional Potential of the Coral-Associated Microbiome. mSystems 2022, 7, e00327-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrow, K.M.; Pankey, M.S.; Lesser, M.P. Community Structure of Coral Microbiomes Is Dependent on Host Morphology. Microbiome 2022, 10, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiner, K. Catalase Test Protocol; American Society for Microbiology: Washington, DC, USA, 2010; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Ratnakaran, P.; Bhoir, M.; Durve-Gupta, A. Isolation and Characterization of Pigment Producing Bacteria Isolated from Waste. Int. J. Appl. Res. 2020, 6, 252–260. [Google Scholar]
- Velho-Pereira, S.; Kamat, N.M. Antimicrobial Screening of Actinobacteria Using a Modified Cross-Streak Method. Indian. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 73, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesa-Luna, C.; Baez, A.; Aguayo-Acosta, A.; Llano-Villarreal, R.C.; Juárez-González, V.R.; Gaytán, P.; del Rocío Bustillos-Cristales, M.; Rivera-Urbalejo, A.; Muñoz-Rojas, J.; Quintero-Hernández, V. Growth Inhibition of Pathogenic Microorganisms by Pseudomonas Protegens EMM-1 and Partial Characterization of Inhibitory Substances. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0240545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodl, E.; Winkler, A.; Macheroux, P. Molecular Mechanisms of Bacterial Bioluminescence. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2018, 16, 551–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunlap, P. Biochemistry and Genetics of Bacterial Bioluminescence. Adv. Biochem. Eng. Biotechnol. 2014, 144, 37–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajivgandhi, G.; Vijayan, R.; Maruthupandy, M.; Vaseeharan, B.; Manoharan, N. Antibiofilm Effect of Nocardiopsis sp. GRG 1 (KT235640) Compound against Biofilm Forming Gram Negative Bacteria on UTIs. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 118, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwyn, B.; Neilands, J.B. Universal Chemical Assay for the Detection and Determination of Siderophores. Anal. Biochem. 1987, 160, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Miranda, S.; Cabirol, N.; George-Téllez, R.; Zamudio-Rivera, L.S.; Fernández, F.J. O-CAS, a Fast and Universal Method for Siderophore Detection. J. Microbiol. Methods 2007, 70, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, J.A.; Reich, C.I.; Sharma, S.; Weisbaum, J.S.; Wilson, B.A.; Olsen, G.J. Critical Evaluation of Two Primers Commonly Used for Amplification of Bacterial 16S RRNA Genes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 2461–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, T.A. BioEdit: A User-Friendly Biological Sequence Alignment Editor and Analysis Program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser. 1999, 41, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Yarza, P.; Yilmaz, P.; Pruesse, E.; Glöckner, F.O.; Ludwig, W.; Schleifer, K.; Whitman, W.; Euzéby, J.; Amann, R.; Rosselló-Móra, R. Uniting the Classification of Cultured and Uncultured Bacteria and Archaea Using 16S RRNA Gene Sequences. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2014, 12, 635–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, S.H.; Ha, S.M.; Kwon, S.; Lim, J.; Kim, Y.; Seo, H.; Chun, J. Introducing EzBioCloud: A Taxonomically United Database of 16S RRNA Gene Sequences and Whole-Genome Assemblies. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 1613–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweet, M.; Villela, H.; Keller-Costa, T.; Costa, R.; Romano, S.; Bourne, D.G.; Cárdenas, A.; Huggett, M.J.; Kerwin, A.H.; Kuek, F.; et al. Insights into the Cultured Bacterial Fraction of Corals. mSystems 2021, 6, e01249-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree of Life (ITOL) v3: An Online Tool for the Display and Annotation of Phylogenetic and Other Trees. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W242–W245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comba González, N.; Ramírez Hoyos, M.L.; López Kleine, L.; Montoya Castaño, D. Production of Enzymes and Siderophores by Epiphytic Bacteria Isolated from the Marine Macroalga Ulva Lactuca. Aquat. Biol. 2018, 27, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munn, C.B. The Role of Vibrios in Diseases of Corals. Microbiol. Spectr. 2015, 3, 3–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaffelke, B.; Klumpp, D.W. Nutrient-Limited Growth of the Coral Reef Macroalga Sargassum Baccularia and Experimental Growth Enhancement by Nutrient Addition in Continuous Flow Culture. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1998, 164, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Angelo, C.; Wiedenmann, J. Impacts of Nutrient Enrichment on Coral Reefs: New Perspectives and Implications for Coastal Management and Reef Survival. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2014, 7, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashida, H.; Matear, R.J.; Strutton, P. Background Nutrient Concentration Determines Phytoplankton Bloom Response to Marine Heatwaves. Glob. Change Biol. 2020, 26, 4800–4811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalley, E.M.; Tuttle, L.J.; Conklin, E.E.; Barkman, A.L.; Wulstein, D.M.; Schmidbauer, M.C.; Donahue, M.J. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Direct Effects of Nutrients on Corals. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 856, 159093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipp, E.; Griffin, D.W. Analysis of Coral Mucus as an Improved Medium for Detection of Enteric Microbes and for Determining Patterns of Sewage Contamination in Reef Environments. Ecohealth 2004, 1, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beurmann, S.; Ushijima, B.; Videau, P.; Svoboda, C.M.; Chatterjee, A.; Aeby, G.S.; Callahan, S.M. Dynamics of Acute Montipora White Syndrome: Bacterial Communities of Healthy and Diseased M. Capitata Colonies during and after a Disease Outbreak. Microbiology 2018, 164, 1240–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buccheri, M.A.; Salvo, E.; Coci, M.; Quero, G.M.; Zoccarato, L.; Privitera, V.; Rappazzo, G. Investigating Microbial Indicators of Anthropogenic Marine Pollution by 16S and 18S High-Throughput Sequencing (HTS) Library Analysis. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2019, 366, fnz179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Numberger, D.; Ganzert, L.; Zoccarato, L.; Mühldorfer, K.; Sauer, S.; Grossart, H.P.; Greenwood, A.D. Characterization of Bacterial Communities in Wastewater with Enhanced Taxonomic Resolution by Full-Length 16S RRNA Sequencing. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orel, N.; Fadeev, E.; Klun, K.; Ličer, M.; Tinta, T.; Turk, V. Bacterial Indicators Are Ubiquitous Members of Pelagic Microbiome in Anthropogenically Impacted Coastal Ecosystem. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 765091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, K. Regulation of Microbial Populations by Coral Surface Mucus and Mucus-Associated Bacteria. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2006, 332, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narváez, S.; Gómez, M.; Acosta, J. Coliformes Termotolerantes En Aguas de Las Poblaciones Costeras y Palafíticas de La Ciénaga Grande de Santa Marta, Colombia. Acta Biol. Colomb. 2008, 13, 113–122. [Google Scholar]
- INVEMAR Análisis Histórico 2001–2021 de La Calidad de Las Aguas Marinas y Costeras En El Caribe y Pacífico Colombianos. Red de Vigilancia para la Conservación y Protección de las Aguas Marinas y Costeras de Colombia; Serie de Publicaciones Periódicas No. 4 del INVEMAR. Invemar: Santa Marta, Colombia, 2022; p. 208. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/362157282_Analisis_historico_2001-2021_de_la_calidad_de_las_aguas_marinas_y_costeras_en_el_Caribe_y_Pacifico_Colombianos_Informe_REDCAM_2021 (accessed on 26 September 2023).
- INVEMAR Diagnóstico y Evaluación de La Calidad de Las Aguas Marinas y Costeras En El Caribe y Pacífico Colombianos. In Red. de Vigilancia para la Conservación y Protección de las Aguas Marinas y Costeras de Colombia; Serie de Publicaciones Periódicas No. 4 del INVEMAR; Invemar: Santa Marta, Colombia, 2020; p. 171. Available online: https://www.invemar.org.co/documents/10182/14479/Informe+REDCAM+2016.pdf/b21d50f5-cd2d-4926-a016-b321cc9659e7 (accessed on 26 September 2023).
- Stewart, J.R.; Gast, R.J.; Fujioka, R.S.; Solo-Gabriele, H.M.; Meschke, J.S.; Amaral-Zettler, L.A.; Del Castillo, E.; Polz, M.F.; Collier, T.K.; Strom, M.S.; et al. The Coastal Environment and Human Health: Microbial Indicators, Pathogens, Sentinels and Reservoirs. Environ. Health 2008, 7, S3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraus, R.; Baljak, V.; Vukić Lušić, D.; Kranjčević, L.; Cenov, A.; Glad, M.; Kauzlarić, V.; Lušić, D.; Grbčić, L.; Alvir, M.; et al. Impacts of Atmospheric and Anthropogenic Factors on Microbiological Pollution of the Recreational Coastal Beaches Neighboring Shipping Ports. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 8552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fudjaja, L.; Viantika, N.M.; Rani, C.; Nurdin, N.; Priosambodo, D.; Tenriawaru, A.N. Anthropogenic Activity and the Destruction of Coral Reefs in the Waters of Small Islands. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 575, 012057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tout, J.; Siboni, N.; Messer, L.F.; Garren, M.; Stocker, R.; Webster, N.S.; Ralph, P.J.; Seymour, J.R. Increased Seawater Temperature Increases the Abundance and Alters the Structure of Natural Vibrio Populations Associated with the Coral Pocillopora Damicornis. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, D.C.A.; Salles, J.F.; Calderon, E.N.; Castro, C.B.; Bianchini, A.; Marques, J.A.; van Elsas, J.D.; Peixoto, R.S. Coral Bacterial-Core Abundance and Network Complexity as Proxies for Anthropogenic Pollution. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunphy, C.M.; Gouhier, T.C.; Chu, N.D.; Vollmer, S.V. Structure and Stability of the Coral Microbiome in Space and Time. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohwer, F.; Seguritan, V.; Azam, F.; Knowlton, N. Diversity and Distribution of Coral-Associated Bacteria. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2002, 243, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Littman, R.A.; Willis, B.L.; Pfeffer, C.; Bourne, D.G. Diversities of Coral-Associated Bacteria Differ with Location, but Not Species, for Three Acroporid Corals on the Great Barrier Reef. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2009, 68, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, M.J.; Yu, Y.T.; Chen, C.A.; Chiang, P.W.; Tang, S.L. Influence of Species Specificity and Other Factors on Bacteria Associated with the Coral Stylophora Pistillata in Taiwan. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 7797–7806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunagawa, S.; Woodley, C.M.; Medina, M. Threatened Corals Provide Underexplored Microbial Habitats. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blackall, L.L.; Wilson, B.; Van Oppen, M.J.H. Coral-the World’s Most Diverse Symbiotic Ecosystem. Mol. Ecol. 2015, 24, 5330–5347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourne, D.G.; Munn, C.B. Diversity of Bacteria Associated with the Coral Pocillopora Damicornis from the Great Barrier Reef. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 7, 1162–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollock, F.J.; McMinds, R.; Smith, S.; Bourne, D.G.; Willis, B.L.; Medina, M.; Thurber, R.V.; Zaneveld, J.R. Coral-Associated Bacteria Demonstrate Phylosymbiosis and Cophylogeny. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Agreda, A.; Gates, R.D.; Ainsworth, T.D. Defining the Core Microbiome in Corals’ Microbial Soup. Trends Microbiol. 2017, 25, 125–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez-Agreda, A.; Leggat, W.; Bongaerts, P.; Herrera, C.; Ainsworth, T.D. Rethinking the Coral Microbiome: Simplicity Exists within a Diverse Microbial Biosphere. mBio 2018, 9, e00812-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lampert, Y.; Kelman, D.; Dubinsky, Z.; Nitzan, Y.; Hill, R.T. Diversity of Culturable Bacteria in the Mucus of the Red Sea Coral Fungia Scutaria. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2006, 58, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Oppen, M.J.H.; Blackall, L.L. Coral Microbiome Dynamics, Functions and Design in a Changing World. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 557–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arboleda, M.; Reichardt, W. Epizoic Communities of Prokaryotes on Healthy and Diseased Scleractinian Corals in Lingayen Gulf, Philippines. Microb. Ecol. 2009, 57, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenig, J.E.; Bourne, D.G.; Curtis, B.; Dlutek, M.; Stokes, H.W.; Doolittle, W.F.; Boucher, Y. Coral-Mucus-Associated Vibrio Integrons in the Great Barrier Reef: Genomic Hotspots for Environmental Adaptation. ISME J. 2011, 5, 962–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvennefors, E.C.E.; Sampayo, E.; Ridgway, T.; Barnes, A.C.; Hoegh-Guldberg, O. Bacterial Communities of Two Ubiquitous Great Barrier Reef Corals Reveals Both Site-and Species-Specificity of Common Bacterial Associates. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solano, F. Melanin and Melanin-Related Polymers as Materials with Biomedical and Biotechnological Applications—Cuttlefish Ink and Mussel Foot Proteins as Inspired Biomolecules. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Lin, Z.J.; Cai, Z.H.; Zeng, Y.H.; Zhu, J.M.; Du, X.P. Opportunistic Bacteria Use Quorum Sensing to Disturb Coral Symbiotic Communities and Mediate the Occurrence of Coral Bleaching. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 22, 1944–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anithajothi, R.; Duraikannu, K.; Umagowsalya, G.; Ramakritinan, C.M. The Presence of Biomarker Enzymes of Selected Scleractinian Corals of Palk Bay, Southeast Coast of India. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 684874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmer, B.L.; May, A.L.; Bhedi, C.D.; Dearth, S.P.; Prevatte, C.W.; Pratte, Z.; Campagna, S.R.; Richardson, L.L. Quorum Sensing Signal Production and Microbial Interactions in a Polymicrobial Disease of Corals and the Coral Surface Mucopolysaccharide Layer. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e108541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Diaz, J.M.; Brighi, C.; Parsons, R.J.; McNally, S.; Apprill, A.; Hansel, C.M. Dark Production of Extracellular Superoxide by the Coral Porites Astreoides and Representative Symbionts. Front. Mar. Sci. 2016, 3, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hansel, C.M.; Diaz, J.M. Production of Extracellular Reactive Oxygen Species by Marine Biota. Ann. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2021, 13, 177–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, D.A.; Petrou, K.; Gates, R.D. Coral Bleaching from a Single Cell Perspective. ISME J. 2018, 12, 1558–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Imlay, J.A. Improved Measurements of Scant Hydrogen Peroxide Enable Experiments That Define Its Threshold of Toxicity for Escherichia Coli. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 120, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, Y. Metal Ions Driven Production, Characterization and Bioactivity of Extracellular Melanin from Streptomyces Sp. ZL-24. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 123, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, K.J. Detection and Measurement of Carotenoids by UV/VIS Spectrophotometry. Curr. Protoc. Food Anal. Chem. 2001, 1, F2.2.1–F2.2.10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen Gupta, S.; Ghosh, M. In Vitro Antioxidative Evaluation of α- and β -Carotene, Isolated from Crude Palm Oil. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2013, 2013, 351671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misawa, N.; Shimada, H. Metabolic Engineering for the Production of Carotenoids in Non-Carotenogenic Bacteria and Yeasts. J. Biotechnol. 1998, 59, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dieser, M.; Greenwood, M.; Foreman, C.M. Carotenoid Pigmentation in Antarctic Heterotrophic Bacteria as a Strategy to Withstand Environmental Stresses. Arct. Antarct. Alp. Res. 2010, 42, 396–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillyer, K.E.; Dias, D.A.; Lutz, A.; Wilkinson, S.P.; Roessner, U.; Davy, S.K. Metabolite Profiling of Symbiont and Host during Thermal Stress and Bleaching in the Coral Acropora Aspera. Coral Reefs 2017, 36, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bana, H.Z. Isolation of Pigment-Producing Bacteria from Surface Water and Study Sun Protection Factor (SPF) of the Purified Pigments. Int. J. Adv. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2017, 5, 2321–9009. [Google Scholar]
- Reis-Mansur, M.C.P.P.; Cardoso-Rurr, J.S.; Silva, J.V.M.A.; de Souza, G.R.; Cardoso, V.S.; Mansoldo, F.R.P.; Pinheiro, Y.; Schultz, J.; Lopez Balottin, L.B.; da Silva, A.J.R.; et al. Carotenoids from UV-Resistant Antarctic Microbacterium Sp. LEMMJ01. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bythell, J.C.; Wild, C. Biology and Ecology of Coral Mucus Release. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2011, 408, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweet, M.; Ramsey, A.; Bulling, M. Designer Reefs and Coral Probiotics: Great Concepts but Are They Good Practice? Biodiversity 2017, 18, 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Patel, N.P.; Kumar, S.B.; Haldar, S. Role of Bacteria in Coral Ecosystem. In Systems Biology of Marine Ecosystems; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 317–341. ISBN 9783319620947. [Google Scholar]
- Matthews, J.L.; Raina, J.B.; Kahlke, T.; Seymour, J.R.; van Oppen, M.J.H.; Suggett, D.J. Symbiodiniaceae-Bacteria Interactions: Rethinking Metabolite Exchange in Reef-Building Corals as Multi-Partner Metabolic Networks. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 22, 1675–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höfte, M. Classes of Microbial Siderophores. In Iron Chelation in Plants and Soil Microorganisms; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1993; pp. 3–26. [Google Scholar]
- Golberg, K.; Pavlov, V.; Marks, R.S.; Kushmaro, A. Coral-Associated Bacteria, Quorum Sensing Disrupters, and the Regulation of Biofouling. Biofouling 2013, 29, 669–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golberg, K.; Eltzov, E.; Shnit-Orland, M.; Marks, R.S.; Kushmaro, A. Characterization of Quorum Sensing Signals in Coral-Associated Bacteria. Microb. Ecol. 2011, 61, 783–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega Thurber, R.; Mydlarz, L.D.; Brandt, M.; Harvell, D.; Weil, E.; Raymundo, L.; Willis, B.L.; Langevin, S.; Tracy, A.M.; Littman, R.; et al. Deciphering Coral Disease Dynamics: Integrating Host, Microbiome, and the Changing Environment. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 8, 575927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Fu, K.; Wu, C.; Qin, K.; Li, F.; Zhou, L. “In-Group” Communication in Marine Vibrio: A Review of N-Acyl Homoserine Lactones-Driven Quorum Sensing. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervino, J.M.; Thompson, F.L.; Gomez-Gil, B.; Lorence, E.A.; Goreau, T.J.; Hayes, R.L.; Winiarski-Cervino, K.B.; Smith, G.W.; Hughen, K.; Bartels, E. The Vibrio Core Group Induces Yellow Band Disease in Caribbean and Indo-Pacific Reef-Building Corals. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 105, 1658–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Certner, R.H.; Vollmer, S.V. Inhibiting Bacterial Quorum Sensing Arrests Coral Disease Development and Disease-Associated Microbes. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 20, 645–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Certner, R.H.; Vollmer, S.V. Evidence for Autoinduction and Quorum Sensing in White Band Disease-Causing Microbes on Acropora Cervicornis. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ringø, E.; Van Doan, H.; Lee, S.H.; Soltani, M.; Hoseinifar, S.H.; Harikrishnan, R.; Song, S.K. Probiotics, Lactic Acid Bacteria and Bacilli: Interesting Supplementation for Aquaculture. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 129, 116–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glasl, B.; Herndl, G.J.; Frade, P.R. The Microbiome of Coral Surface Mucus Has a Key Role in Mediating Holobiont Health and Survival upon Disturbance. ISME J. 2016, 10, 2280–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Toquica, J.S.; Becerra-Real, L.M.; Díaz, L.M.V. Effect of Bacillus Firmus C101 on the Growth of Litopenaeus Vannamei Boone (White Shrimp) Post-Larvae, and Brachionus Plicatilis s.s. Müller (Rotifer). Bol. Investig. Mar. Costeras 2020, 49, 63–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, X.; He, J.; Lu, J.; Chen, Z.; Jin, M.; Jiao, L.; Masagounder, K.; Liu, W.; Zhou, Q. Effects of Bacillus Subtilis DSM 32315 (Gutcare®) on the Growth Performance, Antioxidant Status, Immune Ability and Intestinal Function for Juvenile Litopenaeus Vannamei Fed with High/Low-Fishmeal Diets. Aquac. Rep. 2022, 26, 101282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chimetto, L.A.; Brocchi, M.; Thompson, C.C.; Martins, R.C.R.; Ramos, H.R.; Thompson, F.L. Vibrios Dominate as Culturable Nitrogen-Fixing Bacteria of the Brazilian Coral Mussismilia Hispida. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 31, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olson, N.D.; Ainsworth, T.D.; Gates, R.D.; Takabayashi, M. Diazotrophic Bacteria Associated with Hawaiian Montipora Corals: Diversity and Abundance in Correlation with Symbiotic Dinoflagellates. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2009, 371, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).