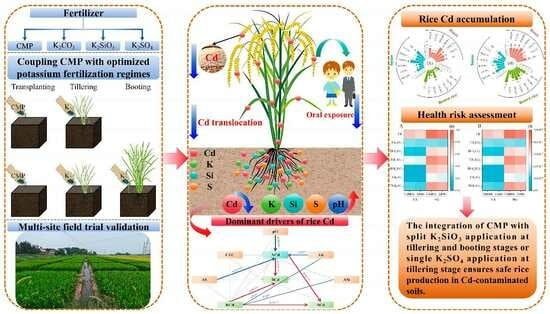
Optimizing Potassium Fertilization Combined with Calcium–Magnesium Phosphate Fertilizer Mitigates Rice Cadmium Accumulation: A Multi-Site Field Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Sites and Materials
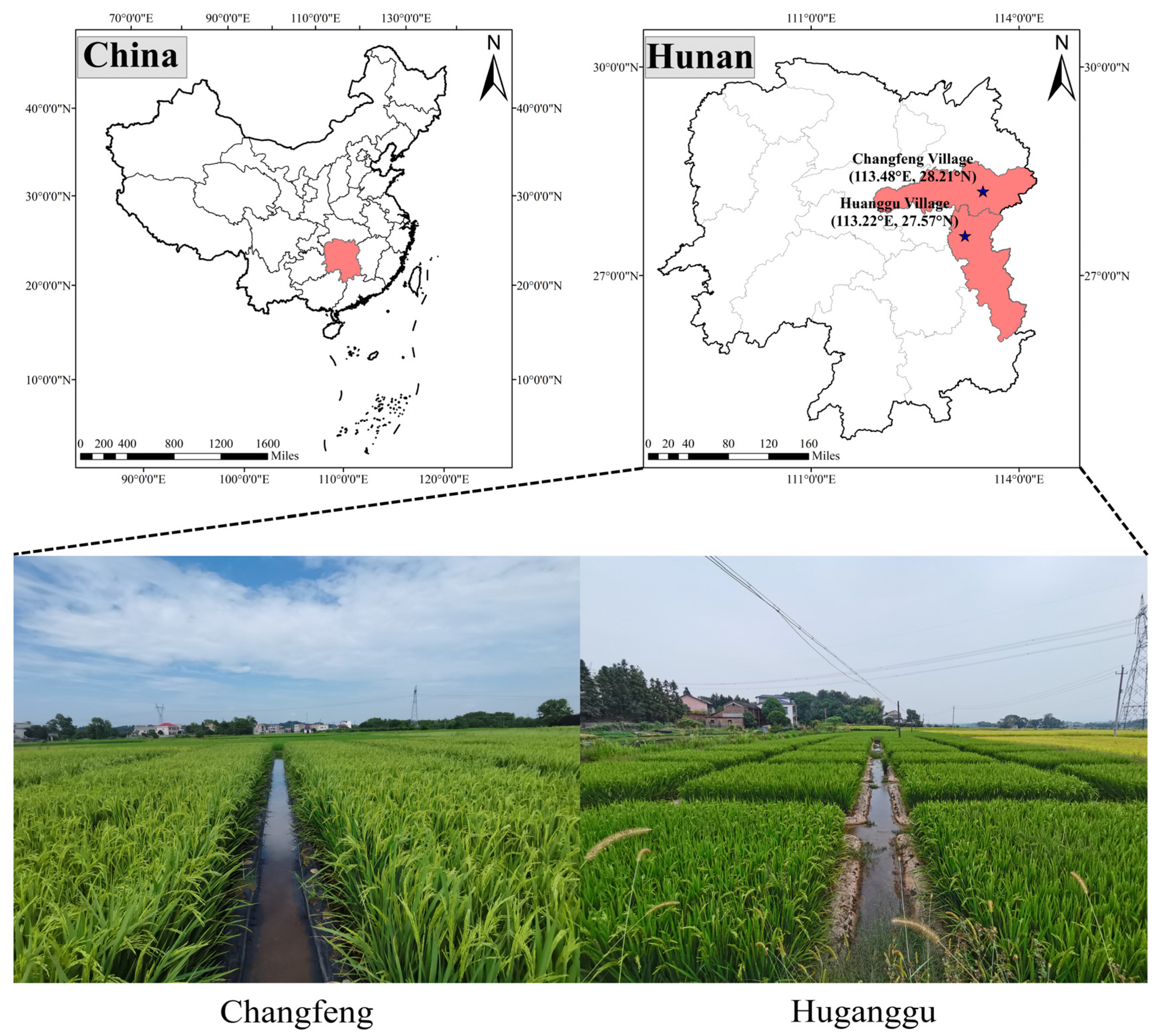
2.2. Field Plot Experimental Design
2.3. Sample Collection and Preparation
2.3.1. Plant Sampling and Preparation
2.3.2. Soil Sampling and Preparation
2.4. Sample Digestion and Determination of Soil Characteristics
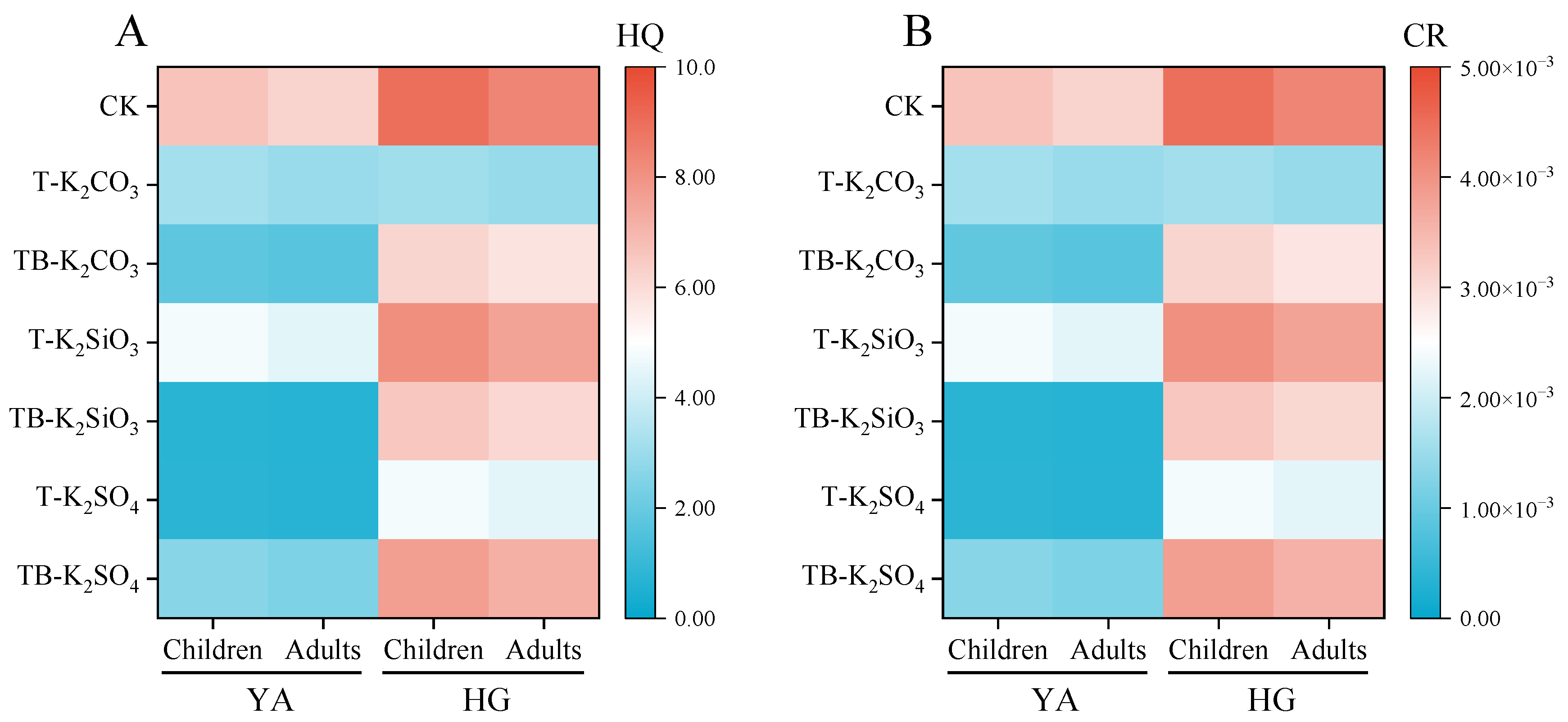
2.5. Health Risk Assessment
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Cd Accumulation in Rice and Health Risk Assessment
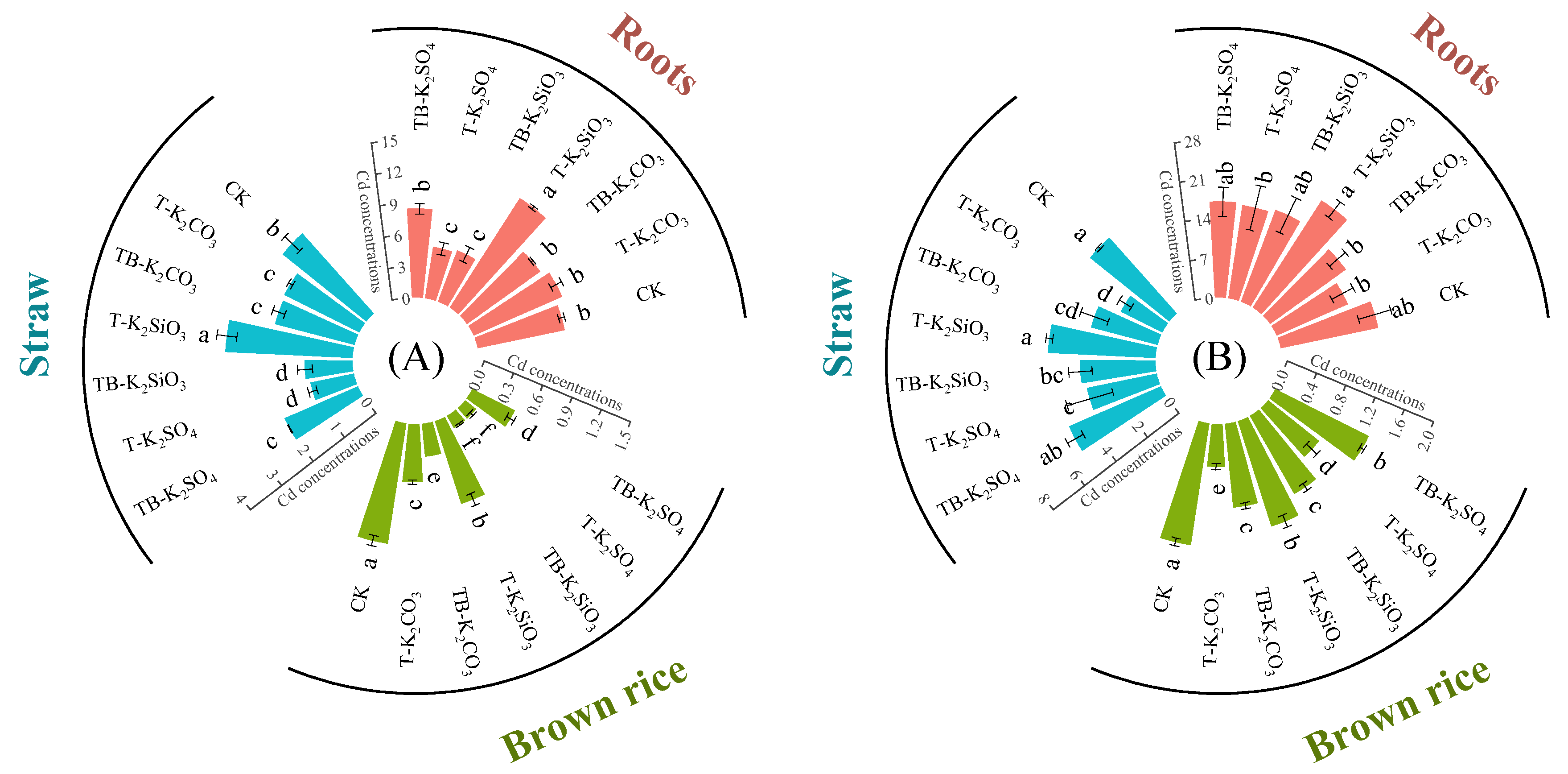
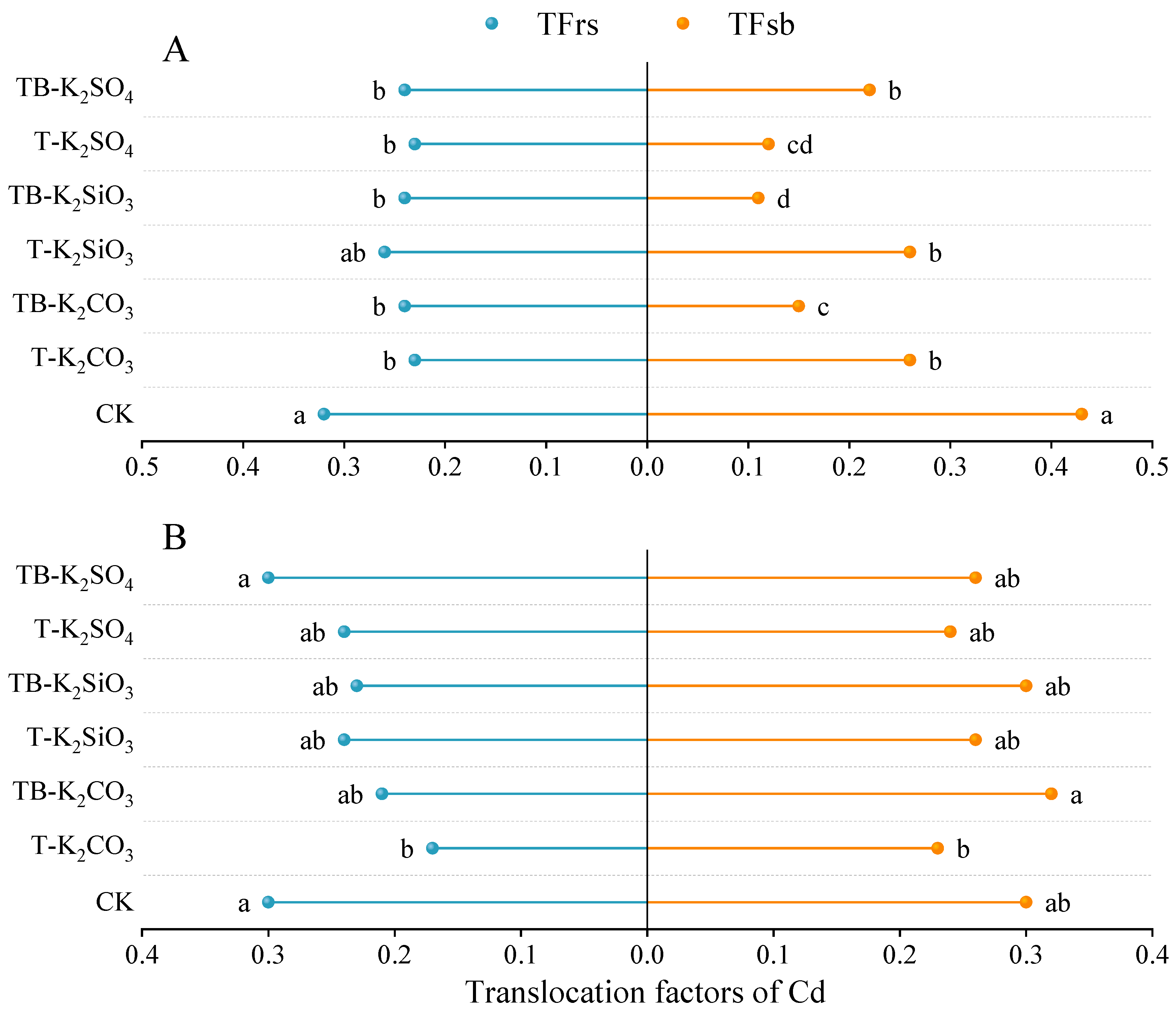
3.2. Changes in Cd Translocation in Rice Tissues
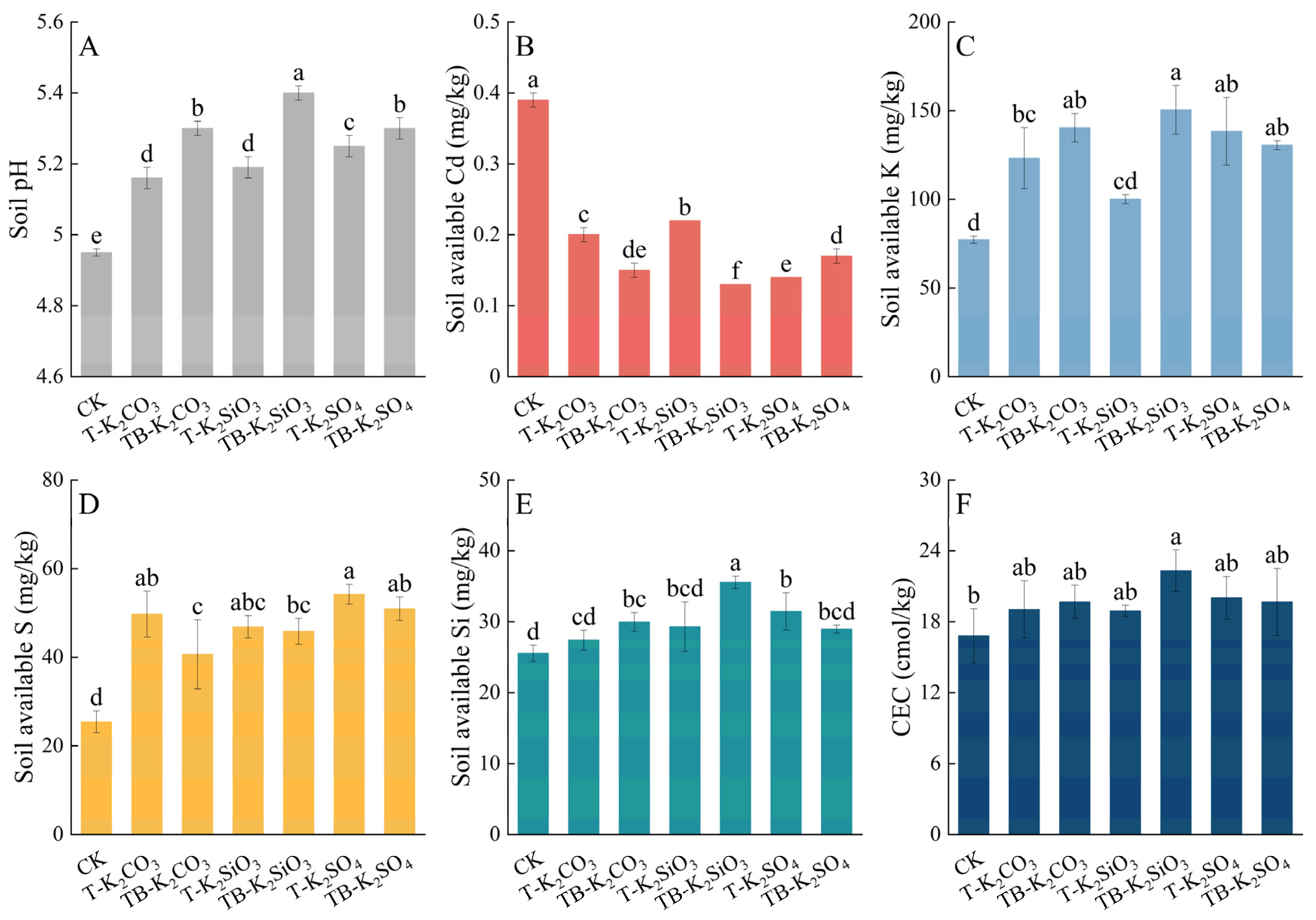
3.3. Variation in Soil Cd Bioavailability and Soil Characteristics
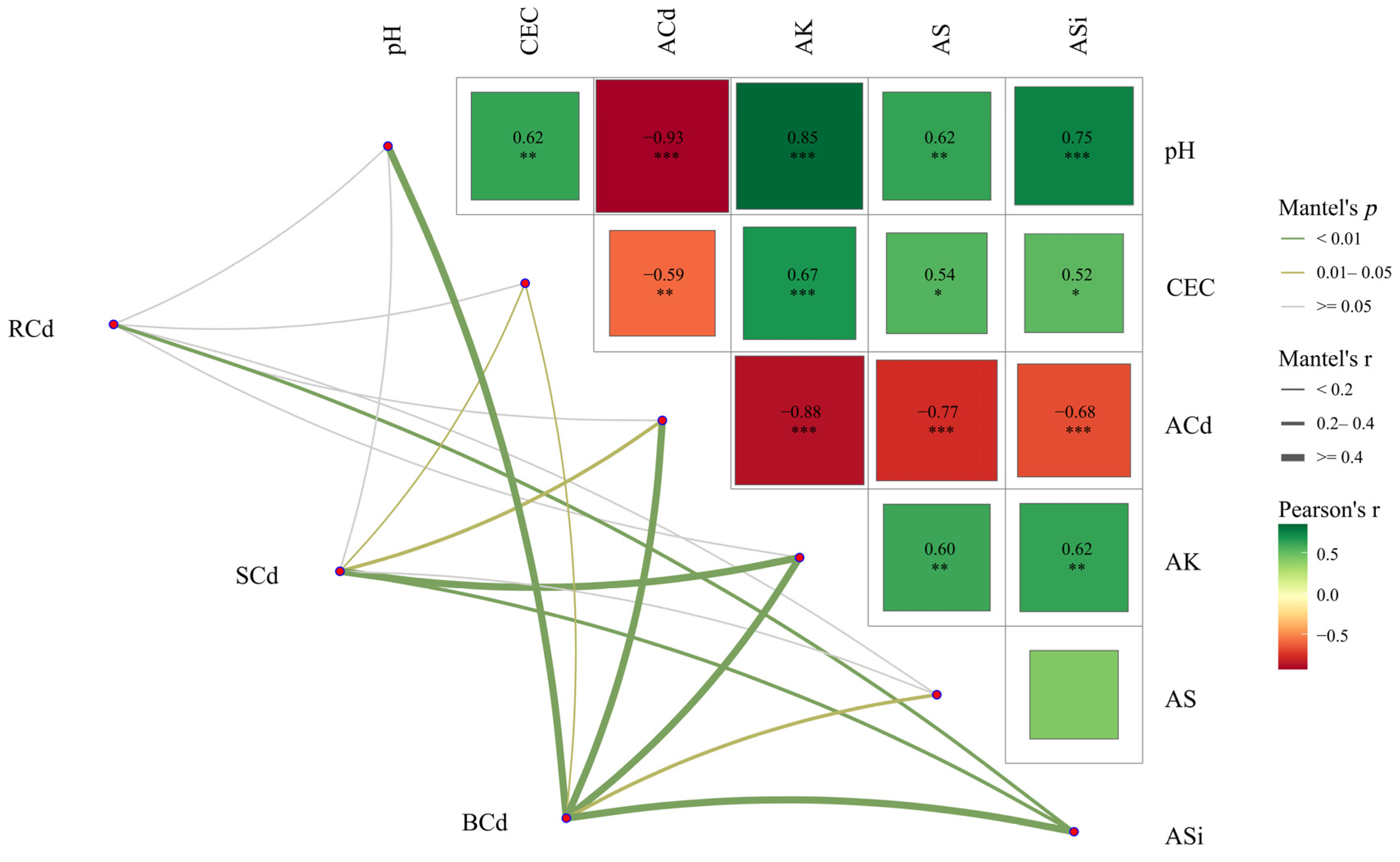
3.4. Relationship Between Soil Properties and Cd Accumulation in Rice
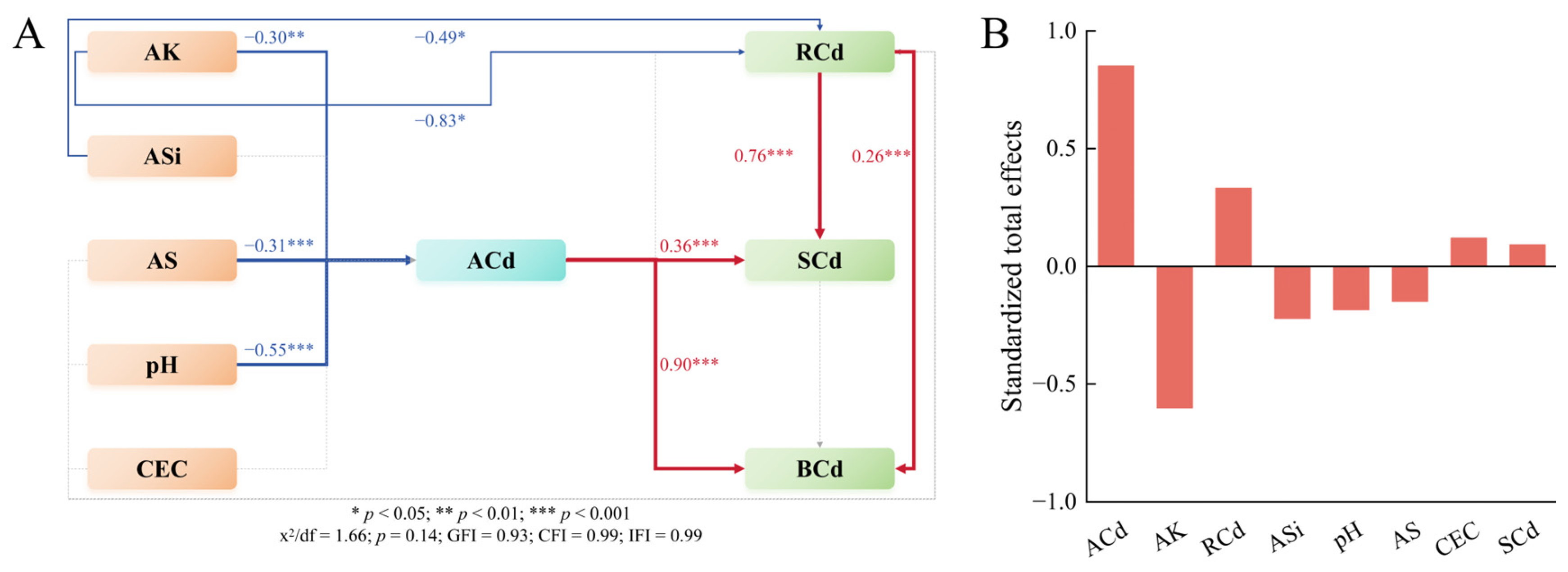
3.5. Integrated Pathway Analysis of Cd Accumulation in Rice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jing, H.; Yang, W.; Chen, Y.; Yang, L.; Zhou, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Wu, P.; Zia-ur-Rehman, M. Exploring the mechanism of Cd uptake and translocation in rice: Future perspectives of rice safety. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 897, 165369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Wang, S.; Zhou, H.; Zeng, M.; Zhang, J.; Huang, F.; Shan, S.; Guo, Z.; Yi, H.; Sun, Z.; et al. Combined amendment reduces soil Cd availability and rice Cd accumulation in three consecutive rice planting seasons. J. Environ. Sci. 2022, 111, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Wu, P.; Yang, W. Study on safe usage of agricultural land in typical Karst areas based on Cd in soil and maize: A case study of Northwestern Guizhou, China. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NaziaTahir; Ullah, A.; Tahir, A.; Rashid, H.U.; Rehman, T.U.; Danish, S.; Hussain, B.; Akca, H. Strategies for reducing Cd concentration in paddy soil for rice safety. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 316, 128116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Peng, P.; Long, J.; Dong, X.; Jiang, K.; Hou, H. Plant-induced insoluble Cd mobilization and Cd redistribution among different rice cultivars. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 256, 120494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, M.; Zhou, S.; Zhou, Y.; Jia, Z.; Guo, T.; Wang, J. Cadmium pollution of soil-rice ecosystems in rice cultivation dominated regions in China: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 280, 116965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Chen, C.; Xu, C.; Zhu, Q.; Huang, D. Effects of soil acidification and liming on the phytoavailability of cadmium in paddy soils of central subtropical China. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 219, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Yang, X.; Wang, P.; Wang, Z.; Li, M.; Zhao, F.-J. Dietary cadmium intake from rice and vegetables and potential health risk: A case study in Xiangtan, southern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 639, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palansooriya, K.N.; Shaheen, S.M.; Chen, S.S.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Hashimoto, Y.; Hou, D.; Bolan, N.S.; Rinklebe, J.; Ok, Y.S. Soil amendments for immobilization of potentially toxic elements in contaminated soils: A critical review. Environ. Int. 2020, 134, 105046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Naushad, M.; Lima, E.C.; Zhang, S.; Shaheen, S.M.; Rinklebe, J. Global soil pollution by toxic elements: Current status and future perspectives on the risk assessment and remediation strategies—A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 417, 126039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Xu, M.; Yang, L.; Jing, H.; Mao, W.; Liu, J.; Zou, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, H.; Yang, W.; et al. A Critical Review of Biochar Application for the remediation of greenhouse gas emissions and nutrient loss in rice paddies: Characteristics, mechanisms, and future recommendations. Agronomy 2023, 13, 893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamid, Y.; Tang, L.; Hussain, B.; Usman, M.; Lin, Q.; Rashid, M.S.; He, Z.; Yang, X. Organic soil additives for the remediation of cadmium contaminated soils and their impact on the soil-plant system: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 707, 136121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Yang, W.; Zhou, H.; Zia-ur-Rehman, M.; Salam, M.; Ouyang, L.; Chen, Y.; Yang, L.; Wu, P. Exploring the mechanisms of organic fertilizers on Cd bioavailability in rice fields: Environmental behavior and effect factors. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 285, 117094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, F.; Lu, S. Soil inorganic amendments produce safe rice by reducing the transfer of Cd and increasing key amino acids in brown rice. J. Environ. Sci. 2024, 136, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabagala, F.S.; Zhang, T.; Zeng, X.; He, C.; Shan, H.; Qiu, C.; Gao, X.; Zhang, N.; Su, S. A review of amendments for simultaneously reducing Cd and As availability in paddy soils and rice grain based on meta-analysis. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 366, 121661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, P.; Liu, J.; Zhou, H.; Wang, Y.; Ni, L.; Liao, Y.; Gu, J.; Liao, B.; Li, Q. Long-term effects of compound passivator coupled with silicon fertilizer on the reduction of cadmium and arsenic accumulation in rice and health risk evaluation. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 922, 171245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, R.; Huang, Z.; Li, X.; Chen, W.; Deng, Y.; Han, C. Lime and phosphate amendment can significantly reduce uptake of Cd and Pb by field-grown rice. Sustainability 2017, 9, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, S.; Qiang, R.; Lu, E.; Li, C.; Zhang, J.; Gao, Q. Response of soil microbial community structure to phosphate fertilizer reduction and combinations of microbial fertilizer. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 899727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Chen, P.; Zhou, W.; Liu, H.; Cheng, K.; Xiao, X.; Tang, H.; Yi, Z. Response characteristics of soil Cd availability to microbes in paddy soil with long-term fertilization and its impact on Cd uptake in rice. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 957, 177680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Y.; Lu, L.; Yuan, X.; Zeng, H.; Zeng, Q. Cadmium accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.) alleviated by basal alkaline fertilizers followed by topdressing of manganese fertilizer. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 262, 114289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Zhu, L.; Zhao, T.; Dahlgren, R.A.; Xu, J. Fertilizer application alters cadmium and selenium bioavailability in soil-rice system with high geological background levels. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 350, 124033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Wu, Q.-T.; Lee, C.C.C.; Jiang, C.A.; Wei, Z. Evaluation of manganese application after soil stabilization to effectively reduce cadmium in rice. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Z.; Gao, Z.; Lu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X. Straw return combined with potassium fertilization improves potassium stocks in large-macroaggregates by increasing complex iron oxide under rice–oilseed rape rotation system. Soil Tillage Res. 2025, 248, 106404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellarby, J.; Surridge, B.W.J.; Haygarth, P.M.; Liu, K.; Siciliano, G.; Smith, L.; Rahn, C.; Meng, F. The stocks and flows of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium across a 30-year time series for agriculture in Huantai county, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 619–620, 606–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, C.A.; Sheppard, S.C. Fertilizer impacts on cadmium availability in agricultural soils and crops. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2008, 14, 210–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Fu, G.; Yu, Y.; Wan, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Li, H. Effects of different potassium fertilizers on cadmium uptake by three crops. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 27014–27022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, B.; Wang, W.; Liu, B.; Cai, K.; Tian, J.; Cai, Y. Significant difference in the efficacies of silicon application regimes on cadmium species and environmental risks in rice rhizosphere. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 327, 121521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Pan, B.; Liu, B.; Cai, K.; Tian, J.; Wang, W. The Cd sequestration effects of rice roots affected by different Si management in Cd-contaminated paddy soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 849, 157718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, B.; Cai, Y.; Liu, B.; Cai, K.; Lv, W.; Tian, J.; Wang, W. Abatement of Cd in rice grain and toxic risks to human health by the split application of silicon at transplanting and jointing period. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 302, 114039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, M.Z.U.; Rizwan, M.; Rauf, A.; Ayub, M.A.; Ali, S.; Qayyum, M.F.; Waris, A.A.; Naeem, A.; Sanaullah, M. Split application of silicon in cadmium (Cd) spiked alkaline soil plays a vital role in decreasing Cd accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.) grains. Chemosphere 2019, 226, 454–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Wang, H.; Xu, C.; Zheng, S.; Wu, M.; Zhang, Q.; Liao, Y.; Zhu, H.; Zhu, Q.; Huang, D. Nitrogen application practices to reduce cadmium concentration in rice (Oryza sativa L.) grains. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 50530–50539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Deng, X.; Ma, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, A.; Zhang, X.; Zeng, Q. Cadmium accumulation in brown rice (Oryza sativa L.) depends on environmental factors and nutrient transport: A three-year field study. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 903, 166942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 15618-2018; Soil Environmental Quality–Risk Control Standard for Soil Contamination of Agricultural Land. China Environment Publishing Group: Beijing, China, 2018.
- Wang, J.; Yu, L.; Qin, L.; Sun, X.; Zhou, W.; Wang, M.; Chen, S. Low pe+pH inhibits Cd transfer from paddy soil to rice tissues driven by S addition. Chemosphere 2023, 335, 139126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Bai, L.; Wei, X.; Li, T.; Tang, Y.; Zeng, X.; Lei, Z.; Wen, J.; Su, S. Promoted decomposition in straw return to double-cropped rice fields controls soil acidity, increases soil fertility and improves rice yield. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 509, 161309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Yu, B.; Wang, X.; Chen, L.; Akhtar, K.; Tang, S.; Lu, H.; He, J.; Wen, R.; He, B. Differences in the response mechanism of cadmium uptake, transfer, and accumulation of different rice varieties after foliar silicon spraying under cadmium-stressed soil. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 13, 1064359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USEPA. Exposure Factors Handbook 2011 Edition; US Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, R.; Chen, C.; Kou, M.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Cai, J.; Tan, W. Heavy metal concentrations in rice that meet safety standards can still pose a risk to human health. Commun. Earth Environ. 2023, 4, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, C.; Song, Y.; Chen, L.; Ji, J.; Li, J.; Yuan, X.; Yang, Z.; Ayoko, G.A.; Frost, R.L.; Theiss, F. Human health risks of heavy metals in paddy rice based on transfer characteristics of heavy metals from soil to rice. CATENA 2019, 175, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.; Wang, X.; Chen, J.; Fang, Q.; Liu, J.; Tang, L.; Liu, L.; Cao, W.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, B. Extreme low-temperature events can alleviate micronutrient deficiencies while increasing potential health risks from heavy metals in rice. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 334, 122165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 2762-2022; National Standard for Food Safety: Limit of Contaminants in Food. NHFPCPRC and CFDA: Beijing, China, 2022.
- Hamid, Y.; Tang, L.; Hussain, B.; Usman, M.; Gurajala, H.K.; Rashid, M.S.; He, Z.; Yang, X. Efficiency of lime, biochar, Fe containing biochar and composite amendments for Cd and Pb immobilization in a co-contaminated alluvial soil. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 257, 113609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, J.; Huang, Q.; Tang, S.; Wang, J.; Hu, P.; Shao, G. Can liming reduce cadmium (Cd) accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa) in slightly acidic soils? A contradictory dynamic equilibrium between Cd uptake capacity of roots and Cd immobilisation in soils. Chemosphere 2018, 193, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhuang, P.; Li, Z.; Zou, B.; Wang, G.; Li, N.; Qiu, J. Effects of fertiliser and intercropping on cadmium uptake by maize. Chem. Ecol. 2013, 29, 489–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahedifar, M.; Akbar, M.A.; Mahshid, S.; Zahra, Z.; Karimian, F. Cadmium accumulation and partitioning in Ocimum basilicum as influenced by the application of various potassium fertilizers. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2016, 62, 663–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettigrew, W.T. Potassium influences on yield and quality production for maize, wheat, soybean and cotton. Physiol. Plant. 2008, 133, 670–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zörb, C.; Senbayram, M.; Peiter, E. Potassium in agriculture-status and perspectives. J. Plant Physiol. 2014, 171, 656–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaheer, M.M.; Ahmad, Y.N.; Rashid, A.S.; Ullah, K.W.; Aqeel, A.; Aamir, A.; Rehman, S.U. Amelioration of cadmium stress in gladiolus (Gladiolus grandiflora L.) by application of potassium and silicon. J. Plant Nutr. 2018, 41, 461–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S. Effects of Anion Attendant, pH Value, and Concentrations of Ca and K in Rhizosphere on Cd Uptake Andtanslolcation in Rice Root; Zhejiang University: Hangzhou, China, 2020. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.; Chen, M.; Huang, Y.; Xie, S.; Zhang, X.; Zuo, T.; Hu, C.; Wang, G. Chloride application weakens cadmium immobilization by lime in paddy rice soil. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 241, 113761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlin, A.S.; Eriksson, J.; Campbell, C.D.; Öborn, I. Soil amendment affects Cd uptake by wheat—Are we underestimating the risks from chloride inputs? Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 554–555, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, Z.; Khaliq, M.A.; Xie, T.; Chen, Y.; Wang, G. Chlorine weaken the immobilization of Cd in soil-rice systems by biochar. Chemosphere 2019, 235, 1172–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Ge, C.; Abulimiti, M.; Zhou, D.; Hu, C.; Wang, G. Detrimental effect of chloride on suppressing cadmium accumulation in rice grains: A field-based investigations. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2024, 36, 103883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, F.; Zhang, X.; Fu, Q.; Hu, H.; Islam, M.S.; Fang, L.; Zhu, J. Sulfur enhances iron plaque formation and stress resistance to reduce the transfer of Cd and As in the soil-rice system. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 927, 171689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Lin, Q.; Li, G.; Guo, C.; Li, L.; Wang, J. Evaluating water management efficiency in regulating cadmium and arsenic accumulation in rice in typical Japonica paddy soils at varied pH levels. Agriculture 2024, 14, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Ji, X.-B.; Cheng, L.-Y.; Zhao, F.-J.; Wang, P. Free radicals produced from the oxidation of ferrous sulfides promote the remobilization of cadmium in paddy soils during drainage. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 9845–9853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Rizwan, M.; Hussain, A.; Zia ur Rehman, M.; Ali, B.; Yousaf, B.; Wijaya, L.; Alyemeni, M.N.; Ahmad, P. Silicon nanoparticles enhanced the growth and reduced the cadmium accumulation in grains of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Plant Physiol Biochem. 2019, 140, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peera Sheikh Kulsum, P.G.; Khanam, R.; Das, S.; Nayak, A.K.; Tack, F.M.G.; Meers, E.; Vithanage, M.; Shahid, M.; Kumar, A.; Chakraborty, S.; et al. A state-of-the-art review on cadmium uptake, toxicity, and tolerance in rice: From physiological response to remediation process. Environ. Res. 2023, 220, 115098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Liu, T.; Li, F.; Yi, J.; Liu, C.; Yu, H. Silica nanoparticles alleviate cadmium toxicity in rice cells: Mechanisms and size effects. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 228, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xu, H.; Tang, J.; Yang, J.; Guo, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Ge, Y.; Liu, T.; Hu, Q.; Ao, H.; et al. Cadmium absorption and translocation in rice plants are influenced by lower air temperatures during grain filling stage. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 954, 176742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.-Y.; Zhao, F.-J.; Wang, P. The relative contributions of root uptake and remobilization to the loading of Cd and As into rice grains: Implications in simultaneously controlling grain Cd and As accumulation using a segmented water management strategy. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 293, 118497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Chen, M.; Dai, H.; Tian, T.; Pan, W.; Xu, J.; Lin, D. Safe production of rice in Cd-polluted paddy fields by rhizosphere application of zero-valent iron nanoplates at specific growth stages. Nano Today 2024, 56, 102289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, L.; Xiao, H.; Ao, H.; Tian, W.; Xiao, F.; Xiang, Y.; Zhang, X. Effect of nitrogen fertilizer on iron plaque formation on the root surface of double cropping rice and cadmium accumulation in double-season rice. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2021, 40, 260–268. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Wang, K.; Li, G.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, W.; Jiang, J.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, L. Stabilization of arsenic, antimony, and lead in contaminated soil with montmorillonite modified by ferrihydrite: Efficiency and mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 457, 141182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Q.; Wu, W.; Zhao, Y.; Tan, X.; Yang, Y.; Zeng, Q.; Deng, X. Optimizing Potassium Fertilization Combined with Calcium–Magnesium Phosphate Fertilizer Mitigates Rice Cadmium Accumulation: A Multi-Site Field Trial. Agriculture 2025, 15, 1052. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15101052
Zhang Q, Wu W, Zhao Y, Tan X, Yang Y, Zeng Q, Deng X. Optimizing Potassium Fertilization Combined with Calcium–Magnesium Phosphate Fertilizer Mitigates Rice Cadmium Accumulation: A Multi-Site Field Trial. Agriculture. 2025; 15(10):1052. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15101052
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Qiying, Weijian Wu, Yingyue Zhao, Xiaoyu Tan, Yang Yang, Qingru Zeng, and Xiao Deng. 2025. "Optimizing Potassium Fertilization Combined with Calcium–Magnesium Phosphate Fertilizer Mitigates Rice Cadmium Accumulation: A Multi-Site Field Trial" Agriculture 15, no. 10: 1052. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15101052
APA StyleZhang, Q., Wu, W., Zhao, Y., Tan, X., Yang, Y., Zeng, Q., & Deng, X. (2025). Optimizing Potassium Fertilization Combined with Calcium–Magnesium Phosphate Fertilizer Mitigates Rice Cadmium Accumulation: A Multi-Site Field Trial. Agriculture, 15(10), 1052. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15101052