Research on Wheat Spike Phenotype Extraction Based on YOLOv11 and Image Processing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Dataset Construction
2.2.1. Data Acquisition
2.2.2. Data Enhancement
2.3. Research Methodology
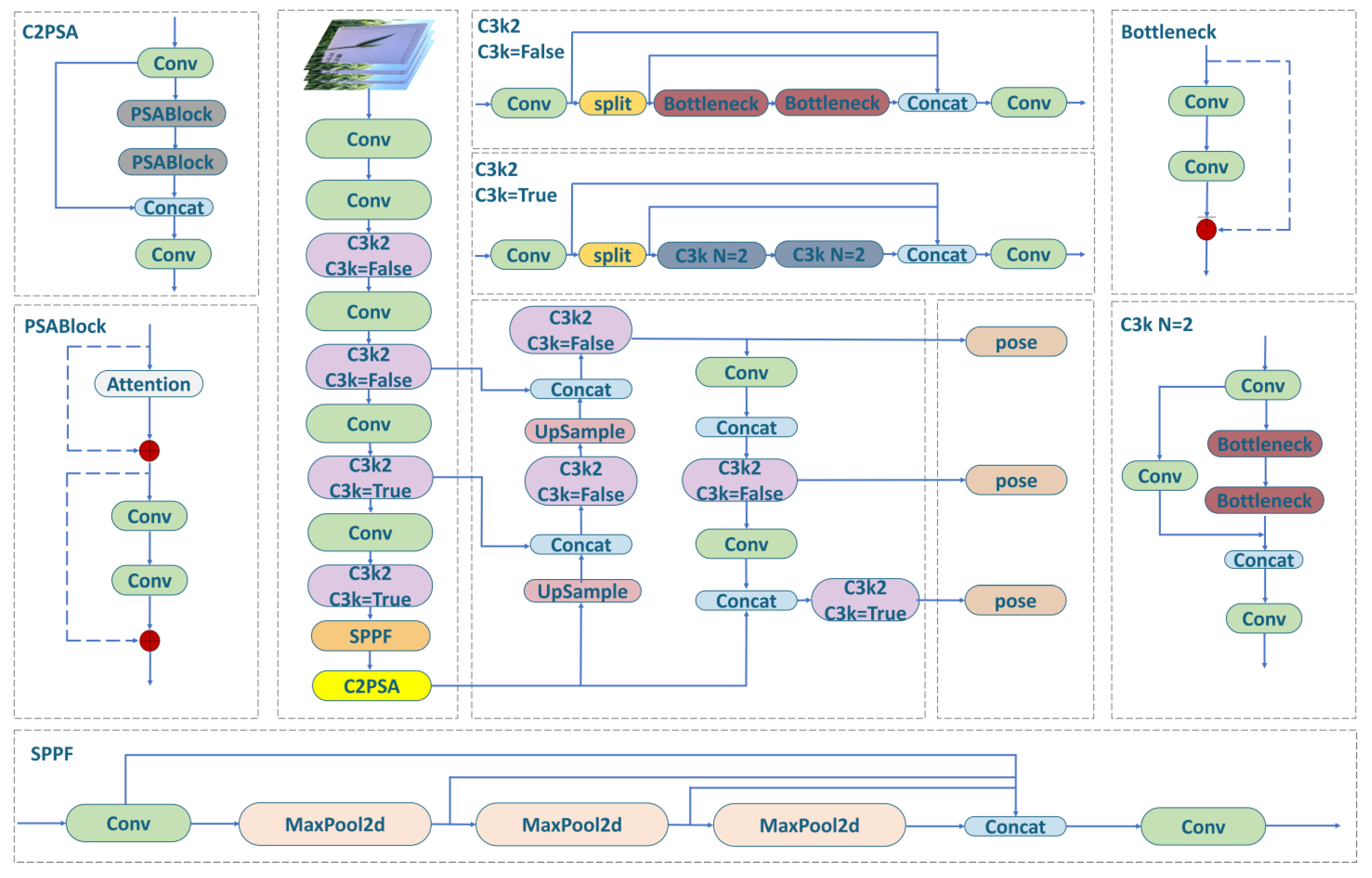
2.3.1. YOLOv11 Keypoint Detection Algorithm
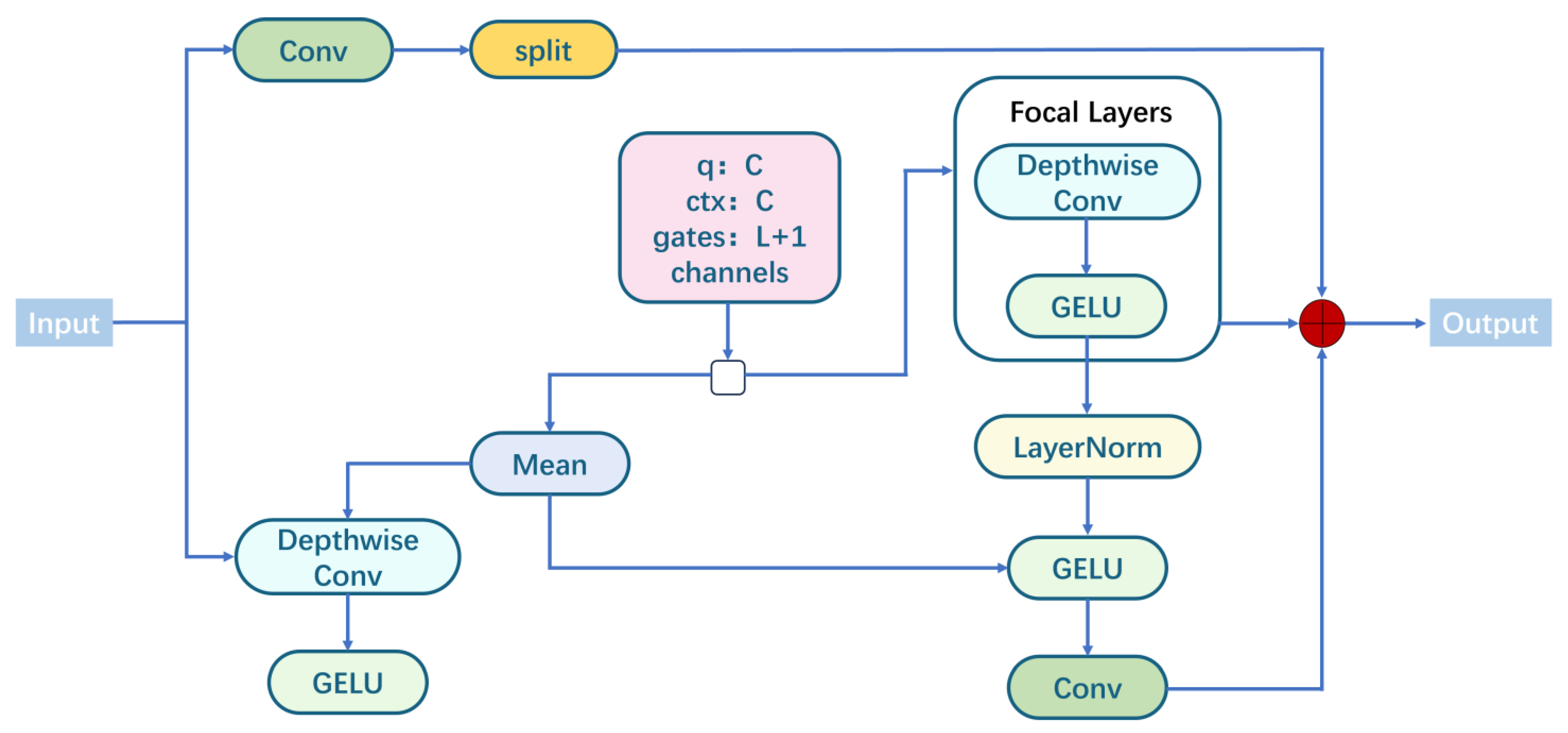
2.3.2. Improving the YOLOv11 Network Model
3. Model Training
3.1. Parameter Setting
3.2. Evaluation Indicator
3.3. Analysis of Experimental Results
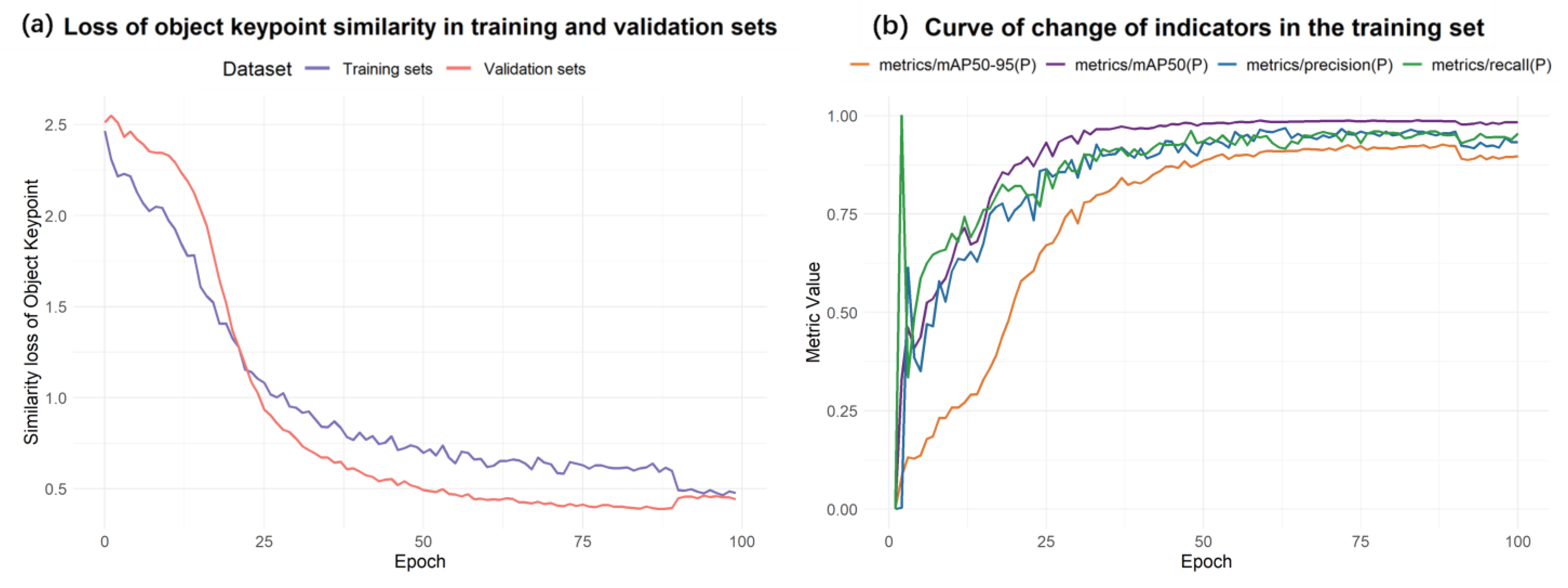
3.3.1. Training Results
3.3.2. Analysis of Ablation Experiment Results
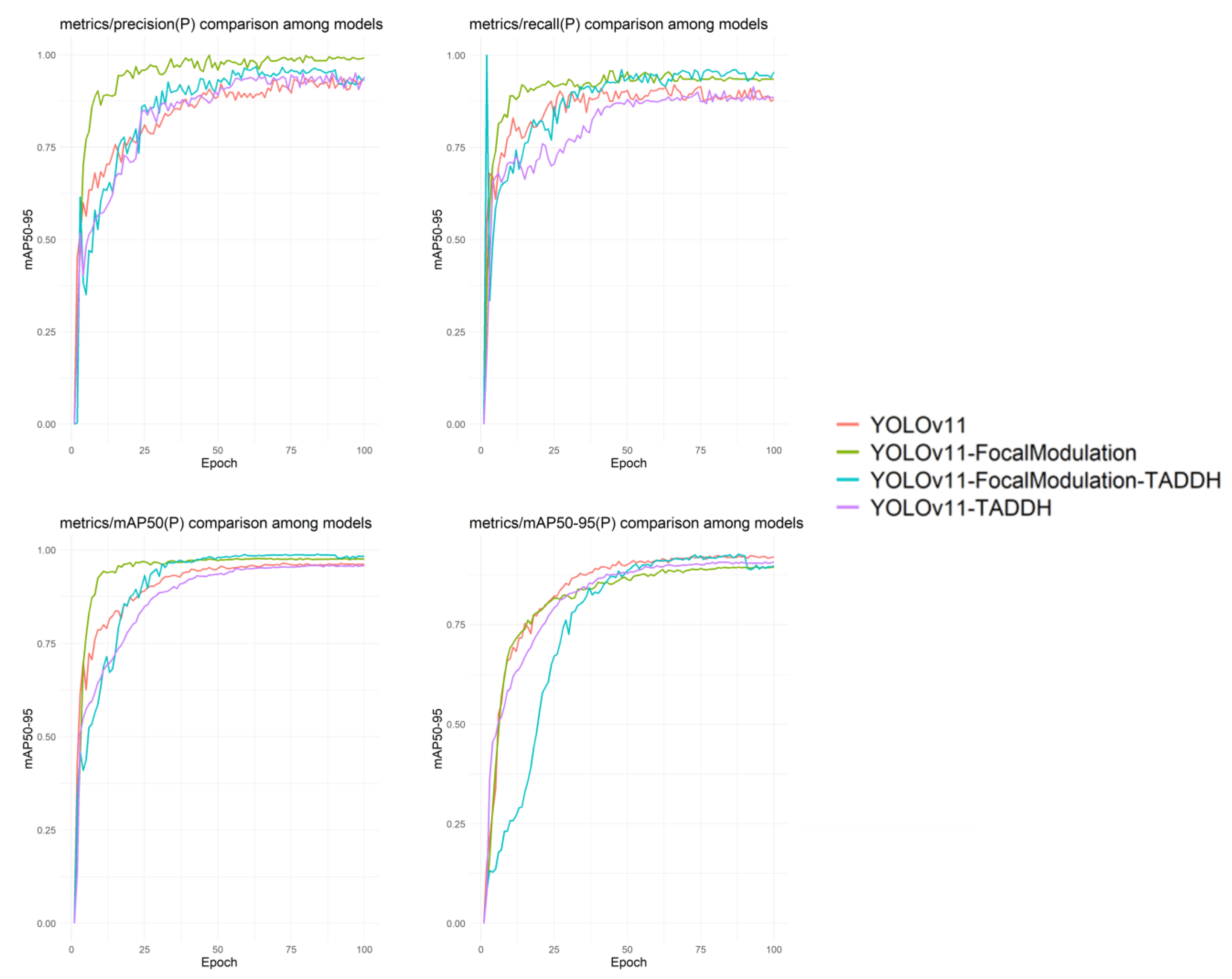
3.3.3. Comparative Experimental Analysis of Different Models
4. Extraction of Spike Phenotype Parameters
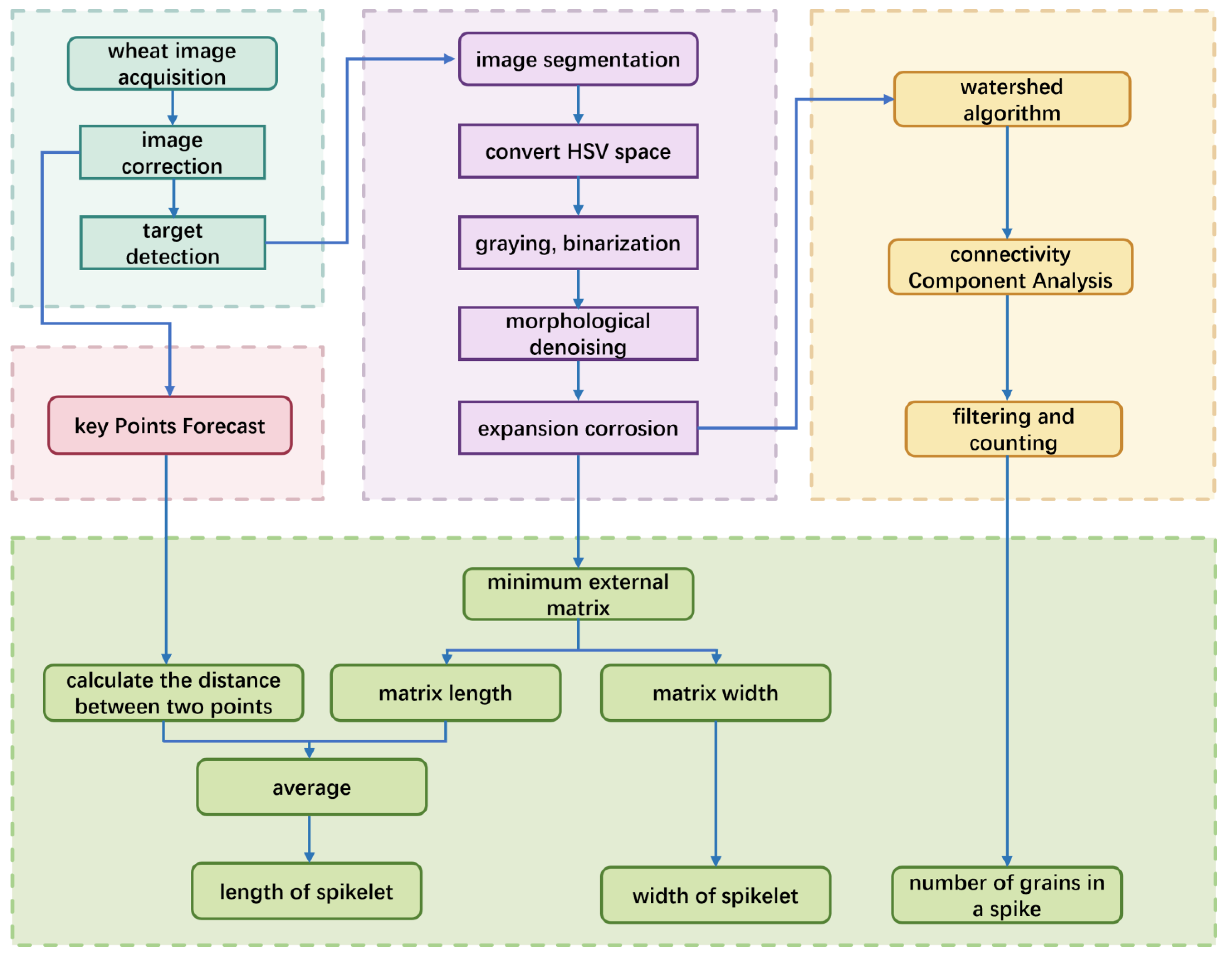
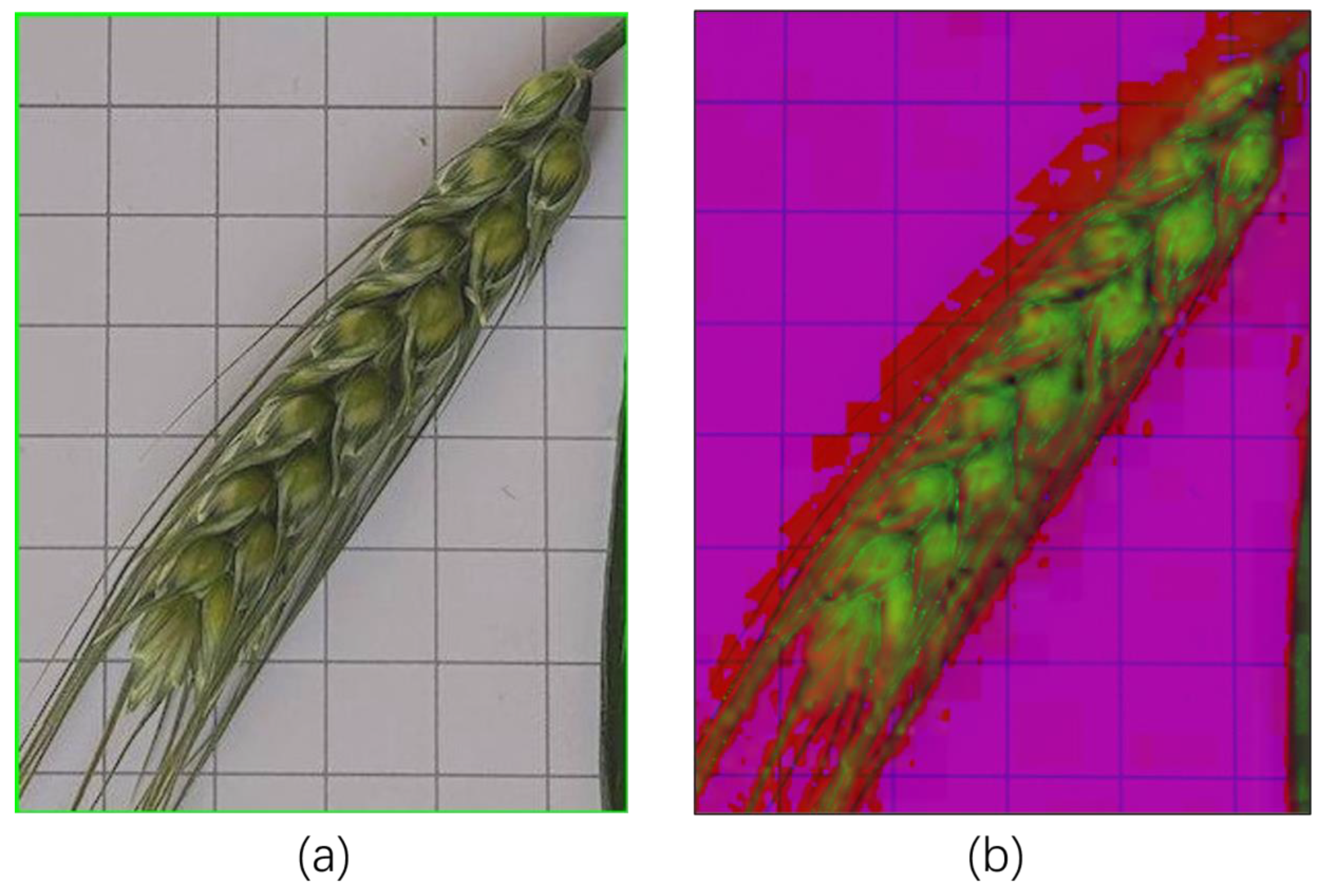
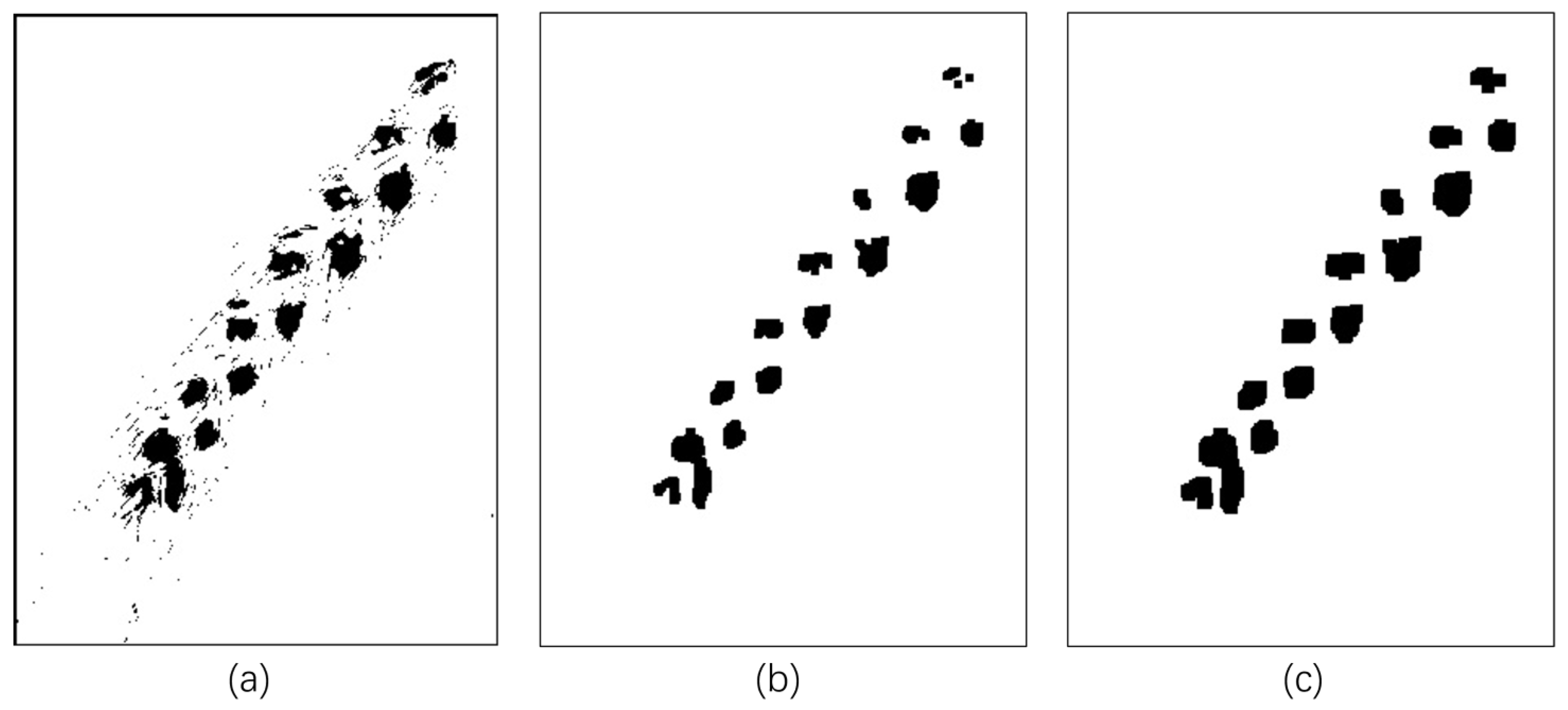
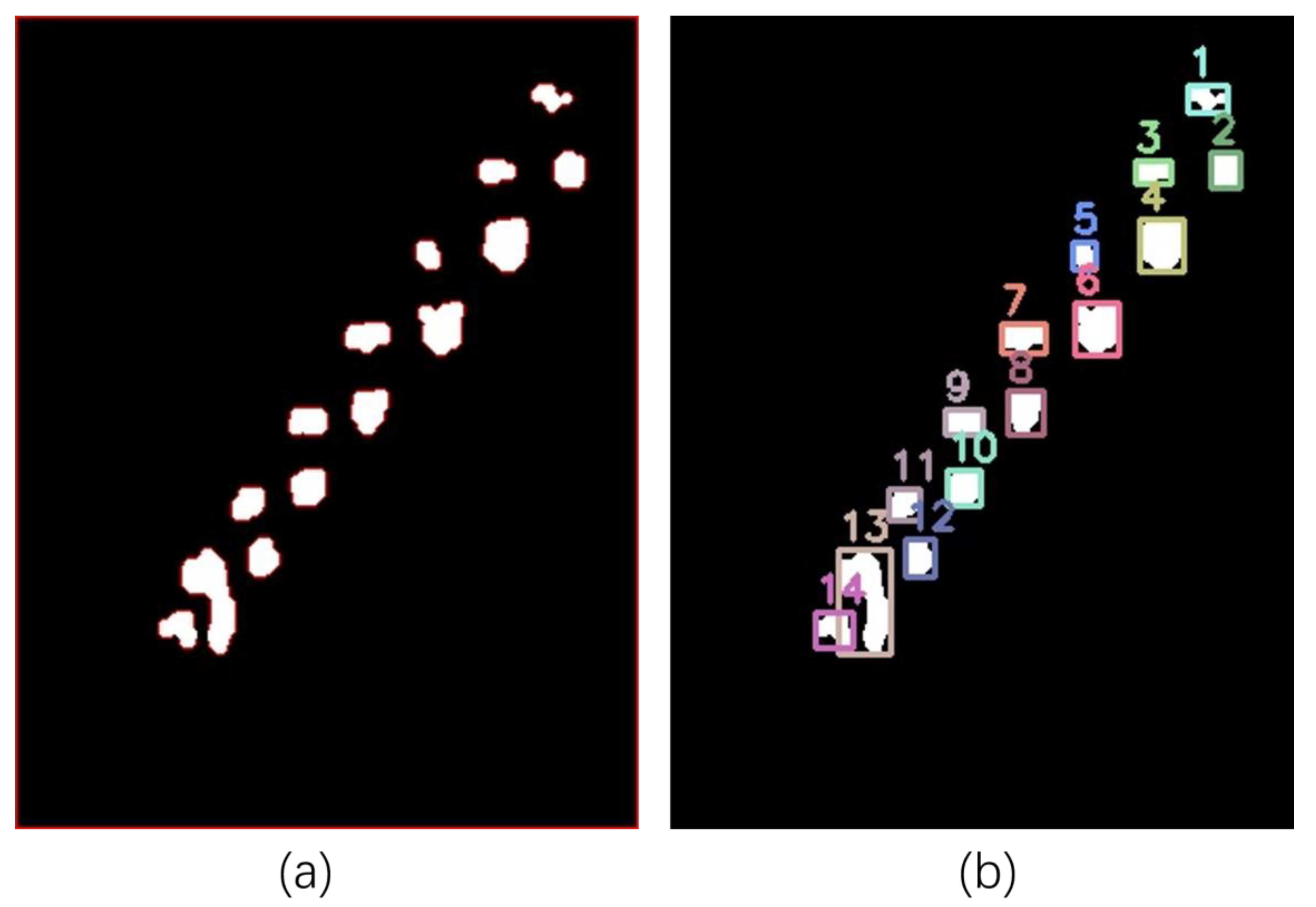
4.1. Image Processing
- (1)
- Image correction
- (2)
- Color Space Conversion
- (3)
- Morphological operation
4.2. Extraction of Phenotypic Parameters
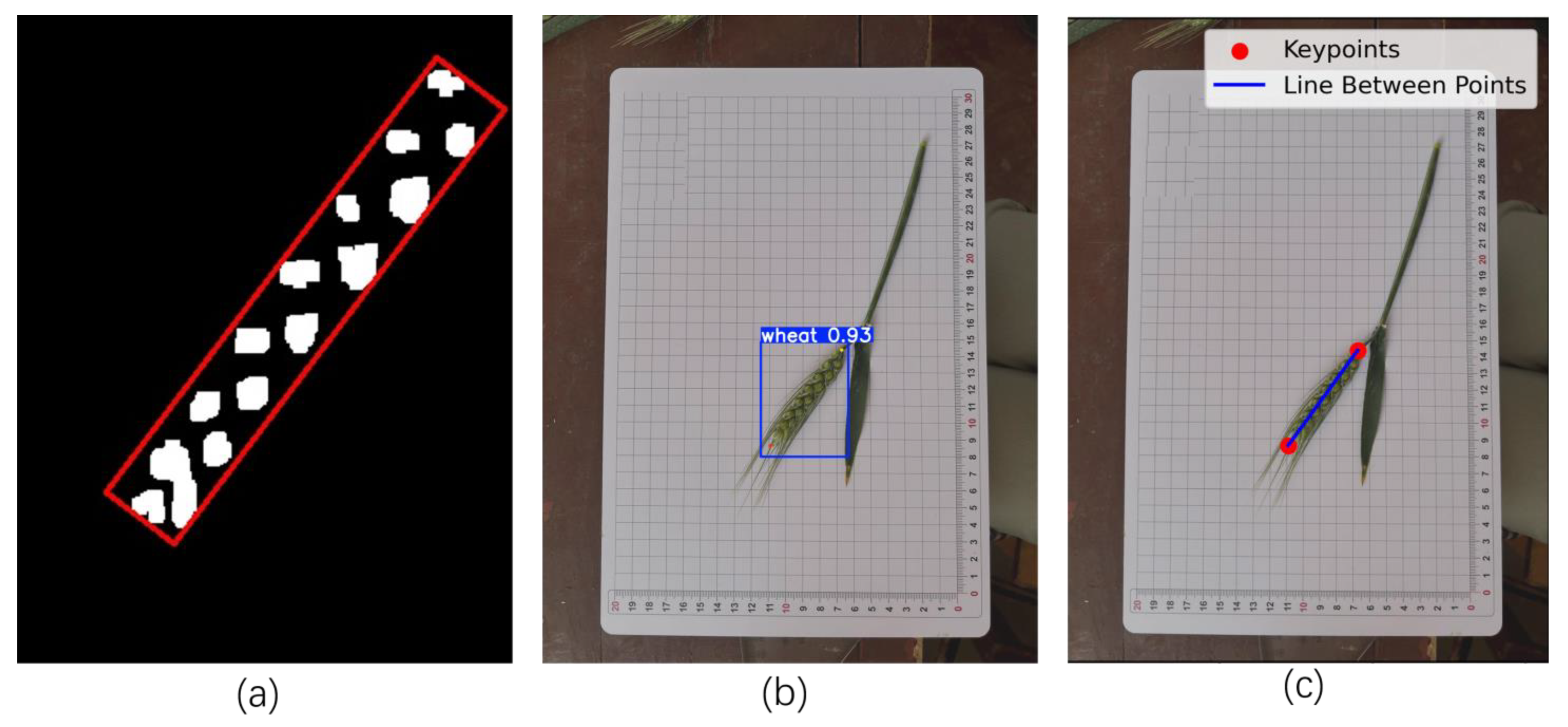
4.2.1. Extraction of Spike Length and Width
4.2.2. Grain Number Extraction
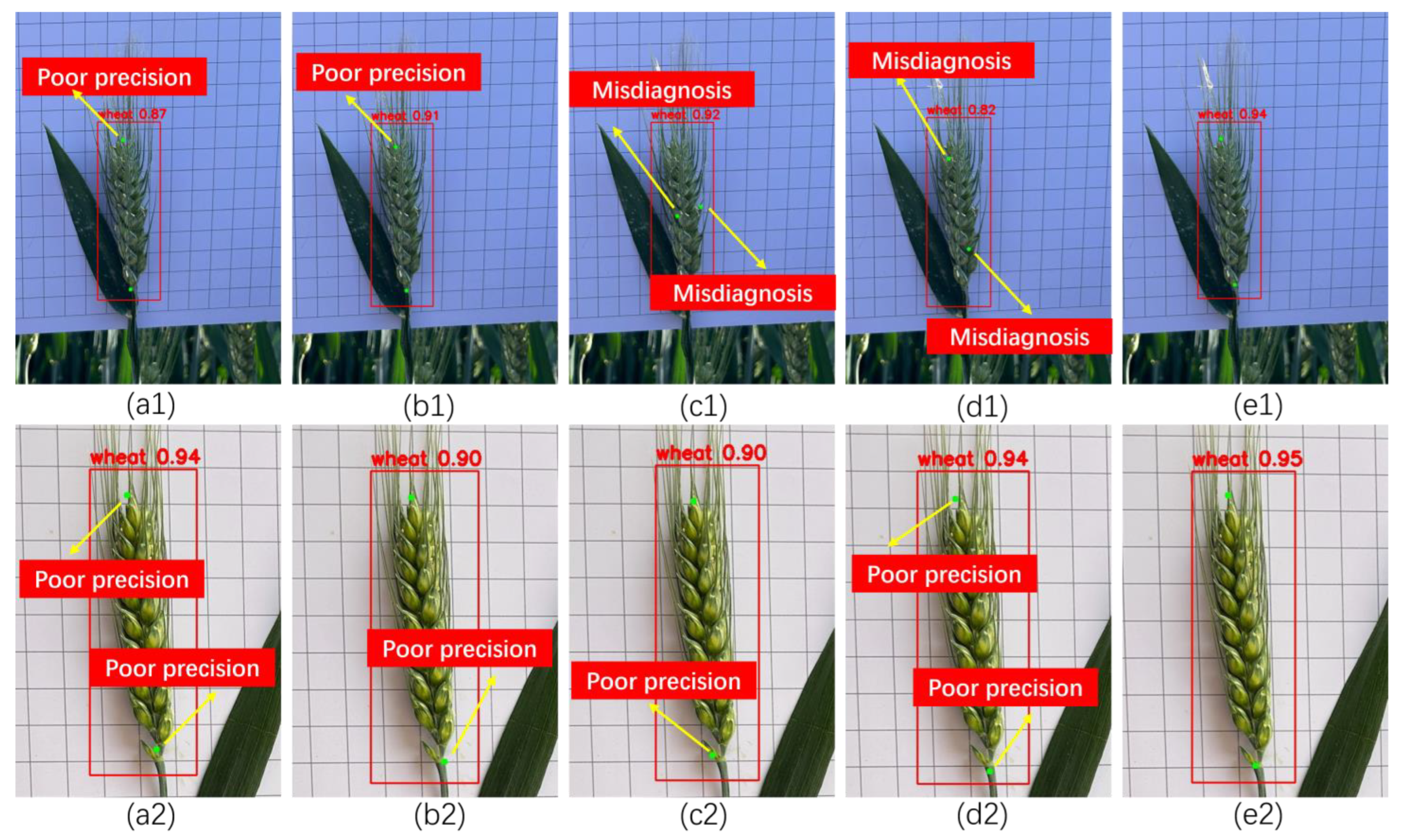
4.3. Experimental Results and Error Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hickey, L.T.; Hafeez, A.N.; Robinson, H.; Jackson, S.A.; Leal-Bertioli, S.C.M.; Tester, M.; Gao, C.; Godwin, I.D.; Hayes, B.J.; Wulff, B.B.H. Breeding crops to feed 10 billion. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 744–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, X.; Liu, C.; Han, J.; Feng, Q.; Lu, Q.; Feng, Y. Wheat-Seed Variety Recognition Based on the GC_DRNet Model. Agriculture 2023, 13, 2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Luo, B.; Pan, D.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, C.; Wang, C. Synchronous measurement of wheat ear length and spikelets number based on image processing. J. Chin. Agric. Mech. 2016, 37, 210–215. [Google Scholar]
- Du, S.; Li, Y.; Yao, M.; Li, L.; Ding, Q.; He, R. Counting method of grain number based on wheatear spikelet image segmentation. J. Nanjing Agric. Univ. 2018, 41, 742–751. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; Deng, G.; Su, Y.; Yang, Z.; Tang, Y.; Wang, J.; Qiu, X.; Pu, X.; Li, J.; Liu, Z.; et al. Identification and validation of two major QTLs for spike compactness and length in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) showing pleiotropic effects on yield-related traits. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2021, 134, 3625–3641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Bragado, R.; Vicente, R.; Molero, G.; Serret, M.D.; Maydupe, M.L.; Araus, J.L. New avenues for increasing yield and stability in C3 cereals: Exploring ear photosynthesis. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2020, 56, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansoor, S.; Karunathilake, E.M.; Tuan, T.T.; Chung, Y.S. Genomics, phenomics, and machine learning in transforming plant research: Advancements and challenges. Hortic. Plant J. 2025, 11, 486–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Li, X.J.; Zhang, D.H.; Zhao, J.S.; Jiang, X.L.; Sun, H.L.; Ru, Z.G. Identification and validation of QTLs for kernel number per spike and spike length in two founder genotypes of wheat. BMC Plant Biol. 2022, 22, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Qi, X.; Nabaei, S.H.; Liu, M.; Chen, D.; Zhang, X.; Yin, X.; Li, Z. A Survey on 3D Reconstruction Techniques in Plant Phenotyping: From Classical Methods to Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF), 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS), and Beyond. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2505.00737. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Gao, L.; Li, X. A Generative Adversarial Network Based Deep Learning Method for Low-Quality Defect Image Reconstruction and Recognition. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2021, 17, 3231–3240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Jin, S.; Liu, X.; Yang, Q.; Li, Q.; Zang, J.; Li, Z.; Hu, T.; Guo, Z.; Wu, J.; et al. Extraction of Wheat Spike Phenotypes From Field-Collected Lidar Data and Exploration of Their Relationships With Wheat Yield. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 4410813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, K.M.; Ludwig, E.; Gutierrez, J.; Gehan, M.A. Deep Learning in Image-Based Plant Phenotyping. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2024, 75, 771–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.Q.; Zheng, P.; Xu, S.T.; Wu, X.D. Object Detection with Deep Learning: A Review. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2019, 30, 3212–3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, H. Review of applying YOLO family algorithms to analyze animal and plant phenotype. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2024, 55, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Chu, Z.; Cui, M.; Yang, Q.; Wang, J.; Yang, H. Red Ripe Strawberry Recognition and Stem Detection Based on Improved YOLO v8—Pose. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2023, 54, 244–251. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Y.; Fu, K.; Lan, H.; Wang, X.; Su, Z. Maize tassel detection with CA-YOLO for UAV images in complex field environments. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 217, 108562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, N.; Su, Y.; Yang, L.; Li, Z.; Yan, H. Wheat Seed Detection and Counting Method Based on Improved YOLOv8 Model. Sensors 2024, 24, 1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Yang, F.; Li, F. Overview of crop image segmentation algorithm. Mod. Comput. 2020, 19, 72–75. [Google Scholar]
- Song, C.; Yu, C.; Xing, Y.; Li, S.; He, H.; Yu, H.; Feng, X. Algorith for acquiring multi-phenotype parameters of soybean seed based on OpenCV. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2022, 38, 156–163. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, Y.-H.; Li, Y.-N.; Zou, W.; Liu, Y.-Y.; He, R.-Y. Determination method on thousand-seed weight of rapeseed based on image processing. Chin. J. Oil Crop Sci. 2022, 44, 201–210. [Google Scholar]
- Bi, K.; Jiang, P.; Li, L.; Shi, B.; Wang, C. Non-destructive measurement of wheat spike characteristics based on morphological image processing. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2010, 26, 212–216. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, P.; Zhang, B.; Bi, K. Wheat ear-length measurements based on image processing. J. Commun. Univ. China 2010, 4, 69–73. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Feng, T.C.; Wang, Y.B.; Li, Y.T.; Chen, D. Wheat grain counting method based on YOLO v7-ST model. Nongye Jixie Xuebao/Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2023, 54, 188–197+204. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, Q.; Zhang, H.; Gao, M.; Qiao, H.; Xu, X.; Ma, X. A rapid, low-cost wheat spike grain segmentation and counting system based on deep learning and image processing. Eur. J. Agron. 2024, 156, 127158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Wu, W.; Chen, C.; Yang, T.; Zhu, S.; Shen, J.; Kehtarnavaz, N.; Shah, M. Deep Learning-based Human Pose Estimation: A Survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 2024, 56, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, B.; Xiao, B.; Wang, J.; Shi, H.; Huang, T.S.; Zhang, L. Higherhrnet: Scale-aware representation learning for bottom-up human pose estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 5385–5394. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Yuag, D.-G.; Wang, E. Automatic counting method of wheat grain based on improved bayes matting algorithm. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2020, 22, 75–82. [Google Scholar]
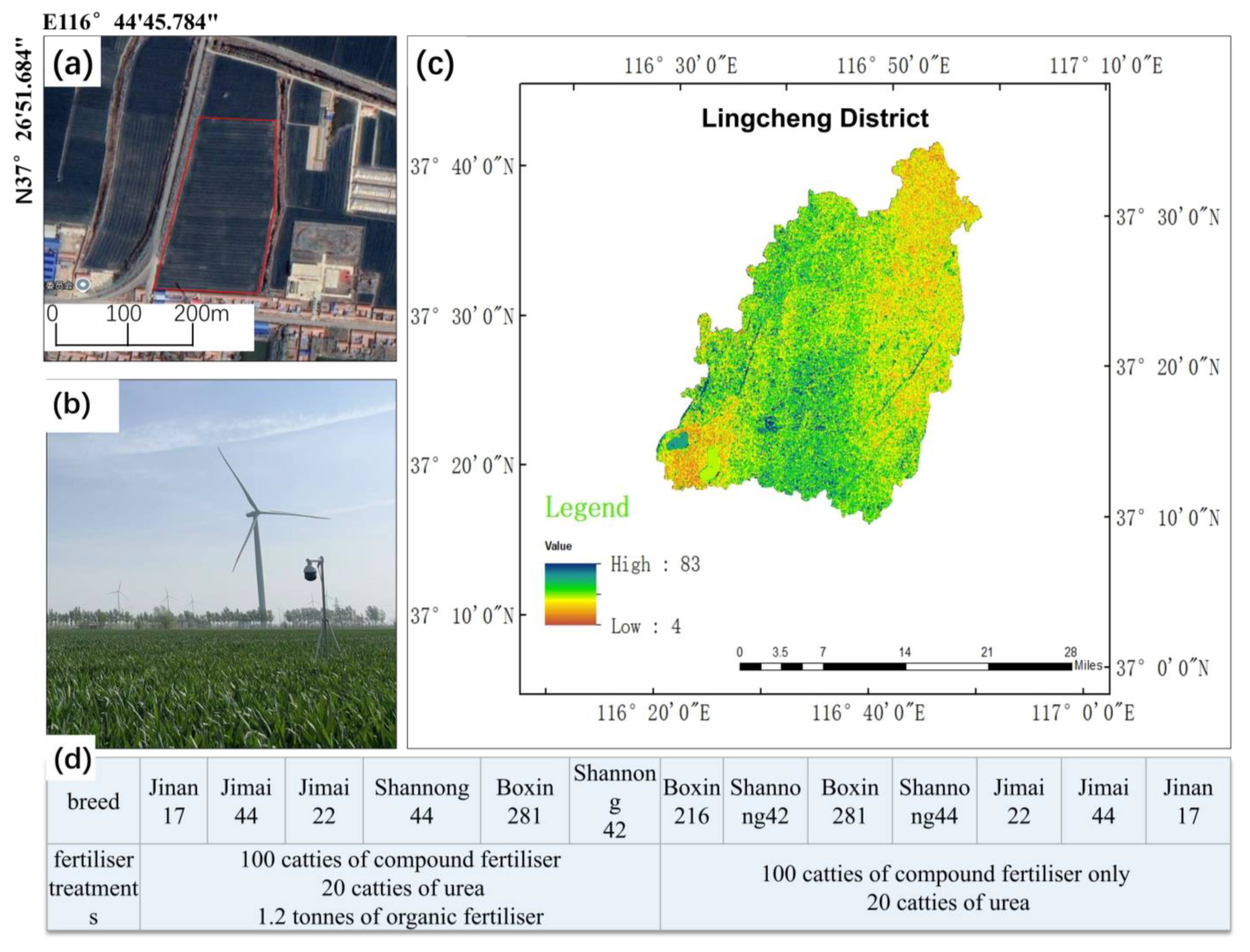

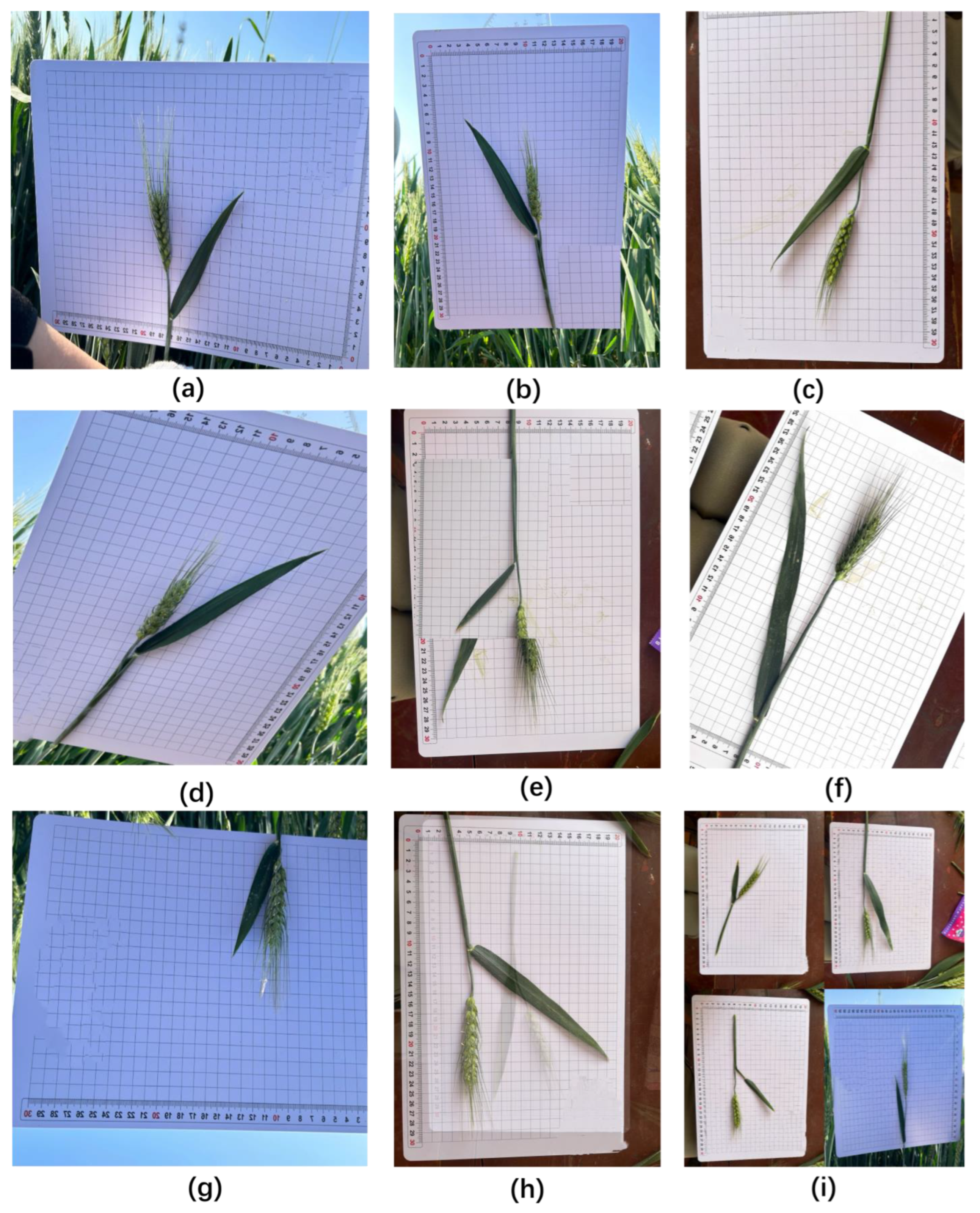


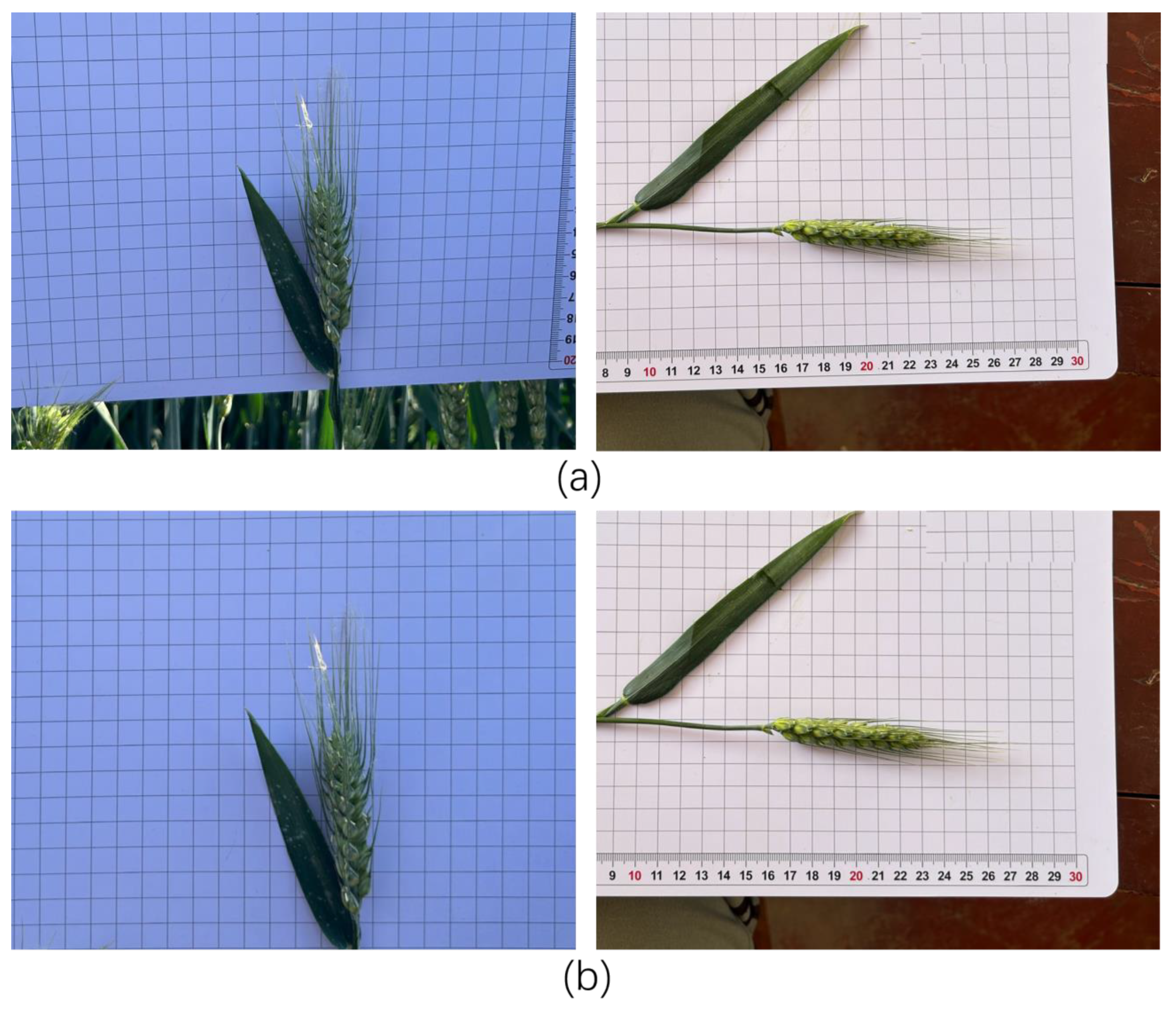

| Wheat Variety | Non-Destructive Images (Sheets) | Degradation Images (Sheets) | Total Images (Sheets) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Jinan 17 (organic fertilizer applied) | 50 | 31 | 81 |
| Jinan 17 (no organic fertilizer applied) | 48 | 30 | 78 |
| Jimai 44 (organic fertilizer applied) | 50 | 30 | 80 |
| Jimai 44 (no organic fertilizer applied) | 53 | 30 | 83 |
| Shannong 44 (organic fertilizer applied) | 53 | 33 | 86 |
| Shannong 44 (no organic fertilizer applied) | 49 | 29 | 78 |
| Boxin 281 (organic fertilizer applied) | 50 | 27 | 77 |
| Boxin 281 (no organic fertilizer applied) | 46 | 30 | 76 |
| Shannong 42 (organic fertilizer applied) | 51 | 31 | 82 |
| Shannong 42 (no organic fertilizer applied) | 51 | 30 | 81 |
| Boxin 216 (no organic fertilizer applied) | 55 | 28 | 83 |
| Models | Precision/% | Recall/% | mAP50/% | mAP50-95/% | Model Storage Size/M | Detection Time/ms |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 89.40 | 89.50 | 95.90 | 91.60 | 5.40 | 41.20 |
| 2 | 98.40 | 94.60 | 97.60 | 89.30 | 5.60 | 39.80 |
| 3 | 91.30 | 90.00 | 96.00 | 91.50 | 4.60 | 62.70 |
| 4 | 96.00 | 95.00 | 98.70 | 92.60 | 4.80 | 57.70 |
| Models | Precision/% | Recall/% | mAP50/% | mAP50-95/% | Inference/ms |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv8 | 90.50 | 90.50 | 87.20 | 84.50 | 33.30 |
| YOLOv9 | 90.40 | 90.50 | 87.70 | 86.20 | 213.40 |
| Hourglass | 83.30 | 83.00 | 77.30 | 74.30 | 33.20 |
| HRNet-W32 | 87.50 | 87.40 | 84.50 | 82.30 | 34.40 |
| YOLOv11-FocalModulation-TADDH | 96.00 | 95.00 | 98.70 | 92.60 | 57.70 |
| Number | Spike Length Measurement | Matrix Error Analysis | Critical Point Error Analysis | Mean Length Error Analysis | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Matrix Length/cm | Key Point Length/cm | Average Length/cm | Actual Length/cm | Absolute Error/cm | Relative Error/% | Absolute Error/cm | Relative Error/% | Absolute Error/cm | Relative Error/% | |
| 1 | 6.98 | 7.05 | 7.015 | 7.00 | 0.020 | 0.286 | 0.050 | 0.714 | 0.015 | 0.214 |
| 2 | 6.82 | 7.57 | 7.195 | 7.90 | 1.080 | 13.671 | 0.330 | 4.177 | 0.705 | 8.924 |
| 3 | 7.03 | 7.39 | 7.210 | 7.20 | 0.170 | 2.361 | 0.190 | 2.639 | 0.010 | 0.139 |
| 4 | 7.33 | 7.00 | 7.165 | 7.60 | 0.270 | 3.553 | 0.600 | 7.895 | 0.435 | 5.724 |
| 5 | 6.95 | 6.90 | 6.925 | 7.00 | 0.050 | 0.714 | 0.100 | 1.429 | 0.075 | 1.071 |
| 6 | 7.36 | 7.41 | 7.385 | 7.80 | 0.440 | 5.641 | 0.390 | 5.000 | 0.415 | 5.321 |
| 7 | 7.32 | 7.62 | 7.470 | 7.40 | 0.080 | 1.081 | 0.220 | 2.973 | 0.070 | 0.946 |
| 8 | 6.98 | 6.95 | 6.965 | 7.00 | 0.020 | 0.286 | 0.050 | 0.714 | 0.035 | 0.500 |
| 9 | 6.38 | 7.33 | 6.855 | 7.00 | 0.620 | 8.857 | 0.330 | 4.714 | 0.145 | 2.071 |
| 10 | 6.79 | 6.94 | 6.865 | 7.10 | 0.310 | 4.366 | 0.160 | 2.254 | 0.235 | 3.310 |
| Number | Spike Width Measurement | Error Analysis | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Measured Length/cm | Actual Length/cm | Absolute Error/cm | Relative Error/% | |
| 1 | 1.36 | 1.40 | 0.040 | 2.857 |
| 2 | 1.01 | 1.00 | 0.010 | 1.000 |
| 3 | 1.25 | 1.20 | 0.050 | 4.167 |
| 4 | 1.14 | 1.20 | 0.060 | 5.000 |
| 5 | 1.50 | 1.55 | 0.050 | 3.226 |
| 6 | 1.44 | 1.50 | 0.060 | 4.000 |
| 7 | 1.04 | 1.20 | 0.160 | 13.333 |
| 8 | 1.38 | 1.30 | 0.080 | 6.154 |
| 9 | 1.28 | 1.30 | 0.020 | 1.538 |
| 10 | 1.45 | 1.40 | 0.050 | 3.571 |
| Number | Grain Count Measurement | Error Analysis | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Measurements/per | Number of Calculations/per | Actual Number/per | Absolute Error/per | Relative Error/% | |
| 1 | 17 | 33 | 32 | 1 | 3.125 |
| 2 | 15 | 29 | 31 | 2 | 6.452 |
| 3 | 16 | 31 | 29 | 2 | 6.897 |
| 4 | 14 | 27 | 28 | 1 | 3.571 |
| 5 | 15 | 29 | 31 | 2 | 6.452 |
| 6 | 16 | 31 | 32 | 1 | 3.125 |
| 7 | 16 | 31 | 33 | 2 | 6.061 |
| 8 | 18 | 35 | 31 | 4 | 12.903 |
| 9 | 14 | 27 | 29 | 2 | 6.897 |
| 10 | 15 | 29 | 31 | 2 | 6.452 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Liu, L.; Liu, P. Research on Wheat Spike Phenotype Extraction Based on YOLOv11 and Image Processing. Agriculture 2025, 15, 2295. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15212295
Li X, Zhang Z, Wang J, Liu L, Liu P. Research on Wheat Spike Phenotype Extraction Based on YOLOv11 and Image Processing. Agriculture. 2025; 15(21):2295. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15212295
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xuanxuan, Zhenghui Zhang, Jiayu Wang, Lining Liu, and Pingzeng Liu. 2025. "Research on Wheat Spike Phenotype Extraction Based on YOLOv11 and Image Processing" Agriculture 15, no. 21: 2295. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15212295
APA StyleLi, X., Zhang, Z., Wang, J., Liu, L., & Liu, P. (2025). Research on Wheat Spike Phenotype Extraction Based on YOLOv11 and Image Processing. Agriculture, 15(21), 2295. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15212295





