Relationship between Large-Scale Variability of North Pacific Waves and El Niño-Southern Oscillation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. North Pacific Wave Field
3.1. Spatial and Temporal Distribution of Wave Height
3.2. Spatial and Temporal Distribution of Swells and Wind Waves
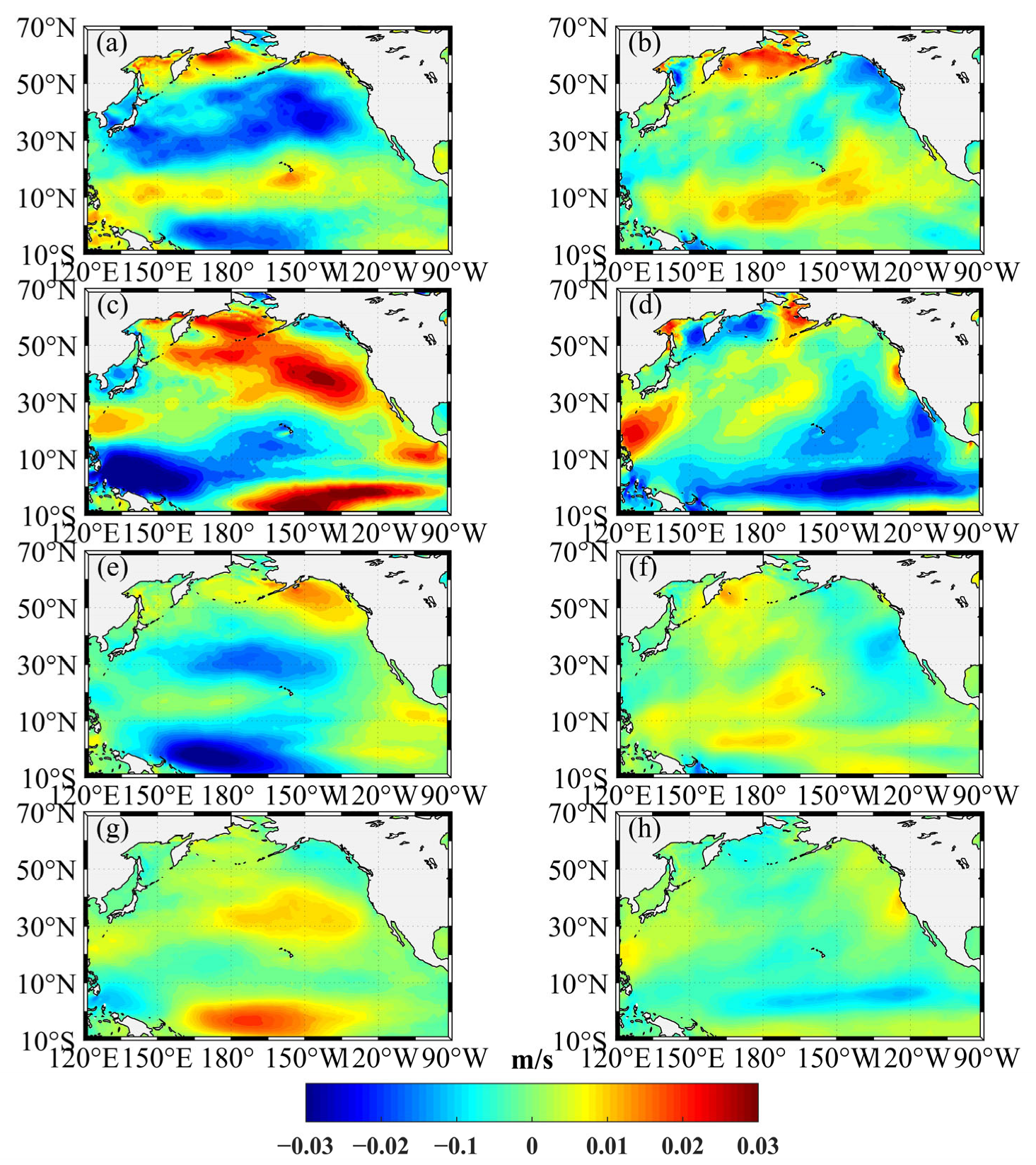
3.3. Wave-Induced Water Transport
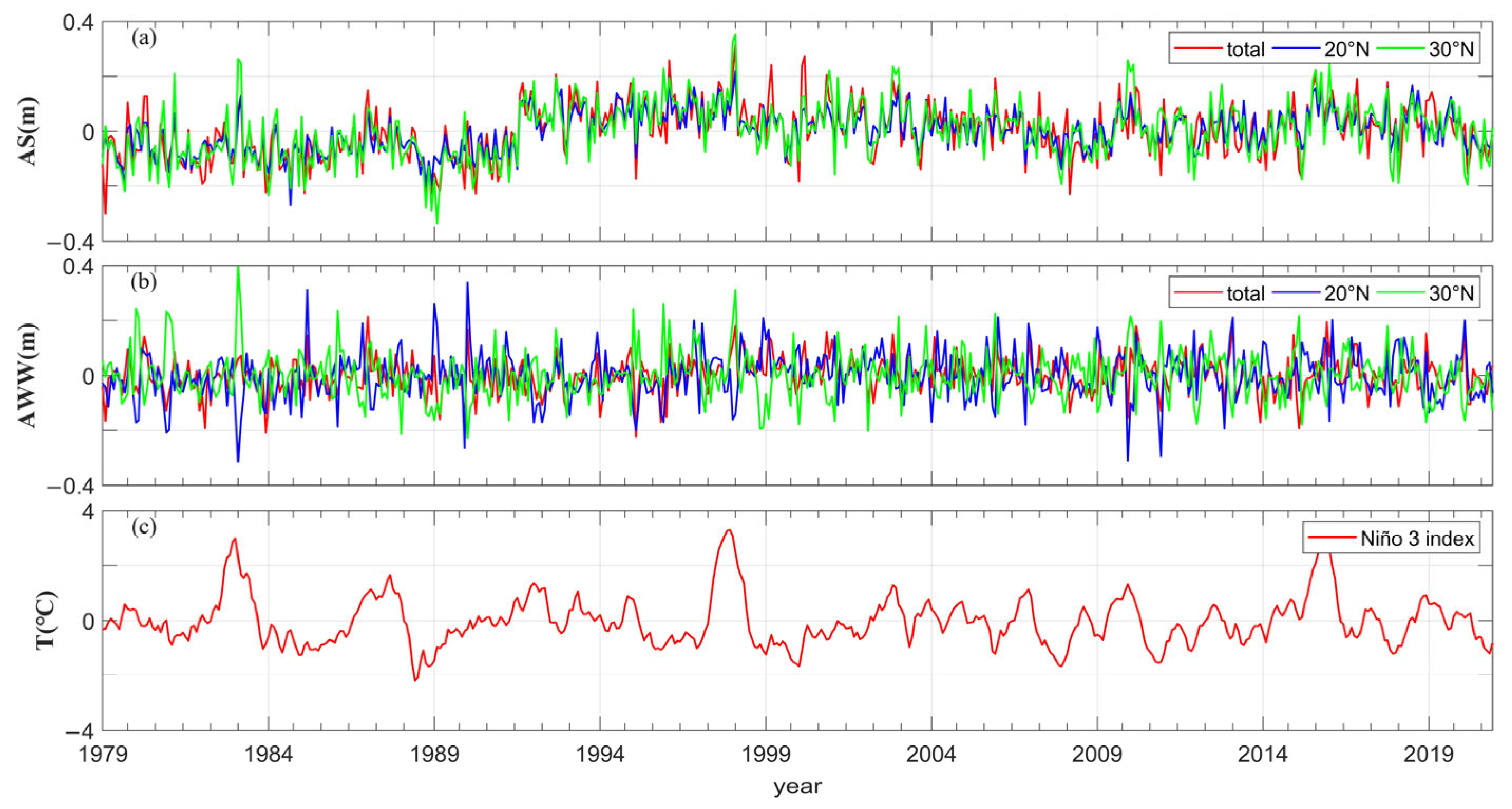
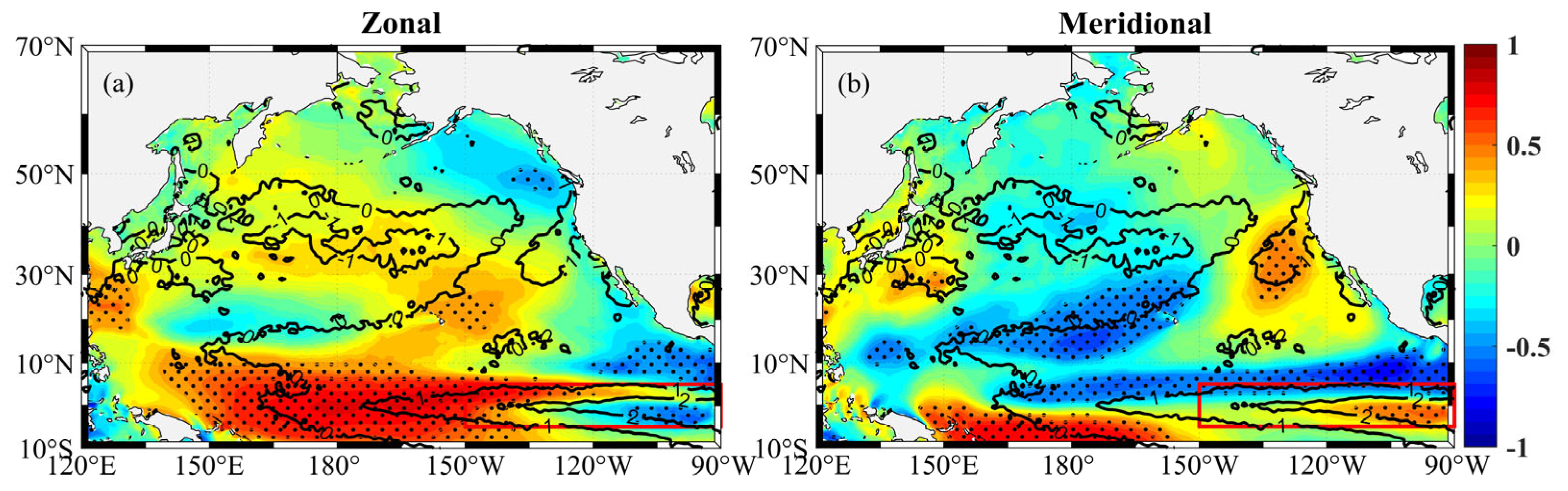
4. The Relationship between Surface Stokes Drift and ENSO
4.1. Correlation between Surface Stokes Drift and ENSO
4.2. Case Study
5. Discussion
6. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mcwilliams, J.C.; Restrepo, J.M. The wave-driven ocean circulation. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1999, 29, 2523–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Liu, B. Stokes drift–induced and direct wind energy inputs into the Ekman layer within the Antarctic Circumpolar Current. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Wu, K.; Guan, C. Global estimates of wind energy input to subinertial motions in the Ekman-Stokes layer. J. Oceanogr. 2007, 63, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polton, J.A.; Lewis, D.M.; Belcher, S.E. The role of wave-induced Coriolis-Stokes forcing on the wind-driven mixed layer. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2005, 35, 444–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, R.H. Laboratory measurement of heat transfer and thermal structure near an Air-Water interface. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1972, 2, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, H.; Miyazawa, Y.; Oey, L.Y. The Stokes drift and wave induced-mass flux in the North Pacific. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, P.A.E.M.; Breivik, Ø.; Mogensen, K.; Vitart, F.; Balmaseda, M.; Bidlot, J.-R.; Keeley, S.; Leutbecher, M.; Magnusson, L.; Molteni, F. Air-Sea Interaction and Surface Waves; European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts: Reading, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, C.; Wu, D.; Wu, H.; Guo, J.; Shen, C.; Tian, C.; Tian, X.; Xiao, Z.; Zhou, W.; Li, C. Propagation and attenuation of swell energy in the Pacific Ocean. Renew. Energ. 2022, 188, 750–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Wu, K.; Li, J.; Akhter, S.; Dong, X.; Sun, J.; Cao, T. Large-scale signals in the south pacific wave fields related to ENSO. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2021, 126, e2021JC017643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bromirski, P.D.; Flick, R.E.; Graham, N. Ocean wave height determined from inland seismometer data; Implications for investigating wave climate changes in the NE Pacific. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 1999, 104, 20753–20766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan, J.; Komar, P. Are ocean wave heights increasing in the eastern North Pacific? Eos Trans. Amer. Geophys. Union. 2000, 81, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggiero, P.; Komar, P.D.; Allan, J.C. Increasing wave heights and extreme value projections: The wave climate of the U.S. Pacific Northwest. Coast. Eng. 2010, 57, 539–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemer, M.A.; Church, J.A.; Hunter, J.R. Variability and trends in the directional wave climate of the Southern Hemisphere. Int. J. Climatol. 2010, 30, 475–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, W. Changes in the North Pacific wave climate since the mid-1990s. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 7854–7860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulev, S.K.; Grigorieva, V. Last century changes in ocean wind wave height from global visual wave data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kako, S.; Kubota, M. Relationship between an El niño event and the interannual variability of significant wave heights in the north pacific. Atmos. Ocean 2006, 44, 377–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasselmann, K. On the mass and momentum transfer between short gravity waves and larger-scale motions. J. Fluid Mech. 1971, 50, 189–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Wu, K.; Zhu, X.; Yang, F.; Zhang, Y. Study of relationship between wave transport and sea surface temperature anomaly (SSTA)in the tropical Pacific. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2016, 35, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukas, R.; Yamagata, T.; Mccreary, J.P. Pacific low-latitude western boundary currents and the Indonesian throughflow. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 1996, 101, 11867–12488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Cai, W.; Zhang, L.; Nakamura, H.; Timmermann, A.; Joyce, T.; Mcphaden, M.J.; Alexander, M.; Qiu, B.; Visbeck, M.; et al. Enhanced warming over the global subtropical western boundary currents. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2012, 2, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Wu, R. Spatial scale dependence of the relationship between turbulent surface heat flux and SST. Clim. Dynam. 2022, 58, 1127–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco, A.; Semedo, A.; Isachsen, P.E.; Christensen, K.H.; Saetra, Ø. Global surface wave drift climate from ERA-40: The contributions from wind-sea and swell. Ocean Dynam. 2014, 64, 1815–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Hu, Z.; Huang, B. Contributions of Atmosphere–Ocean Interaction and Low-Frequency Variation to Intensity of Strong El Niño Events since 1979. J. Clim. 2019, 32, 1381–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, I.; An, S. Kelvin and rossby wave contributions to the SST oscillation of ENSO. J. Clim. 1998, 11, 2461–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.Y.; Kim, Y.Y. Mechanism of Kelvin and Rossby waves during ENSO events. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2002, 81, 169–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Sung, M.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, J.; An, S.; Kug, J. Role of the climatological intertropical convergence zone in the seasonal footprinting mechanism of the El Niño-Southern Oscillation. J. Clim. 2021, 5243–5256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aramburo, D.; Montoya, R.D.; Osorio, A.F. Impact of the ENSO phenomenon on wave variability in the Pacific Ocean for wind sea and swell waves. Dynam. Atmos. Oceans 2022, 100, 101328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izaguirre, C.; Méndez, F.J.; Menéndez, M.; Losada, I.J. Global extreme wave height variability based on satellite data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dee, D.P.; Uppala, S.M.; Simmons, A.J.; Berrisford, P.; Poli, P.; Kobayashi, S.; Andrae, U.; Balmaseda, M.A.; Balsamo, G.; Bauer, P.; et al. The ERA-Interim reanalysis: Configuration and performance of the data assimilation system. Q. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc. 2011, 137, 553–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Hirahara, S.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D.; et al. The ERA5 global reanalysis. Q. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc. 2020, 146, 1999–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semedo, A.K.S.A. Variability of Wind Sea and Swell Waves in the North Atlantic Based on ERA-40 Re-analysis. In Proceedings of the 8th European Wave and Tidal Energy, Uppsala, Sweden, 7–10 September 2009; pp. 119–129. [Google Scholar]
- Breivik, Ø.; Janssen, P.A.E.M.; Bidlot, J. Approximate stokes drift profiles in deep water. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2014, 44, 2433–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, N.; Rader, C. A New Principle for Fast Fourier Transformation. IEEE Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 1976, 24, 264–266. [Google Scholar]
- Lorenz, E.N. Empirical Orthogonal Functions, and Statistical Weather Prediction; Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Department of Meteorology: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1956. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Xu, D. The response of surface chlorophyll to mesoscale eddies generated in the eastern South China Sea. J. Oceanogr. 2020, 76, 211–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, H.; Lin, P.; Yuan, Y.; Chai, F. Seasonal and interannual variability in the sea surface temperature front in the eastern Pacific Ocean. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2021, 126, e2020JC016356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreelakshmi, S.; Bhaskaran, P.K. Regional wise characteristic study of significant wave height for the Indian Ocean. Clim. Dynam. 2020, 54, 3405–3423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Meucci, A.; Young, I.R. A comparison of multiple approaches to study the modulation of ocean waves due to climate variability. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2023, 1489, e2023JC019843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, J.G.M. Numerical modeling of ocean swell contributions to the global wind-wave climate. Ocean Model. 2006, 11, 98–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavaleri, L.; Fox-Kemper, B.; Hemer, M. Wind waves in the coupled climate system. B. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2012, 93, 1651–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babanin, A.V.; Onorato, M.; Qiao, F. Surface waves and wave-coupled effects in lower atmosphere and upper ocean. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenberth, K.; National Center for Atmospheric Research Staff. The Climate Data Guide: Nino SST Indices (Nino 1+2, 3, 3.4, 4; ONI and TNI). Available online: https://climatedataguide.ucar.edu/climate-data/nino-sst-indices-nino-12-3-34-4-oni-and-tni (accessed on 25 July 2023).
- Li, R.; Wu, K.; Li, J.; Dong, X.; Sun, J.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Q. Relating a large-scale variation of waves in the indian ocean to the IOD. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2022, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Meucci, A.; Young, I.R. Projected wave climate of Bass Strait and south-east Australia by the end of the twenty-first century. Clim. Dyn. 2022, 60, 393–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Meucci, A.; Young, I.R. Projected 21st century wind-wave climate of Bass Strait and south-east Australia: Comparison of EC-Earth3 and ACCESS-CM2 climate model forcing. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2023, 128, e2022JC018996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

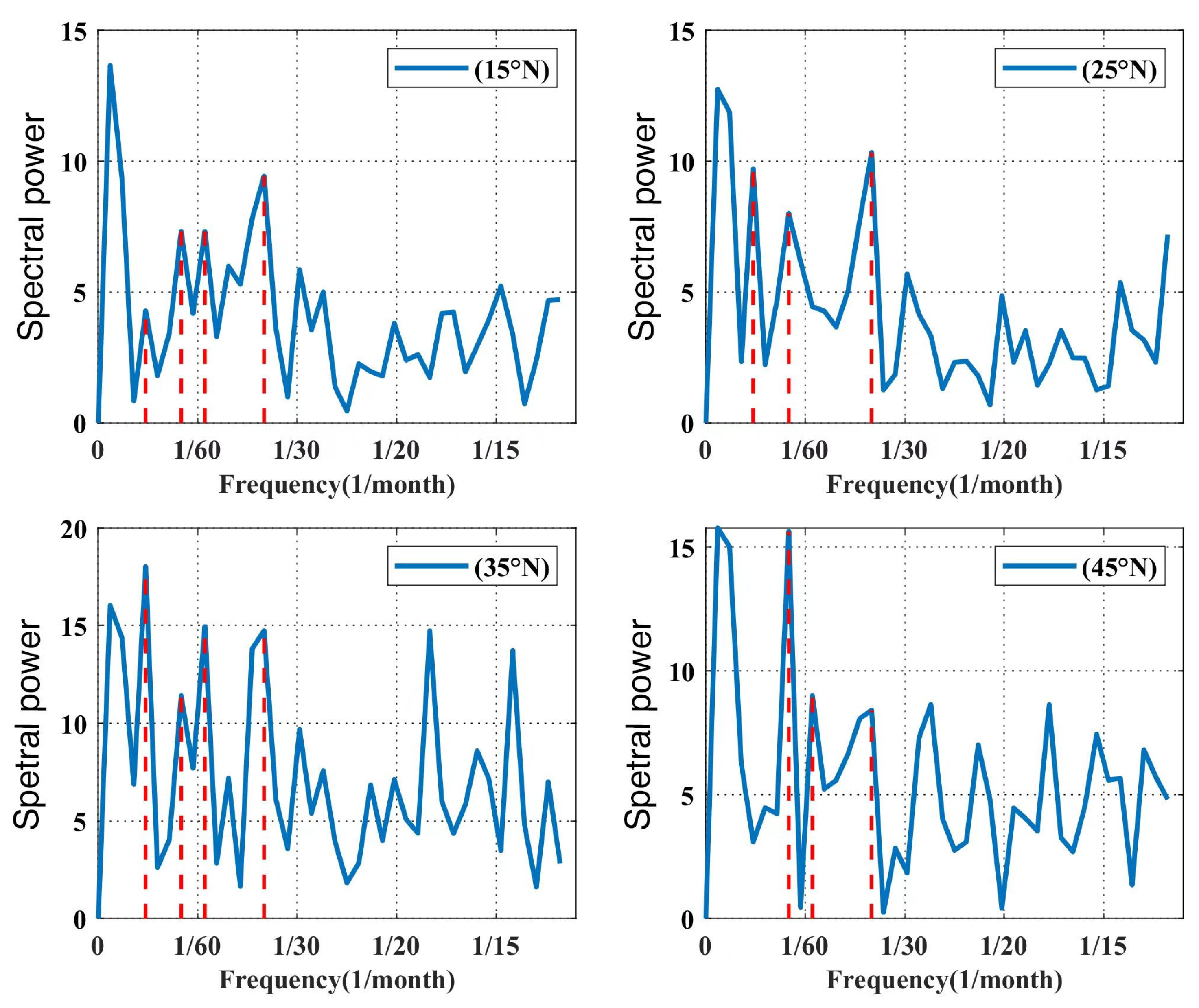



| Latitude | Frequency (1/Month) | Period/(Month) | Period/(Year) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 15° N | 0.028 | 36 | 3.0 |
| 0.014 | 72 | 6.0 | |
| 0.018 | 56 | 4.7 | |
| 0.008 | 126 | 10.5 | |
| 25° N | 0.028 | 36 | 3.0 |
| 0.008 | 126 | 10.5 | |
| 0.014 | 72 | 6.0 | |
| 35° N | 0.008 | 126 | 10.5 |
| 0.028 | 36 | 3.0 | |
| 0.018 | 56 | 4.7 | |
| 0.014 | 72 | 6.0 | |
| 45° N | 0.008 | 126 | 10.5 |
| 0.014 | 72 | 6.0 | |
| 0.028 | 36 | 3.0 |
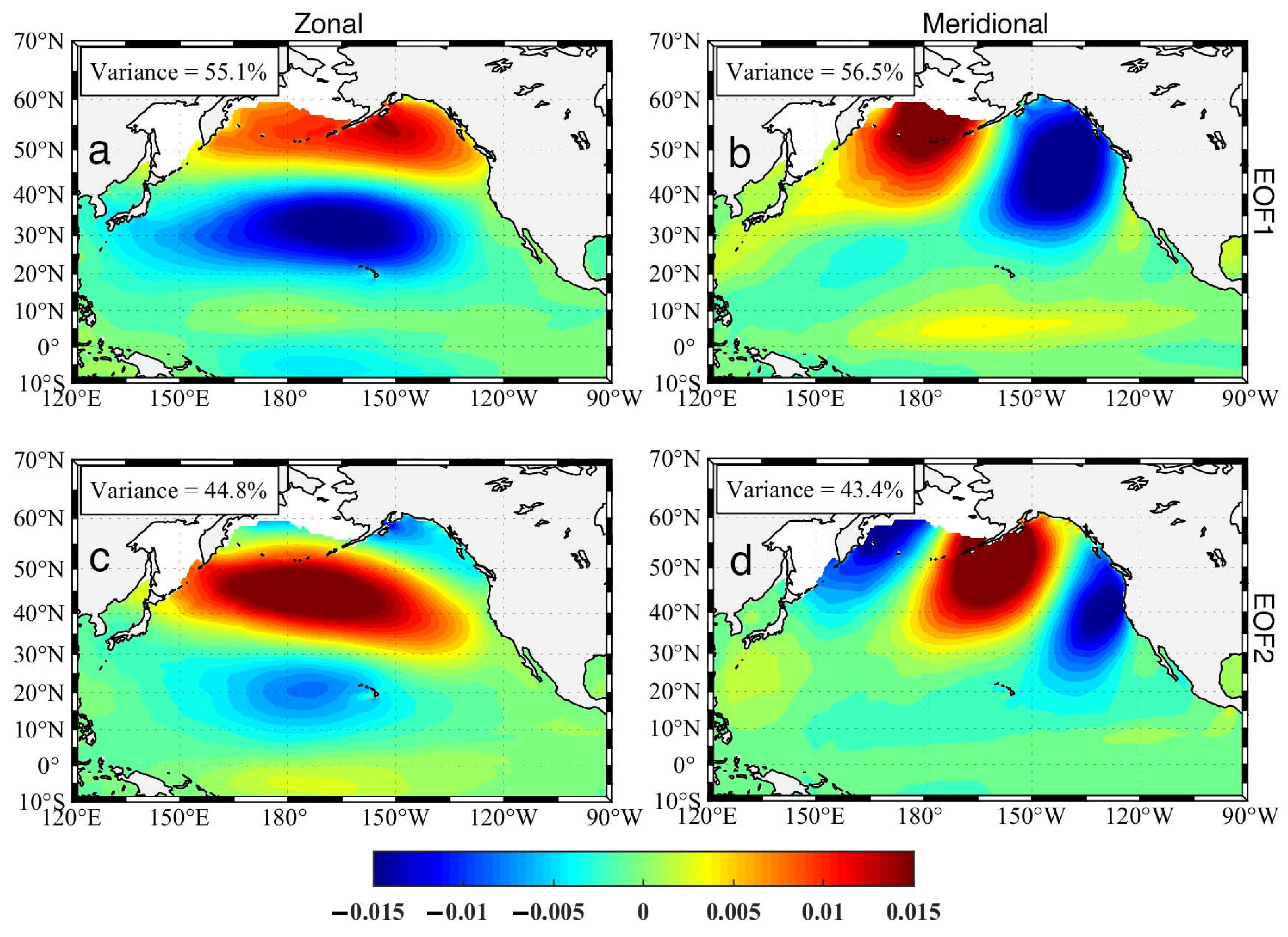
| PC | Frequency (1/Month) | Period/(Year) |
|---|---|---|
| PC1 | 0.014 | 6.0 |
| 0.028 | 3.0 | |
| 0.018 | 4.7 | |
| PC2 | 0.008 | 10.5 |
| 0.056 | 1.5 | |
| 0.02 | 4.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Wu, K.; Li, R.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, R.; Liu, J.; Babanin, A.V. Relationship between Large-Scale Variability of North Pacific Waves and El Niño-Southern Oscillation. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 1848. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11101848
Zhang X, Wu K, Li R, Zhang S, Zhang R, Liu J, Babanin AV. Relationship between Large-Scale Variability of North Pacific Waves and El Niño-Southern Oscillation. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2023; 11(10):1848. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11101848
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xin, Kejian Wu, Rui Li, Shuai Zhang, Ruyan Zhang, Jin Liu, and Alexander V. Babanin. 2023. "Relationship between Large-Scale Variability of North Pacific Waves and El Niño-Southern Oscillation" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 11, no. 10: 1848. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11101848
APA StyleZhang, X., Wu, K., Li, R., Zhang, S., Zhang, R., Liu, J., & Babanin, A. V. (2023). Relationship between Large-Scale Variability of North Pacific Waves and El Niño-Southern Oscillation. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 11(10), 1848. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11101848






