Constitute Variety and Nutrient Analysis of the Different Main Plant Parts of Caragana korshinskii for Animal Feed
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Material Collection and Preparation
2.2. Nutrient Analysis
2.3. Protein Fractions in CNCPS
2.4. Determination of Amino Acid Content
2.5. In Vitro Protein Simulation Digestion
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Variety in the Main Different Plant Parts
3.2. Protein Fraction Analysis and Comparison in Different Plant Parts
3.3. Amino Acid Composition in Different Plant Parts
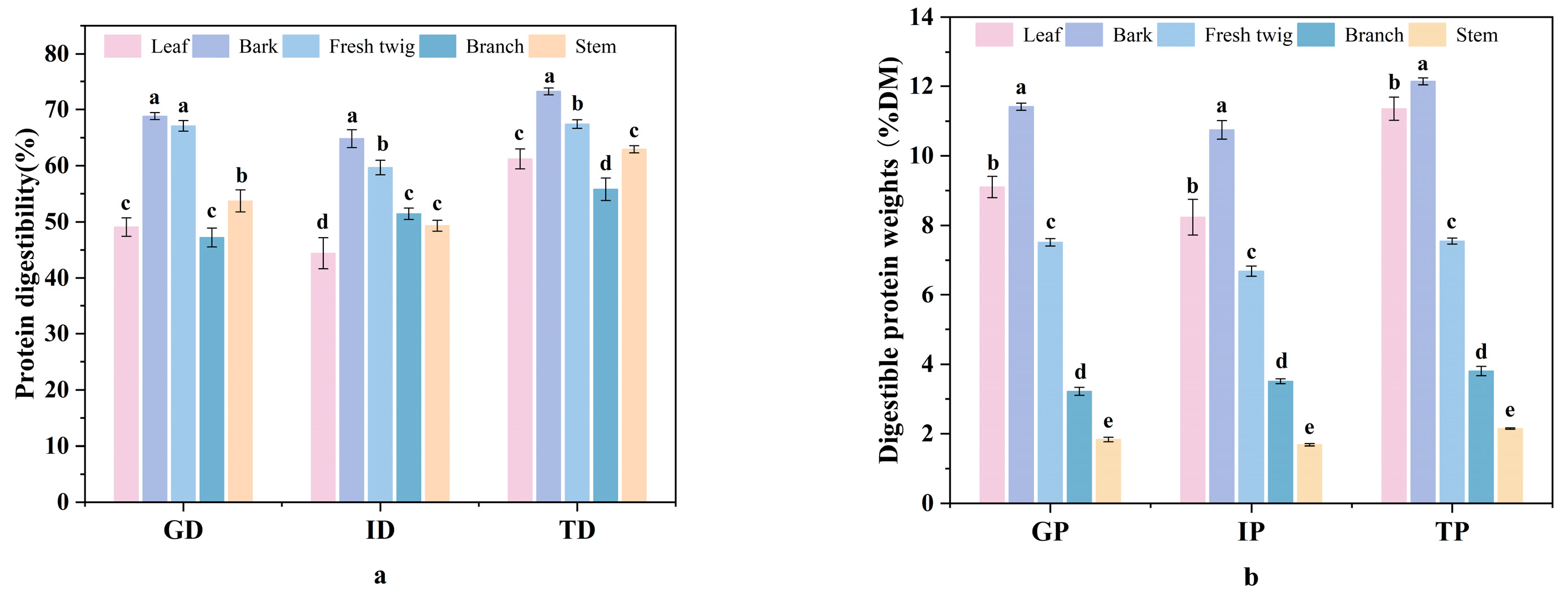
3.4. In Vitro Digestibility of Protein from Different Plant Parts
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Godfray, H.C.J.; Beddington, J.R.; Crute, I.R.; Haddad, L.; Lawrence, D.; Muir, J.F.; Pretty, J.; Robinson, S.; Thomas, S.M.; Toulmin, C. Food Security: The Challenge of Feeding 9 Billion People. Science 2010, 327, 812–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, B.; Chang, L.; Ohm, J.B.; Chen, B.; Rao, J. Structural, functional properties, and volatile profile of hemp protein isolate as affected by extraction method: Alkaline extraction-isoelectric precipitation vs salt extraction. Food Chem. 2023, 405, 135001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santamaría-Fernández, M.; Lübeck, M. Production of leaf protein concentrates in green biorefineries as alternative feed for monogastric animals. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2020, 268, 114605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAOSTAT. 2023. Available online: https://www.fao.org/faostat/zh/#country/41 (accessed on 21 July 2023).
- Gurgel, A.C.; Reilly, J.; Blanc, E. Challenges in simulating economic effects of climate change on global agricultural markets. Clim. Change 2021, 166, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hal, O.; Weijenberg, A.A.A.; De Boer, I.J.M.; Van Zanten, H.H.E. Accounting for feed-food competition in environmental impact assessment: Towards a resource efficient food-system. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 240, 118241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, T.; Shen, Y.; Han, L.; Peng, Z.; Xie, Z.; Zhong, C.; Jia, S. Bacterial cellulose production from ethylenediamine pretreated Caragana korshinskii Kom. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 164, 113340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.J.; Chaudhry, A.S.; Osman, A.; Shi, C.Q.; Edwards, G.R.; Dewhurst, R.J.; Cheng, L. Associative effects of ensiling mixtures of sweet sorghum and alfalfa on nutritive value, fermentation and methane characteristics, Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2015, 206, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, C.; Sun, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Jin, M.J.; Tan, Z.L.; Jia, S.R. Chemical characterization and nutritional analysis of protein isolates from Caragana korshinskii Kom. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 3217–3222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Yin, J.; Li, G.; Qi, L.; Yang, F.; Wang, R.; Li, G. Reference gene selection for qRT-PCR in Caragana korshinskii Kom. under different stress conditions. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2014, 41, 2325–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Huang, M.; Si, B.C.; Yu, M.; Shao, M. The differences of water balance components of Caragana korshinkii grown in homogeneous and layered soils in the desert-Loess Plateau transition zone. J. Arid Environ. 2013, 98, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, H.; Xue, Y.; Cai, Y.; Zhang, G. Microbial community, fermentation quality, and in vitro degradability of ensiling caragana with lactic acid bacteria and rice bran. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 804429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Ma, L.; Fan, S.; Ma, W.; Zhang, X. Effects of fermented Caragana korshinskii feed on meat quality characteristics in different muscles of Tan sheep. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2020, 19, 1036–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, X.; Li, H.; Kang, J.; Yang, J. Experimental Study on the Cutting and Crushing Performance of Caragana korshinskii Strips. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, B.; Qiu, R.; Sun, L.; Bao, J.; Liu, Y.; Ge, G.; Jia, Y.; Wang, Z. Effect isolated lactic acid bacteria inoculation on the quality, bacterial composition and metabolic characterization of Caragana korshinskii silage. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2024, 11, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC. Association of Official Analytical Chemists. In Official Methods of Analysis; AOAC International: Rockville, MD, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- UNE-EN ISO 16472:2007; Animal feeding stuffs—Determination of amylase-treated neutral detergent fibre content (aNDF). International Organization for Standardization (ISO), 2007.
- Sluiter, J.B.; Ruiz, R.O.; Scarlata, C.J.; Sluiter, A.D.; Templeton, D.W. Compositional analysis of lignocellulosic feedstocks. 1. Review and description of methods. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 9043–9053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licitra, G.; Hernandez, T.M.; Van Soest, P.J. Standardization of procedures for nitrogen fractionation of ruminant feeds. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 1996, 57, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sniffen, C.J.; O’Connor, J.D.; Van Soest, P.J.; Fox, D.G.; Russell, J.B. A net carbohydrate and protein system for evaluating cattle diets: II. Carbohydrate and protein availability. J. Anim. Sci. 1992, 70, 3562–3577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marambe, H.K.; Shand, P.J.; Wanasundara, J.P.D. Release of Angiotensin I-Converting Enzyme Inhibitory Peptides from Flaxseed (Linum usitatissimum L.) Protein under Simulated Gastrointestinal Digestion. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 9596–9604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Wang, J.; Xu, C.; Duan, D.; Xu, W.; Tian, P. Effects of Epichloë endophyte and repeated cutting on nutrition compositions of Festuca sinensis. Plant Soil Environ. 2020, 66, 526–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catunda, K.L.; Churchill, A.C.; Zhang, H.; Power, S.A.; Moore, B.D. Short-term drought is a stronger driver of plant morphology and nutritional composition than warming in two common pasture species. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2022, 208, 841–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva Perez, D.; Dupont, C.; Guillemain, A.; Jacob, S.; Labalette, F.; Briand, S.; Marsac, S.; Guerrini, O.; Broust, F.; Commandre, J.-M. Characterisation of the Most Representative Agricultural and Forestry Biomasses in France for Gasification. Waste Biomass Valorization 2015, 6, 515–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenorio, A.T.; Kyriakopoulou, K.E.; Suarez-Garcia, E.; Van den Berg, C.; Van der Goot, A.J. Understanding differences in protein fractionation from conventional crops, and herbaceous and aquatic biomass—Consequences for industrial use. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 71, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Du, Z.; Yamasaki, S.; Nguluve, D.; Tinga, B.; Macome, F.; Oya, T. Community of natural lactic acid bacteria and silage fermentation of corn stover and sugarcane tops in Africa. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2020, 33, 1252–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrenková, M.; Ceresnakova, Z.; Weisbjerg, M.R.; Formelová, Z.; Polacikova, M.; Vondráková, M. Characterization of proteins in feeds according to the CNCPS and comparison to in situ parameters. Czech J. Anim. Sci. 2014, 59, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanyasunya, T.P.; Rong, H.W.; Abdulrazak, S.A.; Mukisira, E.A. The potential of the weed, Commelina diffusa L., as a fodder crop for ruminants. S. Afr. J. Anim. Sci. 2006, 36, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebeid, H.M.; Kholif, A.E.; Chrenkova, M.; Anele, U.Y. Ruminal fermentation kinetics of Moringa oleifera leaf and seed as protein feeds in dairy cow diets: In sacco degradability and protein and fiber fractions assessed by the CNCPS method. Agrofor. Syst. 2020, 94, 905–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamoorthy, U.; Muscato, T.V.; Sniffen, C.J.; Van Soest, P.J. Nitrogen Fractions in Selected Feedstuffs. J. Dairy Sci. 1982, 65, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebeid, H.M.; Kholif, A.E.; El-Bordeny, N.; Chrenkova, M.; Mlynekova, Z.; Hansen, H.H. Nutritive value of quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa) as a feed for ruminants: In sacco degradability and in vitro gas production. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 35241–35252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmunds, B.; Südekum, K.H.; Bennett, R.; Schröder, A.; Spiekers, H.; Schwarz, F.J. The amino acid composition of rumen-undegradable protein: A comparison between forages. J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96, 4568–4577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, S.U.; Jørgensen, H.; Bukh, C.; Schjoerring, J.K. Green biorefining: Effect of nitrogen fertilization on protein yield, protein extractability and amino acid composition of tall fescue biomass. Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 130, 642–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Item | Leaf | Bark | Fresh Twigs | Branch | Stem |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ash | 11.2 ± 0.1 a | 4.2 ± 0.0 b | 3.2 ± 0.2 c | 2.1 ± 0.0 d | 1.0 ± 0.0 e |
| CP | 18.6 ± 0.1 a | 16.6 ± 0.2 b | 11.2 ± 0.0 c | 6.8 ± 0.1 d | 3.4 ± 0.0 e |
| NPN | 2.2 ± 0.2 c | 6.4 ± 0.3 a | 5.1 ± 0.1 b | 1.9 ± 0.2 c | 1.0 ± 0.1 d |
| SP | 4.9 ± 0.3 b | 6.9 ± 0.0 a | 6.1 ± 0.3 a | 2.5 ± 0.3 c | 1.2 ± 0.1 d |
| CF | 10.5 ± 0.2 a | 7.1 ± 0.1 b | 5.9 ± 0.1 c | 5.8 ± 0.2 c | 7.1 ± 0.2 b |
| NDF | 38.2 ± 0.4 e | 54.5 ± 0.2 d | 70.5 ± 0.1 c | 80.5 ± 0.5 b | 81.9 ± 0.3 a |
| ADF | 34.8 ± 0.5 d | 44.5 ± 0.9 c | 58.7 ± 0.6 b | 65.0 ± 0.1 a | 65.0 ± 1.0 a |
| NDICP | 3.8 ± 0.1 a | 3.3 ± 0.0 b | 2.2 ± 0.0 c | 2.3 ± 0.1 c | 1.3 ± 0.1 d |
| ADICP | 3.5 ± 0.2 a | 1.3 ± 0.0 bc | 1.4 ± 0.3 bc | 1.9 ± 0.0 b | 0.8 ± 0.0 c |
| Cellulose | 22.0 ± 0.2 e | 35.2 ± 0.1 b | 33.6 ± 0.2 c | 32.8 ± 0.1 d | 43.9 ± 0.2 a |
| Hemicellulose | 15.2 ± 0.4 d | 19.4 ± 0.0 b | 20.4 ± 0.3 b | 16.8 ± 0.8 c | 22.2 ± 0.1 a |
| ADL | 22.0 ± 1.8 b | 15.4 ± 0.5 c | 21.5 ± 0.1 b | 27.6 ± 0.5 a | 17.2 ± 0.9 c |
| Amino Acid Composition (mg/g DM) | Leaf | Bark | Fresh Twigs | Branch | Stem |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alanine | 7.5 ± 0.2 a | 2.9 ± 0.2 b | 2.2 ± 0.2 c | 0.8 ± 0.2 d | 0.6 ± 0.0 d |
| Arginine | 7.6 ± 0.1 a | 2.6 ± 0.1 b | 2.2 ± 0.0 c | 0.9 ± 0.0 d | 0.4 ± 0.0 e |
| Aspartic acid | 26.3 ± 0.3 a | 17.2 ± 0.7 c | 23.8 ± 0.4 b | 3.2 ± 0.3 d | 1.7 ± 0.1 e |
| Cysteine | 1.2 ± 0.0 a | 0.7 ± 0.0 b | 0.7 ± 0.0 b | 0.3 ± 0.0 c | 0.1 ± 0.0 d |
| Glutamic acid | 19.2 ± 0.4 a | 7.2 ± 0.2 b | 5.6 ± 0.3 c | 2.3 ± 0.1 d | 1.3 ± 0.1 e |
| Glycine | 9.0 ± 0.1 a | 3.2 ± 0.1 b | 2.4 ± 0.0 c | 1.1 ± 0.1 d | 0.7 ± 0.1 e |
| Histidine | 3.7 ± 0.1 a | 2.5 ± 0.2 b | 1.5 ± 0.2 c | 0.6 ± 0.0 d | 0.4 ± 0.0 d |
| Isoleucine | 8.3 ± 0.5 a | 4.1 ± 0.3 b | 2.8 ± 0.1 c | 1.1 ± 0.1 d | 0.6 ± 0.0 d |
| Leucine * | 12.3 ± 0.2 a | 5.3 ± 0.1 b | 3.6 ± 0.1 c | 1.4 ± 0.3 d | 0.9 ± 0.2 e |
| Lysine * | 9.5 ± 0.4 a | 5.4 ± 0.3 b | 3.3 ± 0.2 c | 1.3 ± 0.0 d | 0.8 ± 0.1 d |
| Methionine * | 2.9 ± 0.0 a | 1.1 ± 0.1 b | 0.9 ± 0.1 b | 0.4 ± 0.1 c | 0.1 ± 0.0 d |
| Phenylalanine * | 11.1 ± 0.2 a | 4.1 ± 0.2 b | 3.0 ± 0.3 c | 1.2 ± 0.2 d | 0.7 ± 0.1 d |
| Proline | 5.6 ± 0.7 b | 16.8 ± 0.4 a | 17.1 ± 0.2 a | 2.8 ± 0.0 c | 1.4 ± 0.2 d |
| Serine | 8.4 ± 0.0 a | 4.2 ± 0.6 b | 3.3 ± 0.0 b | 1.1 ± 0.0 c | 0.8 ± 0.1 c |
| Threonine * | 8.4 ± 0.1 a | 5.6 ± 0.5 b | 3.2 ± 0.1 c | 1.3 ± 0.1 d | 0.8 ± 0.0 d |
| Tyrosine | 8.7 ± 0.4 a | 5.4 ± 0.0 b | 2.8 ± 0.4 c | 1.1 ± 0.2 d | 0.4 ± 0.0 d |
| Valine * | 11.1 ± 0.1 a | 6.4 ± 0.3 b | 4.3 ± 0.1 c | 1.7 ± 0.1 d | 0.8 ± 0.1 e |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Ding, Z.; Hua, X.; Yang, F.; Zhou, X.; Xu, Y. Constitute Variety and Nutrient Analysis of the Different Main Plant Parts of Caragana korshinskii for Animal Feed. Agriculture 2025, 15, 1455. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15131455
Zhang Y, Ding Z, Hua X, Yang F, Zhou X, Xu Y. Constitute Variety and Nutrient Analysis of the Different Main Plant Parts of Caragana korshinskii for Animal Feed. Agriculture. 2025; 15(13):1455. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15131455
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yifan, Zhijia Ding, Xia Hua, Fuyu Yang, Xin Zhou, and Yong Xu. 2025. "Constitute Variety and Nutrient Analysis of the Different Main Plant Parts of Caragana korshinskii for Animal Feed" Agriculture 15, no. 13: 1455. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15131455
APA StyleZhang, Y., Ding, Z., Hua, X., Yang, F., Zhou, X., & Xu, Y. (2025). Constitute Variety and Nutrient Analysis of the Different Main Plant Parts of Caragana korshinskii for Animal Feed. Agriculture, 15(13), 1455. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15131455





