Detection of Copy Number Variations from HIF1A and HIF2A Gene as Genetic Determinants of Bovine Carcass Traits
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
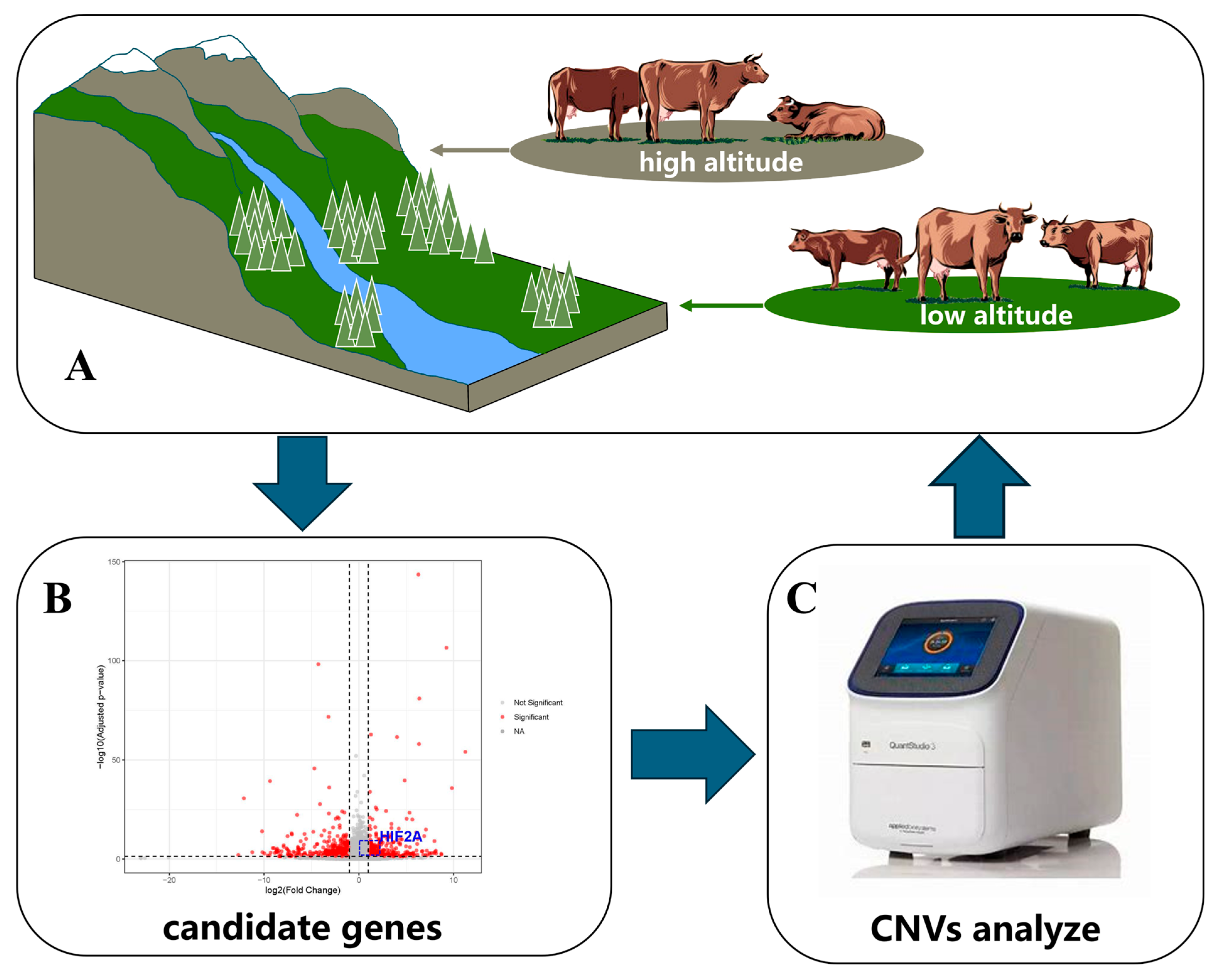
2.1. Screening of Candidate Genes
2.2. Tissue Sample and Data Collection
2.3. Extraction of Genomic DNA
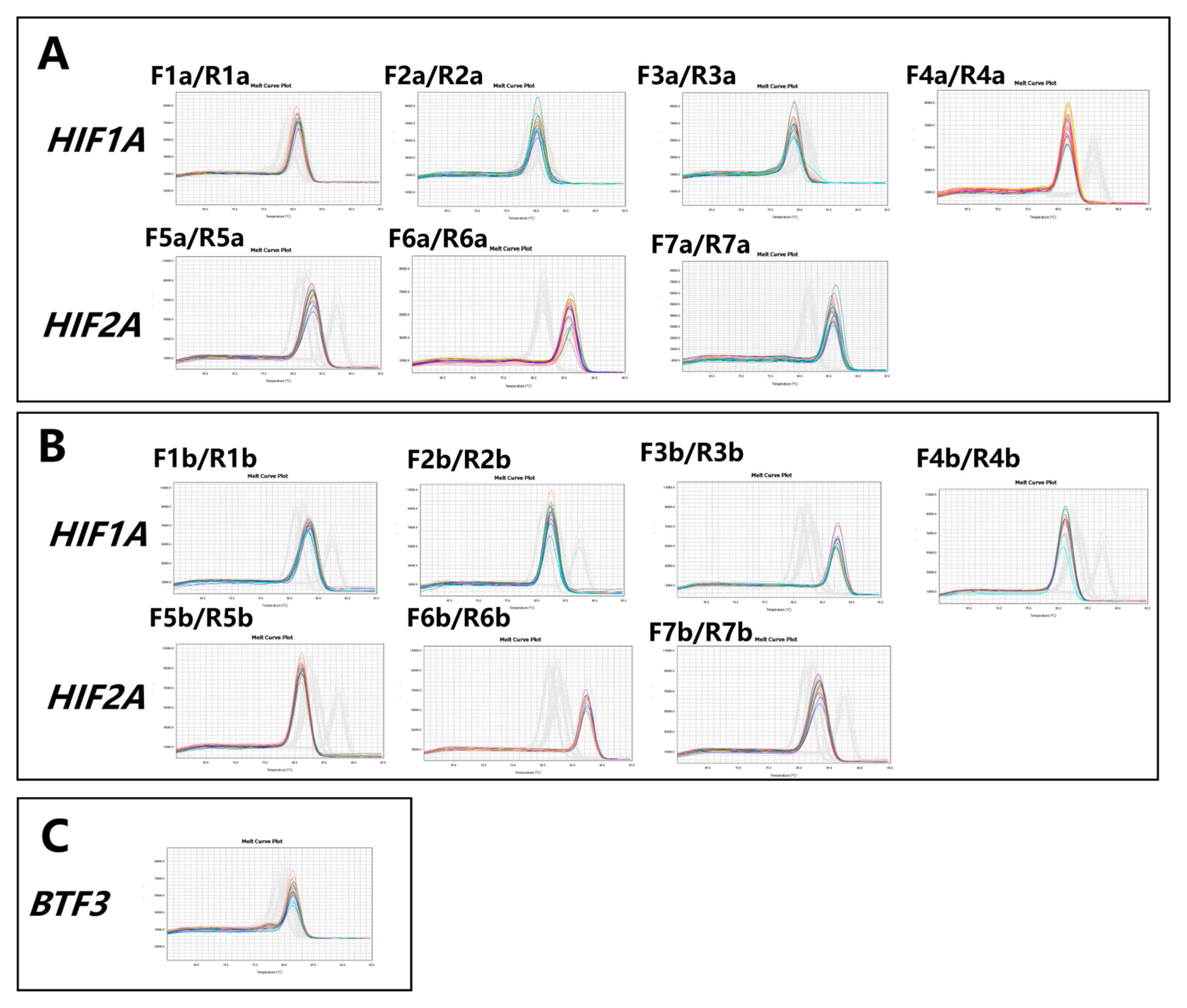
2.4. Identification and Genotyping of Copy Number Variants of Bovine HIF1A and HIF2A Genes
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Identification of the CNVs of the HIF1A and HIF2A Genes
3.2. Validation of the Accuracy of CNV Detection by qPCR
3.3. CNV Polymorphisms of the HIF1A and HIF2A Genes in Gaoqing Black Cattle
3.4. Association Between HIF1A CNV Polymorphisms and Carcass Traits in Gaoqing Black Cattle
3.5. Association Between HIF2A CNV Polymorphisms and Carcass Traits in Gaoqing Black Cattle
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peng, S.J.; Cao, X.K.; Dong, D.; Liu, M.; Hao, D.; Shen, X.M.; Huang, Y.Z.; Lei, C.Z.; Ma, Y.; Bai, Y.Y.; et al. Integrative analysis of APOL3 gene CNV for adult cattle stature. Anim. Biotechnol. 2020, 31, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ladeira, G.C.; Pilonetto, F.; Fernandes, A.C.; Bóscollo, P.P.; Dauria, B.D.; Titto, C.G.; Coutinho, L.L.; e Silva, F.F.; Pinto, L.F.B.; Mourão, G.B. CNV detection and their association with growth, efficiency and carcass traits in Santa Inês sheep. J. Anim. Breed. Genet. 2022, 139, 476–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, E.; Zhang, C.; He, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Pan, C.; Jiang, F.; Song, E.; Zhang, S.; Lan, X. A novel A-to-G mutation in circBDP1 alters adipocyte proliferation and differentiation and affects bovine carcass traits. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B, 2025. (in press) [Google Scholar]
- Song, X.; Bai, Y.; Yuan, R.; Zhu, H.; Lan, X.; Qu, L. InDel and CNV within the AKAP13 gene revealing strong associations with growth traits in goat. Animals 2023, 13, 2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Yang, P.; Sun, H.; Zhang, Z.; Cai, C.; Xu, J.; Ding, X.; Wang, X.; Lyu, S.; Li, Z.; et al. CNV analysis of VAMP7 gene reveals variation associated with growth traits in Chinese cattle. Anim. Biotechnol. 2023, 34, 1095–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Liu, Y.; Chen, W.; Shao, J.; Zhuoma, P.; Zhao, D.; Yu, Y.; Liu, T.; Yu, R.; Gan, Y.; et al. How Placenta Promotes the Successful Reproduction in High-Altitude Populations: A Transcriptome comparison between adaptation and acclimatization. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2022, 39, msac120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basse, A.L.; Isidor, M.S.; Winther, S.; Skjoldborg, N.B.; Murholm, M.; Andersen, E.S.; Pedersen, S.B.; Wolfrum, C.; Quistorff, B.; Hansen, J.B. Regulation of glycolysis in brown adipocytes by HIF-1α. Sci Rep. 2017, 7, 4052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Luo, X.; Xie, M.; Zhang, T.; Chen, X.; Zhang, B.; Sun, M.; Wang, Y.; Feng, Y.; Ji, X.; et al. HNRNPC downregulation inhibits IL-6/STAT3-mediated HCC metastasis by decreasing HIF1A expression. Cancer Sci. 2022, 113, 3347–3361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mole, D.R.; Blancher, C.; Copley, R.R.; Pollard, P.J.; Gleadle, J.M.; Ragoussis, J.; Ratcliffe, P.J. Genome-wide association of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1alpha and HIF-2alpha DNA binding with expression profiling of hypoxia-inducible transcripts. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 16767–16775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, H.; Holt-Martyn, J.P.; Dembitz, V.; Kabayama, Y.; Wang, L.M.; Bellani, A.; Atwal, S.; Saffoon, N.; Durko, J.; van de Lagemaat, L.N.; et al. The selective prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor IOX5 stabilizes HIF-1α and compromises development and progression of acute myeloid leukemia. Nat. Cancer. 2024, 5, 916–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoud, G.N.; Li, W. HIF-1α pathway: Role, regulation and intervention for cancer therapy. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2015, 5, 378–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rainville, N.; Jachimowicz, E.; Wojchowski, D.M. Targeting EPO and EPO receptor pathways in anemia and dysregulated erythropoiesis. Expert. Opin. Ther. Targets 2016, 20, 287–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, M.; Galy, B.; Muckenthaler, M.U.; Hentze, M.W. Iron-regulatory proteins limit hypoxia-inducible factor-2alpha expression in iron deficiency. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2007, 14, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Guo, Y.; Shi, X.; Guo, Z.; Ma, G.; Yu, Q. Glycolysis capacity of bovine muscle during early stage of postmortem aging under action of HIF1α. Transactions of the Chinese society for agriculture machinary (In Chinese). Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2022, 53, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.; Liang, Y.; Huerta-Sanchez, E.; Jin, X.; Cuo, Z.X.; Pool, J.E.; Xu, X.; Jiang, H.; Vinckenbosch, N.; Korneliussen, T.S.; et al. Sequencing of 50 human exomes reveals adaptation to high altitude. Science 2010, 329, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Duan, Q.; Li, B.; Wang, Y.; Bu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Kuang, Z.; Mao, L.; An, X.; Wang, H.; et al. Genomic structural variation contributes to evolved changes in gene expression in high-altitude Tibetan sheep. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2322291121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, J.H.; Holt, T.N.; Cogan, J.D.; Womack, B.; Phillips, J.A., 3rd; Li, C.; Kendall, Z.; Stenmark, K.R.; Thomas, M.G.; Brown, R.D.; et al. Increased prevalence of EPAS1 variant in cattle with high-altitude pulmonary hypertension. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomc, J.; Debeljak, N. Molecular Insights into the Oxygen-Sensing Pathway and Erythropoietin Expression Regulation in Erythropoiesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, H.M.; Pan, S.Y.; Wu, C.J.; Chou, Y.H.; Chen, C.Y.; Chang, F.C.; Chen, Y.T.; Chiang, W.C.; Tsai, H.C.; Chen, Y.M.; et al. Transforming growth factor-β1 decreases erythropoietin production through repressing hypoxia-inducible factor 2α in erythropoietin-producing cells. J. Biomed. Sci. 2021, 28, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirri, D.; Tian, S.; Tardajos-Ayllon, B.; Irving, S.E.; Donati, F.; Allen, S.P.; Mammoto, T.; Vilahur, G.; Kabir, L.; Bennett, J.; et al. EPAS1 Attenuates Atherosclerosis Initiation at Disturbed Flow Sites Through Endothelial Fatty Acid Uptake. Circ. Res. 2024, 135, 822–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javerzat, S.; Franco, M.; Herbert, J.; Platonova, N.; Peille, A.L.; Pantesco, V.; De Vos, J.; Assou, S.; Bicknell, R.; Bikfalvi, A.; et al. Correlating global gene regulation to angiogenesis in the developing chick extra-embryonic vascular system. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellwig-Bürgel, T.; Stiehl, D.P.; Wagner, A.E.; Metzen, E.; Jelkmann, W. Review: Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1): A novel transcription factor in immune reactions. J. Interf. Cytokine Res. 2005, 25, 297–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, J.; Wang, Y.; Anwar, N.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, D.; Ma, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Xiao, L.; et al. The role of autophagy in bone metabolism and clinical significance. Autophagy. 2023, 19, 2409–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Li, J.; Costa, M.; Gao, J.; Huang, C. JNK1 mediates degradation HIF-1alpha by a VHL-independent mechanism that involves the chaperones Hsp90/Hsp70. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 813–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, J.; Li, L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L. Genetic and immune changes in Tibetan high-altitude populations contribute to biological adaptation to hypoxia. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2022, 27, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhasuran, B.; Subramanian, D.; Natarajan, J. Text mining and network analysis to find functional associations of genes in high altitude diseases. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2018, 75, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhong, J.; Wang, J.; Chai, Z.; Zhang, C.; Xin, J.; Wang, J.; Cai, X.; Wu, Z.; Ji, Q. Whole-Transcriptome Analysis of Yak and Cattle Heart Tissues Reveals Regulatory Pathways Associated With High-Altitude Adaptation. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 579800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koshy, L.; Anju, A.L.; Harikrishnan, S.; Kutty, V.R.; Jissa, V.T.; Kurikesu, I.; Jayachandran, P.; Jayakumaran Nair, A.; Gangaprasad, A.; Nair, G.M.; et al. Evaluating genomic DNA extraction methods from human whole blood using endpoint and real-time PCR assays. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2017, 44, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Z.; Wang, X.; Cheng, Y.; Wei, C.; Hou, D.; Li, T.; Li, W.; Han, R.; Li, H.; Sun, G.; et al. Detection of CNV in the SH3RF2 gene and its effects on growth and carcass traits in chickens. BMC Genet. 2020, 21, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhang, B.; Li, H.; Hu, Z.; Jiang, H.; Stablewski, A.B.; Marzullo, B.J.; Yergeau, D.A.; Feng, J. Generation of mouse-human chimeric embryos. Nat. Protoc. 2021, 16, 3954–3980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, Q.; Pan, C.; Lan, X. The free fatty acid receptor 2 (FFA2): Mechanisms of action, biased signaling, and clinical prospects. Pharmacol. Ther. 2025, 272, 108878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; You, L.; Nepovimova, E.; Heger, Z.; Wu, W.; Kuca, K.; Adam, V. Hypoxia-inducible factors: Master regulators of hypoxic tumor immune escape. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 15, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Han, X.; Wu, Q.; Liu, H.; Han, J.; Zhou, H. Effects of Copy Number Variations in the Plectin (PLEC) Gene on the Growth Traits and Meat Quality of Leizhou Black Goats. Animals 2023, 13, 3651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]

| Genes | Loci | Primer Sequences (5′–3′) | Size (bp) | Position |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HIF1A | CNV1 | F1a: TACGTGTGCAGTGCTCCTTT | 155 | NC_037337.1 73835197-73835352 |
| R1a: GGCAGCAGTATTGCCTGTTT | ||||
| CNV2 | F2a: CGTGCAGGTTTGGTTTGGTT | 220 | NC_037337.1 73837401-73837621 | |
| R2a: AGCCATCCGCTACGTTTTC | ||||
| CNV3 | F3a: TACAGCCTAACAGTCCCAGT | 195 | NC_037337.1 73875262-73875457 | |
| R3a: GTTAAACCCACAGCCACTTGAG | ||||
| CNV4 | F4a: TGGGTGTTTCTTATCCCGCC | 211 | NC_037337.1 73889164-73889375 | |
| R4a: GAGGCCCCAAAATGGATGGA | ||||
| HIF2A | CNV1 | F5a: CGTTCAAGAAGTGGGCAGGA | 155 | NC_037337.1 28738050-28738205 |
| R5a: AGTGGTAGTGGGCATTCGTG | ||||
| CNV2 | F6a: GGGTGGAAATCACCACACCA | 205 | NC_037337.1 28759005-28759210 | |
| R6a: TCAGGTGTCAAGGGCCTCTA | ||||
| CNV3 | F7a: ATGGTAAGGTGTTCTTCGGTGT | 172 | NC_037337.1 28797001-28797173 | |
| R7a: GGGCCCTTGATCTCATCTCC | ||||
| BTF3 | Reference gene | F8a: AACCAGGAGAAACTCGCCAA | 166 | NC_037347.1 8122394-8122559 |
| R8a: TTCGGTGAAATGCCCTCTC |
| Loci | Primer Sequences (5′–3′) | Size (bp) | Position | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HIF1A | CNV1 | F1b: AGTGTGGGAACACTGTGAGC | 151 | NC_037337.1_ 73834371-73834522 |
| R1b: CTCCAAATTTGTGCCACTGCT | ||||
| CNV2 | F2b: TGTAACCCTGTTCCTTTTAGTGA | 243 | NC_037337.1_ 73847365-73847608 | |
| R2b: GGGAGTTAACATGGCAGGCT | ||||
| CNV3 | F3b: GCTTTAACTTTGCTGGCCCC | 252 | NC_037337.1_ 73872952-73873204 | |
| R3b: GTGCAGAAAACATGGCAGCA | ||||
| CNV4 | F4b: GCCTTTGCCTGGCTACCTTA | 224 | NC_037337.1_ 73889766-73889990 | |
| R4b: AGGGAGTGGGGCTCCATAAT | ||||
| HIF2A | CNV1 | F5b: CGAAGCAGGGAAGGGACTTT | 193 | NC_037337.1_ 28737151-28737344 |
| R5b: CGATTGCAACATTCGCCGAT | ||||
| CNV2 | F6b: CAAGAGGGAGCAGGTGTCTG | 225 | NC_037337.1_ 28761404-28761629 | |
| R6b: TCAGGTGTCAAGGGCCTCTA | ||||
| CNV3 | F7b: CCTAGCAACCACCTCCACAG | 275 | NC_037337.1_ 28795090-28795365 | |
| R7b: AGACACTGGAAAGCACGGAG |
| Loci | Primer Pairs | Loss | Medium | Gain | Accuracy Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HIF1A–CNV1 | F/R1b | 0.200 (n = 6) | 0.767 (n = 23) | 0.033 (n = 1) | 29/30 = 96.7% |
| HIF1A–CNV2 | F/R2b | 0.111 (n = 3) | 0.889 (n = 24) | 0.000 (n = 0) | 26/27 = 96.3% |
| HIF1A–CNV3 | F/R3b | 0.125 (n = 4) | 0.688 (n = 22) | 0.188 (n = 6) | 32/32 = 100% |
| HIF1A–CNV4 | F/R4b | 0.000 (n = 0) | 0.567 (n = 17) | 0.433 (n = 13) | 30/30 = 100% |
| HIF2A–CNV1 | F/R5b | 0.344 (n = 11) | 0.469 (n = 15) | 0.188 (n = 6) | 32/32 = 100% |
| HIF2A–CNV2 | F/R6b | 0.100 (n = 3) | 0.533 (n = 16) | 0.367 (n = 11) | 29/30 = 96.7% |
| HIF2A–CNV3 | F/R7b | 0.065 (n = 2) | 0.710 (n = 22) | 0.226 (n = 7) | 30/31 = 96.8% |
| Genes | Loci | Sizes (bp) | Genotypic Frequencies | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Loss | Medium | Gain | |||
| HIF1A | CNV1 | 4399 | 0.110 (n = 36) | 0.702 (n = 229) | 0.187 (n = 61) |
| CNV2 | 12,797 | 0.134 (n = 43) | 0.680 (n = 219) | 0.186 (n = 60) | |
| CNV3 | 6800 | 0.228 (n = 74) | 0.502 (n = 163) | 0.271 (n = 88) | |
| CNV4 | 14,800 | 0.208 (n = 64) | 0.476 (n = 146) | 0.316 (n = 97) | |
| HIF2A | CNV1 | 8003 | 0.342 (n = 104) | 0.411 (n = 125) | 0.247 (n = 75) |
| CNV2 | 3200 | 0.174 (n = 53) | 0.454 (n = 138) | 0.372 (n = 113) | |
| CNV3 | 2800 | 0.260 (n = 79) | 0.421 (n = 128) | 0.319 (n = 97) | |
| CNVs | Traits | Loss | Median | Gain | p Values |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNV1 | Cervical vertebrae | 10.99 a ± 1.91 (n = 11) | 7.94 a ± 0.57 (n = 114) | 5.44 b ± 0.82 (n = 44) | 0.009 |
| Oxtail | 0.73 a ± 0.04 (n = 33) | 0.64 b ± 0.01 (n = 204) | 0.64 b ± 0.02 (n = 61) | 0.042 | |
| Rendered fat | 84.80 b ± 1.93 (n = 28) | 89.00 b ± 1.46 (n = 174) | 96.93 a ± 3.05 (n = 56) | 0.009 | |
| Flank steak | 2.10 a ± 0.10 (n = 33) | 1.95 b ± 0.03 (n = 205) | 1.89 b ± 0.05 (n = 60) | 0.023 | |
| CNV2 | Initial weight (kg) | 335.53 ab ± 7.97 (n = 40) | 325.18 b ± 3.83 (n = 202) | 342.90 a ± 6.48 (n = 57) | 0.026 |
| Beef diaphragm (kg) | 2.07 ab ± 0.07 (n = 40) | 1.93 b ± 0.03 (n = 201) | 2.07 a ± 0.05 (n = 57) | 0.030 | |
| Beef knuckle bone (kg) | 2.03 b ± 0.13 (n = 5) | 2.06 ab ± 0.05 (n = 55) | 2.56 a ± 0.18 (n = 19) | 0.001 | |
| Beef tendon (kg) | 0.06 b ± 0.03 (n = 27) | 0.16 b ± 0.05 (n = 163) | 0.51 a ± 0.17 (n = 47) | 4.59 × 10−4 | |
| Cervical vertebrae (kg) | 9.26 a ± 1.27 (n = 21) | 8.07 a ± 0.64 (n = 103) | 5.36 b ± 0.68 (n = 44) | 0.017 | |
| Flank steak (kg) | 6.96 a ± 0.23 (n = 39) | 6.97 a ± 0.10 (n = 200) | 6.38 b ± 0.14 (n = 57) | 0.017 | |
| CNV3 | Initial weight (kg) | 344.73 a ± 7.21 (n = 60) | 328.38 b ± 3.87 (n = 163) | 320.18 b ± 6.42 (n = 78) | 0.024 |
| Slaughter weight (kg) | 100.46 a ± 11.68 (n = 74) | 85.94 b ± 6.73 (n = 163) | 80.70 b ± 8.60 (n = 88) | 0.020 | |
| Chuck (kg) | 9.71 a ± 0.40 (n = 56) | 8.21 b ± 0.27 (n = 133) | 7.70 b ± 0.46 (n = 67) | 0.003 | |
| Flank steak (kg) | 7.26 a ± 0.16 (n = 58) | 6.73 b ± 0.12 (n = 167) | 6.72 b ± 0.14 (n = 77) | 0.032 | |
| Beef brisket (kg) | 2.06 a ± 0.07 (n = 60) | 1.92 ab ± 0.03 (n = 160) | 1.86 b ± 0.05 (n = 77) | 0.025 | |
| Chuck roll (kg) | 17.80 a ± 0.40 (n = 60) | 16.80 ab ± 0.22 (n = 162) | 16.41 b ± 0.35 (n = 77) | 0.019 | |
| Patellar tendon (kg) | 1.16 a ± 0.03 (n = 59) | 1.14 a ± 0.02 (n = 156) | 1.07 b ± 0.04 (n = 72) | 0.035 | |
| CNV4 | Femur (kg) | 16.80 a ± 2.47 (n = 35) | 12.53 b ± 0.64 (n = 105) | 11.13 b ± 0.59 (n = 77) | 0.001 |
| Chuck (kg) | 9.51 a ± 0.48 (n = 55) | 7.94 b ± 0.28 (n = 126) | 8.47 ab ± 0.39 (n = 72) | 0.003 | |
| Coccygeal meat (kg) | 0.70 a ± 0.03 (n = 62) | 0.63 b ± 0.01 (n = 145) | 0.64 b ± 0.02 (n = 87) | 0.011 | |
| Patellar tendon (kg) | 1.18 a ± 0.04 (n = 63) | 1.04 b ± 0.02 (n = 139) | 1.04 b ± 0.04 (n = 82) | 0.003 |
| CNVs | Traits | Loss | Median | Gain | p Values |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNV1 | Beef diaphragm (kg) | 2.06 a ± 0.04 (n = 103) | 1.97 ab ± 0.04 (n = 125) | 1.92 b ± 0.04 (n = 75) | 0.030 |
| Beef knuckle bone (kg) | 2.45 a ± 0.07 (n = 86) | 2.26 ab ± 0.10 (n = 95) | 2.04 b ± 0.10 (n = 56) | 0.004 | |
| Beef tendon (kg) | 0.42 a ± 0.04 (n = 36) | 0.27 b ± 0.06 (n = 39) | 0.10 c ± 0.06 (n = 32) | 1.345 × 10−4 | |
| Chuck (kg) | 9.07 a ± 0.37 (n = 85) | 8.20 ab ± 0.37 (n = 108) | 7.70 b ± 0.44 (n = 65) | 0.024 | |
| Flank steak (kg) | 6.61 a ± 0.13 (n = 103) | 6.69 ab ± 0.12 (n = 123) | 7.063 b ± 0.16 (n = 75) | 0.028 | |
| Patellar tendon (kg) | 1.21 a ± 0.04 (n = 100) | 1.07 b ± 0.03 (n = 115) | 0.97 c ± 0.03 (n = 71) | 8.900 × 10−7 | |
| Striploin (kg) | 13.27 a ± 0.2 (n = 102) | 12.6 b ± 0.25 (n = 125) | 12.66 ab ± 0.26 (n = 75) | 0.040 | |
| CNV2 | Longissimus dorsi width (cm) | 6.07 a ± 0.19 (n = 38) | 5.7 b ± 0.09 (n = 59) | 5.54 b ± 0.11 (n = 39) | 0.007 |
| Beef diaphragm (kg) | 2.07 a ± 0.05 (n = 53) | 2.02 ab ± 0.04 (n = 138) | 1.93 b ± 0.04 (n = 112) | 0.042 | |
| Beef knuckle bone (kg) | 2.56 a ± 0.2 (n = 40) | 2.19 b ± 0.07 (n = 107) | 2.26 ab ± 0.07 (n = 90) | 0.017 | |
| Chuck (kg) | 9.54 a ± 0.64 (n = 43) | 7.86 b ± 0.31 (n = 121) | 8.48 ab ± 0.37 (n = 94) | 0.010 | |
| Flank steak (kg) | 6.39 a ± 0.17 (n = 53) | 6.78 ab ± 0.12 (n = 137) | 6.89 b ± 0.12 (n = 112) | 0.023 | |
| Chuck roll (kg) | 17.74 a ± 0.44 (n = 53) | 16.73 ab ± 0.27 (n = 137) | 16.48 b ± 0.35 (n = 113) | 0.027 | |
| CNV3 | Slaughter weight (kg) | 681.09 ab ± 9.42 (n = 78) | 694.2 a ± 7.8 (n = 128) | 671.03 b ± 7.18 (n = 97) | 0.036 |
| Left forelimb weight (kg) | 210.71 ab ± 3.86 (n = 78) | 214.29 a ± 2.94 (n = 128) | 205.53 b ± 2.84 (n = 97) | 0.042 | |
| Right forelimb weight (kg) | 211.24 ab ± 3.97 (n = 78) | 215.36 a ± 3.03 (n = 128) | 206.43 b ± 2.96 (n = 97) | 0.045 | |
| Longissimus dorsi width (cm) | 5.86 a ± 0.13 (n = 53) | 5.83 ab ± 0.13 (n = 50) | 5.47 b ± 0.10 (n = 31) | 0.049 | |
| Beef Diaphragm (kg) | 1.96 ab ± 0.06 (n = 78) | 2.07 a ± 0.04 (n = 128) | 1.92 b ± 0.03 (n = 97) | 0.010 | |
| Chuck (kg) | 9.14 a ± 0.5 (n = 62) | 8.38 ab ± 0.36 (n = 115) | 7.74 b ± 0.35 (n = 81) | 0.024 | |
| Chuck roll (kg) | 17.13 ab ± 0.41 (n = 79) | 17.12 a ± 0.3 (n = 128) | 16.16 b ± 0.32 (n = 96) | 0.036 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, E.; Zhou, Y.; He, Y.; He, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhu, L.; Pan, C.; Lei, C.; Jiang, F.; Lan, X. Detection of Copy Number Variations from HIF1A and HIF2A Gene as Genetic Determinants of Bovine Carcass Traits. Agriculture 2025, 15, 1240. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15121240
Jiang E, Zhou Y, He Y, He Z, Wang H, Zhu L, Pan C, Lei C, Jiang F, Lan X. Detection of Copy Number Variations from HIF1A and HIF2A Gene as Genetic Determinants of Bovine Carcass Traits. Agriculture. 2025; 15(12):1240. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15121240
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Enhui, Yingjie Zhou, Yunan He, Zhuoyuan He, Hongyang Wang, Leijing Zhu, Chuanying Pan, Chuzhao Lei, Fugui Jiang, and Xianyong Lan. 2025. "Detection of Copy Number Variations from HIF1A and HIF2A Gene as Genetic Determinants of Bovine Carcass Traits" Agriculture 15, no. 12: 1240. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15121240
APA StyleJiang, E., Zhou, Y., He, Y., He, Z., Wang, H., Zhu, L., Pan, C., Lei, C., Jiang, F., & Lan, X. (2025). Detection of Copy Number Variations from HIF1A and HIF2A Gene as Genetic Determinants of Bovine Carcass Traits. Agriculture, 15(12), 1240. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15121240






