Investigation and Analysis of Microbial Diversity in Rice Husk-Based Fermentation Bed Material
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
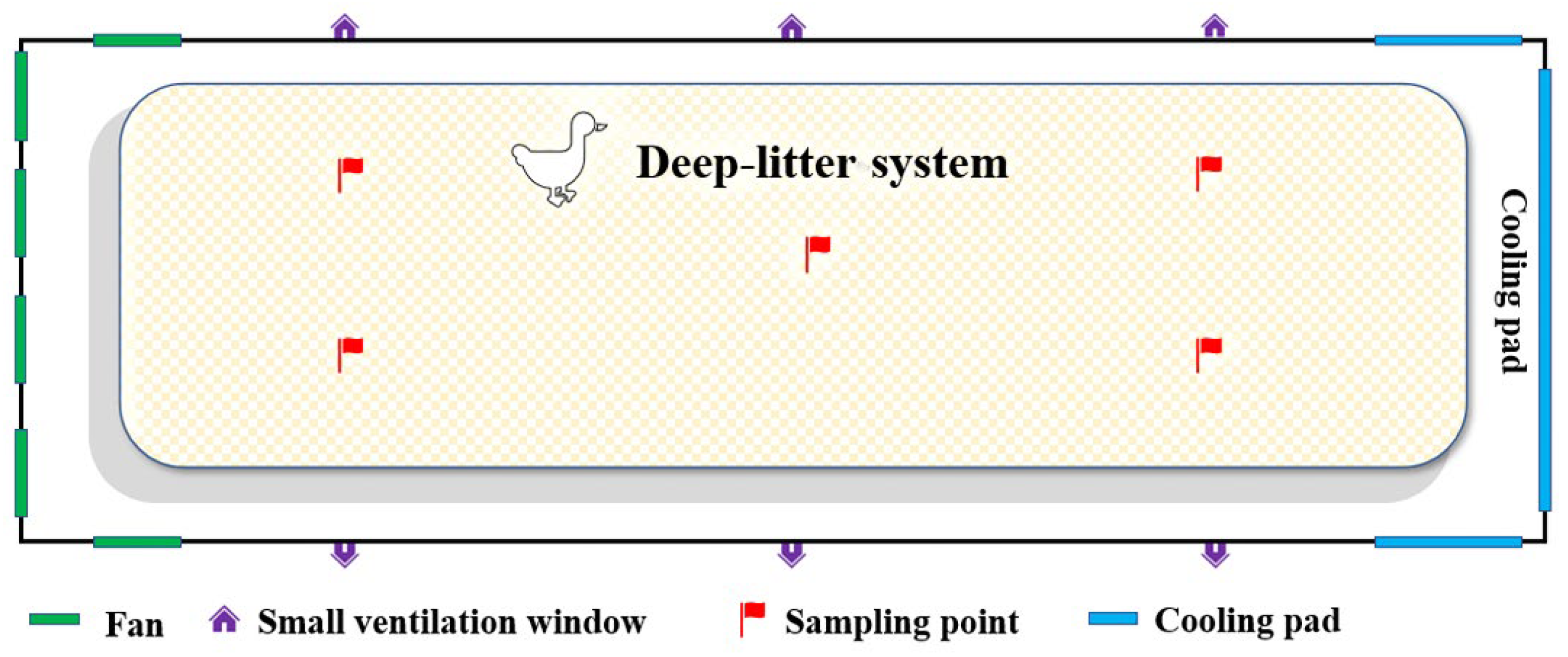
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Main Reagents and Instruments
2.3. DNA Extraction and PCR Amplification of Bacterial 16S rDNA Fragments
2.4. Denaturing Gradient Gel Electrophoresis
2.5. Principal Component Analysis and Calculation of the Shannon Index, Abundance and Evenness Index
3. Results
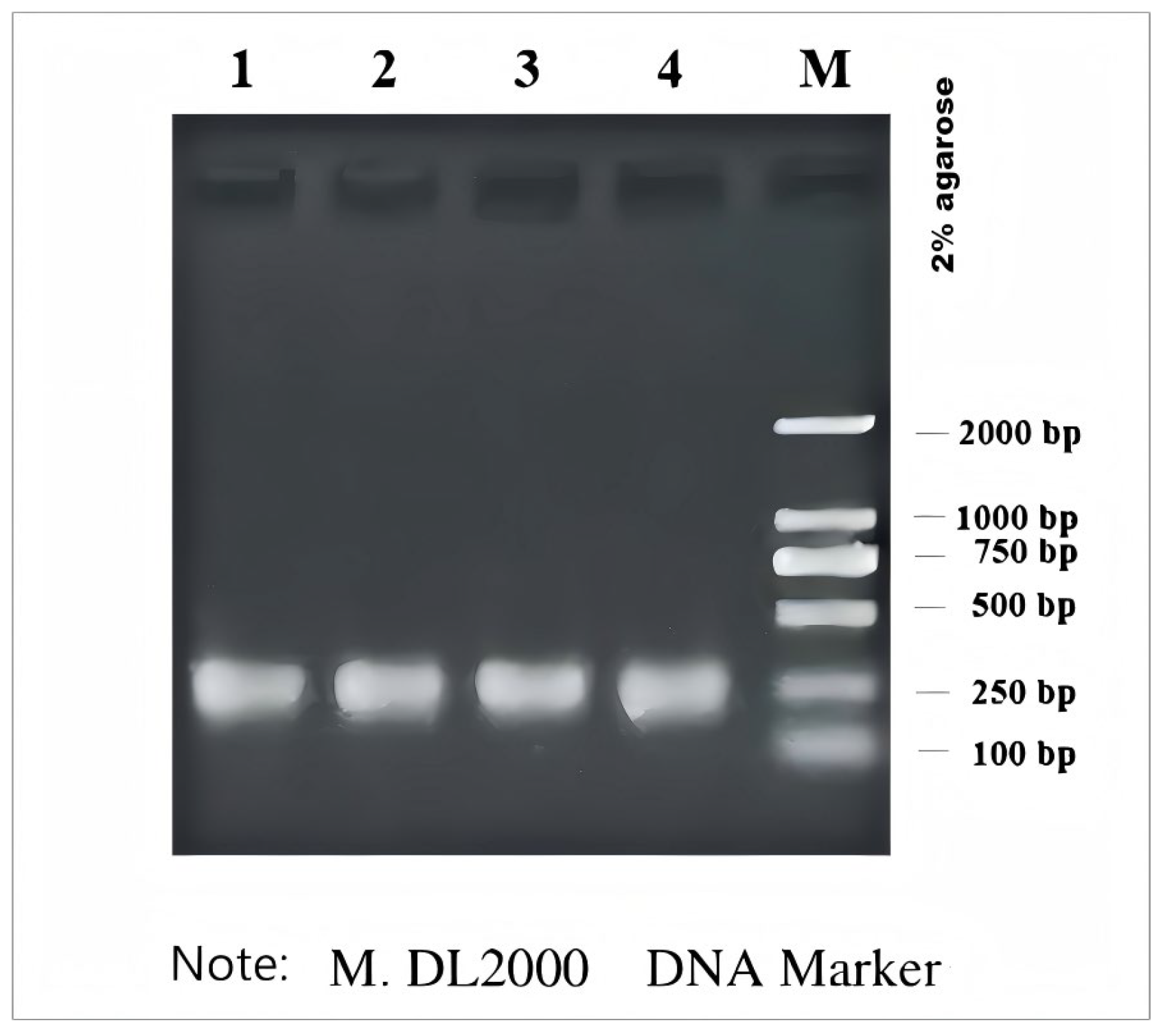
3.1. PCR Amplification of 16S rDNA of Bacteria
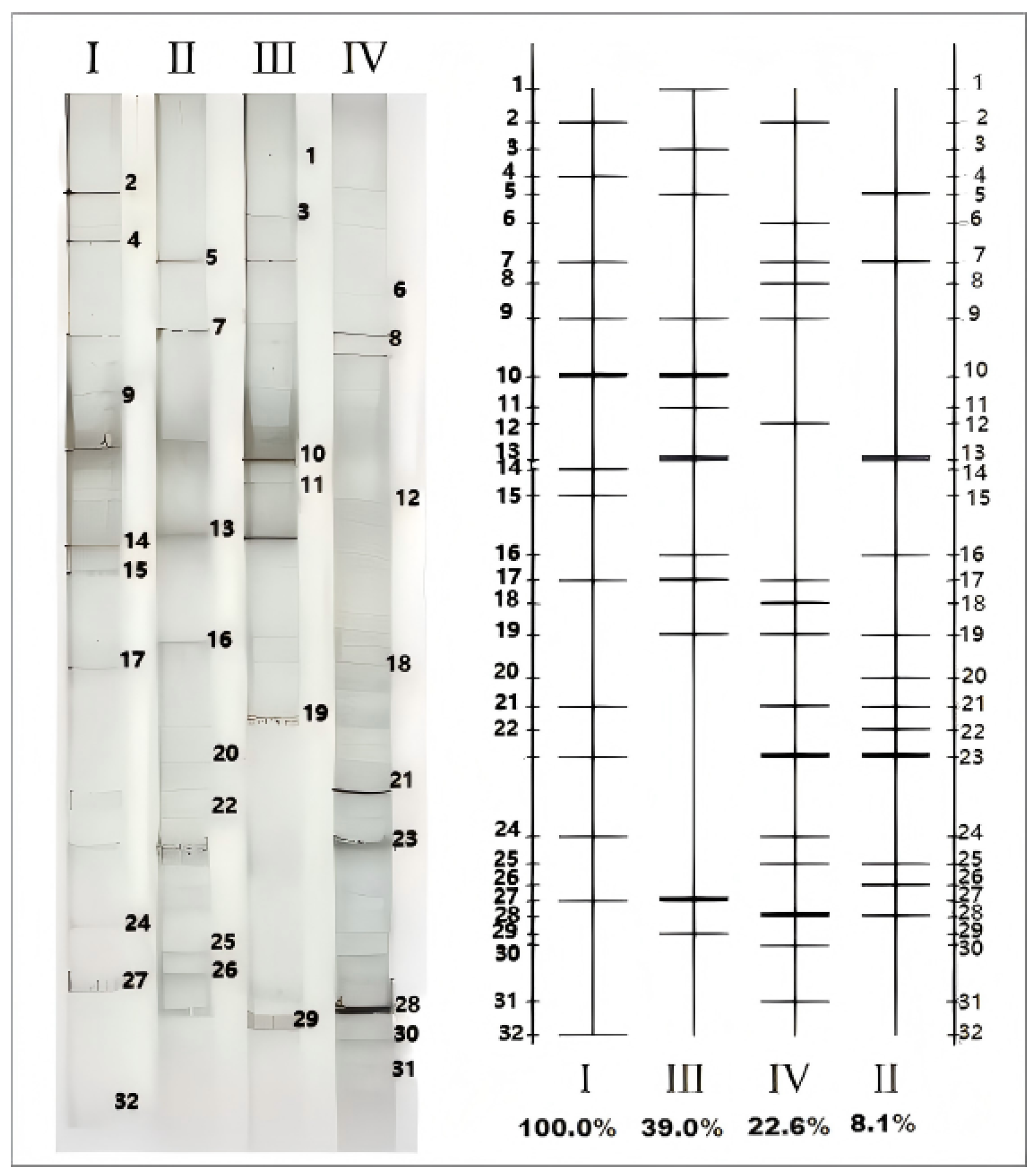
3.2. DGGE of PCR Products
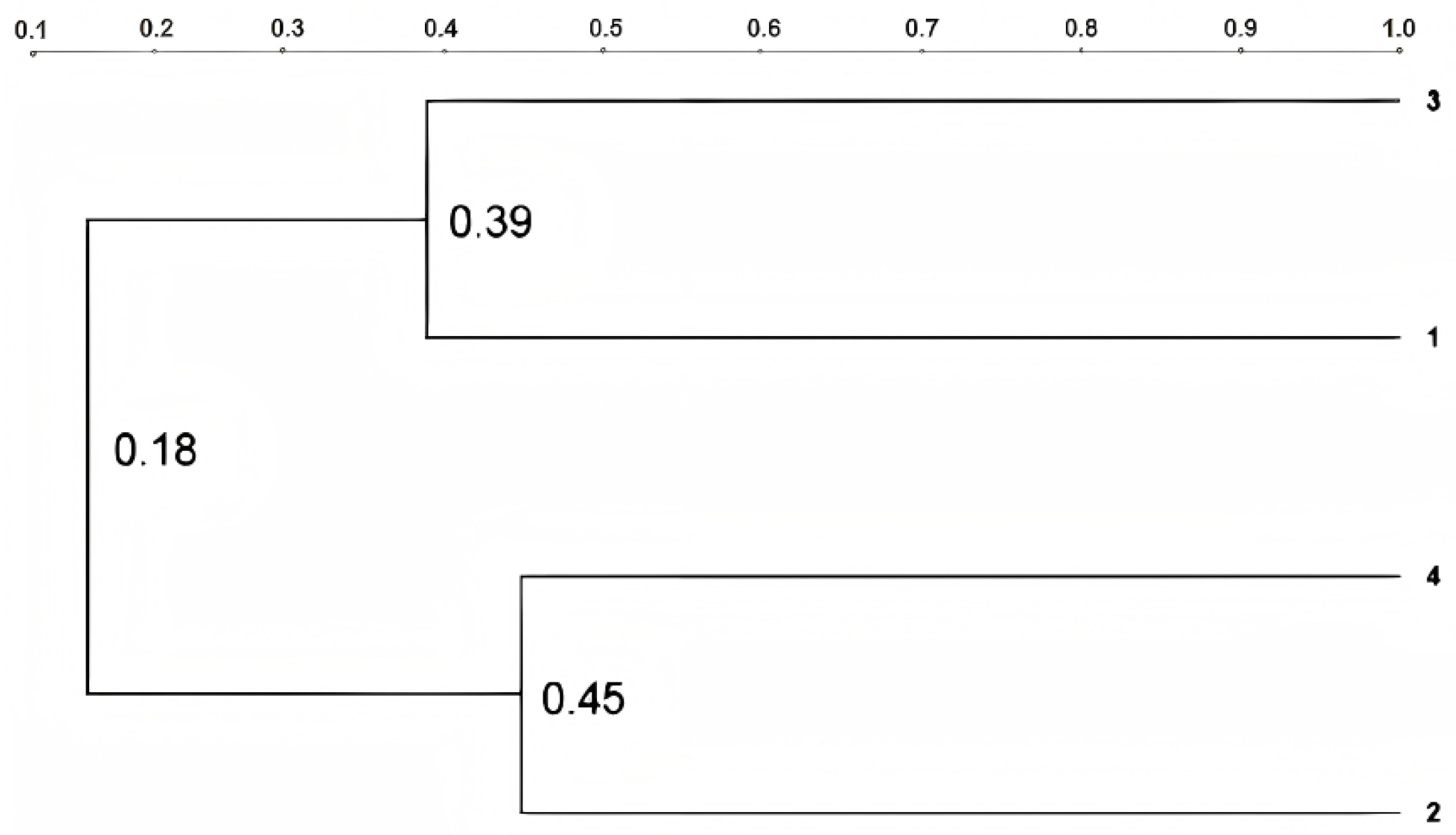
3.3. Construction of the Cluster Diagram
3.4. Analysis of Microbial Diversity Index
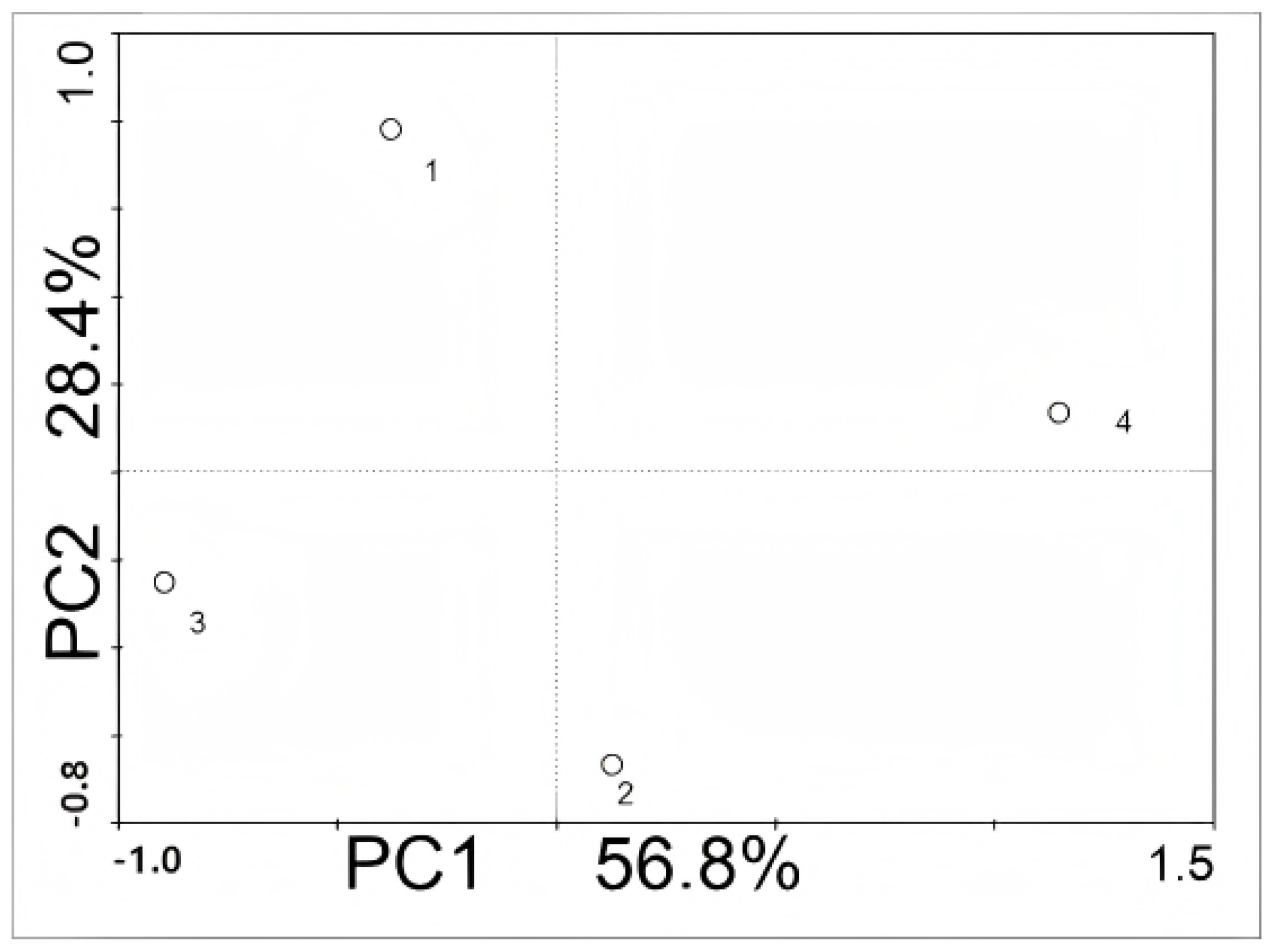
3.5. PCA
3.6. Determination of the Electrophoretic Band Sequence
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fouad, A.M.; Ruan, D.; Wang, S.; Chen, W.; Xia, W.G.; Zheng, C.T. Nutritional requirements of meat-type and egg-type ducks: What do we know? J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2018, 9, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, T.; Chen, L.; Du, X.; Lai, S.J.; Huang, S.P.; Liu, Y.L.; Lu, L.Z. Association analysis between feed efficiency studies and expression of hypothalamic neuropeptide genes in laying ducks. Anim. Genet. 2016, 47, 606–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eratalar, S.A. The effects of plastic slatted floor and a deep-litter system on the growth performance of hybrid Pekin ducks. Arch. Anim. Breed. 2021, 64, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, D.L.M.; de Haas, E.N.; Lee, C. A review of environmental enrichment for laying hens during rearing in relation to their behavioral and physiological development. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 9–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, S.; Guo, Y.; Yan, P. Comparison of two housing systems on behaviour and performance of fattening pigs. J. Appl. Anim. Res. 2019, 47, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Hamid, S.E.; Saleem, A.S.Y.; Youssef, M.I.; Mohammed, H.H.; Abdelaty, A.I. Influence of housing systems on duck behavior and welfare. J. Adv. Vet. Anim. Res. 2020, 7, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Wen, X.; Alphin, R.; Zhu, Z.; Zhou, Z. Effects of two different broiler flooring systems on production performances, welfare, and environment under commercial production conditions. Poult. Sci. 2017, 96, 1108–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, R.S.; Hemsworth, P.H.; Cronin, G.M.; Campbell, R.G. The social and feeding behaviour of growing pigs in deep-litter, group housing systems. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2003, 82, 173–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlen, G.A.M.; Hemsworth, P.H.; Gonyou, H.W.; Fabrega, E.; Strom, A.D.; Smits, R.J. The welfare of gestating sows in conventional stalls and large groups on deep litter. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2007, 105, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.Y.; Zheng, Z.W.; Li, H.C.; Xu, D.; Li, X.; Xiang, L.J.; Tu, S.X. Review on Rice Husk Biochar as an Adsorbent for Soil and Water Remediation. Plants 2023, 12, 1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, S.; Ubeyitogullari, A. Extraction of phenolic compounds from rice husk via ethanol-water-modified supercritical carbon dioxide. Heliyon 2023, 9, e14196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satbaev, B.; Yefremova, S.; Zharmenov, A.; Kablanbekov, A.; Yermishin, S.; Shalabaev, N.; Satbaev, A.; Khen, V. Rice husk research:From environmental pollutant to a promising source of organo-mineral raw materials. Materials 2021, 14, 4119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Guo, X.B.; Liu, Y.; Fang, Z.Q.; Zhang, M.W.; Zhang, R.F.; You, L.J.; Li, T.; Liu, R.H. A full utilization of rice husk to evaluate phytochemical bioactivities and prepare cellulose nanocrystals. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, Y.B.; Xu, L.; Qiang, Z.M.; Dong, H.Y.; Shi, H.L. Preparation of green biosorbent using rice hull to preconcentrate, remove and recover heavy metal and other metal elements from water. Chemosphere 2021, 262, 127940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiquia, S.M.; Tam, N.F.Y.; Hodgkiss, I.J. Effects of bacterial inoculum and mixture adjustment on composting of pig manure. Environ. Pollut. 1997, 96, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, S.G.; Lerman, L.S. DNA fragments differing by single base-pair substitutions separated in denaturing gradient gels: Correspondence with melting theory. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 80, 1579–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.; Saha, A.; Ananthram, A.N. Comparison of DNA extraction methods for non-marine molluscs: Is modified CTAB DNA extraction method more efficient than DNA extraction kits? 3 Biotech 2020, 10, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muyzer, G.; De Waal, E.C.; Uitterlinden, A.G. Profiling of complex microbial populations by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis analysis of polymerase chain reaction–amplified genes coding for 16S rRNA. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1993, 59, 695–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.F.; Jia, T.Z.; Chen, J.N.; Liu, X.Y.; Zhao, M.J.; Liu, P.P. Analysis of microbial diversity in Shenqu with different fermentation times by PCR-DGGE. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2017, 48, 246–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Wu, F.Z.; Zhou, X.G.; Fu, X.P.; Tao, Y.; Xu, W.H.; Pan, K.; Liu, S.W. Effects of Intercropping with Potato Onion on the Growth of Tomato and Rhizosphere Alkaline Phosphatase Genes Diversity. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuang, Y.; Tani, K.; Synnott, A.J.; Ohshima, K.; Higuchi, H.; Nagahata, H.; Tanji, Y. Characterization of bacterial population of raw milk from bovine mastitis by culture-independent PCR-DGGE method. Biochem. Eng. J. 2009, 45, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, N.F.Y.; Vrijmoed, L.L.P. Effects of commercial bacterial products on nutrient transformations of pig manure in a pig-on-litter system. Water Manag. Res. 1990, 8, 363–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, D.K.O.; Chaw, D.; Lo, C.Y. Development of an environmentally friendly and cost effective system for the treatment of waste in pig farming. J. Agric. Eng. Res. 1995, 56, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deininger, A.; Tamm, M.; Krause, R.; Sonnenberg, H. Penetration resistance and water-holding capacity of differently conditioned straw for deep litter housing systems. J. Agric. Eng. Res. 2000, 77, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Liu, B.; Wang, J.; Che, J.; Liu, G.; Guan, X. Diversity and dynamics of the bacterial community involved in pig manure biodegradation in a microbial fermentation bed system. Ann. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biesek, J.; Banaszak, M.; Grabowicz, M.; Wlaźlak, S. Chopped straw and coffee husks affect bedding chemical composition and the performance and foot pad condition of broiler chickens. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 6600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aziz, A.; Akter, M.R.; Rahaman, M.S. Identification and Antibiogram Profiles of Staphylococcus aureus From Commercial Broiler Flocks in Dinajpur District of Bangladesh with Special Focus on the Determination of Lethal Effect of Extracted Toxin. Sci. J. Microbiol. 2023, 4, 74–82. [Google Scholar]
- Sankomkai, W.; Boonyanugomol, W.; Kraisriwattana, K. Characterisation of Classical Enterotoxins, Virulence Activity, and Antibiotic Susceptibility of Isolated from Thai Fermented Pork Sausages, Clinical Samples, and Healthy Carriers in Northeastern Thailand. J. Vet. Res. 2020, 2, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mousavi, B.S.M.; Rahimi, E.; Seyed, M.H.; Zia, J.N. Investigating the Prevalence of Enterotoxin and Antibiotic Resistance in Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Isolated from Meat and Edible Viscera of Broiler Chickens. Vet. Med. Sci. 2025, 11, e70413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiner-Lastinger, L.M.; Abner, S.; Benin, A.L.; Edwards, J.R.; Kallen, A.J.; Karlsson, M.; Magill, S.S.; Pollock, D.; See, I.; Soe, M.M.; et al. Antimicrobial-resistant pathogens associated with pediatric healthcare-associated infections: Summary of data reported to the National Healthcare Safety Network, 2015–2017. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2020, 41, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Poddar, N.; Panigrahi, K.; Pathi, B.; Ravi Nayak, S.; Dandapat, R.; Pattnaik, D.; Praharaj, A.K.; Patro, A.R.K. Evaluation of In-Vitro Activity of Ceftaroline Against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Clinical Isolates. Cureus 2023, 15, e49859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Group | Aroma Concentration Index | Evenness | Abundance |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2.53 ± 0.01 ab | 0.96 ± 0.00 b | 13.15 ± 0.03 ab |
| 2 | 2.44 ± 0.01 b | 0.99 ± 0.01 a | 12.22 ± 0.02 b |
| 3 | 2.40 ± 0.01 b | 0.97 ± 0.00 b | 12.67 ± 0.03 b |
| 4 | 2.68 ± 0.02 a | 0.98 ± 0.01 a | 16.33 ± 0.58 a |
| Band Number | Similar Strain | Accession Number | Similarity | Classification |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Pedobacter ginsenosidimutans | NR_108685 | 92 | Bacteroidetes; Sphingobacteriia Pedobacter |
| 2 | Actinomadura sputi | NR_116929 | 98 | Actinobacteria; Streptosporangiales Actinomadura |
| 3 | Bacillus oleronius | NR_119157 | 94 | Firmicutes; Bacilli; Bacillus |
| 4 | Uncultured Desulfomicrobium sp. | LC001580 | 99 | Proteobacteria; Deltaproteobacteria Desulfomicrobium |
| 5 | Glycomyces arizonensis | NR_025791 | 98 | Actinobacteria; Glycomycetales; Glycomyces |
| 6 | Pedobacter kyungheensis | NR_132668 | 92 | Bacteroidetes; Sphingobacteriia; Pedobacter |
| 7 | Xylanimonas cellulosilytica | NR_074544 | 95 | Actinobacteria; Micrococcales |
| 8 | Pedobacter antarcticus | NR_104917 | 92 | Bacteroidetes; Sphingobacteriia; Pedobacter |
| 9 | Pedobacter antarcticus | NR_113717 | 91 | Bacteroidetes; Sphingobacteriia Pedobacter |
| 10 | Uncultured Sphingobacteriaceae bacterium | KF508174 | 98 | Bacteroidetes; Sphingobacteriia; environmental samples |
| 11 | Conexibacter arvalis | NR_113264 | 92 | Actinobacteria; Thermoleophilia Conexibacter |
| 12 | Uncultured bacterium | KJ454285 | 97 | Bacteria; environmental samples |
| 13 | Uncultured bacterium | JF417963 | 99 | Bacteria; environmental samples |
| 14 | Corynebacterium casei | NR_122062 | 99 | Actinobacteria; Corynebacteriales Corynebacterium |
| 15 | Silicibacter lacuscaerulensis | NR_118852 | 96 | Proteobacteria; Alphaproteobacteria Ruegeria |
| 16 | Staphylococcus sciuri | NR_025520 | 97 | Firmicutes; Bacilli; Staphylococcus |
| 17 | Serinibacter tropicus | NR_134805 | 97 | Actinobacteria; Micrococcales Serinibacter |
| 18 | Streptomyces spectabilis | NR_115463 | 99 | Actinobacteria; Streptomycetales Streptomyces |
| 19 | Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus str. Tiberius | NR_102470 | 93 | Proteobacteria; Deltaproteobacteria Bdellovibrio |
| 20 | Gracilibacillus halotolerans | NR_024876 | 98 | Firmicutes; Bacilli; Gracilibacillus |
| 21 | Virgibacillus zhanjiangensis | NR_116658 | 98 | Firmicutes; Bacilli; Virgibacillus |
| 22 | Oceanobacillus indicireducens | NR_113330 | 99 | Firmicutes; Bacilli; Oceanobacillus |
| 23 | Jeotgalicoccus nanhaiensis | NR_116596 | 96 | Firmicutes; Bacilli; Jeotgalicoccus |
| 24 | Brachybacterium faecium | NR_027599 | 97 | Actinobacteria; Micrococcales; Brachybacterium |
| 25 | Uncultured bacterium | AB518162 | 99 | Bacteria; environmental samples |
| 26 | Fodinibius salinus | NR_117802 | 97 | Bacteroidetes; Sphingobacteriia; Fodinibius |
| 27 | Thermomonas koreensis | NR_113982 | 97 | Proteobacteria; Gammaproteobacteria; Thermomonas |
| 28 | Shewanella amazonensis | NR_074842 | 94 | Proteobacteria; Gammaproteobacteria; Shewanella |
| 29 | Brevibacterium avium | NR_026485 | 99 | Actinobacteria; Micrococcales; Brevibacterium |
| 30 | Herbaspirillum rubrisubalbicans | NR_114141 | 89 | Proteobacteria; Betaproteobacteria; Herbaspirillum |
| 31 | Brevibacterium linens | NR_026166 | 98 | Actinobacteria; Micrococcales; Brevibacterium |
| 32 | Brevibacterium marinum | NR_042586 | 97 | Actinobacteria; Micrococcales; Brevibacterium |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, J.; Liu, W.; Li, F.; Wang, Z.; Guo, G.; Geng, B.; Sun, J.; Guo, G. Investigation and Analysis of Microbial Diversity in Rice Husk-Based Fermentation Bed Material. Agriculture 2025, 15, 1828. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15171828
Gao J, Liu W, Li F, Wang Z, Guo G, Geng B, Sun J, Guo G. Investigation and Analysis of Microbial Diversity in Rice Husk-Based Fermentation Bed Material. Agriculture. 2025; 15(17):1828. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15171828
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Jinbo, Wei Liu, Fuwei Li, Zhaohong Wang, Guang Guo, Bing Geng, Jingshi Sun, and Genglin Guo. 2025. "Investigation and Analysis of Microbial Diversity in Rice Husk-Based Fermentation Bed Material" Agriculture 15, no. 17: 1828. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15171828
APA StyleGao, J., Liu, W., Li, F., Wang, Z., Guo, G., Geng, B., Sun, J., & Guo, G. (2025). Investigation and Analysis of Microbial Diversity in Rice Husk-Based Fermentation Bed Material. Agriculture, 15(17), 1828. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15171828





