Impacts of River Discharge on the Sea Temperature in Changjiang Estuary and Its Adjacent Sea
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
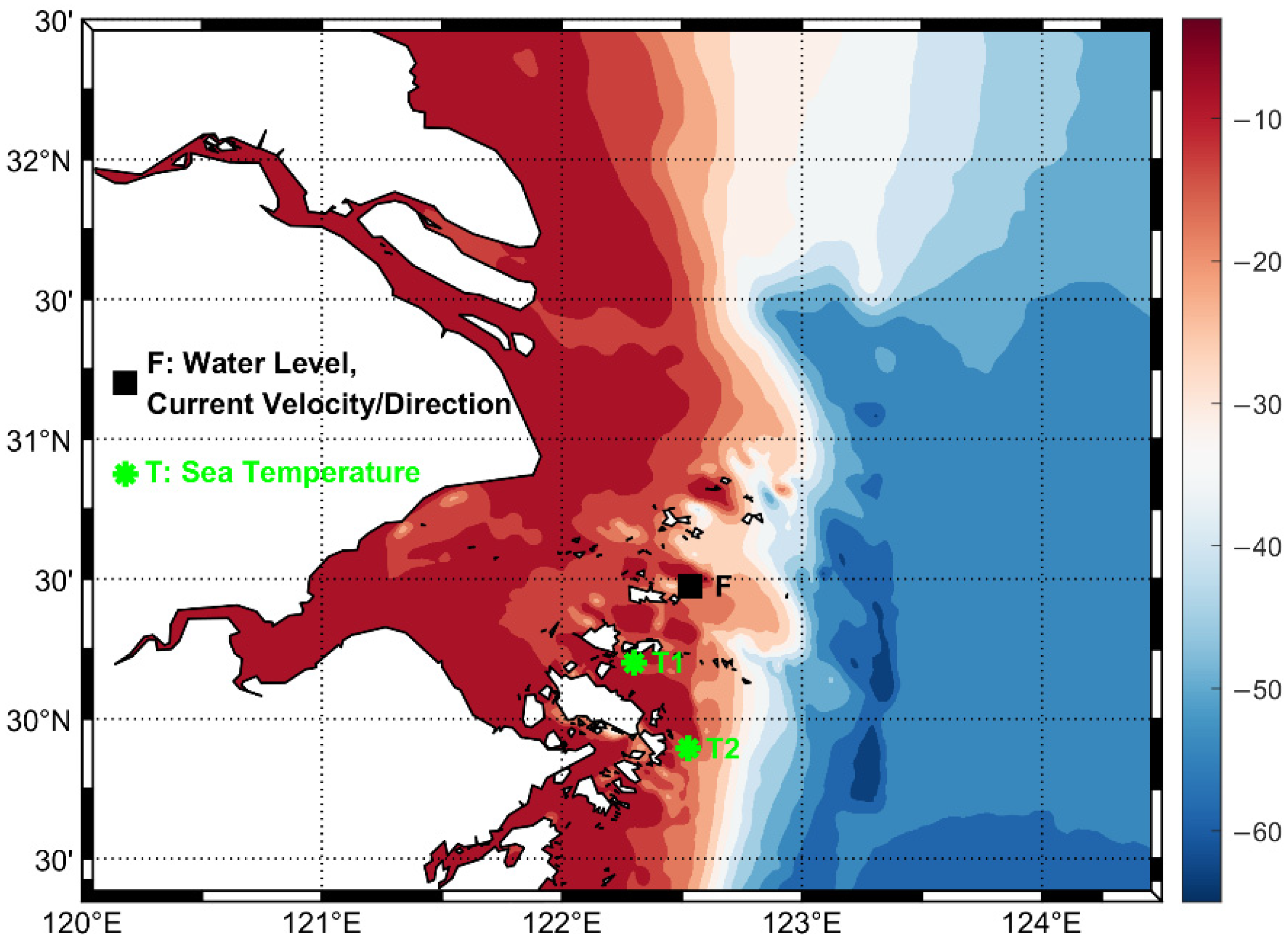
2.1. Model Domain and Configuration
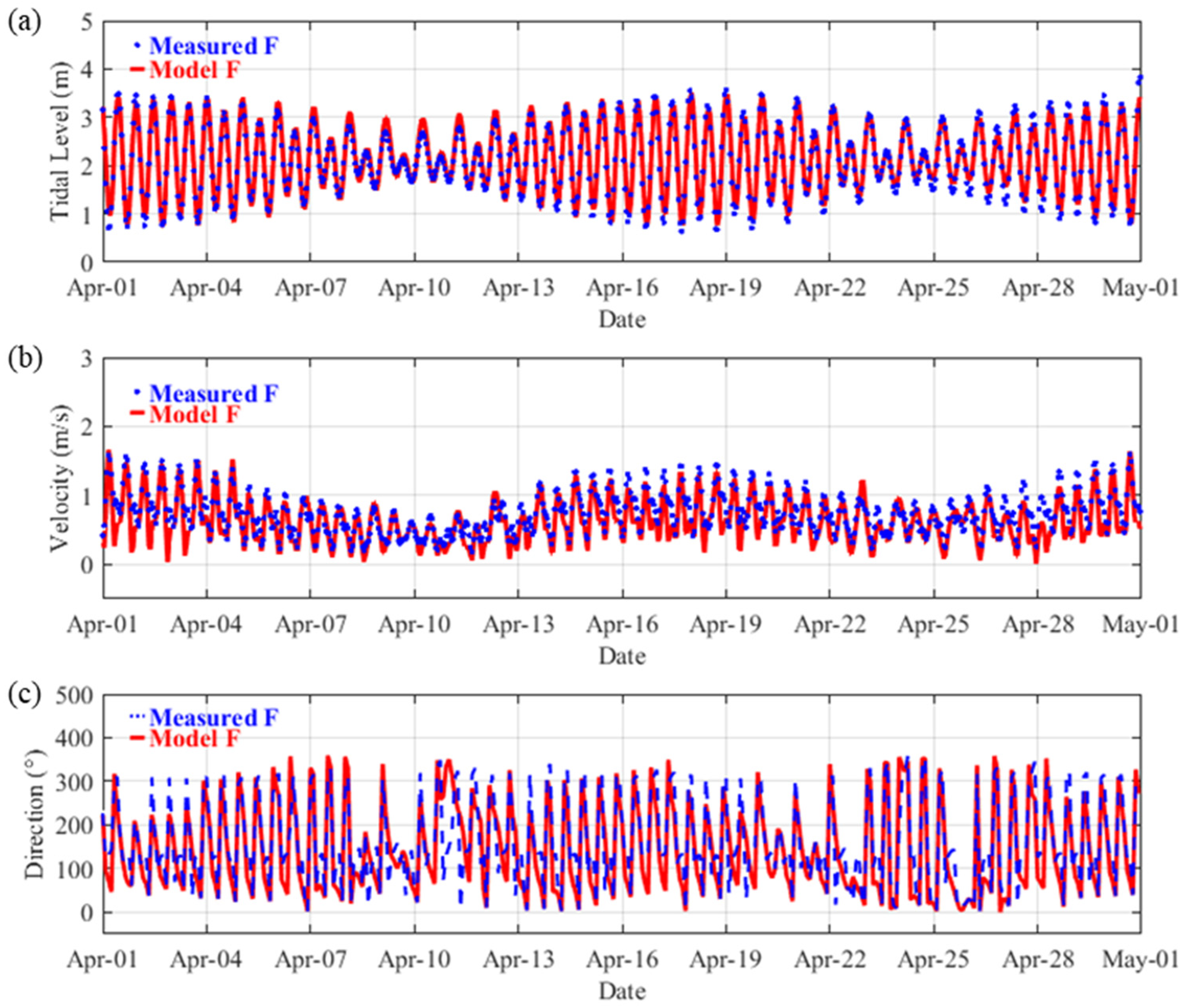
2.2. Model Validation
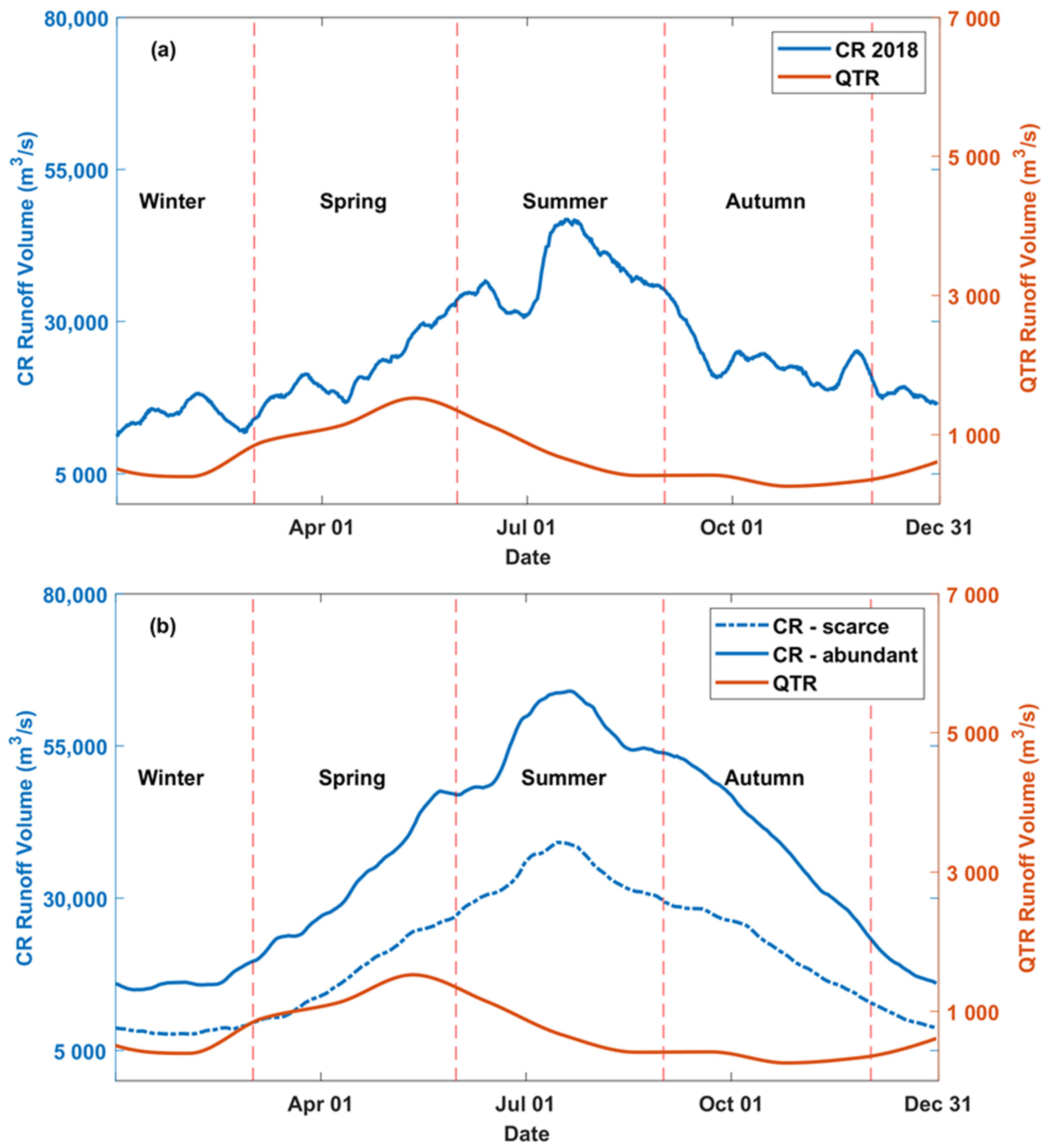
2.3. Numerical Tests
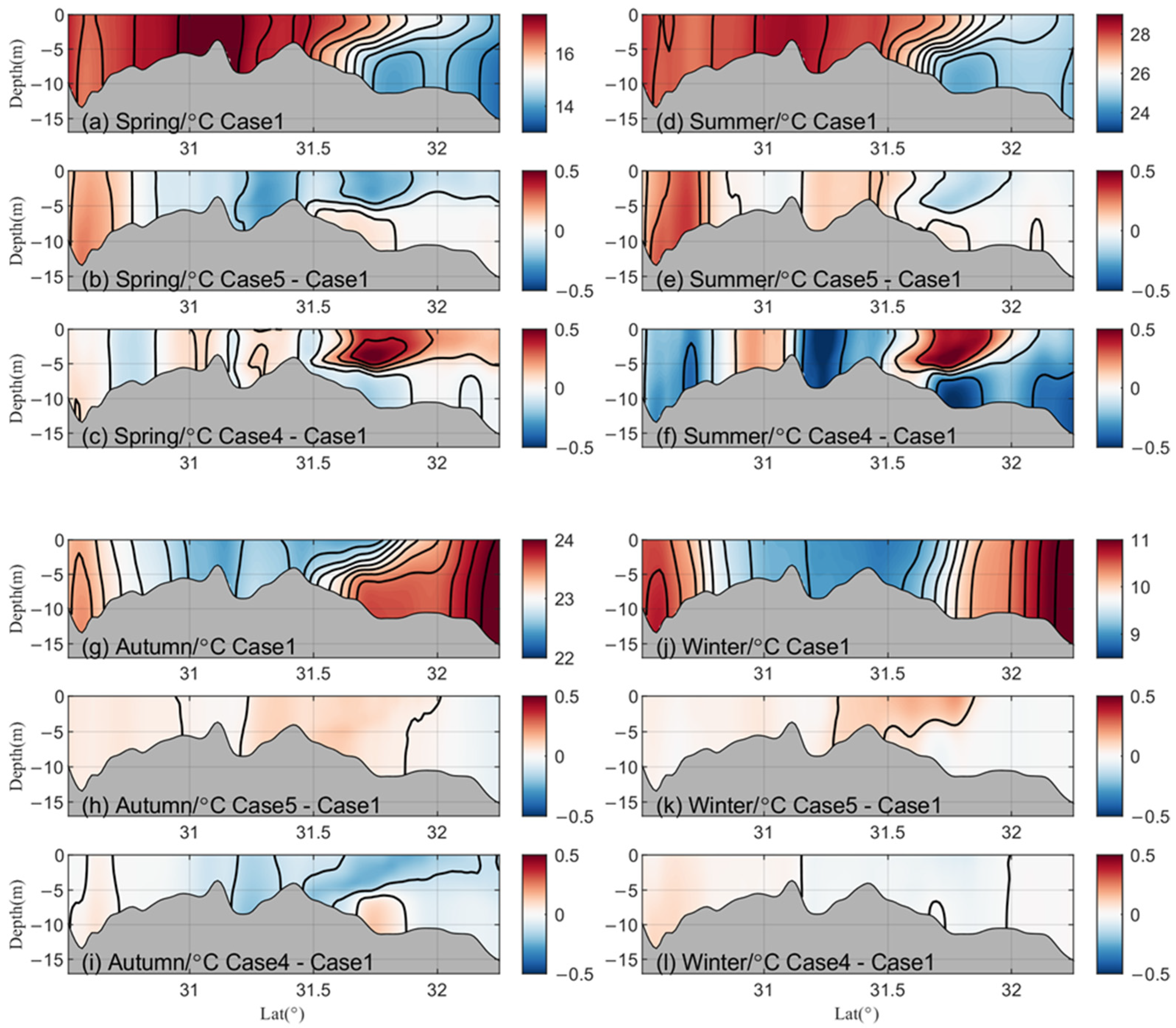
3. Results and Discussion
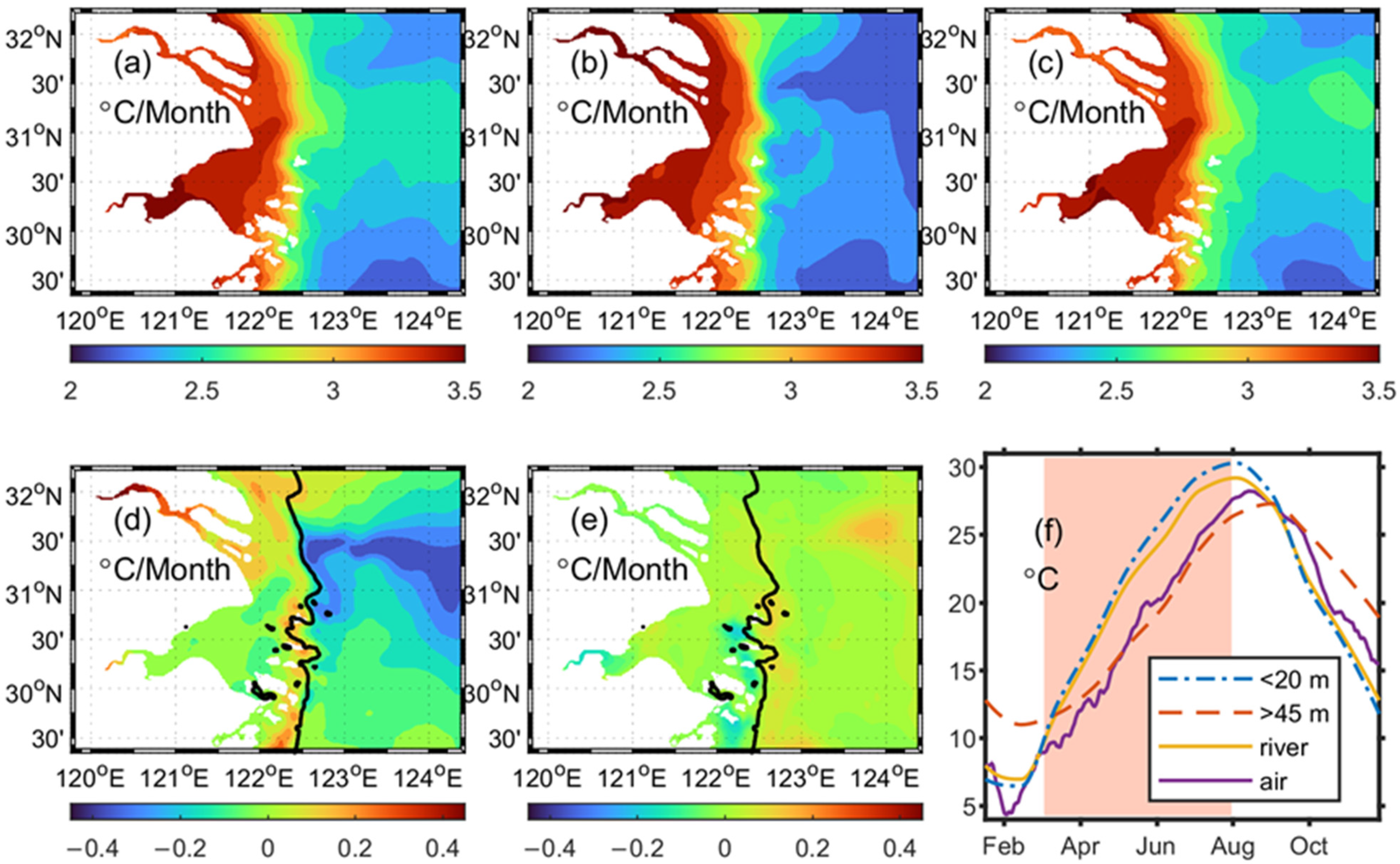
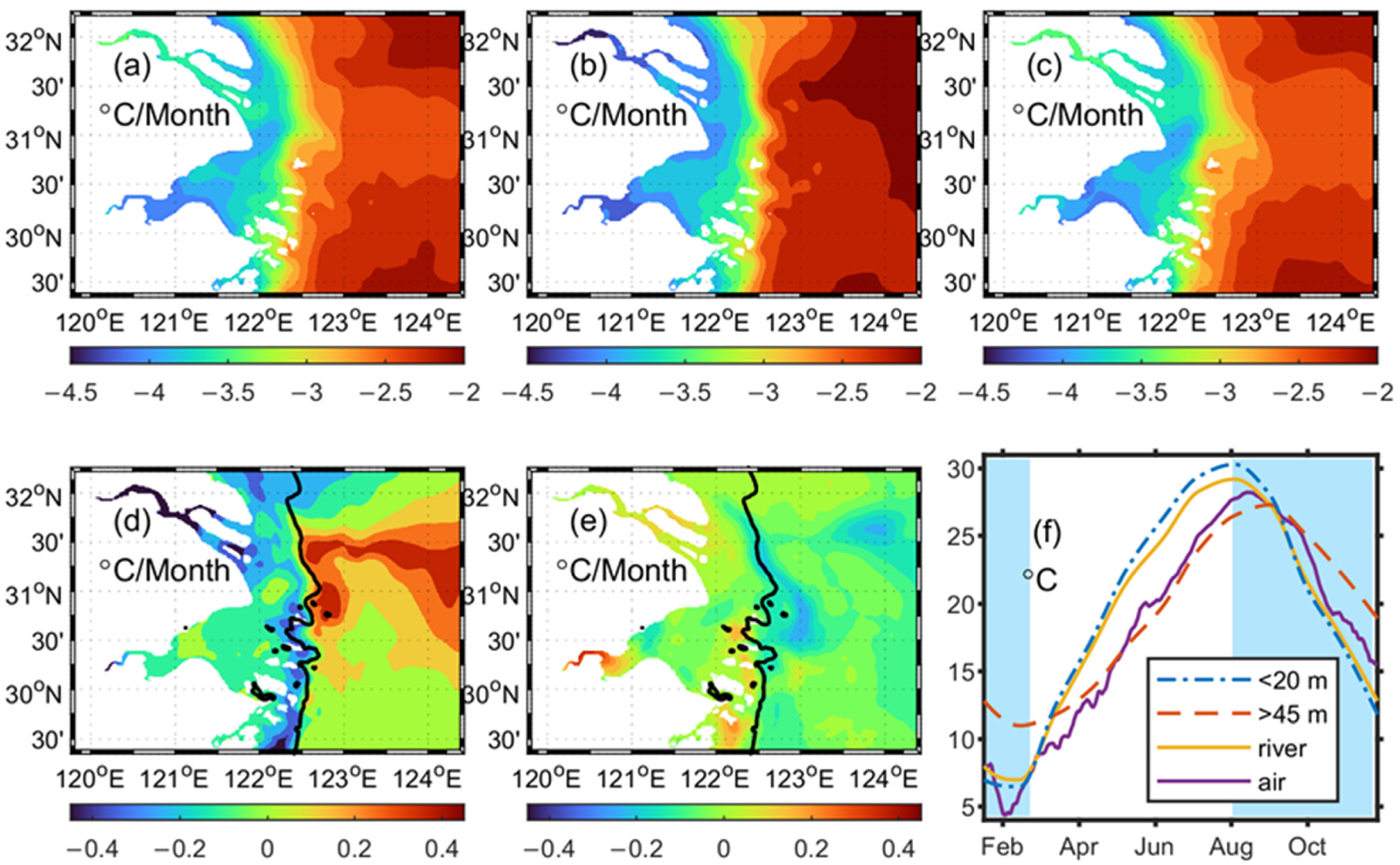
3.1. Influence of CR Runoff on SST
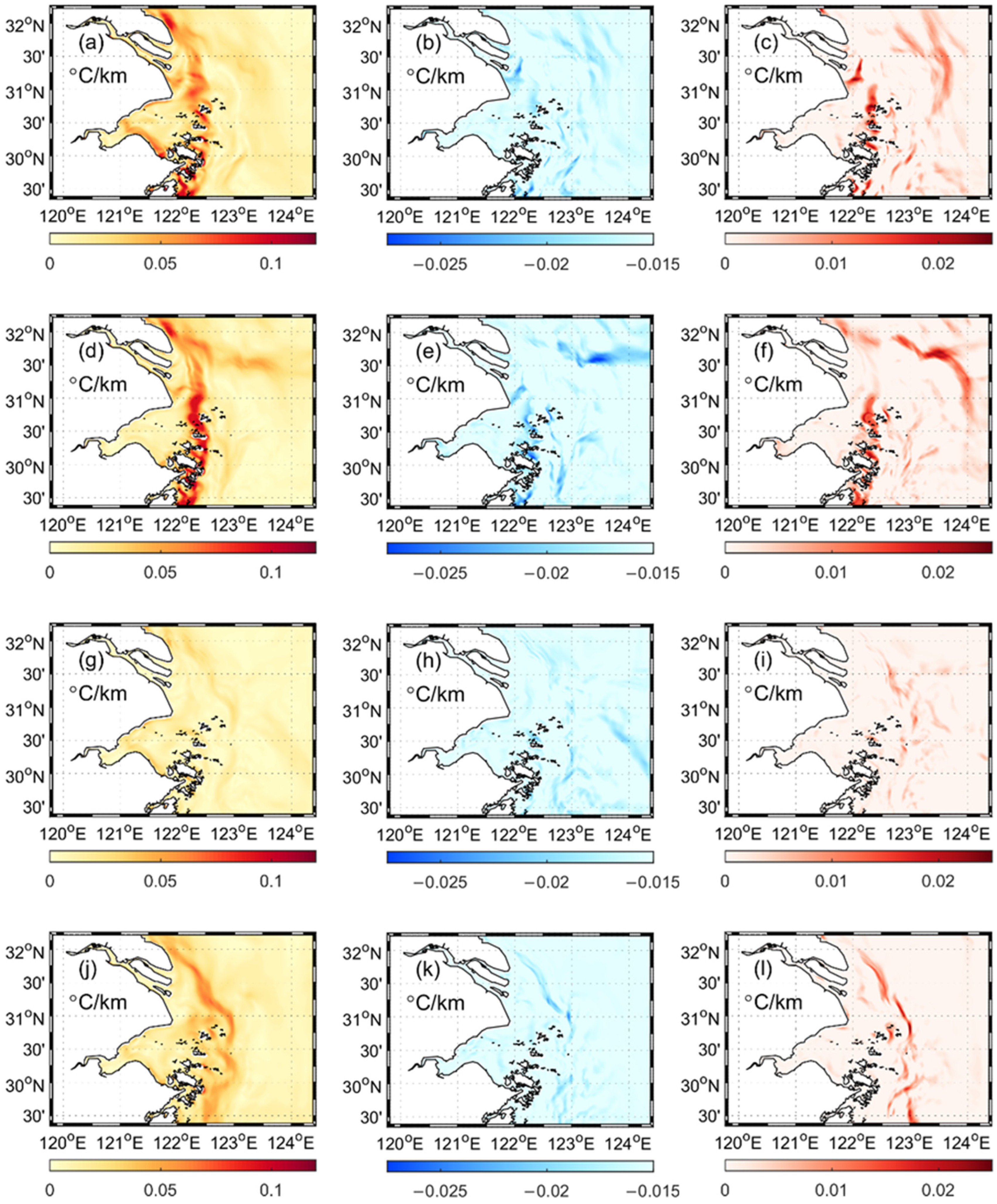
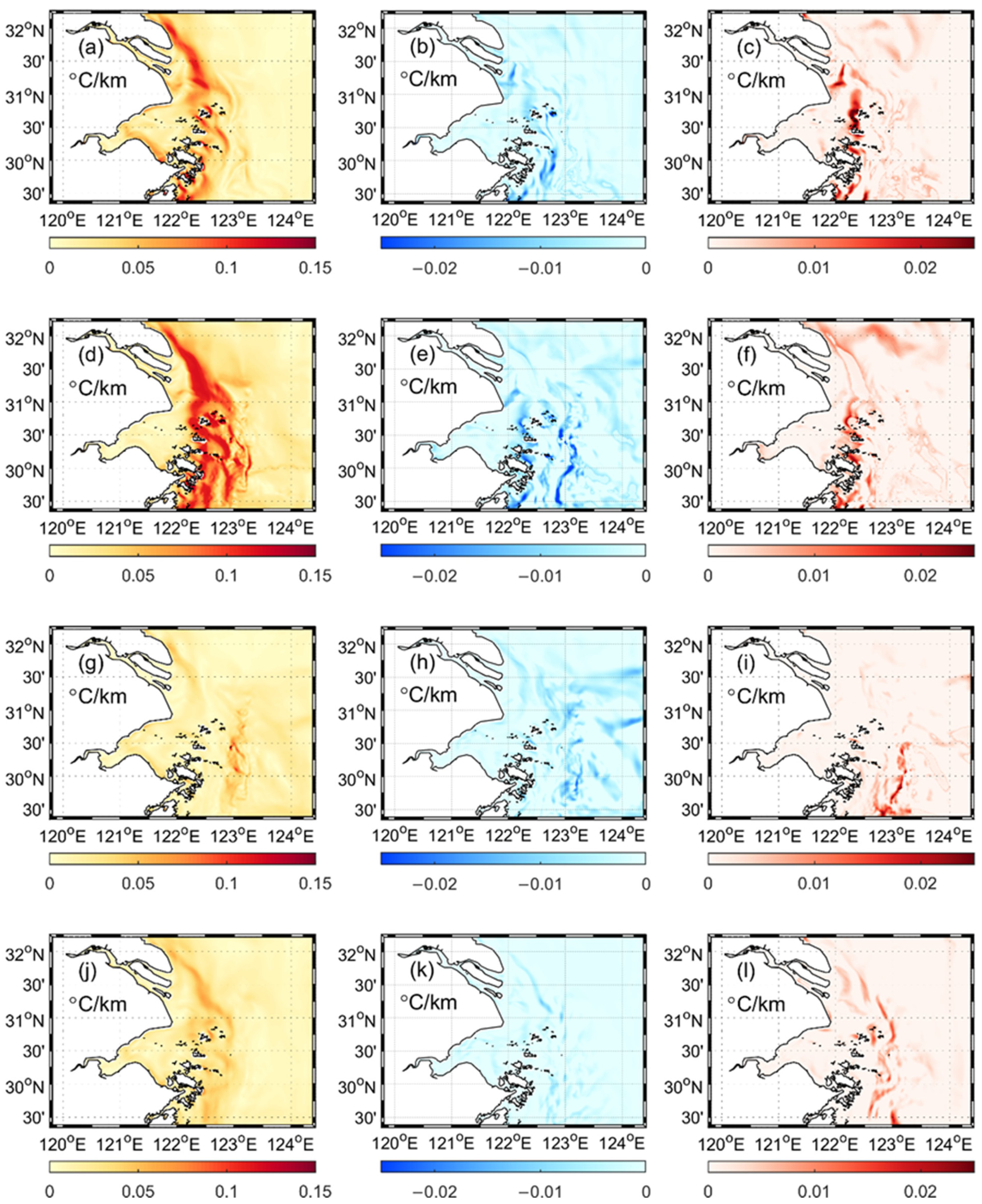
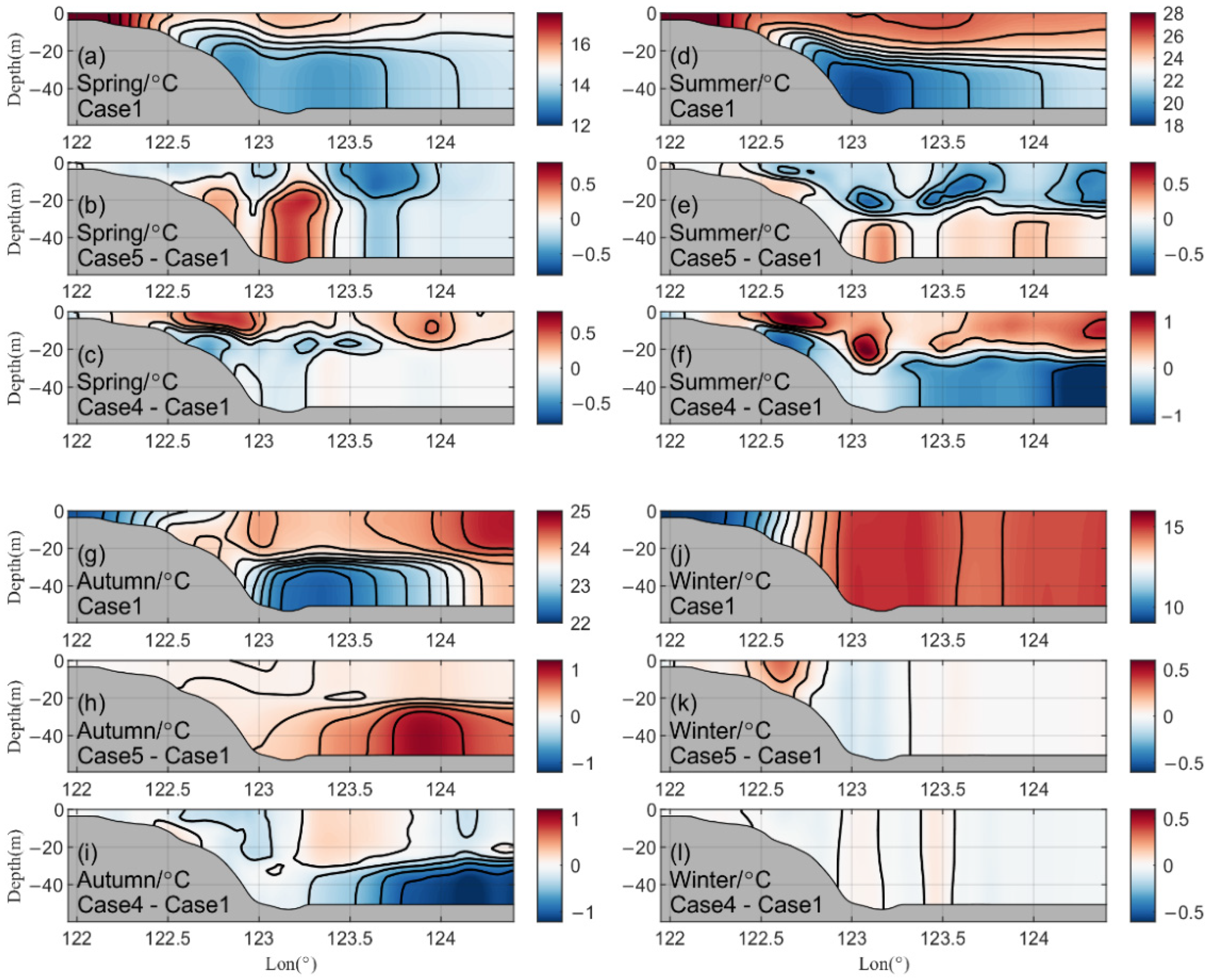
3.2. Influence of CR Runoff on Fronts and Vertical Structure of Sea Temperature
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Beardsley, R.; Limeburner, R.; Yu, H.; Cannon, G. Discharge of the Changjiang (Yangtze river) into the East China sea. Cont. Shelf Res. 1985, 4, 57–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Kangshan, W. Changjiang river plume and suspended sediment transport in Hangzhou Bay. Cont. Shelf Res. 1989, 9, 93–111. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Hou, Y.; Yin, B.; Yang, D. Dynamics of circulation and temperature-salinity structures in Changjiang river mouth and its adjacent sea: III. The temperature structure. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2015, 46, 526–533. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Beardsley, R.; Limeburner, R.; Kim, K. Comparison of winter and summer hydrographic observations in the Yellow and East China Seas and adjacent Kuroshio during 1986. Cont. Shelf Res. 1994, 14, 909–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, P.; Isobe, A. A numerical study on the Changjiang diluted water in the Yellow and East China Seas. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2003, 108, 3299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; He, R.; Zong, H. Variability of Changjiang Diluted Water revealed by a 45-year long-term ocean hindcast and Self-Organizing Maps analysis. Cont. Shelf Res. 2017, 146, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; He, X.; Pan, D.; Chen, C.; Kang, Y.; Chen, X.; Cai, W. Summertime Changjiang River plume variation during 1998–2010. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2014, 119, 6238–6257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Xue, P.; Ding, P.; Beardsley, R.; Xu, Q.; Mao, X.; Gao, G.; Qi, J.; Li, C.; Lin, H. Physical mechanisms for the offshore detachment of the Changjiang Diluted Water in the East China Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2008, 113, C02002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shen, J.; He, Q.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, D. Seasonal variations of transport time of freshwater exchanges between Changjiang Estuary and its adjacent regions. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 157, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Zhang, T.; Zhou, F. Sea-surface temperature fronts in the Yellow and East China Seas from TRMM microwave imager data. Deep Sea Res. Part II 2010, 57, 1017–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B. Hydromorphological mechanisms leading to hypoxia off the Changjiang estuary. Mar. Environ. Res. 2009, 67, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, F.; Xuan, J.; Ni, X.; Huang, D. A preliminary study of variations of the Changjiang Diluted Water between August of 1999 and 2006. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2009, 28, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Moon, J.; Pang, I.; Yoon, J. Response of the Changjiang diluted water around Jeju Island to external forcings: A modeling study of 2002 and 2006. Cont. Shelf Res. 2009, 29, 1549–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukigara, C.; Mino, Y.; Tripathy, S.; Ishizaka, J.; Matsuno, T. Impacts of the Changjiang diluted water on sinking processes of particulate organic matters in the East China Sea. Cont. Shelf Res. 2017, 151, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Cai, Y.; Sun, T.; Xu, W.; Yang, Z. Impacts of Temperature Gradient on the Intensity of Physical Disturbance and the Water Ecological Biodiversity in the River Estuary. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 7, 595–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wu, H.; Wu, T.; Bai, M. Mega Estuarine Constructions Modulate the Changjiang River Plume Extension in Adjacent Seas. Estuaries Coasts 2018, 41, 1234–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornerdevine, A.; Hetland, R.; Macdonald, D. Mixing and Transport in Coastal River Plumes. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2015, 47, 569–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, J.; Hunter, J. Fronts in the Irish sea. Nature 1974, 250, 404–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, C.; Zhu, J. Influence of seasonal runoff regulation by the Three Gorges Reservoir on saltwater intrusion in the Changjiang River Estuary. Cont. Shelf Res. 2013, 71, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herb, W.; Stefan, H. Modified equilibrium temperature models for cold-water streams. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47, W06519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haidvogel, D.; Arango, H.; Hedstrom, K.; Beckmann, A.; Malanotte-Rizzoli, P.; Shchepetkin, A. Model evaluation experiments in the North Atlantic Basin: Simulations in nonlinear terrain-following coordinates. Dyn. Atmos. Oceans 2000, 32, 239–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di-Lorenzo, E. Seasonal dynamics of the surface circulation in the southern California Current System. Deep Sea Res. Part II 2003, 50, 2371–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkin, J.; Arango, H.; Haidvogel, D.; Lichtenwalner, C.; Durski, S.; Hedstrom, K. A regional Ocean Modeling System for the Long-term Ecosystem Observatory. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 110, C06S91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, D.; Zhu, J.; Li, C.; Hu, D. Cross-shelf circulation in the Yellow and East China Seas indicated by MODIS satellite observations. J. Marine Syst. 2008, 70, 134–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlowicz, R.; Beardsley, B.; Lentz, S. Classical tidal harmonic analysis including error estimates in MATLAB using T_TIDE. Comput. Geosci. 2002, 28, 929–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willmott, C. On the validation of models. Phys. Geogr. 1981, 2, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, J.; Geyer, W.; Lerczak, J. Numerical modeling of an estuary: A comprehensive skill assessment. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2005, 110, C5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamurti, T.; Rajendran, K.; Vijaya Kumar, T.; Lord, S.; Toth, Z.; Zou, X.; Cocke, S.; Ahlquist, J.E.; Navon, I.M. Improved skill for the anomaly correlation of geopotential heights at 500 hPa, Mon. Weather Rev. 2003, 131, 1082–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Hafner, J.; Tanimoto, Y.; Liu, W.; Tokinaga, H.; Xu, H. Bathymetric effect on the winter sea surface temperature and climate of the Yellow and East China Seas. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29, 2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, H.; Qin, S.; Yang, D.; Liu, Z. The study on seasonal characteristics of water masses in the western East China Sea shelf area. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2014, 33, 54–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Model Parameters | Parameter Configuration |
|---|---|
| Model domain | 29°–32.5° N, 120°–124°30′ E |
| Grid resolution | 50″ × 50″ in each horizontal direction, 20 sigma layer, θs 7.0, θb 2.0, the minimum depth 3 m |
| Initial conditions | water level, current and sea surface level were 0, temperature and salinity were interpolated from HYCOM |
| Boundary conditions | Datong, Fuchunjiang hydrology station as two points source in the lateral boundary; Tidal forcing K1, O1, P1, Q1, M2, S2, N2, K2 |
| Climate Data | Open boundary: temperature and salinity from JCOPE2Air temperature, air pressure, wind data, relative humidity and radiation flux used NOAA-released NCEP/NCAR reanalysis data. |
| Water Level | Current Velocity | Current Direction | Sea Temperature | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Skill | 0.981 | 0.901 | 0.922 | 0.929/0.932 |
| January | February | March | April | May | June |
| 0.613 | 0.712 | 0.788 | 0.828 | 0.617 | 0.737 |
| July | August | September | October | November | December |
| 0.789 | 0.796 | 0.766 | 0.684 | 0.758 | 0.769 |
| Test | CR | QTR | Tidal Forcing | Climate Forcing |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case 1 | 2019 | 2019 | 2019 | 2019 |
| Case 2 | Off | 2019 | 2019 | 2019 |
| Case 3 | Maximum | 2019 | 2019 | 2019 |
| Case 4 | Abundant | 2019 | 2019 | 2019 |
| Case 5 | Scare | 2019 | 2019 | 2019 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shen, H.; Zhu, Y.; He, Z.; Li, L.; Lou, Y. Impacts of River Discharge on the Sea Temperature in Changjiang Estuary and Its Adjacent Sea. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 343. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10030343
Shen H, Zhu Y, He Z, Li L, Lou Y. Impacts of River Discharge on the Sea Temperature in Changjiang Estuary and Its Adjacent Sea. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2022; 10(3):343. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10030343
Chicago/Turabian StyleShen, Hui, Ye Zhu, Zhiguo He, Li Li, and Yingzhong Lou. 2022. "Impacts of River Discharge on the Sea Temperature in Changjiang Estuary and Its Adjacent Sea" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 10, no. 3: 343. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10030343
APA StyleShen, H., Zhu, Y., He, Z., Li, L., & Lou, Y. (2022). Impacts of River Discharge on the Sea Temperature in Changjiang Estuary and Its Adjacent Sea. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 10(3), 343. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10030343








