Abstract
Plant respiratory burst oxidase homolog (Rboh) genes are integral to the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and the regulation of stress responses. Here, bioinformatic techniques were employed to identify eight PgRboh genes (PgRbohA–H) in the genome of pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) and conduct a systematic analysis of this family. The findings showed that all PgRbohs proteins possess characteristic NADPH oxidase domains and are predicted to be localized on the cell membrane. Experimental verification confirmed the membrane localization of PgRbohD and PgRbohE proteins. Phylogenetic analysis categorized the PgRbohs proteins into six distinct groups, suggesting potential functional divergence among these groups. Promoter analysis revealed a significant presence of cis-acting elements responsive to low-temperature and methyl jasmonate (MeJA). The expression of PgRboh genes was found to be tissue-specific. Additionally, real-time PCR (RT-qPCR) was used to analyze expression patterns in response to low-temperature stress that involves multiple PgRboh genes in the cold response process. Overall, our results lay an important foundation for subsequent studies on the cold resistance function of pomegranate Rboh genes and provides new ideas for the breeding of new cold-resistant pomegranate varieties.
1. Introduction
Plants are routinely subjected to a variety of abiotic stresses, such as low temperature, salinity, and high temperature, which profoundly affect their growth, development, and crop yields [1]. To overcome these limitations, plants have evolved complex defense mechanisms, with reactive oxygen species (ROS) playing a pivotal role in stress-responsive signal transduction [2]. ROS perform dual roles in plant cells [3]. At low concentrations, ROS act as signaling molecules regulating physiological processes [4]. They also function as second messengers in mediating plant defense responses, stomatal movement, programmed cell death (PCD), and systemic acquired acclimation (SAA) [5]. For instance, ROS function as signals for stomatal closure, prompting plants to adjust stomatal aperture and reduce transpiration to cope with drought and other stresses [6]. Conversely, excessive buildup of ROS can lead to oxidative damage to cellular components, including lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids, and eventually result in cell death [7].
The production of ROS in plants is primarily driven by NADPH oxidases, which are also known as respiratory burst oxidase homologs (Rbohs) [8]. These plasma membrane-localized proteins catalyze NADPH-dependent oxygen reduction reactions to produce superoxide (O2−). They collaborate with signaling molecules such as calcium ions (Ca2+), nitric oxide (NO), ethylene, and jasmonic acid (JA), as well as transcription factors, to regulate plant growth, development, and resistance to environmental stresses [9]. The Rboh gene family was initially identified in mammals as the NOX (NADPH oxidase) family, which plays a role in immune defense [10]. Plant Rbohs share structural similarities with animal NOXs, including N-terminal EF-hand motifs for calcium binding, a transmembrane domain, and C-terminal domains for binding domains of FAD and NADPH [11]. Notably, plant Rbohs feature a distinctive N-terminal extension, which may facilitate protein interactions and post-translational modifications [12].
The identification and characterization of the Rboh gene family have been carried out extensively in various plant species, including Arabidopsis thaliana (AtRboh), Oryza sativa (OsRboh), and Malus domestica (MdRboh) [13,14]. In the Arabidopsis species, ten Rboh genes have been identified, each demonstrating unique expression profiles and functional roles in mediating various stresses responses [15]. Specifically, AtRbohF is implicated in the regulation of stomatal closure via ROS signaling, thereby enhancing drought resistance [16]. AtRbohD is involved in activating the CBF/DREB1 pathway through ROS signaling to augment cold tolerance, while AtRbohI is essential for hypoxia tolerance under low-oxygen conditions [17,18]. In rice, among the nine members of the OsRboh family, OsRbohA facilitates H2O2 accumulation, which enhances salt tolerance by regulating potassium (K+) homeostasis [19]. OsRbohC contributes to improved drought resistance by promoting stomatal closure through ROS signaling [20]. Additionally, OsRbohE and OsRbohF are linked to salt tolerance, whereas OsRbohH aids in boosting heat and drought tolerance through the modulation of ROS homeostasis [21,22]. Similar functions of Rbohs are observed in other species: under low-temperature stress, Rboh genes expression in cucumber seedlings leads to H2O2 accumulation, which increases photosynthetic rates and enhances cold tolerance [23]. In tobacco, NtbHLH123 functions as a molecular switch that positively regulates the salt-stress response pathway of NtRbohE [24], and under drought and cold stress, the majority of tobacco Rbohs are notably upregulated [25]. In watermelon, melatonin and Ca2+ induce RbohD expression and H2O2 production during early cold stress responses [26]. In tomato, Rboh1 enhances low-nitrogen tolerance through ROS production [27]. In maize, ZmRbohs are rapidly induced by cold stress [28]. In Strychnos nux-vomica, MpPBLa phosphorylates MpRboh1 to initiate ROS production [29]. TaRbohs demonstrate significant drought tolerance under drought stress, with a positive correlation to the duration of stress [30]. Melatonin has been shown to suppress MaRboh expression in postharvest bananas, thereby reducing reactive oxygen species (ROS) production [31]. Furthermore, CsRbohD is key to maintaining the structural integrity of cell membranes in sweet oranges under cold stress [32]. In terms of biotic stress responses, OsRbohA-RNAi plants exhibit increased susceptibility to sheath blight, while OsRbohB is essential for blast resistance [33,34]. Recent research indicates that OsRbohI is a pivotal gene for pathogen-associated molecular pattern (PAMP)-induced ROS production in rice innate immunity [35]. During the phases of growth and development, Arabidopsis RbohE is involved in pollen grain formation and development, with AtRbohE mutants showing reduced ROS accumulation in anthers, thereby impairing pollen viability [36]. Collectively, these studies demonstrate that Rboh genes play significant roles in plant adaptation to environmental stresses, defense against pathogen invasion, and regulation of growth and development [9].
Pomegranates are crucial economically and are known for their rich nutritional and medicinal properties [37]. The Tunisian soft-seed variety is favored for its edible seeds and market appeal. Rich in antioxidants with anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer benefits, pomegranates face challenges in temperate regions due to cold sensitivity, affecting its quality and yield [38,39]. Cold stress disrupts cellular balance, causing membrane issues and excessive ROS [40]. While cold tolerance is well-studied in plants like Arabidopsis and rice, pomegranate research is limited. With the advancement of pomegranate genomics, several gene families connected to stress responses have been found and studied [41]; for example, PgBAM and PgNAC, among others [42,43]. However, the role of the Rboh gene family in cold stress remains unknown.
The study employed bioinformatics tools to determine the members of the PgRboh gene family, with analyses conducted on their properties, domains, phylogeny, and cis-elements. Subcellular localization of these members was confirmed using localization assays. Furthermore, RT-qPCR technology was utilized to analyze the expression patterns of the PgRboh genes under cold stress conditions. These findings lay a substantial groundwork for understanding the role of PgRbohs in pomegranate stress responses and provide valuable insights into the biological functions of pomegranate Rboh genes.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Analysis of Identification and Physicochemical Properties in Pomegranate Rboh Gene Family
Pomegranate genome sequences and protein sequences, with their annotations, were downloaded from the NCBI (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/, accessed on 21 December 2024), while genome data (sequences and annotations) of Arabidopsis and rice were sourced from Ensembl Plants (http://plants.ensembl.org/, accessed on 21 December 2024).
Using 10 Rboh protein sequences from Arabidopsis as queries, BLAST searches the pomegranate protein database with TBtools v2.332 at an E-value threshold of e-5 to find PgRboh proteins. HMM profiles of the Rboh gene-related domains were downloaded from Pfam (http://pfam.xfam.org/, accessed on 21 December 2024). HMMER v3.3.2 was used to build a Markov model for screening candidate sequences containing these four domains, followed by confirmation of conserved domains via NCBI.
Genes were named PgRbohA–H based on their chromosomal positions. Physicochemical properties were predicted using TBtools software. Subcellular localization of PgRboh proteins was predicted with Plant-mPLoc (http://www.csbio.sjtu.edu.cn/bioinf/plant-multi/, accessed on 21 December 2024).
2.2. Phylogenetic Analysis of PgRbohs
Genome data for Arabidopsis, rice, and grape were obtained from NCBI (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/, accessed on 21 December 2024) and conduct sequence alignment. Subsequently, a phylogenetic tree was generated employing the Maximum Likelihood (ML) method, while maintaining default settings for other parameters. The resulting phylogenetic tree was visualized using Evolview (http://www.evolgenius.info/evolview/#/treeview, accessed on 24 December 2024).
2.3. Analysis of Motifs, Gene Structures, and Conserved Domains
Intron–exon distribution was extracted from pomegranate GFF files. Motif analysis was conducted using MEME (https://meme-suite.org/meme/tools/meme, accessed on 21 December 2024), and motifs/gene structures were visualized with TBtools. Multiple sequence alignment of 8 PgRboh proteins and Arabidopsis AtRbohA was carried out using DNAMAN 9.0.
2.4. Prediction of PgRboh Protein Structures
The protein of secondary and tertiary structures of PgRboh was conducted utilizing SOPMA (https://npsa.lyon.inserm.fr/, accessed on 7 June 2025) and SWISS-MODEL (https://swissmodel.expasy.org/, accessed on 7 June 2025), respectively. Phosphorylation sites were analyzed via CBS-NetPhos 3.1 (https://services.healthtech.dtu.dk/services/NetPhos-3.1/, accessed on 7 June 2025).
2.5. Identification of Cis-Acting Elements
A 2000 bp sequence upstream of the transcription start site of each PgRboh gene was designated as the promoter region. Important responsive elements within these regions were screened out using PlantCARE website (http://bioinformatics.psb.ugent.be/webtools/plantcare/html/, accessed on 7 January 2025) and statistically analyzed.
2.6. Tissue-Specific Expression Analysis
RNA-seq data for “Dabenzi” pomegranate including samples of root (SRR5279396), fresh leaf (SRR5279397), and flower (SRR5279395), were retrieved from NCBI (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sra, accessed on 8 July 2025). Transcript assembly and PgRboh expression levels across tissues were determined using the Hisat2 and StringTie plugins in TBtools. A heatmap was generated using TBtools’ HeatMap function.
2.7. Plant Materials and Low-Temperature Treatment
The seeds were extracted from fruits of the pomegranate, followed by treatment with 1 mol/L NaOH to remove pectin, and subsequently disinfected with a 17% sodium hypochlorite solution. The processed seeds were sown on the 1/2 MS medium containing 1.0 mg/L GA3 (pH 5.8). After true leaf emergence, seedlings were transplanted into a substrate mixture (matrix/vermiculite/perlite = 3:1:1) and grown for 2 months. Seedlings were then subjected to 4 °C cold treatment with time points at 0, 2, 4, 6, 8, 12, and 24 h with 3 biological replicates. The pomegranate materials used were collected in 2024 from the fruit tree cultivation greenhouse located at 32.3892° N, 119.4233° E within the College of Horticulture and Landscape Architecture at Yangzhou University.
2.8. RNA Extraction and RT-qPCR Analysis
Obtain the cDNA of pomegranate leaves using Vazyme kit (Vazyme, Nanjing, China). Gene-specific primers for RT-qPCR are listed in Table S1. RT-qPCR was conducted on a CFX96 system (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA) with PgActin as the reference gene. Each reaction had 3 technical replicates, and gene expression was determined using the 2−ΔΔCt method [44].
2.9. Subcellular Localization
Tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.) seeds were sown in soil and germinated at 25 °C in darkness. After reaching the eight-leaf stage, the seedlings were transferred to a growth chamber maintained at a constant temperature of 25 °C with 16 h in the light and 8 h in the dark. The CDS of PgRbohD and PgRbohE were amplified from pomegranate leaf cDNA, while the pCAMBIA1300-35S-EGFP vector was digested with restriction enzymes SacI and XbaI (Takara, Kusatsu, Japan) in a water bath pot under 37 °C overnight. PgRbohD and PgRbohE were inserted into the linearized vector using the ClonExpress II recombination kit (Vazyme, Nanjing, China). The primers used for vector construction are listed in Table S1. PgRbohD-GFP and PgRbohE-GFP were introduced into A. tumefaciens GV3101 (Tsingke, Beijing, China) and incubated at 28 °C for 2 days. The constructs, along with the EGFP control in 5 mL of LB liquid medium, were incubated at 200 rpm for 16 h, centrifuged, and resuspended in 10 mM MgCl2 and the OD600 adjusted to 1.5. The prepared bacterial suspension was injected into the lower epidermal cells of tobacco. For each treatment, 2–3 leaves were injected, randomly distributed across plants to minimize error. EGFP signals were imaged 36 h post-injection using a Leica LSM-880 confocal microscope (Leica, Germany) to detect GFP fluorescence.
3. Results
3.1. Identification and Basic Information of PgRboh Genes Members
Eight PgRboh genes were identified in the pomegranate through BLAST and conserved domain analyses, named PgRbohA–H based on their chromosomal locations and the widely accepted nomenclature system (Figure 1).
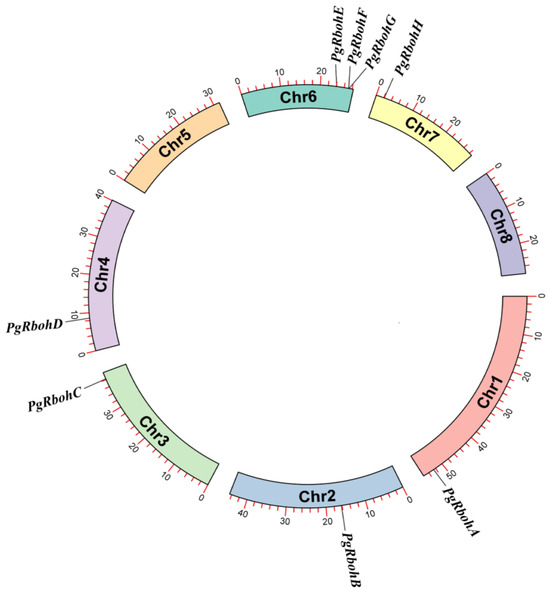
Figure 1.
Distribution of PgRboh genes on pomegranate chromosomes. Chr1–8 represent pomegranate chromosomes 1–8.
As shown in Table 1, the PgRboh proteins, comprising 811–969 amino acids, have molecular weights of 92.33 to 109.36 kDa, isoelectric points from 8.92 to 9.40, and hydrophilicity values (GRAVY) from −0.273 to −0.083. Only PgRbohC protein is predicted to be stable. The negative GRAVY values indicate hydrophilicity, and all proteins are predicted to localize to the cell membrane.

Table 1.
Basic information of PgRbohs.
3.2. Phylogenetic Analysis of Pomegranate Rboh Family Members
To elucidate the evolutionary relationships among Rbohs proteins in pomegranate, Arabidopsis, rice, and grape, a phylogenetic tree was constructed ustilizing 27 predicted Rboh protein sequences (Figure 2). These proteins are categorized into six distinct groups: PgRbohE is classified under Group 1; PgRbohA under Group 2; PgRbohB under Group 3; PgRbohD under Group 4; PgRbohC, PgRbohF, and PgRbohG under Group 5; and PgRbohH is uniquely assigned to Group 6.
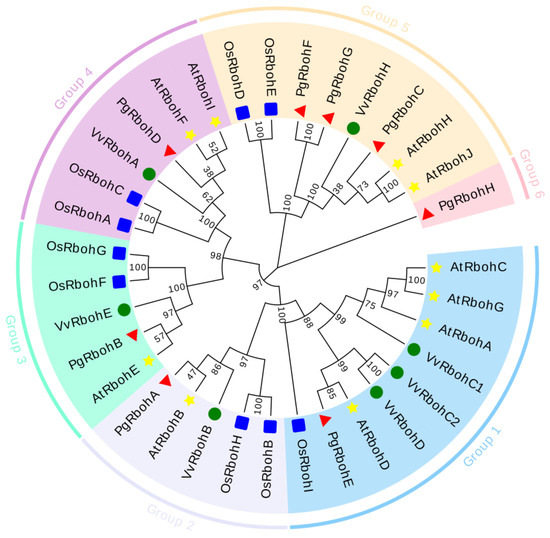
Figure 2.
Phylogenetic tree of Rboh proteins family members in pomegranate (Pg), Oryza sativa (Os), Vitis vinifera (Vv) and Arabidopsis (At). AtRbohs, OsRbohs, PgRbohs, and VvRbohs proteins are indicated by yellow stars, blue squares, red triangles, and green circles, respectively. The PgRboh proteins were classified into 6 families (Group I–VI), with each subfamily indicated by different colors.
3.3. The Structural Domains of PgRboh Exhibit Similarity to Those of Other Plant Rboh Proteins
The sequence alignment of PgRboh proteins with Arabidopsis AtRbohA revealed four conserved domains (Figure 3): the NADPH_Ox and EF-hand domains located in the N-terminal region, and the FAD_binding_8 and NAD_binding_6 domains in the C-terminal region.
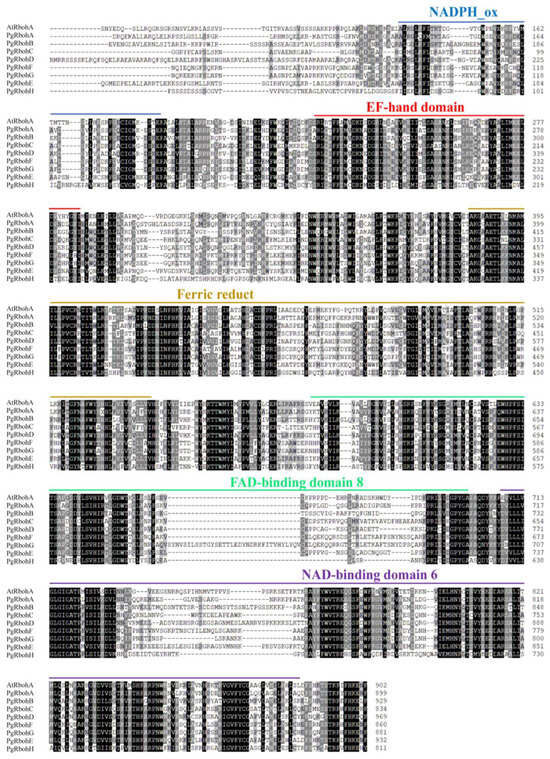
Figure 3.
Sequence alignment of PgRbohs. Protein sequences alignment between Arabidopsis AtRbohA and PgRbohs. Black shading indicates identical residues, while lighter shading represents sites with lower conservation.
3.4. Analysis of Motifs, Gene Structures, and Conserved Domains of PgRbohs
Among the eight identified motifs (Figure 4a), all members of the PgRboh family exhibit the complete set of motifs. Motif 6 is located within the NADPH_Ox domain; Motif 3, 4, and 8 constitute the ferric reductase domain; Motif 1 and 5 are within the FAD_binding_8 domain; and Motif 5 and 7 form the NAD_binding_6 domain in all PgRboh proteins. PgRboh genes contain 11–14 exons and 10–13 introns (Figure 4b).
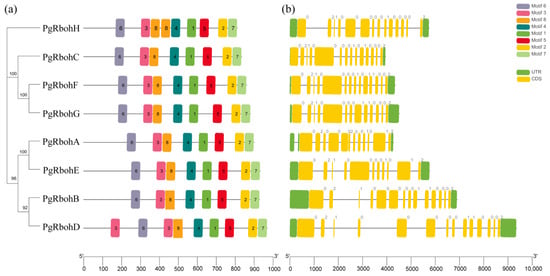
Figure 4.
Motifs and gene structures of PgRboh family members. (a) Motif analysis; (b) gene structure. Yellow and green parts represent coding sequences (CDS) and untranslated regions (UTRs), respectively.
3.5. Prediction of Protein Secondary/Tertiary Structures and Phosphorylation Sites of PgRbohs
PgRbohs mainly consist of α-helices, extended strands, and random coils. In PgRbohA, PgRbohD, and PgRbohE, random coils are most abundant, followed by α-helices and extended strands. In the other five proteins, α-helices are most abundant. PgRbohE has the highest random coils (46.78%), while PgRbohF has the lowest (43.14%). PgRbohB has the most α-helices (44.99%), and PgRbohA the least (41.38%). Phosphorylation site prediction shows serine and threonine are most common, with lysine being least common (Table 2). Tertiary structure analysis indicated a high degree of similarity between PgRbohF and PgRbohG, with reduced similarity observed among the other six proteins (Figure 5).

Table 2.
Structural characteristics of PgRboh proteins.
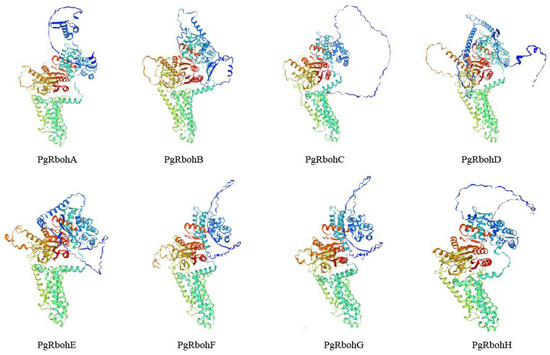
Figure 5.
Tertiary structure of PgRboh proteins. A blue-to-red color gradient (blue-green-yellow-red) is used to depict the polypeptide chain from the N- to the C-terminus.
3.6. Analysis of Cis-Acting Elements of the Pomegranate Rboh Genes
Cis-acting elements are key in gene expression regulation. To investigate PgRboh genes transcriptional regulation, 2000 bp upstream sequences were analyzed with PlantCARE. As shown in Figure 6, 22 representative cis-acting elements were identified, including 7 stress-responsive elements, 12 hormone-responsive elements, and 3 growth/development-related elements. The growth and development elements mainly include circadian rhythm-responsive elements (circadian, two), meristem-specific elements (CAT-box, one), and the cis-acting regulatory element involved in zein metabolism regulation (O2-site, six). The hormone response elements mainly consist of abscisic acid-responsive elements (ABRE, 26), MeJA-responsive elements (TGACG-motif and CGTCA-motif, 32), auxin-responsive elements (AuxRR-core and TGA-element, 9), salicylic acid-responsive elements (TCA-element, 2), and gibberellin-responsive elements (P-box, 1). Stress-responsive elements primarily included light-responsive elements (such as 3-AF1 binding site, AAAC-motif, G-Box), anaerobic induction elements (ARE, 14), low-temperature responsive elements (LTR, 7), and drought-induced elements (MBS, 8). Light-, MeJA-, and abscisic acid-responsive elements are highly enriched in most PgRboh promoters, while low-temperature responsive elements are enriched in PgRbohA–D and PgRbohH.
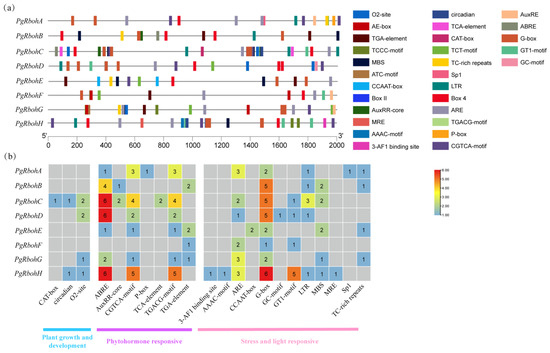
Figure 6.
Cis-acting elements of PgRboh family members. (a) Distribution of cis-acting elements identified in the 2000 bp upstream promoter region of the Rboh genes in pomegranate; (b) the number of cis-acting elements on the putative promoters of the Rboh genes in pomegranate. Differential quantities of elements in each gene are represented by distinct colors in the grid. The color gradient (blue, green, chartreuse, yellow, orange, red) represents the increase in the number of corresponding cis-elements.
3.7. Tissue-Specific Expression of PgRboh Genes
PgRboh expression varies significantly across tissues (Figure 7). PgRbohA and PgRbohH are only expressed at low levels in roots, with PgRbohA more highly expressed. PgRbohC is expressed at low levels exclusively in flowers, while PgRbohF is expressed in both roots and flowers, but its expression level is lower than that of the aforementioned tissue-specific genes. PgRbohB and PgRbohG are not expressed in any tissue. In contrast, PgRbohD and PgRbohE are expressed in all tissues, and their expression levels are significantly higher than those of the other genes across all tissues.
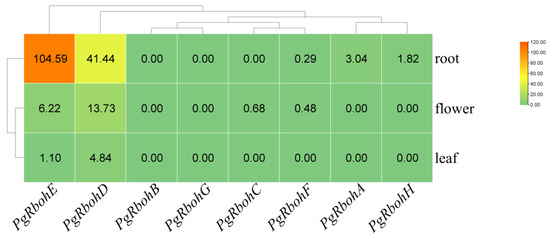
Figure 7.
Expression of PgRbohs in various pomegranate tissues. Gene expression levels were calculated as FPKM values obtained from the corresponding transcriptome data. The color gradient (green to orange) represents the increase in gene expression levels.
3.8. Subcellular Localization of PgRbohs
Due to the relatively high expression levels of PgRbohD and PgRbohE in all the tissues mentioned above, these two PgRboh genes were selected for fusion with pCAMBIA1300-35S-EGFP and transiently expressed in tobacco epidermal cells. In cells expressing the empty GFP vector, fluorescence was detected in both the nucleus and cell membrane (Figure 8a–c). In contrast, GFP signals from PgRbohD-GFP and PgRbohE-GFP were restricted to the cell membrane, with no nuclear localization (Figure 8d–i), confirming their membrane localization.
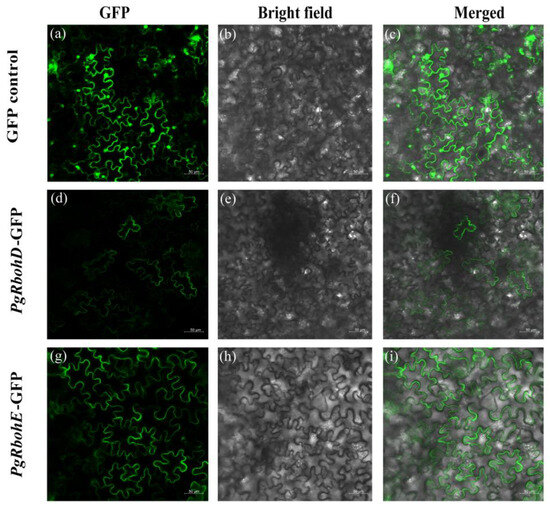
Figure 8.
Subcellular localization of PgRbohs. (a) GFP control; (d,g) PgRbohs-GFP fusion proteins; (b,e,h) bright field; (c,f,i) merged images of bright field with GFP fluorescence.
3.9. Expression Patterns of Pomegranate Rboh Family Genes in Response to Low-Temperature Stress
To elucidate the role of PgRboh genes in the cold response, members with low-temperature responsive elements (PgRbohA, PgRbohB, PgRbohC, PgRbohD, and PgRbohH) were analyzed via RT-qPCR under 4 °C treatment (Figure 9). PgRbohA and PgRbohC exhibited analogous expression trajectories characterized by an increase–decrease–increase–decrease pattern, with expression peaks observed at 8 h (43.23-fold and 40.16-fold, respectively). PgRbohD demonstrated an increase–decrease–increase pattern, peaking at 2 h (4.3-fold). PgRbohB expression decreased initially, then increased, and finally decreased, with significantly lower levels at 12 h and 24 h compared to the control. Remarkably, PgRbohH maintained low expression within 24 h of treatment but increased dramatically at 24 h, reaching 479.26-fold from the control and exceeding the expression of other Rboh genes. These findings suggest that multiple PgRbohs respond to low-temperature stress.
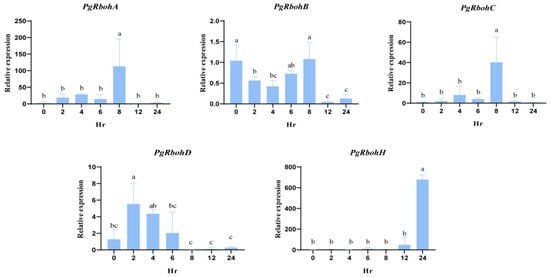
Figure 9.
Expression analysis of Rboh family members in pomegranate under cold treatment. Two-month-old pomegranate seedlings were subjected to 4 °C treatment at time intervals of 0, 2, 4, 6, 8, 12, and 24 h. Fifteen seedlings were used at each time point, and every five seedlings were pooled as one biological replicate, with a total of three biological replicates set up. Different letters indicate significant differences (ANOVA analysis, p < 0.05).
4. Discussion
Pomegranates, known for their nutritional and medicinal benefits, cause ROS-mediated DNA damage and mitochondrial dysfunction in seed cells, promoting apoptosis and inhibiting cell growth, which contributes to anti-cancer effects [45,46]. The Rboh gene family is crucial for plant stress responses, mediating ROS signaling under stress [47]. This study identified and characterized eight PgRboh genes (PgRbohA–H) in pomegranate, distributed unevenly across chromosomes. The gene count is between that of Arabidopsis, rice, chinese indigo, and apple [14,19,48,49], and fewer than in peach and barrel medic [14,50], reflecting different evolutionary needs for ROS signaling.
PgRboh proteins possess conserved domains—NADPH_Ox, Ferric_reduct, FAD_binding_8, and NAD_binding_6—that are also found in Rbohs proteins of other plant species, suggesting a functional conservation in ROS production [51]. The presence of N-terminal EF-hand motifs indicates potential regulation by Ca2+, a characteristic feature of Rboh activity. Consistent with Rbohs proteins from other species, PgRbohs exhibit canonical NADPH oxidase domains. However, in contrast to tomato Rbohs [52], the predicted secondary structures of PgRbohs lack β-pleated sheets (β-sheets), suggesting a unique evolutionary adaptation in pomegranate.
Phylogenetic analysis clustered PgRbohs proteins into six subgroups, with closer evolutionary affinity to AtRbohs and VvRbohs than OsRbohs. Except for PgRbohH, which forms a distinct clade, subgroup classifications align with those of other species, suggesting functional conservation within clades [53]. PgRbohE and PgRbohB cluster with Arabidopsis AtRbohD and AtRbohE, respectively, suggesting that they may have potential functional similarities, though this requires validation.
PgRboh promoter regions are rich in stress- and light-responsive cis-elements, comprising 54.27% of identified elements, including those for cold and drought, aligning with Rboh traits in many species [54,55]. This observation indicates that PgRbohs may play a role in various stresses, both biotic (pathogen-induced) and abiotic (damage, cold, hypoosmotic medium, salinity, etc.). Five PgRbohs have LTR motifs, prompting RT-qPCR analysis, which showed that cold stress (4 °C) significantly altered PgRbohs expression, with PgRbohH upregulated 479.26-fold at 24 h; the results suggest that PgRbohH plays a critical role in the later stages. PgRbohH may be a key gene that is strongly induced by low temperature and involved in the response to cold stress. This delayed induction is similar to the low-temperature response pattern of Rboh in some species. For instance, in pepper (Capsicum annuum), the expression level of CaRbohB was significantly higher after 24 h of cold stress compared to 6 h [56]; the transcript abundance of CsRbohD and CsRbohE in sweet orange (Citrus sinensis) showed a significant increase at 24 h [32]. However, it remains to be further confirmed how PgRbohH gene functions under the low-temperature stress conditions of the pomegranate. Furthermore, it was observed that PgRbohA and PgRbohC reached peak expression levels at 8 h, showing upregulation by 43.23-fold and 40.16-fold, respectively. It is hypothesized that their expression may exhibit rhythmic changes. However, this requires further experimental investigation.
Most PgRbohs are highly expressed in roots, similar to HvRbohs and NtabRbohs [25,57]. PgRbohD and PgRbohE have been found throughout roots, leaves, and flowers, with higher levels in roots and leaves, indicating that they play important roles in these areas. In particular, PgRbohE, which is expressed the most, is closely related to AtRbohD. AtRbohD is expressed in all organs of Arabidopsis, suggesting that their functions may be similar [58]. Both PgRbohD and PgRbohE are located on the plasma membrane in tobacco cells, aligning with other plants’ Rboh localization and supporting their role in apoplastic ROS production [59,60]. Unlike some ZmRbohs that localize to nuclei and mitochondria, PgRbohD and PgRbohE do not, as indicated by the absence of nuclear GFP signals, confirming their main role in plasma membrane ROS generation [28]. However, we cannot exclude the possibility that other uncharacterized PgRbohs might localize to mitochondria, and this will be experimentally addressed in future studies.
In summary, our study presented the first characterization of the pomegranate Rboh gene family, encompassing physicochemical properties, gene structures, phylogeny, promoter cis-elements, and cold-responsive expression patterns. We found that PgRbohH exhibited a significant response to cold stress at a low temperature for 24 h, while PgRbohD responded rapidly to low temperatures, indicating that they might be crucial cold response genes, warranting further investigation into its functional mechanisms.
5. Conclusions
Eight members of the PgRboh family were identified in pomegranate through bioinformatics analysis, and their expression patterns under cold stress were systematically characterized. All PgRboh proteins possess canonical NADPH oxidase domains, including NADPH_Ox and FAD_binding_8, and are localized to the plasma membrane, aligning with the conserved characteristics of Rboh proteins in most plant species. Phylogenetic analysis categorized the PgRboh genes into six subgroups. Promoter analysis revealed an enrichment of cis-acting elements to light, abscisic acid (ABA), cold, and MeJA, suggesting that PgRboh gene expression may be regulated by multiple environmental signals and hormonal pathways. RT-qPCR assays demonstrated that PgRbohs exhibited distinct temporal dynamic characteristics in the cold stress response. PgRbohH showed marked upregulation at 24 h, indicating its potential key role in long-term cold adaptation, while PgRbohD was significantly upregulated at 2 h, indicating its role in rapid cold perception. Subcellular localization experiments confirmed the plasma membrane targeting of PgRbohD and PgRbohE, supporting their involvement in stress responses through apoplastic reactive oxygen species (ROS) production.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/agriculture15171883/s1, Table S1: Primers used in this study.
Author Contributions
Methodology and software, Y.S. and X.W.; collection and analysis of the bibliography, Y.S. and C.W.; validation, Y.S.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.S. and X.W.; writing—review and editing, L.J. and X.X.; supervision, L.J.; project administration, L.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2023M742962); the Key Research and Development Program of Jiangsu Province (BE2023328); and the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20230571).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data, tables, and figures in this manuscript are original and are contained within the article and the Supplementary Materials.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Shiade, S.R.G.; Zand-Silakhoor, A.; Fathi, A.; Rahimi, R.; Minkina, T.; Rajput, V.D.; Zulfiqar, U.; Chaudary, T. Plant metabolites and signaling pathways in response to biotic and abiotic stresses: Exploring bio stimulant applications. Plant Stress 2024, 12, 100454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahanmmed, G.J.; Li, Z.; Chen, J.Y.; Dong, Y.F.; Qu, K.H.; Guo, T.M.; Wang, F.H.; Liu, A.R.; Chen, S.C.; Li, X. Reactive oxygen species signaling in melatonin-mediated plant stress response. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2024, 207, 108398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, F.K.; Rivero, R.M.; Blumwald, E.; Mittler, R. Reactive oxygen species, abiotic stress and stress combination. Plant J. 2016, 90, 856–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noctor, G.; Foyer, C.H. Intracellular Redox Compartmentation and ROS-Related Communication in Regulation and Signaling. Plant Physiol. 2016, 171, 1581–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turkan, I. ROS and RNS: Key signalling molecules in plants. J. Exp. Bot. 2018, 69, 3313–3315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sierla, M.; Waszczak, C.; Vahisalu, T.; Kangasjärvi, J. Reactive Oxygen Species in the Regulation of Stomatal Movements. Plant Physiol. 2016, 171, 1569–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, K.; Roychoudhury, A. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) and response of antioxidants as ROS-scavengers during environmental stress in plants. Front. Environ. Sci. 2014, 2, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagi, M.; Fluhr, R. Production of Reactive Oxygen Species by Plant NADPH Oxidases. Plant Physiol. 2006, 141, 336–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadota, Y.; Sklenar, J.; Derbyshire, P.; Stransfeld, L.; Asai, S.; Ntoukakis, V.; Jones, J.D.G.; Shirasu, K.; Menke, F.; Jones, A.; et al. Direct Regulation of the NADPH Oxidase RBOHD by the PRR-Associated Kinase BIK1 during Plant Immunity. Mol. Cell 2014, 54, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedard, K.; Krause, K.H. The NOX family of ROS-Generating NADPH Oxidases: Physiology and Pathophysiology. Physiol. Rev. 2007, 87, 245–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.Y.; Li, P.; Htwe, N.M.P.S.; Shangguan, K.K.; Liang, Y. Antepenultimate residue at the C-terminus of NADPH oxidase RBOHD is critical for its function in the production of reactive oxygen species in Arabidopsis. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2019, 20, 713–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oda, T.; Hashimoto, H.; Kuwabara, N.; Akashi, S.; Hayashi, K.; Kojima, C.; Wong, H.L.; Kawasaki, T.; Shimamoto, K.; Sato, M.; et al. Structure of the N-terminal Regulatory Domain of a Plant NADPH Oxidase and Its Functional Implications. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 1435–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittler, R.; Vanderauwera, S.; Gollery, M.; Breusegem, F.V. Reactive oxygen gene network of plants. Trends Plant Sci. 2004, 9, 490–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, X.Y.; Tang, C.; Lv, S.Z.; Zhang, S.L.; Wu, J.Y.; Wang, P. PbRbohH/J mediates ROS generation to regulate the growth of pollen tube in pear. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2024, 207, 108342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, M.A.; Dangl, J.L.; Jones, J.D.G. Arabidopsis gp91phox homologues AtrbohD and AtrbohF are required for accumulation of reactive oxygen intermediates in the plant defense response. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 517–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnaud, D.; Deeks, M.J.; Smirnoff, N. RBOHF activates stomatal immunity by modulating both reactive oxygen species and apoplastic pH dynamics in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2023, 116, 404–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sagi, M.; Davydov, O.; Orazova, S.; Yesbergenova, Z.; Ophir, R.; Stratmann, J.W.; Fluhr, R. Plant respiratory burst oxidase homologs impinge on wound responsiveness and development in Lycopersicon esculentum. Plant Cell 2004, 16, 616–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, I.S.; Wu, Y.S.; Chen, C.T.; Chen, G.H.; Hwang, S.G.; Jauh, G.Y.; Tzen, J.T.C.; Yang, C.Y. AtRBOH I confers submergence tolerance and is involved in auxin-mediated signaling pathways under hypoxic stress. Plant Growth Regul. 2017, 83, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.W.; Ni, L.; Cui, Z.Z.; Jiang, J.J.; Chen, C.; Jiang, M.Y. The NADPH oxidase OsRbohA increases salt tolerance by modulating K+ homeostasis in rice. Crop J. 2019, 10, 1611–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, G.; Pati, P.K. Analysis of Cis-acting regulatory elements of Respiratory burst oxidase homolog (Rboh) gene families in Arabidopsis and rice provides clues for their diverse functions. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2016, 62, 104–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshie, Y.; Goto, K.; Takai, R.; Iwano, M.; Takayama, S.; Isogai, A.; Che, F.S. Function of the rice gp91phox homologs OsrbohA and OsrbohE genes in ROS-dependent plant immune responses. Plant Biotechnol. 2005, 22, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.T.; Zhang, R.; Wang, R.J.; Li, J.D.; Wu, B.; Zhang, H.W.; Xiao, G.Q. Overexpression of OsRbohH Enhances Heat and Drought Tolerance through ROS Homeostasis and ABA Mediated Pathways in Rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plants 2024, 13, 2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, Q.H.; Li, Y.S.; Li, S.Z.; Shi, A.K.; Zhou, M.D.; Ren, H.Z.; Yan, Y.; He, C.X.; Wang, J.; Sun, M.T.; et al. Photosynthesis Mediated by RBOH-Dependent Signaling Is Essential for Cold Stress Memory. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Li, Y.Y.; Zhou, Z.C.; Xiang, X.H.; Liu, X.; Wang, J.; Hu, Z.R.; Xiang, S.P.; Li, W.; Xiao, Q.Z.; et al. Tobacco transcription factor bHLH123 improves salt tolerance by activating NADPH oxidase NtRbohE expression. Plant Physiol. 2021, 186, 1706–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.Z.; Kakar, K.U.; Yang, Z.X.; Nawaz, Z.; Lin, S.F.; Guo, Y.S.; Ren, X.L.; Baloch, A.A.; Han, D.J. Systematic study of the stress-responsive Rboh gene family in Nicotiana tabacum: Genome-wide identification, evolution and role in disease resistance. Genomics 2020, 112, 1404–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.J.; Guo, Y.L.; Li, J.Y.; Su, Z.Z.; Wang, C.X.; Zhang, R.M.; Wei, C.H.; Ma, J.X.; Zhang, X.; Li, H. Positive Interaction between H2O2 and Ca2+ Mediates Melatonin-Induced CBF Pathway and Cold Tolerance in Watermelon (Citrullus lanatus L.). Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.L.; Yang, H.F.; Zou, J.P.; Jin, J.P.; Qi, Z.Y.; Yang, P.; Yu, J.Q.; Zhou, J. SnRK1α1-mediated RBOH1 phosphorylation regulates reactive oxygen species to enhance tolerance to low nitrogen in tomato. Plant Cell 2025, 37, koae321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.Y.; Wang, X.; Yan, A.; Deng, J.; Xie, Y.Q.; Liu, S.Y.; Liu, D.B.; He, L.; Weng, J.F.; Xu, J.Y. Evolutionary analysis of Respiratory Burst Oxidase Homolog (RBOH) genes in plants and characterization of ZmRBOHs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, J.S.; Monte, I.; DeFalco, T.A.; Köster, P.; Derbyshire, P.; Menke, F.L.H.; Zipfel, F. Conservation of the PBL-RBOH immune module in land plants. Curr. Biol. 2023, 33, 1030–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, Y.; Ishu; Shumayla; Dixit, S.; Singh, K.; Upadhyay, S.K. Decoding the features and potential roles of respiratory burst oxidase homologs in bread wheat. Curr. Plant Biol. 2024, 37, 100315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.T.; Bai, L.J.; Dai, X.Z.; Ba, L.J.; Wan, J.H.; Liang, W.Q.; Lin, H.T.; Fan, Z.Q. Comparative transcriptomic analysis reveals the reactive oxygen species metabolism involving in melatonin-alleviated chilling injury in postharvest banana fruit. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2025, 222, 10993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Zhang, Y.W.; Luo, L.; Lu, C.Y.; Kong, W.W.; Cheng, L.B.; Xu, X.Y.; Liu, J.H. Genome Wide Identification of Respiratory Burst Oxidase Homolog (Rboh) Genes in Citrus sinensis and Functional Analysis of CsRbohD in Cold Tolerance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Lin, Q.J.; Li, Z.; Chu, J.; Dong, H.; Mei, Q.; Xuan, Y.H. Calcineurin B-like interacting protein kinase 31 confers resistance to sheath blight via modulation of ROS homeostasis in rice. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2023, 24, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Su, H.; Liu, X.X.; Sun, J.F.; Xiang, L.; Liu, Y.J.; Hu, Z.W.; Xiong, X.Y.; Yang, X.M.; Bhutto, S.H.; et al. Identification of NADPH Oxidase Genes Crucial for Rice Multiple Disease Resistance and Yield Traits. Rice 2024, 17, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.F.; Sun, A.Q.; Shan, W.F.; Zheng, X.H.; Wang, Y.; Bai, L.; Xu, Y.C.; An, Z.; Wang, X.Y.; Wang, Y.M.; et al. OsRbohI is the indispensable NADPH oxidase for molecular-patterns-induced reactive oxygen species production in rice. Plant Commun. 2024, 5, 101129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.T.; Wan, Z.Y.; Li, S.; Zhang, Y. Spatiotemporal production of reactive oxygen species by NADPH oxidase is critical for Tapetal programmed cell death and Pollen Development in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2014, 26, 2007–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, P.; McClees, S.F.; Afaq, F. Pomegranate for Prevention and Treatment of Cancer: An Update. Molecules 2017, 22, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaygannia, E.; Bahmani, M.; Zamanzad, B.; Rafieian-Kopaei, M. A Review Study on Punica granatum L. J. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 21, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, S.H.; Chai, Y.Q.; Hao, Q.; Ma, Y.D.; Wang, W.L.; Liu, H.Y.; Diao, M. Transcriptomic and physiological analysis reveals crucial biological pathways associated with low-temperature stress in Tunisian soft-seed pomegranate (Punica granatum L.). J. Plant Interact. 2023, 18, 2152887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnusamy, V.; Zhu, J.H.; Zhu, J.K. Cold stress regulation of gene expression in plants. Trends Plant Sci. 2007, 12, 444–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.S.; Lu, R.; Feng, L.J.; Zheng, M.Y.; Zhang, H.; Yin, Y.L.; Zheng, L. Functional Characterization of Pomegranate CAMTA3 in Cold Stress Responses. Plants 2025, 14, 813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.B.; Xu, S.W.; Zhang, L.H.; Zheng, J. A Genome-Wide Analysis of the BAM Gene Family and Identification of the Cold-Responsive Genes in Pomegranate (Punica granatum L.). Plants 2024, 13, 1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.; Shua, Z.Y.; Zhao, D.G.; Liu, B.B.; Luo, H.; Chen, Y.; Meng, D.; Song, Z.H.; Yang, Q.; Wang, Z.C.; et al. Genome assembly of pomegranate highlights structural variations driving population differentiation and key loci underpinning cold adaption. Hortic. Res. 2025, 12, uhaf022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2−∆∆CT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kshirsagar, K.R.; Pathak, S.S.; Patil, S.M. Pomegranate (Punica granatum L): A fruitful fountain of remedial potential. Cureus 2023, 15, e45677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqahtani, R.A.; Almutairi, B.; Al-Zharani, M.; Alkahtane, A.A.; AL-Johani, N.S.; Alkeraishan, N.; Yaseen, K.N.; Aljarba, N.H.; Almasoud, H.; Aljuhani, B.; et al. The Potential Therapeutic Efficacy of Pomegranate (Punica granatum) Seeds on MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cell Line. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2024, 19, 1934578X241302555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, J.M.; Muhlemann, J.K.; Gayomba, S.R.; Muday, G.K. RBOH-Dependent ROS synthesis and ROS scavenging by Plant Specialized metabolites to modulate Plant Development and stress responses. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2019, 32, 370–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.B.; Ren, W.C.; Jiang, S.; Kong, L.Y.; Ma, L.L.; He, J.J.; Wang, D.L.; Liu, W.L.; Ma, W.; Liu, X.B. Identification and expression analysis of the RBOH gene family of Isatis indigotica Fort. and the potential regulation mechanism of RBOH gene on H2O2 under salt stress. Plant Cell Rep. 2025, 44, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, J.; Kadota, Y.; Zipfel, C.; Molina, A.; Torres, M.A. The Arabidopsis NADPH oxidases RbohD and RbohF display differential expression patterns and contributions during plant immunity. J. Exp. Bot. 2016, 67, 1663–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, D.; Andrio, E.; Danchin, E.G.J.; Oger, E.; Gucciardo, S.; Lambert, A.; Puppo, A.; Pauly, N. A Medicago truncatula NADPH oxidase is involved in symbiotic nodule functioning. New Phytol. 2011, 189, 580–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, S.; Sharma, B.; Gupta, A.K.; Kaur, S.; Kaur, J. Nodule metabolism in cold stress tolerant and susceptible chickpea cultivars. Symbiosis 2014, 64, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.H.; Liu, Z.S.; Li, L.; Pan, X.J.; Yao, K.D.; Wei, W.Y.; Liao, W.B.; Wang, C.L. The Characteristics and Expression Analysis of the Tomato SlRBOH Gene Family under Exogenous Phytohormone Treatments and Abiotic Stresses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camejo, D.; Guzmán-Cedeño, Á.; Moreno, A. Reactive oxygen species, essential molecules, during plant-pathogen interactions. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zou, X.X.; Yin, H.P.; Yin, Y.; Li, Z.Q.; Xiao, W.J.; Liu, S.C.; Li, Y.L.; Guo, X.H. Genome-Wide Identification, Classification, Expression Analysis, and Screening of Drought and Heat Resistance-Related Candidates of the Rboh Gene Family in Wheat. Plants 2024, 13, 3377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.M.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, T.; Li, Y.Y.; Hong, Y.H.; Chen, W.J.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, G.J.; Shabala, S.; Yu, M. Genome-wide analysis of respiratory burst oxidase homolog gene family in pea (Pisum sativum L.). Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1321952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.W.; Xie, Y.D.; Ali, B.; Ahmed, W.; Tang, Y.; Li, H.X. Genome-wide Identification, Classification, Evolutionary Expansion and Expression of Rboh Family Genes in Pepper (Capsicum annuum L.). Trop. Plant Biol. 2021, 14, 251–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahalingam, R.; Graham, D.; Walling, J.G. The Barley (Hordeum vulgare ssp. vulgare) Respiratory Burst Oxidase Homolog (HvRBOH) Gene Family and Their Plausible Role on Malting Quality. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 608541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.K.; He, C.Z. Regulation of plant reactive oxygen species (ROS) in stress responses: Learning from AtRBOHD. Plant Cell Rep. 2016, 35, 995–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, K.; Das, A.; Ahmed, R.; Akhtar, S.; Kulkarni, R.; Banu, S. Genome-wide analysis of respiratory burst oxidase homolog (Rboh) genes in Aquilaria species and insight into ROS-mediated metabolites biosynthesis and resin deposition. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 14, 1326080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.Q.; Zhang, F.; Yang, M.; He, Y.Y.; Li, Z.Y.; Yang, J.L.; Wang, X.F. The NADPH-oxidase LsRbohC1 plays a role in lettuce (Lactuca sativa) seed germination. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2024, 154, 751–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).