Differences in Bacterial Growth and Mortality between Seagrass Meadows and Adjacent Unvegetated Areas
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
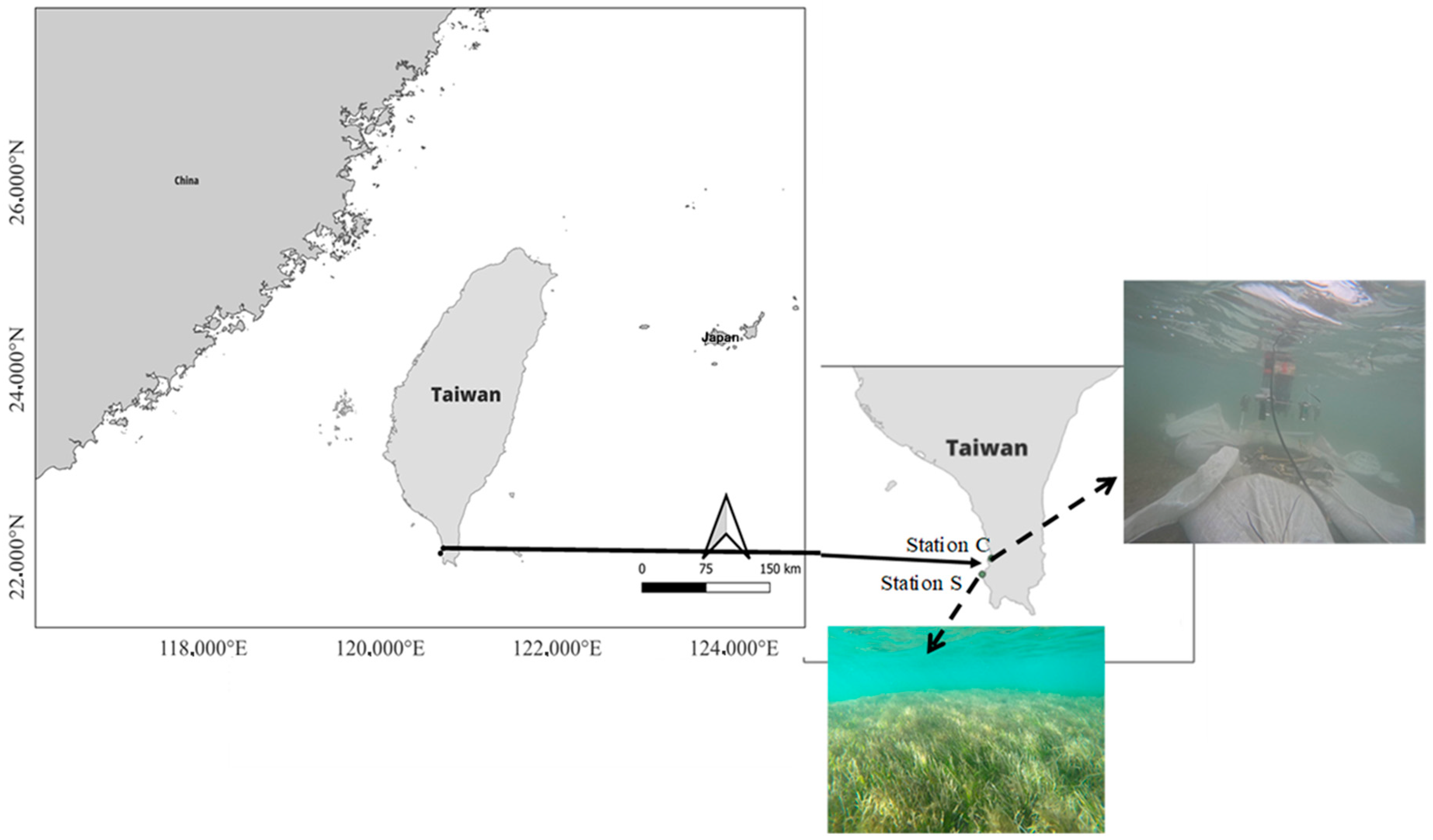
2.1. Study Site and Samplings
2.2. Modified Dilution Experiments
2.3. Flow Cytometric Analyses
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Station Characteristics
3.2. Bacterial Growth Rates
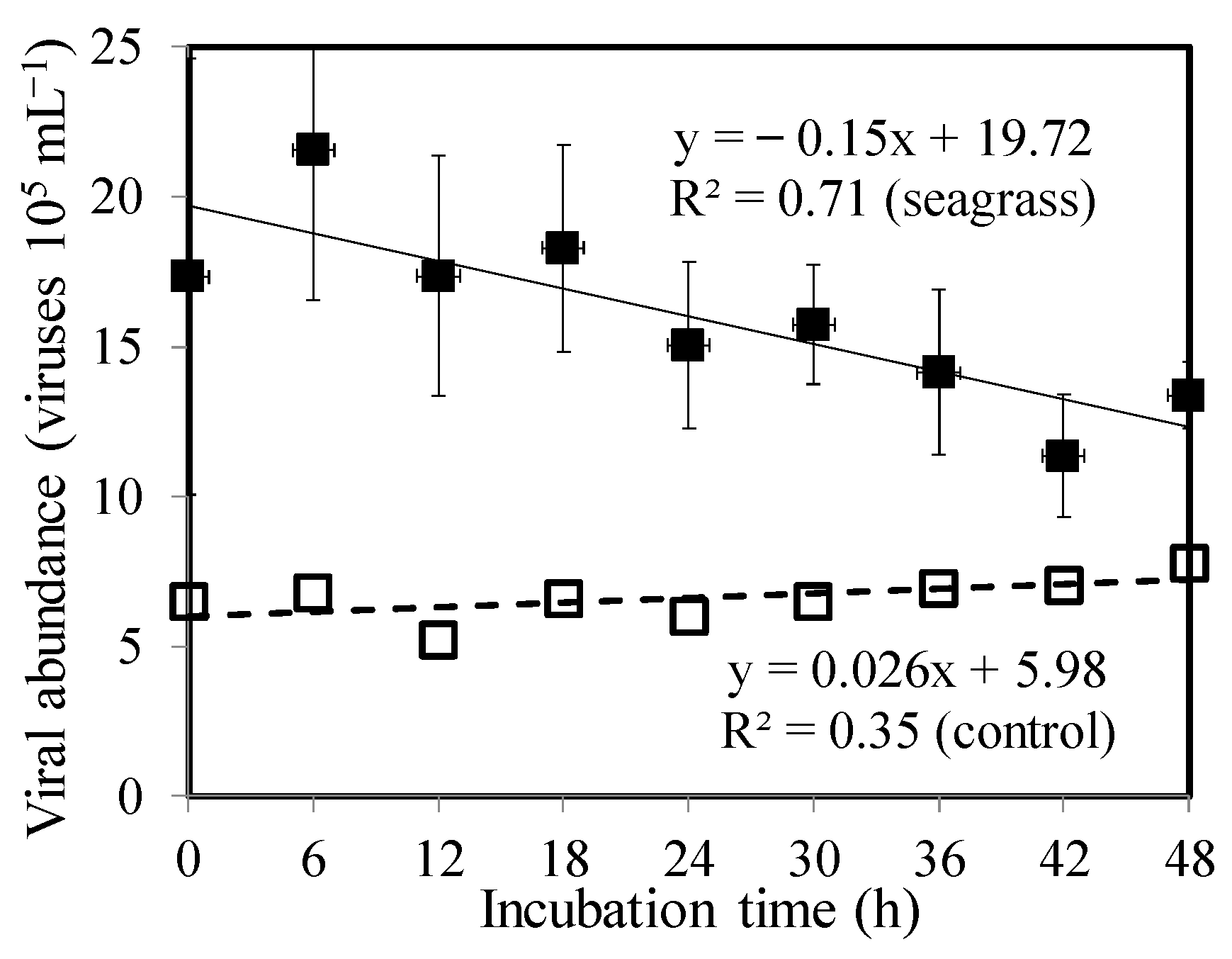
3.3. Bacterial Mortality
4. Discussion
4.1. Bacterial Growth and Mortality
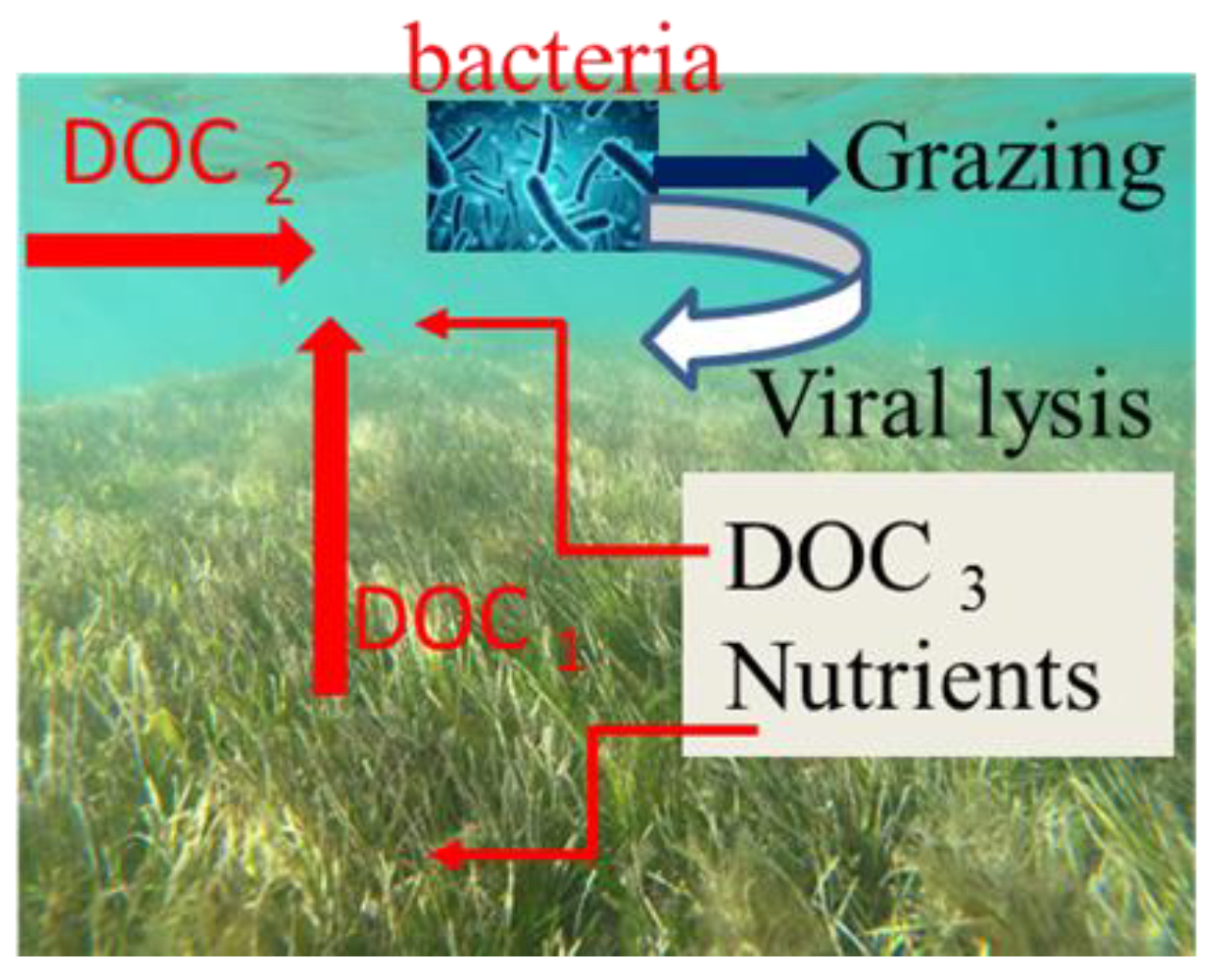
4.2. Microbial Ecology in Seagrass Meadows
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Russell, B.D.; Connell, S.D.; Uthicke, S.; Muehllehner, N.; Fabricius, K.E.; Hall-Spencer, J.M. Future seagrass beds: Can increased productivity lead to increased carbon storage? Mar. Poll. Bull. 2013, 73, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lohrer, A.M.; Townsend, M.; Hailes, S.F.; Rodil, I.F.; Cartner, K.; Pratt, D.R.; Hewitt, J.E. Influence of New Zealand cockles (Austrovenus stutchburyi) on primary productivity in sandflat-seagrass (Zostera muelleri) ecotones. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2016, 181, 238–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, M.W.; Heck, K.L., Jr.; Able, K.W.; Childers, D.L.; Eggleston, D.B.; Gillanders, B.M.; Halpern, B.; Hays, C.G.; Hoshino, K.; Minello, T.J.; et al. The identification, conservation and management of estuarine and marine nurseries for fish and invertebrates. Biosciences 2001, 51, 633–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentine, J.F.; Duffy, J.E. The central role of grazing in seagrass ecology. In Seagrasses: Biology, Ecologyand Conservation; Springer: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 463–501. [Google Scholar]
- Mazarrasa, I.; Marba, N.; Lovelock, C.E.; Serrano, O.; Lavery, P.S.; Fourqurean, J.W.; Kennedy, H.; Mateo, M.A.; Krause-Jensen, D.; Steven, A.D.L.; et al. Seagrass Meadows as a Globally Significant Carbonate Reservoir. Biogeosciences 2015, 12, 4993–5003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricart, A.M.; York, P.H.; Bryant, C.V.; Rasheed, M.A.; Ierodiaconou, D.; Macreadie, P.I. High variability of Blue Carbon storage in seagrass meadows at the estuary scale. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egan, S.; Harder, T.; Burke, C.; Steinberg, P.; Kjelleberg, S.; Thomas, T. The seaweed holobiont: Understanding seaweed–bacteria interactions. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 37, 462–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Church, M.J. Resource control of bacterial dynamics in the sea. In Microbial Ecology of the Ocean, 2nd ed.; Kirchman, D.L., Ed.; John Wiley and Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008; pp. 335–382. [Google Scholar]
- Barrón, C.; Duarte, C. Dissolved organic matter release in a Posidonia oceanica meadow. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2009, 374, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmer, M.; Andersen, F.Ø.; Nielsen, S.L.; Boschker, H.T.S. The importance of mineralization based on sulphate reduction for nutrient regeneration in tropical seagrass sediments. Aquat. Bot. 2001, 71, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemminga, M.A.; Duarte, C.M. Seagrass Ecology; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Boschker, H.T.S.; Wielemaker, A.; Schaub, B.E.M.; Holmer, M. Limited Coupling of Macrophyte Production and Bacterial Carbon Cycling in the Sediments of Zostera spp. Meadows. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2000, 203, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmer, M.; Duarte, C.M.; Boschker, H.T.S.; Barrón, C. Carbon Cycling and Bacterial Carbon Sources in Pristine and Impacted Mediterranean Seagrass Sediments. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2004, 36, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarquinio, F.; Hyndes, G.A.; Laverock, B.; Koenders, A.; Säwström, C. The seagrass holobiont: Understanding seagrass-bacteria interactions and their role in seagrass ecosystem functioning. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2019, 366, fnz057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koopmans, D.; Holtappels, M.; Chennu, A.; Weber, M.; De Beer, D. High net primary production of Mediterranean seagrass (Posidonia oceanica) meadows determined with aquatic eddy covariance. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, W.C.; Fan, L.F.; Yang, C.C.; Chen, Y.H.; Hung, C.C.; Huang, W.J.; Shih, Y.Y.; Soong, K.; Tseng, H.C.; Gong, G.C.; et al. A unique diel pattern in carbonate chemistry in the seagrass meadows of dongsha island: The enhancement of metabolic carbonate dissolution in a semienclosed lagoon. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 717685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriarty, D.J.W.; Pollard, P.C. Diel Variation of Bacterial Productivity in Seagrass (Zostera capricorni) BedsMeasured by Rate of Thymidine Incorporation into DNA. Mar. Biol. 1982, 72, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, C.; Archer, S.D.; Jacquet, S.; Wilson, W.H. Direct estimates of the contribution of viral lysis and microzooplankton grazing to the decline of a Micromonas spp. population. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2003, 30, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiu, R.-F.; Lee, C.-L. Role of microgel formation in scavenging of chromophoric dissolved organic matter and heavy metals in a river-sea system. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 328, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiu, R.-F.; Vazquez, C.I.; Tsai, Y.-Y.; Torres, G.V.; Chen, C.-S.; Santschi, P.; Quigg, A.; Chin, W.-C. Nano-plastics induce aquatic particulate organic matter (microgels) formation. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 706, 135681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brussaard, C.P.D. Optimization of procedures for counting viruses by flow cytometry. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 1506–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammes, F.; Egli, T. Cytometric methods for measuring bacteria in water: Advantages, pitfalls and applications. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 397, 1083–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dierssen, H.M.; Zimmerman, R.C.; Drake, L.A.; Burdige, D. Benthic ecology from space: Optics and net primary production in seagrass and benthic algae across the Great Bahama Bank. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2010, 411, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barron, C.; Apostolaki, E.T.; Duarte, C.M. Dissolved organic carbon fluxes by seagrass meadows and macroalgal beds. Front. Mar. Sci. 2014, 1, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriarty, D.J.W.; Roberts, D.G.; Pollard, P.C. Primary and bacterial seagrass communities in the Gulf of Carpentaria, Australia. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1990, 61, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharek, R.; Latasa, M. Growth, grazing and carbon flux of high and low nucleic acid bacteria differ in surface and deep chlorophyll maximum layers in the NW Mediterranean Sea. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2007, 46, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, I.; Davidson, A.T.; Thomson, P.G.; Wright, S.; van den Enden, R. Marine microbial ecology in the sub-Antarctic Zone: Rates of bacterial and phytoplankton growth and grazing by heterotrophic protists. Deep Sea Res. II 2011, 58, 2248–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, A.-Y.; Mukhanov, V. Response of Growth and Grazing Rate of Nanoflagellates on Synechococcus spp. to Experimental Nutrient Enrichment. Water 2021, 13, 2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landry, M.R. Estimating rate of growth and grazing mortality of phytoplankton by the dilution method. In Handbook of Methods in Aquatic Microbial Ecology; Kemp, P.F., Sherr, B.F., Sherr, E.B., Cole, J.J., Eds.; Routledge: Abingdon, UK, 1993; pp. 114–135. [Google Scholar]
- Ayukai, T. Possible limitation of the dilution technique for estimating growth and grazing mortality rates of picoplanktonic cyanobacteria in oligotrophic tropical waters. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1996, 198, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landry, M.R.; Hassett, R.P. Estimating the grazing impact of marine microzooplankton. Mar. Biol. 1982, 67, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landry, M.R.; Kirshtein, J.; Constantinou, J. A refined dilution technique for measuring the community grazing impact of microzooplankton, with experimental tests in the central Equatorial Pacific. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1995, 120, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuhrman, J.A. Marine viruses and their biogeochemical and ecological effects. Nature 1999, 399, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middelboe, M.; Lyck, P.G. Regeneration of dissolved organic matter by viral lysis in marine microbial communities. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2002, 27, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fourqurean, J.W.; Zieman, J.C.; Powell, G.V. Phosphorus limitation of primary production in Florida Bay: Evidence from C:N:P ratios of the dominant seagrass Thalassia testudinum. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1992, 37, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welsh, D. Nitrogen fixation in seagrass meadows: Regulation, plant-bacteria interactions and significance to primary productivity. Ecol. Lett. 2000, 3, 58–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, L.W.; McGlathery, K.J. Nitrogen fixation in restored eelgrass meadows. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2012, 448, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinbauer, M.G.; Höfle, M.G. Significance of viral lysis and flagellate grazing as factors controlling bacterioplankton pro duction in a eutrophic lake. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| DOC | Bacteria | Viruses | VBR | Growth Rate | Grazing Rate | Viral Lysis | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| μg L−1 | 105 cells mL−1 | 106 viruses mL−1 | (d−1) | (d−1) | (d−1) | ||
| Station C | 1196 | 7.3 | 3.4 | 4.7 | 1.35 * | 0.007 | nd |
| Station S | 1685 | 5.2 | 8.9 | 17.1 | 2.05 | 0.007 | 0.005 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, P.W.-Y.; Olivia, M.; Chou, W.-C.; Shiu, R.-F.; Mukhanov, V.; Tsai, A.-Y. Differences in Bacterial Growth and Mortality between Seagrass Meadows and Adjacent Unvegetated Areas. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 1979. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11101979
Chen PW-Y, Olivia M, Chou W-C, Shiu R-F, Mukhanov V, Tsai A-Y. Differences in Bacterial Growth and Mortality between Seagrass Meadows and Adjacent Unvegetated Areas. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2023; 11(10):1979. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11101979
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Patrichka Wei-Yi, Madeline Olivia, Wen-Chen Chou, Ruei-Feng Shiu, Vladimir Mukhanov, and An-Yi Tsai. 2023. "Differences in Bacterial Growth and Mortality between Seagrass Meadows and Adjacent Unvegetated Areas" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 11, no. 10: 1979. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11101979
APA StyleChen, P. W.-Y., Olivia, M., Chou, W.-C., Shiu, R.-F., Mukhanov, V., & Tsai, A.-Y. (2023). Differences in Bacterial Growth and Mortality between Seagrass Meadows and Adjacent Unvegetated Areas. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 11(10), 1979. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11101979










