Erosion Assessment by a Fast and Low-Cost Procedure in a Vineyard Under Different Soil Management
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
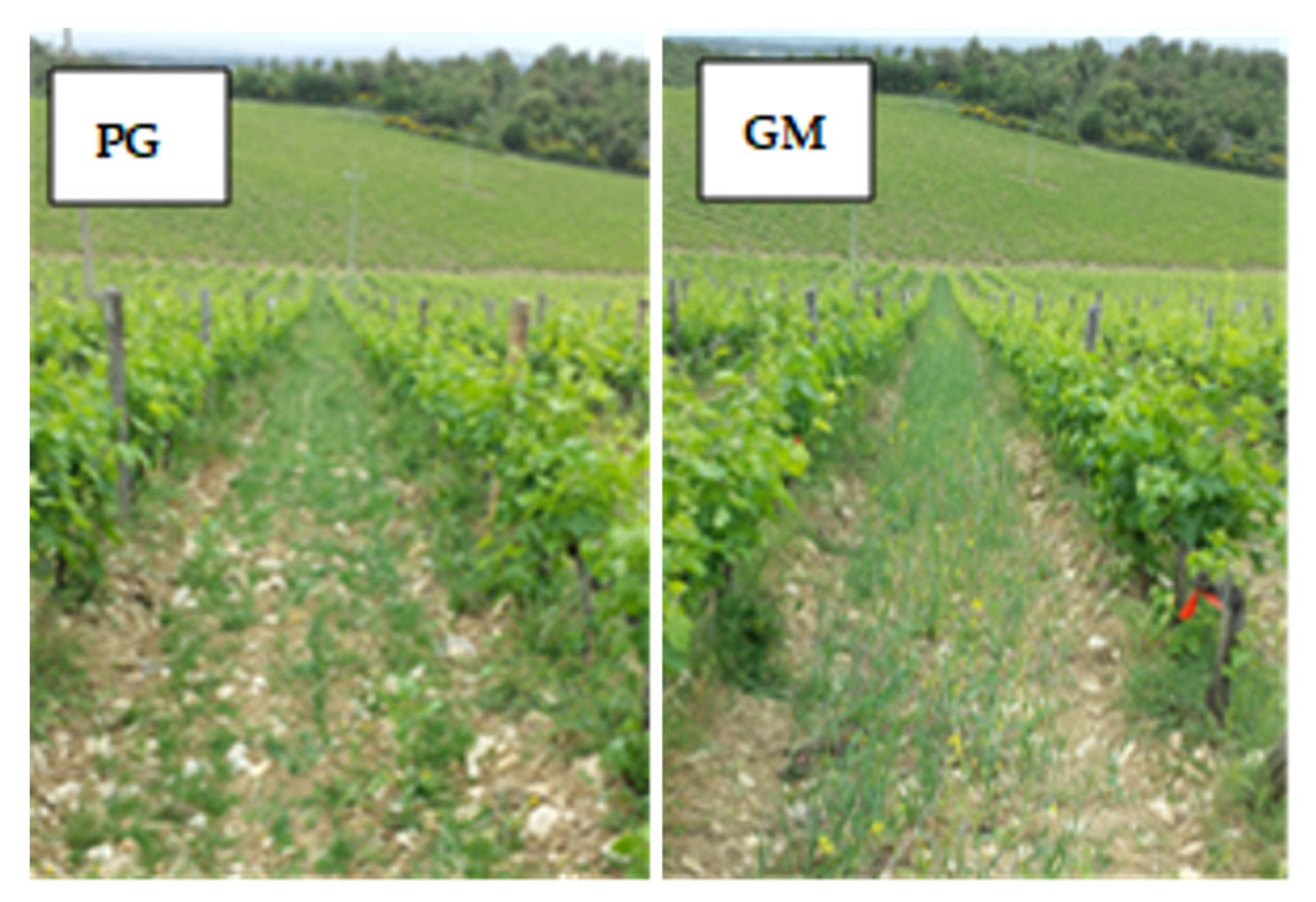
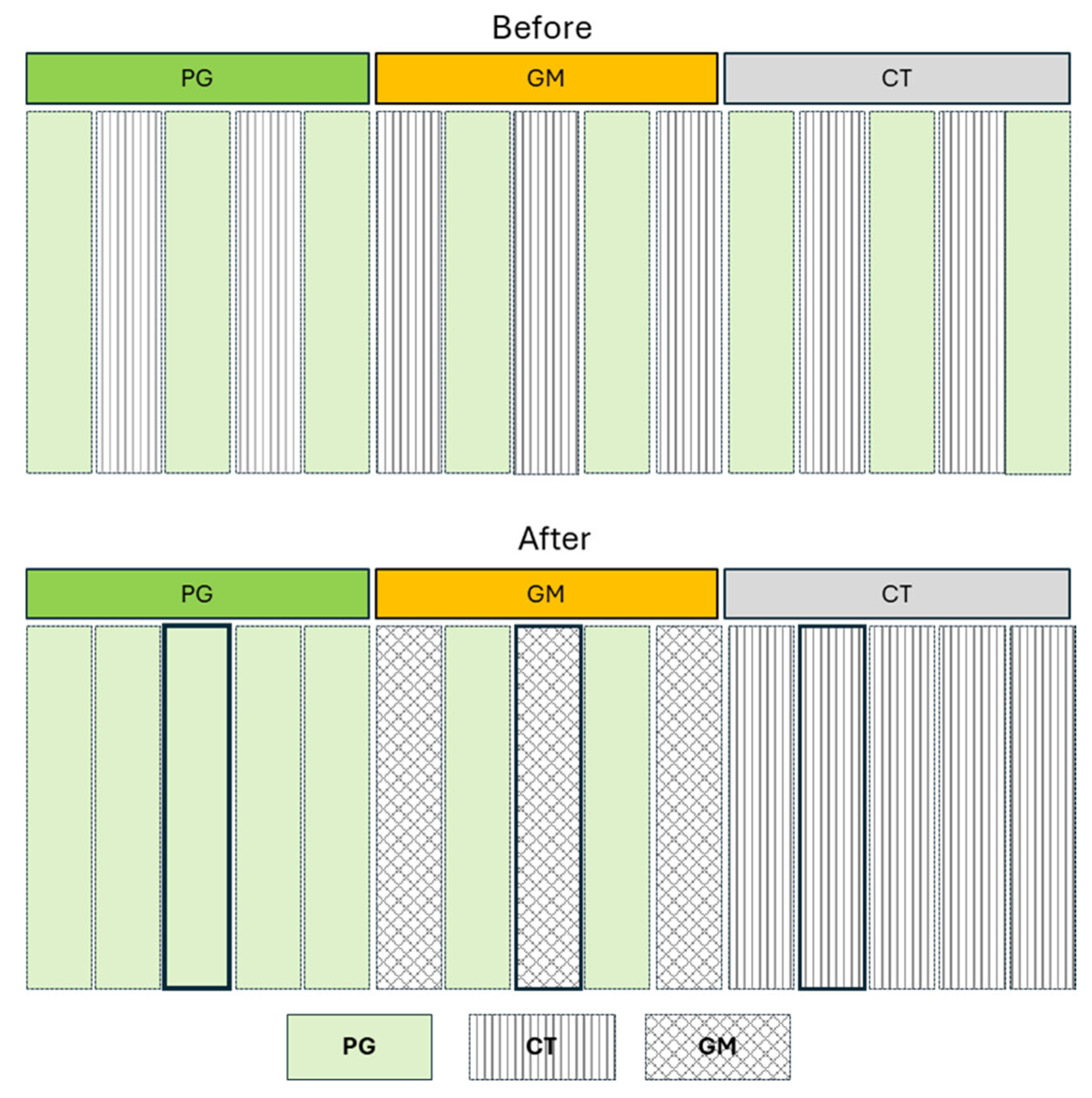
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Soil Sampling and Analyses
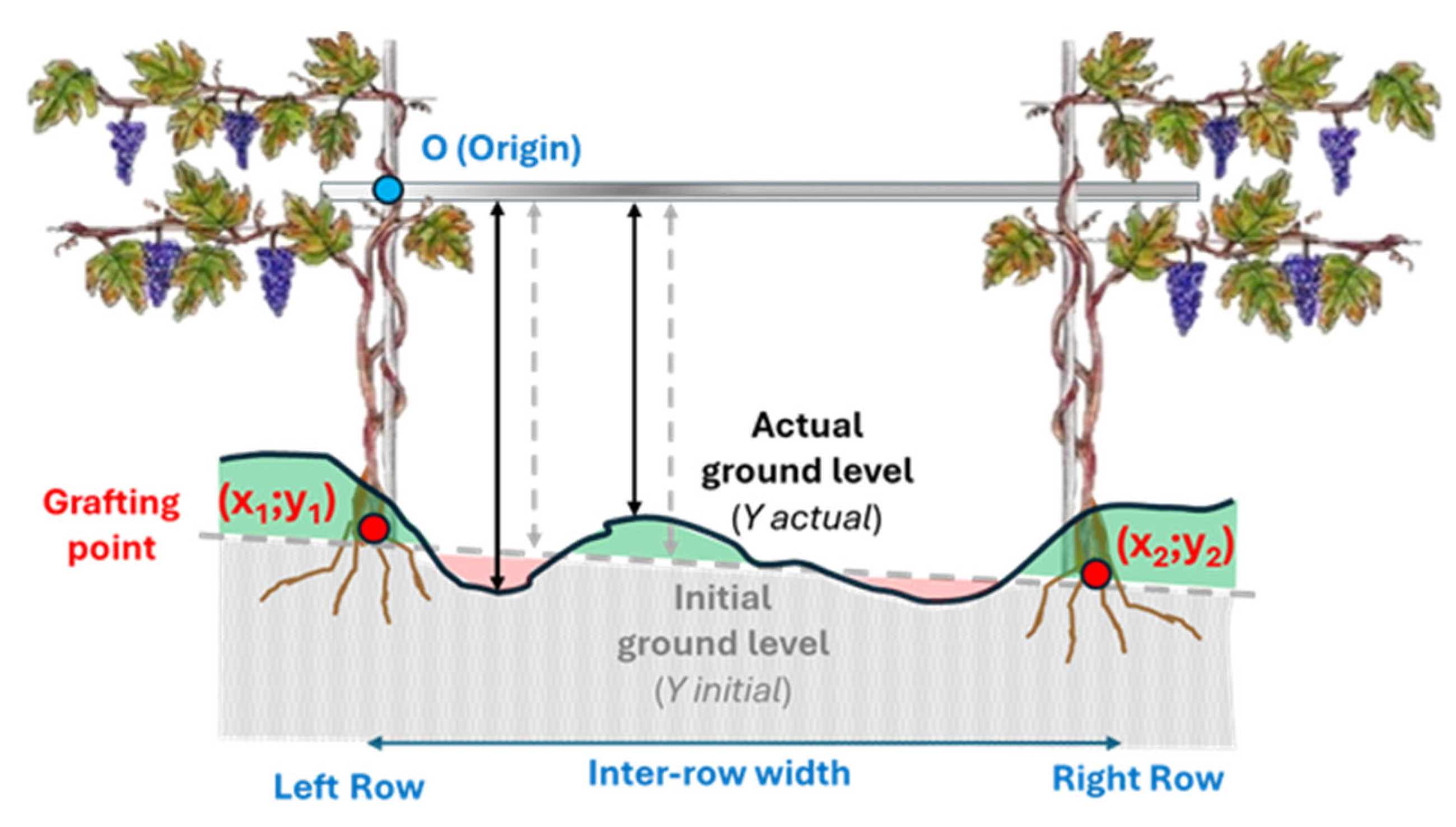
2.3. Soil Surface Survey
2.4. Data Elaboration with ISUMmate_1.1
- (a)
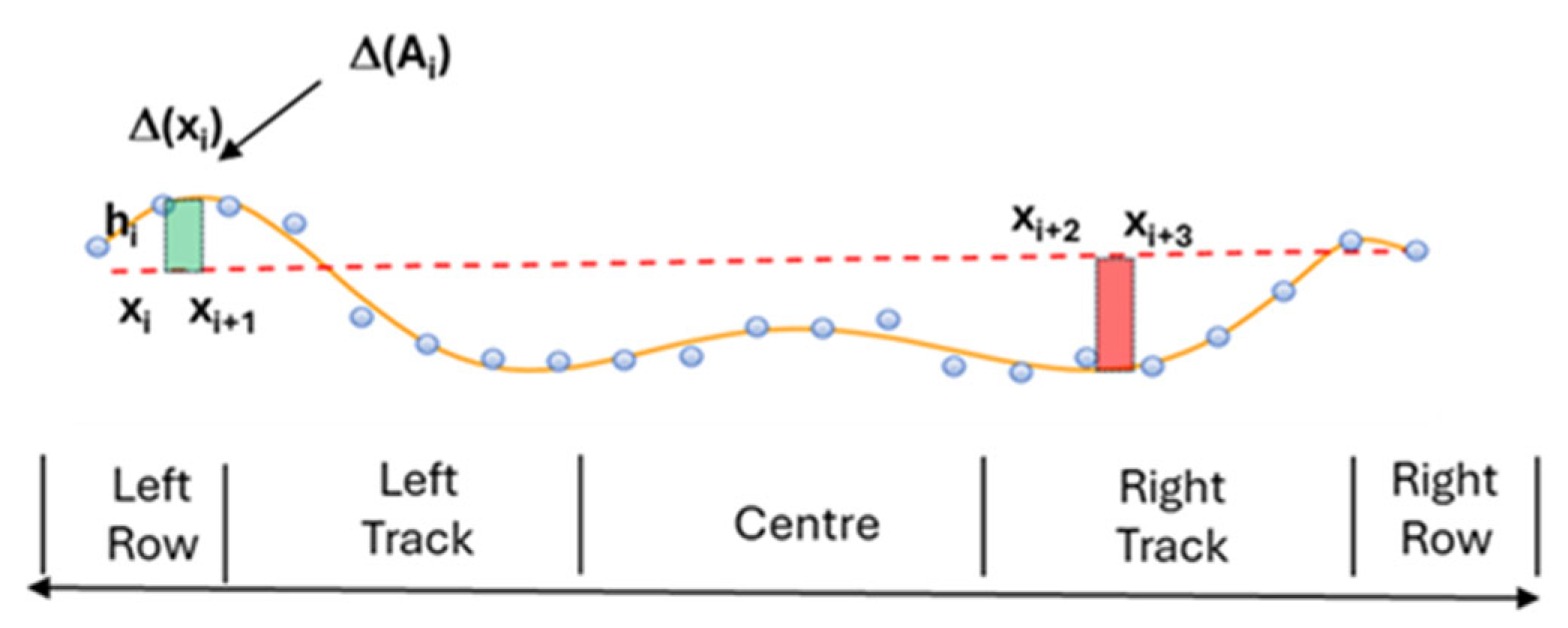
- Calculation of the cross-sectional area
- (b)
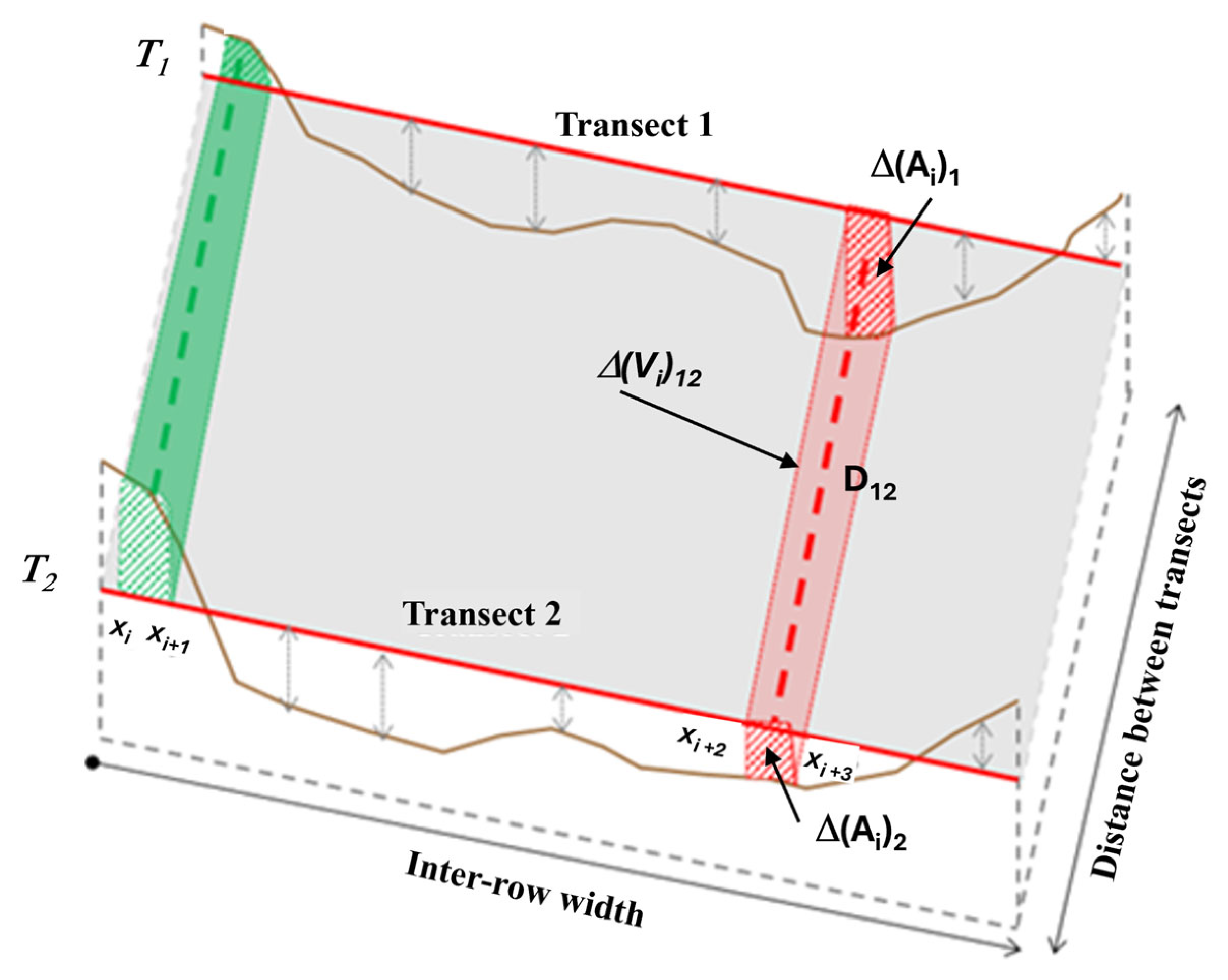
- Volume of soil mobilized between two consecutive transects
- (c)
- Average rate of soil mobilized between consecutive transects T1 and T2
- (d)
- Total volume of mobilized soil
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
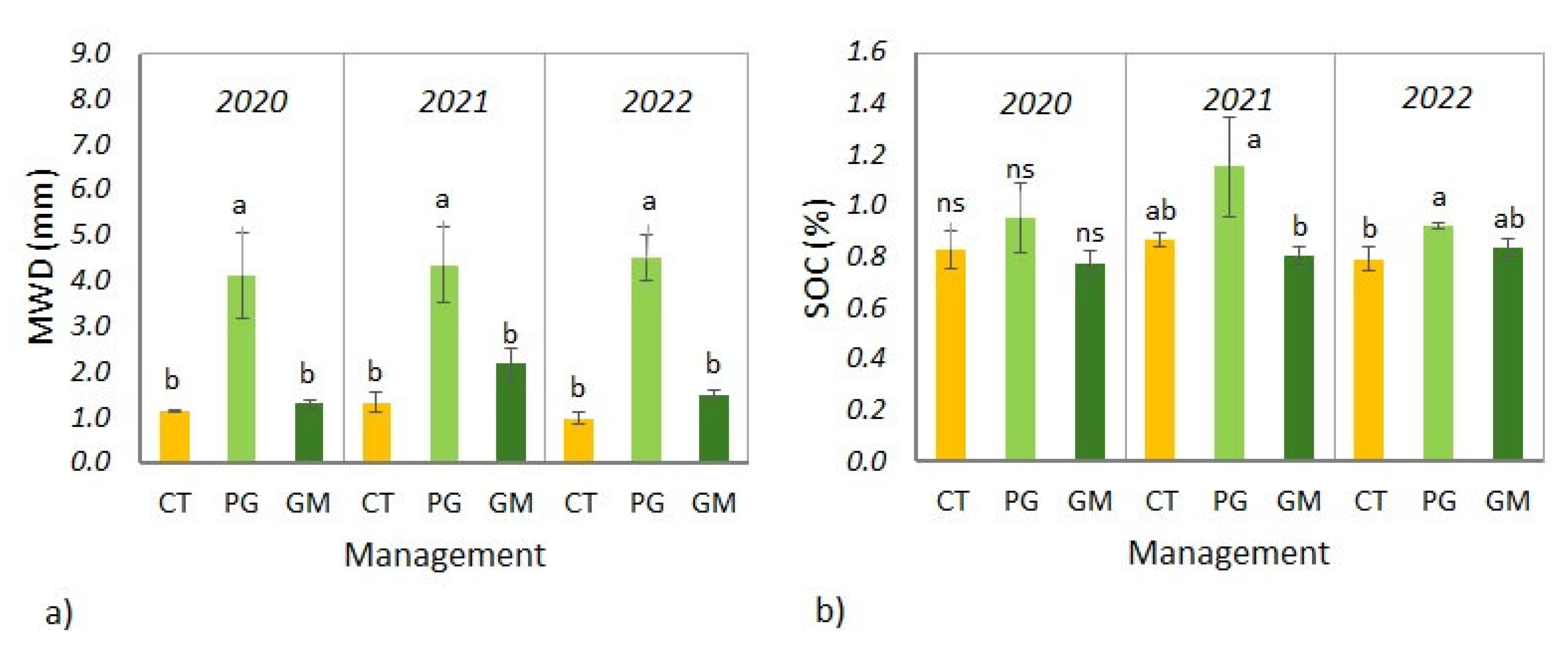
3.1. Dynamics of Soil Aggregate Stability and Organic Carbon Content
3.2. Soil Erosion Quantification
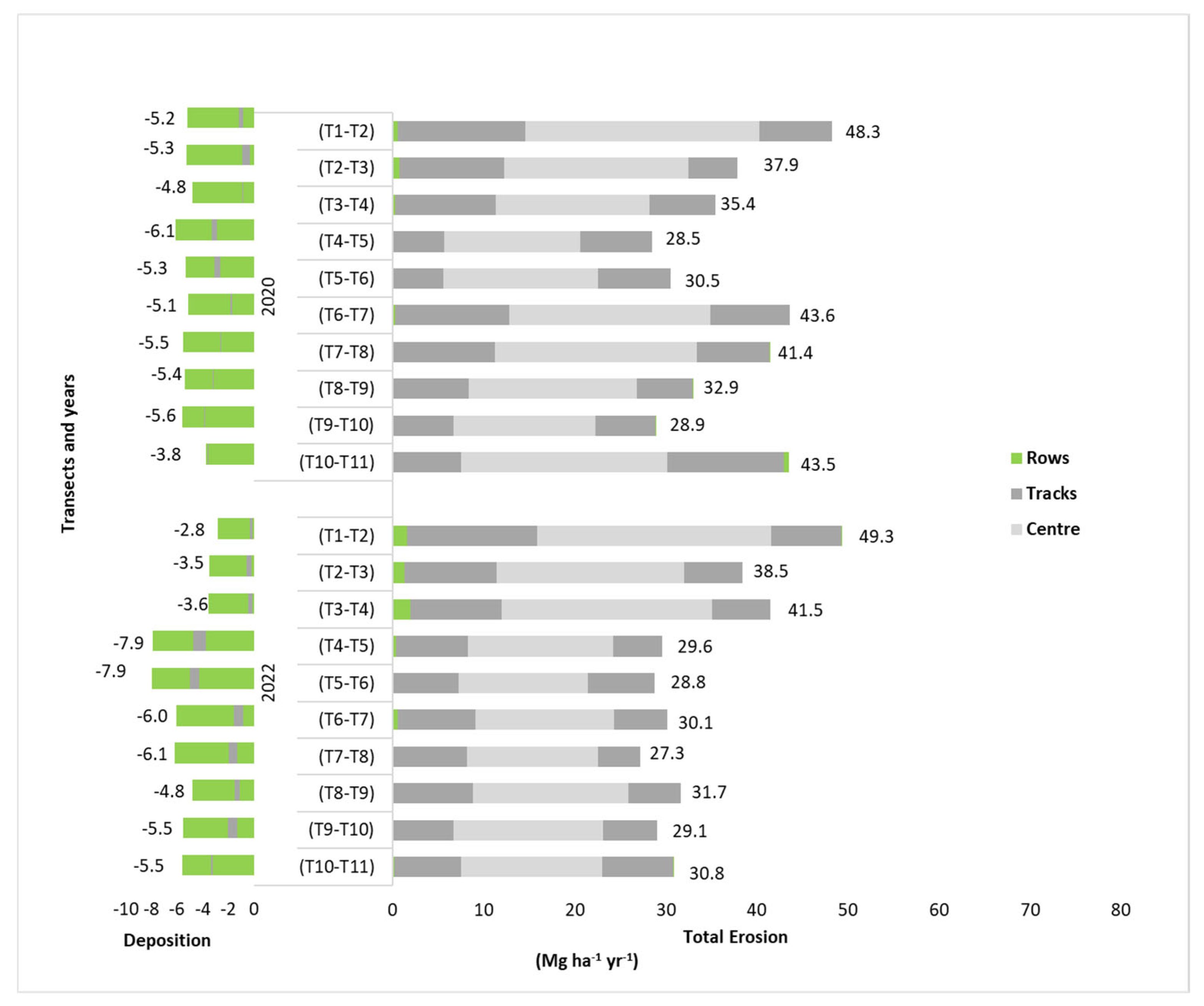
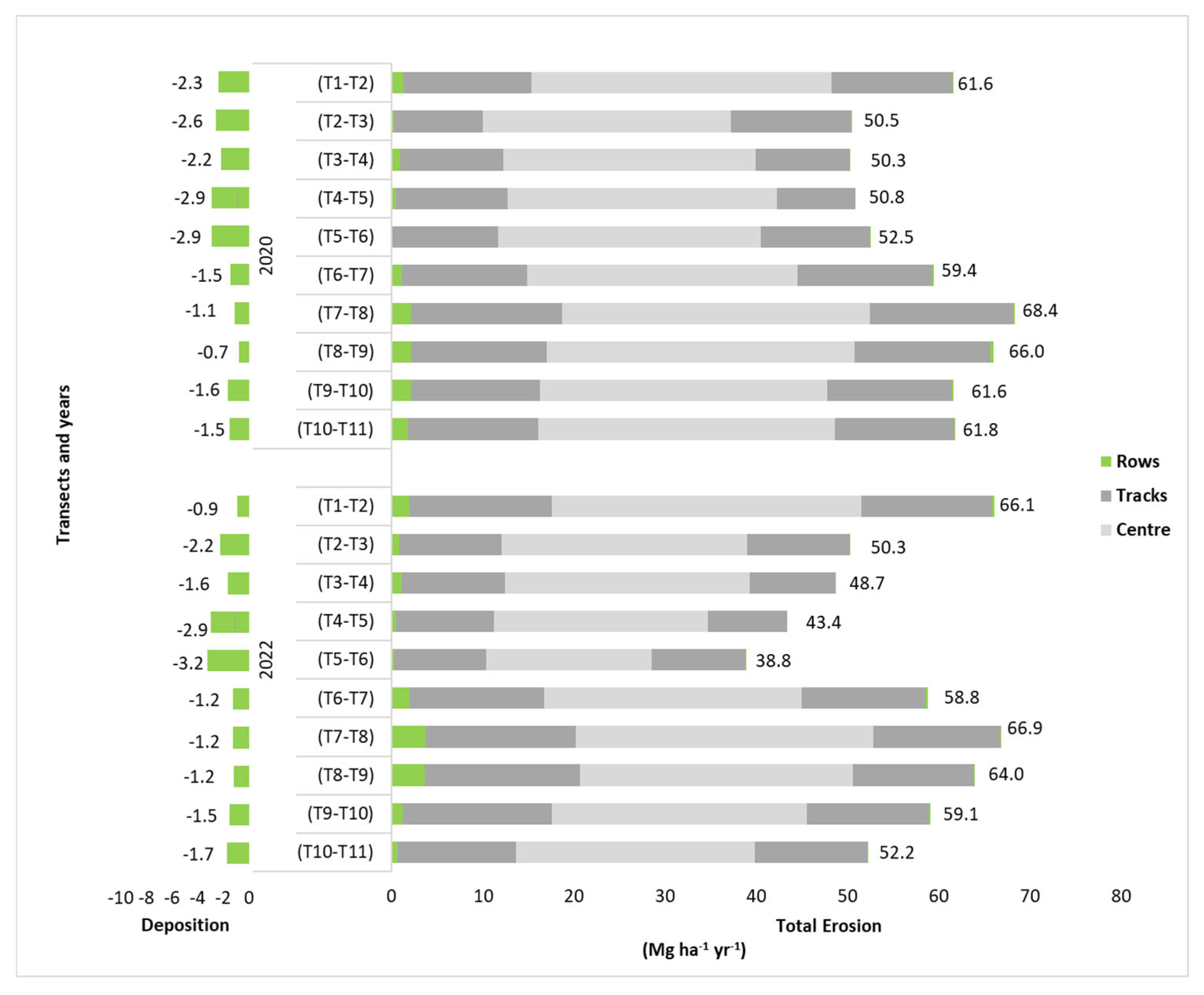
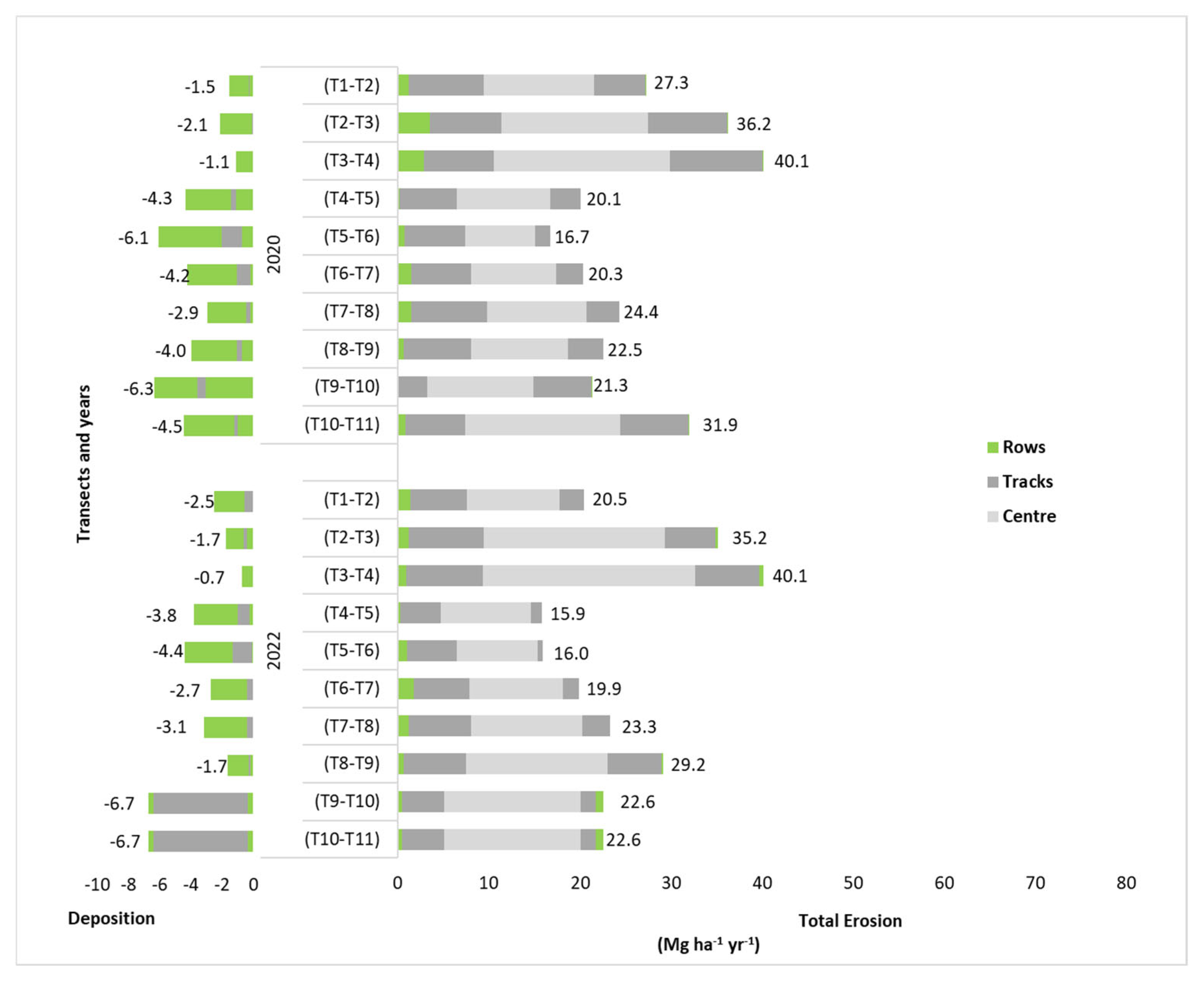
3.3. Distribution of Eroded and Deposited Soil Along the Slope and Within the Inter-Row
3.4. Correlation Between Redistributed Soil Mass and Main Vineyard Geometric Properties for Each Management System
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| A | Surface of the vineyard |
| BD | Bulk density |
| CT | Continuous tillage |
| D | Distance |
| D_Total | Total deposition rate |
| E_Totat | Total erosion rate |
| GM | Green manure |
| MWD | Mean weight diameter |
| P | Total annual rainfall depth |
| PG | Permanent grass cover |
| PTF | Pedotransfer function |
| SOC | Soil organic carbon |
| T(n) | Transect (number) |
| V | Volume |
Appendix A
Appendix A.1

Appendix A.2
| Theses | GM | PG | CT | |
| RRMSE (%) | 1.69 | 1.39 | 1.80 |
References
- Panagos, P.; Ballabio, C.; Poesen, J.; Lugato, E.; Scarpa, S.; Montanarella, L.; Borrelli, P. A Soil Erosion Indicator for Supporting Agricultural, Environmental and Climate Policies in the European Union. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigo-Comino, J. Five Decades of Soil Erosion Research in “Terroir”. The State-of-the-Art. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2018, 179, 436–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corti, G.; Cavallo, E.; Cocco, S.; Biddoccu, M.; Brecciaroli, G.; Agnelli, A. Evaluation of Erosion Intensity and Some of Its Consequences in Vineyards from Two Hilly Environments Under a Mediterranean Type of Climate, Italy. In Soil Erosion Issues in Agriculture; Godone, D., Ed.; InTech: London, UK, 2011; ISBN 978-953-307-435-1. [Google Scholar]
- Pessina, D.; Galli, L.E.; Santoro, S.; Facchinetti, D. Sustainability of Machinery Traffic in Vineyard. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prosdocimi, M.; Jordán, A.; Tarolli, P.; Keesstra, S.; Novara, A.; Cerdà, A. The Immediate Effectiveness of Barley Straw Mulch in Reducing Soil Erodibility and Surface Runoff Generation in Mediterranean Vineyards. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 547, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrelli, P.; Robinson, D.A.; Panagos, P.; Lugato, E.; Yang, J.E.; Alewell, C.; Wuepper, D.; Montanarella, L.; Ballabio, C. Land Use and Climate Change Impacts on Global Soil Erosion by Water (2015–2070). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 21994–22001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intergovernmental Panel On Climate Change (IPCC). Climate Change 2021—The Physical Science Basis: Working Group I Contribution to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, 1st ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2023; ISBN 978-1-009-15789-6. [Google Scholar]
- Panagos, P.; Ballabio, C.; Meusburger, K.; Spinoni, J.; Alewell, C.; Borrelli, P. Towards Estimates of Future Rainfall Erosivity in Europe Based on REDES and WorldClim Datasets. J. Hydrol. 2017, 548, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, R. Soil Organic Matter Content and Crop Yield. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2020, 75, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baloch, S.B.; Ali, S.; Bernas, J.; Konvalina, P.; Naveed, M.; Baloch, F.B.; Jamali, Z.H.; Lošák, T.; Roubík, H.; Ghafoor, A.; et al. Crop Residue Management for Soil Health and Environmental Sustainability: A Comprehensive Review. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2025, 25, 7808–7828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, H.; Lal, R. Tillage Erosion. In Soil Conservation and Management; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 103–125. ISBN 978-3-031-30340-1. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, T.P.; Bressiani, D.; Ebling, É.D.; Reichert, J.M. Best Management Practices to Reduce Soil Erosion and Change Water Balance Components in Watersheds under Grain and Dairy Production. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2024, 12, 121–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaye, J.P.; Quemada, M. Using Cover Crops to Mitigate and Adapt to Climate Change. A Review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2017, 37, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Vicente, M.; Calvo-Seas, E.; Álvarez, S.; Cerdà, A. Effectiveness of Cover Crops to Reduce Loss of Soil Organic Matter in a Rainfed Vineyard. Land 2020, 9, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cárceles Rodríguez, B.C.; Durán Zuazo, V.H.D.; Herencia Galán, J.F.H.; Lipan, L.; Soriano, M.; Hernández, F.; Sendra, E.; Carbonell-Barrachina, Á.A.; Ruiz, B.G.; García-Tejero, I.F. Soil Management Strategies in Organic Almond Orchards: Implications for Soil Rehabilitation and Nut Quality. Agronomy 2023, 13, 749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagliai, M.; Vignozzi, N.; Pellegrini, S. Soil Structure and the Effect of Management Practices. Soil Tillage Res. 2004, 79, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amézketa, E. Soil Aggregate Stability: A Review. J. Sustain. Agric. 1999, 14, 83–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthès, B.; Roose, E. Aggregate Stability as an Indicator of Soil Susceptibility to Runoff and Erosion; Validation at Several Levels. CATENA 2002, 47, 133–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Six, J.; Bossuyt, H.; Degryze, S.; Denef, K. A History of Research on the Link between (Micro)Aggregates, Soil Biota, and Soil Organic Matter Dynamics. Soil Tillage Res. 2004, 79, 7–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagagiolo, G.; Biddoccu, M.; Rabino, D.; Cavallo, E. Effects of Rows Arrangement, Soil Management, and Rainfall Characteristics on Water and Soil Losses in Italian Sloping Vineyards. Environ. Res. 2018, 166, 690–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biddoccu, M.; Ferraris, S.; Opsi, F.; Cavallo, E. Long-Term Monitoring of Soil Management Effects on Runoff and Soil Erosion in Sloping Vineyards in Alto Monferrato (North–West Italy). Soil Tillage Res. 2016, 155, 176–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biddoccu, M.; Guzmán, G.; Capello, G.; Thielke, T.; Strauss, P.; Winter, S.; Zaller, J.G.; Nicolai, A.; Cluzeau, D.; Popescu, D.; et al. Evaluation of Soil Erosion Risk and Identification of Soil Cover and Management Factor (C) for RUSLE in European Vineyards with Different Soil Management. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2020, 8, 337–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanchi, S.; Zecca, O.; Hudek, C.; Pintaldi, E.; Viglietti, D.; D’Amico, M.E.; Colombo, N.; Goslino, D.; Letey, M.; Freppaz, M. Effect of Soil Management on Erosion in Mountain Vineyards (N-W Italy). Sustainability 2021, 13, 1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebhard, G.; Guzmán, G.; Gómez, J.A.; Winter, S.; Zaller, J.G.; Bauer, T.; Nicolai, A.; Cluzeau, D.; Popescu, D.; Bunea, C.; et al. Vineyard Cover Crop Management Strategies and Their Effect on Soil Properties across Europe. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2024, 75, e13573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Colmenero, M.; Bienes, R.; Marques, M.J. Soil and Water Conservation Dilemmas Associated with the Use of Green Cover in Steep Vineyards. Soil Tillage Res. 2011, 117, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salomé, C.; Coll, P.; Lardo, E.; Metay, A.; Villenave, C.; Marsden, C.; Blanchart, E.; Hinsinger, P.; Le Cadre, E. The Soil Quality Concept as a Framework to Assess Management Practices in Vulnerable Agroecosystems: A Case Study in Mediterranean Vineyards. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 61, 456–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, N.S.; Yadav, D.; Chouhan, M.; Bhagat, C.; Kochale, P. Understanding Potential Impact of Green Manuring on Crop and Soil: A Comprehensive Review. Biol. Forum-Int. J. 2023, 15, 832–839. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Yu, A.; Shang, Y.; Wang, P.; Wang, F.; Yin, B.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, D.; Chai, Q. Research Progress on the Improvement of Farmland Soil Quality by Green Manure. Agriculture 2025, 15, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boix-Fayos, C.; Martínez-Mena, M.; Arnau-Rosalén, E.; Calvo-Cases, A.; Castillo, V.; Albaladejo, J. Measuring Soil Erosion by Field Plots: Understanding the Sources of Variation. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2006, 78, 267–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, N.J.; Greenwood, P.; Fister, W. Use of Field Experiments in Soil Erosion Research. In Developments in Earth Surface Processes; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; Volume 18, pp. 175–200. ISBN 978-0-444-63402-3. [Google Scholar]
- Bailey, G.; Li, Y.; McKinney, N.; Yoder, D.; Wright, W.; Washington-Allen, R. Las2DoD: Change Detection Based on Digital Elevation Models Derived from Dense Point Clouds with Spatially Varied Uncertainty. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Nearing, M.A.; Nichols, M.H.; Polyakov, V.O.; Cavanaugh, M.L. Using Terrestrial LiDAR to Measure Water Erosion on Stony Plots under Simulated Rainfall. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2020, 45, 484–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Guan, Y.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, C.; Bai, J.; Chen, K. Determining the Influence of Catchment Area on Intensity of Gully Erosion Using High-Resolution Aerial Imagery: A 40-Year Case Study from the Loess Plateau, Northern China. Geoderma 2019, 347, 90–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadal-Romero, E.; Revuelto, J.; Errea, P.; López-Moreno, J.I. The Application of Terrestrial Laser Scanner and SfM Photogrammetry in Measuring Erosion and Deposition Processes in Two Opposite Slopes in a Humid Badlands Area (Central Spanish Pyrenees). Soil 2015, 1, 561–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Ren, F.; Hu, J.; Yan, L.; Hao, M.; Liu, L.; Gao, J.; Dang, T. Monitoring Soil Erosion on Field Slopes by Terrestrial Laser Scanning and Structure-from-motion. Land Degrad. Dev. 2023, 34, 3663–3680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Li, P.; Hu, J.; Yan, L.; Latifi, H.; Yao, W.; Hao, M.; Gao, J.; Dang, T.; Zhang, S. Development of Gully Erosion Processes: A 3D Investigation Based on Field Scouring Experiments and Laser Scanning. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 265, 112683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigo-Comino, J.; Davis, J.; Keesstra, S.D.; Cerdà, A. Updated Measurements in Vineyards Improves Accuracy of Soil Erosion Rates. Agron. J. 2018, 110, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinnell, P.I.A. A Review of the Design and Operation of Runoff and Soil Loss Plots. CATENA 2016, 145, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenot, J.; Quiquerez, A.; Petit, C.; Garcia, J.-P. Erosion Rates and Sediment Budgets in Vineyards at 1-m Resolution Based on Stock Unearthing (Burgundy, France). Geomorphology 2008, 100, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantini, E.A.C. Linee Guida dei Metodi di Rilevamento e Informatizzazione dei Dati Pedologici; S.EL.CA.: Firenze, Italy, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Diodato, N.; Bellocchi, G. Estimating Monthly (R)USLE Climate Input in a Mediterranean Region Using Limited Data. J. Hydrol. 2007, 345, 224–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemper, W.D.; Rosenau, R.C. Aggregate Stability and Size Distribution. In Methods of Soil Analysis; American Society of Agronomy: Madison WI, USA, 1986; Volume 1, pp. 425–442. [Google Scholar]
- Legout, C.; Leguédois, S.; Le Bissonnais, Y. Aggregate Breakdown Dynamics under Rainfall Compared with Aggregate Stability Measurements. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2005, 56, 225–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigo-Comino, J.; Keshavarzi, A.; Zeraatpisheh, M.; Gyasi-Agyei, Y.; Cerdà, A. Determining the Best ISUM (Improved Stock Unearthing Method) Sampling Point Number to Model Long-Term Soil Transport and Micro-Topographical Changes in Vineyards. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2019, 159, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxton, K.E.; Rawls, W.J.; Romberger, J.S.; Papendick, R.I. Estimating Generalized Soil-water Characteristics from Texture. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1986, 50, 1031–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paroissien, J.-B.; Lagacherie, P.; Le Bissonnais, Y. A Regional-Scale Study of Multi-Decennial Erosion of Vineyard Fields Using Vine-Stock Unearthing–Burying Measurements. CATENA 2010, 82, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Notaris, C.; Jensen, J.L.; Olesen, J.E.; Stumpf Da Silva, T.; Rasmussen, J.; Panagea, I.; Rubæk, G.H. Long-Term Soil Quality Effects of Soil and Crop Management in Organic and Conventional Arable Cropping Systems. Geoderma 2021, 403, 115383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, K.E.; Brennan, E.B.; Cavigelli, M.A.; Smith, R.F. Winter Cover Crops Increase Readily Decomposable Soil Carbon, but Compost Drives Total Soil Carbon during Eight Years of Intensive, Organic Vegetable Production in California. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0228677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Chu, M.L.; Guzman, J.A.; Flanagan, D.C. Modeling Soil Erodibility and Critical Shear Stress Parameters for Soil Loss Estimation. Soil Tillage Res. 2022, 218, 105292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.H.; Zhang, Z.H.; Jia, L.Z. Impact of Tillage Erosion on Water Erosion in a Hilly Landscape. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 551–552, 522–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Napoli, M.; Cecchi, S.; Orlandini, S.; Mugnai, G.; Zanchi, C.A. Simulation of Field-Measured Soil Loss in Mediterranean Hilly Areas (Chianti, Italy) with RUSLE. CATENA 2016, 145, 246–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrena-González, J.; Rodrigo-Comino, J.; Gyasi-Agyei, Y.; Pulido Fernández, M.; Cerdà, A. Applying the RUSLE and ISUM in the Tierra de Barros Vineyards (Extremadura, Spain) to Estimate Soil Mobilisation Rates. Land 2020, 9, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torri, D.; Sfalanga, M.; Chisci, G. Threshold Conditions for Incipient Rilling. In Rill Erosion: Processes and Significance; Catena, Supplement; Bryan, R.B., Ed.; Catena Verlag: Cremlingen, Germany, 1987; Volume 8, pp. 97–105. ISBN 3-923381-07-7. [Google Scholar]
- Capello, G.; Biddoccu, M.; Ferraris, S.; Cavallo, E. Effects of Tractor Passes on Hydrological and Soil Erosion Processes in Tilled and Grassed Vineyards. Water 2019, 11, 2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, I.; Gunal, H.; Budak, M.; Akpinar, C. Effects of Long-Term Organic and Mineral Fertilizers on Bulk Density and Penetration Resistance in Semi-Arid Mediterranean Soil Conditions. Geoderma 2010, 160, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillel, D.I. Fundamentals of Soil Physics; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1980; ISBN 978-0-08-091870-9. [Google Scholar]
- Brunori, F.; Penzo, M.C.; Torri, D. Soil Shear Strength: Its Measurement and Soil Detachability. CATENA 1989, 16, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Jia, Y.; Fan, H.; Guo, C.; Su, F.; Li, S.; Fu, J.; Zhang, X.; Yu, M.; Yang, M.; et al. Impact of Soil Compaction on the Rill Erosion of Mollisol by Waterflow: A Comparative Analysis before and after the Seasonal Freezing and Thawing. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2025, 13, 756–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigo Comino, J.; Keesstra, S.D.; Cerdà, A. Connectivity Assessment in Mediterranean Vineyards Using Improved Stock Unearthing Method, LiDAR and Soil Erosion Field Surveys. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2018, 43, 2193–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Crop | Plant Species | Family | Seed (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PG | Lolium perenne L. (perennial ryegrass) | Poaceae | 33 |
| Trifolium subterraneum L. (subterranean clover) | Fabaceae | 33 | |
| Festuca rubra L. (red fescue) | Poaceae | 33 | |
| GM | Vicia faba L. var. “Minor” Beck (fava bean) | Fabaceae | 40 |
| Lupinus albus L. (white lupine) | Fabaceae | 8 | |
| Pisum sativum L. (garden pea) | Fabaceae | 18 | |
| x Triticosecale Wittm. [Secale × Triticum] (triticale) | Poaceae | 15 | |
| Hordeum vulgare L. (common barley) | Poaceae | 13 | |
| Sinapis alba L. (white mustard) | Brassicaceae | 3.6 | |
| Brassica napus L. (rape) | Brassicaceae | 2.4 |
| Year | Monthly Erosivity (MJ mm ha−1 h−1) | Annual Erosivity | P (mm) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D | |||
| 2019 | 25 | 160 | 41 | 169 | 286 | 2 | 96 | 16 | 36 | 93 | 552 | 148 | 1624 | 1054 |
| 2020 | 51 | 48 | 189 | 137 | 45 | 278 | 17 | 86 | 105 | 334 | 13 | 296 | 1600 | 1075 |
| 2021 | 295 | 279 | 4 | 249 | 93 | 9 | 10 | 13 | 10 | 30 | 160 | 246 | 1398 | 918 |
| 2022 | 37 | 92 | 66 | 244 | 23 | 0 | 6 | 112 | 249 | 0 | 147 | 62 | 1039 | 754 |
| Long term | 67 | 159 | 180 | 224 | 153 | 70 | 33 | 33 | 103 | 124 | 135 | 71 | 1353 | 955 |
| Total Erosion | Total Deposition | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Year | n.s. | n.s. | |
| Management | *** | *** | |
| Year × Management | n.s. | n.s. | |
| 2020 | CT | 37.1 (2.2) b | 5.2 (0.2) a |
| GM | 58.3 (2.1) a | 2.3 (0.2) c | |
| PG | 26.1 (2.4) c | 3.7 (0.6) b | |
| 2022 | CT | 33.7 (2.2) b | 5.4 (0.6) a |
| GM | 54.8 (3.1) a | 1.8 (0.2) c | |
| PG | 24.5 (2.5) c | 3.4 (0.6) b | |
| Mean | CT | 35.4 (1.6) b | 5.3 (0.3) a |
| GM | 56.6 (1.9) a | 2.1 (0.2) c | |
| PG | 25.3 (1.7) c | 3.6 (0.4) b | |
| Treatments | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| CT | PG | GM | |
| Total erosion | |||
| Year | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. |
| Zone | *** | *** | *** |
| Year × Zone | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. |
| Centre | 18.68 (0.84) a | 13.25 (0.94) a | 29.09 (0.87) a |
| Track | 16.23 (0.71) b | 10.79 (0.81) a | 25.97 (0.91) b |
| Row | 0.47 (0.12) c | 1.27 (0.19) b | 1.5 (0.24) c |
| Total deposition | |||
| Year | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. |
| Zone | *** | *** | *** |
| Year × Zone | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. |
| Centre | 0 (0) b | 0 (0) b | 0 (0) b |
| Track | 0.38 (0.06) b | 0.98 (0.39) b | 0.21 (0.08) b |
| Row | 4.9 (0.25) a | 2.57 (0.32) a | 1.84 (0.17) a |
| CT | E_Total | D_Total | Slope | Length |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| E_Total | ||||
| D_Total | −0.675 ** | |||
| Slope | 0.637 ** | −0.43 n.s. | ||
| Length | −0.38 n.s. | 0.141 n.s. | −0.875 *** | |
| PG | E_Total | D_Total | Slope | Length |
| E_Total | ||||
| D_Total | −0.641 ** | |||
| Slope | 0.494 * | −0.708 *** | ||
| Length | −0.22 n.s. | 0.656 ** | −0.912 *** | |
| GM | E_Total | D_Total | Slope | Length |
| E_Total | ||||
| D_Total | −0.645 ** | |||
| Slope | −0.158 n.s. | 0.085 n.s. | ||
| Length | 0.310 n.s. | −0.307 n.s. | −0.871 *** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Andrenelli, M.C.; Pellegrini, S.; Fila, G.; Becagli, C.; Valboa, G.; Vignozzi, N. Erosion Assessment by a Fast and Low-Cost Procedure in a Vineyard Under Different Soil Management. Agriculture 2025, 15, 2218. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15212218
Andrenelli MC, Pellegrini S, Fila G, Becagli C, Valboa G, Vignozzi N. Erosion Assessment by a Fast and Low-Cost Procedure in a Vineyard Under Different Soil Management. Agriculture. 2025; 15(21):2218. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15212218
Chicago/Turabian StyleAndrenelli, Maria Costanza, Sergio Pellegrini, Gianni Fila, Claudia Becagli, Giuseppe Valboa, and Nadia Vignozzi. 2025. "Erosion Assessment by a Fast and Low-Cost Procedure in a Vineyard Under Different Soil Management" Agriculture 15, no. 21: 2218. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15212218
APA StyleAndrenelli, M. C., Pellegrini, S., Fila, G., Becagli, C., Valboa, G., & Vignozzi, N. (2025). Erosion Assessment by a Fast and Low-Cost Procedure in a Vineyard Under Different Soil Management. Agriculture, 15(21), 2218. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15212218









