Effects of Phenanthrene Soil Pollution on Cadmium Bioaccumulation and Metabolic Responses in Maize (Zea mays L.)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Test Materials
2.2. Pot Experiments
2.3. Quantitative Analysis of Indicators
2.4. Statistical Analysis Methods
RI = OB/Cexp
3. Results
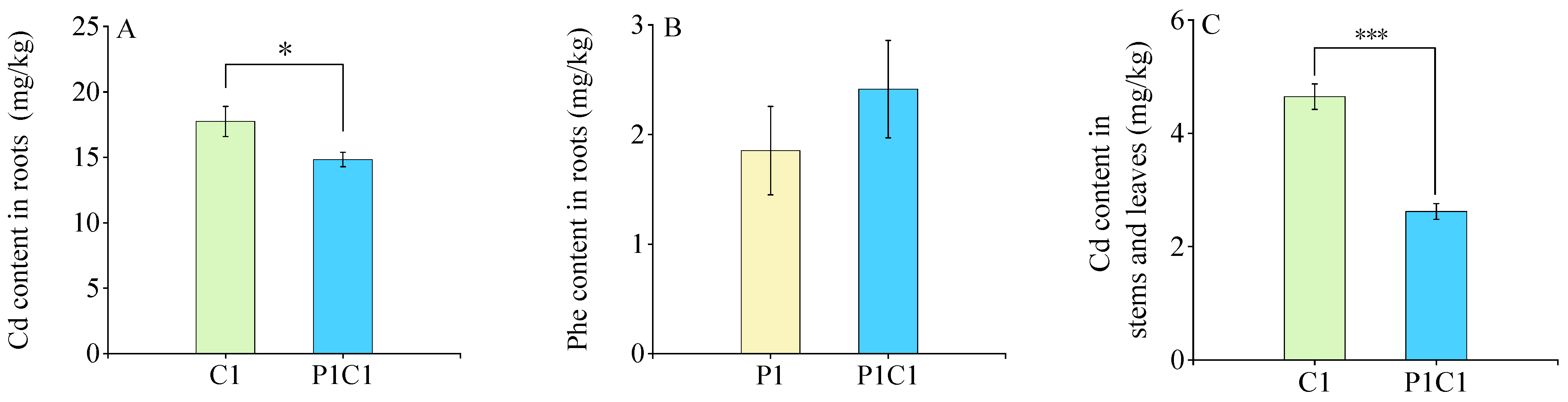
3.1. Accumulation Characteristics of Cd and Phe in HY702
3.2. Effects on HY702 Growth, Physiological, and Biochemical Responses
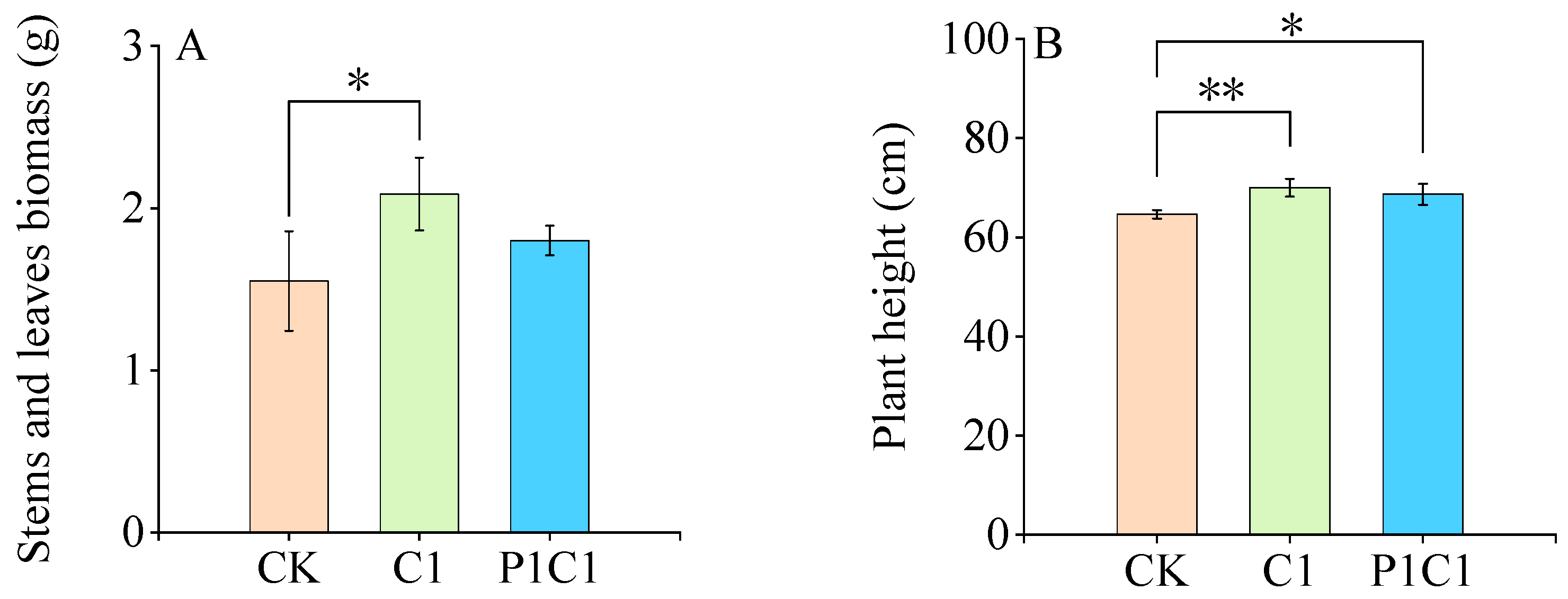
3.2.1. Growth Responses
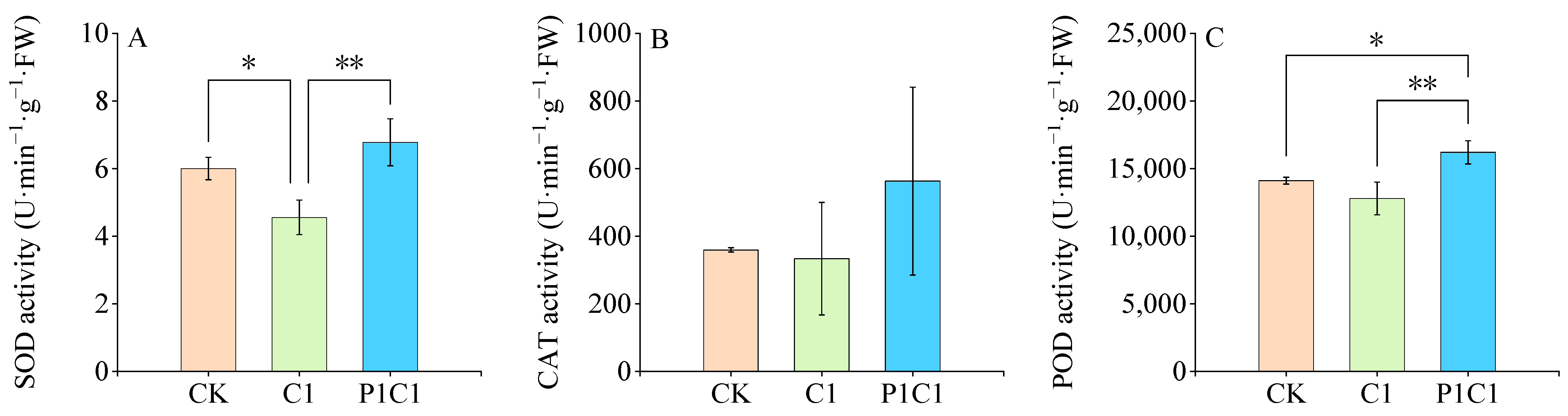
3.2.2. Physiological and Biochemical Responses
3.3. Characterization of Metabolic Differences in HY702 in Response to Cd-Phe Co-Pollution
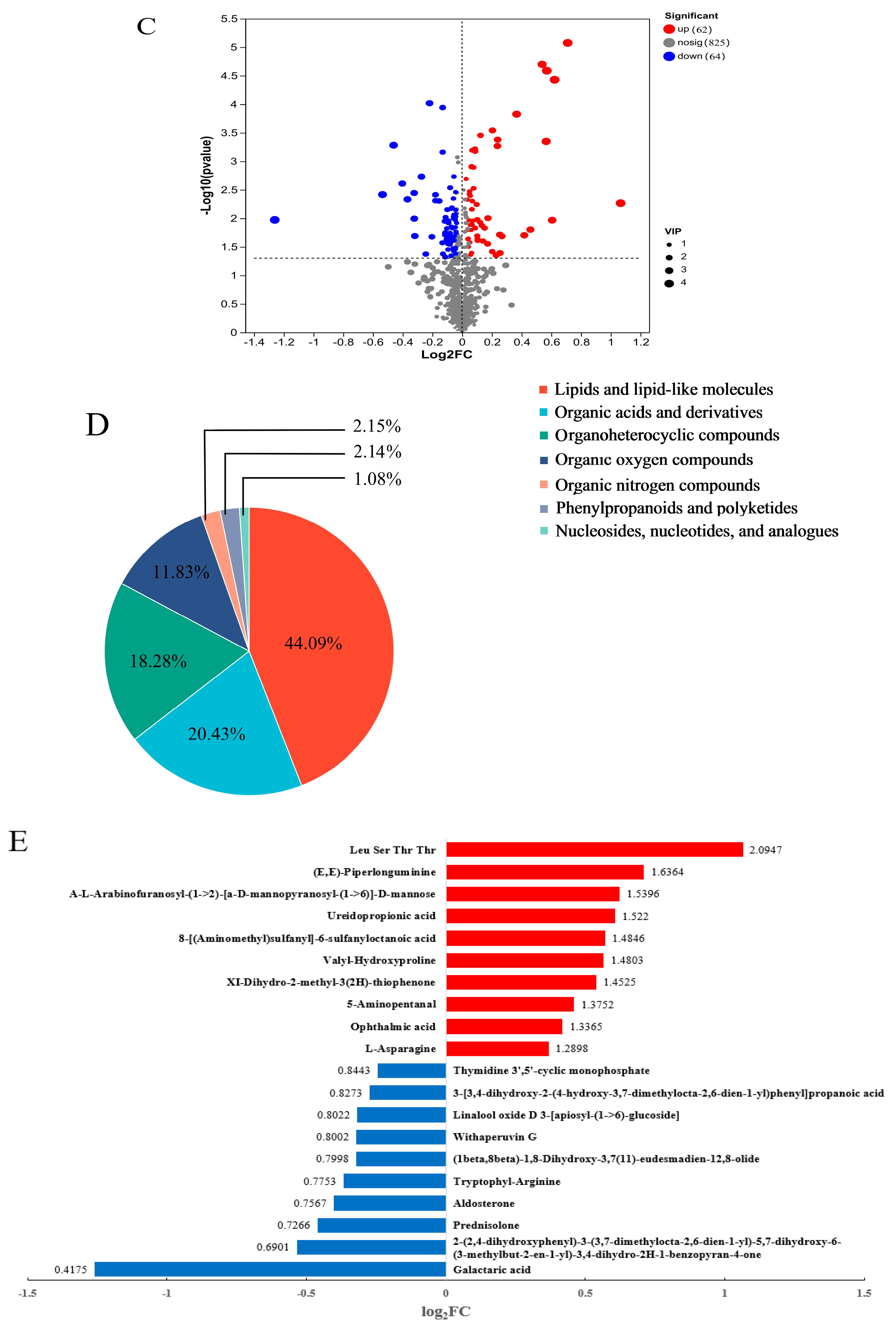
3.3.1. Differential Metabolites of HY702 Under Cd-Phe Co-Pollution
3.3.2. Key Metabolic Pathways of HY702 Under Cd-PheCo-Pollution
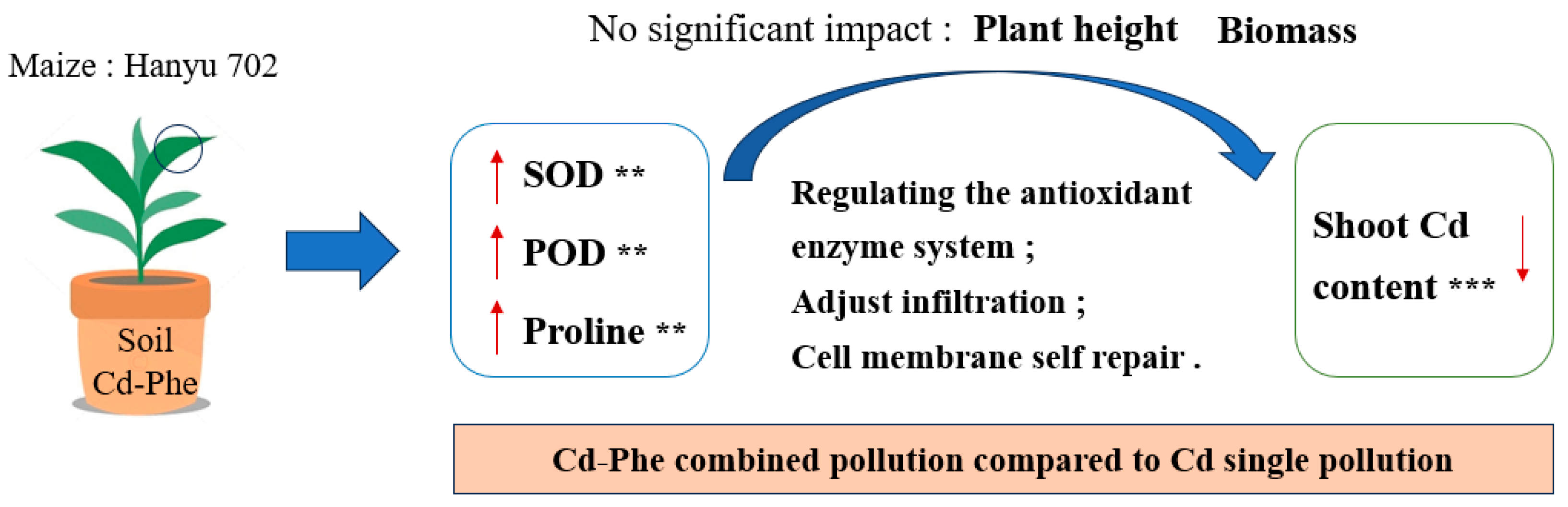
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peng, L.; Fu, D.; Qi, H.; Lan, C.-Q.; Yu, H.; Ge, C. Micro- and nano-plastics in marine environment: Source, distribution, and threats—A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 698, 134254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Shafy, H.I.; Mansour, M.S.M. A review on polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: Source, environmental impact, effect on human health, and remediation. Egypt. J. Pet. 2016, 25, 107–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaco, D.; Chianese, E.; Riccio, A.; Delgado-Sanchez, A.; Lacorte, S. Spatial distribution of heavy hydrocarbons, PAHs, and metals in polluted areas. The case of “Galicia”, Spain. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 121, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Naushad, M.; Lima, E.C.; Zhang, S.; Shaheen, S.M.; Rinklebe, J. Global soil pollution by toxic elements: Current status and future perspectives on the risk assessment and remediation strategies—A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 417, 126039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, X.; Xue, N.; Han, Z. A meta-analysis of heavy metals pollution in farmland and urban soils in China over the past 20 years. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 101, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Sharma, A.; Kaur, P.; Sidhu, G.P.S.; Bali, A.S.; Bhardwaj, R.; Thukral, A.K.; Cerda, A. Pollution assessment of heavy metals in soils of India and ecological risk assessment: A state-of-the-art. Chemosphere 2019, 216, 449–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Yang, G.; Chen, H.; Zhai, Y.; Teng, Y.; Li, J.; Chen, R. Source apportionment and source specific health risk assessment of HMs and PAHs in soils with an integrated framework in a typical cold agricultural region in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 904, 167337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bund/Länder-ArbeitsgemeinschaftBodenschutz (LABO), Kennzahlen der Altlastenstatistik. 2023. Available online: https://www.labo-deutschland.de/Veroeffentlichungen-Daten-Informationssysteme.html (accessed on 20 April 2024).
- Madrid, F.; Ballesteros, R.; Lacorte, S.; Villaverde, J.; Morillo, E. Extraction of PAHs from an aged creosote-polluted soil by cyclodextrins and rhamnolipids: Side effects on removal and availability of potentially toxic elements. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 653, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subashchandrabose, S.R.; Venkateswarlu, K.; Venkidusamy, K.; Palanisami, T.; Naidu, R.; Megharaj, M. Bioremediation of soil long-term contaminated with PAHs by algal–bacterial synergy of Chlorella sp. MM3 and Rhodococcuswratislaviensis strain 9 in slurry phase. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 659, 724–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, S.; Ma, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Liu, G.-J.; Chen, F. Spatial assessment of farmland soil pollution and its potential human health risks in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 687, 642–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, S.; Cao, Z.; Yang, Y.; Wei, G.; Wang, X.M. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, heavy metals, and genotoxicity of the suburban soils from Guangzhou, China. Polycycl. Aromat. Compd. 2013, 33, 501–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Li, H.; Yang, X.; Qiu, H.; Liu, Y. Spatial interaction and risk zoning of compound pollutants in farmland soils: Insights from heavy metals and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in Hezhang County, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 285, 116380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Li, C.; Chen, W. Phytoremediation potential of Bermuda grass (Cynodondactylon (L.) Pers.) in soils co-contaminated with polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and cadmium. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 234, 113389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Environmental Protection of China (MEP of China). National Soil Pollution Survey Bulletin. 2014. Available online: https://www.mee.gov.cn/gkml/sthjbgw/qt/201404/t20140417_270670.htm (accessed on 30 April 2024).
- Lin, C.; Zhang, F.; Zhu, X.; Baitao, L. Characteristics and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons contaminations in agricultural soils and crops in China. Chin. Bioprocess, J. Eng. 2021, 19, 440–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wei, H.; Pan, B. Accumulation characteristics and probabilistic risk assessment of Cd in agricultural soils across China. Environ. Sci. 2023, 44, 4006–4016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhtiar, A.; Song, X.; Ding, D.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Tang, Z. Bioremediation of PAHs and heavy metals co-contaminated soils: Challenges and enhancement strategies. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 295, 118686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Cui, X.; Xie, M.; Zhao, R.; Xu, L.; Ni, S.; Cui, Z. Amendments and bioaugmentation enhanced phytoremediation and micro-ecology for PAHs and heavy metals co-contaminated soils. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 426, 128096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Ke, T.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Hu, Z.; Yin, H.; Guo, L.; Chen, L.; Zhang, D. Heavy metal exposure alters the uptake behavior of 16 priority polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) by Pak Choi (Brassica chinensis L.). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 13457–13468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, M.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, J.; Chen, Y. Interactions between pyrene and heavy metals and their fates in a soil-maize (Zea mays L.) system: Perspectives from the root physiological functions and rhizosphere microbial community. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 287, 117616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, X.; Huang, J.; Yan, C.; Zhang, Q.; Lu, H.; Liu, J. Interactive effects of cadmium and pyrene on contaminant removal from co-contaminated sediment planted with mangrove Kandeliaobovata (S.; L.) Yong seedlings. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 84, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeelani, N.; Yang, W.; Qiao, Y.; Li, J.; An, S.; Leng, X. Individual and combined effects of cadmium and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons on the phytoremediation potential of Xanthium sibiricum in co-contaminated soil. Int. J. Phytoremediat. 2018, 20, 773–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Z. Effects of cadmium and benzo[a]pyrene stress on physiological characteristics of wheat seedlings. J. Agro. Environ. Sci. 2012, 31, 464–467. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Xu, D.; Wang, X.; Wu, J.; Lin, R. Biological responses of maize seedlings to single and combined stress of cadmium and phenanthrene. Environ. Sci. 2011, 32, 1471–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeelani, N.; Yang, W.; Xu, L.; Qiao, Y.; An, S.; Leng, X. Phytoremediation potential of Acorus calamus in soils co-contaminated with cadmium and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Cao, X.; Tan, C.; Deng, Y.; Cai, R.; Peng, X.; Bai, J. Analysis of the effect of cadmium stress on root exudates of Sedum plumbizincicola based on metabolomics. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 205, 111152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivaram, A.K.; Logeshwaran, P.; Lockington, R.; Naidu, R.; Megharaj, M. Metabolomics reveals defensive mechanisms adapted by maize on exposure to high molecular weight polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Chemosphere 2019, 214, 771–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olaf, E.; Jordan, C.; Kai, S. Estimating the global number and distribution of maize and wheat farms. Glob. Food Sec. 2021, 30, 100558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivaram, A.K.; Logeshwaran, P.; Lockington, R.; Naidu, R.; Megharaj, M. Impact of plant photosystems in the remediation of benzo[a]pyrene and pyrene spiked soils. Chemosphere 2018, 193, 625–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.K. Accumulation Characteristics and Metabolic Response Mechanism of Maize to Cadmium Phenanthrene in Complex Contaminated Soil. Master’s Thesis, Hebei Agricultural University, Baoding, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Beiyuan, J.; Ju, W.; Qiu, T.; Cui, Q.; Chen, L.; Chao, H.; Shen, Y.; Fang, L. Inoculation with Bacillus thuringiensis reduces uptake and translocation of Pb/Cd in soil-wheat system: A life cycle study. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 945, 173665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, D.; Wang, Q.; Yang, D. Exogenous salicylic acid improves chilling tolerance in maize seedlings by improving plant growth and physiological characteristics. Plants 2021, 10, 1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Zhang, G.; Gao, X.; Gao, J.; Mi, L.; Chen, L.; Yang, Z. Effects of two Cd-accumulating varieties of tomato combined with indigenous microorganisms on soil available Cd. Chin. J. Eco.-Agric. 2024, 32, 1227–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Guo, Y.; Ning, G.; Li, C.; Li, Y.; Ren, Y.; Zhao, O.; Yang, Z. Remediation of soil polluted with HMW-PAHs by alfalfa or brome in combination with fungi and starch. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 360, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Ning, G.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, W.; Yang, Z. Differences in adsorption, transmembrane transport, and degradation of pyrene and benzo[a]pyrene by Bacillus sp. strain M1. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 248, 114328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, C.; Fu, W.; Zhang, X.; Li, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, F.; Ji, J.; Wang, G.; Gao, X. Enhanced phytoremediation efficiency of PHE-contaminated soil by rape (Brassica napus L.) assisted with PHE-degradable PGPR through modulating rhizobacterial communities. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2023, 202, 117057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Zhang, G.; Dominik, P. Four barley genotypes respond differently to cadmium: Lipid peroxidation and activities of antioxidant capacity. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2003, 50, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, T.; Frenkle, C. Involvement of hydrogen peroxide in the regulation of senescence in pear. Plant Physiol. 1977, 59, 411–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Peng, F.; Wang, L. Regulation of POD activity by pelargonidin during vegetative growth in radish (Raphanus sativus L.). Sci. Hortic. 2014, 174, 105111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papastergiadis, A.; Mubiru, E.; Van Langenhove, H.; De Meulenaer, B. Malondialdehyde measurement in oxidized foods: Evaluation of the spectrophotometric thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS) test in various foods. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 9589–9594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabnam, N.; Tripathi, I.; Sharmila, P.; Pardha-Saradhi, P. A rapid, ideal, and eco-friendlier protocol for quantifying proline. Protoplasma 2016, 253, 1577–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Zhong, G.; Zhou, J.; Liu, Y.; Pang, Y.; Cai, H.; Wu, Z. Separate and combined effects of glyphosate and copper on growth and antioxidative enzymes in Salvinia natans (L.) All. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 655, 1448–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; He, S.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, H.; Wang, J.; Chen, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, Y. Glycine transformation induces repartition of cadmium and lead in soil constituents. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 251, 930–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Yu, S.; Lian, J.; Wang, Q.; He, Z.; Feng, Y.; Yang, X. Physiological and metabolomics responses of two wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) genotypes differing in grain cadmium accumulation. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 769, 145345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhong, Z. Molecular dissection of cadmium-responsive transcriptome profile in a low-cadmium-accumulating cultivar of Brassica parachinensis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 180, 388–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebert, D.N.; Garman, S.C.; Molinari, M. The glycan code of the endoplasmic reticulum: Asparagine-linked carbohydrates as protein maturation and quality-control tags. Trends Cell Biol. 2005, 15, 364–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.H.; Yu, X.Z.; Wu, S.C.; Wang, X.R.; Wang, S.H.; Tam, N.F.Y.; Wong, M.H. Responses of bioaugmented ryegrass to PAH soil contamination. Int. J. Phytoremediat. 2011, 13, 441–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.H.; Gao, Y.; Wu, S.C.; Cheung, K.C.; Wang, X.R.; Wong, M.H. Physiological and biochemical responses of rice (Oryza sativa L.) to phenanthrene and pyrene. Int. J. Phytoremediat. 2008, 10, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabados, L.; Savour, A. Proline: A multifunctional amino acid. Trends Plant Sci. 2010, 15, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Jiang, L.; Sarkodie, E.K.; Guo, Z.; Yang, J.; Shi, J.; Liu, X. Comprehensive insight into the transformation mechanism of Cd fractionation in the components of paddy soils under cysteine leaching. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 112652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.X.; Yang, C.; Li, H.F.; Liu, C.P.; Dang, Z. Influences of single and combined pollution of sulfamethazine and cadmium on seedling growth of Lactuca sativa L. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2019, 28, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, X.; Wu, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, K.; Guo, M.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, J.; Li, X.; Miao, R. Rice husk and its derived biochar assist phytoremediation of heavy metals and PAHs co-contaminated soils but differently affect bacterial community. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 466, 133684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, F.; Yin, W.; Song, S.; Zhang, Z.; Ye, P.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, J.; He, F.; Li, P.; Deng, Y. Ralstonia solanacearum promotes pathogenicity by utilizing L-glutamic acid from host plants. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2020, 21, 1099–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Chen, H.; Kopittke, P.M.; Zhao, F.-J. Cadmium contamination in agricultural soils of China and the impact on food safety. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 249, 1038–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.-Q.; Bai, Z.-Y.; Xiao, Y.-F.; Li, Y.; Liu, Q.-L.; Zhang, L.; Pan, Y.-Z.; Jiang, B.-B.; Zhang, F. Transcriptomic analysis of Verbena bonariensis roots in response to cadmium stress. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jozefczak, M.; Bohler, S.; Schat, H.; Horemans, N.; Guisez, Y.; Remans, T.; Vangronsveld, J.; Cuypers, A. Both the concentration and redox state of glutathione and ascorbate influence the sensitivity of Arabidopsis to cadmium. Ann. Bot. 2015, 116, 601–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seth, C.S.; Remans, T.; Keunen, E.; Jozefczak, M.; Gielen, H.; Opdenakker, K.; Weyens, N.; Vangronsveld, J.; Cuypers, A. Phytoextraction of toxic metals: A central role for glutathione. Plant Cell Environ. 2012, 35, 334–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaufichon, L.; Rothstein, S.J.; Suzuki, A. Asparagine metabolic pathways in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Physiol. 2016, 57, 675–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.C.; Han, J.M.; Kim, S. Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases and amino acid signaling. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2021, 1868, 118889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, N.; Huang, F.; Du, J.; Huang, C.; Yang, Q.; Zhan, X.; Xing, B. Expeditious profiling of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons transport and obstruction mechanisms in crop xylem sap proteins via proteomics and molecular docking. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 340, 122854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.X.; Zhang, S.R.; Wang, Y.J.; Zhong, Q.M.; Feng, C. Effects of folic acid and methionine on chelating agents in the removal of heavy metals. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2018, 37, 1622–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brosnan, M.E.; Brosnan, J.T. Histidine metabolism and function. J. Nutr. 2020, 150, 2570S–2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tronconi, M.A.; Wheeler, M.C.; Martinatto, A.; Zubimendi, J.P.; Andreo, C.S.; Drincovich, M.F. Allosteric substrate inhibition of Arabidopsis NAD-dependent malic enzyme 1 is released by fumarate. Phytochemistry 2015, 111, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strassman, M.; Ceci, L.N. Enzymatic formation of α-isopropylmalic acid, an intermediate in leucine biosynthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 1963, 238, 2445–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Treatment Number | Treatment Description | Phenanthrene Concentration | Cadmium Concentration |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | Control without pollution | 0 | 0 |
| P1 | Single phenanthrene pollution | 1 | 0 |
| C1 | Single cadmium pollution | 0 | 2.5 |
| P1C1 | Cadmium and phenanthrene combined pollution | 1 | 2.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, G.; Ning, G.; Zhang, Y.; Meng, Q.; Li, J.; Qi, M.; Chen, L.; Mi, L.; Gao, J.; Zhang, M.; et al. Effects of Phenanthrene Soil Pollution on Cadmium Bioaccumulation and Metabolic Responses in Maize (Zea mays L.). Agriculture 2025, 15, 1957. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15181957
Zhang G, Ning G, Zhang Y, Meng Q, Li J, Qi M, Chen L, Mi L, Gao J, Zhang M, et al. Effects of Phenanthrene Soil Pollution on Cadmium Bioaccumulation and Metabolic Responses in Maize (Zea mays L.). Agriculture. 2025; 15(18):1957. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15181957
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Guangwei, Guohui Ning, Yukun Zhang, Qingyu Meng, Jiahui Li, Mingyue Qi, Liqian Chen, Liang Mi, Jiayuan Gao, Meng Zhang, and et al. 2025. "Effects of Phenanthrene Soil Pollution on Cadmium Bioaccumulation and Metabolic Responses in Maize (Zea mays L.)" Agriculture 15, no. 18: 1957. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15181957
APA StyleZhang, G., Ning, G., Zhang, Y., Meng, Q., Li, J., Qi, M., Chen, L., Mi, L., Gao, J., Zhang, M., Zhang, X., Wang, X., & Yang, Z. (2025). Effects of Phenanthrene Soil Pollution on Cadmium Bioaccumulation and Metabolic Responses in Maize (Zea mays L.). Agriculture, 15(18), 1957. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15181957





