Abstract
Tadpole shrimp (Triops longicaudatus) has become a major pest for California rice farmers. Currently, management relies solely on the insecticide lambda-cyhalothrin. However, resistance to this pyrethroid was confirmed in 2016; thus, identifying an effective and practical biological control method for TPS is a priority. Field trials were conducted from 2017 to 2018 to (1) evaluate the efficacy of the predatory fish Gambusia affinis and the predatory beetles, Laccophilus maculosus (Say) and Tropisternus lateralis (Fabricius), in controlling TPS, (2) test the efficacy of several inoculation rates of Gambusia affinis at controlling TPS and (3) to explore early indicators of TPS activity and damage as monitoring tools. Both Gambusia affinis and the predatory beetle treatments were not significantly different from the commercial standard (lambda-cyhalothrin). Both four and five Gambusia per 1 m2 controlled TPS as well as lambda-cyhalothrin, and we observed that Gambusia affinis was able to reproduce in the field. Water turbidity was significantly correlated with TPS counts (R = 0.85, N = 20, p < 0.0001 (2017); R = 0.58, N = 30, p = 0.0007 (2018)). The number of dislodged seedlings was less reliably correlated with TPS count; in 2017, correlations were significant (R = 0.84, N = 20, p < 0.0001); however, in 2018, correlations were not significant (R = 0.18, N = 30, p = 0.35). With further refinement, water turbidity could play a valuable role in monitoring TPS populations.
1. Introduction
The tadpole shrimp (Notostraca: Triopsidae: Triops longicaudatus (LeConte); TPS) is a small vernal pool crustacean. TPS has been a part of the California rice ecosystem since the industry’s inception during the gold rush [1,2]. Adapted to vernal pools, TPS are opportunistic omnivores, grow very quickly, and can reach sexual maturity in as few as 6–7 days [3,4]. They are a well-established biological control agent for mosquitoes [5,6,7,8,9], and in many areas, their eggs are commercially available for inoculating rice fields and other ponds to manage local mosquito populations [4,10].
However, over the past several decades, TPS’s status has changed from being a sporadic pest [11] to a significant pest for California rice farmers. TPS damages rice by feeding directly on germinating rice seeds and seedlings, by stirring up silt that reduces the photosynthetic capacity of rice seedlings while growing underwater, and by dislodging rice seedlings through their swimming and burrowing behaviors [12,13,14]. In California, over 90% of rice is aerial/direct seeded [15,16], meaning rice basins are flooded before seeding. Depending on the size of the rice basin, it can take 1–4 days to flood a field [17]. Once fields are flooded, pre-germinated rice seeds are aerially dropped over the fields [17]. What ensues is essentially a growth race between the TPS and the young rice seedling. TPS eggs hatch soon after flooding, giving them a head start over the rice seedlings. Tadpole shrimp grow very quickly, up to several millimeters in a day [18]. If the young rice seedling is unable to grow fast enough to establish a firm root system before the TPS is large enough to uproot it, TPS can demolish entire fields, requiring farmers to reseed. If reseeding is required, young rice seedlings also face the challenge of depleted available oxygen soil levels, leaving insufficient oxygen for adequate seedling growth [19]. When reseeding, growers are advised to drain the field completely and aerate the soil before reflooding, which often reduces yield due to delayed planting and a shortened growing season [17].
TPS has become an increasing problem for farmers over the past decade as changes in rice cultivation have affected farmers’ management of TPS populations. The Connelly-Areias-Chandler Rice Straw Burning Reduction Act of 1991 mandated that rice straw burning in the Sacramento Valley be reduced to a maximum of 25% of total acreage burned by 2001 [20,21]. Prior to this mandate, nearly all rice fields were burned in the fall to remove excess straw waste following harvest. In 1999, 13% of farmers’ fields were burned post-harvest [21]; currently, less than 10% of farmers’ fields are burned following harvest [22]. Rice straw is resistant to decay [23], and reduced burning has resulted in straw accumulation in fields. It is suspected that copper sulfate, traditionally used to control TPS, has become less effective because it binds to the organic matter resulting from the surplus straw [11,14,20,24] and has consequently been replaced by pyrethroids [25]. For the past decade, pyrethroids, primarily lambda-cyhalothrin, have been used as the sole management strategy for TPS in California rice [25]. Thus, it is not surprising that in 2016, farmers noticed possible resistance of TPS to lambda-cyhalothrin after several applications at label rate failed to control TPS in their fields within a single growing season [26]. Resistance was confirmed in laboratory bioassays using field-collected individuals when five times the label rate of lambda-cyhalothrin failed to kill TPS [26]. Given growing concerns over resistance, an alternative management strategy must be developed. The alternative strategy should ideally (1) have a reduced impact on the rice production environment, (2) be practical, sustainable, and economical, and (3) manage mosquito as well as TPS populations. Here, we report tests to develop a sustainable biological control strategy for TPS in rice.
1.1. TPS Biology
Understanding TPS biology is requisite to developing an informed biological control experiment. TPS’ basic morphology has changed little over the last 50 million years or more, leading to their common characterization as “living fossils” [27,28]. Believed to have evolved for vernal pool life to escape predation from fish [29], TPS have evolved a strategy for coping with unpredictable weather/rain events. As a type of bet-hedging strategy, a portion of TPS eggs from every brood goes into a diapause that is broken after varying numbers of wetting-drying cycles [30]. That is, some eggs will hatch following the initial flooding event, while others require several flooding and drying events before being triggered to hatch [31,32,33].
1.2. TPS Monitoring
Currently, prophylactic pesticide spraying for TPS is common, as there are no adequate monitoring protocols to assess TPS populations accurately until the crop is damaged; this likely contributes to the development of insecticide-resistant populations. Sampling of TPS populations is challenging due to their small size and the transparency of young immature stages, making them nearly invisible in field conditions. Additionally, since TPS are adapted to vernal pool environments, they can reach damaging stages within five days of egg hatch under typical field conditions. Consequently, harmful populations can appear suddenly and unexpectedly in commercial rice fields, uprooting seedlings and causing water turbidity. These sampling difficulties are further exacerbated by older TPS stages exhibiting increased photonegativity, with adults spending more time near the rice paddy floor in flooded fields [34]. Taking soil samples and performing egg counts as a sampling method presents its own challenges, as TPS eggs exhibit a staggered diapause, and that staggered diapause can change due to environmental cues (i.e., dissolved oxygen, available food, water temperature) [32]. Thus, it is unknown which eggs will hatch the following season and which will remain dormant. Furthermore, the establishment of TPS as a “pest” is dependent on its growth rate. Thus, we cannot rely only on TPS egg counts to establish a threshold but must take into account factors (e.g., temperature, food availability) that may affect their growth rate. The challenges in monitoring TPS field populations prompted us to seek an early-season indicator of TPS activity, aiming to minimize the reliance on prophylactic sprays.
Field studies conducted in 2017–2018 examined (1) the efficacy of Gambusia fish and predatory beetles (Coleoptera: Dytiscidae: Laccophilus maculosus and Coleoptera: Hydrophilidae: Tropisternus lateralis) as biological controls of TPS, and (2) the relative efficacy of different initial Gambusia affinis (Cyprinodontiformes: Poecilidae) inoculation rates, and (3) the utility of a water turbidity score or a count of dislodged seedlings as monitoring techniques for TPS in California rice.
2. Materials and Methods
Field experiments were conducted in 2017–2018 at the Rice Experiment Station in Biggs, CA, USA. The 2017 field trial compared the efficacy of Gambusia affinis and two predatory beetles (Laccophilus maculosus and Tropisternus lateralis) to the industry standard pesticide lambda-cyhalothrin (Warrior II with Zeon Technology, Syngenta, Greensboro, NC, USA) and untreated control, while the 2018 field trial examined the efficacy of different inoculation rates of Gambusia affinis in controlling TPS (Table 1).

Table 1.
Treatments (Trt) by Trial Year.
2.1. 2017 Field Trial: Efficacy of Gambusia affinis and Predatory Beetles at Controlling TPS
A randomized complete block design consisting of five replications of four treatments was deployed on June 15 in an untreated rice field at the Rice Experiment Station in Biggs, CA, USA. Treatments consisted of mosquito fish (Gambusia affinis), a combination of predatory beetles (three adult Laccophilus maculosus Say and two adults Tropisternus lateralis (Fabricius)), an untreated control, and the industry-standard pesticide (lambda-cyhalothrin) at a rate of 75.7 mL per ring. Gambusia utilized in this study were laboratory-reared to adulthood from stream populations and averaged roughly 4 cm (measured using calipers). Beetles were collected from light traps deployed at the Rice Experiment Station in Biggs, CA, USA, during spring months. Aluminum rings, 1 m2 in area and 61 cm high, acted as experimental plots within the field in accordance with previous rice invertebrate research methods [35,36,37]. Aluminum rings are installed in dry rice fields prior to flooding using wooden stakes secured into the clay soil to hold their cylindrical shape. Clay soil is packed around the bottom of each aluminum ring to ensure study species are unable to immigrate or emigrate from each ring (Supplementary Material Figures S1–S3). The entire experiment occupied a 7 × 9 m grid in the field. Aluminum rings effectively captured TPS, preventing them from moving in or out of the ring. No TPS were added or removed from rings during the experiment; thus, this study embraces the full, natural spatial heterogeneity in TPS densities. Both L. maculosus and T. lateralis beetles are naturally occurring in rice fields throughout the season and are capable of flying in and out of aluminum rings. Five beetles were consistently observed in designated beetle treatment rings throughout the study, suggesting that none emigrated from the ring during our study. Rings were deployed in a research field that had a high-density population of TPS the previous season. Each ring was seeded with rice variety M206 at a commercial rate of 10.8 g/ring one day after flooding (DAF). Treatments were applied 2 DAF, with the exception of lambda-cyhalothrin, which was applied at a commercial rate (0.139 L/ha) prior to flooding. The number of surviving TPS per ring was recorded as 3, 5, 7, and 9 DAF.
2.2. 2018 Field Trial: Comparing Different Application Rates against Previous Successful Rates
The 2018 study was initiated on June 13 and consisted of six treatments, including four application rates of Gambusia fish (1, 2, 4, and 5 fish/ring), an industry-standard pesticide (lambda-cyhalothrin at a commercial rate of 0.139 L/ha), and an untreated control. Gambusia utilized were laboratory-reared adult fish that roughly averaged 2 cm in length (measured using calipers). All treatments were replicated five times and arranged in a completely randomized block design. Aluminum rings (1 m2) were used as experimental units and seeded with rice variety M206 at a commercial rate of 10.8 g/ring one DAF. Application rates and timings of applications were chosen based on their performance in the 2017 study. All treatments were applied 2 DAF, except for the lambda-cyhalothrin, which was applied prior to flooding the field at the same rate that was used in the 2017 trial. Surviving numbers of TPS per ring were recorded as 5, 7, 9, and 11 DAF.
2.3. Assessing Monitoring Practices
During the 2017 field trial, dislodged seedlings and water turbidity per ring were recorded at 3, 5, 7, and 9 DAF. Dislodged seedlings were identified as seedlings floating on the surface of the water. The mean of these four measurements was used in subsequent statistical analyses. During the 2018 field trial, dislodged seedlings and water turbidity were recorded once at 8 DAF. In both trials, turbidity was scored on a scale of 1–4 in increments of one, with 1 representing completely clear water and 4 representing a nearly opaque solution. Scores of 2–3 represent in-between turbidity measurements that are slightly translucent, 2 being closer to clear than opaque, and a score of 3 representing definitively murky but not opaque water clarity [35].
2.4. Statistical Analysis
Both trials were analyzed using the SAS 9.4 statistical package (SAS Institute Inc., 2016, Cary, NC, USA). Analysis of variance (ANOVA) was performed to test for significant differences among treatments. Tukey’s HSD tests were used for pairwise comparisons among the treatments. Upper Dunnett’s comparisons were performed to contrast treatments with the negative control (lambda-cyhalothrin). Lower Dunnett’s comparisons were performed to contrast treatments with the positive (untreated) control. Simple Pearson correlations were computed to examine the linear relationships between the number of dislodged seedlings, water turbidity, and the number of surviving TPS. In the 2017 trial, TPS counts, turbidity readings, and number of dislodged seedlings were averaged across all sampling dates for each ring (i.e., 3, 5, 7, and 9 DAF), and means were used to compute all correlations. In the 2018 trial, turbidity was measured at 8 DAF, and these values were used to compute correlations.
3. Results
There were significant differences among treatments in TPS counts for the 2017 field study (ANOVA, F = 12.69, df = 3, 11, p = 0.0007). Tukey’s HSD and the lower Dunnett’s test both demonstrated that all treatments were significantly different from the untreated control (Figure 1). The Gambusia treatment had zero surviving TPS across all replications and sampling dates.
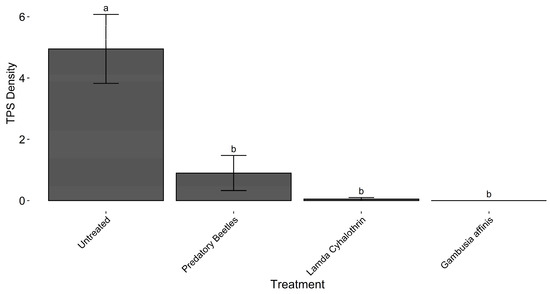
Figure 1.
TPS densities following treatment applications in the 2017 field trial at the UC Davis Rice Experiment Station in Biggs, CA, USA. Bars with the same letter are not significantly different at α = 0.05, according to Tukey’s HSD.
There were significant differences among treatments in TPS counts for the 2018 field trial assessing the efficacy of different application rates of Gambusia spp. (ANOVA, F = 4.82, df = 5, 20, p = 0.0047). TPS suppression had a positive relationship with Gambusia numbers (Figure 2). Dunnett’s test found significant differences (α = 0.05) between the four fish, five fish, and lambda-cyhalothrin treatments when compared to the untreated control.
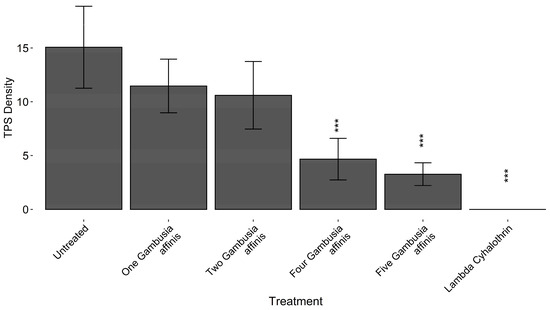
Figure 2.
TPS densities following varying inoculation rates of Gambusia spp. against a positive (untreated) and negative (lambda-cyhalothrin) control in the 2018 field trial at the UC Davis Rice Experiment Station in Biggs, CA, USA. Bars with *** denote treatments determined to be significantly different (α = 0.05) than the Untreated control by Dunnett’s test.
In the 2017 field trial, both turbidity and dislodged seedlings were highly correlated with TPS counts within rings (Pearson correlation, R = 0.85 (turbidity), R = 0.84 (dislodged seedlings), N = 20, p < 0.0001; Figure 3). In the 2018 field trial, turbidity was significantly correlated with TPS counts within the rings, but the relationship was more variable (R = 0.58, N = 30, p = 0.0007); however, dislodged seedlings counts were not significantly correlated with TPS counts (R = 0.18, N = 30, p = 0.35; Figure 3).
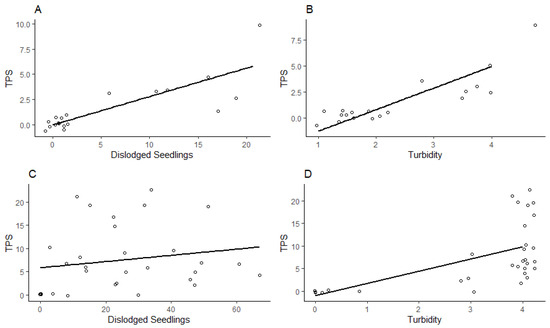
Figure 3.
Linear regressions between TPS counts dislodged seedling counts, and turbidity scores across 2017 and 2018 field trials. (A) Correlation between mean dislodged seedlings and TPS counts (R = 0.84, N = 20, p < 0.0001) in the 2017 study. (B) Correlation between mean turbidity scores (scale 1–4) and TPS counts for the 2017 study (R = 0.85, N = 20, p < 0.0001). (C) Correlation between mean TPS counts (5, 7, 9, and 11 DAF) and dislodged seedlings 8 DAF (R = 0.18, N = 30, p = 0.35) in the 2018 study. (D) Correlation between mean TPS counts (5, 7, 9, and 11 DAF) and turbidity rankings (scale 1–4) 8 DAF (R = 0.58, N = 30, p = 0.0007) in the 2018 study. Points were jittered to avoid excessive overlap.
4. Discussion
The biological control treatments tested here generated effective control of TPS in both the 2017 and 2018 studies, suggesting that both predatory beetles (L. maculosus and T. lateralis) and Gambusia fish have potential as biological control agents. Gambusia affinis consistently controlled TPS as effectively as lambda-cyhalothrin at a rate of five fish per 1 m2. All Gambusia deployed in the field were sexually mature adult fish that averaged 4 cm in size in 2017 and 2 cm in 2018. We observed juvenile Gambusia affinis (which are substantially smaller than the adult fish) in several of the rings when we were taking TPS counts, indicating that Gambusia had already successfully reproduced. A combination of three L. maculosus and two T. lateralis adult beetles was also as effective as lambda-cyhalothrin at controlling TPS. Gambusia produced complete control of TPS in the 2017 trial across all replicates.
Although both biological control treatments proved effective in the 2017 season, the unpredictable occurrence of predatory beetle populations and the inefficiency of current collection methods make them a less predictable biological control method for TPS in rice. We were unable to collect sufficient numbers of adult beetles from light traps to include them in the 2018 field study, and commercial sources of these natural TPS enemies are not available. Alternative methods of collecting and/or rearing these beetles could prove useful in the future. Additional studies examining different combinations of biological control agents would be helpful in gaining greater insight into the dynamics of these organisms with TPS in rice fields. Incorporating treatments such as immature stages of L. maculosus and T. lateralis and different treatment rates and timings could help meet this objective.
Further consideration should be given to enhancing predatory beetle conservation in the rice agroecosystem, either through reduced pyrethroid use or as an augmented biological control. Both modifications to the landscape and cultivation practices could preserve these natural predators already present in rice paddies. Further research should investigate these strategies.
Considerations for the Use of Gambusia in Rice Paddies
Gambusia is especially suited as a biological control agent in rice fields due to several characteristics: (1) Gambusia are remarkably resilient and tolerant of poor water quality, including wide ranges in pH, alkalinity, and total water hardness [38,39,40,41], (2) they birth live young, thus requiring no specific environment for eggs, (3) they can live, grow and thrive under a large variety of conditions, including rice fields, (4) they can live and reproduce in environments with other predators, such as backswimmers, water bugs, some water beetles and crayfish, which are all present in rice fields, (5) they can be easily reared; the Sacramento-Yolo Mosquito Vector-Control District maintains 23 ponds for rearing Gambusia year round, producing several thousand pounds of mosquito fish per year, and (6) there is generally no negative affect of Gambusia on the rice ecosystem; at a stocking rate of 0.22 kg/ha (approximately 100 per acre), Gambusia had no significant effect on copepods, ostracods, corixids, dragonflies, belostomatids or aquatic beetles within the rice ecosystem [42].
Given these characteristics of Gambusia, there are still several factors that must be considered for the effective use of Gambusia to control TPS. These factors include fish size at application, timing of the application, application rate, current weed management strategies, and commercial availability of Gambusia. These factors are addressed in the order below.
Control of TPS by Gambusia is likely affected by fish size. Adult Gambusia fish in the 2018 study were half the size (2 cm) of the adult fish (4 cm) in the 2017 study. We observed no TPS in the rings in 2017 (larger Gambusia) and a mean of 3.27 ± 1.10 TPS per ring in 2018 (smaller Gambusia) for the rate of five fish per ring. Prey size selection is positively correlated with Gambusia size, as Gambusia choose the largest prey they can successfully capture [43,44]. Future studies should explore the effects of Gambusia size at the time of inoculation on TPS control. Ideally, inoculating fields with larger adult fish are one DAF when TPS remains comparatively smaller.
Timing is another consideration if Gambusia are to be used to control TPS. Gambusia are commonly introduced to rice fields 15 to 25 DAF for mosquito control. Farley and Younce (1977) found that Gambusia had the best population growth and mosquito control when introduced to rice fields 15 to 25 DAF, as there was insufficient food in the fields when Gambusia was introduced earlier [45]. These studies were conducted when TPS was classified as a sporadic pest [11,12]. As previously mentioned, TPS hatch almost immediately upon flooding, and Gambusia would likely have to be applied within one or two DAFs to prevent serious TPS damage. Our studies suggest that TPS-infested fields would be able to support early applications of Gambusia. Gambusia are commonly applied for mosquito control at rates from 247 to 2471 fish per ha (0.224 to 2.24 kg per ha) [46,47]. In the 2017 field study, we arbitrarily chose five Gambusia affinis per ring. The results of the 2018 field study found that four fish per 1 m2 provides effective control and would be an absolute maximum rate because many other factors play a role in determining an effective fish inoculation rate. Thus, a simple extrapolation would likely not provide an accurate inoculation rate, and instead, a model that considers fish size, timing of application, water and air temperature, mobility, reproduction, and survivability of early season introductions of Gambusia is required. Further studies that consider the inoculation rate at whole field scales are required to determine the most economically effective rate at the field level for TPS control. It should be noted that free from the constraints of the aluminum rings, Gambusa could readily find shade and cooler water at inlets to enhance growth and survival.
A common weed management strategy in California rice is the post-sowing, early-season draining of fields for herbicide applications. In these cases, fish would not be an applicable management strategy for TPS; draining the field effectively eliminates any TPS pest pressure. Remaining herbicides are usually applied 35–45 DAF once TPS are no longer a problem for farmers. The effect of these herbicides on Gambusia survivorship could be more closely examined if sustained Gambusia populations throughout the growing season are desired by farmers. Not all vector control and mosquito abatement facilities stock, rear, and use Gambusia. The vector control agencies in California’s main rice-growing counties (Butte, Glenn, Colusa, and Yolo) are funded differently, some by property taxes and others through cost-benefit assessments. Many of the smaller districts that are located in large rice-growing counties do not currently have the resources for a Gambusia program as large as the Sacramento-Yolo District’s program. Providing Gambusia across the counties will require coordination, resources, and infrastructure if farmers and these facilities collaborate to control TPS and mosquitoes in rice fields simultaneously. Farmer cooperatives may be an option to consider.
Improved monitoring methods for TPS could reduce the need for prophylactic sprays. In both studies, turbidity was strongly correlated with TPS counts; however, in 2018, this relationship was somewhat more variable. Dislodged seedling counts were also strongly correlated with TPS counts in 2017 but not in 2018. Stronger correlations in 2017 could be due to earlier-season sampling (counts were averaged across 3, 5, 7, and 9 DAF) compared to 2018 (8 DAF only). Field turbidity measurements could be taken with a Secchi disk device (United Scientific Suppliers. INC., Waukegan, IL, USA) for more precise measurements, and drastic changes in turbidity from one day to the next could be indicative of rising TPS populations. Wind can also contribute to turbid water within rice fields, but only at windspeeds above 35 mph. This should be taken into consideration when relying on turbidity measurement as part of a monitoring system for TPS in rice, and it could be used as a covariate in future models. We did not experience any high winds throughout the duration of either trial. Rain is usually not a considerable factor during the rice growing season in California.
5. Summary
The effectiveness of Gambusia affinis as a biological control for both mosquitoes and TPS, coupled with their commercial availability, suggests that Gambusia offers farmers the attractive option of controlling two important pests with a single agent. Further research is required to determine their effectiveness on an operational scale. Improvements in developing a monitoring protocol and introduction of Gambusia to the rice agroecosystem could also help farmers by mitigating the growing pyrethroid resistance problem in TPS populations.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/agriculture14071136/s1, Figure S1: TPS Experimental Unit Aluminum Ring Size; Figure S2: TPS Field Experiment; Figure S3: TPS Experimental Unit Aluminum Rings in Field.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.B. and K.G.; methodology, J.B., K.G. and L.G.; validation, J.B. and K.G.; formal analysis, J.B.; investigation, J.B.; resources, J.B. and L.G.; data curation, J.B.; writing—original draft preparation, J.B.; writing—review and editing, J.B. and K.G.; visualization, J.B.; supervision, J.B. and L.G.; project administration, J.B.; funding acquisition, J.B. and L.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Western Sustainable Agriculture Research and Education (WSARE), project number GW16-044, sub-award no. 130676024, and the California Rice Research Board. The APC was funded by the University of Hawaii at Manoa.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors upon request.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Jay Rosenheim, Frank Zalom, and Luis Espino for their mentorship and guidance during my Ph.D. at the University of California, Davis. Their continued support and expertise informed this work. The authors would also like to thank Paul Bloese for reviewing the manuscript for organization and clarity.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that this research was performed in the absence of any financial or commercial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Linder, F. Contributions to the morphology and taxonomy of the Branchiopoda Notostraca with special reference to the North American species. Proc. U. S. Natl. Mus. 1952, 102, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longhurst, A.R. A review of the Notostraca. Bull. Br. Mus. Zool. 1955, 3, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholnick, D.A. Sensitivity of metabolic rate, growth and fecundity of tadpole shrimp, Triops longicaudatus to environmental variation. Biol. Bull. 1995, 189, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Fry, L.L.; Mulla, M.S. Optimal conditions for rearing the tadpole shrimp, Triops longicaudatus (Notostraca: Triopsidae), A biological control agent against mosquitoes. J. Am. Mosq. Control Assoc. 1996, 12, 446–453. [Google Scholar]
- Maffi, M. Triops granaries (Lucas) (Crustacea) as a natural enemy of mosquito larvae. Nature 1962, 195, 722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tietze, N.S.; Mulla, M.S. Prey size selection by Triops longicaudatus (Notostraca: Triopsidae) feeding on immature stages of Culex quinquefasciatus. J. Am. Mosq. Control Assoc. 1989, 5, 392–396. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tietze, N.S.; Mulla, M.S. Influence of the tadpole shrimp, Triops longicaudatus (Notostraca: Triopsidae), stocking rate of Culex tarsalis development in experimental field microcosms. J. Am. Mosq. Control Assoc. 1990, 6, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tietze, N.S.; Mulla, M.S. Biological control of Culex mosquitoes (Diptera: Culicidae) by the tadpole shrimp, Triops longicaudatus (Notostraca: Triopsidae). J. Med. Entomol. 1991, 28, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fry, L.L.; Mulla, M.S.; Adams, C.W. Field introduction and establishment of the tadpole shrimp, Triops longicaudatus (Notostraca: Triopsidae), a biological control agent of mosquitoes. Biol. Control 1994, 4, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amazon Inc. Toyops. 2019. Available online: https://www.amazon.com/Toyops-HG24TRI-Triops-Hanging-Kit/dp/B003L2CQBK/ref=sr_1_3?keywords=Tadpole+shrimp&qid=1553536366&s=hpc&sr=8-3/ (accessed on 25 March 2019).
- Grigarick, A.A.; Lange, W.H.; Finfrock, D.C. Control of the tadpole shrimp, Triops longicaudatus, in California rice fields. J. Econ. Entomol. 1961, 54, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, L.E. Apus as a pest in California rice fields. Calif. Dep. Agric. Bull. 1947, 36, 42–48. [Google Scholar]
- Grigarick, A.A. Rice plant injury: By invertebrate pests. Calif. Agric. 1963, 17, 6–7. [Google Scholar]
- Grigarick, A.A.; Lynch, J.H.; Way, J.O. Controlling Tadpole Shrimp. California Agriculture March–April 1985; pp. 12–13. Available online: http://calag.ucanr.edu/archive/?type=pdf&article=ca.v039n03p12 (accessed on 5 March 2019).
- Linquist, B.; Fischer, A.; Godfrey, L.D.; Greer, C.; Hill, J.; Koffler, K.; Moeching, M.; Mutters, R.; van Kessel, C. Minimum tillage could benefit California rice farmers. Calif. Agric. 2008, 62, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UCCE. University of California Cooperative Extension (UCCE) Rice Production Manual. 2015. Available online: http://rice.ucanr.edu/Stand_Establishment/ (accessed on 23 February 2019).
- UCCE. University of California Cooperative Extension (UCCE) Rice Production Manual. 2018. Available online: http://rice.ucanr.edu/Stand_Establishment/ (accessed on 23 February 2019).
- Takahashi, F. Pioneer life of tadpole shrimp, Triops spp. (Notostraca:Triopsidea). Appl. Entomol. Zool. 1977, 12, 104–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linquist, B.; Koffler, K.; Hill, J.; van Kessel, C. Rice field drainage affects nitrogen dynamics and management. Calif. Agric. 2011, 65, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bird, J.A.; Eagle, A.J.; Horwath, W.R.; Hair, M.W.; Zilbert, E.E.; van Kessel, C. Long-term studies find benefits, challenges in alternative rice straw management. Calif. Agric. 2002, 56, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Report to the Legislature. Progress Report of the Phase Down of Rice Straw Burning in the Sacramento Valley Air Basin; California Air Resources Board; California Department of Food and Agriculture: Sacramento, CA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- ACC, American Commodity Company LCC. The Facts About California Rice Production, As Reported in Part from May 2012, Environmental Sustainability Report Prepared by the California Rice Commission. 2012. Available online: http://www.accrice.com/sustainability/the-facts-about-california-rice-production/ (accessed on 10 January 2019).
- Van Soest, P.J. Rice straw, the role of silica and treatments to improve quality. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2006, 130, 137–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blank, R. Spatial and temporal variation in the composition and biomass of algae present in selected California rice fields. J. Freshw. Ecol. 2006, 21, 649–656. [Google Scholar]
- DPR, Department of Pesticide Regulation. Summary of Pesticide Use Report Data. 2015. Available online: https://www.pesticidereform.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/ex_sum_15.pdf (accessed on 5 November 2016).
- Espino, L. TPS Control Issues. University of California, Agriculture and Natural Resources (UCANR) UC Rice Blog, California Rice Production. 2016. Available online: https://ucanr.edu/blogs/blogcore/postdetail.cfm?postnum=21130/ (accessed on 14 February 2019).
- Fischer, D.C. Rate of Evolution in Living Fossils. In Paleobiology; Briggs, D.E.G., Krauther, P.R., Eds.; Blackwell Scientific: London, UK, 1990; pp. 152–159. [Google Scholar]
- Mantovani, B.; Cesar, M.; Scanabissi, F. Molecular taxonomy and phylogeny of the ‘living fossil’ lineages Triops and Lepidurus (Branchiopoda: Notostraca) Academy of Science and Letter. Zool. Scr. 2004, 33, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boix, D.; Sala, J.; Gascón, S.; Brucet, S. Predation in a Temporary pond with special attention to the trophic role of Triops cancriformis (Crustacea: Branchiopoda: Notostraca). Hydrobiologia 2006, 571, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hengherr, S.; Heyer, A.G.; Brümmer, F.; Schill, R.O. Trehalose and Vitreous States: Desiccation Tolerance of Dormant Stages of the Crustaceans Triops and Daphnia. J. Physiol. Biochem. Zool. 2011, 84, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Igarishi, K. Ecological studies on Triops longicaudatus (Notostraca) inhabiting Shonai District, Japan. J. Yamagata Agric. Soc. 1970, 23, 33–39. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, S.R.; Grigarick, A.A. Laboratory studies of factors affecting egg hatch of Triops longicaudatus (LeConte) (Notostraca: Triopsidae). Hydrobiologia 1979, 63, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fry, L.L.; Mulla, M.S. Effect of drying period and soil moisture on egg hatch of the tadpole shrimp (Notostraca: Triopsidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 1992, 85, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, J.M.; Madison, D. The Ontogeny of Light-Dark Response in Triops longicaudatus as a Response to Changing Selective Pressures. Crustaceana 2000, 73, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloese, J.B.; Goding, K.M.; Godfrey, L.D. Alternative Chemical Control Options and Monitoring Techniques for Triops longicaudatus (Notostraca: Triopsidae) in California Rice. J. Econ. Entomol. 2022, 115, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aghaee, M.A.; Godfrey, L.D. The Efficacy of Bacillus thuringiensis spp. Galleriae Against Rice Water Weevil (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) for Integrated Pest Management in California Rice. J. Econ. Entomol. 2015, 108, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aghaee, M.A.; Espino, L.; Goding, K.M.; Goldman, E.; Godfrey, L.D. Effects of Seeding Rates and Rice Water Weevil (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) Density on Damage in Two Medium Grain Varieties of Rice. J. Econ. Entomol. 2016, 109, 667–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- California Mosquito & Vector Control. Controlling Mosquitoes with Mosquito Fish. Clarkcountynv.gov. 1991. Available online: https://webfiles.clarkcountynv.gov/Public%20Works/Vector/Controlling%20Mosquitoes%20with%20Mosquito%20Fish.pdf (accessed on 2 March 2021).
- Pyke, G.H. A review of the biology of Gambusia affinis and G. holbrooki. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2005, 15, 339–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, R.G. Temperature tolerance of the mosquitofish, Gambusia affinis (Baird and Girard). J. Fish Biol. 1973, 5, 575–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stearns, S.C.; Sage, R.D. Maladaption in a marginal population of the mosquito fish Gambusia affinis. Evolution 1980, 34, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miura, T.; Takahashi, R.M.; Wilder, W.H. Impact of the mosquito fish (Gambusia affinis) on a rice field ecosystem when used as a mosquito control agent. Mosq. News. 1984, 44, 510–517. [Google Scholar]
- Bence, J.R.; Murdoch, W.W. Prey size selection by the mosquitofish Gambusia affinis relation to optimal diet theory. Ecology 1986, 67, 324–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurtsbaugh, W.; Cech, J.J.; Compton, J. Effect of fish size on prey size selection in Gambusia affinis. Proc. Calif. Mosq. Vector Control Assoc. 1980, 48, 48–51. [Google Scholar]
- Farley, D.G.; Younce, L.C. Stocking date versus efficacy of Gambusia affinis in Fresno County rice fields. Proc. Calif. Mosq. Vector Control Assoc. 1977, 45, 83–86. [Google Scholar]
- Hoy, J.B.; Reed, D.E. Biological control of Culex tarsalis in a California rice field. Mosq. News. 1970, 30, 222–230. [Google Scholar]
- Hoy, J.B.; Reed, D.E. The efficacy of mosquitofish for control of Culex tarsalis in California rice fields. Mosq. News. 1971, 31, 567–572. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).