Exploring the Impact of Green Technology Innovation on Rural Habitat System Resilience
Abstract
1. Introduction
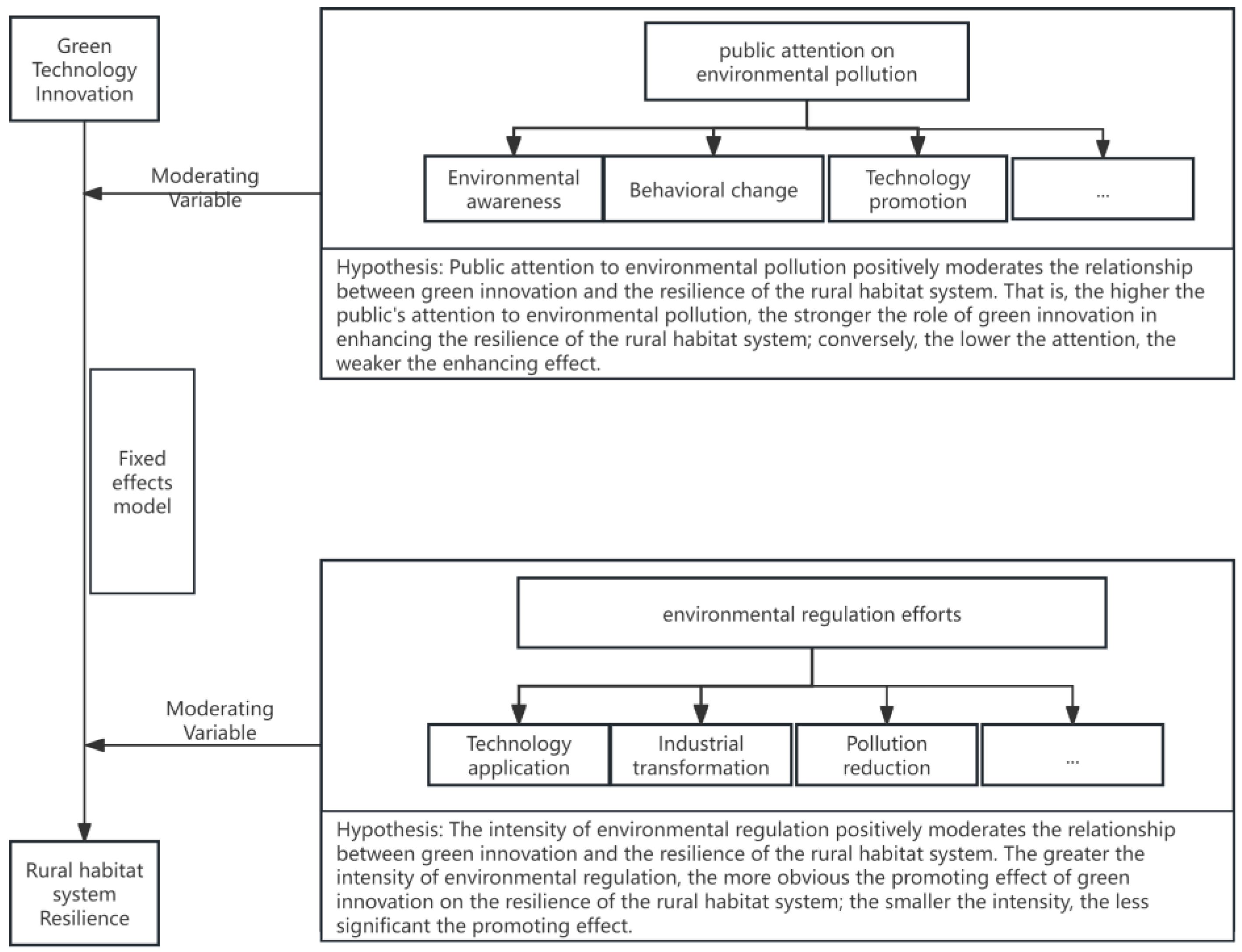
2. Literature Review and Research Hypothesis
2.1. Green Technology Innovations
2.2. Rural Habitat System Reliance
2.3. Research Contributions
3. Model Selection and Data Sources
3.1. Empirical Framework
3.2. Data Measurement and Description
3.2.1. Indicator System for Evaluating Rural Habitat Resilience
3.2.2. Selection of Green Innovation Levels
3.2.3. Selection of Control Variables
3.2.4. Selection of Moderating Variables
3.3. Sources of Variables and Descriptive Statistics
4. Empirical Analysis
4.1. Cluster Analysis
4.2. Benchmark Regression Model Analysis
4.3. Robustness Tests
4.3.1. Replacement of Core Explanatory Variables
4.3.2. Core Explanatory Variables Lagged by One Period
4.3.3. Replacement of the Fixed Effects Model
4.4. Endogeneity Test
4.5. Heterogeneity Test
4.5.1. Regional Heterogeneity Across Eastern, Central, and Western China
4.5.2. Regional Heterogeneity in the Yangtze River Economic Belt
5. Further Analysis
6. Conclusions and Research Outlook
6.1. Conclusions
6.2. Research Outlooks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, M.; Pelz, S.; Lamboll, R.; Wang, C.; Rogelj, J. A principle-based framework to determine countries’ fair warming contributions to the Paris Agreement. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, S. The Possibility and Improvement Directions of Achieving the Paris Agreement Goals from the Perspective of Climate Policy. Sustainability 2024, 16, 4212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulme, M. 1.5 °C and climate research after the Paris Agreement. Nat. Clim. Change 2016, 6, 222–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Gan, J.; Liu, B.; Zhao, K. Environmental policy and green development in urban and rural construction: Beggar-thy-neighbor or win-win situation? J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 446, 141201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.; Lin, C.; Bin, Y. Harmony with nature: Disentanglement the influence of ecological perception and adaptation on sustainable development and circular economy goals in country. Heliyon 2024, 10, e26034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayyab Ayaz, M.; Prodromou, T.; Le, T.; Nepal, R. Energy security dimensions and economic growth in Non-OECD Asia: An analysis on the role of institutional quality with energy policy implications. Energy Policy 2024, 188, 114090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antončič, J.A.; Hojnik, J.; Ruzzier, M.; Ruzzier, M.K.; Soltwisch, B. The Role of Demographic Changes and Digitalization in Eco-Innovations and Their Effects on the Growth of Companies. Sustainability 2024, 16, 6203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, J.; Xin, B.; Xin, B.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, M. Research on the coordinated development of provincial urbanization and carbon emission efficiency of construction industry in China. Carbon Balance Manag. 2024, 19, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Shi, F. New urbanization and high-quality urban and rural development: Based on the interactive coupling analysis of industrial green transformation. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 156, 111044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Qu, Y.; Zhan, L. Great transition and new pattern: Agriculture and rural area green development and its coordinated relationship with economic growth in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 344, 118563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Azam, S.M.F. The impact of green-listed companies on rural ecological environments in China: A spatial heterogeneity and empirical analysis. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 356, 120687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michalewska-Pawlak, M. Evolution of the European Union’s policy for development of rural communities in the context of the European Green Deal strategy implementation. Przegląd Eur. 2024, 3, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.; You, Y. The Impact of the Rural Digital Economy on Agricultural Green Development and Its Mechanism: Empirical Evidence from China. Sustainability 2024, 16, 3594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Xiong, M.; Li, X. Energy transition policy and rural revitalization of Chinese ethnic regions. Financ. Res. Lett. 2025, 71, 106439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, X. Research on Auditing of Special Agricultural Funds under the Background of Rural Revitalization—Taking S City in Yunnan Province as an Example. Sustain. Dev. 2023, 13, 951–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Huang, X.; Li, R.; Cheng, W. Assessing the effectiveness of targeted poverty alleviation policies in Xinjiang, China. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2023, 10, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Yang, H.; Su, L.; Pei, H. Household residential energy choices in green transition: Insights from a household survey in rural China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 60539–60554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.; Dong, S.; Xu, S.X.; Kraemer, K.L. Innovation diffusion in global contexts: Determinants of post-adoption digital transformation of European companies. Eur. J. Inform. Syst. 2017, 15, 601–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alola, A.A. Global urbanization and ruralization lessons of clean energy access gap. Energ. Policy 2024, 188, 114101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahmi, M.; Bruno, B.; Dhayal, K.S.; Esposito, L.; Parziale, A. From manure to megawatts: Navigating the sustainable innovation solution through biogas production from livestock waste for harnessing green energy for green economy. Heliyon 2024, 10, e34504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Cui, C.; Xu, M.; Cheng, B.; Zhuang, M. Key technologies improvements promote the economic-environmental sustainability in wheat production of China. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 443, 141230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Xie, C.; Qin, Y.; Zhou, R.; Wu, H.; Che, S. Study on temperature regulation function of green spaces at community scale in high-density urban areas and planning design strategies. Urban For. Urban Green. 2024, 101, 128511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Huang, X.; Xie, M.; Cheng, W.; Shu, Q. A study on the effects of regional differences on agricultural water resource utilization efficiency using super-efficiency SBM model. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.W.; Rhee, J.H.; Park, C.H. How Does Digital Transformation Improve Supply Chain Performance: A Manufacturer’s Perspective. Sustainability 2024, 16, 3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Huang, J.; Jiao, M.; Yang, Q. The Effects of Urbanization on Urban Land Green Use Efficiency of Yangtze River Delta Urban Agglomeration: Mechanism from the Technological Innovation. Sustainability 2024, 16, 2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ji, M.; Wang, S. Can Environmental, Social, and Governance Ratings Promote Green Innovation in Chinese Heavy Polluters? Perspectives from “Greening” Behaviors. Sustainability 2024, 16, 2842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Chen, C.; Du, P.; Song, L.; Zhang, Y. Evaluation of Rural Human Settlement Environment in the Middle and Lower Reaches of the Yellow River. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2023, 32, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L. Overall Thoughts on the Planning and Construction of Beijing. Beijing Plan. Rev. 1996, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Li, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X. Land use policy as an instrument of rural resilience—The case of land withdrawal mechanism for rural homesteads in China. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 87, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, D.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, S.; Fu, J.; Su, F. Spatio-Temporal Pattern and Influence Mechanism of Rural Human Settlements System Resilience: Case from China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 14533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Rong, F.; Li, S. Driving Force–Pressure–State–Impact–Response-Based Evaluation of Rural Human Settlements’ Resilience and Their Influencing Factors: Evidence from Guangdong, China. Sustainability 2024, 16, 813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streimikiene, D.; Baležentis, T.; Volkov, A.; Morkūnas, M.; Žičkienė, A.; Streimikis, J. Barriers and Drivers of Renewable Energy Penetration in Rural Areas. Energies 2021, 14, 6452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Nie, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Luo, F.; Wei, J.; Cui, Y. Spatiotemporal Dynamics and Spatial Spillover Effects of Resilience in China’s Agricultural Economy. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yan, C.; Guo, Q.; Zhang, J.; Ruiz-Menjivar, J. The impact of agricultural chemical inputs on environment: Global evidence from informetrics analysis and visualization. Int. J. Low-Carbon Technol. 2018, 13, 338–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, D.; Feng, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Xue, L. Local implementation for green-manufacturing technology diffusion policy in China: From the user firms’ perspectives. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 129, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Block, J.; Lambrecht, D.; Willeke, T.; Cucculelli, M.; Meloni, D. Green patents and green trademarks as indicators of green innovation. Res. Policy 2025, 54, 105138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Liu, X.; Yang, Z. An integrated indicator on regional ecological civilization construction in China. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. World Ecol. 2015, 23, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wainger, L.A.; Secor, D.H.; Gurbisz, C.; Kemp, W.M.; Glibert, P.M.; Houde, E.D.; Richkus, J.; Barber, M.C. Resilience indicators support valuation of estuarine ecosystem restoration under climate change. Ecosyst. Health Sustain. 2017, 3, e01268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bizikova, L.; Larkin, P.; Mitchell, S.; Waldick, R. An indicator set to track resilience to climate change in agriculture: A policy-maker’s perspective. Land Use Policy 2019, 82, 444–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Zhu, F.; Qiu, X.; Zhao, S. Effects of natural disasters on livelihood resilience of rural residents in Sichuan. Habitat Int. 2018, 76, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Hu, Z.; Cao, J.; Xu, X. The impact of environmental accountability on air pollution: A public attention perspective. Energ. Policy 2022, 161, 112733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhou, H.; Hua, G.; Wu, Q. What is the relationship among environmental pollution, environmental behavior, and public health in China? A study based on CGSS. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 20299–20312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, T.; Chen, M.; Wang, F.; Cheng, S. The impact of public demands on local environmental governance performance: Evidence from civil environmental complaints placed on leaders at different government levels in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 360, 121216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, W.; Zhang, Z. Environmental regulation intensity, green finance, and environmental sustainability: Empirical evidence from China based on spatial metrology. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 66228–66253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Yang, M.; Wang, C. Strategic interaction of environmental regulation and its influencing mechanism: Evidence of spatial effects among Chinese cities. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 312, 127668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Tian, P. How does heterogeneous environmental regulation affect net carbon emissions: Spatial and threshold analysis for China. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 330, 117161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Wang, D. How does environmental regulation influence China’s carbon productivity? An empirical analysis based on the spatial spillover effect. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 257, 120484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, C.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, J. Dual driving forces for corporate environmental responsibility performance: The synergistic effects of government environmental regulation and market multi-agent green supervision. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 949, 174790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Li, J.; Luo, X. How Top-Down Water Regulation Affects the Financial Performance of Enterprises: The River Chief System in China as an Example. Water 2024, 16, 2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blundell, R.; Bond, S. Initial Conditions and Moment Restrictions in Dynamic Panel Data Models. J. Econom. 1998, 87, 115–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhou, H. The Impact of Rural Industrial Revitalization on the Consumption Upgrade of Rural Residents. J. Jiangxi Univ. Financ. Econ. 2022, 103–115. [Google Scholar]
| Subsystems | Factor Layer | Indicator Layer | Unit of Measure | Interpretation of Indicators | Indicator Properties |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Economic systems | Production conditions | Cropland water intensity | Thousands of hectares/billion cubic meters | Reservoir capacity/cultivated land area | Forward |
| Economic development | Per capita production of agriculture, forestry, animal husbandry, and fisheries | Million dollars per person | Gross value of agricultural, forestry, livestock, and fisheries production/rural population | Forward | |
| Rural disposable income per capita | Yuan/r person | Disposable income/rural population | Forward | ||
| Agricultural efficiency | Level of agricultural mechanization | Million kilowatts/thousand hectares | Total power of agricultural machinery/area of agricultural land | Forward | |
| Grain production per unit area | Tons/thousand hectares | Total grain production/total area sown to grain | Forward | ||
| Society systems | Demographic composition of the population | Percentage of rural population | % | Rural population/total population | Forward |
| Elderly dependency ratio (population sample survey) | % | Ratio of the old-age component of the non-working-age population to the working-age population | Negative direction | ||
| Social security | Minimum living standard for rural residents | Ten thousand dollars | Direct access to the yearbook | Forward | |
| Grass-roots organization | Number of village committees for 10,000 people | Per 10,000 persons | Number of village committees/village population | Forward | |
| Ecological systems | Resource endowment | Water resources per capita | m3 | Water resources per capita | Forward |
| Cultivated land area per capita | Thousands of hectares/ten thousand people | Cultivated land area/rural population | Forward | ||
| Ecological preservation | Pesticide application intensity | Tons/thousand hectares | Pesticide application/total sown area of crops | Negative direction | |
| Film use strength | Tons/thousand hectares | Film use/total sown area of crops | Negative direction | ||
| Intensity of fertilizer use | Tons/thousand hectares | Fertilizer use/total sown area of crops | Negative direction | ||
| Environmental governance | Public toilets per 10,000 population | Collars | Public toilets per 10,000 population | Forward | |
| Soil and water management loss intensity | % | Soil erosion control area/total arable land area | Forward | ||
| Infrastructure systems | Transportation | Transportation and communication expenditures | Yuan/person | Consumption expenditure on cash transportation and communications by rural residents in the Urban–Rural Integration Household Income, Expenditure and Living Conditions Survey (URBIS) | Forward |
| Residence | Expenditure on housing for rural residents | Yuan/person | Cash residential consumption expenditures of rural residents from the Urban–Rural Integration Household Income, Expenditure and Living Conditions Survey (URBIS) | Forward | |
| Education | Expenditures on education, culture, and recreation | Yuan/person | Rural residents’ cash expenditure on education, culture, and recreation from the Urban–Rural Integration Household Income, Expenditure, and Living Conditions Survey (URBIS) | Forward | |
| Health care | Number of beds in medical institutions per 10,000 persons in rural areas | Sheet of paper | Number of beds in medical institutions per 10,000 persons in rural areas (beds) | Forward | |
| Village health center personnel per 1000 agricultural population | Man | Village health center personnel per 1000 agricultural population | Forward | ||
| Informatization level | Rural internet penetration | % | Number of rural internet access users/internet access users | Forward | |
| Rural cable broadcasting and television penetration rate/% | % | Number of rural cable radio and television subscribers as a percentage of total households | Forward | ||
| Energy system | Rural energy use | Mechanization of agriculture | kWh/ha | Total power of agricultural machinery/total sown area of crops | Forward |
| Rural social electricity consumption | Million kWh | Direct access to the yearbook | Forward | ||
| Rural electricity generation | Million kWh | Direct access to the yearbook | Forward |
| VarName | Full Form | Obs | Mean | SD | P5 | Median | P95 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RHSES | Rural Human Settlements Environmental Resilience System | 360 | 0.287 | 0.073 | 0.190 | 0.283 | 0.416 |
| lnGP | Natural Logarithm of Green Patent Grants | 360 | 7.532 | 1.409 | 5.034 | 7.604 | 9.655 |
| lnAP | Natural Logarithm of Agricultural Productivity | 360 | 6.666 | 1.295 | 4.474 | 6.667 | 8.640 |
| PEUAFHFU | Proportion of Employed in Agricultural, Forestry, Animal Husbandry, and Fishery in Urban Units | 360 | 0.021 | 0.038 | 0.001 | 0.006 | 0.109 |
| AGDP | Agricultural GDP Proportion | 360 | 9.651 | 5.177 | 0.600 | 9.250 | 18.000 |
| LEP | Local Environmental Protection Expenditure Ratio | 360 | 0.029 | 0.009 | 0.017 | 0.027 | 0.048 |
| lnLRI | Natural Logarithm of Rural Infrastructure Index | 349 | 5.986 | 2.166 | 1.099 | 6.263 | 8.785 |
| PPIAP | Producer Price Index for Agricultural Products | 360 | 104.059 | 6.335 | 95.850 | 102.900 | 116.650 |
| PAEP | Public Attention to Environmental Pollution | 360 | 105.795 | 38.226 | 40.708 | 105.599 | 168.943 |
| IER | Intensity of Environmental Regulation | 360 | 0.951 | 0.272 | 0.568 | 0.915 | 1.388 |
| Rural Habitat System Resilience Category | Provinces |
|---|---|
| Demonstration and leading category | Zhejiang Province, Jilin Province, Qinghai Province |
| Key enhancement category | Chongqing Municipality, Liaoning Province, Gansu Province, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, Shanghai Municipality |
| Actively promoting category | Shandong Province, Hebei Province, Jiangxi Province, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, Jiangsu Province, Heilongjiang Province, Tianjin Municipality, Guizhou Province, Shanxi Province |
| Basic consolidation category | Sichuan Province, Fujian Province, Beijing Municipality, Hunan Province, Guangdong Province, Yunnan Province, Hubei Province, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region |
| To-be-breakthrough-and-improved category | Henan Province, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, Anhui Province, Hainan Province, Shaanxi Province |
| Test Type | p-Value |
|---|---|
| F-test | 0 |
| Hausman test | 0.000 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RHSES | RHSES | RHSES | RHSES | RHSES | RHSES | RHSES | |
| lnGP | 0.018 ** | 0.014 * | 0.014 * | 0.012 * | 0.012 * | 0.012 ** | 0.012 ** |
| (2.521) | (1.936) | (1.940) | (1.658) | (1.660) | (2.023) | (2.087) | |
| lnAP | 0.010 ** | 0.013 *** | 0.012 ** | 0.012 ** | 0.009 * | 0.009 * | |
| (2.578) | (2.726) | (2.521) | (2.490) | (1.872) | (1.806) | ||
| PEUAFHFU | 0.106 | 0.085 | 0.088 | 0.098 | 0.098 | ||
| (1.091) | (0.871) | (0.899) | (1.059) | (1.052) | |||
| AGDP | −0.002 * | −0.002 * | −0.003 *** | −0.003 *** | |||
| (−1.861) | (−1.897) | (−2.727) | (−2.777) | ||||
| LEP | −0.133 | −0.017 | −0.016 | ||||
| (−0.520) | (−0.069) | (−0.065) | |||||
| lnLRI | 0.004 * | 0.004 * | |||||
| (1.771) | (1.738) | ||||||
| PPIAP | 0.000 | ||||||
| (0.159) | |||||||
| _cons | 0.183 *** | 0.151 *** | 0.130 ** | 0.171 *** | 0.176 *** | 0.174 *** | 0.169 *** |
| (4.086) | (3.281) | (2.590) | (3.130) | (3.170) | (3.574) | (2.698) | |
| N | 360 | 360 | 360 | 360 | 360 | 360 | 360 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| RHSES | RHSES | RHSES | |
| lnNGPA | 0.015 ** | ||
| (2.145) | |||
| L.lnGP | 0.013 * | ||
| (1.696) | |||
| lnGP | 0.010 ** | ||
| (2.516) | |||
| lnAP | 0.012 ** | 0.011 ** | −0.010 ** |
| (2.275) | (2.049) | (−2.067) | |
| PEUAFHFU | 0.120 | 0.110 | 0.362 ** |
| (1.243) | (1.021) | (2.416) | |
| AGDP | −0.002 * | −0.003 ** | −0.007 *** |
| (−1.925) | (−2.050) | (−6.393) | |
| LEP | −0.020 | 0.079 | −0.264 |
| (−0.082) | (0.303) | (−0.672) | |
| lnLRI | 0.005 ** | 0.004 * | 0.007 *** |
| (2.115) | (1.797) | (3.745) | |
| PPIAP | 0.000 | 0.000 | −0.001 *** |
| (0.048) | (1.256) | (−2.759) | |
| _cons | 0.117 * | 0.104 | 0.464 *** |
| (1.679) | (1.517) | (6.840) | |
| N | 349 | 320 | 349 |
| RHSES | |
|---|---|
| L.RHSES | 0.191 ** |
| (2.24) | |
| lnGP | 0.01 ** |
| (2.20) | |
| Control Variable | Y |
| _cons | 0.603 *** |
| (9.90) | |
| N | 349 |
| AR (1) | 0.000 |
| AR (2) | 0.560 |
| Hansen Test | 0.180 |
| VarName | First Step | Second Step |
|---|---|---|
| L.lnGP | 0.963 *** | - |
| (65.96) | ||
| lnGP | - | 0.189 *** |
| (11) | ||
| lnAP | 0.003 | −0.002 |
| (0.26) | (−0.79) | |
| PEUAFHFU | −0.439 | 0.421 *** |
| (−1.49) | (4.34) | |
| AGDP | −0.004 | −0.005 *** |
| (−0.10) | (−5.86) | |
| LEP | −0.313 | 0.336 |
| (−0.35) | (1.10) | |
| lnLRI | 0.001 | 0.005 |
| (0.07) | (3.95) | |
| PPIAP | −0.001 | 0.001 * |
| (0.13) | (1.75) | |
| Weak Instrument Variable (IV) test | - | 12943.10 (16.38) |
| Test for identifiability (p-value) | - | 10.76 (0.001) |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Eastern | Central | Western | |
| lnGP | 0.009 | 0.040 *** | −0.023 *** |
| (0.743) | (2.699) | (−3.475) | |
| lnAP | 0.009 | −0.006 | 0.017 *** |
| (1.357) | (−0.752) | (2.766) | |
| PEUAFHFU | −0.673 *** | 0.095 | 0.478 *** |
| (−3.033) | (0.613) | (4.498) | |
| AGDP | −0.004 * | −0.001 | −0.003 * |
| (−1.708) | (−0.510) | (−1.890) | |
| LEP | 0.358 | −1.430 *** | 0.099 |
| (1.070) | (−3.918) | (0.276) | |
| lnLRI | 0.004 | 0.003 | 0.003 |
| (1.324) | (0.773) | (1.610) | |
| PPIAP | 0.002 *** | −0.000 | −0.000 |
| (2.665) | (−0.533) | (−0.651) | |
| (−2.141) | (−0.839) | (2.571) | |
| _cons | 0.006 | 0.094 | 0.312 *** |
| (0.050) | (0.896) | (4.664) | |
| N | 121 | 96 | 132 |
| (1) | (2) | |
|---|---|---|
| RHSES | RHSES | |
| lnGP | 0.061 *** | 0.011 ** |
| (5.632) | (1.967) | |
| lnAP | 0.030 ** | −0.003 |
| (2.459) | (−0.658) | |
| PEUAFHFU | 2.989 ** | −0.066 |
| (1.974) | (−0.719) | |
| AGDP | −0.002 | −0.003 *** |
| (−0.847) | (−2.604) | |
| LEP | −1.397 | −0.238 |
| (−1.390) | (−1.036) | |
| lnLRI | 0.007 | 0.002 |
| (1.560) | (1.016) | |
| PPIAP | −0.000 | 0.000 |
| (−0.229) | (0.710) | |
| (−3.904) | (−1.150) | |
| _cons | −0.309 | 0.245 *** |
| (−1.535) | (3.610) | |
| N | 121 | 228 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| RHSES | lnPAEP | IER | |
| lnGP | 0.012 ** | 0.106 *** | 0.162 *** |
| (2.087) | (6.951) | (3.066) | |
| lnAP | 0.009 * | 0.046 *** | 0.020 |
| (1.806) | (3.622) | (0.508) | |
| PEUAFHFU | 0.098 | 0.760 *** | 0.228 |
| (1.052) | (3.053) | (0.310) | |
| AGDP | −0.003 *** | −0.006 ** | 0.009 |
| (−2.777) | (−2.187) | (1.069) | |
| LEP | −0.016 | −0.494 | −0.174 |
| (−0.065) | (−0.764) | (−0.093) | |
| lnLRI | 0.004 * | 0.003 | −0.024 |
| (1.738) | (0.506) | (−1.284) | |
| PPIAP | 0.000 | −0.000 | 0.002 |
| (0.159) | (−0.396) | (0.733) | |
| _cons | 0.169 *** | 3.357 *** | −0.524 |
| (2.698) | (19.989) | (−1.010) | |
| N | 349 | 349 | 349 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, C.; Xu, N.; Shen, S.; He, W.; Su, Y. Exploring the Impact of Green Technology Innovation on Rural Habitat System Resilience. Agriculture 2025, 15, 925. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15090925
Chen C, Xu N, Shen S, He W, Su Y. Exploring the Impact of Green Technology Innovation on Rural Habitat System Resilience. Agriculture. 2025; 15(9):925. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15090925
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Chulin, Nanyang Xu, Shouyun Shen, Wei He, and Yang Su. 2025. "Exploring the Impact of Green Technology Innovation on Rural Habitat System Resilience" Agriculture 15, no. 9: 925. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15090925
APA StyleChen, C., Xu, N., Shen, S., He, W., & Su, Y. (2025). Exploring the Impact of Green Technology Innovation on Rural Habitat System Resilience. Agriculture, 15(9), 925. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15090925





