Abstract
Weeds pose a significant threat to the production of the medicinal crop Ophiopogon japonicus. Due to the scarcity of registered herbicides for this crop, farmers heavily rely on manual weeding. This study evaluated a novel acetochlor nanocapsule formulation for weed control in Sichuan O. japonicus fields, comparing it to a conventional acetochlor emulsifiable concentrate (EC). Treatments included manual weeding (weed-free control), conventional EC (900 g a.i. ha−1), and three nanocapsule doses (450, 900, and 1800 g a.i. ha−1). Weed control efficacy was assessed at 15, 30, 45, and 60 days after application, followed by the measurement of agronomic traits, yield, and the content of bioactive compounds (saponins, flavonoids, and polysaccharides) post-harvest. The high-dose nanocapsules (1800 g a.i. ha−1) provided excellent weed control (96.54% at 45 days), which was better than the EC and lower nanocapsule doses, and extended the control duration. It did not negatively affect key agronomic traits, root tuber morphology, final yield, nor the content of key bioactive compounds compared to the weed-free control. In conclusion, acetochlor nanocapsules, especially at 1800 g a.i. ha−1, offer an effective and safe weed management strategy for O. japonicus. They provide superior, prolonged weed control without harming crop yield or quality.
1. Introduction
Acetochlor is a widely used pre-emergent selective amide herbicide that is primarily absorbed through the shoots and roots of weeds, inhibiting protein synthesis and leading to weed mortality. It is currently extensively applied in corn, soybean, cotton, and rapeseed fields to control annual grass weeds and certain small-seeded broadleaf weeds [1].
However, conventional herbicide formulations, such as emulsifiable concentrate (EC) and emulsion in water (EW), often pose significant risks, including phytotoxicity to crops, environmental contamination through soil residues and the water cycle system, and necessitating frequent applications due to rapid degradation [2,3,4,5,6]. These limitations have spurred the development of novel, environmentally friendly formulation technologies.
The broader adoption of nanotechnology in agriculture presents an exciting opportunity for innovation. It enables the development of advanced delivery systems that can improve the efficiency and sustainability of agrochemicals, such as fertilizers, biostimulants, and pesticides [7]. To optimize the use of herbicides, controlled-release formulations are vital. One promising approach is nanocapsule technology, which involves encapsulating the active ingredient within a polymeric shell. This method has demonstrated considerable potential by reducing the initial burst effect, prolonging herbicidal activity, minimizing environmental losses, and enhancing crop safety [8,9].
In previous studies, a novel nanocapsule was developed through polymerization between diacetone acrylamide (DAAM) and diacetone acrylamide (BMA), and its in vitro release mechanism was examined. Field efficacy tests demonstrated that, compared to traditional acetochlor emulsifiable concentrate (EC), acetochlor nanocapsules provided a better control of weeds after 30 days of application [10]. However, the critical transition from laboratory-scale development to field-scale evaluation has not been adequately explored. To fully understand the efficacy, physiological impact, and overall benefits of these novel formulations, further validation is necessary under real-world agronomic conditions, especially in high-value specialty crops.
Ophiopogon japonicus (O. japonicus) is a herbaceous plant from the Liliaceae family. Its root tubers are used as medicines and are included in the 2020 edition of the Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China [11]. Numerous pharmacological studies have demonstrated that O. japonicus contains saponins, flavonoids, polysaccharides, volatile oils and amino acids. These compounds exhibit a range of pharmacological effects, including cardiovascular protection as well as anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer, antioxidant, immunoregulatory, antitussive, antibacterial, and anti-diabetic properties [12,13,14]. O. japonicus is categorized into two types based on its region of cultivation: Sichuan O. japonicus and Zhejiang O. japonicus. Sichuan O. japonicus is mainly planted in the plain of Fujiang River Basin in Mianyang City, Sichuan Province, where it accounts for over 70% of the national yield [15].
The expansion of O. japonicus in China has faced significant challenges, particularly due to weed infestations in the crops. A key issue is that the use of herbicides in most traditional Chinese medicine crops is still at a preliminary stage, with few officially registered and approved applications [16]. This limitation makes it time-consuming and labor-intensive for growers to use manual weeding in the cultivation of O. japonicus. According to a survey, growers spend more than USD 300 per year on manual weeding, accounting for more than 20% of their total input cost [17]. Therefore, it is essential to develop a safe and efficient weed control strategy for O. japonicus fields, a task that is both urgent and challenging.
Building upon previous formulation studies, this research aims to bridge the gap between laboratory innovation and field application. We hypothesize that the acetochlor nanocapsule will provide effective and sustained weed control while enhancing crop safety and preserving the medicinal quality of O. japonicus. To test this hypothesis, a comprehensive field experiment was conducted to (1) evaluate the weed control efficacy and persistence of a novel acetochlor nanocapsule formulation applied at three different rates, in comparison with a conventional acetochlor emulsifiable concentrate (EC), in a Sichuan O. japonicus production system; (2) assess the impact of these treatments on the agronomic traits and yield of O. japonicus; and (3) determine the subsequent effects on the quality of the tubers by quantifying the content of key bioactive compounds: saponins, polysaccharides, and flavonoids.
This study provides crucial empirical evidence for the practical application of acetochlor nanocapsule in a medicinal crop system. The findings are anticipated not only to support sustainable weed management in the cultivation of O. japonicus, but also to enhance understanding of how advanced herbicide formulations can be effectively integrated into the production of high-value crops, ensuring both productivity and quality.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
The model herbicide, acetochlor (purity > 98%), was supplied by Jiangsu Tenglong Co., Ltd. (Yancheng, China). Butyl methacrylate (BMA), Diacetone acrylamide (DAAM), Sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS), Potassium persulfate (KPS) were purchased from Kelong Chemical Reagent Chengdou Co. (Chengdu, China). Methylophiopogonanone A, Methylophiopogonanone B, Ophiopogonin D, Ophiopogonin D′, Ophiopogonin B (purities > 98%) were supplied by Desite Biological Technology Co., Ltd. (Chengdu, China). Fructose, Hesperidin and Ruscogenin (purities > 98%) were supplied by Chengdu Purechem-Standard Co., Ltd. (Chengdu, China). Acetonitrile (HPLC grade) was supplied by Thermo Fisher Scientific (Fisher, NJ, USA). Methanol, N-Butanol, Perchloric acid, Ethyl Alcohol, Anthrone, Phosphoric acid, and concentrated sulfuric acid were purchased from Chron Chemicals Co., Ltd. (Chengdu, China). Ultra-pure water was obtained using a UPR-II-20L water purification system (Ulupure, Chengdu, China).
2.2. Preparation of Acetochlor Nanocapsules
The acetochlor nanocapsules were prepared following the method described by Guo et al. [10] employing nanoemulsion polymerization. This formulation was selected for our field study because it had been previously optimized and exhibited excellent sustained-release properties in vitro, making it a suitable candidate for investigating long-term weed control and reduced phytotoxicity in field conditions. First, acetochlor was dissolved in BMA. This solution was then emulsified in an aqueous SDS solution using ultrasonic homogenization. Polymerization was initiated by adding KPS at 60 °C and continued at 70 °C for 2 h. Next, 0.1 g of DAAM was added as a co-monomer and proceeded for another hour. Finally, the nanocapsules were collected by centrifugation, washed, and dried at 45 °C for later use.
2.3. Field Experimental Condition
2.3.1. Field Management and Experimental Design
The experiments were conducted in Mianyang City, Sichuan, China (104°49′3″ E, 31°23′7″ N, 402 m above sea level). The region has a humid subtropical monsoon climate, with a mean annual temperature of 16.7 °C. The annual average sunshine duration is 1376 h, the annual precipitation ranges from 882 to 1134 mm, the frost-free period is 283 days, and the soil type is sandy soil.
Seedlings were prepared from plants of O. japonicus after the previous harvest. The root tubers were removed. The lower rhizomes and fibrous roots were cut off, keeping stem nodes within 1 cm. The selected seedlings had 20 to 22 leaves and were 12 to 14 cm in height. They were planted in the experimental field on April 23, 2024, with a planting density of 120 plants per square meter.
Standard cultivation practices were implemented, including a basal application of compound fertilizer (N:P2O5:K2O = 15:15:15) at 600 kg ha−1. Regular irrigation was conducted to maintain soil moisture.
The experiment employed a randomized complete block design with five treatments and three replications. Each experimental plot measured 3 m × 3 m (9 m2), separated by 1 m wide isolation strips. Approximately 1080 plants were contained within each plot.
2.3.2. Herbicide Treatments and Application
The experiment consisted of five different treatments. These treatments included (1) manual weeding (weed-free control); (2) conventional acetochlor emulsifiable concentrate (EC) applied at 900 g a.i. ha−1; and acetochlor nanocapsules (prepared as described in Section 2.2) applied at (3) 450 g a.i. ha−1, (4) 900 g a.i. ha−1, and (5) 1800 g a.i. ha−1. Additionally, an unweeded control plot was established that received no weeding or herbicide. It was used to calculate weed control efficacy. All herbicide treatments were applied one week after planting using backpack sprayers.
2.3.3. Target Weed Spectrum
The acetochlor formulations were applied as pre-emergence herbicides to control weed germination. The target weed spectrum was determined by monitoring the weed species that emerged in the unweeded control plots throughout the experimental period. The weed community was primarily dominated by annual grasses, primarily Digitaria sanguinalis and Eleusine indica. Common broadleaf weeds such as Portulaca oleracea and Capsella bursa-pastoris were also observed. This composition reflects a typical weed complex in the region. It aligns with the known efficacy profile of acetochlor, which is highly effective against germinating grass and small-seeded broadleaf weeds.
2.4. Herbicide Efficacy in Weed Control
Weed control efficacy was evaluated at 15, 30, 45, and 60 days after application (DAA). A 0.50 m × 0.50 m PVC quadrat (0.25 m2 sampling area) was randomly positioned at three locations within the experimental plot to count weed individuals, thereby facilitating the calculation of weed control rates and species composition. This final assessment at 60 DAA also included cutting the weeds within the quadrat at ground level to determine their fresh weight. After this final assessment, the experiment transitioned to a crop maintenance phase. To prevent weed competition from affecting subsequent crop growth and yield, all herbicide treatment plots were manually weeded every 14 days from 60 DAA until the complete closure of the crop canopy. For the weed-free control treatment, this regime of manual weeding every 14 days had been maintained since O. japonicus planting until the crop canopy was fully closed. Weed control efficacy and fresh weight control efficacy were calculated relative to the unweeded control plot (described in Section 2.3.2) using the following formulas, respectively:
Weed control efficacy (%) = (1 − number of weeds in herbicide-treated plot/
number of weeds in unweeded control plot) × 100
number of weeds in unweeded control plot) × 100
Weight control efficacy (%) = (1 − fresh weight of weeds in herbicide-treated
plot/fresh weight of weeds in unweeded control plot) × 100
plot/fresh weight of weeds in unweeded control plot) × 100
2.5. Effect of Herbicide on the Agronomic Traits and Yield of O. japonicus
The effect of herbicide on the agronomic traits and yield of O. japonicus was studied, focusing on several parameters: leaf length, root length, leaf number, root number, tiller number, root tuber number, leaf width, root tuber diameter, root tuber length, shoot dry weight, root dry weight and root tuber dry weight. Samples were collected on 27 March 2025. At this time, the plants had reached maturity, which is the optimum stage for harvest to determine the final yield. Ten plants were randomly selected at each plot, and the numbers of leaves, roots, tillers and root tubers were counted. The leaf length and root length were measured with a ruler, and the leaf width was measured using a vernier caliper. Three root tubers were randomly selected from each plant, and the length and diameter of root tubers were measured by vernier caliper. Finally, the shoot, root and root tuber of the plant were separated and dried in an 50 °C oven (101-4ARS, Ever Bright Medical Treatment Instrument, Beijing, China) to measure the dry weight of shoot, root and root tuber. After harvesting, all root tubers from each plot were sun-dried. The average ambient temperature during this process was 19 °C. Drying was considered complete when a constant weight was achieved, meeting the standard of moisture content below 18%. The dry weight was then measured for yield calculation.
2.6. Quality Determination of O. japonicus
The primary bioactive compounds in O. japonicus, including saponins, flavonoids, and polysaccharides [13], were analyzed as follows. Total saponins were extracted by heat reflux extraction with n-butanol saturated with water and determined by ultraviolet–visible spectrophotometry using an A360 spectrophotometer (AOE Instruments, Shanghai, China) [11]. Total flavonoids were extracted by ultrasonic-assisted extraction with methanol using a KQ-5200DV numerical control ultrasonic cleaner (Kunshan Ultrasonic Instrument, Suzhou, China) and determined by ultraviolet–visible spectrophotometry using an A360 spectrophotometer (AOE Instruments, Shanghai, China) [18]. Total polysaccharides were extracted by ultrasonic-assisted extraction with 95% ethanol using a KQ-5200DV numerical control ultrasonic cleaner (Kunshan Ultrasonic Instrument, Suzhou, China) and determined by ultraviolet–visible spectrophotometry using an A360 spectrophotometer (AOE Instruments, Shanghai, China) [19]. Ophiopogonin B, Ophiopogonin D, and Ophiopogonin D′ were determined according to the method of Feng [20] using high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with an evaporative light-scattering detector (HPLC-ELSD) on a Thermo UltiMate3000 HPLC system (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) equipped with an Alltech ELSD 6000 detector (Alltech, Chicago, IL, USA). Methylophiopogonanone A and Methylophiopogonanone B were determined according to the method of Wu et al. [18] using high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) on a Thermo UltiMate3000 HPLC system (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA).
2.7. Data Processing
The experimental data were organized and pre-processed using Microsoft Office Excel 2021 (Microsoft Corporation, Redmond, WA, USA). Statistical analyses, including one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), were conducted using SPSS Statistics 27.0 (IBM Corporation, Armonk, NY, USA). Following a significant result from the ANOVA, multiple comparisons were performed using Tukey’s HSD test at a significance level of p < 0.05. Data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD). Graphs were generated with GraphPad Prism 8.0.0 (GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA, USA). Correlation analysis was specifically performed using Origin 2021 (OriginLab Corporation, Northampton, MA, USA).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Control Efficacy of Acetochlor Nanocapsules on Weeds
As shown in Table 1, when applied at 1800 g a.i. ha−1, acetochlor nanocapsules showed significantly higher weed control efficacy and weight control efficacy from 15 DAA to 60 DAA compared to other treatments. The weed control effect reached 96.54% at 45 DAA, indicating that high-dose acetochlor nanocapsules provided excellent weed control in O. japonicus fields. At 15 DAA, the weed control effect of 900 g a.i. ha−1 acetochlor EC was higher, although not statistically significantly, than that of nanocapsules at the same dosage. However, as time progressed, the control efficacy of acetochlor EC decreased, while that of acetochlor nanocapsules remained largely consistent. From 30 to 60 days after application, the weed control effect of acetochlor EC was lower than that of nanocapsules at the same dosage. Although this difference was not statistically significant, the trend suggests that the nanocapsule formulation may extend the duration of weed control. Previous research in rapeseed fields acetochlor nanocapsules provided superior weed control efficacy and a longer persistence compared to the control agent acetochlor EC. These findings are consistent with the results of the present study [10]. This study found that acetochlor nanocapsules provided excellent and lasting control of weeds in O. japonicus fields, a finding consistent with the research by Volova et al. [21] in wheat and barley fields. Their research demonstrated that slow-release formulations of metribuzin and tribenuron methyl herbicides effectively controlled various weed species and exhibited a longer duration of activity compared to conventional formulations. These findings collectively underscore the universal advantage of sustained-release technology across different cropping systems and active ingredients. Furthermore, a study by Zhila et al. [22] showed that experimental formulations containing metribuzin and tribenuron-methyl embedded in a biodegradable poly-3-hydroxybutyrate matrix exhibited significantly higher herbicidal activity against weeds compared to their commercial formulations.

Table 1.
Weed control efficacy of various acetochlor formulations over time.
3.2. Effect of Herbicide on the Agronomic Traits and Yield of O. japonicus
As shown in Table 2, the number of leaves was the only agronomic trait that showed a significant difference among treatments. In contrast, all other measured traits, including leaf length, leaf width, root length, root tuber diameter, root tuber length, and dry weights of shoot, root, and root tuber, showed no significant differences. The high-dose acetochlor nanocapsule treatment (1800 g a.i. ha−1) resulted in a leaf count that was not significantly different from the weed-free control and was significantly higher than the results from the acetochlor EC and low-dose nanocapsule treatments. This result was likely because the weed control efficacy of the EC and low-dose nanocapsule treatments decreased from 30 to 60 DAA, which led to increased weed competition and subsequently inhibited the above ground growth of O. japonicus.

Table 2.
Agronomic traits of O. japonicus as influenced by different acetochlor treatments.
As shown in Figure 1, the yields for both the high-dose (1800 g a.i. ha−1) and medium-dose (900 g a.i. ha−1) acetochlor nanocapsule treatments were not significantly different from the weed-free control. This result demonstrates that these nanocapsule formulations effectively prevented yield loss by suppressing weed competition to a level comparable to complete weed removal.
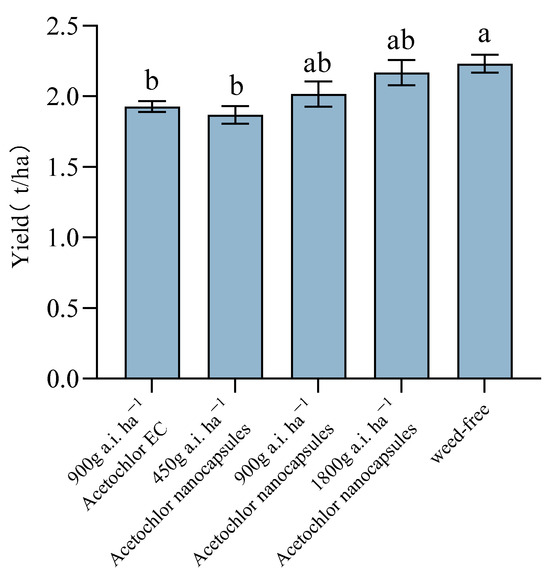
Figure 1.
Root tuber yield of O. japonicus in response to different weed control strategies. Data are presented as mean ± SD (n = 3). Bars sharing the same lowercase letter are not significantly different according to Tukey’s HSD test (p < 0.05).
In the production of Chinese medicinal herbs, “excellent shape” is often regarded as the foundation for “high quality” [23]. Therefore, the impact of agrochemical inputs on the root tuber morphology of O. japonicus is of considerable importance. Zhang et al. [16] conducted a study on the physiological and biochemical effects of paclobutrazol on O. japonicus. They found that while high dosages of paclobutrazol significantly increased the yield, they also resulted in elongated root tubers and abnormal shapes, which do not meet the “excellent shape” standards necessary for medicinal materials. In contrast, this study demonstrated that there were no significant differences in the length and diameter of O. japonicus root tubers across various acetochlor treatments compared to the control group. These results indicate that the applying acetochlor does not negatively impact root tuber morphology, supporting its potential use in cultivating O. japonicus without compromising shape-related quality criteria. Furthermore, the high-dose acetochlor nanocapsule treatment did not show any significant adverse effects on the agronomic traits or yield of O. japonicus, indicating a favorable safety profile. As evidenced by the research of Salac et al. [24], high molecular weight poly (lactic acid)-based metazachlor microparticles not only maintained herbicidal efficacy comparable to that of a commercial formulation but also exhibited lower phytotoxicity during the early growth stages of rapeseed seedlings. This reduced phytotoxicity is attributed to the sustained-release system, which avoids an initial burst release of the active ingredient, thus minimizing potential stress on the crop.
3.3. Correlation Analysis Between Agronomic Traits and Yield of O. japonicus
A correlation analysis was conducted among 12 agronomic traits and the yield of O. japonicus, with the results presented in Figure 2. The yield of O. japonicus showed a highly significant positive correlation with both root tuber dry weight and the number of root tubers. Additionally, there was a significant positive correlation between yield and leaf number. Root tuber dry weight exhibited a highly significant positive correlation with the number of root tubers, and a significant positive correlation with root tuber length, root tuber diameter, and leaf number. Furthermore, root dry weight showed a highly significant positive correlation with shoot dry weight, root tuber number, and root number, along with a significant positive correlation with leaf number. Shoot dry weight displayed a highly significant positive correlation with root number and a significant positive correlation with the number of root tubers. A significant positive correlation was also observed between root tuber length and root tuber diameter. Similarly, Root tuber diameter demonstrated a significant positive correlation with the number of root tubers. Moreover, Root tuber number was highly significantly positively correlated with root number and leaf number, and significantly positively correlated with tiller number and leaf length. Root number also was significantly positively correlated with root length and leaf number, while root length displayed a significant positive correlation with tiller number. Additionally, a highly significant positive correlation was identified between tiller number and leaf number.
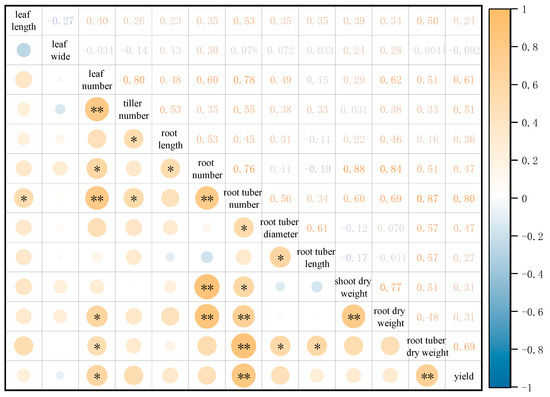
Figure 2.
Correlation matrix between agronomic traits and yield of O. japonicus. The diagonal represents the distribution of each variable. The upper triangle displays the correlation coefficients. The lower triangle displays the significance of correlations, where the size and color intensity of the symbols are proportional to the strength of the correlation. * Denote significant correlations (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01).
Kagimbo et al. [25] conducted a correlation analysis to explore the relationship between yield and yield-related traits in sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas [L.] Lam.). They found significant positive correlations between root yield and the number of roots per plot, as well as between dry mass and ground coverage. Additionally, there was a positive correlation between root yield and ground coverage. Similarly, Zongo et al. [26] investigated the relationship between peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) yield and agronomic traits, and found that pod and kernel yields were significantly positively correlated with hundred-kernel weight and shelling percentage. Consistent with these findings, the present study demonstrated that in O. japonicus, yield showed a highly significant positive correlation with both root tuber dry weight and root tuber number, indicating that these two traits are the most critical agronomic factors influencing the yield potential of this medicinal crop.
3.4. Effect of Herbicide on the Nutritional Quality of O. japonicus
O. japonicus is a Chinese medicinal material known for its active compounds with medicinal properties. It is important to investigate whether the application of acetochlor affects the efficacy and quality of O. japonicus. In this study, we focused on several key constituents with reported anti-cancer properties: Ophiopogonin D [27], Ophiopogonin D′ [28], and Ophiopogonin B [29], Methylophiopogonanone A [30], Methylophiopogonanone B [31]. The experimental results are summarized in Table 3. Statistical analysis revealed that none of the measured quality parameters—including total saponins, total polysaccharides, total flavonoids, and the specific compounds Methylophiopogonanone A, Methylophiopogonanone B, Ophiopogonin D, Ophiopogonin B, and Ophiopogonin D′—showed any statistically significant differences across the various treatments. Siddiqui et al. [32] reported that weed competition not only reduced potato tuber yield but also negatively affected protein, starch, and secondary metabolite levels in the tubers. In this study, the total flavonoid content under the treatments of the acetochlor EC (900 g a.i. ha−1) and low-dose nanocapsule (450 g a.i. ha−1) was lower than that of the control group. However, this difference was not statistically significant. This suggests that weed competition, resulting from compromised weed control, may pose a potential threat to the nutritional quality of O. japonicus, in addition to reducing its yield.

Table 3.
Content of bioactive compounds in O. japonicus as affected by different acetochlor treatments.
The effects of herbicides on crop quality have been documented across various species. For instance, Hamoda et al. [33] reported that the application of post-emergence herbicides in the wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) fields effectively suppressed weeds, reduced weed competition, and negatively impacted the nutritional quality of wheat. In contrast, Shi et al. [34] found that while herbicide use in rice (Oryza sativa L.) fields increased yield, it reduced the nutritional and cooking quality of rice. Noworolnik et al. [35] observed that herbicides increased grain protein content and grain filling in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.), with interactions observed between herbicide treatments and barley varieties. Similarly, Cutulle et al. [36] examined the effects of several herbicides on the nutritional composition of sweet corn (Zea mays L.) and found increased fructose and glucose content but reduced levels of maltose or sucrose. This shift may result from herbicide-induced disruptions in biochemical pathways, ultimately altering the nutritional quality, flavor, and overall plant health of edible crops. In the present study, none of the acetochlor nanocapsule treatments adversely affected the medicinal components of O. japonicus, indicating that this formulation is safe for use and does not compromise the nutritional quality of this medicinal plant.
The development of controlled-release formulations like micro/nanocapsules offers a promising approach to enhancing herbicide performance. For example, Chen et al. [37] reported that pretilachlor polyurea microcapsules provided more sustained weed control than a commercial EC formulation. Similarly, Fogleman et al. [38] observed that an acetochlor microcapsule formulation was safer for rice than the EC formulation. Furthermore, Guo et al. [10] showed that an acetochlor nano-formulation effectively controlled grass weeds like Alopecurus aequalis and Polypogon fugax. Despite these advancements, the performance of such formulations in high-value medicinal crops like O. japonicus remains poorly understood. This study evaluated whether acetochlor nanocapsules could provide effective and safe weed control in this medicinal crop. We found that the nanocapsules offered sustained weed suppression while maintaining both yield and medicinal quality, demonstrating their potential for use in specialized cropping systems.
Our experiment revealed that all treatments exhibited reduced weed control after 45 days. This is typical of pre-emergence herbicides, which naturally degrade in the soil, resulting in lower their concentration and effectiveness over time [39]. Although this degradation presents challenges for achieving complete season-long control from a single application for crops like O. japonicus, the high-dose nanocapsules demonstrated extended efficacy, lasting up to 60 days. This confirms their superior controlled-release properties compared to the EC formulation.
The growing issue of herbicide resistance poses a significant threat to sustainable crop production [40]. In this context, the development of nano-formulations may offer new opportunities associated with resistance management. While target-site resistance to acetochlor is less common, enhanced metabolic detoxification in weeds is a well-known mechanism for amide herbicides [41]. Nano-formulations may offer a strategic advantage by altering the herbicide’s release profile. More controlled and sustained release could minimize the initial, sub-lethal exposure, which often selects for resistant weed biotypes and may ensure a longer window of effective concentration. This might also help in effectively controlling weeds with slightly elevated metabolic resistance. Future research should directly investigate the selection pressure exerted by nanocapsules compared to conventional formulations on resistant weed populations. Furthermore, exploring nano-formulations that combine herbicides with different modes of action could provide a proactive approach to resistance management.
Although acetochlor is not registered for use on O. japonicus in China, it has shown promising results by significantly reducing weed interference without negatively impacting the root tuber shape and nutrient composition of O. japonicus. High-dose (1800 g a.i. ha−1) acetochlor nanocapsule provided the best outcomes in terms of weed control and root tuber productivity, with yields reaching 2.17 t ∙ ha−1. These findings suggest that acetochlor nanocapsule has potential for selective use in O. japonicus production, paving the way for further studies aimed at their registration and incorporation into production systems. The primary objectives in the production of Chinese medicinal herbs are to maximize yield and optimize quality. However, a common and challenging issue in this process is the frequent inconsistency between biomass accumulation and the dynamic changes in the content of bioactive compounds [42]. Therefore, further research is needed to clarify the relationship between weed competition and both the yield and quality of O. japonicus. The ultimate goal is to establish with the ultimate goal of establishing an effective chemical weed control system tailored to its cultivation. Additionally, although acetochlor demonstrated a safety profile in this study, further investigations at the physiological, biochemical, and molecular levels are essential to elucidate the detoxification and metabolic mechanisms of acetochlor in O. japonicus.
It is important to acknowledge the limitations of this study. The evaluation of weed control efficacy was conducted over a 60-day period, which, while covering the critical stages of crop–weed competition, may not fully capture the long-term dynamics of the weed seed bank or later-season weed infestations. As such, the findings primarily reflect the initial and mid-term efficacy of the acetochlor nanocapsules. Future research should involve multi-location and multi-year trials to verify the environmental robustness of the acetochlor nanocapsule formulation and to develop integrated weed management strategies suitable for the entire growth cycle of O. japonicus. Finally, this study concentrated on agronomic and quality parameters, but it did not include a cost–benefit analysis. Assessing the economic viability of producing and applying the nanocapsules compared to conventional weeding methods is crucial for practical adoption and will be an important focus of future research.
4. Conclusions
This study demonstrates that the novel acetochlor nanocapsule formulation is an effective method of weed control in O. japonicus cultivation. The high-dose nanocapsule treatment (1800 g a.i. ha−1) achieved excellent and sustained weed control, which translated directly into economic benefits by preventing yield losses associated with weed competition. Furthermore, the high-dose nanocapsule treatment did not adversely affect the growth, development, or yield of O. japonicus, showing comparable performance to the weed-free control in most measured agronomic traits and root tuber morphology. Additionally, the treatment did not affect the content of key medicinal compounds (saponins, polysaccharides, flavonoids), which are crucial for the quality and efficacy of this Chinese medicinal material.
In conclusion, acetochlor nanocapsules address the primary challenges in the production of O. japonicus: effective weed control, high yield, and maintained medicinal quality. Their use can reduce reliance on labor-intensive manual weeding, providing a more reliable and efficient production strategy. While this study demonstrates these advantages under the specific conditions of a single site and season, future research is essential to validate these findings across diverse environments and to investigate the long-term environmental behavior of the formulation. Furthermore, elucidating the molecular mechanisms of acetochlor metabolism in O. japonicus is crucial for ensuring crop safety and facilitating the registration of this promising technology.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.Q. and S.Z.; methodology, S.Z., Q.L. and D.Z.; investigation, S.Z., Q.L. and D.Z.; resources, Q.L. and D.Z.; data curation, S.Z.; formal analysis, S.Z.; writing—original draft, S.Z.; writing—review and editing, L.H., K.Q. and W.D.; project administration, K.Q.; funding acquisition, K.Q., W.D. and L.H.; supervision, L.H. and W.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the China Agriculture Research System (CARS-21) and Mianyang Central Government-Guided Local Science and Technology Development Fund (2025ZYDF89).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Crop Characteristic Resources Creation and Utilization Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province, Academy of Agricultural Sciences, and the Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Southwest University, for its support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Su, S. Review of amide herbicides. Pesticide 2002, 11, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.S.; Li, C.Y. Cytochrome P450 CYP90D5 Enhances Degradation of the Herbicides Isoproturon and Acetochlor in Rice Plants and Grains. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 17399–17409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Ma, L.; Wei, R.; Xu, L.; Ma, Y.; Dang, J.; Chen, Z.; Ma, S.; Li, S. Physiology, Biochemistry, and Transcriptomics Jointly Reveal the Phytotoxicity Mechanism of Acetochlor on Pisum sativum L. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2024, 43, 2005–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.N.; Zhang, J.J.; Liu, J.T.; Zhang, N.; Ma, L.Y.; Lu, F.F.; Chen, Z.J.; Shi, Z.; Si, W.J.; Liu, C.; et al. Biodegrading Two Pesticide Residues in Paddy Plants and the Environment by a Genetically Engineered Approach. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 4947–4957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Z.; Bai, X.; Zhang, T.; Yang, Z. Ultrasound-assisted extraction and solid-phase extraction for the simultaneous determination of five amide herbicides in fish samples by gas chromatography with electron capture detection. J. Sep. Sci. 2017, 40, 1142–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, F.; Xu, Y.; Tai, Z. Development of a MOF-based SPE method combined with GC-MS for simultaneous determination of alachlor, acetochlor and pretilachlor in field soil. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutasy, B.; Hegedus, G.; Kiniczky, M.; Pallos, J.P.; Nagy, A.; Pocsi, I.; Pakozdi, K.; Kallai, M.; Weingart, C.; Andor, K.; et al. Garlic Extracts Nanoliposome as an Enhancer of Bioavailability of ABA and Thiamine Content and as an Antifungal Agent Against Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. pisi Infecting Pisum sativum. Agronomy 2025, 15, 991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, R.; You, C.; Qu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Deng, Y.; Ma, W.; Huang, C. Recent advances in the design of controlled- and sustained-release micro/nanocarriers of pesticide. Environ. Sci. Nano 2023, 10, 351–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, H.V.; Dhiman, S.; Ansari, N.G. Recent trends in techniques, process and sustainability of slow-release formulation for pesticides. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 216, 118764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Yang, Q.; Yan, W.; Li, B.; Qian, K.; Li, T.; Xiao, W.; He, L. Controlled release of acetochlor from poly (butyl methacrylate-diacetone acrylamide) based formulation prepared by nanoemulsion polymerisation method and evaluation of the efficacy. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2014, 94, 1001–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commission, C.P. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China (Part One); Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission: Beijing, China, 2020.
- Liu, Q.; Lu, J.-J.; Hong, H.-J.; Yang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.-J. Ophiopogon japonicus and its active compounds: A review of potential anticancer effects and underlying mechanisms. Phytomedicine 2023, 113, 154718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, F.; Weckerle, C.S.; Heinrich, M. Liriopogons (Genera Ophiopogon and Liriope, Asparagaceae): A Critical Review of the Phytochemical and Pharmacological Research. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 769929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Qiu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Luo, L.; Tang, H.; Zhou, X.; Yuan, H.; Wang, W.; Liu, P. Characterization of quality differences of Ophiopogonis Radix from different origins by TLC, HPLC, UHPLC-MS and multivariate statistical analyses. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2022, 45, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.-X.; Li, M.-M.; Wang, T.; Wang, T.-L.; Chen, J.-Y.; Francis, F.; Fan, B.; Kong, Z.-Q.; Dai, X.-F. Screening of pesticide residues in Traditional Chinese Medicines using modified QuEChERS sample preparation procedure and LC-MS/MS analysis. J. Chromatogr. B-Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2020, 1152, 122224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, R.; Chen, D.; Chen, J.; Xiao, O.; Kong, Z.; Dai, X. Effect of Paclobutrazol on the Physiology and Biochemistry of Ophiopogon aponicus. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Chen, J.; Ye, S.; Dai, W.; Lai, Q.; Wang, J.; Wang, T.; Chen, F.; Luo, D. Cultivation Status, Existing Problems, and Development Strategies of Ophiopogon japonicus in Fucheng: A Study Based on a Survey of 139 Households. Mod. Chin. Med. 2022, 24, 1083–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Yang, R.; Zhang, S.; Bao, X.; Li, M.; Zhou, J. Simultaneous Determination of Three Flavone Constituents in Ophiopogonis Radix by HPLC Method. Chin. Pharm. J. 2016, 51, 655–658. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Cai, X.; Yang, R.; Tao, L.; Li, M. Commercial grade standard and quality evaluation of Chuanmaidong medicinal materials. Chin. Tradit. Pat. Med. 2023, 45, 641–646. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, T. Comprehensive Evaluation of Agronomic Traits and Quality of 40 O. Japonicus Germplasm Resources. Master’s Thesis, Southwest University of Science and Technology, Mianyang, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Volova, T.; Shumilova, A.; Zhila, N.; Sukovatyi, A.; Shishatskaya, E.; Thomas, S. Efficacy of Slow-Release Formulations of Metribuzin and Tribenuron Methyl Herbicides for Controlling Weeds of Various Species in Wheat and Barley Stands. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 25135–25147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhila, N.; Murueva, A.; Shershneva, A.; Shishatskaya, E.; Volova, T. Herbicidal activity of slow-release herbicide formulations in wheat stands infested by weeds. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part B-Pestic. Food Contam. Agric. Wastes 2017, 52, 729–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Yuan, Y.; Zheng, H.; Huang, L.Q. Review of contributing factors and research model of “excellent shape, high quality, and superior effect” of Dao-di herbs. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2024, 49, 3977–3985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salac, J.; Sopik, T.; Stloukal, P.; Janasova, N.; Jursik, M.; Koutny, M. Slow release formulation of herbicide metazachlor based on high molecular weight poly(lactic acid) submicro and microparticles. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 16, 6135–6144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagimbo, F.M.; Shimelis, H.; Sibiya, J. Diversity assessment of sweetpotato germplasm collections for yield and yield-related traits in western Tanzania. Acta Agric. Scand. Sect. B-Soil Plant Sci. 2018, 68, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zongo, A.; Nana, A.T.; Sawadogo, M.; Konate, A.K.; Sankara, P.; Ntare, B.R.; Desmae, H. Variability and Correlations among Groundnut Populations for Early Leaf Spot, Pod Yield, and Agronomic Traits. Agronomy 2017, 7, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.-Q.; Wang, S.-Z.; Lei, H.-B.; Liu, X. Ophiopogonin D: Review of pharmacological activity. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1401627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Song, F.; Huang, P. Ophiopogonin D′ inhibited tumour growth and metastasis of anaplastic thyroid cancer by modulating JUN/RGS4 signalling. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2024, 28, e70014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Z.; Li, Z.; Gu, L.; Li, L.; Gao, Q.; Zhang, X.; Fu, J.; Guo, Y.; Li, Q.; Shen, X.; et al. Ophiopogonin B alleviates cisplatin resistance of lung cancer cells by inducing Caspase-1/GSDMD dependent pyroptosis. J. Cancer 2022, 13, 715–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Chen, B.; Chen, S.; Liang, Y.; Chen, D.; Li, X. Methylophiopogonanone A Inhibits Ferroptosis in H9c2 Cells: An Experimental and Molecular Simulation Study. Molecules 2024, 29, 5764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Qin, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, B.; Fang, R.; Bai, M. Methylophiopogonanone B of Radix Ophiopogonis protects cells from H2O2-induced apoptosis through the NADPH oxidase pathway in HUVECs. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 20, 3691–3700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, A.O.; Isik, D.; Jabran, K. Impact of Weed Competition on Morphological and Biochemical Traits of Potato: A Review. Potato Res. 2024, 67, 451–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamoda, A.; Khojah, E.Y.; Radhi, K.S. Synergistic effects of herbicides and gibberellic acid on wheat yield and quality. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 7496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Cheng, X.; Xi, X.; Weng, W.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, R. Effects of a Novel Weeding and Fertilization Scheme on Yield and Quality of Rice. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noworolnik, K.; Leszczynska, D. Effect of selected herbicides on yielding and malting quality of spring barley cultivars. Acta Agric. Scand. Sect. B-Soil Plant Sci. 2017, 67, 303–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutulle, M.A.; Armel, G.R.; Kopsell, D.A.; Wilson, H.P.; Brosnan, J.T.; Vargas, J.J.; Hines, T.E.; Koepke-Hill, R.M. Several Pesticides Influence the Nutritional Content of Sweet Corn. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 3086–3092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Liu, X.; Deng, S.; Wang, H.; Ou, X.; Huang, L.; Li, J.; Jin, C. Pretilachlor Releasable Polyurea Microcapsules Suspension Optimization and Its Paddy Field Weeding Investigation. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogleman, M.; Norsworthy, J.K.; Barber, T.; Gbur, E. Influence of Formulation and Rate on Rice Tolerance to Early-Season Applications of Acetochlor. Weed Technol. 2019, 33, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Sun, J.; Xu, J.; Wang, H. Degradation of acetochlor in soil by adding organic fertilizers with different conditioners. Soil Tillage Res. 2023, 228, 105651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutasy, B.; Takacs, Z.; Kovacs, J.; Bogaj, V.; Razak, S.A.; Hegedus, G.; Decsi, K.; Szekvari, K.; Virag, E. Pro197Thr Substitution in Ahas Gene Causing Resistance to Pyroxsulam Herbicide in Rigid Ryegrass (Lolium Rigidum Gaud.). Sustainability 2021, 13, 6648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhala, A.J.; Singh, M.; Shergill, L.; Singh, R.; Jugulam, M.; Riechers, D.E.; Ganie, Z.A.; Selby, T.P.; Werle, R.; Norsworthy, J.K. Very long chain fatty acid-inhibiting herbicides: Current uses, site of action, herbicide-resistant weeds, and future. Weed Technol. 2023, 38, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Cai, X.; Chen, H.; Bao, X.; Li, M.; Zhou, J. Accumulation of Main Chemical Components in Ophiopogonis Radix in the Process of Development. Chin. Pharm. J. 2016, 51, 533–537. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).