Comparative Assessment of Fractional and Erosion Plot Methods for Quantifying Soil Erosion and Nutrient Loss Under Vetiver Grass Technology on Two Contrasting Slopes in Rainforest Agroecology
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
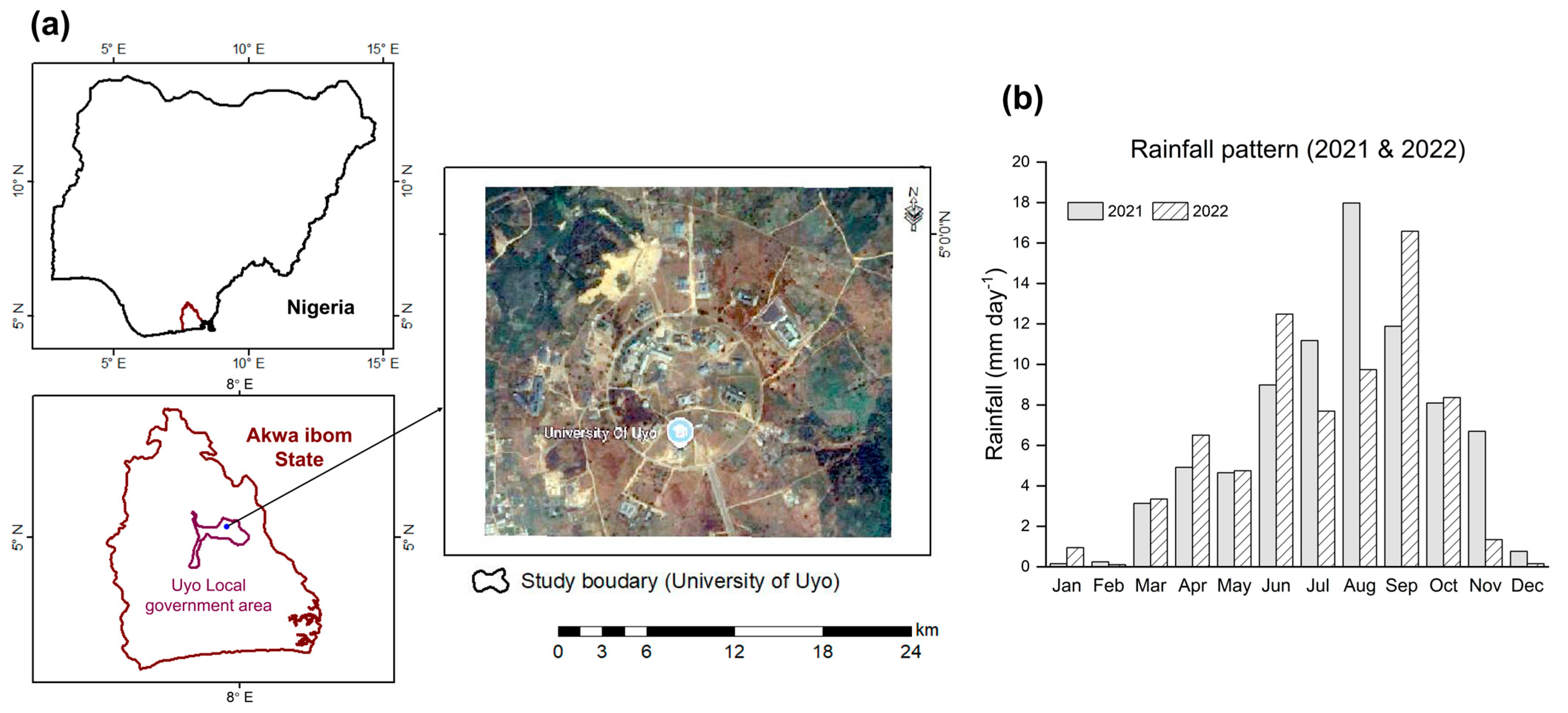
2.1. Experimental Site
2.2. Nursery and Field Establishment of Vetiver Grass Hedgerows
2.3. Rainfall and Precipitation Concentration Index Determination
2.4. Experimental Plot Description, Installations, and Measurement of Soil Erosion
2.5. Determination of Runoff and Sediment Nutrients
2.6. Cost Benefits of Using the Fractional and Erosion Plot Methods
2.7. Statistical Data Analyses
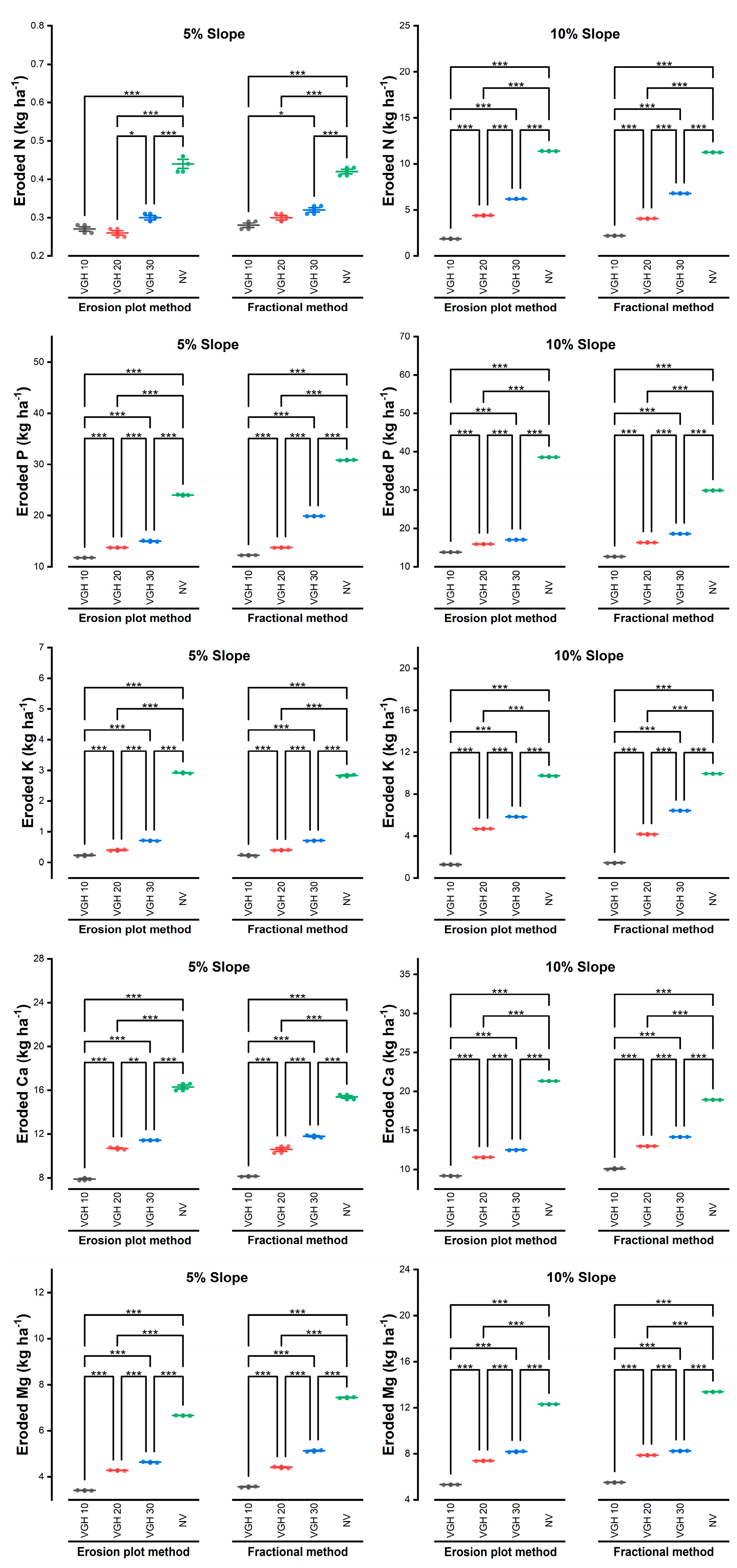
3. Results
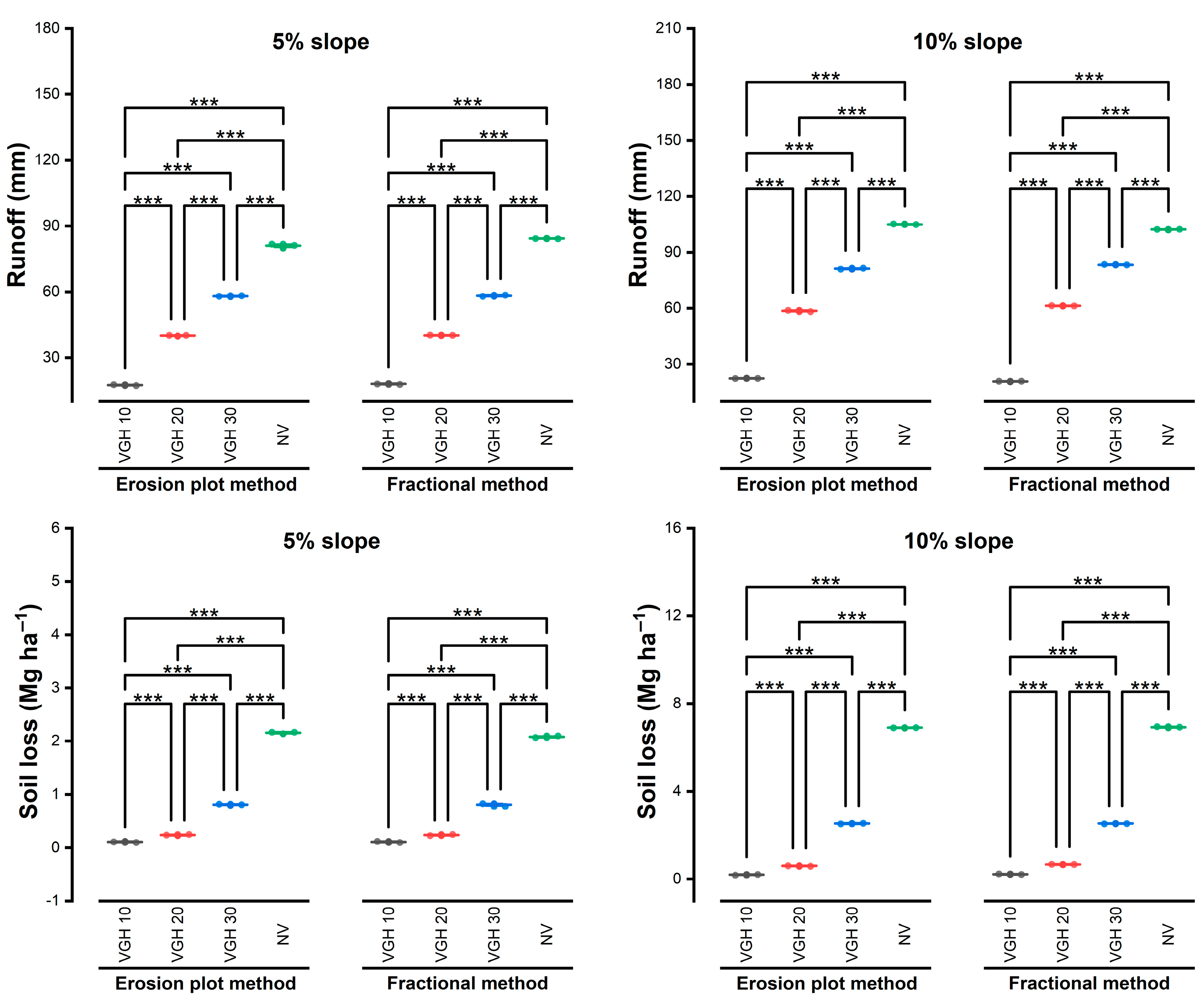
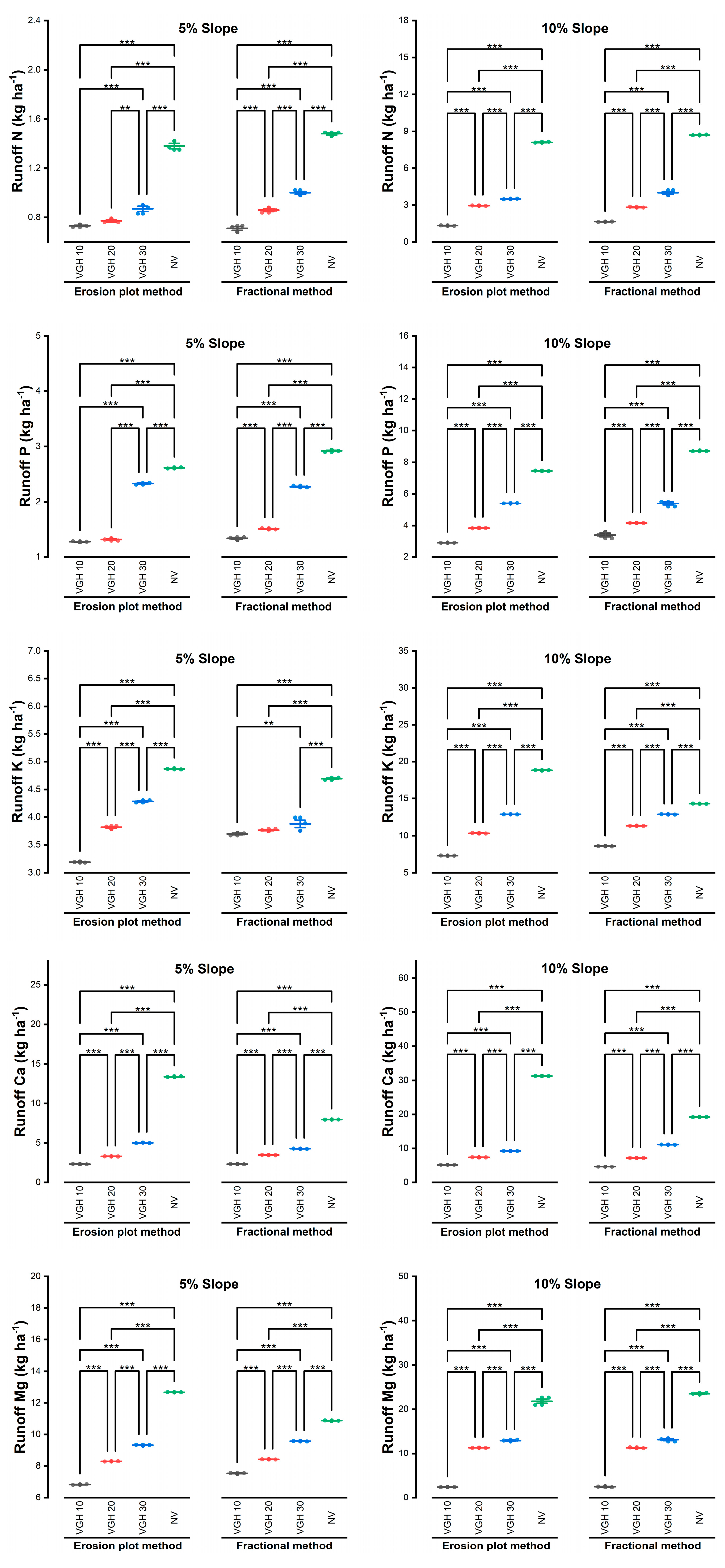
3.1. Comparison of Runoff and Nutrient Loss Discharged Between the Fractional and Erosion Plot Methods
3.2. Differences in Soil and Nutrient Losses Obtained from Fractional and Erosion Plot Methods

| Left-Piped Drum | Central-Piped Drum | Right-Piped Drum | CV (%) | Left-Piped Drum | Central-Piped Drum | Right-Piped Drum | CV (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year 1 | Year 2 | |||||||||||
| 5% Slope | ||||||||||||
| Runoff (mm) | VGH10 | 5.46 ± 0.03 | 5.93 ± 0.03 | 5.80 ± 0.03 | 5.73 ± 0.03 | 5.1 | 5.55 ± 0.00 | 6.13 ± 0.05 | 6.51 ± 0.00 | 6.06 ± 0.02 | 7.3 | |
| VGH20 | 10.81 ± 0.01 | 12.23 ± 0.01 | 12.06 ± 0.01 | 11.70 ± 0.01 | 7.02 | 13.42 ± 0.00 | 14.45 ± 0.00 | 14.74 ± 0.00 | 14.20 ± 0.00 | 6 | ||
| VGH30 | 18.67 ± 0.02 | 17.83 ± 0.02 | 17.70 ± 0.02 | 18.07 ± 0.02 | 2.9 | 21.83 ± 0.00 | 21.41 ± 0.00 | 22.50 ± 0.01 | 21.91 ± 0.01 | 5 | ||
| NV | 26.37 ± 0.01 | 28.17 ± 0.01 | 26.07 ± 0.01 | 26.87 ± 0.01 | 4.65 | 29.65 ± 0.02 | 27.45 ± 0.03 | 28.33 ± 0.01 | 28.48 ± 0.02 | 3.89 | ||
| Soil loss (kg ha−1) | VGH10 | 30.56 ± 0.02 | 31.89 ± 0.04 | 30.75 ± 0.02 | 31.07 ± 0.03 | 5.18 | 33.93 ± 0.01 | 34.13 ± 0.02 | 35.93 ± 0.01 | 34.66 ± 0.01 | 3.18 | |
| VGH20 | 62.15 ± 0.02 | 62.52 ± 0.02 | 61.84 ± 0.02 | 62.17 ± 0.02 | 6.2 | 81.40 ± 0.01 | 79.47 ± 0.01 | 82.13 ± 0.01 | 81.00 ± 0.01 | 1.7 | ||
| VGH30 | 242.67 ± 0.01 | 249.55 ± 0.01 | 261.08 ± 0.01 | 251.10 ± 0.01 | 5.1 | 270.00 ± 0.01 | 274.43 ± 0.01 | 268.57 ± 0.01 | 271.00 ± 0.01 | 1.13 | ||
| NV | 692 ± 0.01 | 671.23 ± 0.01 | 730.47 ± 0.02 | 697.90 ± 0.01 | 4.31 | 737.33 ± 0.01 | 715.15 ± 0.01 | 778.52 ± 0.01 | 743.67 ± 0.01 | 4.32 | ||
| 10% slope | ||||||||||||
| Runoff (mm) | VGH10 | 11.27 ± 0.02 | 11.15 ± 0.01 | 11.18 ± 0.01 | 11.20 ± 0.01 | 8.62 | 12.87 ± 0.01 | 12.25 ± 0.01 | 11.38 ± 0.00 | 12.17 ± 0.01 | 3.9 | |
| VGH20 | 18.52 ± 0.01 | 18.81 ± 0.01 | 18.07 ± 0.00 | 18.47 ± 0.01 | 3.9 | 19.18 ± 0.01 | 18.51 ± 0.00 | 18.03 ± 0.00 | 18.57 ± 0.00 | 4.21 | ||
| VGH30 | 33.00 ± 0.00 | 34.03 ± 0.00 | 33.27 ± 0.02 | 33.43 ± 0.01 | 2.29 | 23.11 ± 0.00 | 22.93 ± 0.00 | 23.87 ± 0.02 | 23.30 ± 0.01 | 2.29 | ||
| NV | 53.40 ± 0.03 | 52.10 ± 0.01 | 51.90 ± 0.02 | 52.47 ± 0.02 | 2.51 | 34.41 ± 0.01 | 34.12 ± 0.01 | 33.93 ± 0.03 | 34.15 ± 0.02 | 2.51 | ||
| Soil loss (kg ha−1) | VGH10 | 74.67 ± 0.01 | 78.11 ± 0.01 | 75.32 ± 0.01 | 76.03 ± 0.01 | 5.58 | 90.27 ± 0.02 | 89.82 ± 0.01 | 86.92 ± 0.01 | 89.00 ± 0.01 | 2.04 | |
| VGH20 | 173.70 ± 0.01 | 175.00 ± 0.01 | 179.30 ± 0.01 | 176.00 ± 0.01 | 3.06 | 216.67 ± 0.02 | 228.00 ± 0.02 | 213.33 ± 0.01 | 219.33 ± 0.02 | 3.51 | ||
| VGH30 | 815.33 ± 0.02 | 800.00 ± 0.00 | 840.67 ± 0.01 | 818.67 ± 0.01 | 6.88 | 866.00 ± 0.01 | 848.67 ± 0.01 | 902.33 ± 0.01 | 872.33 ± 0.01 | 3.14 | ||
| NV | 2090.33 ± 0.00 | 2257.33 ± 0.01 | 2376.33 ± 0.01 | 2241.33 ± 0.01 | 6.41 | 2210.00 ± 0.01 | 2297.00 ± 0.00 | 2367.00 ± 0.01 | 2291.33 ± 0.01 | 3.43 | ||
3.3. Comparison of Soil Erosion Discharged by the Central Pipe and Side Pipes
3.4. The Difference Between the Cost Analyses of the Fractional and Erosion Plot Methods
4. Discussion
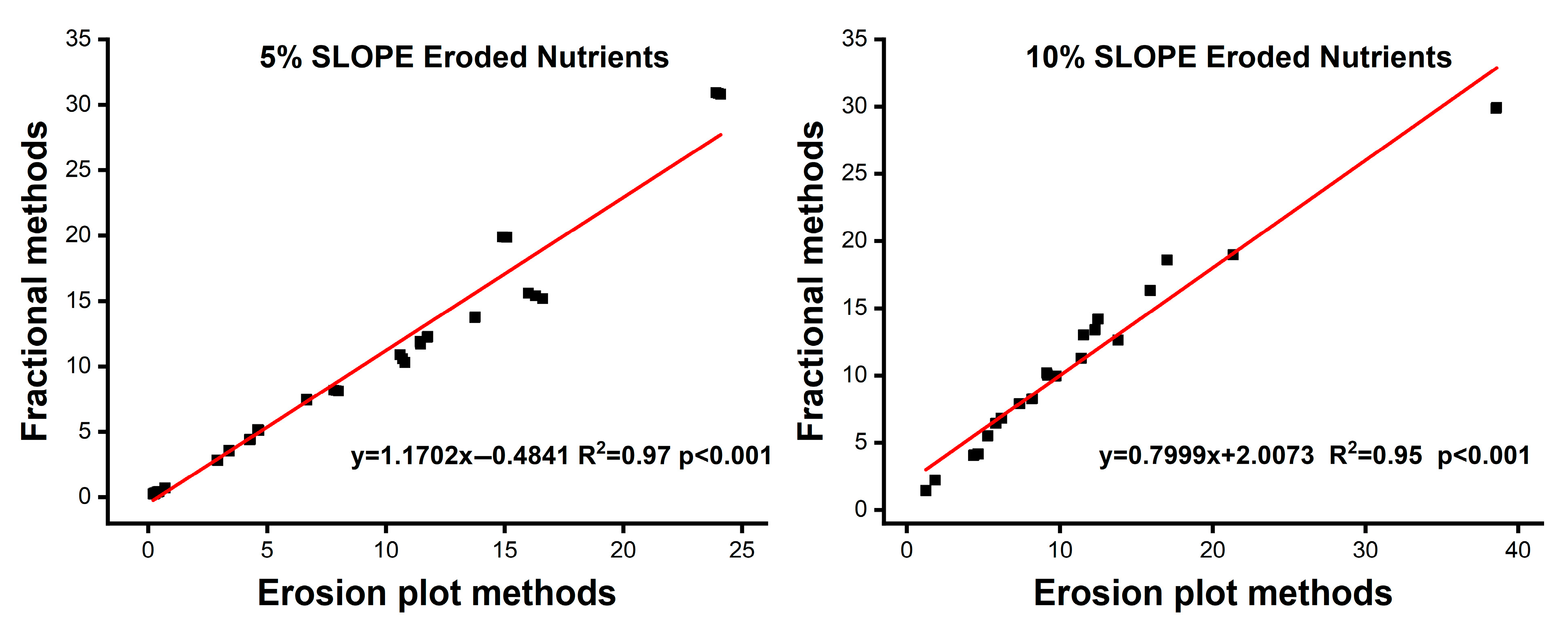
4.1. Relationship Between Soil Erosion Produced by Fractional and Erosion Plot Methods
4.2. Economic Benefit of Replacing the Erosion Plot Method with the Fractional Method
4.3. Limitations of the Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO. Soils for Nutrition: State of the Art; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. Outcome Document of the Global Symposium on Soil Erosion; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- El Mazi, M.; Hmamouchi, M.; Saber, E.; Bouchantouf, S.; Houari, A. Deforestation effects on soil properties and erosion: A case study in the central Rif, Morocco. Eurasian J. Soil Sci. 2022, 11, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimeles, A.; Verdier-Chouchane, A.; Boly, A. Conclusions: Enhancing the resilience and sustainability of the agriculture sector in sub-Saharan Africa. In Building a Resilient and Sustainable Agriculture in Sub-Saharan Africa; Shimeles, A., Verdier-Chouchane, A., Boly, A., Eds.; Palgrave Macmillan: Cham, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adegboyega, E.R. The impact of soil erosion on agricultural land and productivity in Efon Alaaye, Ekiti State. Int. J. Agric. Pol. Res. 2019, 7, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshunsanya, S.O.; Yu, H.; Opara, C.C.; Odebode, A.M.; Oluwatuyi, T.S.; Babalola, O. Integration effect of vetiver grass strips with maize population density on soil erosion under two contrasting slopes of rainforest agroecology. Catena 2023, 221, 106728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Bank. Vetiver Grass: A Method of Vegetative Soil and Soil Moisture Conservation; Asia Technical Department, Agricultural Division; The World Bank NW: Washington, DC, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- NRC (National Research Council). Vetiver Grass: A Thin Green Line Against Erosion; The National Academies Press: Washington DC, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, P. Vetiver Roots: The Vetiver System Technology Hidden Half; The Vetiver Network International: Cedar Crest, NM, USA, 2021; p. 173. [Google Scholar]
- Grimshaw, R.G. Past achievements and future direction of The Vetiver Network International (TVNI). In Proceeding of the First Philippines Vetiver Conference, Manila, Philippines, 12–14 March 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Howeler, R.; Watananonta, W.; Vongkasem, W.; Klakhaeng, K.; Jantawat, S.; Randaway, S.; Vankaew, B. Working with Farmers: The Key to Adoption of Vetiver Grass Hedgerows to Control Erosion in Cassava Fields in Thailand. In Vetiver and Water, Proceeding Third International Conference on Vetiver and Exhibition, Guangzhou, China, 6–9 October 2003; International Center for Tropical Agriculture: Cali, Colombia, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Oshunsanya, S.O. Spacing effects of vetiver grass (Vetiveria nigritana Stapf) hedgerows on soil accumulation and yields of maize-cassava intercropping system in southwest Nigeria. Catena 2013, 104, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Oshunsanya, S.O.; Li, Y.; Yu, H.; Are, K.S. Vetiver grass hedgerows significantly trap P but little N from sloping land: Evidenced from a 10-year field observation. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2019, 281, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, R. Some methods of directly assessing water erosion of cultivated land—A comparison of measurements made on plots and in fields. Prog. Phys. Geog. 1995, 19, 115–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.Y.; Zhao, Y.; Mo, B.; Mi, H.X. An improved experimental method for simulating erosion processes by concentrated channel flow. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e99660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remke, A.A.; Rodrigo-Comino, J.; Wirtz, S.; Ries, J.B. Finding possible weakness in the runoff simulation experiments to assess rill erosion changes with non-intermittent surveying capabilities. Sensors 2020, 20, 6254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, R. Soil Erosion in the Tropics Principles and Management; McGraw Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1990; p. 588. [Google Scholar]
- Lang, R.D. Accuracy of two sampling methods used to estimate sediment concentration in runoff from soil loss plots. Ear. Sur. Proc. Landf. 1992, 17, 841–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babalola, O.; Oshunsanya, S.O.; Are, K. Effects of vetiver grass (Vetiveria nigritana) strips, vetiver grass mulch and an organomineral fertilizer on soil, water and nutrient losses and maize (Zea mays L.) yield. Soil Till. Res. 2007, 96, 6–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciesiolka, C.A.A.; Yu, B.; Rose, C.W.; Ghadiri, H.; Lang, D.; Rosewell, C. Improvement in soil loss estimation in USLE-type experiments. J. Soil Water Conser. 2006, 61, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, C.M.; Giadom, L. Assessment of devastating spectacular gullies scenario in some agro-communities in rural and urban fringes in Akwa Ibom State, Nigeria. Environmental Planning and Resource Development in Niger Delta Region. In A Book of Reading; Uyanga, J., Ikurekong, E., Eds.; University of Uyo: Uyo, Nigeria, 2014; pp. 51–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyth, A.J.; Montgomery, R.F. Soils and Land Use in Central Western Nigeria; Government Printer: Ibadan, Nigeria, 1962; p. 265. [Google Scholar]
- USDA (United States Department of Agriculture). Soil Taxonomy. Keys to Soil Taxonomy, 9th ed.; USDA-NRCS: Washington, DC, USA, 2003; p. 332.
- Soil Survey Staff. Soil Taxonomy: A Basic System of Soil Classification for Making and Interpreting Soil Surveys, 13th ed.; Natural Resources Conservation Service (USDA-NRCS): Washington, DC, USA, 2022. Available online: https://nrcspad.sc.egov.usda.gov/DistributionCenter/pdf.aspx?productID=1709 (accessed on 11 August 2025).
- Abraham, C.M.; Saturday, U.; Tom, A.A.; Ibanga, I. Soil physical properties: A determinant of soils susceptibility to gully erosion menace in Uyo metropolis, Akwa Ibom State, Nigeria. Int. J. Soc. Sci. 2018, 12, 125–138. [Google Scholar]
- Manickam, V.; Kotapati, S.S.; Muralikrishna, I.V.K. Analysis of precipitation concentration index and rainfall prediction in various agro-climatic zones of Andhra Pradesh, India. Int. Res. J. Environ. Sci. 2013, 2, 53–61. [Google Scholar]
- Cleene, A.D.; Helba, A.D.; Palacio, E.M.; de Andrade, J.C.N.; Paulilo, P.B. Characteristics of rainfall and erosion under natural conditions of land use in semiarid regions. Rev. Bras. Eng. Agrícola Ambient. 2013, 17, 1222–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luis, M.; Gonzalez-Hidalgo, J.C.; Brunetti, M.; Longares, L.A. Precipitation concentration changes in Spain 1946–2005. Nat. Haz. Ear. Sys. Sci. 2011, 11, 1259–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, R. Soil degradation by erosion. Land Degrad. Dev. 2001, 12, 519–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyakov, V.O.; Lal, R. Soil organic matter and CO2 emission as affected by water erosion on field runoff plots. Geoderma 2008, 143, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kothyari, B.P.; Verma, P.K.; Joshi, B.K.; Kothyari, U.C. Rainfall–runoff-soil and nutrient loss relationships for plot size areas of Bhetagad watershed in Central Himalaya, India. J. Hydro. 2004, 293, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IITA (International Institute of Tropical Agriculture). Automated and Semi-Automated Methods for Soil and Plant Analysis, Manual Series No. 8; International Institute of Tropical Agriculture: Ibadan, Nigeria, 1991; p. 34. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, D.W.; Sommers, L.E. Total organic carbon and organic matter. In Methods of Soil Analysis; Part 2; Agronomy Monograph 9; ASA: Madison, WI, USA, 1982; pp. 539–594. [Google Scholar]
- Bray, R.H.; Kurtz, L.T. Determinations of total organic and available form of phosphorous in soils. Soil Sci. 1945, 59, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinnell, P.I.A. Laboratory studies on the effect of drop size on splash erosion. J. Agric. Engr. Res. 1982, 27, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roels, J.M.; Jonker, P.J. Representativity and accuracy of measurements of soil loss from runoff plots. Trans. Amer. Soc. Agric. Engr. 1985, 28, 1458–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boardman, J.; Evans, R. The measurement, estimation and monitoring of soil erosion by runoff at field scale: Challenges and possibilities with particular reference to Britain. Prog. Phys. Geog. Ear. Environ. 2019, 44, 31–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pampalone, V.; Carollo, F.G.; Nicosia, A.; Palmeri, V.; Di Stefano, C.; Bagarello, V.; Ferro, V. Measurement of water soil erosion at Sparacia Experimental Area (Southern Italy): A summary of more than twenty years of scientific activity. Water 2022, 14, 1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshunsanya, S.O. Crop yield as influenced by land preparation methods established within vetiver grass alleys for sustainable agriculture in Southwest Nigeria. Agroecol. Sust. Food Sys. 2013, 37, 578–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshunsanya, S.O. Surface soil properties and maize yields in runoff plots planted with vetiver grass (Vetiveria nigritana Stapf) hedges. Soil Sci. 2013, 178, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagarello, V.; Di Piazza, G.V.; Ferro, V. Manual sampling and tank size effects on the calibration curve of plot sediment storage tanks. Trans. Amer. Soc. Agric. Biol. Sci. 2014, 47, 1105–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, N.W. Field Measurement of Soil Erosion and Runoff; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh, Y.P.; Grant, K.T.; Bugna, G.C. A field method for soil erosion measurements in agricultural and natural lands. J. Soil Water 2009, 64, 374–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| S/N | Items | Qty | Cost (₦) | Cost (₦) | Number of Samples | Number of Samples | Total Cost (NGN) for 300 m2 Land Area | Total Cost (USD) for 300 m2 Land Area | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5% Slope | 10% Slope | 5% Slope | 10% Slope | 5% Slope | 10% Slope | 5% Slope | 10% Slope | |||
| Erosion plot method | ||||||||||
| 1 | Drums (250 litres) | 36 | 6600.00 | 6600.00 | - | - | 237,600.00 | 237,600.00 | 1284.00 | 1284.00 |
| 2 | Pipes (100 m) | 36 | 3740.00 | 3740.00 | - | - | 134,640.00 | 134,640.00 | 728.00 | 728.00 |
| 3 | Sampling and emptying the drums per measurement | 36 | 250.00 | 450.00 | 31 | 31 | 279,000.00 | 502,200.00 | 1508.00 | 2715.00 |
| 4 | Analysis (N, P, K, C, Ca, Mg) | 36 | 3000.00 | 3000.00 | 31 | 31 | 3,348,000.00 | 3,348,000.00 | 18,097.00 | 18,097.00 |
| Fractional method | ||||||||||
| 1 | Drums (250 litres) | 12 | 6600.00 | 6600.00 | - | - | 79,200.00 | 79,200.00 | 428.00 | 428.00 |
| 2 | Pipes (100 m) | 36 | 3740.00 | 3740.00 | - | - | 134,640.00 | 134,640.00 | 728.00 | 728.00 |
| 3 | Sampling and emptying the drums per measurement | 12 | 250.00 | 450.00 | 31 | 31 | 93,000.00 | 167,400.00 | 503.00 | 905.00 |
| 4 | Analysis (N, P, K, C, Ca, Mg) | 12 | 3000.00 | 3000.00 | 31 | 31 | 1,116,000.00 | 1,116,000.00 | 6032.00 | 6032.00 |
| 5% slope | 10% slope | 5% slope | 10% slope | |||||||
| Total cost under the erosion plot method | 3,999,240.00 | 4,222,440.00 | 21,618.00 | 22,824.00 | ||||||
| Total cost under the fractional method | 1,422,840.00 | 1,497,240.00 | 7691.00 | 8093.00 | ||||||
| Gross margin | 2,576,400.00 | 2,725,200.00 | 13,926.00 | 14,731.00 | ||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oshunsanya, S.O.; Yu, H.; Odebode, A.M.; Edem, I.D.; Oluwatuyi, T.S.; Imasuen, E.E.; Odeyinka, D.E. Comparative Assessment of Fractional and Erosion Plot Methods for Quantifying Soil Erosion and Nutrient Loss Under Vetiver Grass Technology on Two Contrasting Slopes in Rainforest Agroecology. Agriculture 2025, 15, 1762. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15161762
Oshunsanya SO, Yu H, Odebode AM, Edem ID, Oluwatuyi TS, Imasuen EE, Odeyinka DE. Comparative Assessment of Fractional and Erosion Plot Methods for Quantifying Soil Erosion and Nutrient Loss Under Vetiver Grass Technology on Two Contrasting Slopes in Rainforest Agroecology. Agriculture. 2025; 15(16):1762. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15161762
Chicago/Turabian StyleOshunsanya, Suarau O., Hanqing Yu, Ayodeji M. Odebode, Ini D. Edem, Tunde S. Oluwatuyi, Esther E. Imasuen, and Dorcas E. Odeyinka. 2025. "Comparative Assessment of Fractional and Erosion Plot Methods for Quantifying Soil Erosion and Nutrient Loss Under Vetiver Grass Technology on Two Contrasting Slopes in Rainforest Agroecology" Agriculture 15, no. 16: 1762. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15161762
APA StyleOshunsanya, S. O., Yu, H., Odebode, A. M., Edem, I. D., Oluwatuyi, T. S., Imasuen, E. E., & Odeyinka, D. E. (2025). Comparative Assessment of Fractional and Erosion Plot Methods for Quantifying Soil Erosion and Nutrient Loss Under Vetiver Grass Technology on Two Contrasting Slopes in Rainforest Agroecology. Agriculture, 15(16), 1762. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15161762






