Benthic Microbial Communities and Environmental Parameters of Estuary and Hypoxic Zone in the Bohai Sea, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Nutrient Sampling and Preparation
2.2. High-Throughput Sequencing Analysis
2.3. Analysis Software, Method, and Gene Sequence Process
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Environmental Factor Analysis
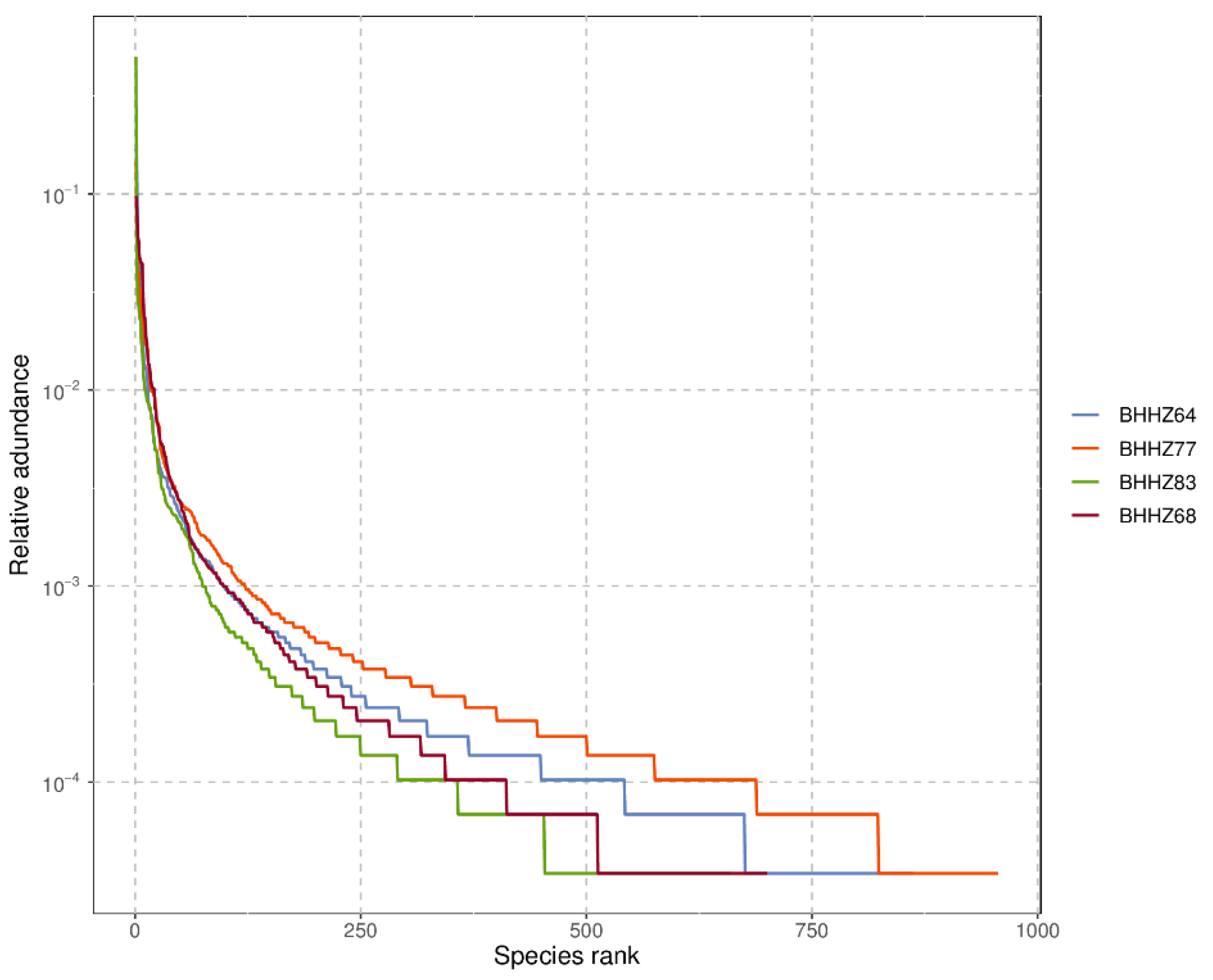
3.2. Microbial Community Abundance and Diversity Analysis of Sediments from Different Areas of the Bohai Sea
3.2.1. Alpha Diversity Analysis
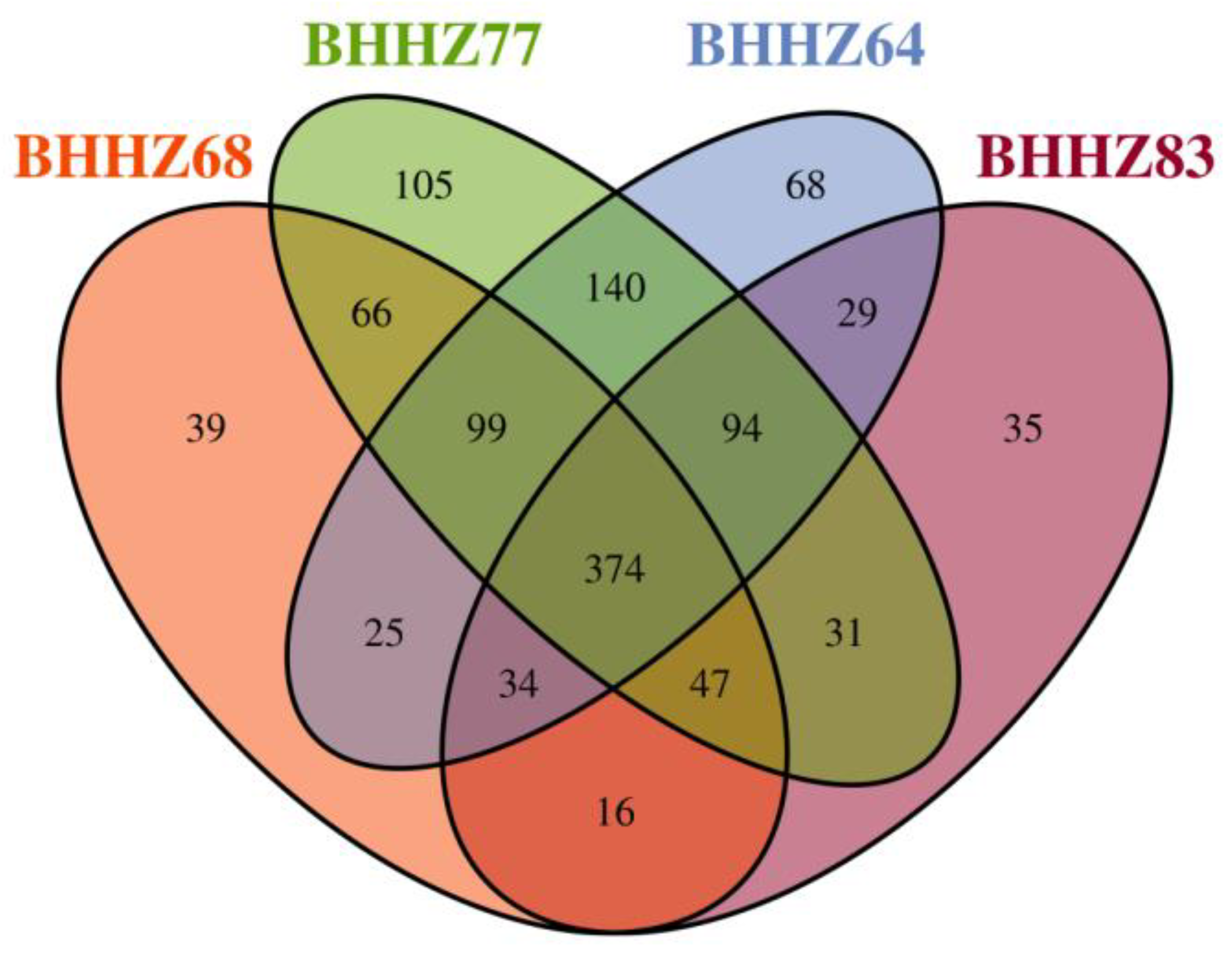
3.2.2. Beta Diversity Analysis
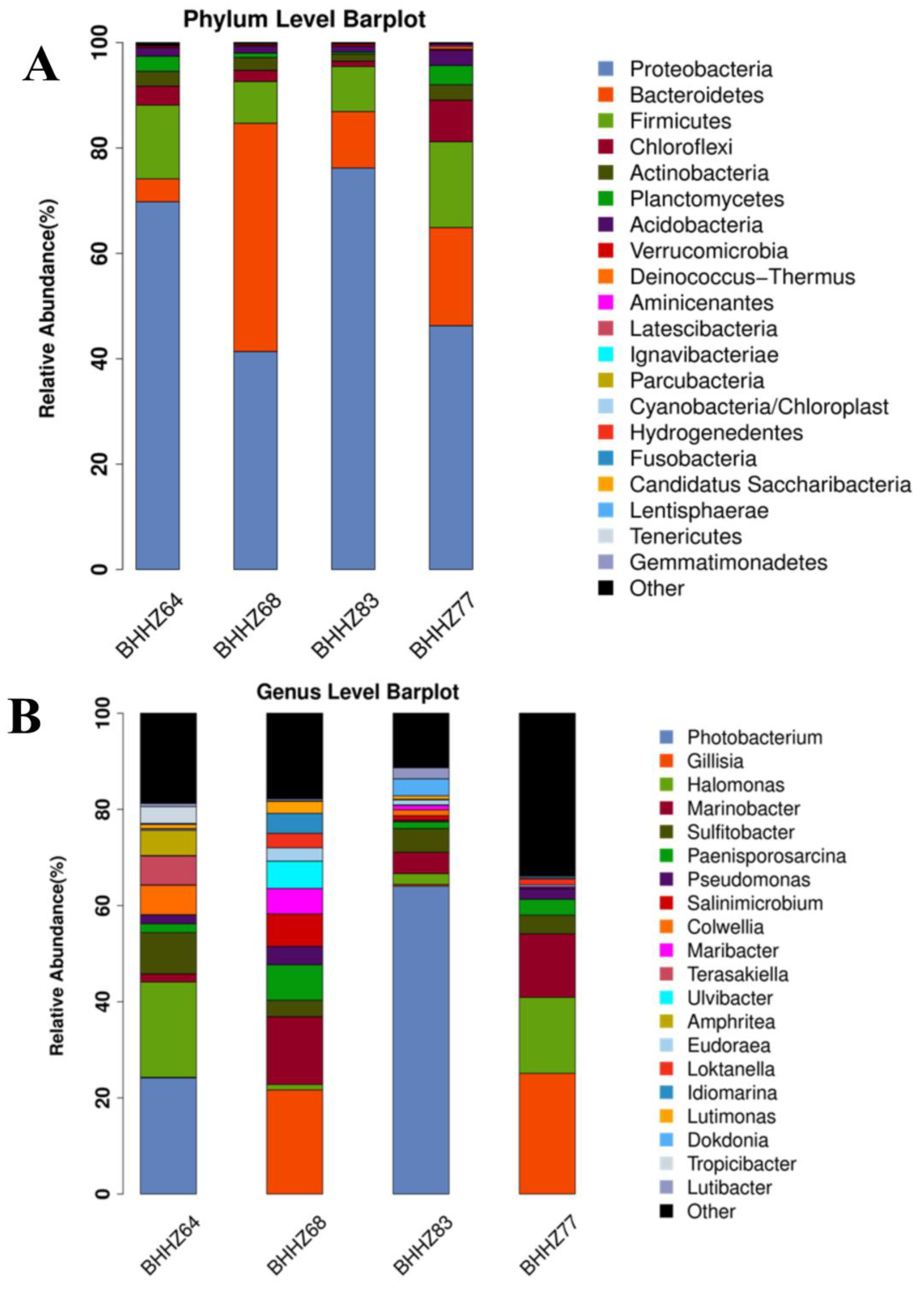
3.2.3. Microbial Community Characteristics in the Sediments of Estuaries and a Hypoxic Zone
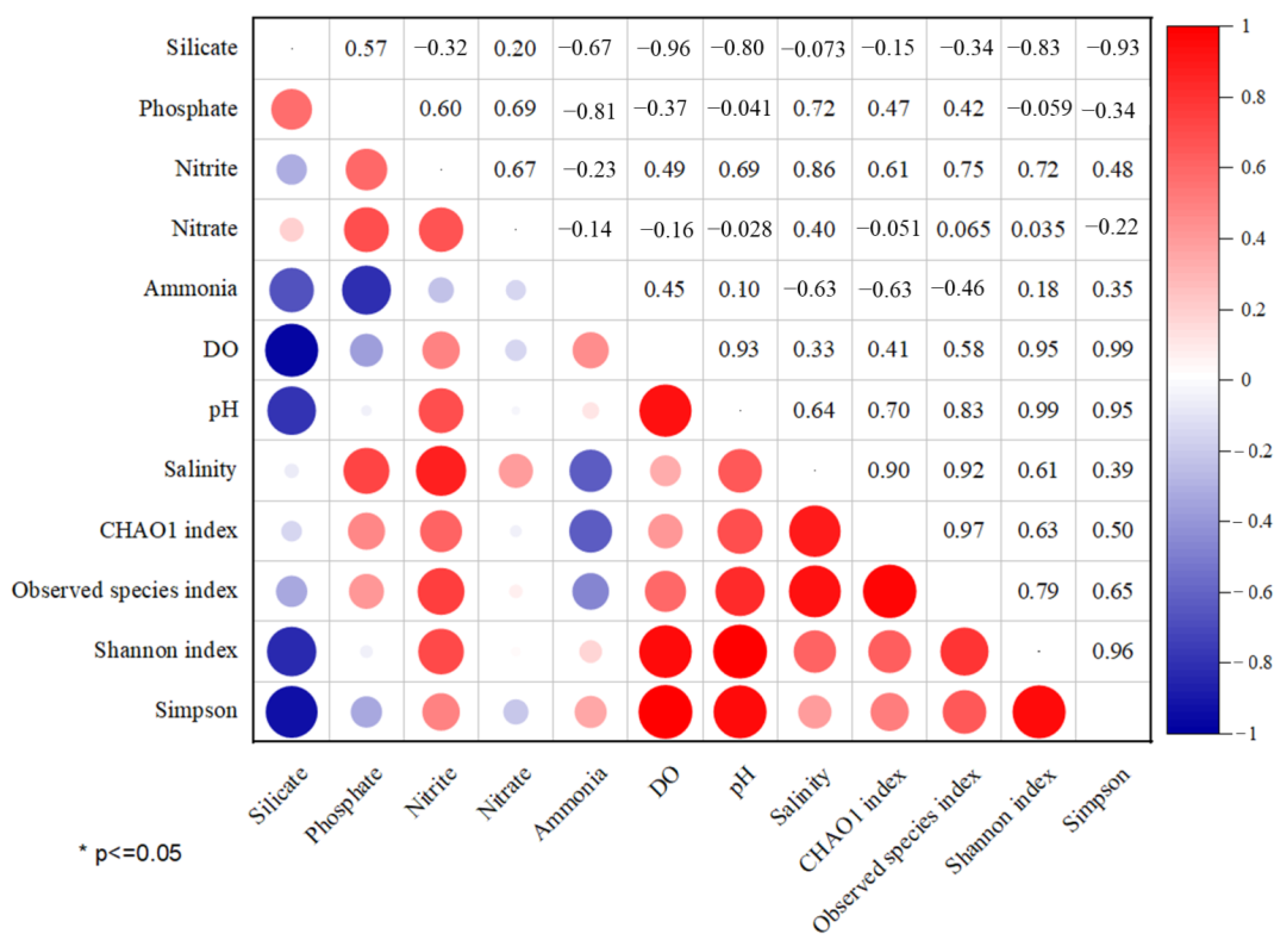
3.3. Effects of Environmental Parameters on Microbial Communities
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wei, M.; Yanwen, Q.; Binghui, Z.; Lei, Z. Heavy metal pollution in Tianjin Bohai Bay, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2008, 7, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, H.; Li, L.; Fu, C.; Tu, C.; Huang, Y.; Wu, L.; Tang, J.; Luo, Y.; Christie, P. Levels, distributions and sources of veterinary antibiotics in the sediments of the Bohai Sea in China and surrounding estuaries. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 109, 597–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Gang, L.; Gao, C.; Sun, W. Analysis of Comparative Advantage of the Main Aquaculture Products in Bohai Rim. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2014, 57, 1093–1096. [Google Scholar]
- Sørensen, K.; Teske, A. Stratified Communities of Active Archaea in Deep Marine Subsurface Sediments. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 4596–4603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Liu, L.; Zheng, B.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, X. Analysis of the bacterial community in the two typical intertidal sediments of Bohai Bay, China by pyrosequencing. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 72, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.D.; Kao, S.J.; Zhai, W.D.; Zang, K.P.; Zheng, N.; Xu, X.M.; Huo, C.; Wang, J.Y. Effects of stratification, organic matter remineralization and bathymetry on summertime oxygen distribution in the Bohai Sea, China. Cont. Shelf Res. 2017, 134, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, T.H.; Yergeau, E.; Maynard, C.; Juck, D.; Whyte, L.G.; Greer, C.W. Predictable bacterial composition and hydrocarbon degradation in Arctic soils following diesel and nutrient disturbance. ISME J. 2013, 7, 1200–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G.; Ren, W.; Teng, Y.; Li, Z. Evident bacterial community changes but only slight degradation when polluted with pyrene in a red soil. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 00022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, Z.; He, T.; Dai, Y.; Xie, S. Sediment Bacterial Communities Associated with Anaerobic Biodegradation of Bisphenol A. Microb. Ecol. 2015, 70, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Xing, R.; Lv, Z.; Shao, Y.; Zhao, X.; Li, C. Analysis of gut microbiota revealed Lactococcus garviaeae could be an indicative of skin ulceration syndrome in farmed sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 80, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Li, Z.; Du, B.; Wang, G.; Ding, Y. Bacterial communities in sediments of the shallow Lake Dongping in China. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2011, 112, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Song, X.; Zhang, C.Y.; Chen, G.F.; Lao, Y.M.; Jin, H.; Cai, Z.H. Distribution Patterns of Microbial Community Structure Along a 7000-Mile Latitudinal Transect from the Mediterranean Sea Across the Atlantic Ocean to the Brazilian Coastal Sea. Microb. Ecol. 2018, 76, 592–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kroeker, K.J.; Kordas, R.L.; Crim, R.N.; Singh, G.G. Meta-analysis reveals negative yet variable effects of ocean acidification on marine organisms. Ecol. Lett. 2010, 13, 1419–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, M.; Bowes, G.; Ross, C.; Zhang, X. Climate change and ocean acidification effects on seagrasses and marine macroalgae. Global Change Biol. 2013, 19, 103–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hale, R.; Calosi, P.; Mcneill, L.; Mieszkowska, N.; Widdicombe, S. Predicted levels of future ocean acidification and temperature rise could alter community structure and biodiversity in marine benthic communities. Oikos 2011, 120, 661–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, L.G.; Thrash, J.C.; Rabalais, N.N.; Mason, O.U. Extent of the annual Gulf of Mexico hypoxic zone influences microbial community structure. Public Libr. Sci. 2019, 14, 0209055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekau, W.; Auel, H.; Pörtner, H.O.; Gilbert, D. Impacts of hypoxia on the structure and processes in pelagic communities (zooplankton, macro-invertebrates and fish). Biogeosciences 2010, 7, 1669–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozupone, C.A.; Knight, R. Global patterns in bacterial diversity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins, T.L.; Katie, C.; Baas, J.H.; Jago, C.F.; Jones, D.L.; Malham, S.K.; Mcdonald, J.E.; Gomes, N. Sediment Composition Influences Spatial Variation in the Abundance of Human Pathogen Indicator Bacteria within an Estuarine Environment. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, 112951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, Q.; Han, T.; Xie, J.; Hu, Y.; Chai, L. Phylogenetic analysis of bacterial community composition in sediment contaminated with multiple heavy metals from the Xiangjiang River in China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 70, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 19th ed.; American Publishers Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 1884–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magoč, T.; Salzberg, S.L. FLASH: Fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C. UPARSE: Highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat. Methods. 2013, 10, 996–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stackebrandt, E.; Goebel, B.M. Taxonomic Note: A Place for DNA-DNA Reassociation and 16S rRNA Sequence Analysis in the Present Species Definition in Bacteriology. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1994, 44, 846–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, J.R.; Wang, Q.; Fish, J.A.; Chai, B.; McGarrell, D.M.; Sun, Y.; Brown, C.T.; Porras-Alfaro, A.; Kuske, C.R.; Tiedje, J.M. Ribosomal Database Project: Data and tools for high throughput rRNA analysis. Nucl. Acids Res. 2014, 42, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, F.K.; Josephine, Y.A. Bacterial diversity in aquatic and other environments: What 16S rDNA libraries can tell us. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2004, 47, 161–177. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Garrity, G.M.; Tiedje, J.M.; Cole, J.R. Naïve Bayesian Classifier for Rapid Assignment of rRNA Sequences into the New Bacterial Taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5261–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannan, X.; Yong, L.; Fan, J.; Yayuan, X.; Zhanhui, Q.; Manogaran, L. Impact of salinity variation and silicate distribution on phytoplankton community composition in Pearl River estuary, China. Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2022, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Gao, F.; Wu, Y.; Xu, G.; Liu, H.; Zhang, H.; Yang, F.; Xu, Y. Small-sized salt-tolerant denitrifying and phosphorus removal aerobic granular sludge cultivated with mariculture waste solids to treat synthetic mariculture wastewater. Biochem. Engin. J. 2022, 181, 108396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Q.; Li, W.; Li, W.; Wu, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y. Salt-tolerance aerobic granular sludge: Formation and microbial community characteristics. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 249, 132–138. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, X.; Kou, W.; Yu, H.; Liu, Y.; Wu, L. Environmental Factors Influencing the Spatial Distribution of Sediment Bacterial Community Structure and Function in Poyang Lake. Res. Environ. Sci. 2017, 30, 529–536. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Wang, L.; Bao, X.; Jiang, N.; Yang, X.; Hao, Z.; Chang, Y.; Ding, J. Microbial communities in sea cucumber (Apostichopus japonicus) culture pond and the effects of environmental factors. Aquac. Res. 2019, 10, 14002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Song, X.; Wang, Y.; Abayneh, B.; Ding, Y.; Yan, D.; Bai, J. Microbial community structure of different electrode materials in constructed wetland incorporating microbial fuel cell. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 221, 697–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kizito, S.; Tao, L.; Wu, S.; Ajmal, Z.; Luo, H.; Dong, R. Treatment of anaerobic digested effluent in biochar-packed vertical flow constructed wetland columns: Role of media and tidal operation. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 592, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, T.; Yoshiguchi, K.; Ariesyady, H.D.; Okabe, S. Identification and quantification of key microbial trophic groups of methanogenic glucose degradation in an anaerobic digester sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 123, 599–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, R.E.; Bofillmas, S.; Egle, L.; Reischer, G.H.; Schade, M.; Fernandez-Cassi, X. Occurrence of human-associated Bacteroidetes genetic source tracking markers in raw and treated wastewater of municipal and domestic origin and comparison to standardand alternative indicators of faecal pollution. Water Res. 2016, 90, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.S.; Parameswaran, P.; Rittmann, B.E. Effects of solids retention time on methanogenesis in anaerobic digestion of thickened mixed sludge. Bioresour Technol. 2011, 102, 10266–10272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skariyachan, S.; Garka, S.; Puttaswamy, S.; Shanbhogue, S.; Devaraju, R.; Narayanappa, R. Environmental monitoring and assessment of antibacterial metabolite producing actinobacteria screened from marine sediments in south coastal regions of Karnataka, India. Environ. Monit. Assessment. 2017, 189, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissbrodt, D.G.; Neu, T.R.; Kuhlicke, U.; Rappaz, Y.; Holliger, C. Assessment of bacterial and structural dynamics in aerobic granular biofilms. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 00175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Tian, C. Analysis of microbial diversity and its correlation with environmental factors in reservoir sediment. Acta Sci. Nat. Univ. Pekinesis 2018, 54, 625–632. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.B.; Yang, Y.; Zhong-Yuan, L.I.; Lin, Y.Q. Analysis of microbial community diversity in the water from Changli coastal area of Bohai Sea, Hebei. J. Saf. Environ. 2019, 19, 1817–1823. [Google Scholar]
- Beman, J.M.; Carolan, M.T. Deoxygenation alters bacterial diversity and community composition in the ocean’s largest oxygen minimum zone. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jessica, A.B.; Frank, J.S.; John, M.E.; Edward, F.D. Microbial community phylogenetic and trait diversity declines with depth in a marine oxygen minimum zone. Ecology 2012, 93, 1659–1673. [Google Scholar]
- Hettinger, A.; Sanford, E.; Hill, T.M.; Lenz, E.A.; Russell, A.D.; Gaylord, B. Larval carry-over effects from ocean acidification persist in the natural environment. Global Chang. Biol. 2013, 19, 3317–3326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, H. Research of Low Heat Portland Cement for Marine Engineering. Master’s Thesis, China Building Materials Academy, Beijing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H. Application of Low-Heat Portland Cement in Marine Engineering Concrete. Master’s Thesis, Guangzhou University, Guangzhou, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Q. Researchon on New Composite Flocculant Material of Modified Layer Silieates and Microorganism. Master’s Thesis, Wuhan University of Technology, Wuhan, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Tian, J.; Yang, G.; Jia, H. Effects of ocean acidification on cycles of carbon, nitrogen and sulfur. T. Oceanol. Limn. 2018, 3, 79–87. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Xie, X.; Li, Q.; Gan, Z.; Hu, T.; Yang, J.; Deng, Y.; Gan, Y.; Zhang, Y. Microbial community structure and its Response to environment in mangrove sediments of Dongzhai Port. Earth Sci. 2022, 3, 1122–1135. [Google Scholar]
- Ceccon, D.M.; Faoro, H.; da Cunha Lana, P. Metataxonomic and Metagenomic Analysis of Mangrove Microbiomes Reveals Community Patterns Driven by Salinity and pH Gradients in Paranaguá Bay, Brazil. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 694, 133609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.N.; Ren, P.; Feng, P.Y. Shift in Rhizospheric and Endophytic Bacterial Communities of Tomato Caused by Salinity and Grafting. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 734, 139388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, P.; Mahapatra, S.; Mohapatra, M. Salinity and Macrophyte Drive the Biogeography of the Sedimentary Bacterial Communities in a Brackish Water Tropical Coastal Lagoon. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 595, 472–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Ke, S.; Yuan, H.; Zhu, J.; Li, W. Effect of ammonia-nitrogen concentration on microbial community structure in a MBBR process. Environ. Eng. 2020, 38, 119–125. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Huang, H.; Bao, S. Microbial Community Structure of Soils in Bamenwan Mangrove Wetland. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Chen, C.T.A. Heavy metal pollution status in surface sediments of the coastal Bohai Bay. Water Res. 2012, 46, 1901–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
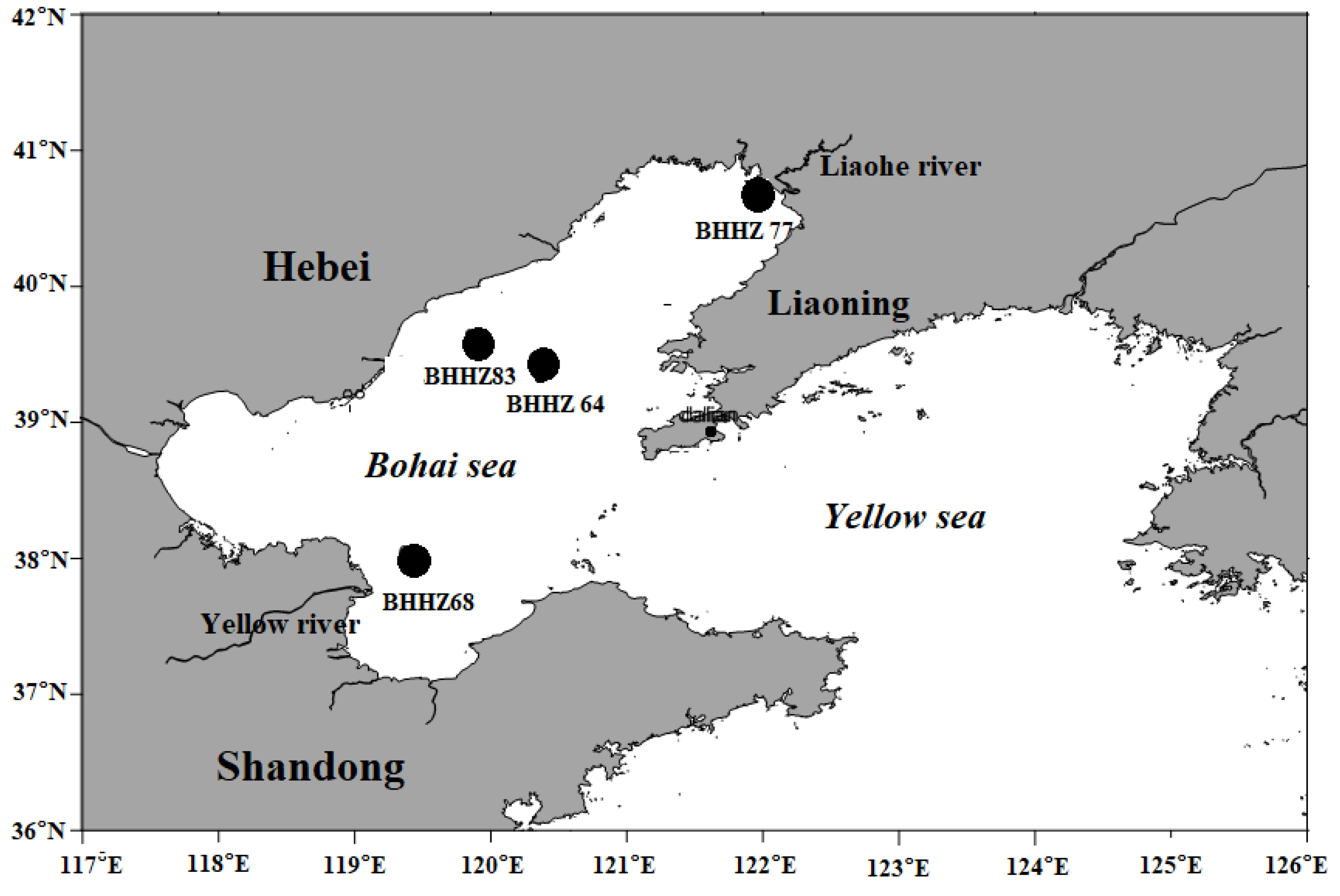


| Station | Longitude (N) | Latitude (E) | Sampling Depth (m) | Time (Year/Month) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BHHZ64 | 120.37 | 39.33 | 20.0 ± 1.0 | 2018.8 |
| BHHZ83 | 119.90 | 39.50 | 23.0 ± 1.0 | 2018.8 |
| BHHZ68 | 119.27 | 38.22 | 17.0 ± 1.0 | 2018.8 |
| BHHZ77 | 121.60 | 40.48 | 10.0 ± 1.0 | 2018.8 |
| ID | Silicate (μM) | Phosphate (μM) | Nitrite (μM) | Nitrate (μM) | Ammonia Avg (μM) | pH | DO (mg/L) | Salinity (‰) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 64-1 | 6.28 | 0.15 | 0.73 | 1.20 | BLQ | 7.93 | 6.16 | 31.1461 |
| 64-2 | 6.26 | 0.13 | 0.74 | 1.18 | BLQ | 7.92 | 6.07 | 31.1448 |
| 77-1 | 4.91 | 0.37 | 4.60 | 6.21 | BLQ | 7.98 | 6.63 | 31.8122 |
| 77-2 | 5.65 | 0.36 | 4.75 | 7.21 | BLQ | 7.98 | 6.57 | 30.7856 |
| 68-1 | 2.04 | BLQ | 1.00 | 4.96 | 0.60 | 7.88 | 6.27 | 30.8148 |
| 68-2 | 4.10 | BLQ | 1.28 | 2.56 | 0.80 | 7.95 | 7.10 | 30.8151 |
| 83-1 | 10.28 | 0.29 | 0.64 | 5.44 | BLQ | 7.78 | 4.23 | 31.5270 |
| 83-2 | 11.34 | 0.30 | 0.65 | 5.47 | BLQ | 7.78 | 4.30 | 31.6682 |
| CHAO1 Index | Observed Species Index | Shannon Index | Simpson Index | Goods Coverage | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BHHZ77 | 1024.21 | 950 | 6.86 | 0.97 | 0.99 |
| BHHZ64 | 1004.16 | 859 | 5.95 | 0.94 | 0.99 |
| BHHZ68 | 852.31 | 690 | 6.09 | 0.96 | 0.99 |
| BHHZ83 | 867.64 | 652 | 4.35 | 0.74 | 0.99 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, F.; Zhao, H.; Zhao, P.; Zhang, C.; Xu, G.; Liu, G.; Guo, X. Benthic Microbial Communities and Environmental Parameters of Estuary and Hypoxic Zone in the Bohai Sea, China. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1862. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10121862
Gao F, Zhao H, Zhao P, Zhang C, Xu G, Liu G, Guo X. Benthic Microbial Communities and Environmental Parameters of Estuary and Hypoxic Zone in the Bohai Sea, China. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2022; 10(12):1862. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10121862
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Fan, Huade Zhao, Pengfei Zhao, Cuiya Zhang, Guangjing Xu, Guize Liu, and Xianyong Guo. 2022. "Benthic Microbial Communities and Environmental Parameters of Estuary and Hypoxic Zone in the Bohai Sea, China" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 10, no. 12: 1862. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10121862
APA StyleGao, F., Zhao, H., Zhao, P., Zhang, C., Xu, G., Liu, G., & Guo, X. (2022). Benthic Microbial Communities and Environmental Parameters of Estuary and Hypoxic Zone in the Bohai Sea, China. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 10(12), 1862. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10121862






