Abstract
The sorghum aphid (Melanaphis sacchari (Zehntner, 1897)), a globally destructive pest, severely compromises sorghum yield and quality. This study compared aphid-resistant (HX133) and aphid-susceptible (HX37) sorghum (Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench) cultivars, revealing that HX133 significantly suppressed aphid proliferation through repellent and antibiotic effects, while aphid populations increased continuously in HX37. Transcriptome analysis identified 2802 differentially expressed genes (DEGs, 45.9% upregulated) in HX133 at 24 h post-infestation, in contrast with only 732 DEGs (21% upregulated) in HX37. Pathway enrichment highlighted shikimate-mediated phenylpropanoid/flavonoid biosynthesis and glutathione metabolism as central to HX133’s defense response, alongside photosynthesis-related pathways common to both cultivars. qRT-PCR validation confirmed activation of the shikimate pathway in HX133, driving the synthesis of dhurrin—a cyanogenic glycoside critical for aphid resistance—and other tyrosine-derived metabolites (e.g., benzyl isoquinoline alkaloids, tocopherol). These findings demonstrate that HX133 employs multi-layered metabolic regulation, particularly dhurrin accumulation, to counteract aphid infestation, whereas susceptible cultivars exhibit limited defense induction. This work provides molecular targets for enhancing aphid resistance in sorghum breeding programs.
1. Introduction
The sorghum aphid (Melanaphis sacchari (Zehntner, 1897)) is a significant worldwide pest, significantly threatening sorghum crops by reducing yield and quality [1]. Over the past decade, this pest has severely impacted sorghum cultivation, expanding across all production regions in the United States, Mexico, and South America, with documented crop losses ranging from 50% to 100%. The insect is characterized by its phloem-feeding behavior, whereby it punctures stems or foliage to access sap, resulting in nutrient depletion that impedes plant growth and development [2,3]. Aphids secrete honeydew on infested sorghum leaves, which promotes the growth of mold and fungi. These microorganisms form a sooty mold layer on the leaf surface, thereby impairing photosynthetic processes and ultimately reducing photosynthetic rates [4,5]. The predominant approach to managing this pest involves chemical insecticides, which leads to environmental contamination and the persistence of pesticide residues [6]. Consequently, deploying aphid-resistant sorghum varieties is the most sustainable and efficacious strategy for controlling aphids [7,8]. Plants have evolved a repertoire of strategies to evade, endure, and combat insect pests, offering valuable genetic resources for comprehensive pest management [9,10,11]. Upon detecting pest-induced damage, plants initiate a complex and coordinated response through a finely tuned network, thereby activating their defense mechanisms [12,13,14].
Many sources of aphid-resistant germplasm have been identified; however, the molecular mechanisms behind plants’ resistance to aphids are still not fully understood [15]. Plants have evolved a range of defense strategies against pests, such as antixenosis, antibiosis, and tolerance [16,17]. Antixenosis involves morphological traits and chemical compounds that deter aphids from settling and feeding, while antibiosis encompasses factors that inhibit aphid growth, development, and reproduction. Tolerance is defined as a plant’s capacity to endure and recover following damage caused by pests [15]. These defense strategies operate at various stages of plant–aphid interactions and are often interwoven, making them challenging to disentangle [18,19]. The initial line of defense in plants includes physical and chemical barriers. Physical barriers consist of specific morphological features, such as trichomes, spines, and waxy coatings [20]. Chemical barriers include volatile and non-volatile secondary metabolites that affect aphid host selection, deter settlement, and enhance the ability of the plant to expel aphids [21,22]. Aphid-resistant varieties predominantly exhibit antixenosis and antibiosis, while tolerance is less common. Several sorghum aphid-resistant strains, such as RT×2783, TAM428, Ent62/SADC, SC110, SC170, M35-1, SAP166, IS5590C, have been identified [23]. Ongoing screening of sorghum aphid-resistant germplasm is essential for future aphid resistance breeding efforts. Identifying aphid-resistant lines, discovering new resistance genes, and developing resistant varieties are crucial [14,24,25,26].
To elucidate the genomic-scale shifts in gene expression in response to aphid infestation, numerous “omics” studies have been performed on diverse plant species, including maize (Zea mays L.) [27,28], wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) [29,30], sorghum (Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench) [31], rose (Rosa chinensis L.) [32], soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merr.) [33], cowpea (Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walp.) [34], and cotton (Gossypium spp.) [35]. These investigations have revealed many genes implicated in the plant’s response to aphids, including hormones, flavonoid biosynthesis, and secondary metabolism [14,36]. However, only a limited number of genes have been cloned and confirmed to confer aphid resistance. ‘HN16’, a Chinese grain sorghum variety, contains the dominant resistance gene RMES1, which provides aphid resistance [37]. Using populations that segregated from ‘HN16’ and the susceptible variety ‘Qianshan’, genetic mapping pinpointed the RMES1 gene on chromosome 6. The RMES1 locus includes five genes, such as Sobic.006g017000, Sobic.006g017100, Sobic.006g017200, Sobic.006g017400, and Sobic.006g017500 [36]. Further research with a sorghum recombinant inbred line (RIL) population from the aphid-resistant line 407B and the aphid-susceptible line 7B validated the RMES1 locus and detected three more associated loci on chromosome 6 [38]. Subsequent analysis of the RIL population derived from Tx2783 and BTx623 identified sequence variations in disease-resistance genes linked to a sorghum aphid-tolerant QTL [39]. A sorghum genome-wide association study identified the WRKY transcription factor WRKY86 as a candidate gene for resistance to the sorghum aphid A genome-wide association study on sorghum found that the WRKY transcription factor WRKY86 is a potential gene for resistance against the sorghum aphid [24]. Despite the existence of useful sources of sorghum aphid resistance in many sorghum lines, the specific genes responsible often remain elusive. Transcriptome sequencing stands out as a rapid and effective method of bioinformatics analysis for anti-aphid-related signaling pathways. To investigate the mechanisms of aphid resistance in sorghum, 244 inbred lines were assessed for aphid infestation during the seedling stage. Transcriptome changes in leaves were analyzed before and after aphid infestation in the aphid-susceptible line HX37 and the aphid-resistant line HX133. This pipeline detected transcriptional variation (DEGs) and critical biological routes.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plants and Aphid Cultivation
The plant materials utilized in this study were obtained from the sorghum germplasm repository at Anhui Science and Technology University. A comprehensive evaluation was conducted on the sensitivity of 244 inbred sorghum lines to aphid infestation during the early stages, aiming to identify the resistant and sensitive strains. The identification method was based on Tetreault H M et al. The method for identification drew on the work of Tetreault H M et al. [40]. The HX133 line demonstrated resistance, while HX37 exhibited susceptibility. We sampled aphids infesting sorghum across cultivated fields within Anhui Science and Technology University and reared on susceptible sorghum in controlled environment chambers set at 25 ± 1 °C, with a photoperiod of 16 h light and 8 h dark, and 60% humidity. This setup ensured continuous cultivation across generations [41].
2.2. Assessment of Sorghum Resistance to Aphids
Two sorghum lines were chosen for this study after initial screening for tolerance levels. These were the aphid-susceptible HX37 (IS5386) and the aphid-resistant HX133 (IS23514). Sorghum seeds were germinated and transplanted in 10 cm diameter plastic pots, with six seedlings per pot, and each setup was replicated three times. The growth substrate consisted of a mixture of soil, vermiculite, and nutrient soil at a ratio of 3:2:1 (v/v). Once the seedlings developed three leaves, adult aphids were manually applied to the plants using a fine brush, at a density of 10 aphids per plant. Plants were secured in clip cages, with aphid population assessments conducted at 2, 4, 7, 14, and 17 days post-infestation (dpi) [42].
2.3. Management of Sorghum Inbred Lines with Varying Resistance Levels
HX133 and HX37 seeds were germinated in controlled-environment chambers under conditions described previously. Sorghum lines were cultivated in 10 cm diameter plastic pots (10 plants per pot) with 3 biological replicates per treatment group. At 14 days post-germination, each plant was infested with 10 apterous adult aphids applied to the stem. Samples from both lines were collected at 0, 24, and 48 h post-infestation (hpi), with three biological replicates per time point. Stems and leaves were harvested during infestation and promptly stored at −80 °C for subsequent RNA extraction [31].
2.4. RNA Extraction and Transcriptome Sequencing
Total RNA was isolated from 100 mg of tissue using TRIzol (T9108, Takara, Kyoto, Japan) reagent following supplier-provided protocols precisely. DNase I (TaKaRa Bio, CA, USA) was employed for genomic DNA removal, while RNA integrity was determined using the NanoPhotometer® spectrophotometer (Implen, CA, USA). Clustering of indexed samples was performed using the Illumina cBot system (San Diego, CA, USA) with TruSeq paired-end cluster generation kit v3-cBot-HS. The library preparations were sequenced on an Illumina NovaSeq 6000 platform, generating 150 bp paired-end reads. The RNA-seq template was prepared and sequencing services were provided by Genepioneer Biotechnologies (Nanjing, China) [43]. The basic next-generation sequencing (NGS) read metrics can be found in Supplementary Table S1.
2.5. Gene Expression Profiling
Gene read counts were quantified using StringTie v2.0 [44] and aligned to the S. bicolor reference genome [S. bicolor_454 v3.1.1], accessible at https://phytozome-next.jgi.doe.gov/, accessed on 10 December 2021. The DESeq2 R package (1.10.1) was employed to carry out differential expression analysis between the two groups [45]. The transcriptional responses of the resistant and susceptible lines were compared at different time points. DESeq2 analysis identified differentially expressed genes meeting the significance threshold of adjusted p < 0.05. The GOseq R package [46] was used for the GO enrichment analysis of the DEGs, applying the Wallenius noncentral hyper-geometric distribution to address gene length bias. DEGs were analyzed for KEGG pathway enrichment using the KEGG Orthology-based Annotation System software version 2.0 [47].
2.6. Quantitative qRT-PCR Expression Analysis
We employed qRT-PCR to assess gene expression related to the shikimic acid and dhurrin biosynthetic pathways in the sorghum lines under aphid infestation, for which relative quantification was performed using eIF4a1 (Sb04g003390) as the reference gene. The expression levels of genes associated with the shikimate and diterpenoid biosynthetic pathways were quantified by qRT-PCR in sorghum lines HX133 and HX37. The ViiA 7 qRT-PCR platform (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA) was utilized to measure gene expression, employing SYBR Green-based master mix reagents supplied by Vazyme Biotech (Nanjing, China). The qRT-PCR protocol followed the manufacturer’s guidelines. The thermal cycling profile began with initial denaturation at 95 °C for 30 s, followed by 40 cycles consisting of 10 s of denaturation at 95 °C and 30 s of annealing/extension at 60 °C. A melting curve analysis was performed by gradually increasing the temperature from 60 to 95 °C at 0.2 °C per second to dissociate the double-stranded DNA. All samples were tested in triplicate, with each qRT-PCR reaction repeated three times to ensure reliability [48].
3. Results
3.1. Evaluation of the Sorghum Lines for Aphid Resistance
This study evaluated the resistance of sorghum lines HX37 and HX133 to aphid infestation. As illustrated in Figure 1, the aphid population on the susceptible sorghum increased steadily during the 2-, 4-, 7-, and 14-day intervals, reaching a peak of 125 aphids per plant by day 14. However, the aphid counts slightly decreased by day 17 post-infestation, primarily due to wilting resulting from early aphid damage and the escape of some aphids, which contributed to reducing the number of aphids. In contrast, the aphid population on the aphid-resistant line (HX133) increased gradually, with counts of 27 and 36 aphids per plant at days 14 and 17, respectively. As presented in Figure 2, the aphid-resistant sorghum (HX133) exhibited both antixenosis and antibiotic effects against the aphids, significantly inhibiting the growth of the aphid populations.
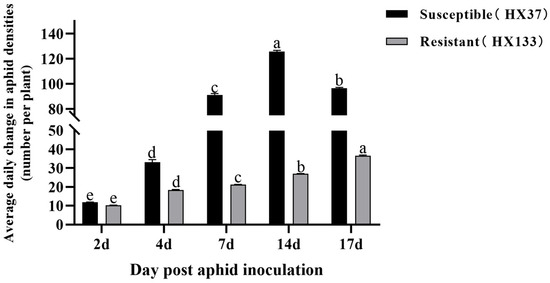
Figure 1.
Evaluation of sorghum line for resistance to sorghum aphid (M. sacchari). A significant difference (p < 0.05) is indicated by different superscript lowercase letters.
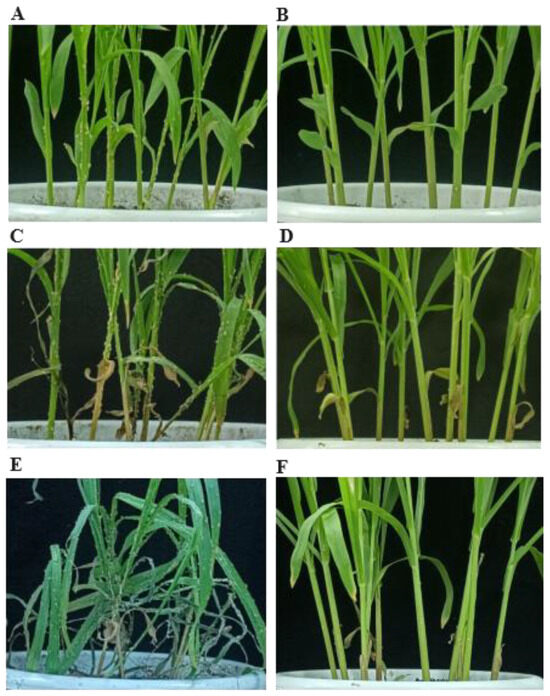

Figure 2.
Resistant (HX133) and susceptible (HX37) sorghum line following aphid infestation at various time points. (A,C,E) Susceptible (HX37) sorghum line after aphid infestation at day 7, 14, and 17. (B,D,F) Resistant (HX133) sorghum line after aphid infestation at day 7, 14, and 17.
The aphid-susceptible (HX37) and aphid-resistant (HX133) lines represent distinct Sorghum bicolor responses to aphid infestation. Daily mean aphid density (expressed as aphids per plant) exhibited significant temporal variations, with statistically divergent time points denoted by different lowercase letters (p < 0.05).
3.2. Differential Gene Expression in the Resistant and Susceptible Sorghum Lines
Comparative analysis was conducted to identify the DEGs between the HX133 resistant line and the HX37 susceptible line as a reaction to aphid infestation at various time points, as shown in Figure 3. Analysis of resistant line HX133 revealed 2802 DEGs between the 0 and 24 h post-infestation time points, with 45.9% of these being upregulated. Between the 0 and 48 h time points, a total of 1309 DEGs were found, with 59.5% upregulated, while 2248 DEGs were detected between the 24 and 48 h time points, with 76.4% upregulated. Notable expression differences were observed in the 732 genes between 0 h and 24 h in susceptible line HX37, with 21% upregulated; in 2844 genes between 0 h and 48 h, with 38.5% upregulated; and in 2432 DEGs between 24 h and 48 h, with 27.5% upregulated. A total of 9274 DEGs were identified when comparing HX37 and HX133 at 0 h, 11,223 DEGs at 24 h, and 7133 DEGs at 48 h. The analysis indicated a significant difference in gene regulation between the resistant and susceptible lines; the resistant lines had a higher proportion of upregulated genes after aphid infestation, while the susceptible lines had fewer upregulated genes than downregulated genes.
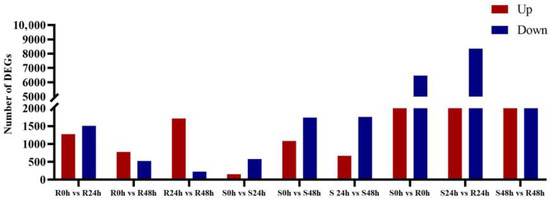
Figure 3.
Number of DEGs in sorghum lines in response to sorghum aphid herbivory at 0, 24, and 48 h. (Supplementary Table S2). S, susceptible sorghum HX37; R, resistant sorghum HX133. Columns show genes upregulated or downregulated after aphid herbivory, versus unexposed lines of the same age. DEGs were identified by a fold change ≥1.9 or ≤−1.9 and an FDR-adjusted p-value < 0.05.
3.3. Venn Diagram Analysis
To compare the gene expression differences and similarities between the aphid-resistant inbred line HX133 and the aphid-susceptible inbred line HX37 at different aphid infestation intervals, a Venn diagram (Figure 4) was constructed. Analysis identified 74 common differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in HX37 across the three aphid infestation time points (0 h, 24 h, and 48 h), with the highest number of DEGs observed at 24 h, which was higher than that at 0 h. HX133 showed 29 common DEGs during the same time period, and the most significant gene expression changes between 0 and 24 h were observed, with a total of 1500 DEGs. Overall, 3815 DEGs were identified across all comparisons.
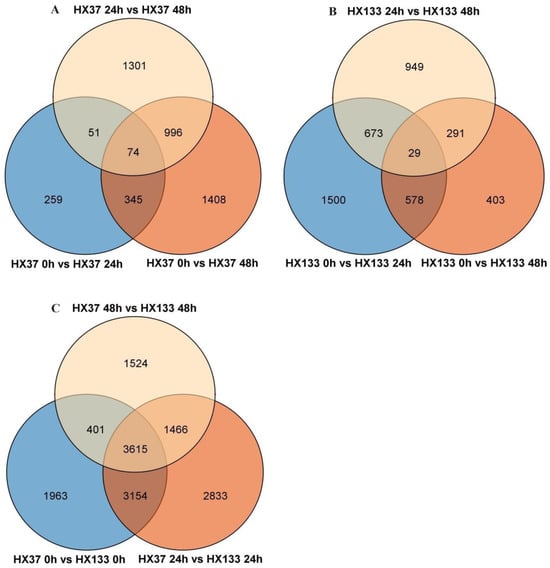
Figure 4.
Venn diagrams of DEGs during resistance and susceptible sorghum line after aphid infestation. (A) DEGs between the different infestation time points in HX37. (B) DEGs between the different infestation time points in HX133. (C) DEGs between HX37 and HX133 at the same time points.
3.4. Gene Ontology Analysis
GO enrichment analysis was performed to categorize the DEGs into biological processes (BP), cellular components (CCs), and molecular functions (MFs). I In the susceptible HX37 line, enriched BP terms included plant-type primary cell wall biogenesis, cellulose, and sphingoid biosynthetic processes, photosynthesis, and responses to abscisic acid and chitin, all linked to plant constitutive resistance (Figure 5A,B). In contrast, resistant line HX133 was enriched in BP terms related to translation, chlorophyll biosynthetic processes, gamma-aminobutyric acid transport, L-lysine transmembrane transport, and sugar biosynthesis processes, indicating a role in plant-induced resistance (Figure 5C,D).
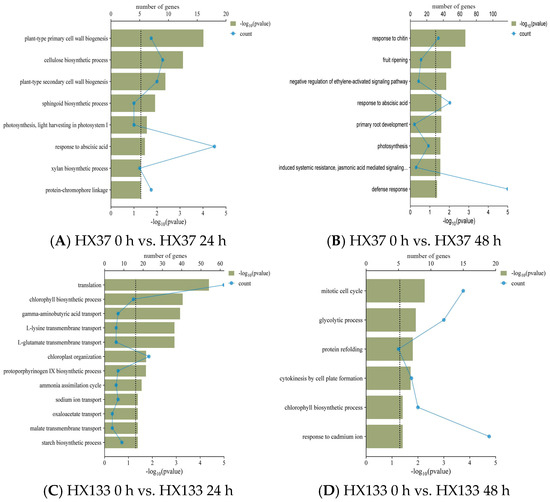
Figure 5.
Functional enrichment of DEGs in Sorghum bicolor lines following aphid infestation (Supplementary Table S3). (A) Significantly enriched GO pathways in HX37 0 h vs. HX37 24 h. (B) Significantly enriched GO pathways in HX37 0 h vs. HX37 48 h. (C) Significantly enriched GO pathways in HX133 0 h vs. HX133 24 h. (D) Significantly enriched GO pathways in HX133 0 h vs. HX133 48 h.
A relative scarcity of enriched terms was detected in CC compared to MF and BP in susceptible line HX37. The CC-enriched terms revealed that the upregulated genes in resistant line HX133 at 24 h were primarily associated with chlorophyll, protoporphyrinogen IX, sterols, and aromatic amino acid families, among others. MF-enriched terms within the BP-enriched terms in the resistant line HX133 during aphid infestation included amino acid transmembrane transporter activity, manganese-ion binding, and protein serine/threonine kinase activity. Conversely, MF terms enriched in the susceptible line HX37 at 24 and 48 hpi highlighted water channel activity and iron-ion binding.
3.5. KEGG Pathway Analysis
To better understand the biological roles of the DEGs, KEGG pathway enrichment analysis was conducted (Figure 6). The DEGs between HX37 0 h and HX133 0 h were mainly associated with photosynthesis, photosynthetic antenna proteins, flavonoid biosynthesis, glutathione metabolism, alpha-linolenic acid metabolism, the MAPK signaling pathway, and linoleic acid metabolism (Figure 6A). Fifteen pathways were identified at HX37 24 h vs. HX133 24 h post-aphid infestation, including flavonoid biosynthesis, photosynthesis, stilbenoid, diarylheptanoid, and gingerol biosynthesis, and phenylpropanoid biosynthesis, among others (Figure 6B), with six of these pathways aligned with those enriched from HX37 0 h vs. HX133 0 h. Photosynthesis was the most enriched pathway among the DEGs between HX37 48 h and HX133 48 h, followed by photosynthesis-antenna proteins, glycolysis/gluconeogenesis, DNA replication, homologous recombination, and starch and sucrose metabolism (Figure 6C). Photosynthesis and proteins of photosynthesis antenna were consistently enriched across all post-infestation time points, suggesting their significance. Phenylpropanoid and flavonoid biosynthesis, along with glutathione and starch and sucrose metabolism are potentially significant in the aphid infestation process.
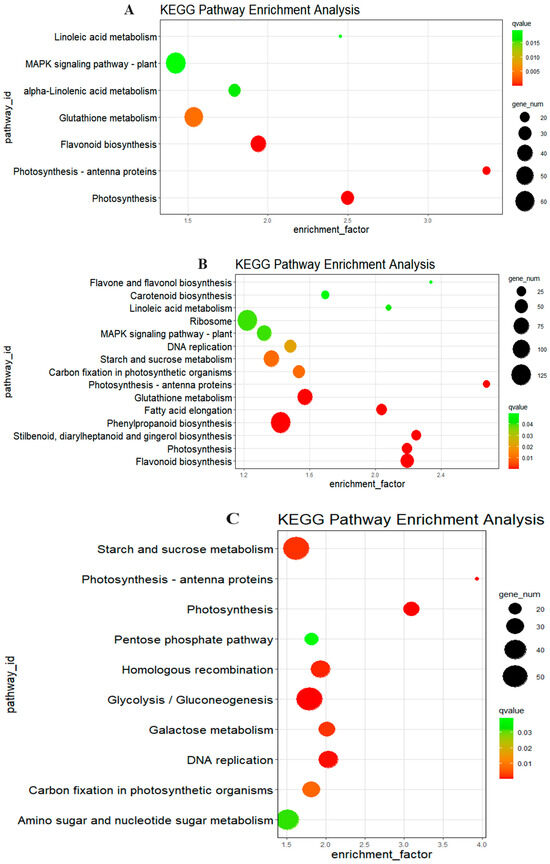
Figure 6.
KEGG enrichment analysis of DEGs after aphid infestation between different comparisons. (A) Significantly enriched KEGG pathways in HX37 0 h vs. HX133 0 h. (B) Significantly enriched KEGG pathways in HX37 24 h vs. HX133 24 h. (C) Significantly enriched KEGG pathways in HX37 48 h vs. HX133 48 h.
The DEGs between HX133 at 0 h and HX133 at 24 hpi were enriched in 16 signaling pathways, with 13 upregulated and 3 downregulated (Table 1). The upregulated pathways primarily encompassed the biosynthesis of phenylalanine, tyrosine, and tryptophan, along with porphyrin and chlorophyll metabolism, the pentose phosphate pathway, and starch and sucrose metabolism. The phenylalanine, tyrosine, and tryptophan biosynthetic pathways were the most enriched among the upregulated pathways. In contrast, the downregulated pathways encompass galactose metabolism, hormone signal transduction, and glutathione metabolism. Gene enrichment analysis revealed nine signaling pathways when comparing HX133 at 0 h to HX133 at 48 h. The results showed that the HX133 line exhibited a stronger defense response at 24 h after aphid infestation with more enriched pathways than at 48 h. Analysis of the susceptible aphid line (HX37) revealed enrichment in six signaling pathways when comparing 0 h to 24 h. Glutathione metabolism was upregulated, whereas photosynthesis-antenna proteins, sphingolipid metabolism, carotenoid biosynthesis, phenylpropanoid biosynthesis, and the MAPK signaling pathway were downregulated. The DEGs between HX37 at 0 h and HX37 at 48 h were enriched in 11 signaling pathways, with four pathways being commonly enriched when comparing HX37 at 0 h versus HX37 at 24 h. These findings indicate that the signaling pathways enriched in the resistant and susceptible inbred lines diverged significantly from the control following aphid infestation, with notable differences in the timing and activation pathways of aphid defenses between the resistant and susceptible strains.

Table 1.
KEGG enrichment signaling pathway of differentially expressed genes from resistant and susceptible aphid inbred lines after aphid infestation.
3.6. Differentially Expressed Genes of Hormone Metabolism Post-Aphid Infestation
The plant hormones jasmonic acid (JA), ethylene (ET), and abscisic acid (ABA) play vital roles in mediating resistance to insect pests [43]. GO enrichment analysis indicated that the signaling pathways of these hormones in sorghum were subjected to differential regulation following aphid infestation. Transcriptional profiles associated with jasmonate, ethylene, and abscisic acid biosynthesis pathways were examined in the HX37 and HX133 genotypes.
3.6.1. Jasmonic Acid Biosynthetic Pathway
Two LOX genes within the JA biosynthetic pathway exhibited differential expression post-aphid infestation (Figure 7A). Specifically, the gene Sobic.001G483400 was downregulated in HX37 24 at 48 hpi, while Sobic.004G078600 was upregulated at 48 hpi in HX37 but downregulated at 24 hpi in HX133. The single AOS gene Sobic.001G449700 was downregulated at 24 hpi in HX133. Among the two identified OPR genes, Sobic.006G091700 demonstrated differential expression at 48 hpi in HX37 and HX133, whereas Sobic.006G091900 was differentially expressed only at 24 hpi in HX37. A multifunctional gene was upregulated at 24 hpi in HX133. Additionally, the ACOX gene (Sobic.005G181000) was downregulated at 24 and 48 hpi in HX133, with no differential expression observed in HX37. The RAN gene (Sobic.003G238000) was upregulated at 24 and 48 hpi in HX133.
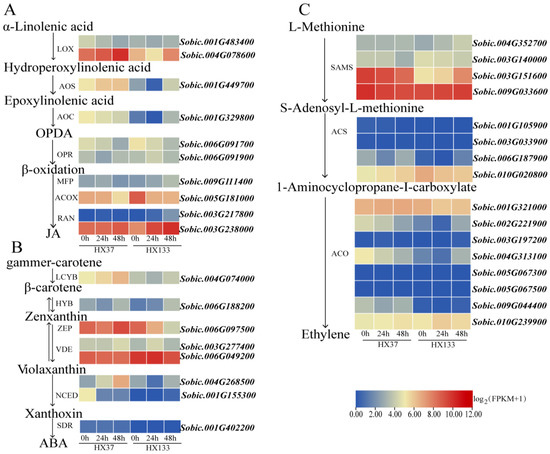
Figure 7.
Relative expression changes in DEGs involved in JA, ABA, and ET biosynthesis after aphid infestation. (A) Differential expressed genes in JA biosynthesis pathway. (B) Differential expressed genes in ABA biosynthesis pathway. (C) Differential expressed genes in ET biosynthesis pathway.
3.6.2. Abscisic Acid Biosynthetic Pathway
Based on our research findings, the single-copy LCYB gene (Sobic.004G074000) exhibited marked transcriptional upregulation at 48 h post-infestation (hpi) in the aphid-susceptible sorghum cultivar HX37. The single LCYB gene, Sobic.004G074000, was significantly upregulated exclusively in susceptible HX37 at 48 hpi. One NCED gene, Sobic.004G268500, was upregulated in HX37 at 24 and 48 hpi, while another NCED gene, Sobic.001G155300, was downregulated during the same period. Sobic.004G268500 expression was downregulated at 24 hpi in the resistant HX133 line, with no significant change at 48 hpi relative to the control. The ZEP gene Sobic.006G097500 was downregulated in HX133 at 24 and 48 hpi compared to the control, while no significant changes were observed in susceptible line HX37 (Figure 7B).
3.6.3. Ethylene Biosynthetic Pathway
No significant changes in gene expression related to the ET biosynthetic pathway were observed in the resistant or susceptible lines at 24 hpi when compared to the control. Four genes in susceptible line HX37 were downregulated at 48 hpi: one SAMS gene (Sobic.003G151600), one ACS gene (Sobic.001G105900), and two ACO genes (Sobic.002G221900, Sobic.004G313100). In contrast, expression of the two SAMS genes was upregulated in the resistant line HX133 at 48 hpi, namely Sobic.004G352700 and Sobic.003G151600 (Figure 7C).
3.6.4. Shikimic Acid Pathway During Aphid Defense
The biosynthetic pathway for phenylalanine, tyrosine, and tryptophan is ranked as the most enriched signaling pathway among upregulated genes when comparing HX133 at 0 h to HX133 at 24 hpi (Figure 8). This pathway is the same as the shikimic acid pathway due to its role in producing these amino acids derived from the shikimic acid metabolic route. Upregulation of 12 genes was observed. Specifically, the genes Sobic.002G279700, Sobic.004G236300, and Sobic.001G433700 are involved in the synthesis of shikimic acid and chorismic acid, while Sobic.004G065500 and Sobic.009G149400 catalyze the conversion of chorismic acid into tyrosine and phenylalanine. The qRT-PCR analysis at 24 hpi revealed that the expression levels of shikimic acid synthetase, chorismic acid synthetase, and tyrosine synthetase were markedly upregulated in the resistant inbred line compared to the control (Figure 9). These results corroborate the transcriptome analysis, confirming that the shikimic acid pathway was activated as part of the defense response to aphid stress.
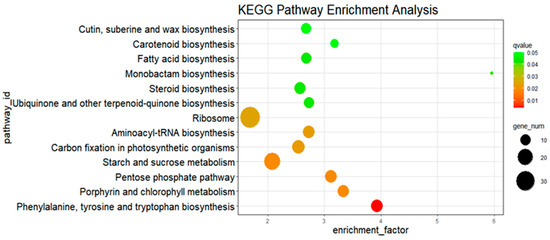
Figure 8.
KEGG enrichment analysis of DEGs after aphid infestation between signaling pathway of upregulated gene enriched from HX133 0 h vs. HX133 24 h. Note that all results presented in the figures were experimentally validated through qRT-PCR.
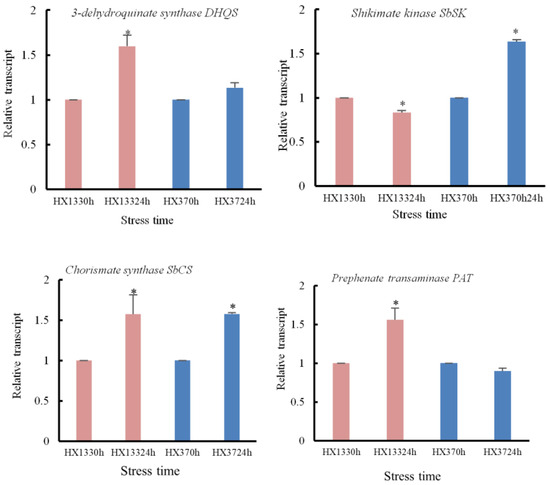
Figure 9.
Expression patterns of the genes related to shikimic acid synthetic pathway in resistant and susceptible sorghum lines following sorghum aphid infestation. This study quantified transcript levels of shikimate pathway-related genes in aphid-stressed sorghum using qRT-PCR. Resistant (HX133) and susceptible (HX37) lines were analyzed at 0 h and 24 h post-inoculation. Statistically significant differences (p < 0.05), indicated by asterisks, exist between the stressed and control groups.
3.6.5. Dhurrin Biosynthesis and Metabolic Pathways
Tyrosine is derived from the shikimic acid pathway [49] and is a precursor for synthesizing several secondary metabolites, such as tocopherol (vitamin E), dhurrin, plastoquinone, ubiquinone, betaine, salidroside, benzyl isoquinoline alkaloids, rosmarinic acid, and related compounds [50]. Further analysis of the transcriptome data revealed that the downstream pathways associated with the biosynthesis of aromatic amino acids encompassed a range of tyrosine metabolic products, such as dhurrin. Dhurrin is the most prevalent cyanogenic compound in sorghum and is linked to resistance against aphid infestation [51,52]. The process requires two multifunctional cytochrome P450 enzymes, CYP79A1 and CYP71E1, plus a family 1 UDP-glucosyltransferase, UGT85B1. The cyanogenic glucoside dhurrin is a principal chemical defense compound in S. bicolor; its hydrolysis by specific β-glucosidases following tissue disruption, such as that caused by chewing insects, releases chemically unstable α-hydroxynitrile [53]. This compound dissociates to form toxic hydrogen cyanide. Dhurrin synthesis, starting from tyrosine, is catalyzed by the cytochrome P450 enzymes CYP79A1 and CYP71E1, along with the UDP-glucosyltransferase UGT85B1. In our data, genes related to dhurrin biosynthesis, i.e., CYP79A1 and CYP71E1, were differentially expressed (Figure 10). Gene expression of CYP79A1 was significantly downregulated in the resistant lines compared to 0 h, while expression in the susceptible strains was downregulated. Gene expression of CYP71E1 was induced and upregulated in the resistant and susceptible lines at 24 hpi compared to 0 h [54].
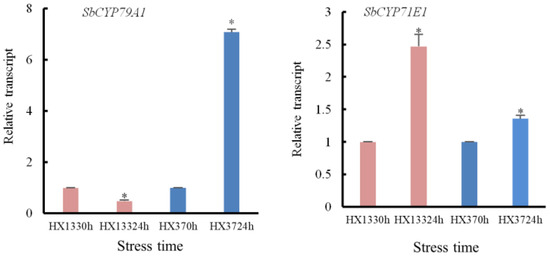
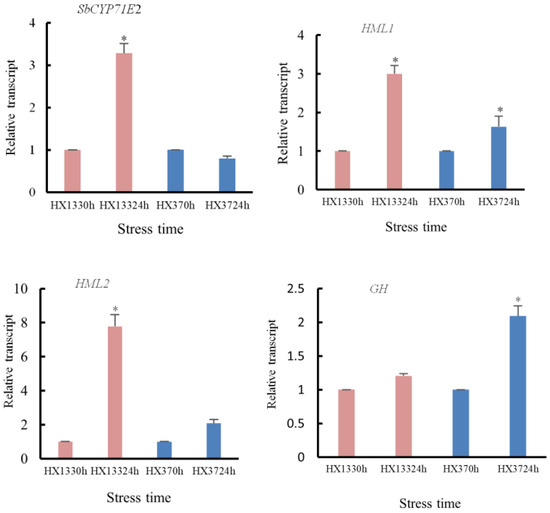
Figure 10.
Expression patterns of the genes related to dhurrin synthetic and metabolic pathways in resistant and susceptible sorghum lines following sorghum aphid infestation. This study quantified transcript levels of dhurrin pathway-related genes in aphid-stressed sorghum using qRT-PCR. Resistant (HX133) and susceptible (HX37) lines were analyzed at 0 h and 24 h post-inoculation. Statistically significant differences (p < 0.05), indicated by asterisks, exist between the stressed and control groups.
The expression of CYP71E2 was significantly upregulated in resistant strains at 24 h compared to 0 h, while no significant change was observed in susceptible strains at 24 hpi. Hydroxymandelonitrile lyase (HML) and glycoside hydrolase (GH), key genes in the dhurrin metabolism pathway of sorghum, both showed upregulated trends in aphid-resistant and aphid-susceptible sorghum strains compared to controls after aphid infestation (Figure 10). At 24 h post-aphid infestation, HML1 gene expression was significantly induced and upregulated in both resistant and susceptible strains, while HML2 expression was significantly upregulated only in resistant strains, with no significant difference observed in susceptible strains. The GH gene exhibited significant upregulation in aphid-susceptible strains.
4. Discussion
The hormone signaling pathways play crucial roles in mediating responses to abiotic and biotic stressors [55]. Previous research has demonstrated that silencing lipoxygenase 3 (LOX3), a key enzyme in jasmonic acid’s (JA) biosynthetic pathway, reduces the production of defensive metabolites in tobacco [56]. This suppression enables enhanced indirect defense across diverse environments and direct deterrence of herbivorous insects through the action of volatile organic compounds (VOCs). In our research, we noted varying expression levels of two. LOXs following aphid infestation. Previous studies indicated that aphids trigger significant defense mechanisms in susceptible BCK60 sorghum, notably through the upregulation of genes associated with JA and ET biosynthesis [40]. In our study, we noted a differential expression of two LOXs within the JA pathway post-aphid infestation, suggesting that induction of JA under aphid attack may bolster the defense of sorghum against aphids. Ethylene response factor 6 (ERF6) is crucial in Arabidopsis thaliana (L.) Heynh for enhancing antioxidant activity during biological stress [57]. Interestingly, when aphids infected the sorghum, two ET pathway transcription factors were significantly upregulated in resistant sorghum HX133, albeit to a lesser extent than in susceptible HX37. However, the expression of the ET biosynthetic genes was higher in HX133 than in HX37, suggesting that the gene products may be associated with resistance. Activation of the ABA signaling pathway enhances water use efficiency in plants by reducing stomatal opening and the transpiration rate [58]. This leads to longer feeding durations for aphids in the xylem and phloem, facilitating population growth [59]. In our study, ABA gene expression was lower in the resistant HX133 line than in the susceptible HX37 line. This observation indicates that the resistant sorghum may modulate stomatal conductance through ABA during aphid feeding, thereby conserving water to avoid aphid infestation.
JA, ABA, and ET constitute a complex hormonal network that underpins various resistance pathways against diverse biotic and abiotic stressors [60]. Mounting evidence indicates that these hormones play significant roles in defense against biological stress [59]. Plant hormone signaling transduction represents one of the most highly prevalent DEG pathways. [61]. We performed RNA-seq analysis at 24 and 48 hpi to identify the DEGs in the aphid-resistant and -susceptible lines, to uncover potential candidate genes. ABA, JA, and ET play essential roles in stress conditions [62]. JA, ET, and ABA are pivotal signaling molecules in the defense of plants against insects. Mao et al. [63]. identified JA as crucial in plant defense against herbivorous insects. JA is the primary defense hormone that triggers defense responses against herbivorous insects and necrotic pathogens and is a key regulator in plant–insect defense dynamics. Numerous studies have highlighted that ET is instrumental in the long-distance signaling mechanisms inherent in plant–insect interactions [64]. Emerging evidence suggests that ABA also has a significant role in biological stress. While ABA usually serves as a negative regulator of disease resistance, it bolsters plant defense and participates in synergistic and antagonistic interactive networks [65]. Previous studies have highlighted the involvement of salicylic acid and jasmonate pathways in aphid resistance [66], which aligns with our finding that differential expression of hormone biosynthesis genes underpins HX133’s resistance.
The feeding of herbivorous insects can cause changes in gene expression, thereby affecting the expression of gene signaling pathways. Shikimic acid is a pivotal regulatory factor associated with insect resistance. Resistant sorghum activates the shikimate pathway to enhance the synthesis of tyrosine-derived cyanogenic glycosides, such as dhurrin, thereby forming a chemical defense barrier [67]. The authors highlighted the involvement of shikimic acid in basal and induced resistance, as well as priming against biotic stress [68]. For example, a derivative of shikimic acid exerts a markedly detrimental effect on grain aphids [69]. Serba’s study shows that in resistant genotype TAM428, shikimate pathway-related genes (like those encoding 3-dehydroquinate synthase, shikimate kinase) are significantly enriched 216 h after inoculation, driving phenylalanine and tyrosine biosynthesis [43]. Our study demonstrated that aphid infestation affected the expression levels of shikimate kinase, chitin synthase, and tyrosine synthetase genes in aphid-resistant inbred lines. Moreover, we observed significant differences in gene expression at various time points, indicating that the shikimic acid pathway is activated to mount a defensive response against aphids.
The metabolism of cyanogenic glycosides in sorghum is central to the defense mechanism of the plant. The chemical name for the cyanogenic glycoside of sorghum is p-hydroxy-(S)-phenylethanol-nitro-β- D-glucoside [70]. After consuming the cell walls, this metabolite decomposes into toxic cyanide, effectively repelling pests [71]. To explore the localization of enzymes in the sorghum cyanogenic glycoside pathway, we transiently expressed CYP79A1, CYP71E1, UGT85B1, POR2b, and various combinations of these enzymes (along with control proteins) in the leaf epidermal cells of the plant. The results revealed that CYP71E1 expression in the resistant line was significantly upregulated at 24 h compared to 0 h, and the expression of CYP71E1 in the susceptible line remained unchanged between 24 and 0 h. Notably, the cyanogenic glycoside accumulation in susceptible line HX37 is low, a phenomenon consistent with the reported susceptible line Tx2737 [43]. This finding suggests that the cyanogenic glycoside response in sorghum may significantly enhance herbivore resistance. This study provides novel experimental evidence supporting the defensive role of cyanogenic glycosides against insect herbivory, thereby confirming their significance in plant defense mechanisms.
5. Conclusions
This study investigates aphid resistance mechanisms in sorghum through transcriptomic comparison between resistant (HX133) and susceptible (HX37) lines. Following aphid infestation, HX133 suppressed aphid proliferation and exhibited 2802 differentially expressed genes (DEGs; 45.9% upregulated) at 24 h, contrasting with 732 DEGs (21% upregulated) in HX37. Pathway analysis revealed conserved enrichment in photosynthesis-related pathways across both lines. Key defense-related pathways, including phenylpropanoid/flavonoid biosynthesis, glutathione metabolism, and plant hormone signaling, were specifically activated in HX133.
Notably, the shikimic acid pathway and downstream aromatic amino acid biosynthesis (e.g., dhurrin production via CYP79A1, CYP71E1, and UGT85B1) were upregulated in resistant plants, validated by qRT-PCR. Dhurrin, a major cyanogenic glucoside in sorghum, emerged as a critical anti-aphid metabolite. These findings highlight a coordinated regulation of hormone signaling and specialized metabolism as central to aphid resistance, providing molecular targets for breeding resistant cultivars.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/agriculture15141502/s1, Table S1: NGS read metrics; Table S2: Number of DEGs in sorghum lines in response to sorghum aphid herbivory at 0, 24 and 48 h; Table S3:(A) Significantly enriched G0 pathways in HX37 0 h vs HX37 24 h. (B) Significantly enriched GO pathways in HX37 0 h vs HX37 48 h. (C) Significantly enriched GO pathways in HX133 0 h vs HX133 24 h. (D) Significantly enriched GO pathways in HX133 0 h vs HX133 48 h.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.D.; methodology, M.G.; validation, T.W.; formal analysis, J.L. and D.W.; investigation, Y.W., L.S. and J.D.; resources, J.L.; data curation, M.G., J.D. and T.W.; writing—original draft preparation, M.G. and J.D.; writing—review and editing, D.W. and J.L.; supervision, L.S.; project administration, Y.W. and D.W.; funding acquisition, J.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32372134), the Natural Science Foundation of Education Department of Anhui Province (2023AH051852), Key Discipline Construction Fund for Crop Science of Anhui Science and Technology University (No. XK-XJGF001), and supported by Anhui Province International Joint Research Center of Forage Bio-breeding (No. AHIJRCFB202303).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets presented in this study are available upon request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank postgraduate students Kunliang Zou and Yang Liu, who have provided great assistance in aphid rearing and sorghum genome extraction. We also thank Xin Wang and Lihua Wang for their careful guidance on the use of experimental instruments.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| RNA-seqI | RNA Sequencing |
| qRT-PCR | Quantitative Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
| DEGs | Differentially Expressed Genes |
| BP | Biological Processes |
| CC | Cellular Components |
| MF | Molecular Functions |
| hpi | Hours Post-Infestation |
| JA | Jasmonic Acid |
| ET | Ethylene |
| ABA | Abscisic Acid |
| LOX | Lipoxygenase |
| AOS | Allene Oxide Synthase |
| OPR | 12-Oxophytodienoate Reductase |
| LCYB | Lycopene Beta-Cyclase |
| ZEP | Zeaxanthin Epoxidase |
| NCED | 9-Cis-Epoxycarotenoid Dioxygenase |
| SAMS | S-Adenosyl-L-Methionine Synthase |
| ACS | ACC Synthase |
| ACO | ACC Oxidase |
| HML | Hydroxymandelonitrile Lyase |
| GH | Glycoside Hydrolase |
References
- Bowling, R.D.; Brewer, M.J.; Kerns, D.L.; Gordy, J.; Seiter, N.; Elliott, N.E.; Buntin, G.D.; Way, M.O.; Royer, T.A.; Biles, S.; et al. Sugarcane Aphid (Hemiptera: Aphididae): A New Pest on Sorghum in North America. J. Integr. Pest Manag. 2016, 7, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balbi, E.I.; Decker-Franco, C.; Szwarc, D.; Casuso, V.M.; Saluso, A.; Arneodo, J.D. Unveiling the occurrence of Melanaphis sorghi in Argentina following a major aphid outbreak. Phytoparasitica 2022, 51, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekarcik, A.J.; Jacobson, A.L.; Giles, K. Evaluating Sugarcane Aphid, Melanaphis sacchari (Hemiptera: Aphididae), Population Dynamics, Feeding Injury, and Grain Yield Among Commercial Sorghum Varieties in Alabama. J. Econ. Entomol. 2021, 114, 757–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña-Martínez, R.; Lomeli-Flores, J.R.; Bujanos-Muñiz, R.; Salas-Monzón, R.; Hernández-Torres, O.E.; Marín-Jarillo, A.; Ibarra, J.E.; Vanegas-Rico, J.M.; Muñoz-Viveros, A.L. Comparative biology and life tables of sorghum aphid Melanaphis sorghi (Theobald) (Hemiptera: Aphididae) from Mexico, at different temperatures. Phytoparasitica 2024, 52, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viswanathan, R.; Nithya, K.; Vishnuvardhan, J.; Balasaravanan, S.; Kaverinathan, K.; Visalatchi, D. Sorghum (Sorghum bicolor) a new host to sugarcane yellow leaf and mosaic viruses in India. Indian Phytopathol. 2023, 76, 867–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, D.A.; Lehmler, H.-J.; Kolpin, D.W.; Hladik, M.L.; Vargo, J.D.; Schilling, K.E.; LeFevre, G.H.; Peeples, T.L.; Poch, M.C.; LaDuca, L.E. A critical review on the potential impacts of neonicotinoid insecticide use: Current knowledge of environmental fate, toxicity, and implications for human health. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2020, 22, 1315–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guden, B.; Yol, E.; Ikten, C.; Erdurmus, C.; Uzun, B. Molecular and morphological evidence for resistance to sugarcane aphid (Melanaphis sacchari) in sweet sorghum [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench]. 3 Biotech 2019, 9, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haar, P.J.; Buntin, G.D.; Jacobson, A.; Pekarcik, A.; Way, M.O.; Zarrabi, A. Evaluation of Tactics for Management of Sugarcane Aphid (Hemiptera: Aphididae) in Grain Sorghum. J. Econ. Entomol. 2019, 112, 2719–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y. Improvement of crop protection against greenbug using the worldwide sorghum germplasm collection and genomics-based approaches. Plant Genet. Resour. 2011, 9, 317–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paudyal, S.; Armstrong, J.S.; Giles, K.L.; Payton, M.E.; Opit, G.P.; Limaje, A. Categories of Resistance to Sugarcane Aphid (Hemiptera: Aphididae) Among Sorghum Genotypes. J. Econ. Entomol. 2019, 112, 1932–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pingault, L.; Palmer, N.A.; Koch, K.G.; Heng-Moss, T.; Bradshaw, J.D.; Seravalli, J.; Twigg, P.; Louis, J.; Sarath, G. Differential Defense Responses of Upland and Lowland Switchgrass Cultivars to a Cereal Aphid Pest. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.; Duan, X.; Cui, J.; Xue, W.; Zhang, Q. Differential molecular responses of aphid-sensitive and aphid-resistant sorghum lines to aphid infestation. Arthropod-Plant Interact. 2011, 6, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pingault, L.; Varsani, S.; Palmer, N.; Ray, S.; Williams, W.P.; Luthe, D.S.; Ali, J.G.; Sarath, G.; Louis, J. Transcriptomic and volatile signatures associated with maize defense against corn leaf aphid. BMC Plant Biol. 2021, 21, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, K.; Huang, Y. Genome-wide characterization of the sorghum JAZ gene family and their responses to phytohormone treatments and aphid infestation. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 3238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paudyal, S.; Armstrong, J.S.; Giles, K.L.; Hoback, W.; Aiken, R.; Payton, M.E. Differential responses of sorghum genotypes to sugarcane aphid feeding. Planta 2020, 252, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triplett, E.; Hayes, C.; Emendack, Y.; Longing, S.; Monclova, C.; Simpson, C.; Laza, H.E. Leaf structural traits mediating pre-existing physical innate resistance to sorghum aphid in sorghum under uninfested conditions. Planta 2023, 258, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palial, S.; Kumar, S.; Atri, C.; Sharma, S.; Banga, S.S. Antixenosis and antibiosis mechanisms of resistance to turnip aphid, Lipaphis erysimi (Kaltenbach) in Brassica juncea-fruticulosa introgression lines. J. Pest Sci. 2021, 95, 749–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knoll, J.E.; Uchimiya, M.; Harris-Shultz, K. Juice chemical properties of 24 sorghum cultivars under varying levels of sugarcane aphid (Melanaphis sacchari) infestation. Arthropod-Plant Interact. 2021, 15, 707–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishnan, D.; Bateman, N.; Kariyat, R.R. Rice physical defenses and their role against insect herbivores. Planta 2024, 259, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardona, J.B.; Grover, S.; Busta, L.; Sattler, S.E.; Louis, J. Sorghum cuticular waxes influence host plant selection by aphids. Planta 2022, 257, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Hereward, J.P.; Wang, D.; Yang, Q.; Wang, Y. A host-specialized aphid lineage helps another conspecific lineage utilize a new host by disrupting the plant defenses. J. Pest Sci. 2023, 97, 1525–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezerra, R.H.S.; Sousa-Souto, L.; Santana, A.E.G.; Ambrogi, B.G. Indirect plant defenses: Volatile organic compounds and extrafloral nectar. Arthropod-Plant Interact. 2021, 15, 467–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, J.S.; Rooney, W.L.; Peterson, G.C.; Villenueva, R.T.; Brewer, M.J.; Sekula-Ortiz, D. Sugarcane Aphid (Hemiptera: Aphididae): Host Range and Sorghum Resistance Including Cross-Resistance from Greenbug Sources. J. Econ. Entomol. 2015, 108, 576–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poosapati, S.; Poretsky, E.; Dressano, K.; Ruiz, M.; Vazquez, A.; Sandoval, E.; Estrada-Cardenas, A.; Duggal, S.; Lim, J.-H.; Morris, G.; et al. A sorghum genome-wide association study (GWAS) identifies a WRKY transcription factor as a candidate gene underlying sugarcane aphid (Melanaphis sacchari) resistance. Planta 2022, 255, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Liu, G.; Wang, X.; Su, Y.; Diao, H.; Sun, D.; Shang, J.; Li, Y.; Guo, Y.; Qiu, L. Identification and characterization of resistance to soybean aphid in 22 highly resistant soybean accessions. Euphytica 2022, 218, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Huang, J.; Huang, Y. Identification and characterization of plant resistance genes (R genes) in sorghum and their involvement in plant defense against aphids. Plant Growth Regul. 2022, 96, 443–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzin, V.; Fernandez-Pozo, N.; Richter, A.; Schmelz, E.A.; Schoettner, M.; Schafer, M.; Ahern, K.R.; Meihls, L.N.; Kaur, H.; Huffaker, A.; et al. Dynamic Maize Responses to Aphid Feeding Are Revealed by a Time Series of Transcriptomic and Metabolomic Assays. Plant Physiol. 2015, 169, 1727–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Wang, K.; Wang, C.; Zhao, Y.; Tao, Z.; Li, J.; Wang, L.; Shi, J.; Huang, S.; Xie, C.; et al. Combining quantitative trait locus mapping with multiomics profiling reveals genetic control of corn leaf aphid (Rhopalosiphum maidis) resistance in maize. J. Exp. Bot. 2023, 74, 3749–3764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batyrshina, Z.S.; Yaakov, B.; Shavit, R.; Singh, A.; Tzin, V. Comparative transcriptomic and metabolic analysis of wild and domesticated wheat genotypes reveals differences in chemical and physical defense responses against aphids. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, S.K.; Weng, Y.; Rudd, J.C.; Akhunova, A.; Liu, S. Transcriptomics of induced defense responses to greenbug aphid feeding in near isogenic wheat lines. Plant Sci. 2013, 212, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiani, M.; Szczepaniec, A. Effects of sugarcane aphid herbivory on transcriptional responses of resistant and susceptible sorghum. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, W.; Sun, L.; Jiao, B.; Zhao, P.; Ma, C.; Gao, J.; Zhou, S. Evaluation of aphid resistance on different rose cultivars and transcriptome analysis in response to aphid infestation. BMC Genom. 2024, 25, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Cassone, B.J.; Wijeratne, A.; Jun, T.-H.; Michel, A.P.; Mian, M.A.R. Transcriptomic dynamics in soybean near-isogenic lines differing in alleles for an aphid resistance gene, following infestation by soybean aphid biotype 2. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacWilliams, J.R.; Nabity, P.D.; Mauck, K.E.; Kaloshian, I. Transcriptome analysis of aphid-resistant and susceptible near isogenic lines reveals candidate resistance genes in cowpea (Vigna unguiculata). BMC Plant Biol. 2023, 23, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, X.; Yang, Y.; Feng, P.; Ma, Q.; Su, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J. Transcriptomic profiling of cotton leaves in response to cotton aphid damage. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2022, 44, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.-R.; Zhao, D.-T.; Zhang, L.-Y.; Chang, J.-H.; Cui, J.-H. Combining transcriptome and metabolome analysis to understand the response of sorghum to Melanaphis sacchari. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Zhao, S.; Han, Y.; Shao, Y.; Dong, Z.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, K.; Liu, X.; Li, D.; Chang, J.; et al. Efficient and fine mapping of RMES1 conferring resistance to sorghum aphid Melanaphis sacchari. Mol. Breed. 2013, 31, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, W.; Lv, P.; Yang, X.; Xu, W.; Ni, X.; Feng, H.; Zhao, G.; Pu, M.; Zhou, S.; et al. Whole-genome resequencing and transcriptome analysis provide insights on aphid-resistant quantitative trait loci/genes in Sorghum bicolor. Plant Breed. 2021, 140, 618–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, K.; Huang, J.; Yan, L.; Doust, A.N.; Huang, Y. Integrated transcriptomic and pathway analyses of sorghum plants revealed the molecular mechanisms of host defense against aphids. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1324085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetreault, H.M.; Grover, S.; Scully, E.D.; Gries, T.; Palmer, N.A.; Sarath, G.; Louis, J.; Sattler, S.E. Global Responses of Resistant and Susceptible Sorghum (Sorghum bicolor) to Sugarcane Aphid (Melanaphis sacchari). Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.-L.; Wu, D.-G.; Li, J.-Q.; Zhan, Q.-W.; Huang, S.-C.; Huang, B.-H.; Wang, X. Effects of aphid disoperation on photosynthetic performance and agronomic traits of different sorghum varieties. Pak. J. Bot. 2021, 53, 2275–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, K.; Liu, Y.; Wang, T.; Guan, M.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Yu, H.; Wu, D.; Du, J. Genomic Identification of Callose Synthase (CalS) Gene Family in Sorghum (Sorghum bicolor) and Comparative In Silico Expression Analysis under Aphid (Melanaphis sacchari) Infestation. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serba, D.D.; Meng, X.; Schnable, J.; Bashir, E.; Michaud, J.P.; Vara Prasad, P.V.; Perumal, R. Comparative Transcriptome Analysis Reveals Genetic Mechanisms of Sugarcane Aphid Resistance in Grain Sorghum. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pertea, M.; Kim, D.; Pertea, G.M.; Leek, J.T.; Salzberg, S.L. Transcript-level expression analysis of RNA-seq experiments with HISAT, StringTie and Ballgown. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 1650–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-Seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, M.D.; Wakefield, M.J.; Smyth, G.K.; Oshlack, A. Gene ontology analysis for RNA-seq: Accounting for selection bias. Genome Biol. 2010, 11, R14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mccormick, R.F.; Truong, S.K.; Sreedasyam, A.; Jenkins, J.; Shu, S.; Sims, D.; Kennedy, M.; Amirebrahimi, M.; Weers, B.D.; Mckinley, B. The Sorghum bicolor reference genome: Improved assembly, gene annotations, a transcriptome atlas, and signatures of genome organization. Plant J. 2018, 93, 338–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, K.; Wang, T.; Guan, M.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Du, J.; Wu, D. Identification and Evaluation of qRT-PCR Reference Genes in Melanaphis sacchari. Insects 2024, 15, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, H.; Dudareva, N. The Shikimate Pathway and Aromatic Amino Acid Biosynthesis in Plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2012, 63, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhrah, S.; Bano, N.; Sarvendra, K.; Lone, R.A.; Nayak, S.P.; Kumari, A.; Rout, P.K.; Mohanty, C.S. Elucidating the Secondary Metabolite Biosynthesis Networks in Underutilized Tree Bean (Parkia timoriana) Through Integrated Metabolomic and Transcriptomic Approaches. Appl. Biochem. 2025, 197, 3521–3547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myrans, H.; Vandegeer, R.K.; Henry, R.J.; Gleadow, R.M. Nitrogen availability and allocation in sorghum and its wild relatives: Divergent roles for cyanogenic glucosides. J. Plant Physiol. 2021, 258–259, 153393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- English, B.; Quinn, A.A.; Warren, C.R.; Gleadow, R.M.; Myrans, H. Do cyanogenic glucosides help sorghum manage a fluctuating nitrogen supply? Funct. Plant Biol. 2025, 52, FP24343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darbani, B.; Motawia, M.S.; Olsen, C.E.; Nour-Eldin, H.H.; Møller, B.L.; Rook, F. The biosynthetic gene cluster for the cyanogenic glucoside dhurrin in Sorghum bicolor contains its co-expressed vacuolar MATE transporter. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gleadow, R.M.; Mckinley, B.A.; Blomstedt, C.K.; Lamb, A.C.; Mller, B.L.; Mullet, J.E. Regulation of dhurrin pathway gene expression during Sorghumbicolor development. Planta 2021, 254, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, Y.-S.; Sintaha, M.; Cheung, M.-Y.; Lam, H.-M. Plant Hormone Signaling Crosstalks between Biotic and Abiotic Stress Responses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onkokesung, N.; Baldwin, I.T.; Gális, I. The role of jasmonic acid and ethylene crosstalk in direct defense ofNicotiana attenuataplants against chewing herbivores. Plant Signal. Behav. 2014, 5, 1305–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiu, S.-H.; Sewelam, N.; Kazan, K.; Thomas-Hall, S.R.; Kidd, B.N.; Manners, J.M.; Schenk, P.M. Ethylene Response Factor 6 Is a Regulator of Reactive Oxygen Species Signaling in Arabidopsis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70289. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, H.; Sun, Y.; Peng, X.; Wang, Q.; Harris, M.; Ge, F. Up-regulation of abscisic acid signaling pathway facilitates aphid xylem absorption and osmoregulation under drought stress. J. Exp. Bot. 2016, 67, 681–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bari, R.; Jones, J.D.G. Role of plant hormones in plant defence responses. Plant Mol. Biol. 2008, 69, 473–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Mostafa, S.; Zeng, W.; Jin, B. Function and Mechanism of Jasmonic Acid in Plant Responses to Abiotic and Biotic Stresses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Zhou, M.; Wei, D.; Chen, H.; You, C.; Lin, J. Transcriptome Profiling Reveals the Negative Regulation of Multiple Plant Hormone Signaling Pathways Elicited by Overexpression of C-Repeat Binding Factors. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Duan, G.; Li, C.; Liu, L.; Han, G.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, C. The crosstalks between jasmonic acid and other plant hormone signaling highlight the involvement of jasmonic acid as a core component in plant response to biotic and abiotic stresses. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.-B.; Liu, Y.-Q.; Chen, D.-Y.; Chen, F.-Y.; Fang, X.; Hong, G.-J.; Wang, L.-J.; Wang, J.-W.; Chen, X.-Y. Jasmonate response decay and defense metabolite accumulation contributes to age-regulated dynamics of plant insect resistance. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 13925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, J.; Basu, S.; Varsani, S.; Castano-Duque, L.; Jiang, V.; Williams, W.P.; Felton, G.W.; Luthe, D.S. Ethylene Contributes to maize insect resistance1-Mediated Maize Defense against the Phloem Sap-Sucking Corn Leaf Aphid. Plant Physiol. 2015, 169, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ton, J.; Flors, V.; Mauch-Mani, B. The multifaceted role of ABA in disease resistance. Trends Plant Sci. 2009, 14, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, C.; Schmidt, A.; Reichelt, M.; Tsai, C.J.; Gershenzon, J. Lack of antagonism between salicylic acid and jasmonate signalling pathways in poplar. New Phytol. 2022, 235, 701–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gleadow, R.M.; Møller, B.L. Cyanogenic Glycosides: Synthesis, Physiology, and Phenotypic Plasticity. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2014, 65, 155–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamir, J.; Sánchez-Bel, P.; Flors, V. Molecular and physiological stages of priming: How plants prepare for environmental challenges. Plant Cell Rep. 2014, 33, 1935–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dangol, A.; Shavit, R.; Yaakov, B.; Strickler, S.R.; Jander, G.; Tzin, V. Characterizing serotonin biosynthesis in Setaria viridis leaves and its effect on aphids. Plant Mol. Biol. 2022, 109, 533–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruss, S.M.; Ghaste, M.; Widhalm, J.R.; Tuinstra, M.R. Seedling growth and fall armyworm feeding preference influenced by dhurrin production in sorghum. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2022, 135, 1037–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laursen, T.; Møller, B.L.; Bassard, J.-E. Plasticity of specialized metabolism as mediated by dynamic metabolons. Trends Plant Sci. 2015, 20, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).