Earthworm (Eisenia fetida) Mediated Macropore Network Formation in Black Soil: Decay Straw as a Trigger for Sustainable Tillage
Abstract
1. Introduction
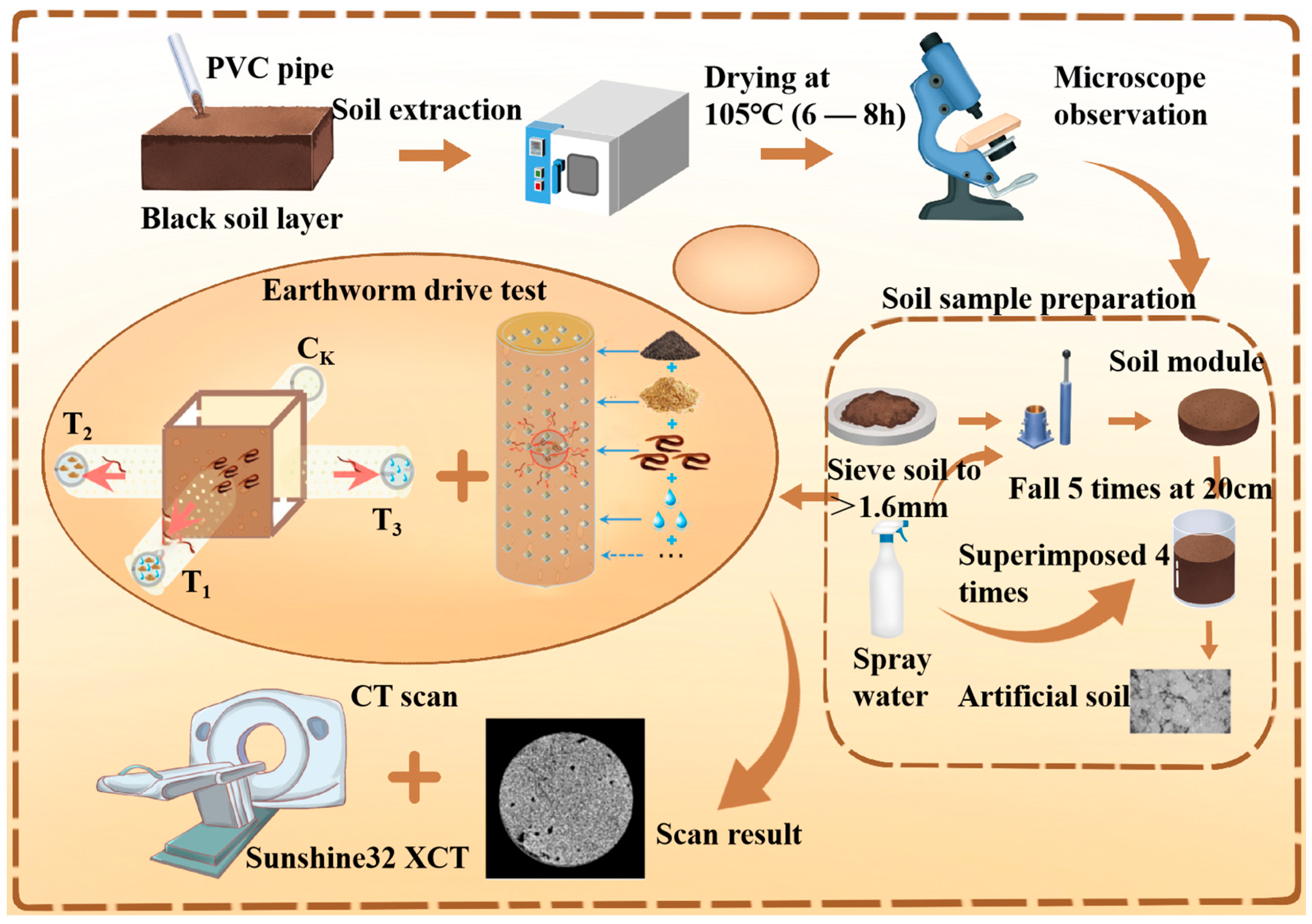
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Measurement of Soil Properties in Tests
2.2. Earthworm Food Attraction Test
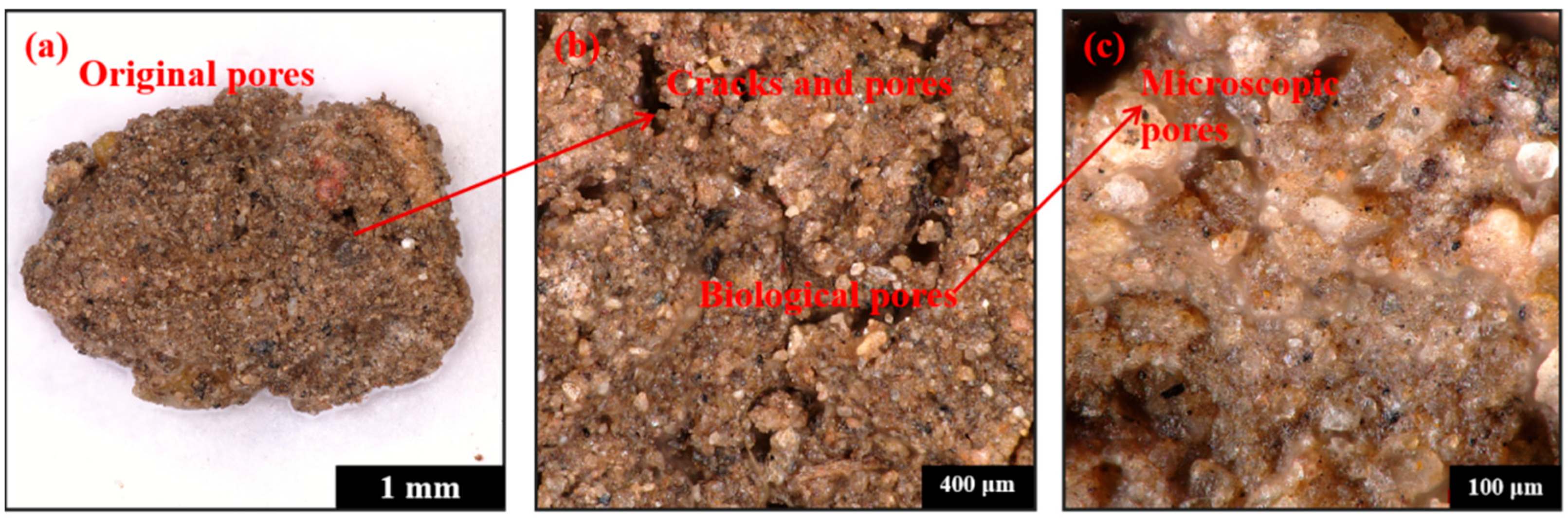
2.3. Image Acquisition and Processing of CT Equipment
2.4. Calculation Formula
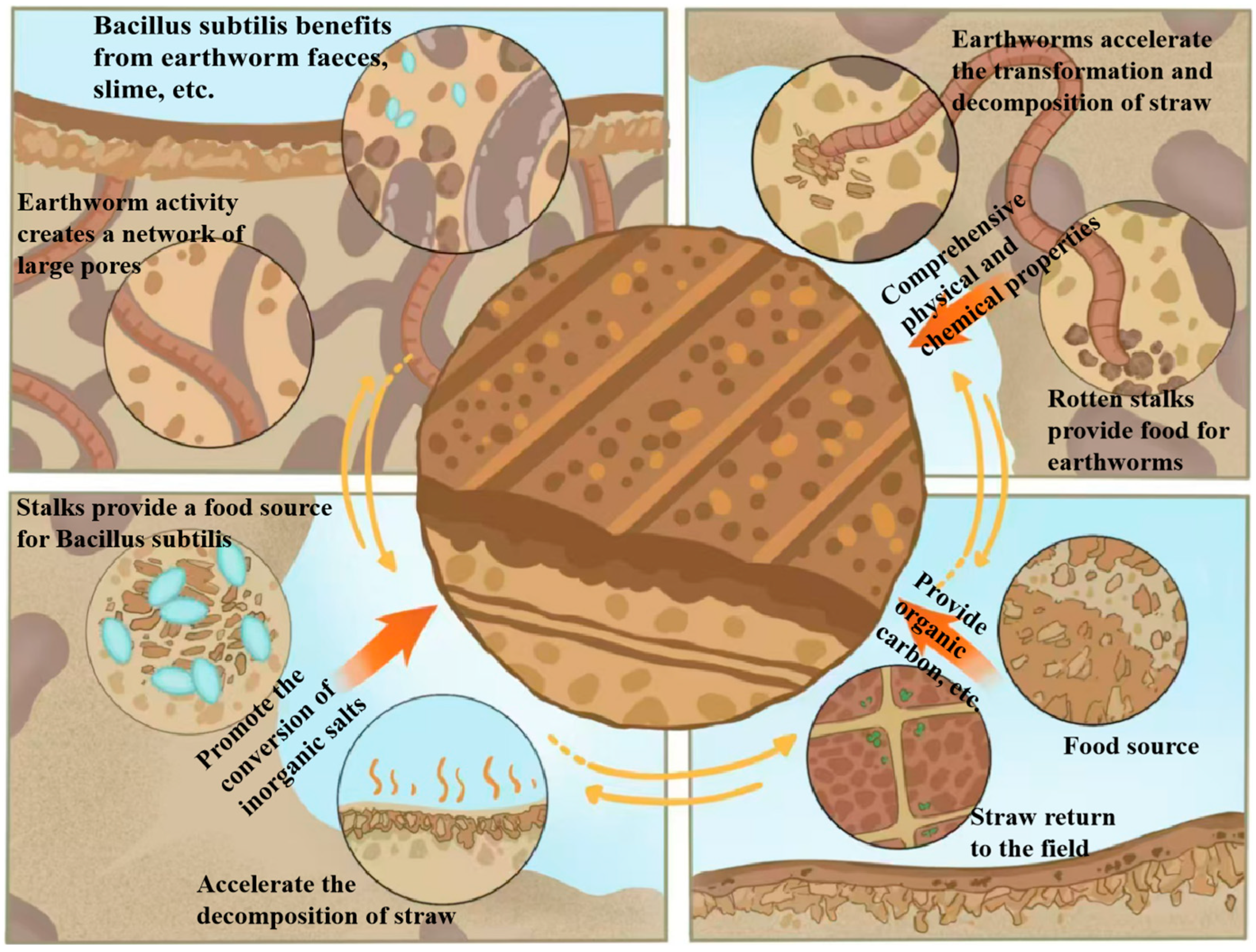
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Earthworm Food Attraction Effect
3.2. Pore Structure After Earthworm Food Attraction (Porosity, Pore Network Model)
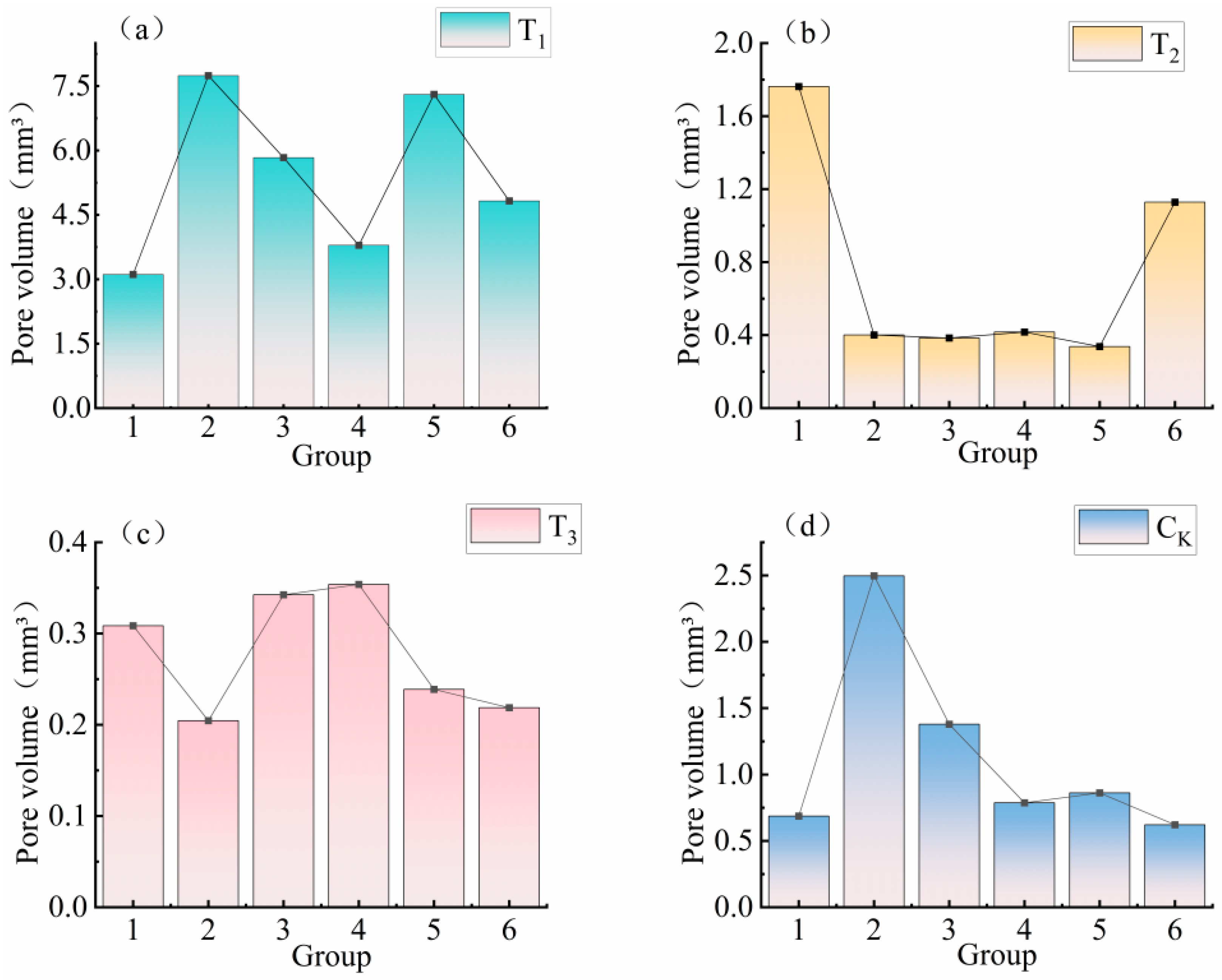
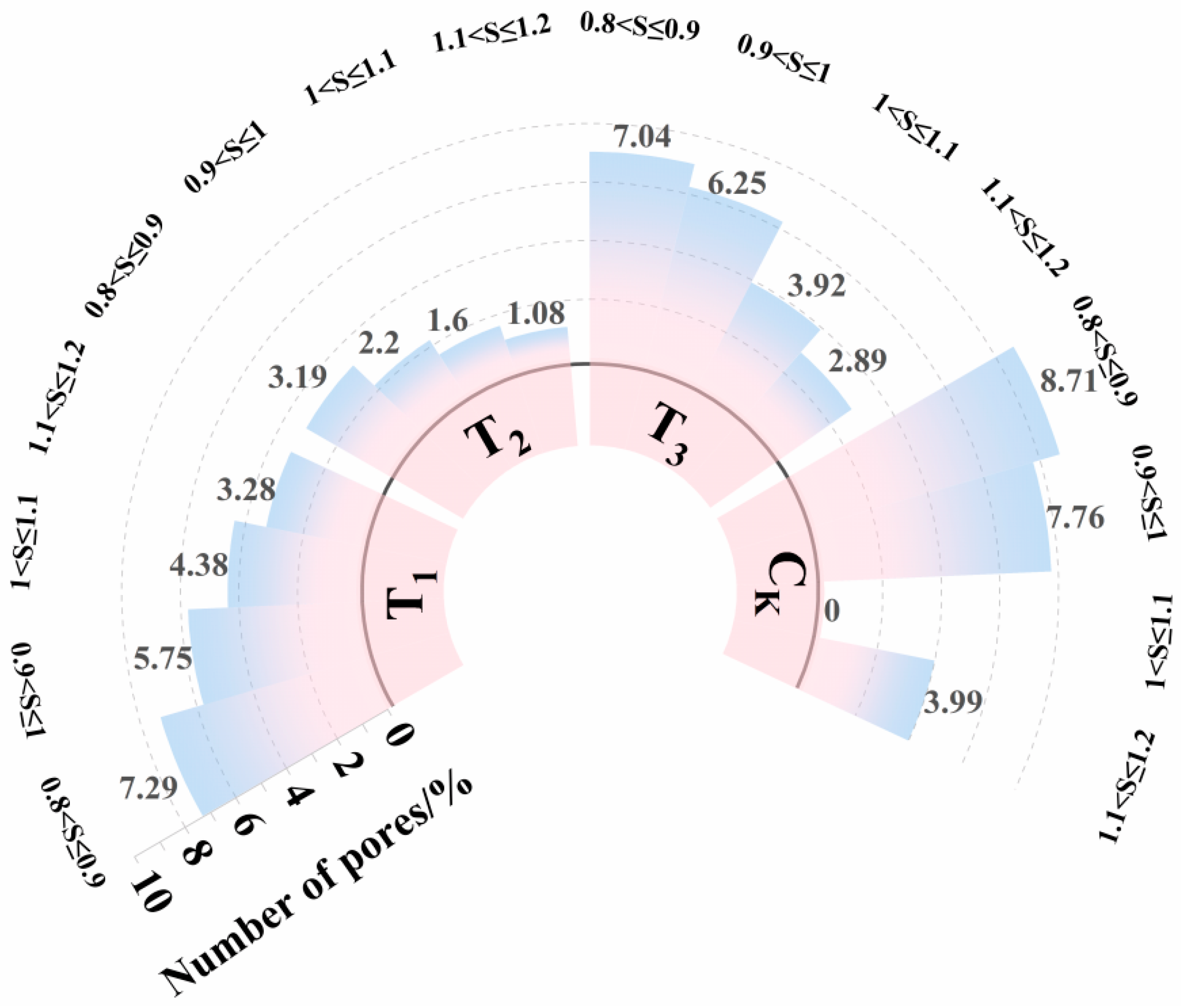
3.3. Quantitative Parameters of Pore Size Distribution (PSD)
3.3.1. Pore Volume Analysis of Earthworm Food Attraction Formation
3.3.2. Pore Equivalent Diameter Analysis
3.3.3. Pore Shape Factor
3.4. Characteristics of Pore Channel Parameters
3.4.1. Analysis of Channel Tortuosity
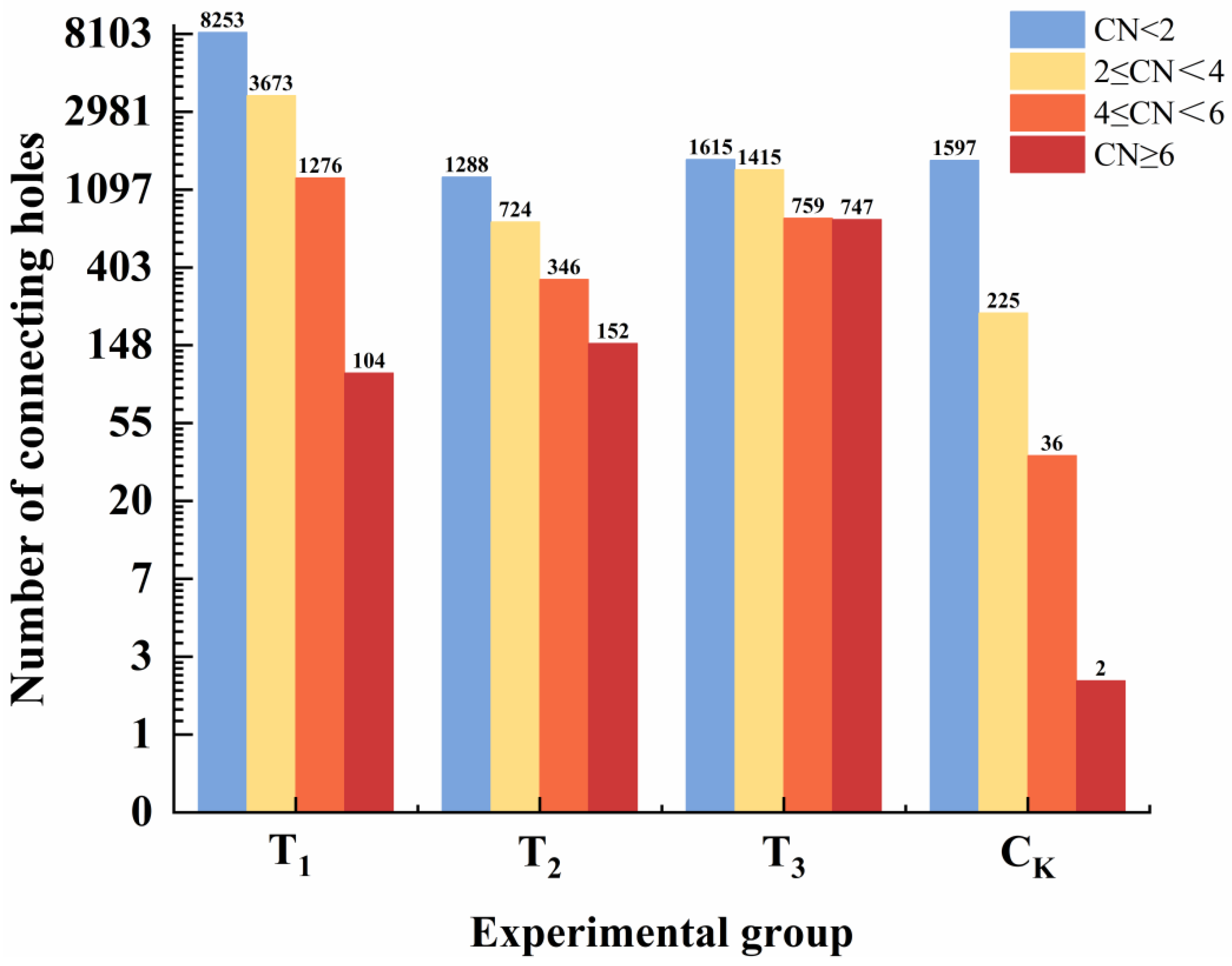
3.4.2. Coordination Number Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO. Global Map of Black Soil; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Pan, C.; Guo, H. Factors Affecting the Promotion of Conservation Tillage in Black Soil—The Case of Northeast China. Sustainability 2021, 13, 9563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.Z.; Xu, Y.; Chen, S.C.; Xu, S.G.; Zhang, H.W. Soil loss and conservation in the black soil region of Northeast China: A retrospective study. Environ. Sci. Policy 2010, 13, 793–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mayahi, A.K.; Al-Ismaily, S.S.; Breitenstein, D.; Al-Busaidi, H.S.; Al-Maktoumi, A.K.; Lehmann, P.; Or, D.; Kacimov, A.R.; Fahrni, S.; Al-Shukaili, A.H. Soil water distribution and dynamics across prescribed capillary barriers under evaporating surfaces. Biosyst. Eng. 2023, 226, 55–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, J.; Wang, Z.; Hu, F.; Huang, J.; Zhao, S.W. Study on soil hydraulic properties of slope farmlands with different degrees of erosion degradation in a typical black soil region. PeerJ 2023, 11, e15930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zang, S.; Chen, Q.; Sun, L. Distributions of Particle Sizes in Black Soil and Their Environmental Significance in Northeast China. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, C.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Wang, K.; Guo, Z. Evaluation and Classification of Black Soil Structure Degradation in Jilin by Factor Analysis & Dynamic Clustering Analysis. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Advanced Measurement and Test (AMT 2011), Nanchang, China, 24–26 June 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Bonachela, S.; Lopez, J.C.; Granados, M.R.; Magan, J.J.; Hernandez, J.; Baille, A. Effects of gravel mulch on surface energy balance and soil thermal regime in an unheated plastic greenhouse. Biosyst. Eng. 2020, 192, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budhathoki, S.; Lamba, J.; Srivastava, P.; Williams, C.; Arriaga, F.; Karthikeyan, K.G. Impact of land use and tillage practice on soil macropore characteristics inferred from X-ray computed tomography. CATENA 2022, 210, 105886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Léonard, J.; Perrier, E.; Rajot, J.L. Biological macropores effect on runoff and infiltration: A combined experimental and modelling approach. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2004, 104, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Shao, M.A.; Fan, J.; Wang, J.; Li, Y. Effects of earthworm (Metaphire guillelmi) density on soil macropore and soil water content in typical Anthrosol soil. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 311, 107338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barron, C.; Clunes, J.; Pinochet, D.; Santelices, M. Does earthworm density change the quality of degraded volcanic soil? Appl. Soil Ecol. 2024, 193, 105154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallam, J.; Berdeni, D.; Grayson, R.; Guest, E.; Holden, J.; Lappage, M.G.; Prendergast-Miller, M.; Robinson, D.A.; Turner, A.; Leake, J.R.; et al. Effect of earthworms on soil physico-hydraulic and chemical properties, herbage production, and wheat growth on arable land converted to ley. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 713, 136491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.Y. An overview of some tillage impacts on earthworm population abundance and diversity-Implications for functioning in soils. Soil Tillage Res. 2001, 57, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottinelli, N.; Hallaire, V.; Menasseri-Aubry, S.; Le Guillou, C.; Cluzeau, D. Abundance and stability of belowground earthworm casts influenced by tillage intensity and depth. Soil Tillage Res. 2010, 106, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scullion, J.; Malik, A. Earthworm activity affecting organic matter, aggregation and microbial activity in soils restored after opencast mining for coal. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2000, 32, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biradar, P.M.; Biradar, V.A. Influence of organic wastes on the biology of epigeic earthworm, Perionyx excavates during different seasons. J. Environ. Biol. 2015, 36, 1095–1100. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Banfield, C.C.; Dippold, M.A.; Pausch, J.; Hoang, D.T.T.; Kuzyakov, Y. Biopore history determines the microbial community composition in subsoil hotspots. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2017, 53, 573–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, Q.V.; Dang, H.X.; Nguyen, A.D.; Capowiez, Y.; Joquet, P.; Tran, T.M.; Rumpel, C.; Bottinelli, N. Interaction Between Anecic and Polyhumic Endogeic Earthworms Can Lead to Synergistic Effects on Soil Functioning. Appl Soil Ecol 2024, 200, 105438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Sun, L.; Lv, W.; Zheng, X.; Sun, Y.; Terzaghi, W.; Qin, Q.; Xue, Y. Earthworms accelerate rice straw decomposition and maintenance of soil organic carbon dynamics in rice agroecosystems. PeerJ 2020, 8, e9870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, S.; Zhu, Q.; Ding, W. Image grey value analysis for estimating the effect of microorganism inoculants on straws decomposition. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2016, 128, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turunen, M.; Hyväluoma, J.; Keskinen, R.; Kaseva, J.; Nikama, J.; Reunamo, A.; Rasa, K. Pore structure of wastewater sludge chars and their water retention impacts in different soils. Biosyst. Eng. 2021, 206, 6–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whalen, J.K. Spatial and temporal distribution of earthworm patches in corn field, hayfield and forest systems of southwestern Quebec, Canada. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2004, 27, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, X.L.; Cheng, Y.F.; Feng, X.P.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, X.; Du, M.J.; Gu, Y.F. The effects of Eisenia fetida and metaphire guillelmi on the soil micro-food web in a microcosm experiment. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0290282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertrand, M.; Barot, S.; Blouin, M.; Whalen, J.; Oliveira, T.; Roger-Estrade, J. Earthworm services for cropping systems. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2015, 35, 553–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Huang, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, Y. The improved remediation effect of the combined use of earthworms with bacillus subtilis -loaded biochar in ameliorating soda saline–alkali soil. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giuliani, L.M.; Hallett, P.D.; Loades, K.W. Effects of soil structure complexity on root growth of plants with contrasting root architecture. Soil Tillage Res. 2024, 238, 106023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torre, I.G.; Losada, J.C.; Tarquis, A.M. Multiscaling properties of soil images. Biosyst. Eng. 2018, 168, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierret, A.; Capowiez, Y.; Belzunces, L.; Moran, C.J. 3D reconstruction and quantification of macropores using X-ray computed tomography and image analysis. Geoderma 2002, 106, 247–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, W.; Zhou, S.; Long, K.; Xie, B.; Ai, C.; Yan, C. Investigation of key morphological parameters of pores in different grades of asphalt mixture based on CT scanning technology. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 434, 136770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Tong, F.; Yan, L.; Zhou, H.; Hao, S. Effect of Porosity on Soil-Water Retention Curves: Theoretical and Experimental Aspects. Geofluids 2020, 2020, 6679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doolittle, J.H. The effect of thigmotaxis on negative phototaxis in the earthworm. Psychon. Sci. 1971, 22, 311–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Schaik, L.; Palm, J.; Klaus, J.; Zehe, E.; Schroeder, B. Linking spatial earthworm distribution to macropore numbers and hydrological effectiveness. Ecohydrology 2014, 7, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazão, J.; de Goedé, R.G.M.; Capowiez, Y.; Pulleman, M.M. Soil structure formation and organic matter distribution as affected by earthworm species interactions and crop residue placement. Geoderma 2019, 338, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvis, N.J. A review of non-equilibrium water flow and solute transport in soil macropores: Principles, controlling factors and consequences for water quality. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2020, 71, 279–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capowiez, Y.; Cadoux, S.; Bouchand, P.; Roger-Estrade, J.; Richard, G.; Boizard, H. Experimental evidence for the role of earthworms in compacted soil regeneration based on field observations and results from a semi-field experiment. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2009, 41, 711–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifzadeh, M.; Mitani, Y.; Esaki, T.; Urakawa, F. An investigation of joint aperture distribution using precise surface asperities measurement and GIS data processing. In Proceedings of the ISRM International Symposium/3rd Asian Rock Mechanics Symposium (ARMS), Kyoto, Japan, 30 November–2 December 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Hallam, J.; Holden, J.; Robinson, D.A.; Hodson, M.E. Effects of winter wheat and endogeic earthworms on soil physical and hydraulic properties. Geoderma 2021, 400, 115126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deks, L.K.; Williams, A.G.; Dowd, J.F.; Scholefield, D. Quantification of pore size distribution and the movement of solutes through isolated soil blocks. Geoderma 1999, 90, 65–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glab, T. Application of image analysis for soil macropore characterization according to pore diameter. Int. Agrophys. 2007, 21, 61–66. [Google Scholar]
- Mele, G.; Buscemi, G.; Gargiulo, L.; Terribile, F. Soil burrow characterization by 3D image analysis: Prediction of macroinvertebrate groups from biopore size distribution parameters. Geoderma 2021, 404, 115292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanbarian, B.; Lin, Q.; Pires, L.F. Scale Dependence of Tortuosity in Soils under Contrasting Cultivation Conditions. Soil Tillage Res. 2023, 233, 105788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.Y.; Dai, S.; Zhan, L.T.; Chen, Y.M. A pore-scale numerical investigation of the effect of pore characteristics on flow properties in soils. J. Zhejiang Univ. 2019, 20, 961–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Symbols | Meanings |
|---|---|
| BD | Volume weight of soil |
| WS | Soil moisture content |
| T | Temperature |
| PH | Soil pH |
| earthworm | Eisenia foetida |
| CT | Computed Tomography |
| straw | Corn stalk powder (1 mm) |
| Micro-organisms | Bacillus subtilis |
| T1 | Fermented corn stover powder after 7 days of mixed fermentation of Bacillus subtilis and water |
| T2 | Corn stalk |
| T3 | Bacillus subtilis mixed with water |
| CK | Control group |
| EC | Earthworm count (strip) |
| EDD | Earthworm food attraction distance (cm) |
| V | Theoretical volume |
| VC | Actual volume |
| AP, A | They are the pore area on each slice and the total area of the slice. |
| A0 | Represents the three-dimensional pore surface area |
| L | The length of a pore throat. |
| LT | The actual path length of the throat. |
| (xi, yi, zi) and (xk, yk, zk) | Represents the starting point and end Point of the three-dimensional Coordinates of the hole section |
| PNM | Equivalent pore-network model |
| PSD | Pore size distribution |
| V′ | Three-dimensional porosity |
| φ | Surface porosity |
| V | Pore volume |
| R | Equivalent diameter |
| S | Shape factor |
| R0 | Throat radius |
| L0 | Throat length |
| V0 | Throat volume |
| τ | Tortuosity |
| CN | Coordination number |
| MP | Micropore |
| PH | Eyelet |
| MH | Middle hole |
| MPS | Macropore |
| SH | Spherical cavity |
| OH | Oval hole |
| CH | Cylindrical hole |
| BH | Branch hole |
| MD | Microporous diameter |
| SA | Small aperture |
| MA | Medium aperture |
| LA | Large aperture |
| BD (g/cm3) | WS (%) | T (°C) | pH | Clay (g/kg) | Sand (g/kg) | Silt (g/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.88–1.26 | 19.6–21.4 | 23.2–24.7 | 6.8–7.9 | 107.1 ± 3 | 823 ± 7 | 69.9 ± 6 |
| Comparative Test Group | T1 | T2 | T3 | CK |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Micro-organisms (g) | 30 | 0 | 30 | 0 |
| Straw (g) | 35 | 35 | 0 | 0 |
| Comparison of the Experimental Group | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EC (Strip) | T1 | T2 | T3 | CK | P |
| 17.66 ± 1.15 | 9 ± 1 | 7 ± 0.58 | 1.33 ± 0.58 | >0.001 | |
| EDD (cm) | 15.43 ± 0.50 | 12.13 ± 0.55 | 10.03 ± 0.60 | 1.7 ± 0.40 | >0.001 |
| Dispose | Volume Fraction | Label Volume (nm3) | Mask Volume (nm3) | Label Voxel Count | Mask Voxel Count |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | 0.069 | 7.2 × 1022 | 1.0 × 1024 | 1.41 × 106 | 2.02 × 107 |
| T2 | 0.019 | 1.7 × 1022 | 8.8 × 1023 | 2.56 × 105 | 1.31 × 107 |
| T3 | 0.015 | 1.6 × 1022 | 1.0 × 1024 | 6.21 × 105 | 3.92 × 107 |
| CK | 0.010 | 6.7 × 1021 | 6.6 × 1023 | 2.30 × 105 | 2.29 × 107 |
| T1 | T2 | T3 | CK | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max-τ | 5.16 | 3.71 | 10.49 | 15.50 |
| Avg-τ | 1.18 | 1.25 | 1.20 | 1.21 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, B.; Chen, P.; Liu, Y.; Yin, Z.; Wang, Q.; Xu, S.; Zhang, J.; Bai, B.; Zhou, D.; Liu, Y. Earthworm (Eisenia fetida) Mediated Macropore Network Formation in Black Soil: Decay Straw as a Trigger for Sustainable Tillage. Agriculture 2025, 15, 1397. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15131397
Wu B, Chen P, Liu Y, Yin Z, Wang Q, Xu S, Zhang J, Bai B, Zhou D, Liu Y. Earthworm (Eisenia fetida) Mediated Macropore Network Formation in Black Soil: Decay Straw as a Trigger for Sustainable Tillage. Agriculture. 2025; 15(13):1397. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15131397
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Baoguang, Pu Chen, Yuping Liu, Zhipeng Yin, Qiuju Wang, Shun Xu, Jinsong Zhang, Bingqi Bai, Deyi Zhou, and Yuxin Liu. 2025. "Earthworm (Eisenia fetida) Mediated Macropore Network Formation in Black Soil: Decay Straw as a Trigger for Sustainable Tillage" Agriculture 15, no. 13: 1397. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15131397
APA StyleWu, B., Chen, P., Liu, Y., Yin, Z., Wang, Q., Xu, S., Zhang, J., Bai, B., Zhou, D., & Liu, Y. (2025). Earthworm (Eisenia fetida) Mediated Macropore Network Formation in Black Soil: Decay Straw as a Trigger for Sustainable Tillage. Agriculture, 15(13), 1397. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15131397






