The Characteristics and Driving Factors of Soil Salinisation in the Irrigated Area on the Southern Bank of the Yellow River in Inner Mongolia: A Assessment of the Donghaixin Irrigation District
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
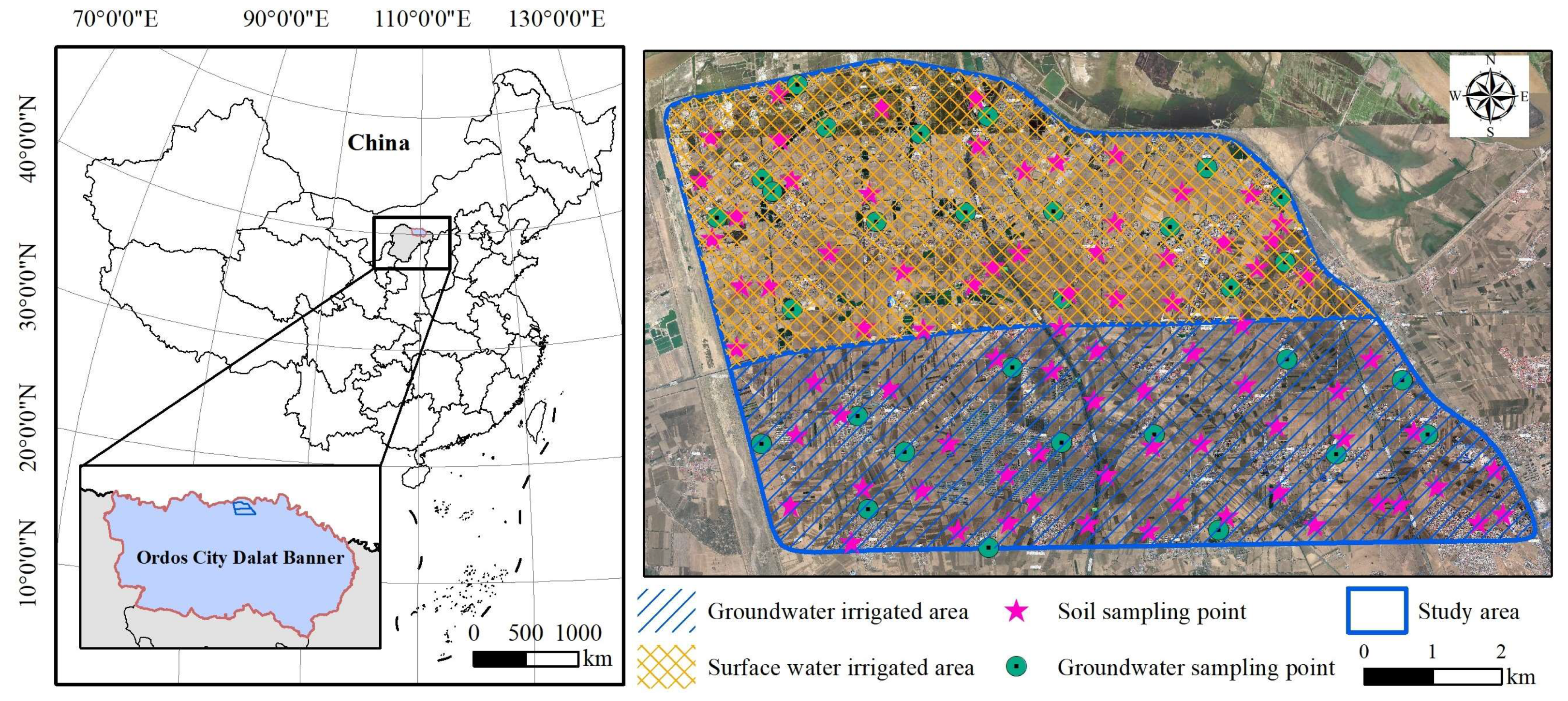
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection and Measurement
2.3. Data Acquisition
2.4. Research Methodology
3. Results
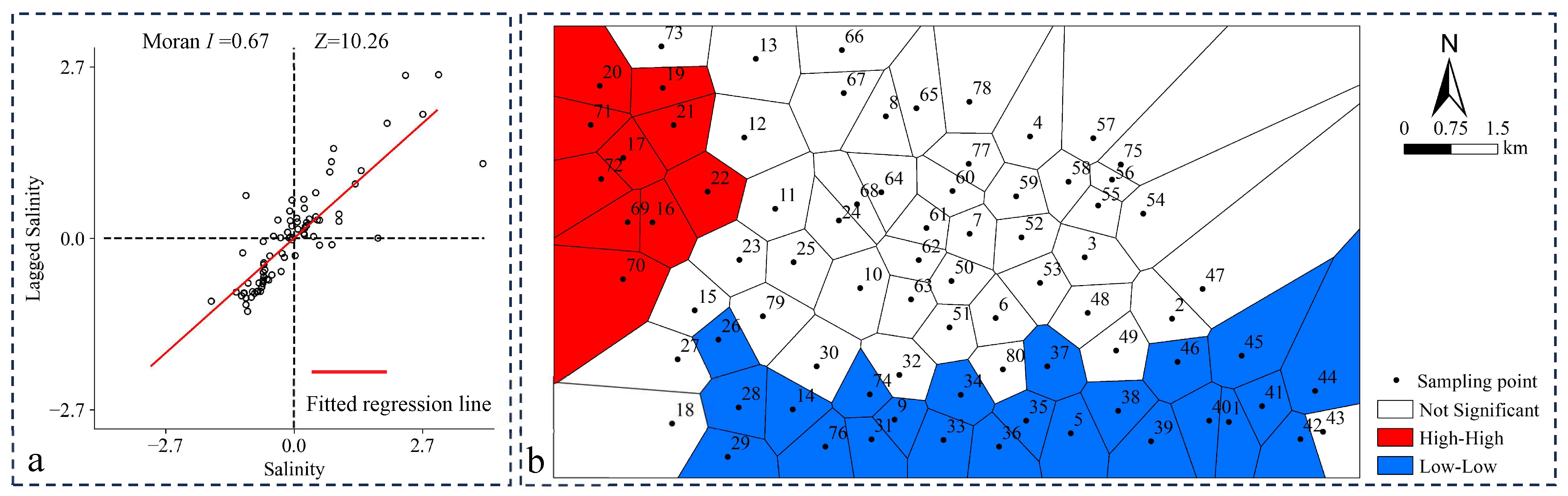
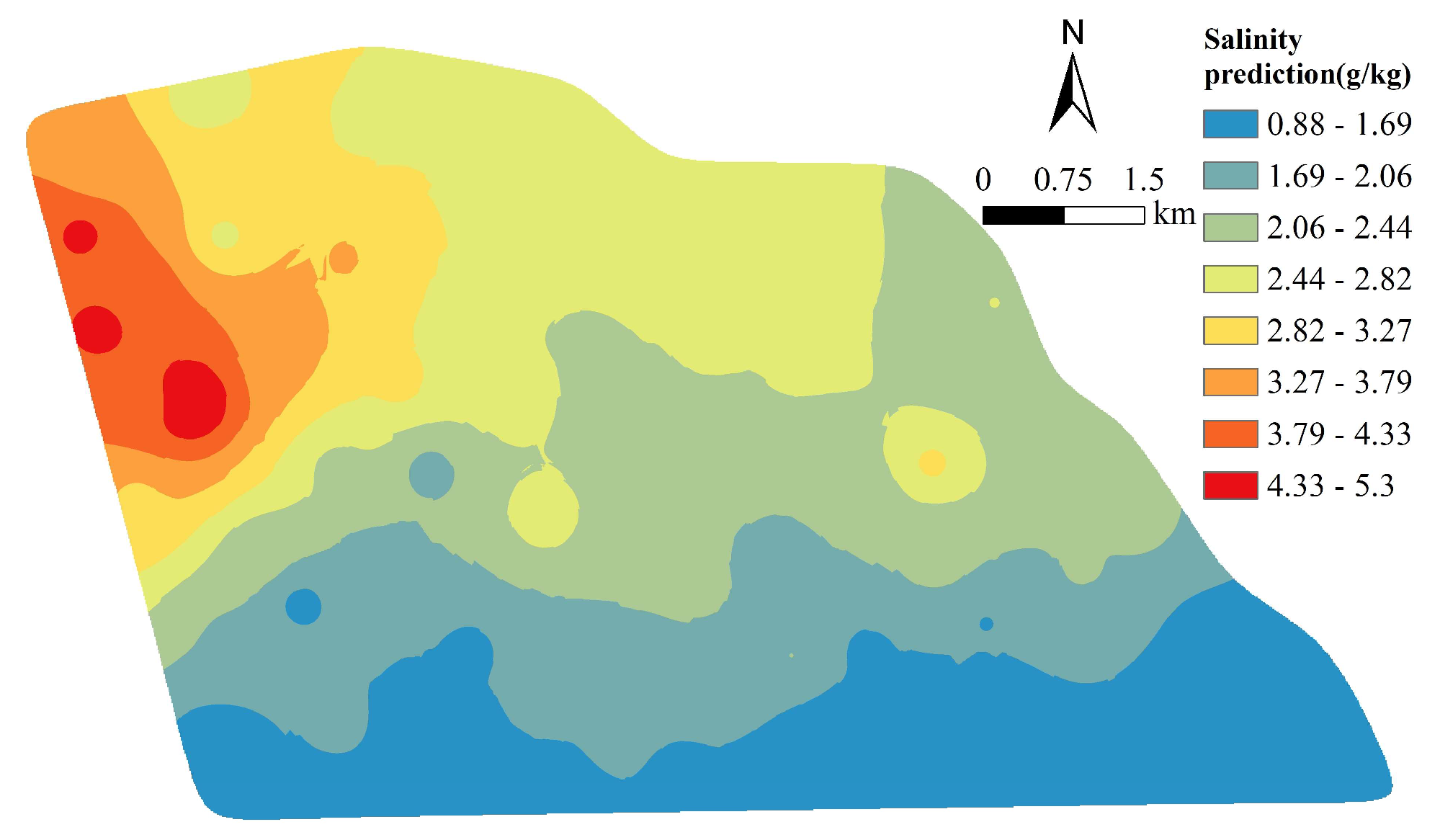
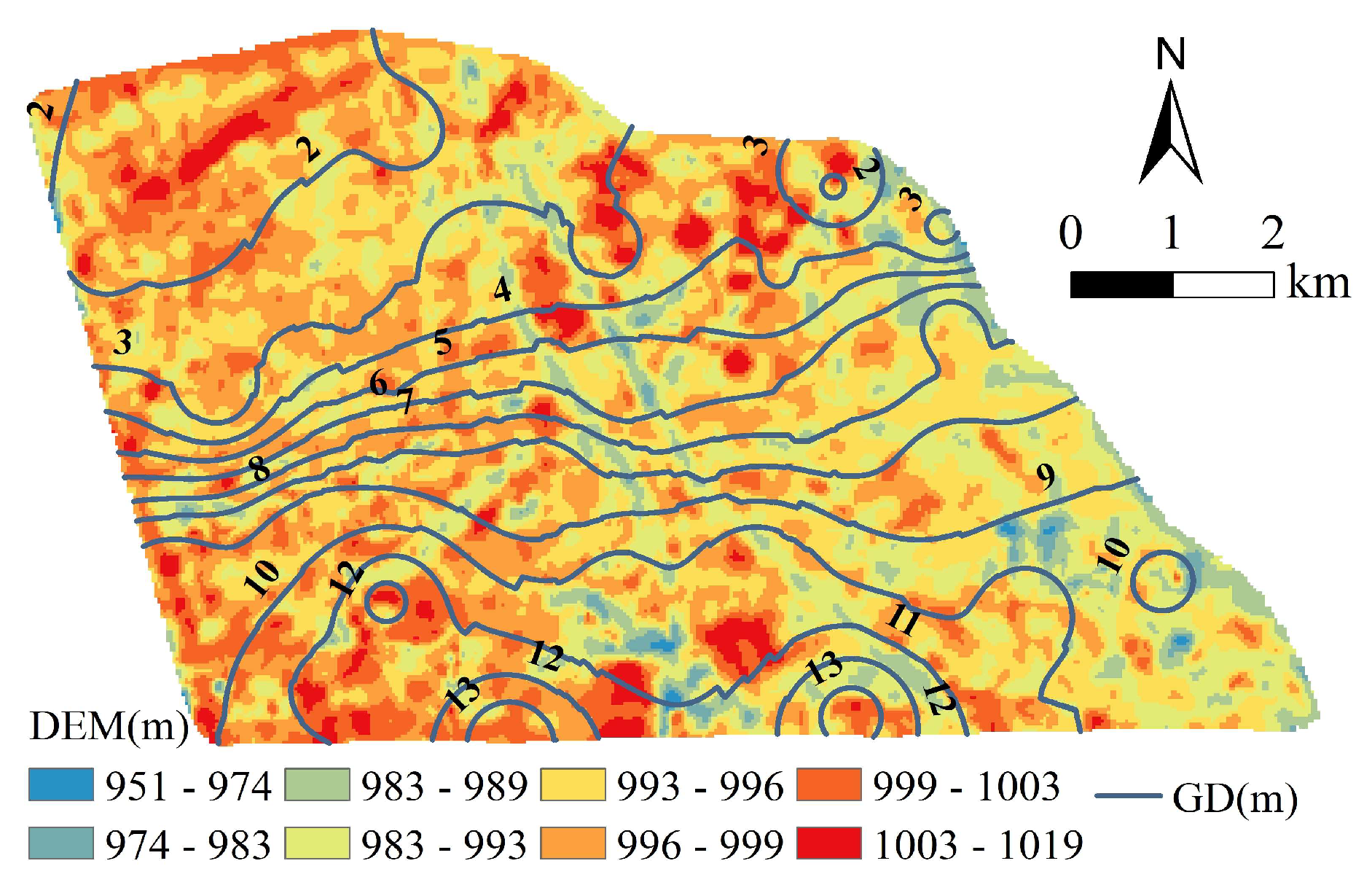
3.1. Soil Salinisation Distribution Characteristics and Spatial Autocorrelation Analysis
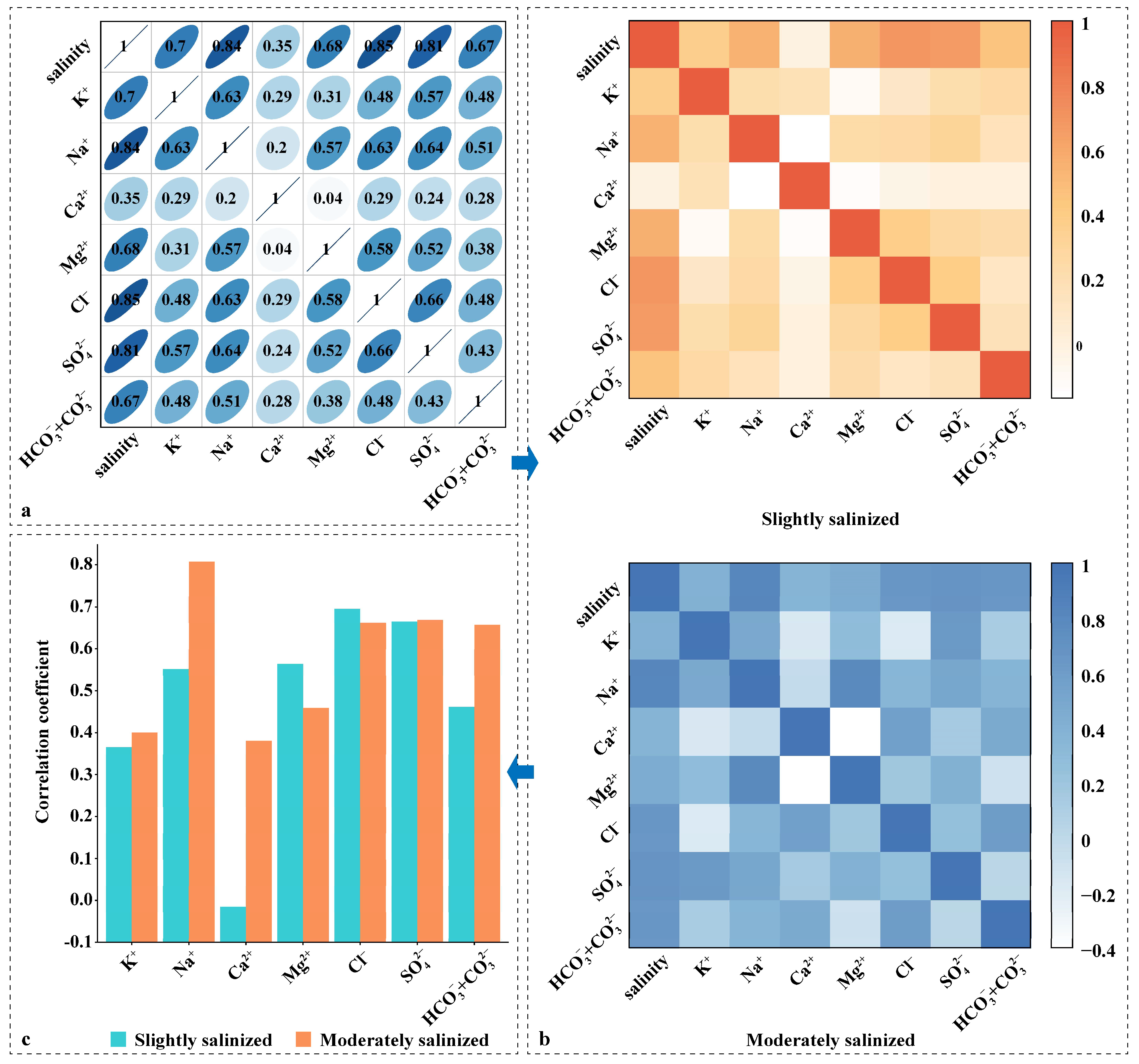
3.2. Correlation Analysis Between Soil Salinity and Micro-Ion Content
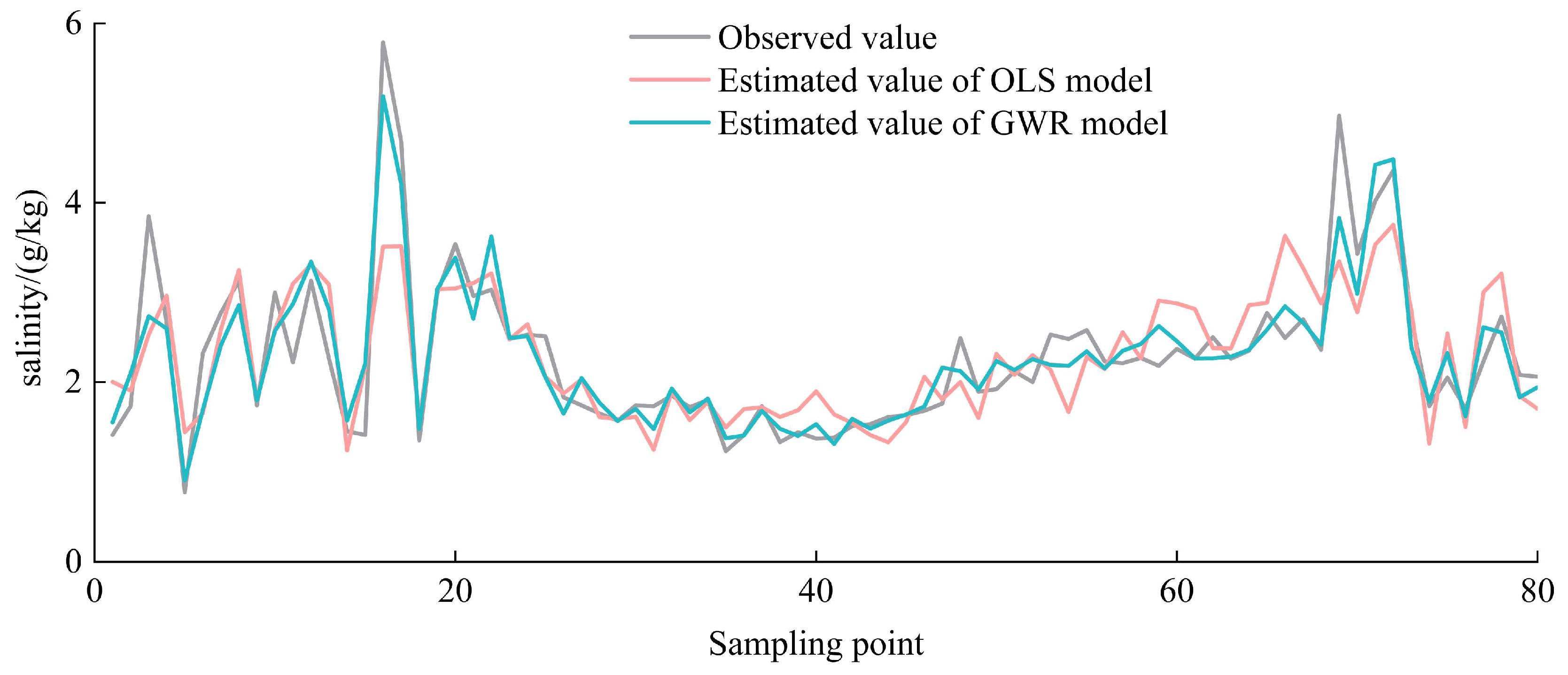
3.3. Regression Analysis and Spatial Prediction of Soil Salinisation
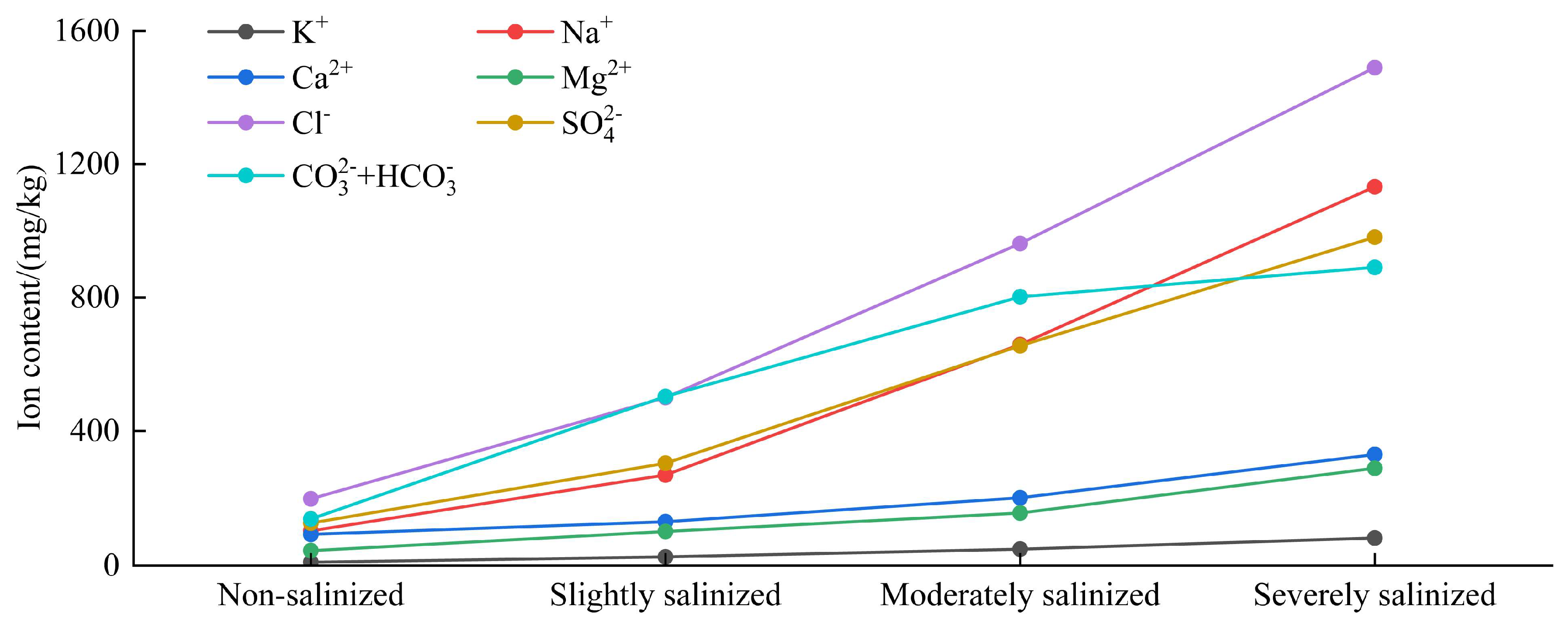
3.4. Analysis of Groundwater and Soil Water-Soluble Ion Characteristics
4. Discussion
4.1. Spatial Heterogeneity of Soil Salinity and Environmental Factors and Their Driving Mechanisms
4.2. The Relationship Between Salinisation and Groundwater
4.3. Comprehensive Control Strategies for Soil Salinisation Management
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wimmler, M.C.; Bathmann, J.; Peters, R.; Jiang, J.; Walther, M.; Lovelock, C.E.; Berger, U. Plant-soil feedbacks in mangrove ecosystems: Establishing links between empirical and modelling studies. Trees-Struct. Funct. 2021, 35, 1423–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heijden, M.G.A.V.D.; Wagg, C. Soil microbial diversity and agro-ecosystem functioning. Plant Soil 2013, 363, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neher, D. Soil community composition and ecosystem processes: Comparing agricultural ecosystems with natural ecosystems. Agrofor. Syst. 1999, 45, 159–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Castellano, M.J.; Yang, G. Coupling soil water processes and the nitrogen cycle across spatial scales: Potentials, bottlenecks and solutions. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2018, 187, 248–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcbratney, A.; Field, D.J.; Koch, A. The dimensions of soil security. Geoderma 2014, 213, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, D.D.L.; Sobral, R. Soil Quality and Methods for its Assessment. In Land Use and Soil Resources; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 167–200. [Google Scholar]
- Adhikari, K.; Hartemink, A.E. Linking soils to ecosystem services—A global review. Geoderma 2016, 262, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A. Soil salinization and waterlogging: A threat to environment and agricultural sustainability. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 57, 128–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanavelu, A.; Naganna, S.R.; Al-Ansari, N. Irrigation Induced Salinity and Sodicity Hazards on Soil and Groundwater: An Overview of Its Causes, Impacts and Mitigation Strategies. Agriculture 2021, 11, 983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ao, C.; Zeng, W.; Srivastava, A.K.; Gaiser, T.; Wu, J.; Huang, J. Simulating water and salt transport in subsurface pipe drainage systems with HYDRUS-2D. J. Hydrol. 2021, 592, 125823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Nigara, T. Current status and development trend of soil salinity monitoring research in China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 5874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Sharma, P.K. Soil Salinity and Food Security in India. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2020, 4, 533781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chartres, C.J.; Noble, A. Sustainable intensification: Overcoming land and water constraints on food production. Food Secur. 2015, 7, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rengasamy, P. World salinization with emphasis on Australia. J. Exp. Bot. 2006, 57, 1017–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, D.; Song, X.; Currell, M.J.; Yang, J.; Xiao, G. Chemical and isotopic constraints on evolution of groundwater salinization in the coastal plain aquifer of Laizhou Bay, China. J. Hydrol. 2014, 508, 12–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A. Soil salinization management for sustainable development: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 277, 111383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Li, Y.; Han, J.; Zhou, D.; Fu, Y.; Guan, B.; Wang, G.; Ning, K.; Wu, H.; Wang, J. The spatial distribution characteristics of soil salinity in coastal zone of the Yellow River Delta. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 72, 589–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wang, T.; Wang, L.; Wu, X.; Zuo, Q.; Shi, J.; Sheng, J.; Jiang, P.; Chen, Q.; Ben-Gal, A. Plant water deficit index-based irrigation under conditions of salinity. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 269, 107669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Mao, X.; Shang, S. Response and contribution of shallow groundwater to soil water/salt budget and crop growth in layered soils. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 266, 107574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, C.; Xiang, W.; Zhang, S. Evaluation of the hydrochemical evolution characteristics and renewable capacity of deep fresh groundwater in the Hangzhou Bay New Zone, China. Environ. Geol. 2019, 78, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, F.; Jia, Y.; Yang, Y.; Huan, H.; Lian, X.; Xu, X.; Xia, F.; Han, X.; Jiang, Y. Hydrogeochemical and statistical analysis of high fluoride groundwater in northern China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 34840–34861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wu, J.; Jia, H. Analysis of spatial variation of soil salinization using a hydrochemical and stable isotopic method in a semiarid irrigated basin, Hetao Plain, inner Mongolia, North China. Environ. Process. 2016, 3, 723–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Pu, L.; Zhu, M.; Xu, Y.; Wang, X. Linkage between soil salinization indicators and physicochemical properties in a long-term intensive agricultural coastal reclamation area, Eastern China. J. Soils Sediments 2019, 19, 3699–3707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pržulj, N.; Tunguz, V.; Jovović, Z.; Velimirović, A. The significance of harvest residues in the sustainable management of arable land. II. Harvest residues management. Arch. Tech. Sci. 2022, 27, 49–56. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, B.; Xu, M.; Zhang, R. Evolution Patterns and Dominant Factors of Soil Salinization in the Yellow River Delta Based on Long-Time-Series and Similar Phenological-Fusion Images. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, A.C.; Jin, L. Chemical and hydrological controls on salt accumulation in irrigated soils of southwestern U. S. Geoderma 2021, 391, 114976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schofield, R.V.; Kirkby, M.J. Application of salinization indicators and initial development of potential global soil salinization scenario under climatic change. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2003, 17, 1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Qi, Z.; Hu, K.; Li, B.; Prasher, S.O. Modelling subsurface drainage and nitrogen losses from artificially drained cropland using coupled DRAINMOD and WHCNS models. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 195, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scanlon, B.R.; Jolly, I.; Sophocleous, M.; Zhang, L. Global impacts of conversions from natural to agricultural ecosystems on water resources: Quantity versus quality. Water Resour. Res. 2007, 43, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Qian, H.; Xu, P.; Li, W.; Feng, W.; Liu, R. Effect of hydrogeological conditions on groundwater nitrate pollution and human health risk assessment of nitrate in Jiaokou Irrigation District. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 298, 126783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Qu, Z.; Yang, W.; Chen, X.; Qiao, T. Inversion of Soil Salinity in the Irrigated Region along the Southern Bank of the Yellow River Using UAV Multispectral Remote Sensing. Agronomy 2024, 14, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.; Feng, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, T.; Yang, A.; Zhang, Z. Spatial distribution and simulation of soil moisture and salinity under mulched drip irrigation combined with tillage in an arid saline irrigation district, northwest China. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 201, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Cheng, Q.; Wang, X.; Li, X. Microwave Radar Inversion of Soil Salinization in Hetao Irrigation Area. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2016, 32, 109–114. [Google Scholar]
- Hardie, M.; Doyle, R. Measuring soil salinity. In Plant Salt Tolerance: Methods and Protocols; Humana: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 415–425. [Google Scholar]
- Endo, T.; Yamamoto, S.; Larrinaga, J.A.; Fujiyama, H.; Honna, T. Status and causes of soil salinization of irrigated agricultural lands in Southern Baja California, Mexico. Appl. Environ. Soil Sci. 2011, 2011, 873625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, G.; Lu, Y.; Zheng, C.; Liu, Z.; Sai, J. Relationship between soil salinization and groundwater hydration in Yaoba Oasis, Northwest China. Water 2019, 11, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokalioğlu, Ş.; Kartal, Ş. Chemometrical interpretation of lake waters after their chemical analysis by using AAS, flame photometry and titrimetric techniques. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2002, 82, 291–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalali, M. Hydrochemical identification of groundwater resources and their changes under the impacts of human activity in the Chah basin in western Iran. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 130, 347–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S. Soil Agricultural Analysis, 3rd ed.; China Agricultural Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Robert, M. O’brien. A caution regarding rules of thumb for variance inflation factors. Qual. Quant. 2007, 41, 673–690. [Google Scholar]
- Ivits, E.; Cherlet, M.; Tóth, T.; Lewińska, K.E.; Tóth, G. Characterisation of productivity limitation of salt-affected lands in different climatic regions of europe using remote sensing derived productivity indicators. Land Degrad. Dev. 2013, 24, 438–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Chu, L.; Zhu, W.; Sun, Q.; Sun, Q. Analysis of Soil Salinity Distribution and Influencing Factors in Coastal Saline-Alkaline Land After Reforestation. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2023, 39, 149–157. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Li, Z.; Fu, W.; Li, F. The Influence of Shallow Groundwater on the Physicochemical Properties of Field Soil, Crop Yield, and Groundwater. Agriculture 2024, 14, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, D.A.; Konukcu, F.; Gowing, J.W. Effect of watertable depth on evaporation and salt accumulation from saline groundwater. Soil Res. 2005, 43, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakr, N.; Ali, R.R. Statistical relationship between land surface altitude and soil salinity in the enclosed desert depressions of arid regions. Arab. J. Geosci. 2019, 12, 715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimaki, H.; Shimano, T.; Inoue, M.; Nakane, K. Effect of a Salt Crust on Evaporation from a Bare Saline Soil. Vadose Zone J. 2006, 5, 1246–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobley, E.; Garcia-Franco, N.; Hübner, R.; Wiesmeier, M. Reviewing our options: Managing water-limited soils for conservation and restoration. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 1041–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Zhang, G.; Wang, J.; Yan, M. Spatial Variation of Soil Salinity and Water Table Depth in the Bohai Rim Plain and Their Co-Kriging Estimation. Acta Geosci. Sin. 2011, 32, 493–499. [Google Scholar]
- Moussa, I.; Walter, C.; Michot, D.; Boukary, I.A.; Nicolas, H.; Pichelin, P.; Guéro, Y. Soil salinity assessment in irrigated paddy fields of the Niger Valley using a four-year time series of sentinel-2 satellite images. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Hou, K.; Qian, H.; Gao, Y.; Fang, Y.; Xiao, S.; Tang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Qu, W.; Ren, W. Characterization of soil salinization and its driving factors in a typical irrigation area of Northwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 837, 155808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Wu, J.; Tan, X.; Huang, J.; Jansson, P.-E.; Zhang, W. Simulation of dynamical interactions between soil freezing/thawing and salinization for improving water management in cold/arid agricultural region. Geoderma 2019, 338, 325–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.; Liu, T.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, C.; Zhang, Q.; Qu, Z.; Liu, X.; Li, C. Analysis of Salinization Dynamics by Remote Sensing in Hetao Irrigation District of North China. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 1952–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, H.; Li, P. Hydrochemical characteristics of groundwater in Yinchuan Plain and their control factors. Asian J. Chem. 2011, 23, 2927–2938. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, Q.; Sang, H. Major ion chemistry of waters and possible controls under winter irrigation in the saline land of arid regions. Water 2023, 15, 3968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanasekarapandian, M.; Chandran, S.; Devi, D.; Kumar, V. Spatial and temporal variation of groundwater quality and its suitability for irrigation and drinking purpose using GIS and WQI in an urban fringe. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2016, 124, 270–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F. Study on the Evaporation Laws and Effects of Bare Soil Under the Influence of Temperature and Humidity. Master’s Thesis, Chang’an University, Xi’an, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Gul, N.; Mangrio, M.A.; Shaikh, I.A.; Siyal, A.G.; Semiromi, M.T. Quantifying the impacts of varying groundwater table depths on cotton evapotranspiration, yield, water use efficiency, and root zone salinity using lysimeters. Agric. Water Manag. 2024, 301, 108933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Qian, H.; Wu, J. Conjunctive use of groundwater and surface water to reduce soil salinization in the Yinchuan Plain, North-West China. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2018, 34, 337–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Li, X.; Šimůnek, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhen, Z.; He, R. Experimental and numerical evaluation of soil water and salt dynamics in a corn field with shallow saline groundwater and crop-season drip and autumn post-harvest irrigations. Agric. Water Manag. 2024, 305, 109119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Gu, S.; Jiang, R.; Zhang, X.; Hatano, R. Saline–Alkali Soil Reclamation Contributes to Soil Health Improvement in China. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Soil Layer Depth (cm) | Soil Particle Size Distribution (%) | Bulk Density (g/cm3) | Texture | Organic Matter (g/kg) | Salinity (g/kg) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <0.002 mm | 0.002–0.05 mm | >0.05 mm | |||||
| 0–20 | 38.3 | 38.4 | 23.3 | 1.441 | Clay loam | 14.8 | 1.82 |
| 20–40 | 37.2 | 38.9 | 23.9 | 1.446 | Clay loam | 15.9 | 2.14 |
| 40–60 | 23.7 | 41.1 | 35.2 | 1.428 | Loam | 15.2 | 2.49 |
| 60–80 | 19.6 | 44.3 | 36.1 | 1.42 | Loam | 14.1 | 2.50 |
| 80–100 | 14.6 | 47.5 | 37.9 | 1.396 | Loam | 13.6 | 2.81 |
| Water Source | TDS (g/L) | pH | Ion Content (mg/L) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K+ | Na+ | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | Cl− | SO42− | HCO3− + CO32− | |||
| Yellow River Water | 0.37 | 7.51 | 0.89 | 97.11 | 13.32 | 6.88 | 38.34 | 140.91 | 71.57 |
| Groundwater (Surface Water Irrigated Area) | 1.86 | 7.88 | 5.07 | 388.59 | 105.04 | 37.55 | 223.65 | 550.59 | 550.82 |
| Groundwater (Groundwater Irrigated Area) | 1.68 | 7.91 | 4.16 | 396.54 | 77.73 | 30.28 | 238.46 | 328.92 | 601.00 |
| Soil Classification | Non-Salinised | Slightly Salinised | Moderately Salinised | Severely Salinised | Extremely Severely Salinised |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Salt Content (g/kg) | <1 | 1–3 | 3–5 | 5–10 | >10 |
| Saturated Extract EC25 (dS/m) | 0–2 | 2–4 | 4–8 | 8–16 | >16 |
| Degree | K+ | Na+ | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | Cl− | SO42− | HCO3− + CO32− |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mg/kg | mg/kg | mg/kg | mg/kg | mg/kg | mg/kg | mg/kg | |
| Non-salinised | 10.16 | 103.24 | 92.84 | 44.27 | 198.20 | 126.15 | 138.47 |
| Slightly salinised | 25.81 | 269.48 | 130.57 | 101.56 | 500.05 | 304.09 | 503.05 |
| Moderately salinised | 48.82 | 658.69 | 201.69 | 156.41 | 962.29 | 655.07 | 802.42 |
| Severely salinised | 81.82 | 1132.39 | 330.11 | 289.23 | 1490.09 | 981.10 | 890.72 |
| Model | AIC | R2 | Adjusted R2 | RSS | df | F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OLS model | 150.26 | 0.61 | 0.56 | 23.87 | 71.00 | 13.85 |
| GWR model | 126.90 | 0.78 | 0.68 | 13.67 | 54.83 | 2.67 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qin, Z.; Nie, T.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, H.; Tong, C.; Wang, J.; Wang, R.; Hou, H. The Characteristics and Driving Factors of Soil Salinisation in the Irrigated Area on the Southern Bank of the Yellow River in Inner Mongolia: A Assessment of the Donghaixin Irrigation District. Agriculture 2025, 15, 566. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15050566
Qin Z, Nie T, Wang Y, Zheng H, Tong C, Wang J, Wang R, Hou H. The Characteristics and Driving Factors of Soil Salinisation in the Irrigated Area on the Southern Bank of the Yellow River in Inner Mongolia: A Assessment of the Donghaixin Irrigation District. Agriculture. 2025; 15(5):566. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15050566
Chicago/Turabian StyleQin, Ziyuan, Tangzhe Nie, Ying Wang, Hexiang Zheng, Changfu Tong, Jun Wang, Rongyang Wang, and Hongfei Hou. 2025. "The Characteristics and Driving Factors of Soil Salinisation in the Irrigated Area on the Southern Bank of the Yellow River in Inner Mongolia: A Assessment of the Donghaixin Irrigation District" Agriculture 15, no. 5: 566. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15050566
APA StyleQin, Z., Nie, T., Wang, Y., Zheng, H., Tong, C., Wang, J., Wang, R., & Hou, H. (2025). The Characteristics and Driving Factors of Soil Salinisation in the Irrigated Area on the Southern Bank of the Yellow River in Inner Mongolia: A Assessment of the Donghaixin Irrigation District. Agriculture, 15(5), 566. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15050566







