Effect of Dietary Supplementation of Enteric Avian-Origin Lactobacillus casei-Fermented Soybean Meal on the Growth Performance and Intestinal Health of Broiler Chickens
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Fermented Soybean Meal
2.2. Experimental Birds and Diets
2.3. Performance and Sample Collection
2.4. Meat Color Measurements
2.5. Morphometric Analysis of the Intestine
2.6. Oxidative Damage and Immune Barrier in the Intestine
2.7. RNA Extraction and Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Amplification
2.8. Microbiological Analysis of the Cecum Microbiota
2.9. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Comparison and Screening of Fermentation Effects of Different Intestinal Probiotics in Chickens
3.2. Effect of Incorporating Varying Levels of Fermented Soybean Meal into Diets on the Growth Performance of Broiler Chickens
3.3. Effect of Incorporating Varying Levels of Fermented Soybean Meal into Diets on the Slaughter Performance and Meat Color of Broiler Chickens
3.4. Effect of Incorporating Varying Levels of Fermented Soybean Meal into Diets on the Intestinal Morphology of Broiler Chickens
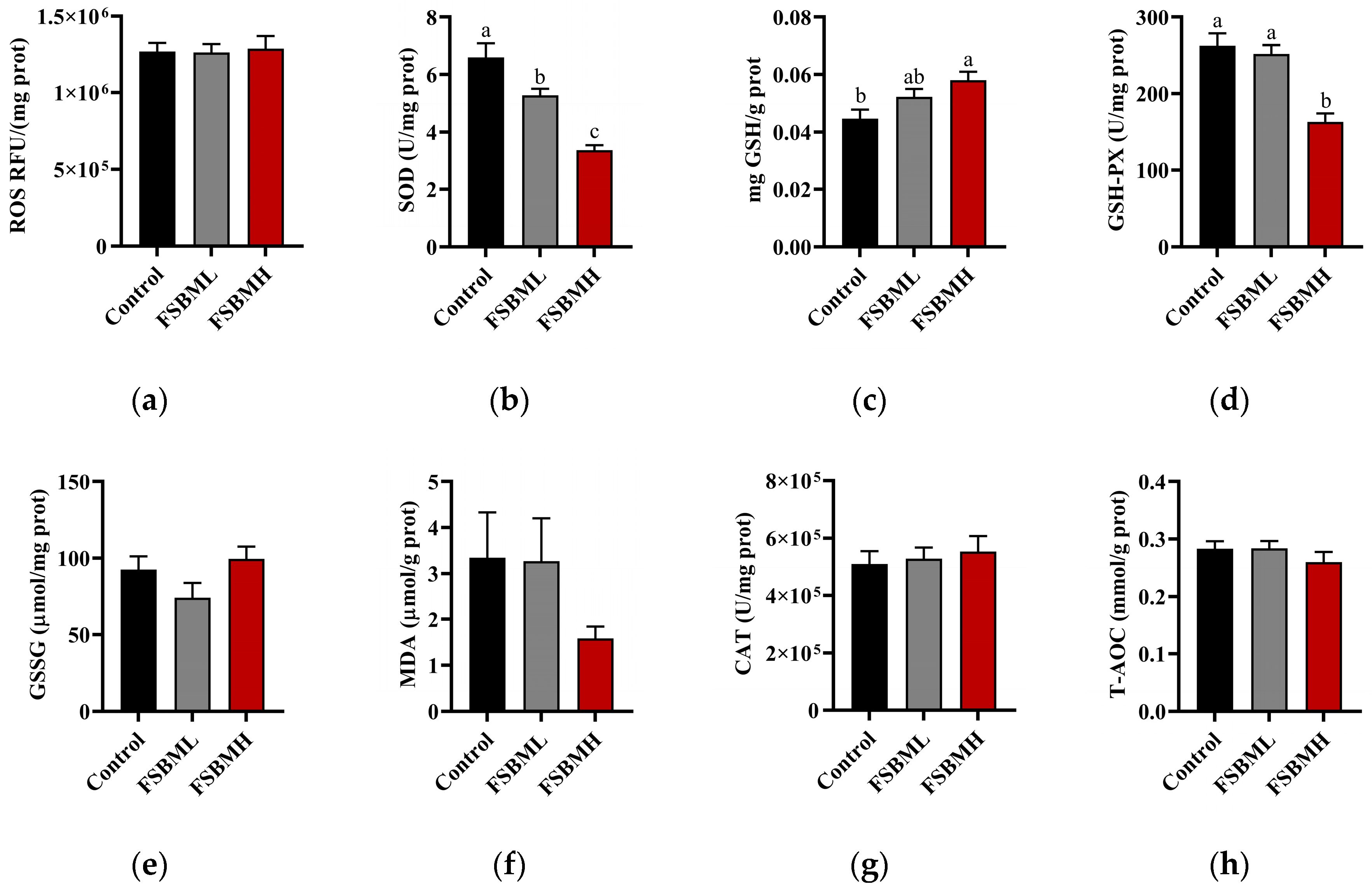
3.5. Effect of Fermented Soybean Meal on Oxidative Damage in the Ileal Intestine of Broiler Chickens
3.6. Effect of Fermented Soybean Meal on the Integrity of the Ileal Intestinal Barrier in Broiler Chickens
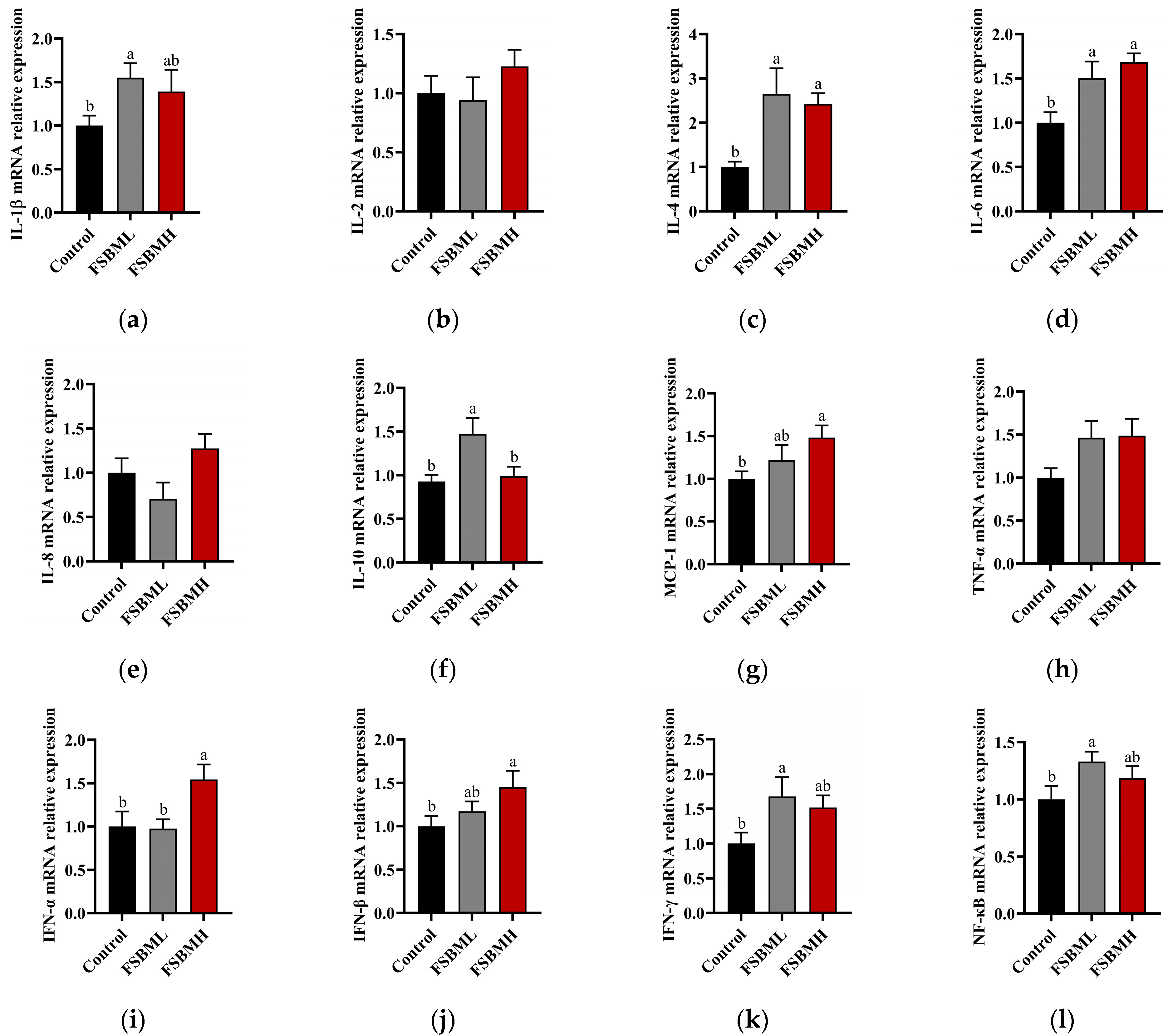
3.7. Effect of Fermented Soybean Meal on Intestinal Inflammation and Immune Factor Expression in Broiler Chickens
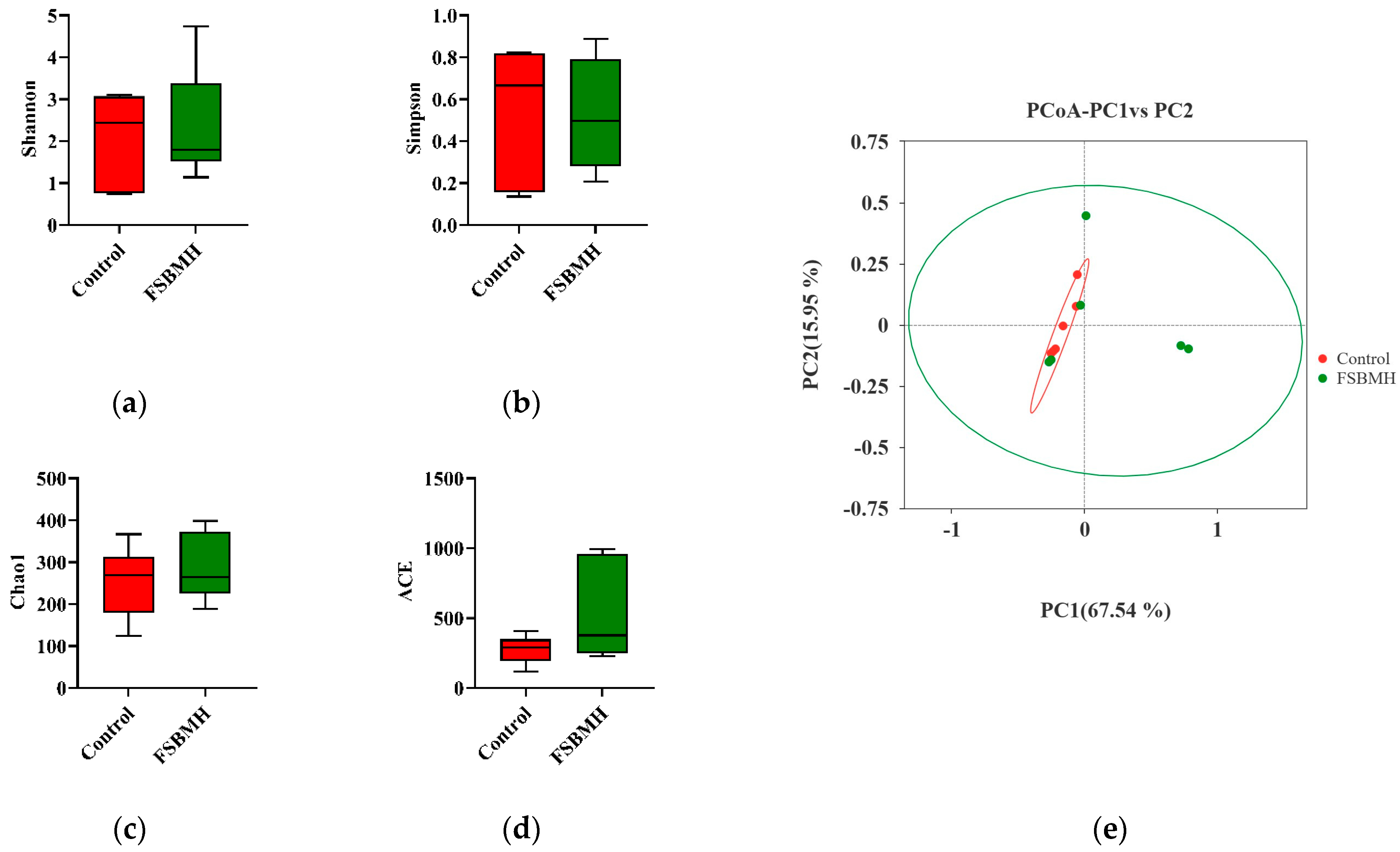
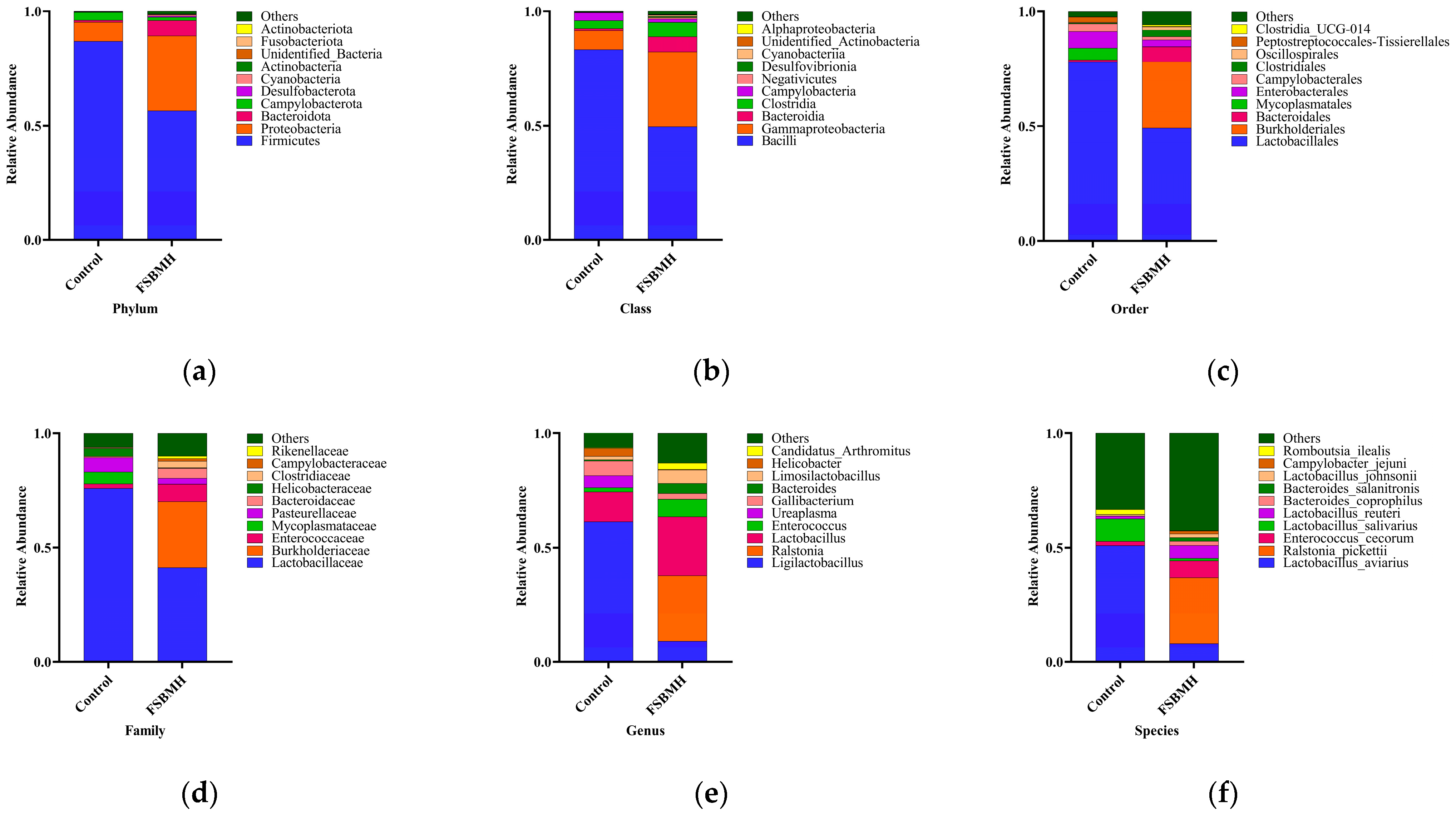
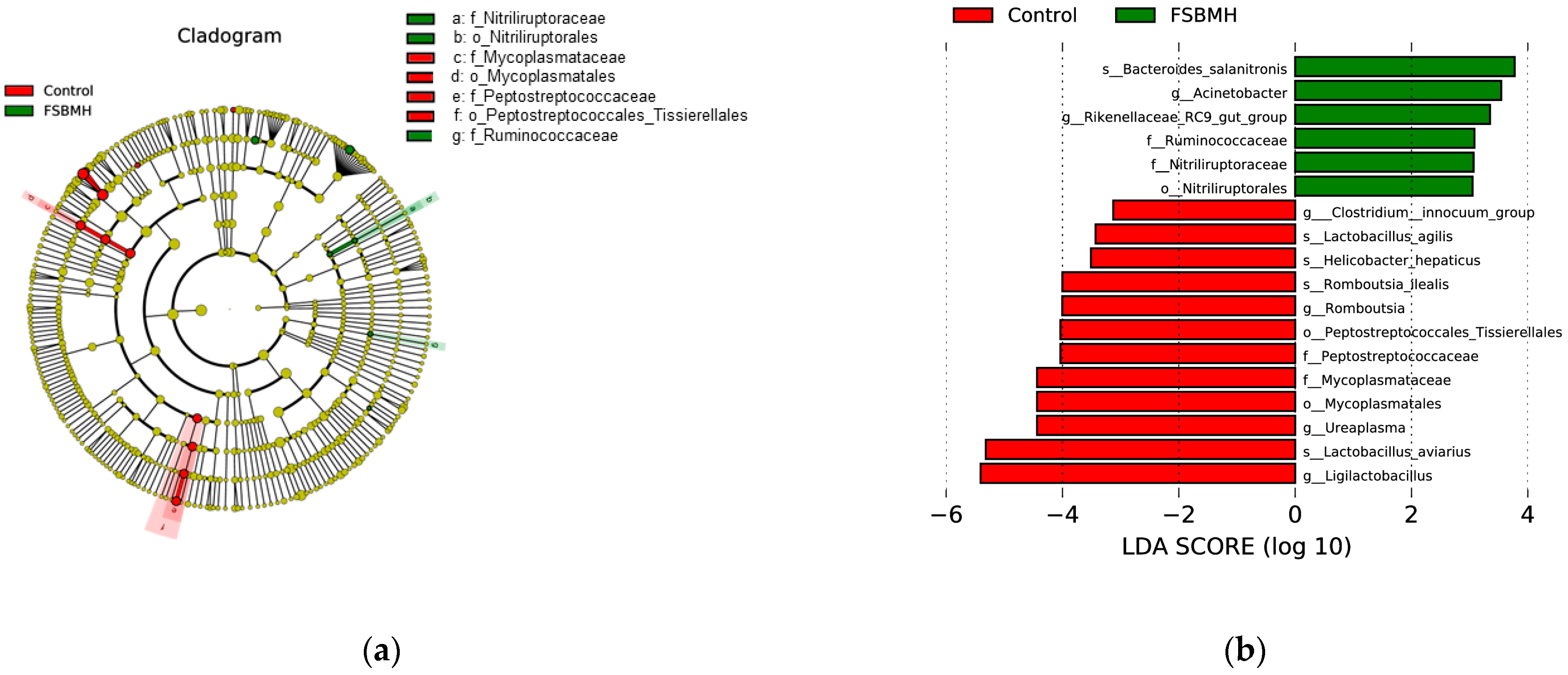
3.8. Effect of Fermented Soybean Meal on the Cecal Microbiota of Broiler Chickens
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparison and Screening of Fermentation Effects of Different Intestinal Probiotics in Chickens
4.2. Effect of Incorporating Varying Levels of Fermented Soybean Meal into Diets on the Growth Performance of Broiler Chickens
4.3. Effect of Incorporating Varying Levels of Fermented Soybean Meal into Diets on the Slaughter Performance and Meat Color of Broiler Chickens
4.4. Effect of Incorporating Varying Levels of Fermented Soybean Meal into Diets on the Intestinal Morphology of Broiler Chickens
4.5. Effect of Fermented Soybean Meal on Oxidative Damage in the Ileal Intestine of Broiler Chickens
4.6. Effect of Fermented Soybean Meal on the Integrity of the Ileal Intestinal Barrier in Broiler Chickens
4.7. Effect of Fermented Soybean Meal on Intestinal Inflammation and Immune Factor Expression in Broiler Chickens
4.8. Effect of Fermented Soybean Meal on the Cecal Microbiota of Broiler Chickens
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shi, C.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, Y.; Wang, C.; Lu, Z.; Wang, F.; Feng, J.; Wang, Y. Amino acid and phosphorus digestibility of fermented corn-soybean meal mixed feed with Bacillus subtilis and Enterococcus faecium fed to pigs. J. Anim. Sci. 2017, 95, 3996–4004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, H.; Zhao, H.; Lu, F.; Zhang, C.; Bie, X.; Lu, Z. Improvement of the Nutritional Quality and Fibrinolytic Enzyme Activity of Soybean Meal by Fermentation of Bacillus subtilis. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2015, 39, 1235–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, C.; Ju, H.K.; Kim, S.C.; Park, J.H.; Lim, J.; Kwon, S.W.; Lee, J. Determination of bioactive compounds in fermented soybean products using GC/MS and further investigation of correlation of their bioactivities. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2012, 880, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Yan, G.; Meng, X.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Z.; Zhou, S.; Li, G.; Zhang, Q.; Wei, X. Effects of Lactobacillus plantarum and Pediococcus acidilactici co-fermented feed on growth performance and gut microbiota of nursery pigs. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 1076906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Missotten, J.A.; Michiels, J.; Degroote, J.; De Smet, S. Fermented liquid feed for pigs an ancient technique for the future. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2015, 6, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasabe, J.; Suzuki, M. Emerging Role of D-Amino Acid Metabolism in the Innate Defense. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallejo-Cordoba, B.; Castro-López, C.; García, H.S.; González-Córdova, A.F.; Hernández-Mendoza, A. Postbiotics and paraprobiotics: A review of current evidence and emerging trends. In Probiotic and Prebiotics in Foods: Challenges, Innovations and Advances; Advances in Food and Nutrition Research; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 1–34. [Google Scholar]
- Szliszka, E.; Czuba, Z.P.; Domino, M.; Mazur, B.; Zydowicz, G.; Krol, W. Ethanolic Extract of Propolis (EEP) Enhances the Apoptosis- Inducing Potential of TRAIL in Cancer Cells. Molecules 2009, 14, 738–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, H.S.; Park, S.Y.; Lee, D.K.; Kim, S.A.; An, H.M.; Kim, J.R.; Kim, M.J.; Cha, M.G.; Lee, S.W.; Kim, K.J.; et al. Hypocholesterolemic effect of sonication-killed Bifidobacterium longum isolated from healthy adult Koreans in high cholesterol fed rats. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2010, 33, 1425–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teame, T.; Wang, A.; Xie, M.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Ding, Q.; Gao, C.; Olsen, R.E.; Ran, C.; Zhou, Z. Paraprobiotics and Postbiotics of Probiotic Lactobacilli, Their Positive Effects on the Host and Action Mechanisms: A Review. Front. Nutr. 2020, 7, 570344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.L.; Kho, W.L.; You, S.H.; Yeh, R.H.; Tang, S.W.; Hsieh, C.W. Effects of Bacillus subtilis var. natto and Saccharomyces cerevisiae mixed fermented feed on the enhanced growth performance of broilers. Poult. Sci. 2009, 88, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Liu, X.; Xu, Z.R.; Wang, Y.Z.; Liu, J.X. Effects of Fermented Soybean Meal on Digestive Enzyme Activities and Intestinal Morphology in Broilers. Poult. Sci. 2007, 86, 1149–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.; Liu, X.; Xu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Lu, Y. Effects of Aspergillus oryzae 3.042 fermented soybean meal on growth performance and plasma biochemical parameters in broilers. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2007, 134, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Wu, H.; Xie, J.; Zeng, T.; Hao, L.; Xu, W.; Lu, L. The Effects of Fermented Feed on the Growth Performance, Antioxidant Activity, Immune Function, Intestinal Digestive Enzyme Activity, Morphology, and Microflora of Yellow-Feather Chickens. Animals 2023, 13, 3545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Chen, D.; Cai, H.; Chang, W.; Wang, Z.; Liu, G.; Deng, X.; Chen, Z. Effects of Fermenting the Plant Fraction of a Complete Feed on the Growth Performance, Nutrient Utilization, Antioxidant Functions, Meat Quality, and Intestinal Microbiota of Broilers. Animals 2022, 12, 2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Missotten, J.A.M.; Goris, J.; Michiels, J.; Van Coillie, E.; Herman, L.; De Smet, S.; Dierick, N.A.; Heyndrickx, M. Screening of isolated lactic acid bacteria as potential beneficial strains for fermented liquid pig feed production. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2009, 150, 122–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.-H.; Yu, B.; Jang, S.-H.; Tsen, H.-Y. Different probiotic properties for Lactobacillus fermentum strains isolated from swine and poultry. Anaerobe 2007, 13, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Lin, Z.; Ali, M.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Li, K.; Kebzhai, F.; Li, J. Effects of lactic acid bacteria isolated from Tibetan chickens on the growth performance and gut microbiota of broiler. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1171074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, W.; Talpur, M.Z.; Zeng, Y.; Xie, P.; Li, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, L.; Zhu, X.; Gao, P.; Jiang, Q.; et al. Influence of fermented feed additive on gut morphology, immune status, and microbiota in broilers. BMC Vet. Res. 2022, 18, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NRCU. Nutrient Requirements of Poultry; National Academy Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, J.; Yi, H.; Gyawali, I.; Lu, J.; Guo, S.; Ji, Y.; et al. Smooth muscle AKG/OXGR1 signaling regulates epididymal fluid acid–base balance and sperm maturation. Life Metab. 2022, 1, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canibe, N.; Jensen, B.B. Fermented and nonfermented liquid feed to growing pigs effect on aspects of gastrointestinal ecology and growth performance. J. Anim. Sci. 2003, 81, 2019–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeddargahi, F.; Darmani Kuhi, H.; Rafiei, F.; Roostaie-Alimehr, M.; Takalu, Z.; Sajedi, R.H.; Mohammadpour, F. The effect of probiotic and fermented soybean meal based on Bacillus subtilis spore on growth performance, gut morphology, immune response and dry matter digestibility in broiler chickens. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2022, 21, 1642–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Feng, J.; Wang, Y.; Lv, J.; Li, J.; Guo, L.; Min, Y. Fermented Corn-Soybean Meal Mixed Feed Modulates Intestinal Morphology, Barrier Functions and Cecal Microbiota in Laying Hens. Animals 2021, 11, 3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Zhang, B.; Li, J.; Zhu, L. Effects of fermented feed on growth performance, immune response, and antioxidant capacity in laying hen chicks and the underlying molecular mechanism involving nuclear factor-κb. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 2573–2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Xin, H.; Yang, C.; Yang, X. Impact of essential oils and organic acids on the growth performance, digestive functions and immunity of broiler chickens. Anim. Nutr. 2018, 4, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunkley, K.D.; Dunkley, C.S.; Njongmeta, N.L.; Callaway, T.R.; Hume, M.E.; Kubena, L.F.; Nisbet, D.J.; Ricke, S.C. Comparison of In Vitro Fermentation and Molecular Microbial Profiles of High-Fiber Feed Substrates Incubated with Chicken Cecal Inocula. Poult. Sci. 2007, 86, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcone, G.L.; Rosini, E.; Crespi, E.; Pollegioni, L. D-amino acids in foods. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 104, 555–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Li, Z.; Wang, C.; Fu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Lu, Z. Effects of fermented feed supplementation on pig growth performance: A meta-analysis. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2020, 259, 114315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiharto, S.; Ranjitkar, S. Recent advances in fermented feeds towards improved broiler chicken performance, gastrointestinal tract microecology and immune responses: A review. Anim. Nutr. 2019, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim, M.M.; Leyva-Jimenez, H.E.; Al-Ajeeli, M.N.; Jameel, Y.J.; Gaydos, T.A.; Bailey, C.A. Performance of broilers fed diets supplemented with two yeast cell wall strains using two feeding strategies. Vet. Med. Sci. 2019, 5, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhang, H.; Li, S.; Jiang, Y.; Kang, L.; Deng, J.; Yang, C.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, J.; Jiang, L.; et al. The effects of fermented feedstuff derived from Citri Sarcodactylis Fructus by-products on growth performance, intestinal digestive enzyme activity, nutrient utilization, meat quality, gut microbiota, and metabolites of broiler chicken. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1231996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Wan, X.L.; Zhang, X.H.; Zhao, L.G.; He, J.T.; Zhang, J.F.; Zhang, L.L.; Wang, T. Effect of supplemental fermented Ginkgo biloba leaves at different levels on growth performance, meat quality, and antioxidant status of breast and thigh muscles in broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 2017, 96, 869–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Sun, X.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y. Age-associated changes in the growth development of abdominal fat and their correlations with cecal gut microbiota in broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 2023, 102, 102900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, X.; Li, H.; Wen, Z.; Hou, Y.; Wang, G.; Fan, J.; Qian, L. Effects of fermented tea residue on fattening performance, meat quality, digestive performance, serum antioxidant capacity, and intestinal morphology in fatteners. Animals 2020, 10, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, J.; Guo, L.; Chen, B.; Hao, K.; Ma, H.; Liu, Y.; Min, Y. Effects of different probiotic fermented feeds on production performance and intestinal health of laying hens. Poult. Sci. 2021, 101, 101570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, H.; Luo, J.; Chen, T.; Xi, Q.; Sun, J.; Wei, L.; Zhang, Y. Synergism of fermented feed and ginseng polysaccharide on growth performance, intestinal development, and immunity of Xuefeng black-bone chickens. BMC Vet. Res. 2024, 20, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Deng, Q.; Song, D.; Wang, W.; Zhou, H.; Wang, L.; Li, A. Effects of fermented cottonseed meal on growth performance serum biochemical parameters immune functions antioxidative abilities and cecal microfl. Food Agric. Immunol. 2017, 28, 725–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, K.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, J.; He, J.; Zhang, L.; Wang, T. Supplemental effects of probiotic Bacillus subtilis fmbJ on growth performance, antioxidant capacity, and meat quality of broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 2017, 96, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagano, T.; Yamao, S.; Terachi, A.; Yarimizu, H.; Itoh, H.; Katasho, R.; Kawai, K.; Nakashima, A.; Iwasaki, T.; Kikkawa, U.; et al. d-amino acid oxidase promotes cellular senescence via the production of reactive oxygen species. Life Sci. Alliance 2019, 2, e201800045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murtas, G.; Sacchi, S.; Tedeschi, G.; Maffioli, E.; Notomista, E.; Cafaro, V.; Abbondi, M.; Mothet, J.P.; Pollegioni, L. Antimicrobial D-amino acid oxidase-derived peptides specify gut microbiota. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2021, 78, 3607–3620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, V.H.; Kan, L.; Huang, J.; Geng, Y.; Zhen, W.; Guo, Y.; Abbas, W.; Wang, Z. Waseem Abbas and Zhong Wang. Dietary encapsulated essential oils and organic acids mixture improves gut health in broiler chickens challenged with necrotic enteritis. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2020, 11, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, B.; Zeng, Z.; Liu, R.; Tang, L.; Gong, L.; Li, W. Effects of probiotics Lactobacillus plantarum 16 and Paenibacillus polymyxa 10 on intestinal barrier function, antioxidative capacity, apoptosis, immune response, and biochemical parameters in broilers. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 5028–5039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Zhang, H.; Li, S.; Jiang, Y.; Deng, J.; Yang, C.; Chen, X.; Jiang, L. Effects of different levels of Citri Sarcodactylis Fructus by-products fermented feed on growth performance, serum biochemical, and intestinal health of cyan-shank partridge birds. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 20130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, C.F.; Lin, L.J.; Wang, C.H.; Tsai, C.S.; Chang, S.C.; Lee, T.T. Assessment of Intestinal Immunity and Permeability of Broilers on Partial Replacement Diets of Two-Stage Fermented Soybean Meal by Bacillus velezensis and Lactobacillus brevis ATCC 367. Animals 2021, 11, 2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, J. d-Amino Acids and Lactic Acid Bacteria. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, J.; Shi, J.; Liu, K.; Li, A.; He, B.; Wang, Y.; Duan, T.; Wang, Y.; He, J. Effects of Solid-State Fermented Wheat Bran on Growth Performance, Immune Function, Intestinal Morphology and Microflora in Lipopolysaccharide-Challenged Broiler Chickens. Animals 2022, 12, 1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamilla, A.; Ruiz-Ruiz, S.; Artacho, A.; Pons, J.; Messina, A.; Lucia Randazzo, C.; Caggia, C.; Lanza, M.; Moya, A. Analysis of the Microbial Intestinal Tract in Broiler Chickens during the Rearing Period. Biology 2021, 10, 942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Zhong, G.; Shao, D.; Wang, Q.; Hu, Y.; Wu, T.; Ji, C.; Shi, S. Dietary supplementation with Bacillus subtilis promotes growth performance of broilers by altering the dominant microbial community. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 100935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, Z.; Yousaf, M.Z.; Gilani, S.M.H.; Zehra, S.; Ali, A.; Azhar, A.; Galani, S. Comparative analysis of chicken cecal microbial diversity and taxonomic composition in response to dietary variation using 16S rRNA amplicon sequencing. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2021, 48, 7203–7214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisinin, V.I.; Il’ina, L.A.; Iyldyrym, E.A.; Nikonov, I.N.; Filippova, V.A.; Laptev, G.Y.; Novikova, N.I.; Grozina, A.A.; Lenkova, T.N.; Manukyan, V.A.; et al. Broiler chicken cecal microbiocenoses depending on mixed fodder. Microbiology 2016, 85, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabour, S.; Tabeidian, S.A.; Sadeghi, G. Dietary organic acid and fiber sources affect performance, intestinal morphology, immune responses and gut microflora in broilers. Anim. Nutr. 2019, 5, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Wang, T.; Aschalew, N.D.; Zhao, W.; Chen, X.; Zhang, X.F.; Zhen, Y.G.; Qin, G.X. Effects of yeast cultures with different fermentation times on the growth performance, caecal microbial community and metabolite profile of broilers. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2020, 104, 212–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.C.; Yu, Y.H. Bacillus licheniformis-fermented products improve growth performance and the fecal microbiota community in broilers. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 1432–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.-D.; Tian, Y.; Jiao, J.-Y.; Zhang, X.-T.; Zhang, Y.-G.; Dong, Z.-Y.; Xiong, M.-J.; Xiao, M.; Shu, W.-S.; Li, W.-J. Comparative genomics analysis of Nitriliruptoria reveals the genomic differences and salt adaptation strategies. Extremophiles 2019, 24, 249–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, M.; Su, N.; Zhang, T.; Chen, L.; Wei, W.; Luo, J.; et al. Quantitative Proteomics Reveals Membrane Protein-Mediated Hypersaline Sensitivity and Adaptation in Halophilic Nocardiopsis xinjiangensis. J. Proteome Res. 2015, 15, 68–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Weirdt, R.; Van de Wiele, T. Micromanagement in the gut: Microenvironmental factors govern colon mucosal biofilm structure and functionality. npj Biofilms Microbiomes 2015, 1, 15026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Sim, J.X.Y.; Lee, W.L.; Cui, L.; Chan, Y.F.Z.; Chang, E.D.; Teh, Y.E.; Zhang, A.-N.; Armas, F.; Chandra, F.; et al. Gut Ruminococcaceae levels at baseline correlate with risk of antibiotic-associated diarrhea. iScience 2022, 25, 103644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Items | Finisher Diet (22 d–42 d) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ingredients (%) | Control | FSBML | FSBMM | FSBMH |
| Corn | 65.80 | 65.78 | 65.68 | 65.49 |
| Soybean meal (46%) | 23.40 | 23.40 | 23.35 | 23.28 |
| Corn gluten powder | 5.00 | 5.00 | 4.99 | 4.98 |
| Soybean Oil | 2.10 | 2.10 | 2.10 | 2.09 |
| FSBM | 0 | 0.02 | 0.20 | 0.50 |
| Limestone | 1.20 | 1.20 | 1.20 | 1.19 |
| Calcium hydrogen phosphate | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Salt | 0.17 | 0.17 | 0.16 | 0.16 |
| Propionic acid antifungal agent 4 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 |
| Premix of trace elements 1 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10 |
| Vitamin premix 2 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 |
| L-Lysine | 0.36 | 0.36 | 0.36 | 0.36 |
| DL Methionine | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.14 | 0.14 |
| L-Threonine | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 |
| Choline chloride | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10 |
| Antioxidants | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| Heat-resistant phytase 4 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| AB enzyme complex 3 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| Sodium humate | 0.21 | 0.21 | 0.21 | 0.21 |
| Mannanase (K302) 4 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| Sodium bicarbonate | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.15 |
| Zeolite 4 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10 |
| Total | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| Nutrient content 5 | ||||
| Metabolizable energy (kcal/kg) | 3050.00 | 3051.00 | 3056.00 | 3066.00 |
| Crude protein (%) | 19.19 | 19.19 | 19.24 | 19.33 |
| Calcium (%) | 0.76 | 0.76 | 0.76 | 0.76 |
| Available phosphorus (%) | 0.49 | 0.49 | 0.49 | 0.49 |
| Lysine (%) | 1.10 | 1.10 | 1.10 | 1.10 |
| Methionine (%) | 0.41 | 0.41 | 0.41 | 0.41 |
| Methionine + cystine (%) | 0.84 | 0.84 | 0.84 | 0.84 |
| Threonine (%) | 0.79 | 0.79 | 0.79 | 0.79 |
| Tryptophan (%) | 0.22 | 0.22 | 0.22 | 0.22 |
| Genes | Sequence Type-Probe/Primer Sequence | Tm | Product Length | Accession Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| β-Actin | forward 5′-CTGTGCCCATCTATGAAGGCTA-3′ | 60 °C | 139 bp | NM_205518.2 |
| reverse 5′-ATTTCTCTCTCGGCTGTGGTG-3′ | ||||
| ZO-1 | forward 5′-TCATCCTTACCGCCGCATAT-3′ | 60 °C | 206 bp | XM_046925214.1 |
| reverse 5′-GTTGACTGCTCGTACTCCCT-3′ | ||||
| ZO-2 | forward 5′-AGTCCACCTCCAGCATTCAA-3′ | 60 °C | 165 bp | XM_046934796.1 |
| reverse 5′-CACAGAAACAGGTGGTGGTG-3′ | ||||
| Claudin-1 | forward 5′-TGGAGGATGACCAGGTGAAG-3′ | 60 °C | 137 bp | NM_001013611.2 |
| reverse 5′-TGTGAAAGGGTCATAGAAGG-3′ | ||||
| Claudin-2 | forward 5′-CGCTCGTATCTCTTGCTTGG-3′ | 60 °C | 185 bp | NM_001277622.1 |
| reverse 5′-AGAGTATGGCTGTGACGAGG-3′ | ||||
| IL-1β | forward 5′-GCTTCATCTTCTACCGCCTG-3′ | 60 °C | 161 bp | XM_046931582.1 |
| reverse 5′-ACTTAGCTTGTAGGTGGCGA-3′ | ||||
| IL-2 | forward 5′-CAAGAGTCTTACGGGTCTAAATCAC-3′ | 60 °C | 100 bp | NM_204153.2 |
| reverse 5′-GTTGGTCAGTTCATGGAGAAAATC-3′ | ||||
| IL-4 | forward 5′-GTGCCCACGCTGTGCTTAC-3′ | 60 °C | 82 bp | NM_001007079.2 |
| reverse 5′-AGGAAACCTCTCCCTGGATGTC-3′ | ||||
| IL-6 | forward 5′-AAATCCCTCCTCGCCAATCT-3′ | 60 °C | 106 bp | NM_204628.2 |
| reverse 5′-CCCTCACGGTCTTCTCCATAAA-3′ | ||||
| IL-8 | forward 5′-ATTCAAGATGTGAAGCTGAC-3′ | 60 °C | 301 bp | NM_205498.2 |
| reverse 5′-AGGATCTGCAATTAACATGAGG-3′ | ||||
| IL-10 | forward 5′-CGCTGTCACCGCTTCTTCA-3′ | 60 °C | 88 bp | NM_001004414.4 |
| reverse 5′-TCCCGTTCTCATCCATCTTCTC-3′ | ||||
| IFN-α | forward 5′-TTCAGCTGCCTCCACACCTT-3′ | 60 °C | 101 bp | XM_046936231.1 |
| reverse 5′-TTGTGGATGTGCAGGAACCA-3′ | ||||
| IFN-β | forward 5′-CAGCTCTCACCACCACCTTCTC-3′ | 60 °C | 100 bp | NM_001024836.2 |
| reverse 5′-GGAGGTGGAGCCGTATTCTG-3′ | ||||
| IFN-γ | forward 5′-GACAAGTCAAAGCCGCACA-3′ | 60 °C | 127 bp | NM_205149.2 |
| reverse 5′-TCAAGTCGTTCATCGGGAGC-3′ | ||||
| TNF-α | forward 5′-TGTTCTATGACCGCCCAGTT-3′ | 60 °C | 164 bp | XM_046927265.1 |
| reverse 5′-AGCATCAACGCAAAAGGGAA-3′ | ||||
| Occludin | forward 5′-CTTCAGGTGTTTCTCTTCCTCCTC-3′ | 60 °C | 131 bp | XM_040680624.2 |
| reverse 5′-CTGTGGTTTCATGGCTGGA-3′ | ||||
| NF-κB | forward 5′-GAAGGAATCGTACCGGGAACA-3′ | 60 °C | 131 bp | XM_046915553.1 |
| reverse 5′-CTCAGAGGGCCTTGTGACAGTAA-3′ |
| Items | Control 2 | FSBML 2 | FSBMM 2 | FSBMH 2 | SEM | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial BW 1 (g) | 451.61 | 449.48 | 449.30 | 448.51 | 4.03 | 0.994 |
| Final BW 1 (g) | 1468.11 b | 1539.88 ab | 1517.75 ab | 1626.02 a | 19.28 | 0.036 |
| ADFI 1 (g/d) | 97.61 b | 109.97 a | 107.61 a | 111.25 a | 1.41 | 0.002 |
| ADG 1 (g/d) | 48.37 b | 51.90 ab | 50.96 b | 56.06 a | 0.82 | 0.011 |
| FCR 1 (g/g) | 2.04 | 2.06 | 2.13 | 2.05 | 0.47 | 0.741 |
| Items | Control 1 | FSBML 1 | FSBMH 1 | SEM | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liver percentage/% | 2.02 | 1.91 | 2.06 | 0.39 | 0.278 |
| Spleen percentage/% | 0.25 | 0.24 | 0.21 | 0.15 | 0.485 |
| Abdominal fat percentage/% | 0.94 c | 1.21 b | 1.65 a | 0.65 | 0.000 |
| Breast muscle percentage/% | 13.58 | 14.01 | 13.33 | 0.16 | 0.226 |
| Thigh muscle percentage/% | 15.33 ab | 15.78 a | 14.84 b | 0.16 | 0.043 |
| Breast muscle luminance /L* | 50.52 | 50.985 | 50.98 | 0.36 | 0.838 |
| Breast muscle redness/a* | 7.21 | 6.85 | 7.53 | 0.20 | 0.376 |
| Breast muscle yellowness/b* | 10.27 | 10.44 | 10.31 | 0.24 | 0.956 |
| Thigh muscle luminance /L* | 57.3 | 56.53 | 56.01 | 0.42 | 0.462 |
| Thigh muscle redness/a* | 11.82 b | 13.62 a | 13.99 a | 0.32 | 0.011 |
| Thigh muscle yellowness/b* | 11.81 | 11.98 | 11.09 | 0.25 | 0.303 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, J.; Yang, X.; Liu, T.; Wang, R.; Chen, X.; Yang, H.; Mo, Z.; Han, D.; et al. Effect of Dietary Supplementation of Enteric Avian-Origin Lactobacillus casei-Fermented Soybean Meal on the Growth Performance and Intestinal Health of Broiler Chickens. Agriculture 2024, 14, 844. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14060844
Zhu Y, Li J, Liu J, Yang X, Liu T, Wang R, Chen X, Yang H, Mo Z, Han D, et al. Effect of Dietary Supplementation of Enteric Avian-Origin Lactobacillus casei-Fermented Soybean Meal on the Growth Performance and Intestinal Health of Broiler Chickens. Agriculture. 2024; 14(6):844. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14060844
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Yunlong, Jincheng Li, Jiaxin Liu, Xue Yang, Tingting Liu, Ran Wang, Xiaoting Chen, Huisi Yang, Ziyi Mo, Dongyue Han, and et al. 2024. "Effect of Dietary Supplementation of Enteric Avian-Origin Lactobacillus casei-Fermented Soybean Meal on the Growth Performance and Intestinal Health of Broiler Chickens" Agriculture 14, no. 6: 844. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14060844
APA StyleZhu, Y., Li, J., Liu, J., Yang, X., Liu, T., Wang, R., Chen, X., Yang, H., Mo, Z., Han, D., Jiang, Q., & Shu, G. (2024). Effect of Dietary Supplementation of Enteric Avian-Origin Lactobacillus casei-Fermented Soybean Meal on the Growth Performance and Intestinal Health of Broiler Chickens. Agriculture, 14(6), 844. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14060844






