Biosolid Mixtures Applied in Tropical Soils and Their Effect on Coriandrum sativum and Ocimum basilicum Nutritional Uptake
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Soil, Compost, and Sludge Mixtures
2.2. Soil Mixture pH
2.3. Soil Mixtures’ Electrical Conductivity
2.4. Plants’ Germination and Harvest
2.5. Nutrient Quantification in Plant Tissues
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of Biosolid Incorporation (Compost and Sludge) into Voladora and Coloso Soils on pH and Electric Conductivity
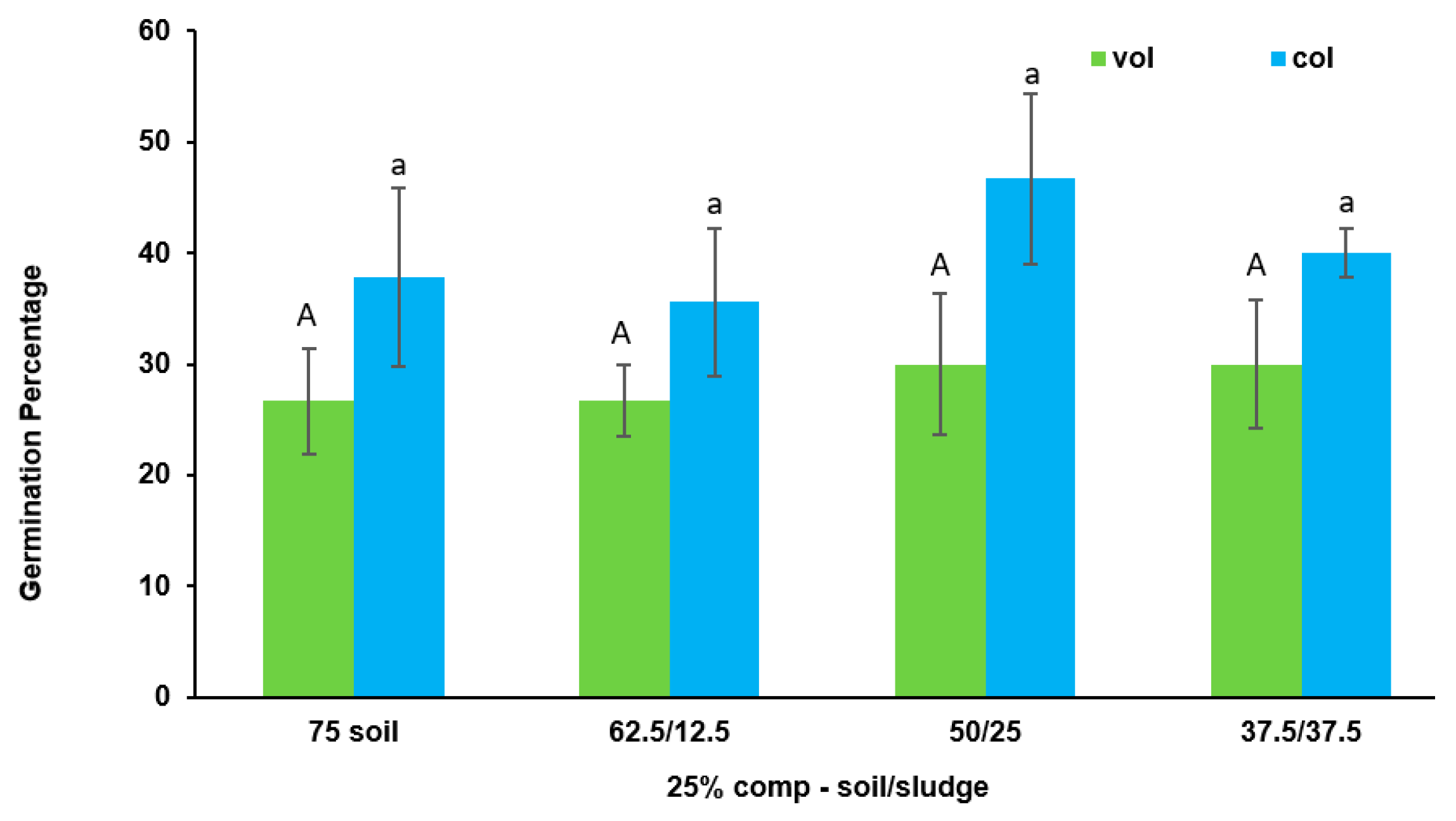
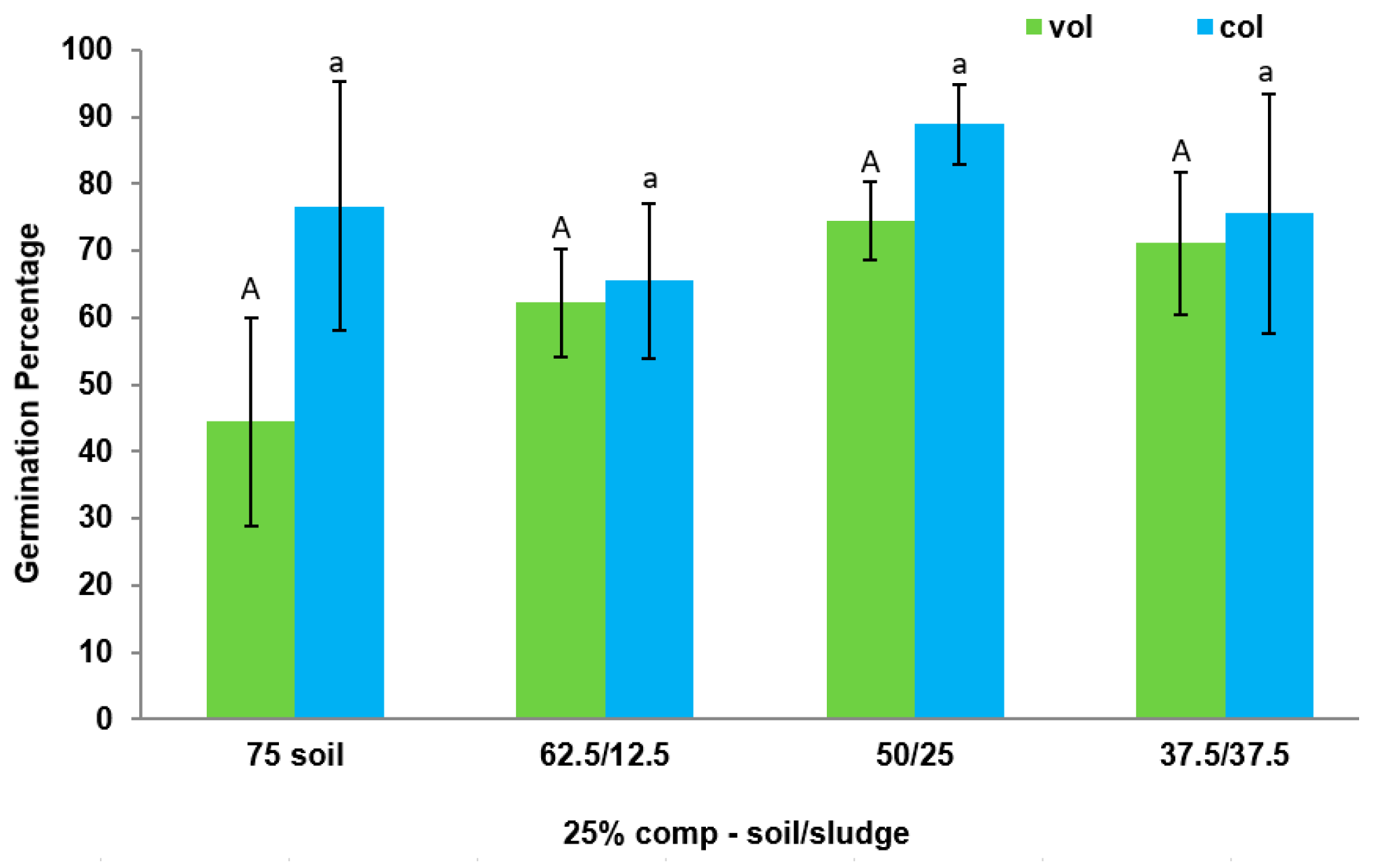
3.2. Effect of Biosolid (Compost and Sludge) Incorporation into Voladora and Coloso Soils in Basil and Coriander Germination Percentages
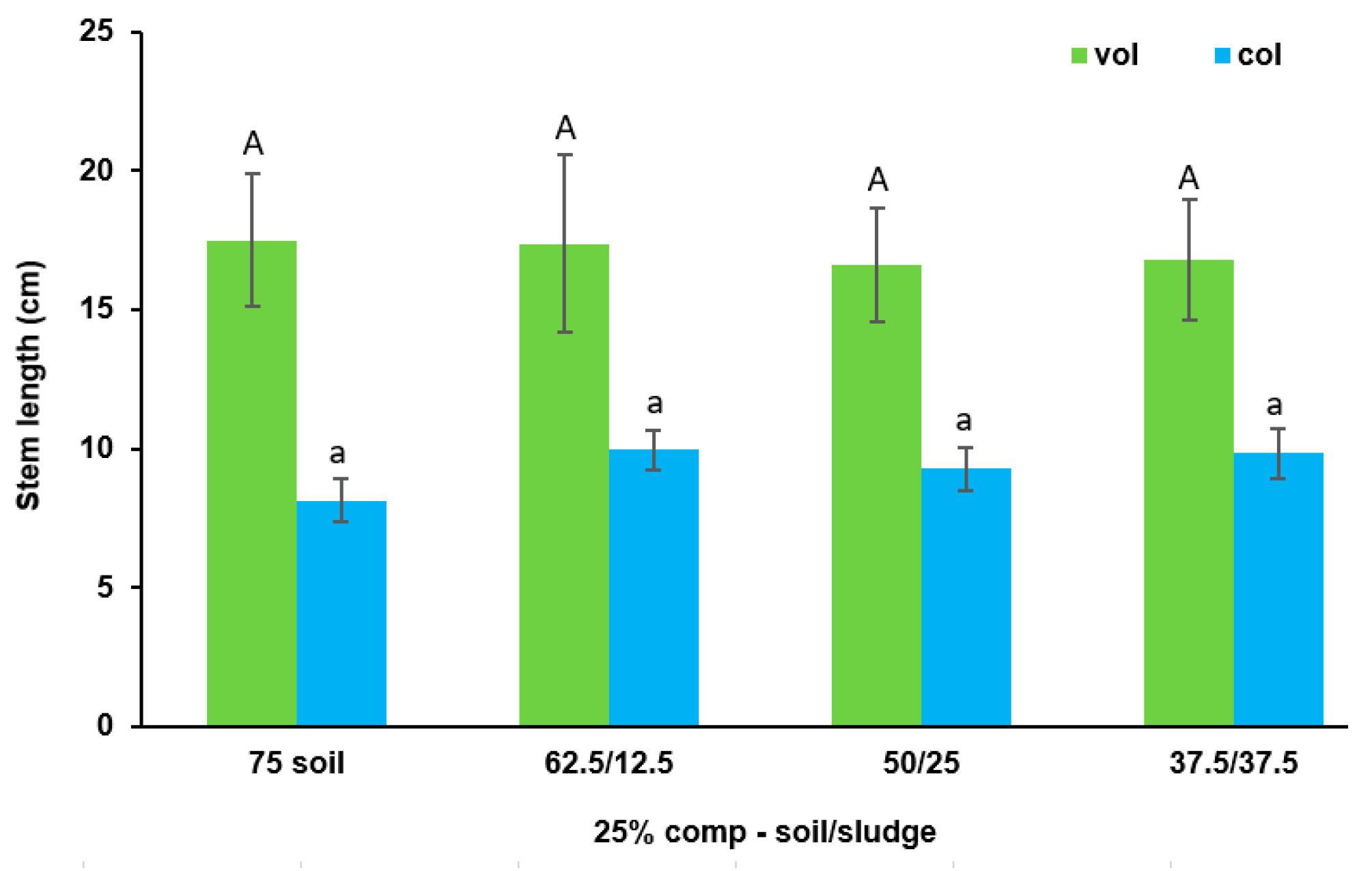
3.3. Effect of Biosolid (Compost and Sludge) Incorporation into Voladora and Coloso Soils on Basil and Coriander Growth
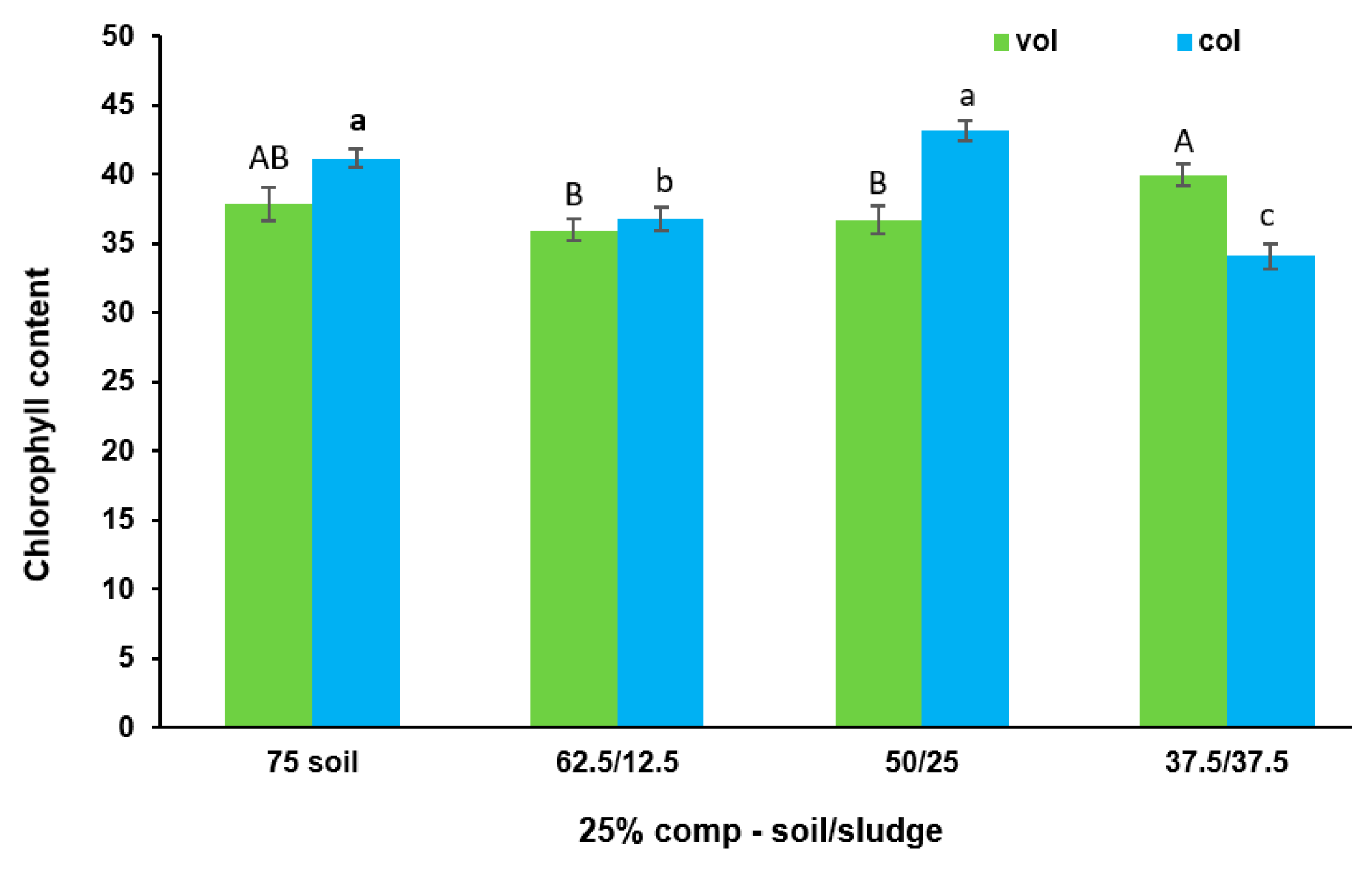
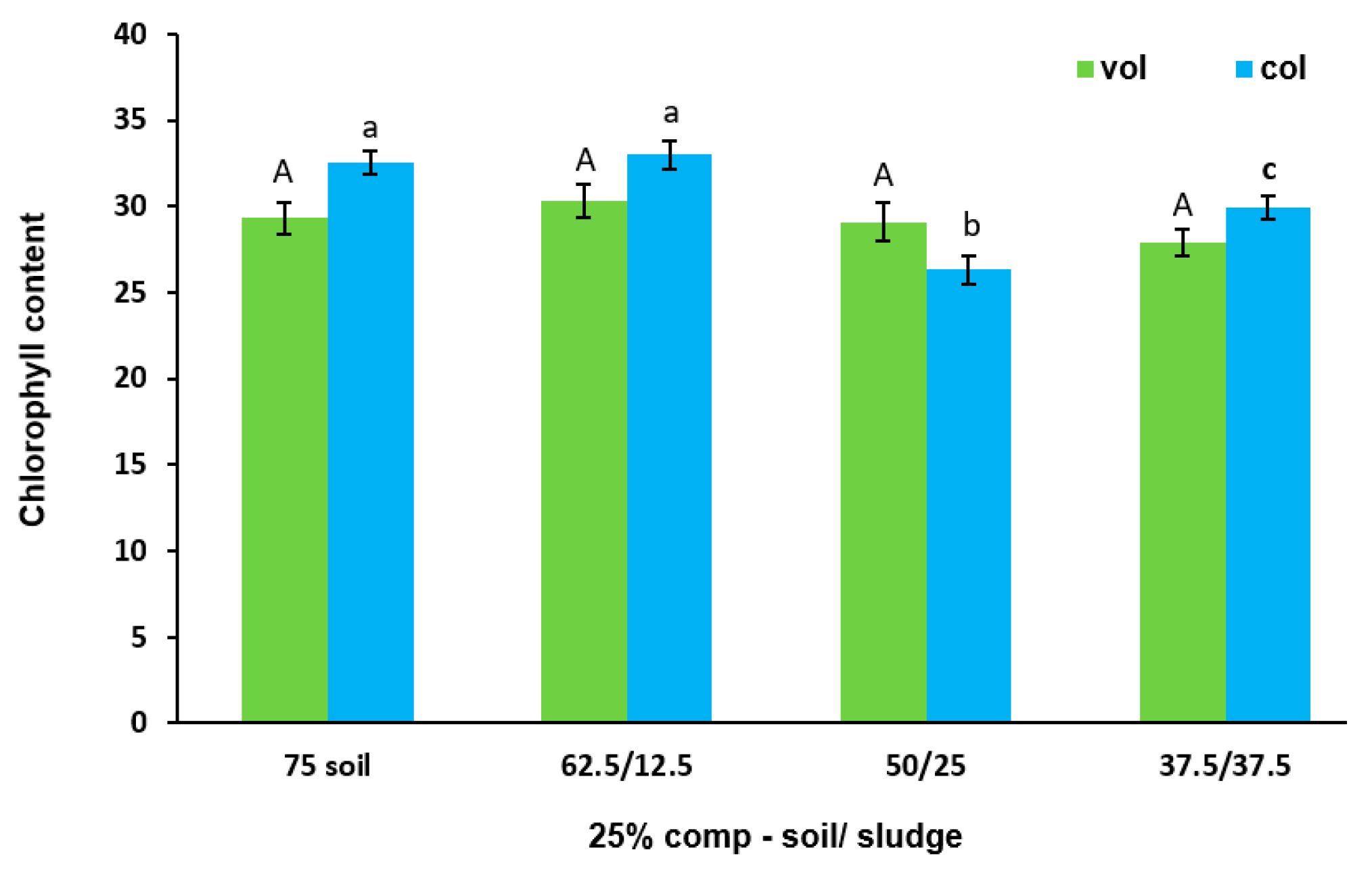
3.4. Effect of Biosolid (Compost and Sludge) Incorporation into Voladora and Coloso Soils on Basil and Coriander Total Chlorophyll Content, SPAD 502
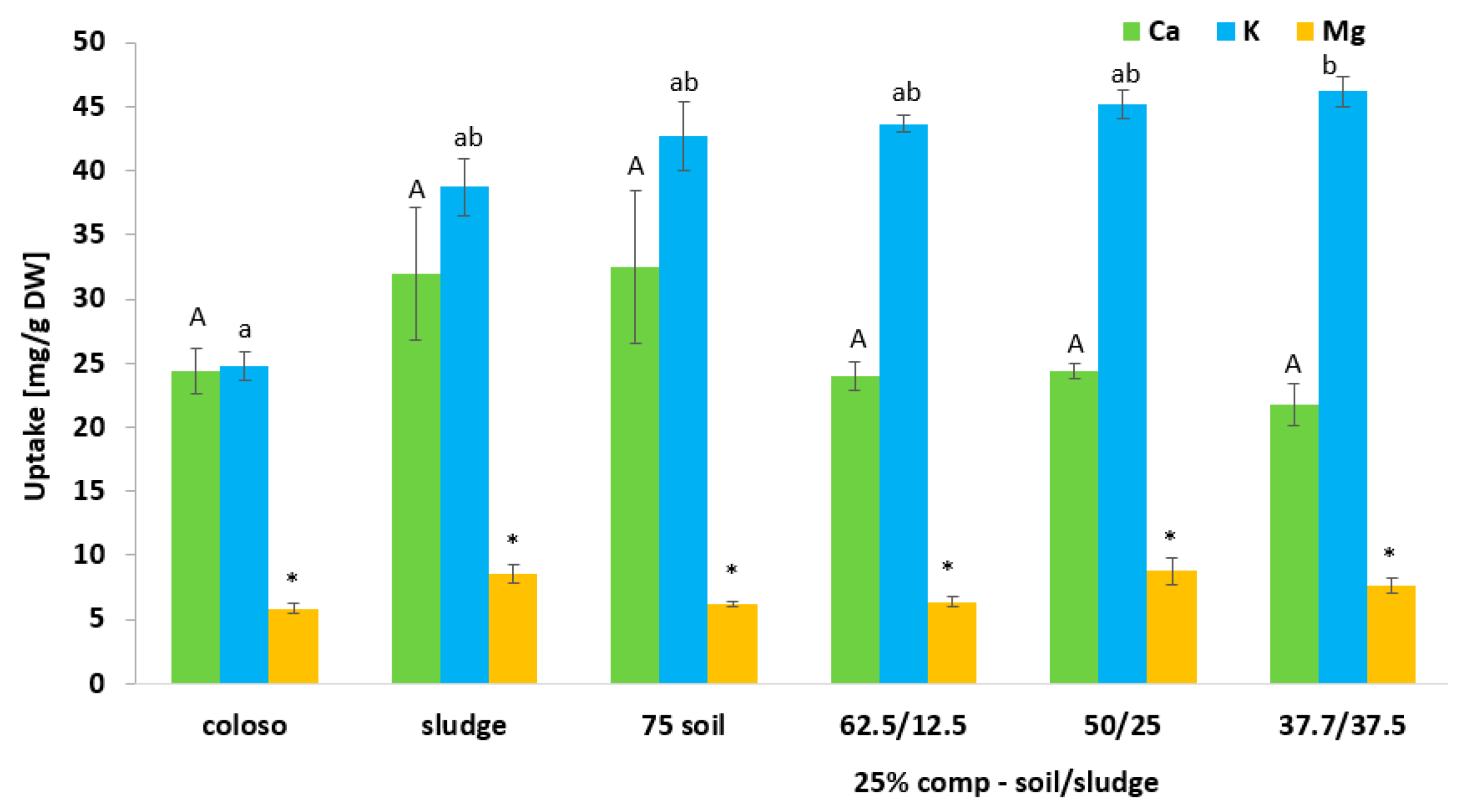
3.5. Effects of Biosolid (Compost and Sludge) Incorporation into Voladora and Coloso Soils on Macronutrient (Ca, K, and Mg) Content in Basil Leaves
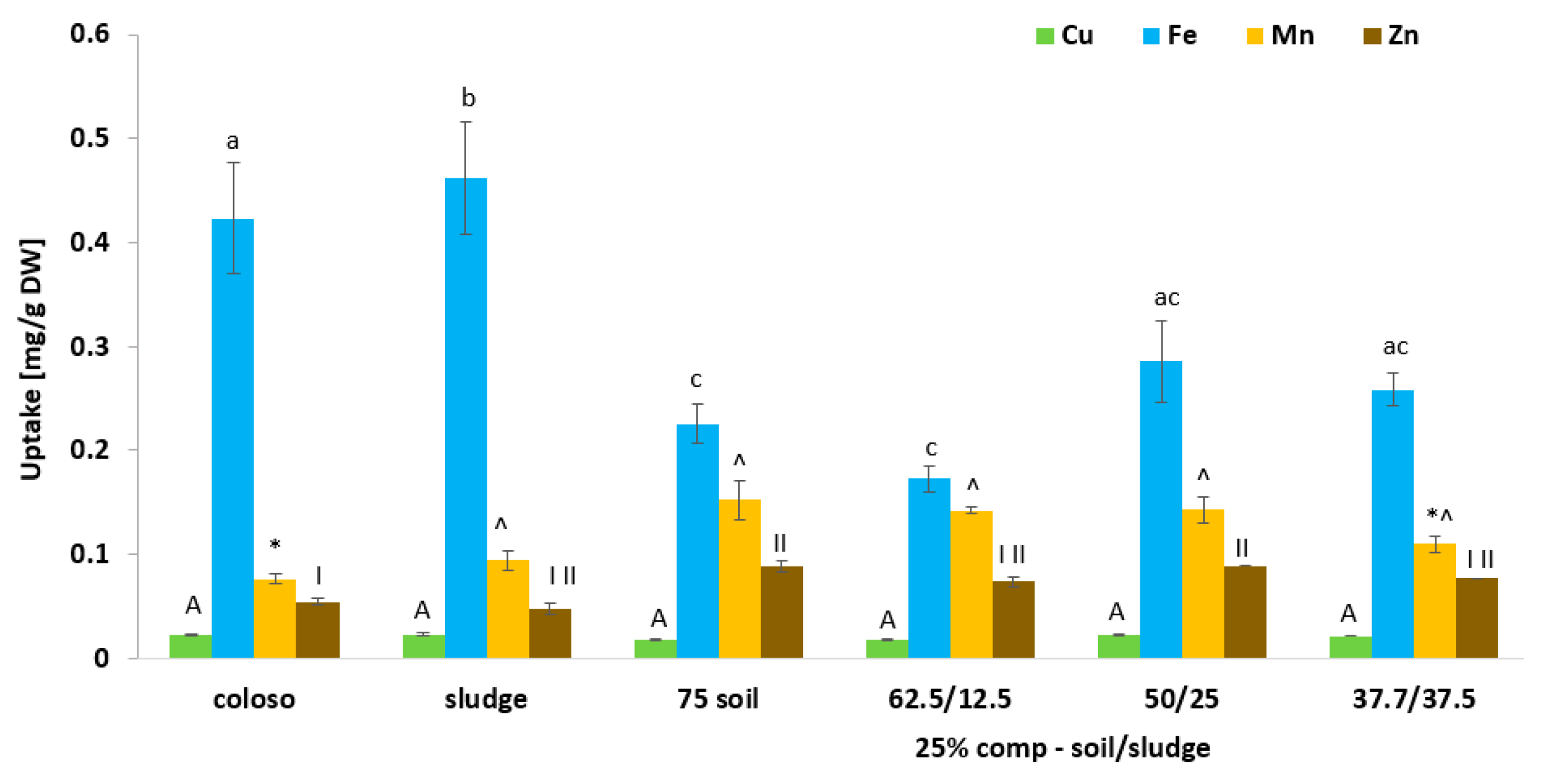
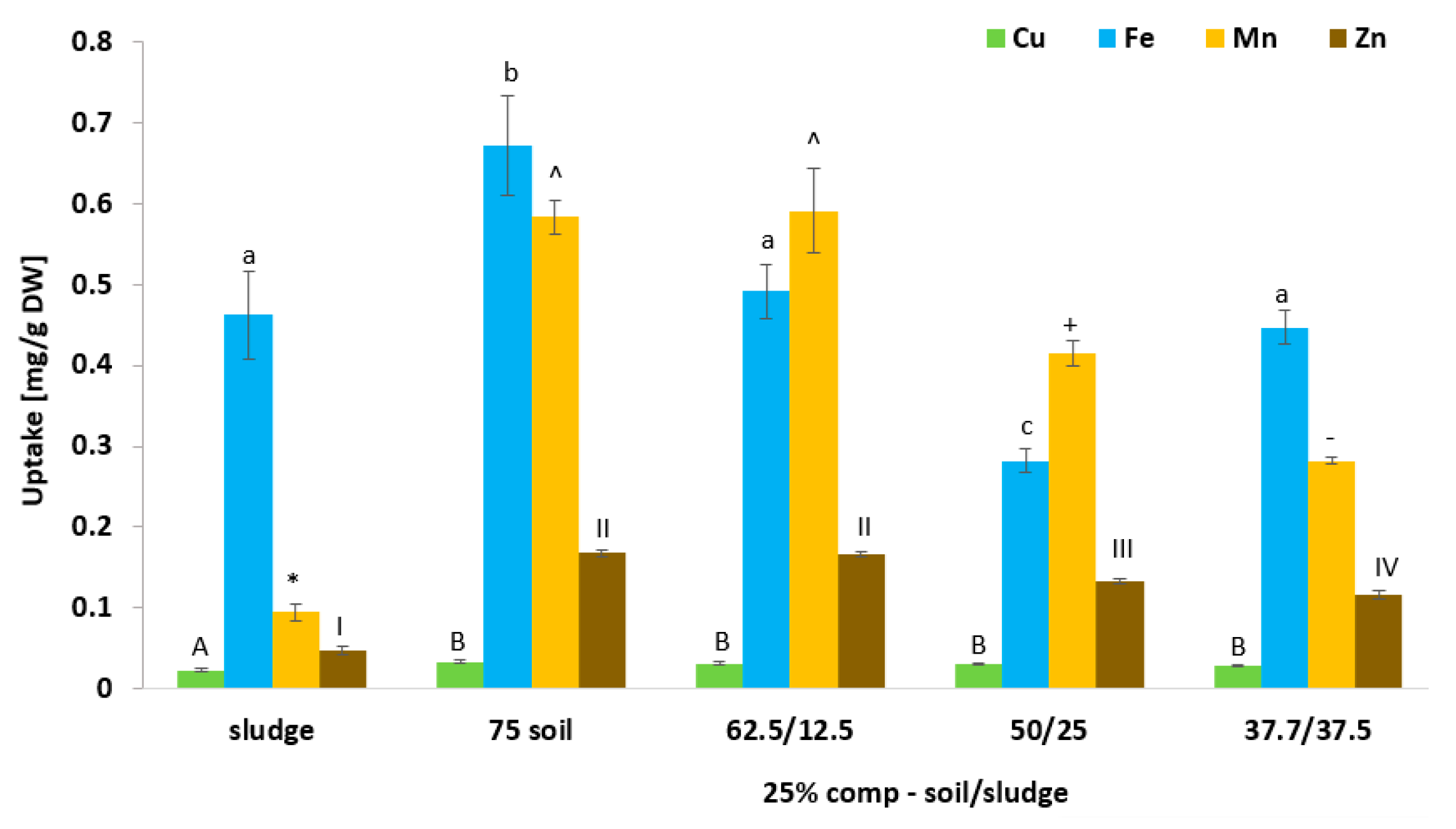
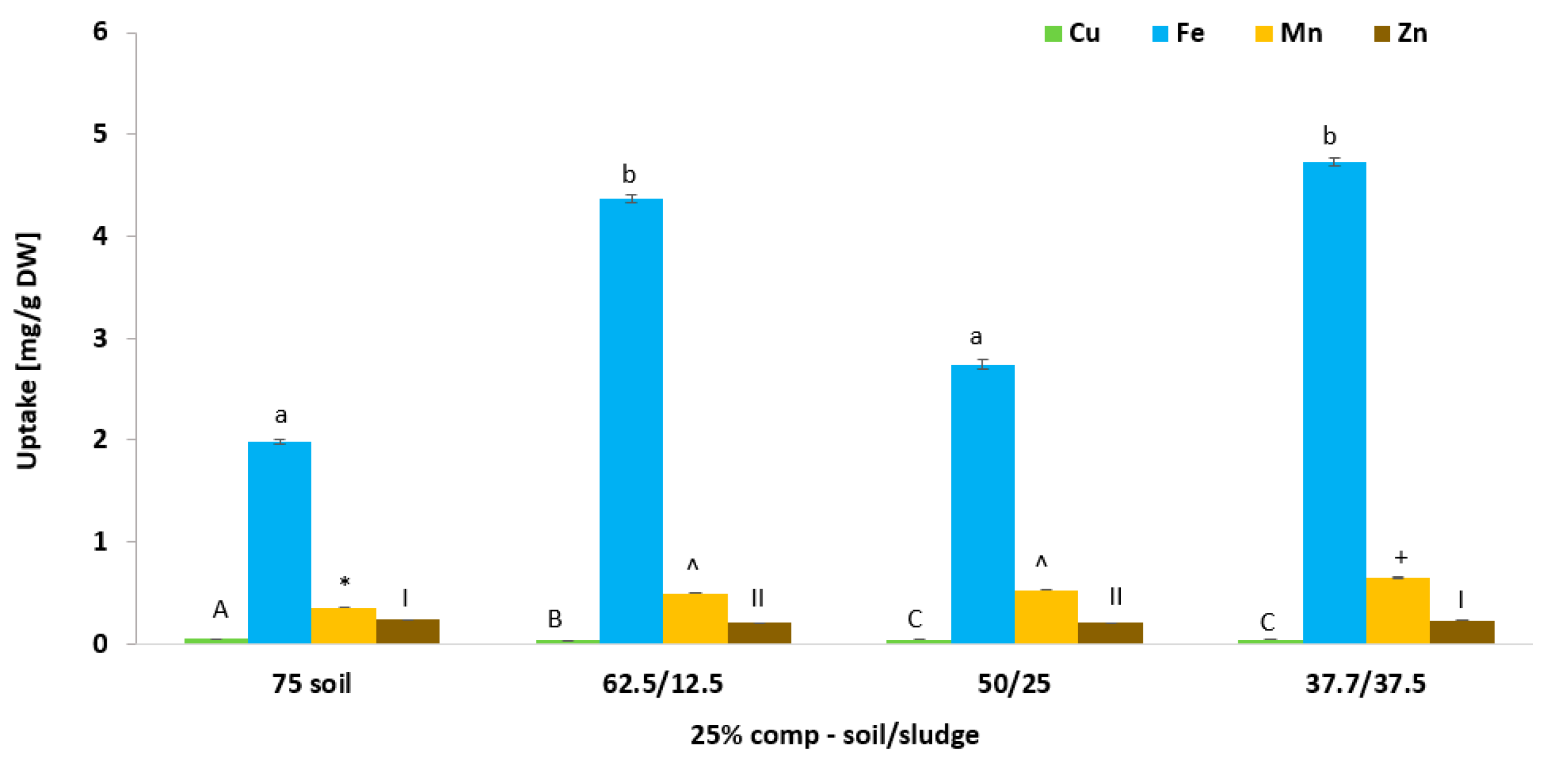
3.6. Effect of Biosolid (Compost and Sludge) Incorporation into Voladora and Coloso Soils on Micronutrients (Cu, Fe, Mn, and Zn) Content in Basil Leaves
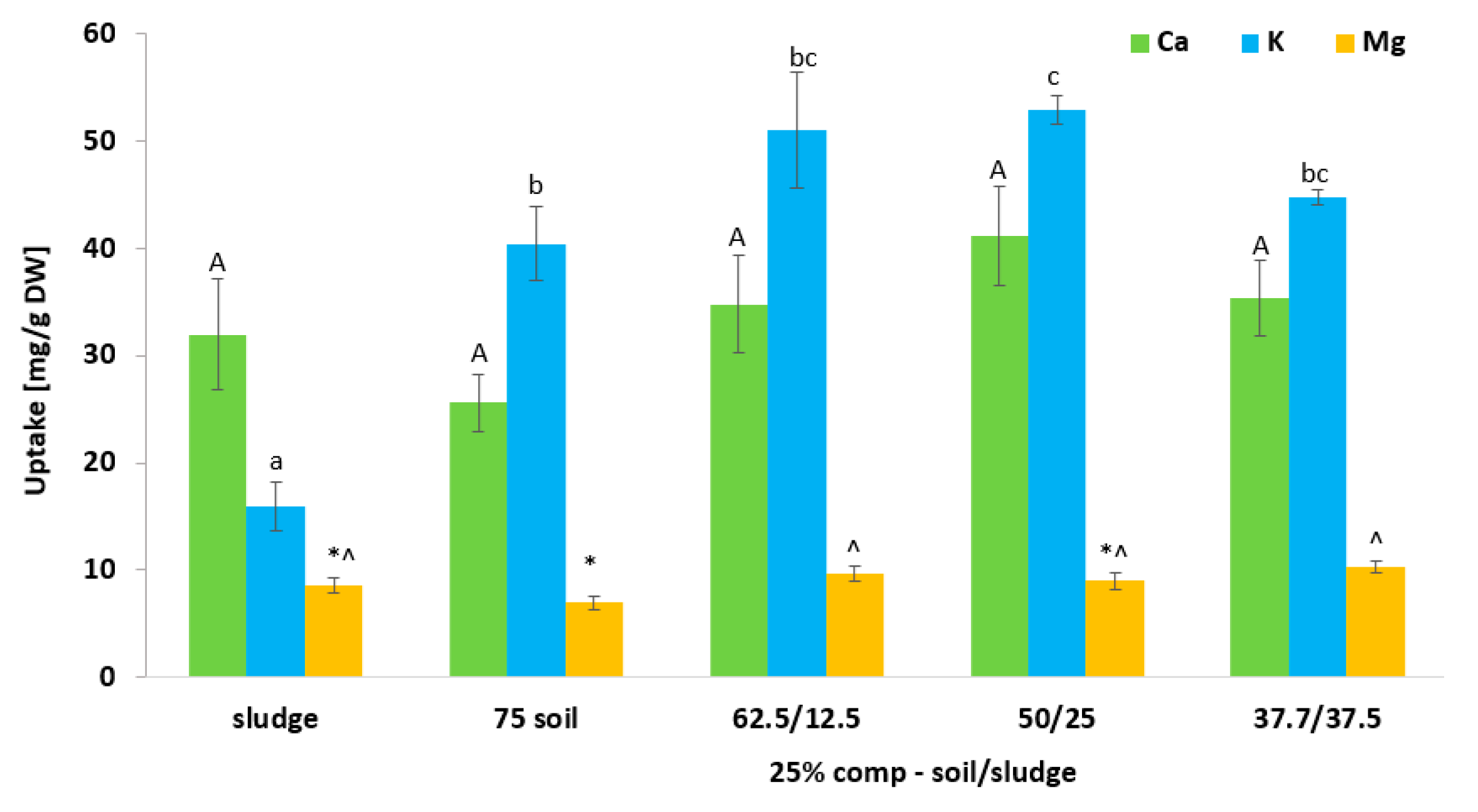
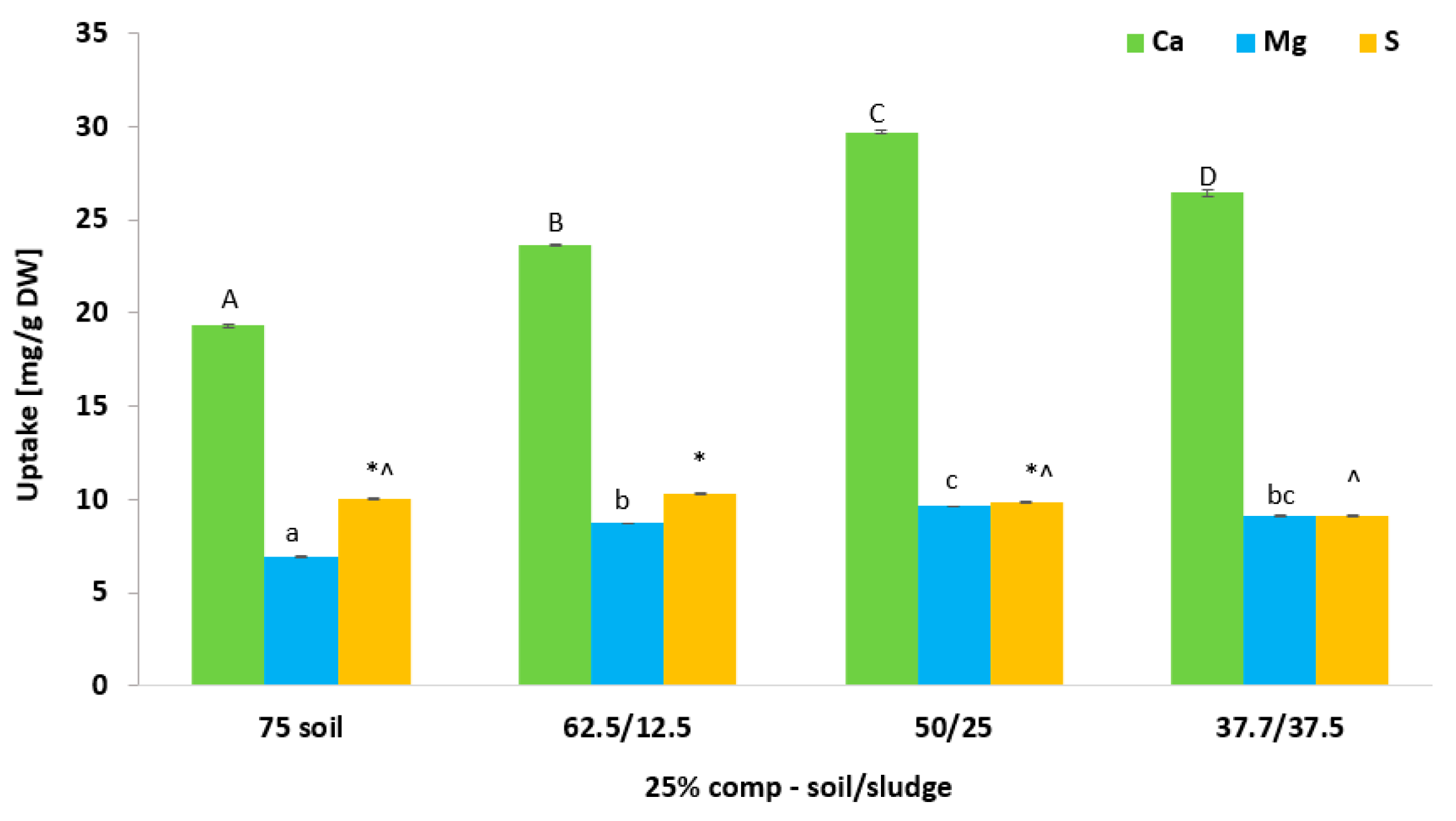
3.7. Effect of Biosolid (Compost and Sludge) Incorporation into Voladora and Coloso Soils on Coriander Leave Macronutrients (Ca, K, and S) Content
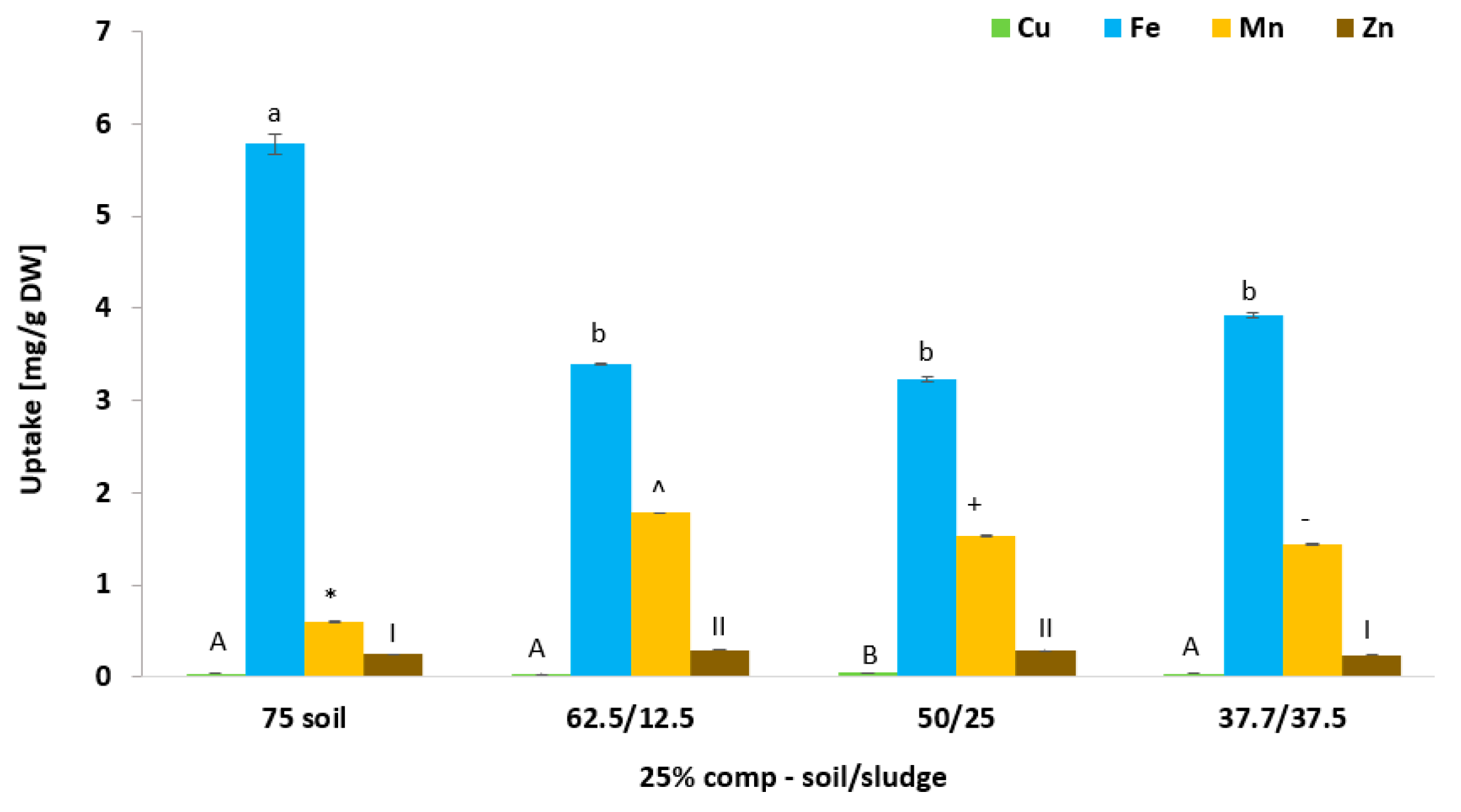
3.8. Effect of Biosolid (Compost and Sludge) Incorporation into Voladora and Coloso Soils on Coriander Leaf Micronutrient (Cu, Fe, Mn, and Zn) Content
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferreira, C.S.; Seifollahi-Aghmiuni, S.; Destouni, G.; Ghajarnia, N.; Kalantari, Z. Soil degradation in the European Mediterranean region: Processes, status and consequences. Sci. Total. Environ. 2022, 805, 150106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soil Survey Staff, Natural Resources Conservation Service, United States Department of Agriculture. Soil Series Classification Database. Available online: https://www.nrcs.usda.gov/resources/data-and-reports/soil-series-classification-database-sc (accessed on 1 March 2023).
- Plummer, C.; Carlson, D.; Hammersley, L. Physical Geology, 15th ed.; McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 123–124. [Google Scholar]
- Beinroth, F.H. An Outline of the Geology of Puerto Rico; University of Puerto Rico, Agricultural Experiment Station Bulletin: San Juan, Puerto Rico, 1969; p. 213. [Google Scholar]
- Mejías, C.; Martín, J.; Santos, J.L.; Aparicio, I.; Alonso, E. Occurrence of pharmaceuticals and their metabolites in sewage sludge and soil: A review on their distribution and environmental risk assessment. Trends Environ. Anal. Chem. 2021, 30, e00125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iranpor, R.; Cox, H.H.J.; Kearney, R.J.; Clark, J.H.; Pincence, A.B.; Diagger, G.T. Regulations for bio-solids land application in U.S. and European Union. J. Residuals Sci. Technol. 2004, 1, 209–222. [Google Scholar]
- Noirot-Cosson, P.E.; Vaudour, E.; Gilliot, J.M.; Gabrielle, B.; Houot, S. Modeling the long-term effect of urban compost applications on carbon and nitrogen dynamics in temperature cropland. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 94, 138–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, T.D. Biosolids in Europe. In Proceedings of the Residuals and Biosolids Conference 2012, Raleigh, NC, USA, 25–28 March 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onchoke, K.K.; Fateru, O.O. Evaluating bioavailability of elements in municipal wastewater sludge (Biosolids) from three rural wastewater treatment plants in East Texas (USA) by a sequential extraction procedure. Results Chem. 2021, 3, 100211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Amorim Júnior, S.S.; Pereira, M.A.d.S.; Lima, P.d.M.; Marishigue, M.; Guilherme, D.d.O.; Filho, F.J.C.M. Evidences on the application of biosolids and the effects on chemical characteristics in infertile tropical sandy soils. Clean. Eng. Technol. 2021, 4, 100245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Figueiredo, C.C.; Chagas, J.K.M.; da Silva, J.; Paz-Ferreiro, J. Short-term effects of a sewage sludge biochar amendment on total and available heavy metal content of a tropical soil. Geoderma 2019, 344, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansen, J.L.; Dam, M.; Kudjordjie, E.N.; Santos, S.S.; Palmqvist, A.; Magid, J.; Vestergård, M. Effects of long-term fertilization with contemporary Danish human urine, composted household waste and sewage sludge on soil nematode abundance and community structure. Sci. Total. Environ. 2023, 860, 160485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouoba, N.; Phung, L.D.; Sasaki, A.; Pham, D.V.; Watanabe, T. Drip fertigation with treated municipal wastewater and soil amendment with composted sewage sludge for sustainable protein-rich rice cultivation. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2022, 28, 102569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, S.; Mandal, M. Coriander (Coriandrum sativum L.) essential oil: Chemistry and biological activity. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2015, 5, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calín-Sánchez, Á.; Lech, K.; Szumny, A.; Figiel, A.; Carbonell-Barrachina, Á.A. Volatile composition of sweet basil essential oil (Ocimum basilicum L.) as affected by drying method. Food Res. Int. 2012, 48, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.L.; Doran, J.W. Measurements and use of pH and electrical conductivity for soil quality analysis. Methods Assess. Soil Qual. 1997, 49, 169–185. [Google Scholar]
- Ecological Effects Test Guidelines OPPTS 850.4100 Terrestrial Plant Toxicity, Tier I (Seedling Emergence) EPA 850.4100—USEPA. 1996. Available online: https://nepis.epa.gov/Exe/ZyNET.exe/P100XGWA.TXT?ZyActionD=ZyDocument&Client=EPA&Index=1995+Thru+1999&Docs=&Query=&Time=&EndTime=&SearchMethod=1&TocRestrict=n&Toc=&TocEntry=&QField=&QFieldYear=&QFieldMonth=&QFieldDay=&IntQFieldOp=0&ExtQFieldOp=0&XmlQuery=&File=D%3A%5Czyfiles%5CIndex%20Data%5C95thru99%5CTxt%5C00000041%5CP100XGWA.txt&User=ANONYMOUS&Password=anonymous&SortMethod=h%7C-&MaximumDocuments=1&FuzzyDegree=0&ImageQuality=r75g8/r75g8/x150y150g16/i425&Display=hpfr&DefSeekPage=x&SearchBack=ZyActionL&Back=ZyActionS&BackDesc=Results%20page&MaximumPages=1&ZyEntry=1&SeekPage=x&ZyPURL (accessed on 1 March 2023).
- Marchuk, S.; Tait, S.; Sinha, P.; Harris, P.; Antille, D.L.; McCabe, B.K. Biosolids-derived fertilisers: A review of challenges and opportunities. Sci. Total. Environ. 2023, 875, 162555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesfahun, W.; Zerfu, A.; Shumuye, M.; Abera, G.; Kidane, A.; Astatkie, T. Effects of brewery sludge on soil chemical properties, trace metal availability in soil and uptake by wheat crop, and bioaccumulation factor. Heliyon 2021, 7, e05989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urionabarrenetxea, E.; Garcia-Velasco, N.; Zaldibar, B.; Soto, M. Impacts of sewage sludges deposition on agricultural soils: Effects upon model soil organisms. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2022, 255, 109276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arlo, L.; Beretta, A.; Szogi, A.; del Pino, A. Biomass production, metal and nutrient content in sorghum plants grown on soils amended with sewage sludge. Heliyon 2022, 8, e08658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoghlami, R.I.; Hamdi, H.; Mokni-Tlili, S.; Hechmi, S.; Khelil, M.N.; Ben Aissa, N.; Moussa, M.; Bousnina, H.; Benzarti, S.; Jedidi, N. Monitoring the variation of soil quality with sewage sludge application rates in absence of rhizosphere effect. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2020, 8, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamizela, T.; Lyng, K.-A.; Saxegård, S.; Švédová, B.; Grobelak, A. Bionor sewage sludge technology—Biomass to fertiliser and a soil addition. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 319, 128655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutgersson, C.; Ebmeyer, S.; Lassen, S.B.; Karkman, A.; Fick, J.; Kristiansson, E.; Brandt, K.K.; Flach, C.-F.; Larsson, D.J. Long-term application of Swedish sewage sludge on farmland does not cause clear changes in the soil bacterial resistome. Environ. Int. 2020, 137, 105339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkhlifi, Z.; Kamran, M.; Maqbool, A.; El-Naggar, A.; Ifthikar, J.; Parveen, A.; Bashir, S.; Rizwan, M.; Mustafa, A.; Irshad, S.; et al. Phosphate-lanthanum coated sewage sludge biochar improved the soil properties and growth of ryegrass in an alkaline soil. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 216, 112173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dad, K.; Wahid, A.; Khan, A.A.; Anwar, A.; Ali, M.; Sarwar, N.; Ali, S.; Ahmad, A.; Ahmad, M.; Khan, K.A.; et al. Nutritional status of different biosolids and their impact on various growth parameters of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 26, 1423–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastida, F.; Jehmlich, N.; Martínez-Navarro, J.; Bayona, V.; García, C.; Moreno, J. The effects of struvite and sewage sludge on plant yield and the microbial community of a semiarid Mediterranean soil. Geoderma 2019, 337, 1051–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marschner, H. (Ed.) Marschner’s Mineral Nutrition of Higher Plants; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012; ISBN 978-0-12384-906-9. [Google Scholar]
- Song, U.; Lee, E.J. Environmental and economical assessment of sewage sludge compost application on soil and plants in a landfill. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2010, 54, 1109–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tepecik, M.; Ongun, A.R.; Kayikcioglu, H.H.; Delibacak, S.; Elmaci, O.L.; Celen, A.E.; Ilker, E. Change in cotton plant quality in response to application of anaerobically digested sewage sludge. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 29, 615–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonkiewicz, J.; Popławska, A.; Kołodziej, B.; Ciarkowska, K.; Gambuś, F.; Bryk, M.; Babula, J. Application of ash and municipal sewage sludge as macronutrient sources in sustainable plant biomass production. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 264, 110450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, J.; Fraga, S.; Zanatta, M.; Martins, M.; Pires, M. Characterization of organic compounds and drugs in sewage sludge aiming for agricultural recycling. Heliyon 2021, 7, e06771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbarick, K.; Ippolito, J.; McDaniel, J.; Hansen, N.; Peterson, G. Biosolids application to no-till dryland agroecosystems. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2012, 150, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Głąb, T.; Żabiński, A.; Sadowska, U.; Gondek, K.; Kopeć, M.; Mierzwa–Hersztek, M.; Tabor, S. Effects of co-composted maize, sewage sludge, and biochar mixtures on hydrological and physical qualities of sandy soil. Geoderma 2018, 315, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilas-Boas, A.C.M.; Tarelho, L.A.C.; Kamali, M.; Hauschild, T.; Pio, D.T.; Jahanianfard, D.; Gomes, A.P.D.; Matos, M.A.A. Biochar from slow pyrolysis of biological sludge from wastewater treatment: Characteristics and effect as soil amendment. Biofuels Bioprod. Biorefin. 2021, 15, 1054–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.-H.; Zhu, G.-Y.; Li, H.-L.; Han, X.-M.; Li, J.-M.; Ma, Y.-B. Accumulation and bioavailability of heavy metals in a soil-wheat/maize system with long-term sewage sludge amendments. J. Integr. Agric. 2018, 17, 1861–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buta, M.; Hubeny, J.; Zieliński, W.; Harnisz, M.; Korzeniewska, E. Sewage sludge in agriculture—The effects of selected chemical pollutants and emerging genetic resistance determinants on the quality of soil and crops—A review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 214, 112070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Controls | Soil Mixtures |
|---|---|
| 100% compost | 25% compost/75% soil |
| 100% sludge | 25% compost/62.5% soil/12.5% sludge |
| 100% Coloso soil | 25% compost/50% soil/25% sludge |
| 100% Voladora soil | 25% compost/37.5% soil/37.5% sludge |
| Samples (%) | pH | EC (dS/m) |
|---|---|---|
| 100 Compost | 6.5 ± 0.02 A | 8.4 ± 0.04 A |
| 100 Sludge | 7.6 ± 0.08 B | 0.32 ± 0.001 B |
| 100 Voladora | 4.55 ± 0.10 C | 0. 0563 ± 0.0003 C |
| 25 Comp/75 Voladora | 4.84 ± 0.11 C | 1.126 ± 0.004 D |
| 25 Comp/62.5 Voladora/12.5 Sludge | 5.15 ± 0.09 D | 0.8330 ± 0.0006 E |
| 25 Comp/50 Voladora/25 Sludge | 5.57 ± 0.02 E | 0.806 ± 0.006 E |
| 25 Comp/37.5 Voladora/37.5 Sludge | 5.64 ± 0.22 E | 1.39 ± 0.01 F |
| Samples (%) | pH | EC (dS/m) |
|---|---|---|
| 100 Compost | 6.5 ± 0.02 a | 8.4 ± 0.04 a |
| 100 Sludge | 7.6 ± 0.08 b | 0.32 ± 0.001 b |
| 100 Coloso | 5.93 ± 0.05 c | 0.117 ± 0.001 c |
| 25 Comp/75 Coloso | 6.38 ± 0.13 c | 0.762 ± 0.002 d |
| 25 Comp/62.5 Coloso/12.5 Sludge | 6.60 ± 0.03 d | 0.699 ± 0.002 e |
| 25 Comp/50 Coloso/25 Sludge | 6.69 ± 0.03 d | 0.588 ± 0.003 f |
| 25 Comp/37.5 Coloso/37.5 Sludge | 6.82 ± 0.07 e | 1.310 ± 0.009 g |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lugo-Avilés, L.E.; López-Moreno, M.L.; Roman-Velazquez, F.R.; Lugo-Rosas, J. Biosolid Mixtures Applied in Tropical Soils and Their Effect on Coriandrum sativum and Ocimum basilicum Nutritional Uptake. Agriculture 2024, 14, 561. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14040561
Lugo-Avilés LE, López-Moreno ML, Roman-Velazquez FR, Lugo-Rosas J. Biosolid Mixtures Applied in Tropical Soils and Their Effect on Coriandrum sativum and Ocimum basilicum Nutritional Uptake. Agriculture. 2024; 14(4):561. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14040561
Chicago/Turabian StyleLugo-Avilés, Leany Enid, Martha Laura López-Moreno, Felix R. Roman-Velazquez, and Joel Lugo-Rosas. 2024. "Biosolid Mixtures Applied in Tropical Soils and Their Effect on Coriandrum sativum and Ocimum basilicum Nutritional Uptake" Agriculture 14, no. 4: 561. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14040561
APA StyleLugo-Avilés, L. E., López-Moreno, M. L., Roman-Velazquez, F. R., & Lugo-Rosas, J. (2024). Biosolid Mixtures Applied in Tropical Soils and Their Effect on Coriandrum sativum and Ocimum basilicum Nutritional Uptake. Agriculture, 14(4), 561. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14040561






