Divergent Impacts and Policy Implications of Rural Shrinkage on Carbon Intensity in the Yellow River Basin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Research Hypotheses
2.1. The Central Role of Rural Population Shrinkage in the Yellow River Basin’s Overall Population Shrinkage
2.2. Rural Population Shrinkage Exerts a Significant Influence on Carbon Emission Intensity in the Yellow River Basin
2.3. Regional Heterogeneity in the Impact of Rural Population Shrinkage on Carbon Emission Intensity in the Yellow River Basin
3. Research Design
3.1. Research Methods
3.1.1. Measurement and Classification of Population Growth and Shrinkage
3.1.2. Benchmark Model
3.2. Variable Selection
3.2.1. Explanatory Variables
3.2.2. Explained Variable
3.2.3. Control Variable
3.3. Study Area
3.4. Data Sources and Descriptive Statistics
4. Results
4.1. Total, Urban, and Rural Population Shrinkage Trends in the Yellow River Basin
4.2. Spatial and Temporal Changes in Carbon Emission Intensity in the Yellow River Basin
4.2.1. Temporal Changes in Carbon Emission Intensity in the Yellow River Basin
4.2.2. Spatial Changes in Carbon Emission Intensity in the Yellow River Basin
4.3. Spatial Correlation Between Rural Population Shrinkage and Carbon Emission Intensity
4.4. Rural Population Shrinkage Impacts on Basin Carbon Emission Intensity
4.4.1. Benchmark Regression Analysis
4.4.2. Regional Heterogeneity Analysis
4.4.3. Robustness Test
5. Discussion
5.1. The Spatial Association Between Rural Population Shrinkage and Carbon Emission Intensity in the Yellow River Basin
5.1.1. The Spatial Distribution of Counties with Different Degrees of Rural Population Shrinkage
5.1.2. The Spatiotemporal Link Between Rural Population Shrinkage and Carbon Emission Intensity
5.2. The Impact of Population Shrinkage on Carbon Emissions
5.3. Regional Identification and Policy Implications for Rural Population Shrinkage and Carbon Emission Intensity
5.4. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qin, D. Climate change science and sustainable development. Prog. Geogr. 2014, 33, 874–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, R.; Andriano, L.; Striessnig, E.; Rüttenauer, T.; Borderon, M.; Grace, K. Climate change and population: Demographic perspectives on the 21st century’s defining challenge. Vienna Yearb. Popul. Res. 2024, 22, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenton, T.M.; Rockström, J.; Gaffney, O.; Rahmstorf, S.; Richardson, K.; Steffen, W.; Schellnhuber, H.J. Climate tipping points—Too risky to bet against. Nature 2019, 575, 592–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Bega, F. China’s Belt & Road Initiative coal power cooperation: Transitioning toward low-carbon development. Energy Policy 2021, 156, 112438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korsbakken, J.I.; Peters, G.P.; Andrew, R.M. Uncertainties around reductions in China’s coal use and CO2 emissions. Nat. Clim. Change 2016, 6, 687–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, G.P.; Marland, G.; Le Quéré, C.; Boden, T.; Canadell, J.G.; Raupach, M.R. Rapid growth in CO2 emissions after the 2008–2009 global financial crisis. Nat. Clim. Change. 2012, 2, 2–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Biru, A.; Lettu, S. Energy poverty and public health: Global evidence. Energy Econ. 2021, 101, 105423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G. Development and Prospect of China’s Carbon Emission Policy under the “Double Carbon” Goal. Technol. Econ. Changjiang 2021, 5, 53–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajlouni, S. Energy Consumption and Economic Growth in Jordan: An ARDL Bounds Testing Approach to Cointegration. Jordan J. Econ. Sci. 2015, 2, 143–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seto, K.C.; Churkina, G.; Hsu, A.; Keller, M.; Newman, P.W.G.; Qin, B.; Ramaswami, A. From low- to net-zero carbon cities: The next global agenda. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2021, 46, 377–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuzcu, M.; Tuzcu, S. Renewable Energy and Proven Oil Reserves Relation: Evidence from OPEC Members. Cankiri Karatekin Univ. IIBF Derg. 2014, 4, 121–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuf, A.M.; Abubakar, A.B.; Mamman, S.O. Relationship between greenhouse gas emission, energy consumption, and economic growth: Evidence from some selected oil-producing African countries. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 15815–15823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.J.; Li, Q.Y.; Fang, C.L.; Zhou, C.S. The relationship between economic growth, energy consumption, and CO2; emissions: Empirical evidence from China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 542, 360–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haase, A.; Rink, D.; Großmann, K.; Bernt, M. Conceptualizing Urban Shrinkage. Environ. Plan A. 2014, 46, 1519–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idowu, A.; Ohikhuare, O.M.; Chowdhury, M.A. Does industrialization trigger carbon emissions through energy consumption? Evidence from OPEC countries and high industrialised countries. Quant. Financ. Econ. 2023, 7, 165–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breuer, M.; Dehaan, E. Using and Interpreting Fixed Effects Models. J. Account. Res. 2024, 62, 1183–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Zhao, X.Z.; Li, T.S.; Yang, L.Y. Spatial temporal patterns and driving mechanisms of multi-scale population shrinkage in the Shaanxi section of the Yellow River Basin. J. Northwest Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2025, 55, 833–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.L.; Pan, T. Accurate identification and characteristic analysis of township population shrinkage from the perspective of dual boundary: A case study of the Yellow River Basin. Econ. Geogr. 2024, 44, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.H.; Yang, Y.H.; Qiao, J.J.; Zhu, X.Y.; Jiang, X.J. Rural hollowing out in the Yellow River Basin and the development path of rural revitalization. Prog. Geogr. 2024, 43, 1049–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.L.; Jia, J.S.; Li, L.; Hu, M.M.; Wu, G. Spatio-temporal pattern and influencing factors of carbon emissions in the middle reaches of the Yellow River from the perspective of urban shrinkage. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2024, 44, 903–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brockway, P.E.; Sorrell, S.; Semieniuk, G.; Heun, M.K.; Court, V. Energy efficiency and economy-wide rebound effects: A review of the evidence and its implications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 141, 110781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekun, F.V.; Uzuner, G.; Onifade, S.T.; Alola, A.A. Carbon emission in MINT economies: The role of poverty, population, energy use and economic factors. OPEC Energy Rev. 2024, 48, 343–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohwasser, J.; Schaffer, A. The varying roles of the dimensions of affluence in air pollution: A regional STIRPAT analysis for Germany. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 19737–19748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, K.; Du, J.G.; Kirikkaleli, D.; Oláh, J.; Altuntas, M. Do green technological innovation, financial development, economic policy uncertainty, and institutional quality matter for environmental sustainability? All Earth 2023, 35, 82–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cumming, G.S.; Epstein, G.; Anderies, J.M.; Apetrei, C.I.; Baggio, J.; Bodin, Ö.; Chawla, S.; Clements, H.; Cox, M.; Egli, L.; et al. Advancing understanding of natural resource governance: A post-Ostrom research agenda. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2020, 44, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.; Wang, R.Q.; Tang, H.C.; Ma, X.; Zeng, X.Y. A study on the potential of higher education in reducing carbon intensity. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0309546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, W. Analysis of influencing factors of carbon emissions in China based on the STIRPAT model. Theor. Nat. Sci. 2023, 25, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGee, J.; Clement, M.; Besek, J. The impacts of technology: A re-evaluation of the STIRPAT model. Environ. Sociol. 2015, 1, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.H.; Ma, L.; Jin, F.J. How Urbanisation Affects Carbon Dioxide Emissions: A Case Study of the Yellow River Basin. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2023, 32, 5261–5272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Guo, C.H.; Chen, X.J.; Jia, L.Q.; Guo, X.N.; Chen, R.S.; Zhang, M.-S.; Chen, Z.-Y.; Wan, H.-D. Carbon peak and carbon neutrality in China: Goals, implementation path and prospects. China Geol. 2021, 4, 720–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Y.L.; Liu, Y.J.; Liu, L.W. The influence of population growth and shrinkage on carbon emission intensity in old industrial cities of China. Geogr. Res. 2024, 43, 558–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, J.; Khan, I.; Alharthi, M.; Zafar, M.W.; Saeed, A. Sustainable energy policy, socio-economic development, and ecological footprint: The economic significance of natural resources, population growth, and industrial development. Util. Policy 2023, 81, 101490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, X.; Li, R. The impact of political, financial, and economic risks on energy transition: The role of natural resource rents. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2025, 12, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haberl, H.; Wiedenhofer, D.; Virág, D.; Kalt, G.; Plank, B.; Brockway, P.; Fishman, T.; Hausknost, D.; Krausmann, F.; Leon-Gruchalski, B.; et al. A systematic review of the evidence on decoupling of GDP, resource use and GHG emissions, part II: Synthesizing the insights. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 065003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, W.L.; Wang, S.; Zhao, W.J. Urban-rural carbon emission differences in China’s urbanization: Spatial effects and influencing factors. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 366, 125423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Dai, Z.; Chen, Y.; Li, Z.; Shan, X.; Wang, X.; Feng, Z.; Wu, K. The Impact of Rural Population Shrinkage on Rural Functions—A Case Study of Northeast China. Land 2025, 14, 1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, J. Geographic detection and optimizing decision of the differentiation mechanism of rural poverty in China. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2017, 72, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpermann, B. China’s Rural-Urban Transformation: New Forms of Inclusion and Exclusion. J. Curr. Chin. Aff. 2021, 49, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Li, W.; Liu, S.H. Effects of regional population shrinkage on economic growth and the underlying mechanism. Geogr. Res. 2024, 43, 949–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, H.V.; Rybski, D.; Kropp, J.P. Effects of changing population or density on urban carbon dioxide emissions. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Testa, R. Consumption and Production Patterns for Agricultural Sustainable Development. Agronomy 2021, 11, 814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, M.; Jiang, J.; Huang, X.; Zhu, F.F.; Wang, Q. Spatial and temporal changes in population distribution and population projection at county level in China. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2024, 11, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.Q.; Xu, C.; Xia, R.; Li, D.; Zhou, J.L. The strategy of synergistic promotion of the ecological conservation and governance in the Yellow River Basin: Problems, challenges and suggestions. Environ. Prot. 2023, 51, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, Z.; Sun, X. Provinces with transitions in industrial structure and energy mix performed best in climate change mitigation in China. Commun. Earth Environ. 2021, 2, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.N. A primary framework on protection of ecological environment and realization of high-quality development for the Yellow River Basin. Environ. Prot. 2020, 48, 18–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Wang, C. Quality evaluation and division of regional types of rural human settlements in China. Habitat Int. 2020, 105, 102278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gozgor, G.; Lau, C.K.M.; Lu, Z. Energy consumption and economic growth: New evidence from the OECD countries. Energy 2018, 153, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mildenberger, M.; Lachapelle, E.; Harrison, K.; Stadelmann-Steffen, I. Limited impacts of carbon tax rebate programmes on public support for carbon pricing. Nat. Clim. Change 2022, 12, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Jiang, Q.Z.; Dong, X.C.; Dong, K.Y.; Jiang, H.D. How does industrial structure adjustment reduce CO2 emissions? Spatial and mediation effects analysis for China. Energy Econ. 2022, 105, 105704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Li, J.; Huang, J. Spatial–Temporal Patterns of Population Aging in Rural China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 15631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.N.; Pan, X.D.; Bai, D.Q. Overview of Basic Education in China. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Modern Education and Social Development, Wuhan, China, 20–22 April 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Işık, C.; Zhang, W.; Han, J.; Kuang, S.; Su, Y.; Ju, G.L.; Ti, L.; Li, S.; Xia, Z.; Muhammad, A. Exploring the impact of sustainable finance on carbon emissions: Policy implications and interactions with low-carbon energy transition from China. Resour. Policy. 2024, 97, 105272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.W.; Zhang, Q.; Hao, J.L.; Ma, W.T.; Sun, Y.; Wang, X.C.; Song, Y. Development of an extended STIRPAT model to assess the driving factors of household carbon dioxide emissions in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 325, 116502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Zhang, J.J.; Yuan, M.J. Carbon emissions and economic growth in the Yellow River Basin: Decoupling and driving factors. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 1089517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T. Types and spatiotemporal change characteristics of population shrinking county seats in the Yellow River Basin. Resour. Sci. 2024, 46, 336–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Ma, L.; Qiao, J.; Li, X. Measurement and optimization paths of the multidimensional development levels of counties in the Yellow River Basin: Based on the sustainable livelihoods framework. Front. Environ. Sci. 2024, 12, 1513411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, W.T.; Yu, W.L.; Xia, X.L. Spatiotemporal differentiation characteristics and driving factors of agricultural green development in the Yellow River Basin from a county perspective. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2024, 32, 1251–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.Q.; Deng, S.Y.; Zhang, S.X.; Shen, Y. Urban Growth and Its Ecological Effects in China. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.W.; Che, L.; Wang, M.; Du, H. Unwrapping the short-term disruptions and long-term implications of the COVID-19 pandemic on China’s rural migrant population. Econ. Anal. Policy 2025, 78, 181–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.J.; Yu, B.; Xin, Z.H.; Cong, M.; Zhang, C. Spatial-temporal variations of river water quality under human-induced land use changes in large river basins. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 36945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, P.L.; Chen, J.Q.; Fung, C.; Naing, Z.; Ouyang, Z.T.; Nyunt, K.M.; Myint, Z.N.; Qi, J.; Messina, J.P.; Myint, S.W.; et al. Urbanization, economic development, and environmental changes in transitional economies in the global south: A case of Yangon. Ecol. Process. 2022, 11, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.C.; Wang, E.Z.; Tang, H.M. Green fiscal policy and carbon emission: Enterprises’ level evidence from China. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2024, 203, 114795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Yu, T.; Li, N. Dynamic Allocation of Medical Resources During the Outbreak of Epidemics. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2022, 19, 663–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zheng, J. The Impact of Technical Progress and Industrial Structure Adjustment on China′s Carbon Emission Intensity. Commer. Res. 2022, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Li, X.; Yang, Y.Q.; Wang, M.X. Analyzing the features of energy consumption and carbon emissions in the Upper Yangtze River Economic Zone. Greenh. Gases Sci. Technol. 2021, 11, 573–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.C.; Nie, X.D. The Impact of Urban Shrinkage on Carbon Emission Intensity and Its Spatial Spillover Effects. Land. 2025, 14, 975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, C.; Xian, G.M.; Chu, X. Foreign Investment Openness, Market Segmentation and Industrial Upgrade: Discussion Basedon the ‘Dual Circulation’ Development Pattern. South China J. Econ. 2022, 7, 69–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachs, J.D.; Schmidt-Traub, G.; Mazzucato, M.; Messner, D.; Nakicenovic, N.; Rockström, J. Six Transformations to achieve the Sustainable Development Goals. Nat. Sustain. 2019, 2, 805–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.H.; Peng, D.Z.; Xu, Z.X.; Liu, W.F. Identification of the impacts of climate changes and human activities on runoff in the upper and middle reaches of the Heihe River basin, China. J. Water Clim. Change 2016, 7, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.P.; Liu, D.D.; Xu, A.T. Will Industrial Structure Upgrading Reduce Carbon Emission Intensity: Investigation from the Perspective of Green Tax. Chin. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 16, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.Y.; Lin, J.Q.; Zhao, Y.F.; Liu, W. Spatiotemporal dynamics and driving mechanisms of coupled coordination between rural–urban integration and rural resilience in Southwest China. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 23944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.F.; Sun, J.; Ma, B.B.; Du, W.P. Assessing the ecological vulnerability of the upper reaches of the Min jiang River. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, T.Y.; Jin, H.; Xu, G.; Kang, Z. County Economy, Population, Construction Land, and Carbon Intensity in a Shrinkage Scenario. Sustainability 2022, 14, 10523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.L.; Liu, S.N.; Wang, J.Y. Study on the synergistic evolution between green development and industrial structure optimization: A case study of resource-based cities in the Yellow River Basin. Macroeconomics 2025, 4, 49–64+111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mente, U.; Wolanin, E.; Eshov, M.; Salahodjaev, R. Industrialization and CO2 Emissions in Sub-Saharan Africa: The Mitigating Role of Renewable Electricity. Energies 2022, 15, 946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann-Pillath, C. The universal commons: An economic theory of ecosystem ownership. Ecol. Econ. 2023, 208, 107822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, Z.H.; Dong, G. Spatial-temporal characteristics of coupling coordination between high-quality economic development and residents’ quality of life in the Yellow River Basin. J. Northwest Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2025, 55, 896–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsompo, T.; Sardianou, E.; Horobet, A.; Zambrano-Monserrate, M.A.; Kostakis, I. Balancing growth and sustainability: The impact of economic status, energy, trade and finance on the ecological footprint in selected ASEAN economies. Sustain. Anal. Model. 2025, 5, 100041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





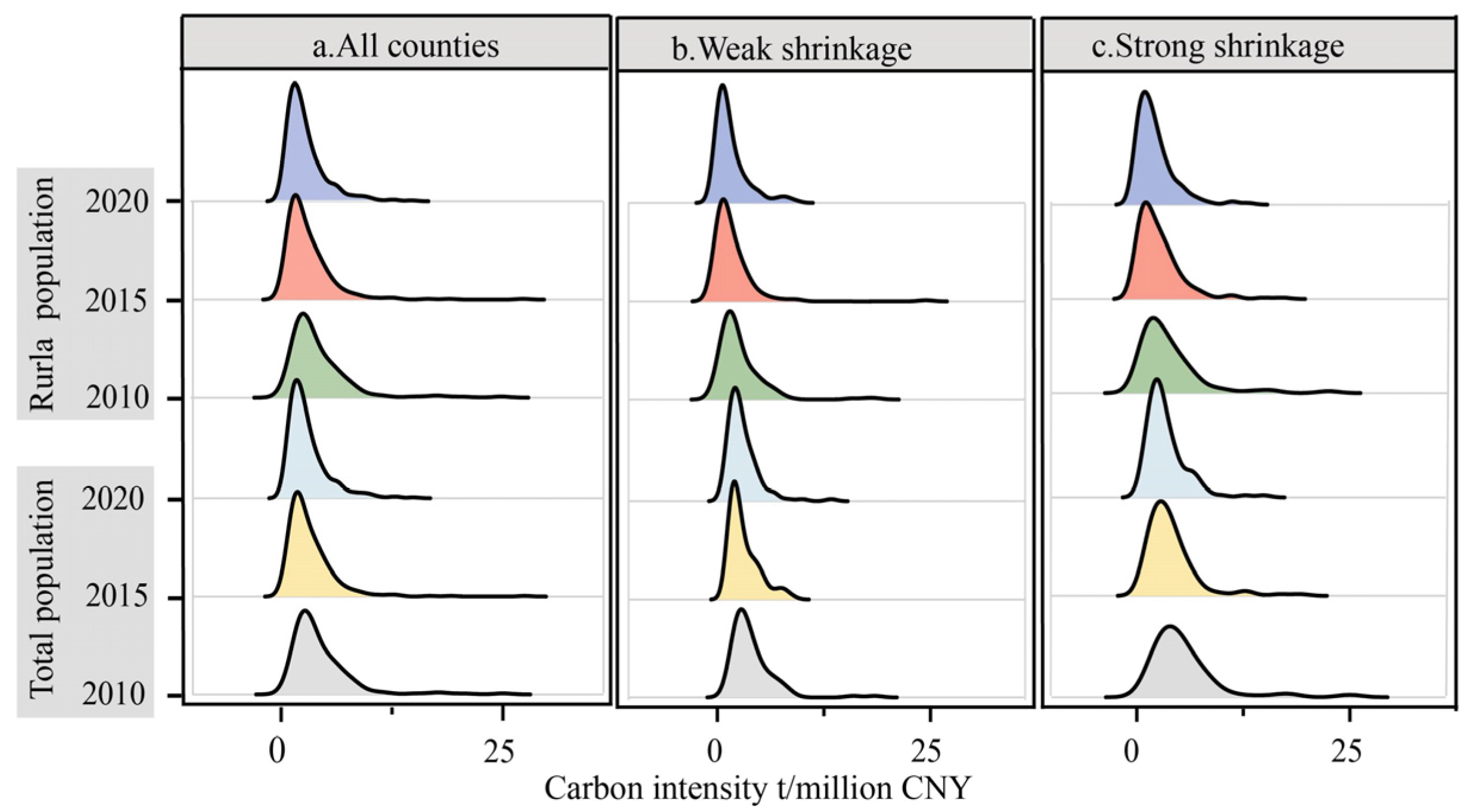
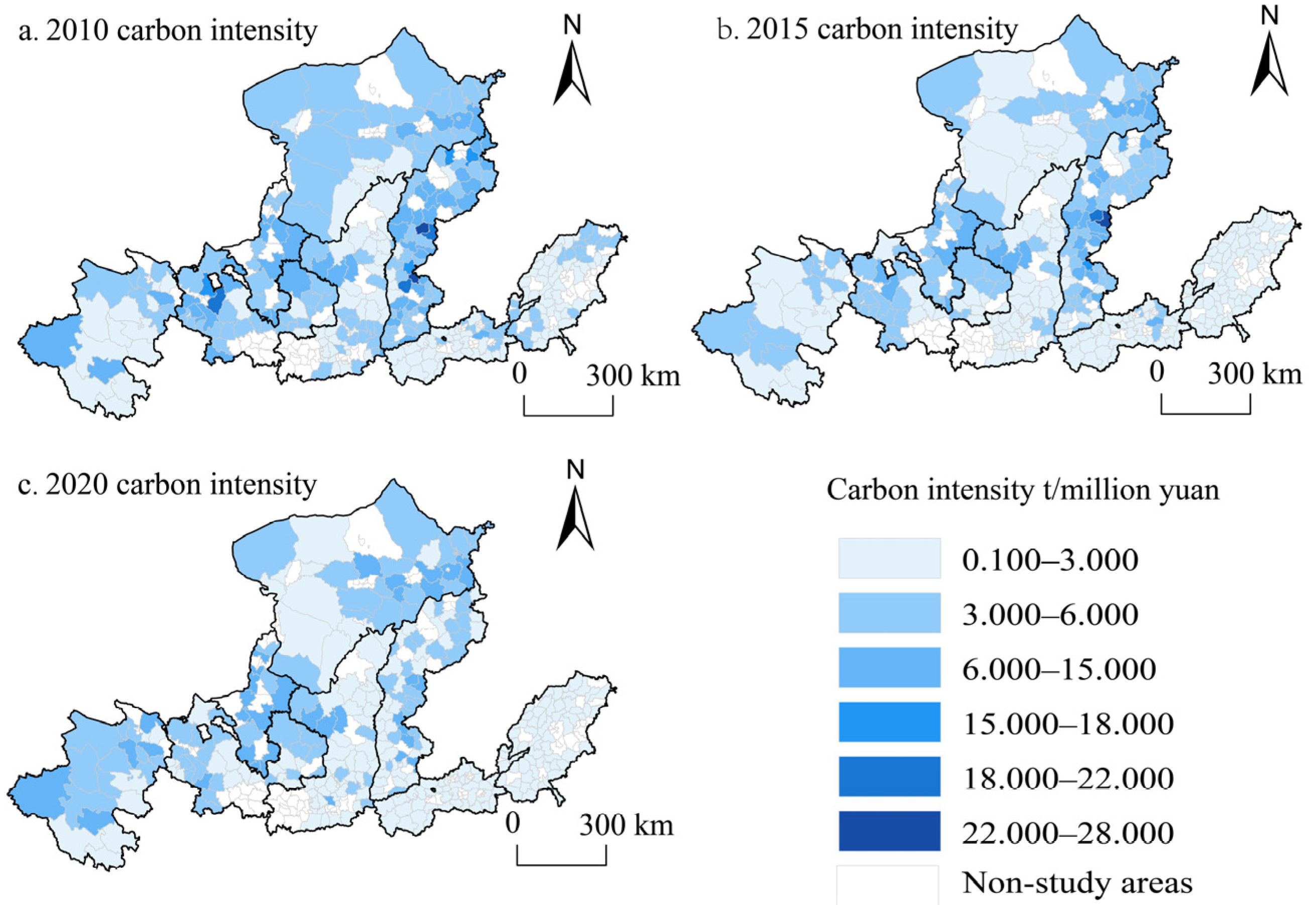




| Category | Variable Name | Symbol | Observations | Average | Standard Deviation | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Explained Variables | Carbon emissions intensity (%) | cei | 960 | 3.554 | 2.943 | 0.146 | 27.466 |
| Explanatory Variables | Total population shrinkage rate (%) | -tpsr | 960 | −0.070 | 0.186 | −0.988 | 0.959 |
| Rural population shrinkage rate (%) | -rpsr | 960 | −0.305 | 0.315 | −1.454 | 1.441 | |
| Variables | Industrial upgrading (%) | ins | 960 | 1.281 | 1.592 | 0.094 | 22.078 |
| Medical level (bed) | med | 960 | 14.891 | 12.670 | 0.440 | 79.170 | |
| Education level (person) | edu | 960 | 49.895 | 39.047 | 1.688 | 250.856 | |
| Financial level (million CNY) | loan | 960 | 87.815 | 138.300 | 0.016 | 2196.770 | |
| Government financial capacity (million CNY) | gov | 960 | 8.986 | 12.753 | 0.033 | 91.615 |
| Category | Total Population | Rural Population | Rural Population Share |
|---|---|---|---|
| YRB | 11,200.6 | 6531.8 | 58.3% |
| 11,309.5 | 5253.7 | 46.5% | |
| Upper | 2768.8 | 1840.9 | 66.5% |
| 2778.5 | 1539.5 | 55.4% | |
| Middle | 3256.8 | 2009.4 | 61.7% |
| 3076.8 | 1519.8 | 49.4% | |
| Lower | 5175.0 | 2661.5 | 51.5% |
| 5454.2 | 2154.4 | 39.5% |
| Variable | (1) All Counties | (2) Population Growth | (3) Weak Shrinkage | (4) Strong Shrinkage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| -tpsr | 1.850 *** (0.630) | 1.038 (1.206) | −0.783 (1.617) | 2.310 ** (0.876) |
| ins | 0.051 (0.072) | −0.128 (0.195) | −0.073 (0.073) | 0.164 (0.104) |
| gov | −0.039 *** (0.009) | −0.008 (0.013) | −0.043 *** (0.012) | −0.146 ** (0.058) |
| med | −0.032 *** (0.008) | −0.035 *** (0.011) | −0.026 (0.016) | 0.022 (0.032) |
| edu | 0.033 *** (0.005) | 0.022 ** (0.009) | 0.023 *** (0.007) | 0.063 *** (0.016) |
| loan | −0.001 (0.001) | −0.002 (0.002) | −0.000 (0.001) | 0.002 (0.005) |
| _cons | 2.922 *** (0.262) | 3.234 *** (0.490) | 2.527 *** (0.447) | 2.623 *** (0.797) |
| N | 960 | 960 | 960 | 960 |
| Variable | (1) All Counties | (2) Population Growth | (3) Weak Shrinkage | (4) Strong Shrinkage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| -rpsr | 0.629 ** (0.263) | −0.312 (0.446) | −0.406 (0.381) | 1.201 *** (0.365) |
| ins | 0.051 (0.071) | 0.995 (0.696) | −0.046 (0.141) | 0.117 (0.080) |
| gov | −0.039 *** (0.009) | −0.034 (0.062) | 0.013 (0.019) | −0.041 *** (0.012) |
| med | −0.030 *** (0.008) | 0.026 (0.024) | −0.032 *** (0.010) | −0.018 (0.013) |
| edu | 0.035 *** (0.005) | −0.000 (0.058) | 0.029 *** (0.006) | 0.042 *** (0.009) |
| loan | −0.000 (0.001) | −0.007 (0.006) | −0.003 (0.003) | 0.001 (0.001) |
| _cons | 2.767 *** (0.273) | 2.975 (1.677) | 2.468 *** (0.388) | 2.861 *** (0.489) |
| N | 960 | 960 | 960 | 960 |
| -tpsr/cei | -rpsr/cei | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | (1) Upper | (2) Middle | (3) Lower | (1) Upper | (2) Middle | (3) Lower |
| -tpsr | −2.364 *** (0.779) | 5.015 *** (1.216) | 0.268 (0.981) | |||
| -rpsr | −1.403 *** (0.372) | 2.521 *** (0.475) | 0.332 * (0.178) | |||
| ins | −0.077 (0.124) | 0.149 (0.105) | −0.134 (0.112) | −0.103 (0.116) | 0.155 (0.105) | −0.230 * (0.121) |
| gov | −0.038 ** (0.018) | −0.060 (0.037) | −0.034 *** (0.008) | −0.024 (0.020) | −0.043 (0.035) | −0.034 *** (0.007) |
| med | −0.020 (0.022) | 0.017 (0.023) | −0.029 *** (0.005) | −0.034 (0.024) | 0.019 (0.025) | −0.029 *** (0.006) |
| edu | 0.053 *** (0.016) | 0.044 *** (0.010) | 0.010 *** (0.003) | 0.047 *** (0.0165) | 0.044 *** (0.011) | 0.010 *** (0.002) |
| loan | −0.002 (0.002) | −0.010 ** (0.004) | 0.001 ** (0.001) | −0.003 (0.002) | −0.006 (0.004) | 0.001 ** (0.001) |
| _cons | 3.178 *** (0.564) | 3.572 *** (0.547) | 2.217 *** (0.291) | 3.347 *** (0.536) | 3.586 *** (0.513) | 2.135 *** (0.287) |
| N | 960 | 960 | 960 | 960 | 960 | 960 |
| Variable | (1) All Counties | (2) Population Growth | (3) Weak Shrinkage | (4) Strong Shrinkage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| -tpsr | 2.870 *** (0.630) | −3.052 *** (1.136) | 1.052 (2.051) | 4.805 *** (1.468) |
| ins | 0.037 (0.072) | −0.229 *** (0.55) | 0.540 (0.324) | 0.108 (0.075) |
| gov | −0.040 *** (0.009) | −0.008 (0.008) | −0.068 *** (0.023) | −0.198 *** (0.061) |
| med | −0.0316 *** (0.008) | −0.027 *** (0.007) | −0.030 * (0.018) | 0.068 * (0.040) |
| edu | 0.032 *** (0.005) | 0.030 *** (0.007) | 0.023 *** (0.007) | 0.052 *** (0.014) |
| loan | −0.001 (0.001) | −0.002 (0.002) | −0.003 (0.005) | 0.001 (0.006) |
| _cons | 2.839 *** (0.267) | 3.234 *** (0.490) | 3.196 *** (0.447) | 2.377 *** (0.789) |
| N | 960 | 960 | 960 | 960 |
| Variable | (1) All Counties | (2) Population Growth | (3) Weak Shrinkage | (4) Strong Shrinkage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| -rpsr | 1.015 *** (0.308) | −2.749 (1.954) | 0.517 (0.441) | 1.501 *** (0.410) |
| ins | 0.057 (0.074) | −0.266 *** (0.082) | 0.183 * (0.104) | 0.145 (0.112) |
| gov | −0.026 *** (0.009) | −0.035 (0.062) | −0.055 *** (0.013) | −0.016 (0.014) |
| med | −0.024 *** (0.008) | 0.021 (0.024) | −0.019 (0.015) | −0.017 (0.012) |
| edu | 0.032 *** (0.005) | −0.025 ** (0.029) | 0.032 *** (0.007) | 0.035 *** (0.008) |
| loan | −0.001 (0.001) | −0.004 (0.002) | −0.002 (0.001) | 0.001 (0.001) |
| _cons | 2.713 *** (0.268) | 3.380 (0.731) | 2.569 *** (0.425) | 2.305 *** (0.443) |
| N | 960 | 960 | 960 | 960 |
| -tpsr/cei | -rpsr/cei | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | (1) Upper | (2) Middle | (3) Lower | (1) Upper | (2) Middle | (3) Lower |
| -tpsr | −5.085 *** (1.387) | 5.840 *** (1.532) | 0.667 (0.775) | |||
| -rpsr | −1.274 *** (0.316) | 2.540 *** (0.476) | 0.002 * (0.195) | |||
| ins | −0.041(0.1111) | 0.150 (0.103) | −0.143 (0.115) | −0.076 (0.020) | 0.152 (0.111) | −0.128(0.123) |
| gov | −0.035 * (0.020) | −0.054 (0.033) | −0.035 *** (0.008) | −0.043 ** (0.021) | −0.027(0.033) | −0.033 *** (0.008) |
| med | −0.011 (0.022) | 0.007 (0.023) | −0.028 *** (0.006) | −0.025 (0.024) | 0.014 (0.026) | −0.028 *** (0.006) |
| edu | 0.048 *** (0.015) | 0.040 *** (0.010) | 0.009 *** (0.002) | 0.048 *** (0.016) | 0.035 *** (0.011) | 0.010 *** (0.002) |
| loan | −0.002 (0.002) | −0.007 * (0.003) | 0.001 ** (0.001) | −0.003 (0.002) | −0.002 (0.003) | 0.001 ** (0.001) |
| _cons | 3.540 *** (0.571) | 3.381 *** (0.507) | 2.221 *** (0.278) | 3.542 *** (0.568) | 3.530 *** (0.511) | 2.166 *** (0.281) |
| N | 960 | 960 | 960 | 960 | 960 | 960 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, H.; Shi, L.; Wen, Q.; Shen, C.; Wu, X.; Wang, C. Divergent Impacts and Policy Implications of Rural Shrinkage on Carbon Intensity in the Yellow River Basin. Agriculture 2025, 15, 2443. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15232443
Yang H, Shi L, Wen Q, Shen C, Wu X, Wang C. Divergent Impacts and Policy Implications of Rural Shrinkage on Carbon Intensity in the Yellow River Basin. Agriculture. 2025; 15(23):2443. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15232443
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Haonan, Linna Shi, Qi Wen, Caiting Shen, Xinyan Wu, and Caijun Wang. 2025. "Divergent Impacts and Policy Implications of Rural Shrinkage on Carbon Intensity in the Yellow River Basin" Agriculture 15, no. 23: 2443. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15232443
APA StyleYang, H., Shi, L., Wen, Q., Shen, C., Wu, X., & Wang, C. (2025). Divergent Impacts and Policy Implications of Rural Shrinkage on Carbon Intensity in the Yellow River Basin. Agriculture, 15(23), 2443. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15232443







