Design and Experiment of Precision Seed Metering Device for Flow Adsorption of Quinoa Seeds
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
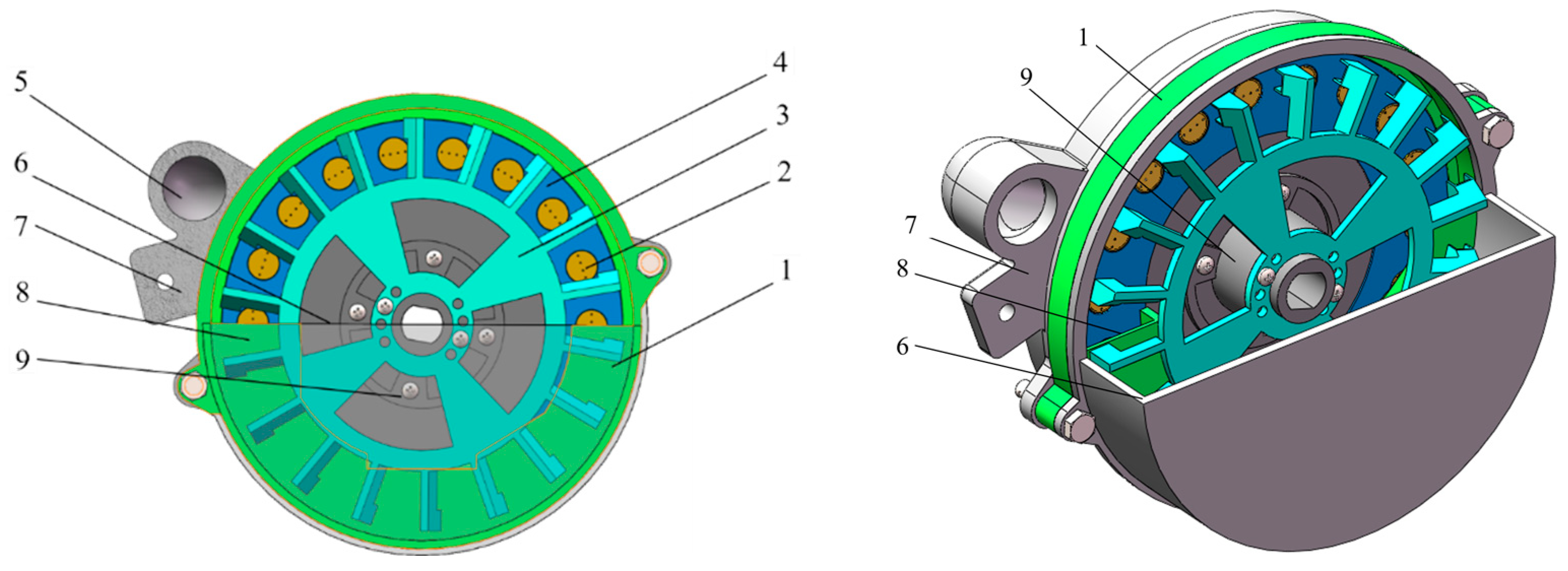
2.1. Structure and Working Principle of Planting Apparatus
2.2. Design of Key Components
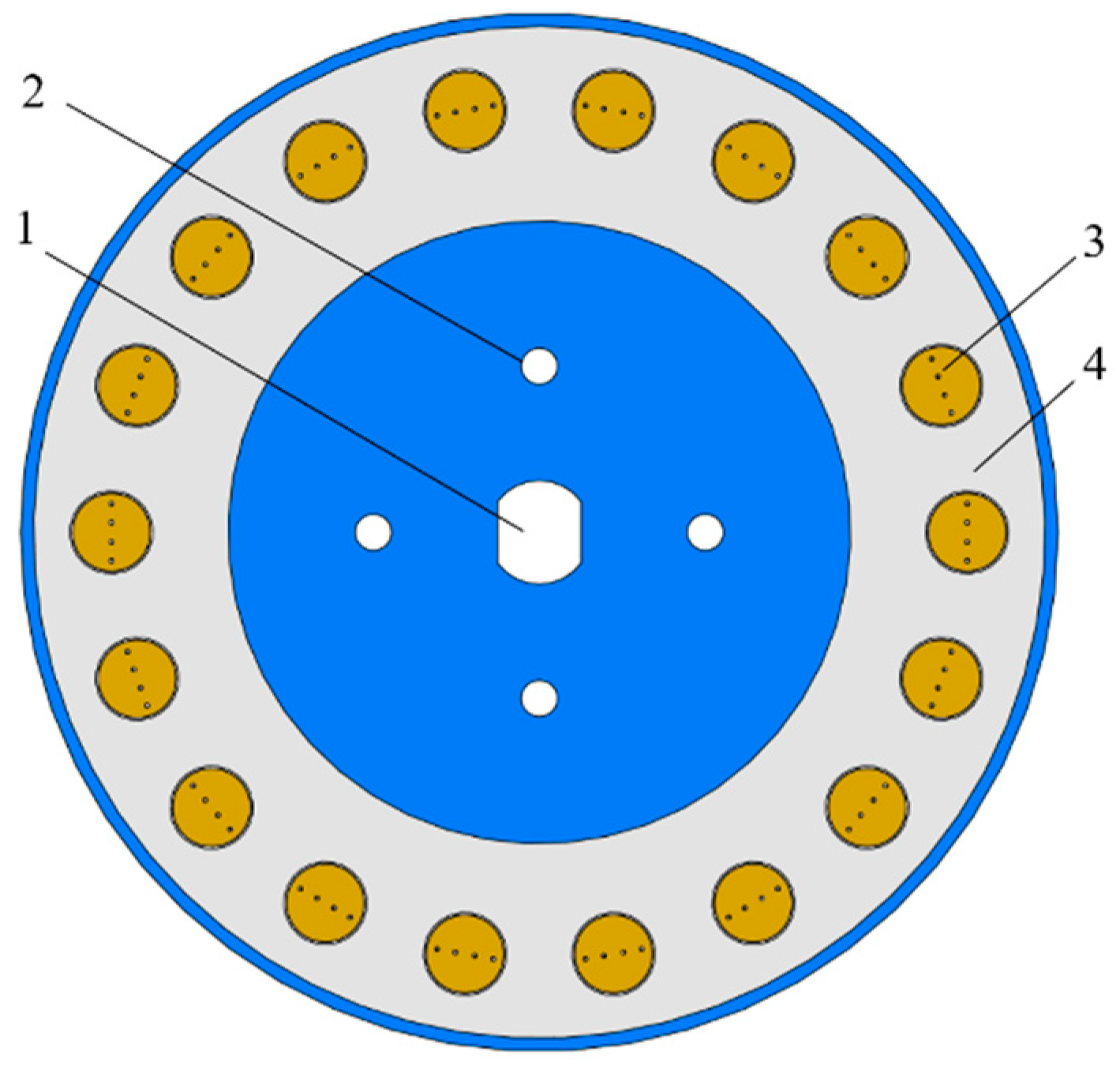
2.2.1. Design of the Seed Chamber Baffle
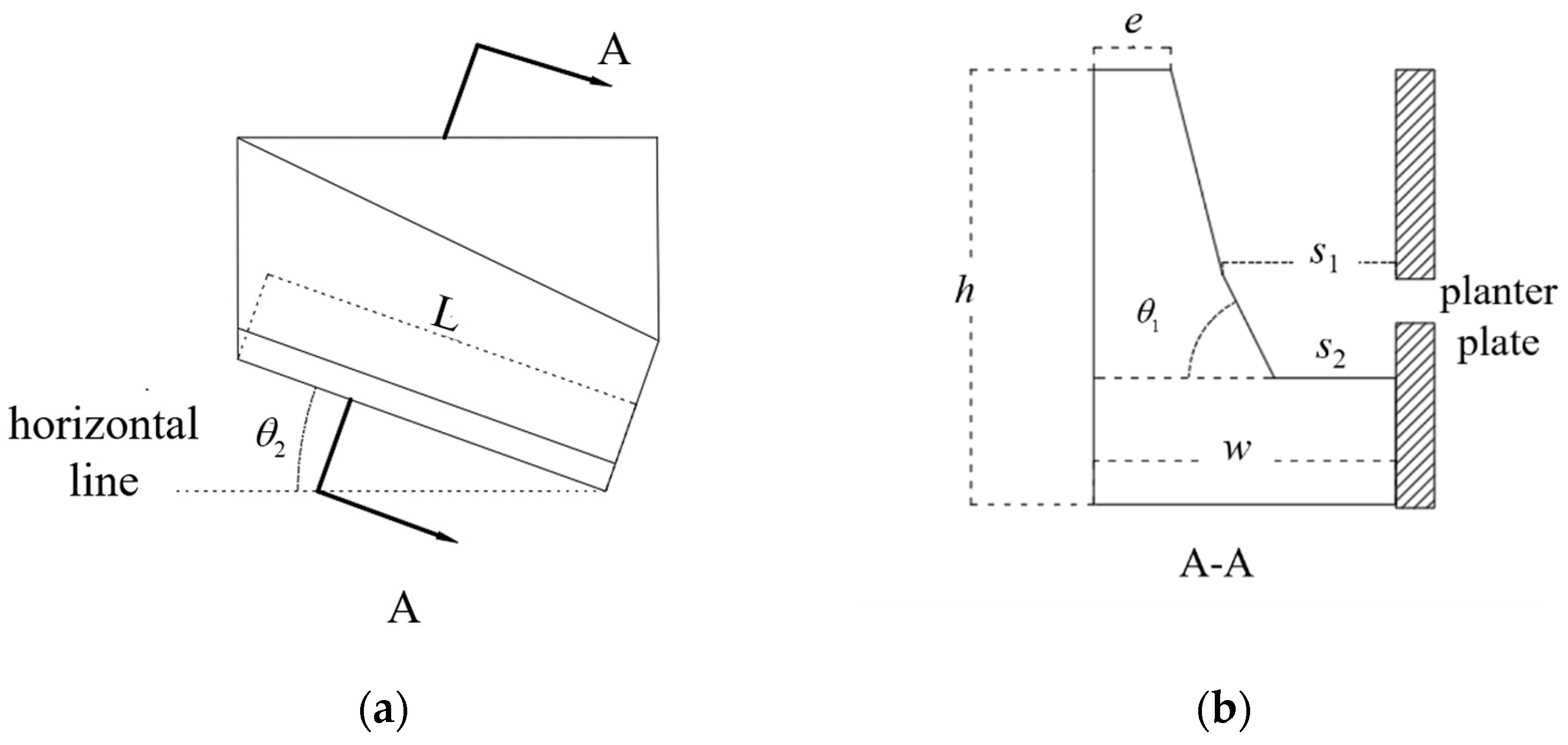
2.2.2. Design of the Scooping Seed Tray
2.2.3. Design of Planter Plate
2.3. Flow Process Analysis
2.4. Seeding Performance Test of Seed-Metering Device
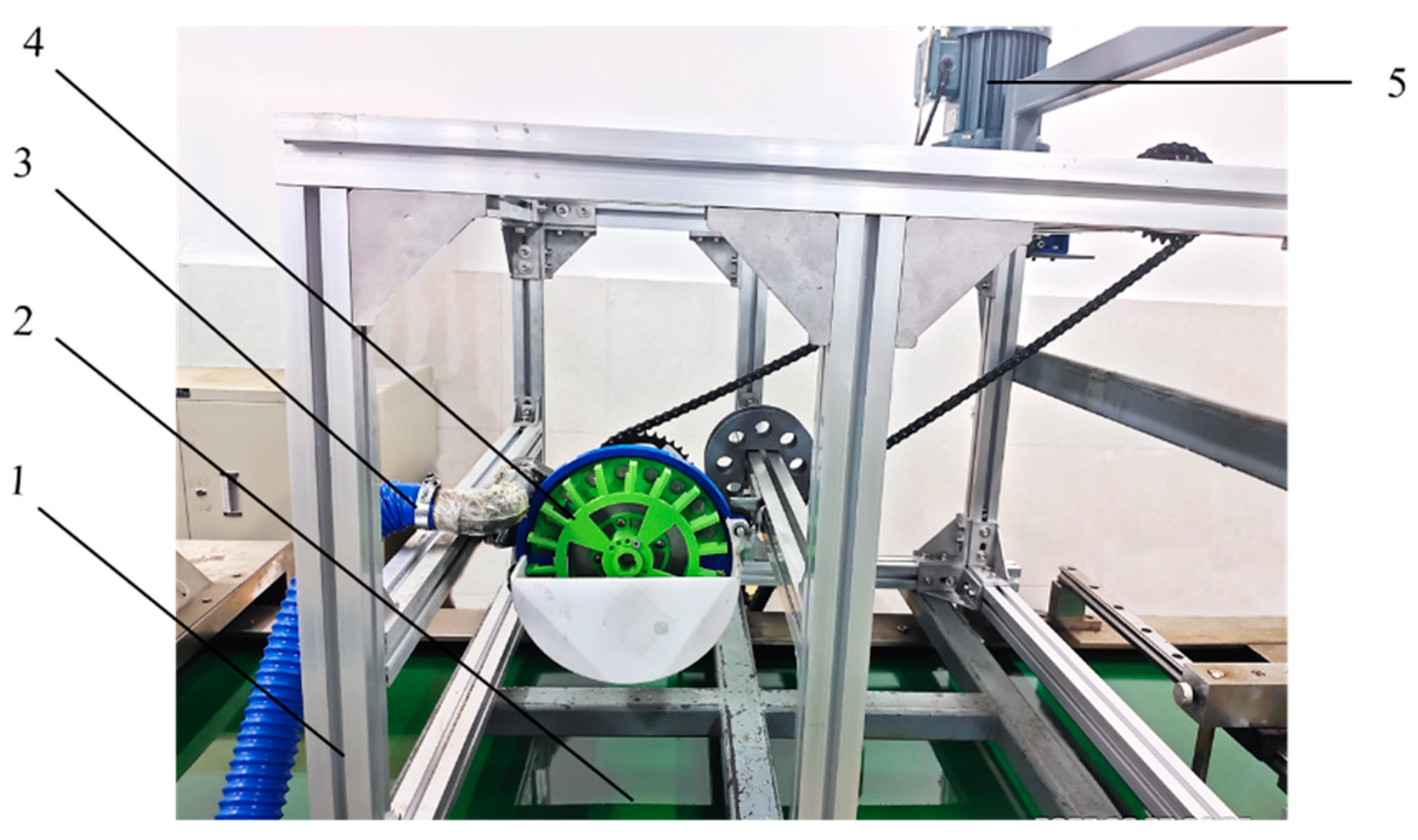
2.4.1. Test Equipment and Materials
2.4.2. Experimental Performance Evaluation Indicators
2.4.3. Single-Factor Experiments
2.4.4. Box–Behnken Central Composite Experiment
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Single-Factor Experimental Results and Analysis
3.1.1. Single-Factor Experiment of the Forward Speed
3.1.2. Single-Factor Experiment of Negative Pressure
3.1.3. Single-Factor Experiment of the Amount of Seeds
3.1.4. Single-Factor Experiment of the Flow Angles
3.2. Experimental Results and Analysis of the Box–Behnken Central Composite Design
3.2.1. Regression Model of Hole Grain Count Qualification Index
| Index | Source | Sum of Squares | df | MS | F | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y1 | Model | 487.698 | 14 | 34.836 | 131.245 | <0.0001 ** |
| A | 64.403 | 1 | 64.403 | 242.644 | <0.0001 ** | |
| B | 0.963 | 1 | 0.963 | 3.629 | 0.0775 | |
| C | 16.662 | 1 | 16.662 | 62.774 | <0.0001 ** | |
| D | 28.398 | 1 | 28.398 | 106.990 | <0.0001 ** | |
| AB | 5.499 | 1 | 5.499 | 20.718 | 0.0005 ** | |
| AC | 8.762 | 1 | 8.762 | 33.010 | <0.0001 ** | |
| AD | 1.836 | 1 | 1.836 | 6.917 | 0.0198 * | |
| BC | 2.924 | 1 | 2.924 | 11.017 | 0.0051 ** | |
| BD | 3.186 | 1 | 3.186 | 12.004 | 0.0038 ** | |
| CD | 2.496 | 1 | 2.496 | 9.405 | 0.0084 ** | |
| A2 | 301.827 | 1 | 301.827 | 1137.154 | <0.0001 ** | |
| B2 | 74.166 | 1 | 74.166 | 279.426 | <0.0001 ** | |
| C2 | 2.627 | 1 | 2.627 | 9.898 | 0.0071 ** | |
| D2 | 55.645 | 1 | 55.645 | 209.645 | <0.0001 ** | |
| Residual | 3.716 | 14 | 0.265 | |||
| Lock of Fit | 2.464 | 10 | 0.246 | 0.787 | 0.6558 | |
| Pure Error | 1.252 | 4 | 0.313 | |||
| Cor Total | 491.414 | 28 |
3.2.2. Regression Model for the Hole Spacing Qualification Index
| Index | Source | Sum of Squares | df | MS | F | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y2 | Model | 390.300 | 14 | 27.879 | 17.090 | <0.0001 ** |
| A | 69.745 | 1 | 69.745 | 42.754 | <0.0001 ** | |
| B | 108.000 | 1 | 108.000 | 66.204 | <0.0001 ** | |
| C | 5.427 | 1 | 5.427 | 3.327 | 0.0896 | |
| D | 4.763 | 1 | 4.763 | 2.920 | 0.1096 | |
| AB | 9.120 | 1 | 9.120 | 5.591 | 0.0330 * | |
| AC | 8.791 | 1 | 8.791 | 5.389 | 0.0359 * | |
| AD | 2.161 | 1 | 2.161 | 1.325 | 0.2690 | |
| BC | 3.168 | 1 | 3.168 | 1.942 | 0.1852 | |
| BD | 1.988 | 1 | 1.988 | 1.219 | 0.2882 | |
| CD | 1.488 | 1 | 1.488 | 0.912 | 0.3557 | |
| A2 | 88.169 | 1 | 88.169 | 54.048 | <0.0001 ** | |
| B2 | 113.773 | 1 | 113.773 | 69.743 | <0.0001 ** | |
| C2 | 21.885 | 1 | 21.885 | 13.416 | 0.0026 ** | |
| D2 | 26.026 | 1 | 26.026 | 15.954 | 0.0013 ** | |
| Residual | 22.838 | 14 | 1.631 | |||
| Lock of Fit | 20.189 | 10 | 2.019 | 3.048 | 0.1471 | |
| Pure Error | 2.649 | 4 | 0.662 | |||
| Cor Total | 413.139 | 28 |
3.2.3. Burrow Distance Coefficient of Variation Regression Models
| Index | Source | Sum of Squares | df | MS | F | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y3 | Model | 84.211 | 14 | 6.015 | 6.897 | 0.0004 ** |
| A | 34.544 | 1 | 34.544 | 39.606 | <0.0001 ** | |
| B | 10.679 | 1 | 10.679 | 12.243 | 0.0035 ** | |
| C | 0.715 | 1 | 0.715 | 0.820 | 0.3804 | |
| D | 0.667 | 1 | 0.667 | 0.765 | 0.3965 | |
| AB | 5.313 | 1 | 5.313 | 6.092 | 0.0271 * | |
| AC | 0.004 | 1 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.9497 | |
| AD | 3.940 | 1 | 3.940 | 4.518 | 0.0518 | |
| BC | 2.789 | 1 | 2.789 | 3.198 | 0.0954 | |
| BD | 3.367 | 1 | 3.367 | 3.861 | 0.0696 | |
| CD | 0.714 | 1 | 0.714 | 0.819 | 0.3809 | |
| A2 | 17.953 | 1 | 17.953 | 20.584 | 0.0005 ** | |
| B2 | 0.095 | 1 | 0.095 | 0.109 | 0.7456 | |
| C2 | 0.193 | 1 | 0.193 | 0.221 | 0.6455 | |
| D2 | 0.685 | 1 | 0.685 | 0.786 | 0.3903 | |
| Residual | 12.211 | 14 | 0.872 | |||
| Lock of Fit | 10.294 | 10 | 1.029 | 2.148 | 0.2400 | |
| Pure Error | 1.917 | 4 | 0.479 | |||
| Cor Total | 96.422 | 28 |
3.3. Impact of Factors on Evaluation Indicators
3.3.1. Influence of Factors on the Qualifying Index of Number of Grains in the Hole
- The interaction of forward speed and negative pressure in the air chamber
- 2.
- The interaction effect of forward speed and seed scooping volume
- 3.
- The interaction effect of forward speed and flow angle
- 4.
- The interaction between negative pressure and the amount of seed scooping
- 5.
- Interaction between negative pressure and flow angle
- 6.
- Interaction between seed scooping volume and flow angle
3.3.2. Influence of Factors on Qualified Index of Hole Distance
- Interaction of forward velocity and negative pressure
- 2.
- Interaction between the amount of seed scooping and forward speed
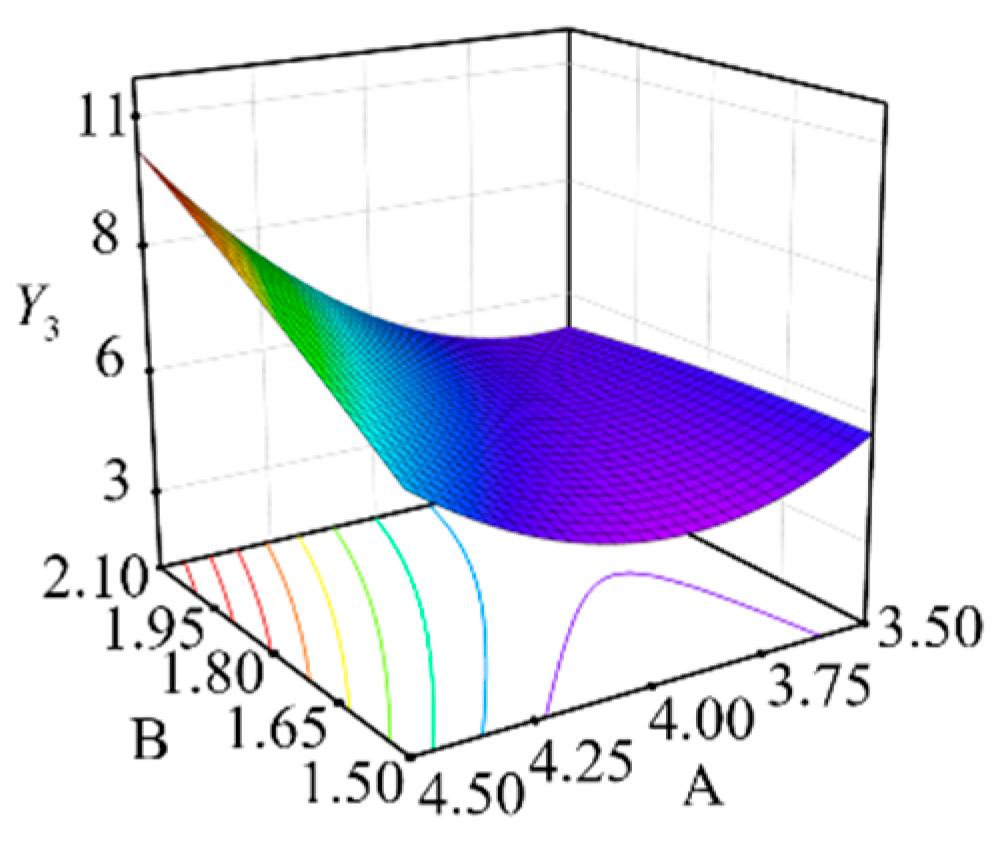
3.3.3. Influence of Various Factors on the Coefficient of Variation of Hole Distance
3.4. Parameter Optimization and Validation Tests
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- A quinoa precision seed-metering device based on the flow adsorption method was designed, and its structure and working principle were described. The phenomenon of multiple adsorption in one hole is solved, which leads to a low qualified index of hole grain number because the traditional small particle size seed-metering device has a high population accumulation density in the seed filling area. The population dispersion is improved by the flow seed device, which improves the adsorption performance of the planting apparatus.
- Through the dynamic analysis of the seed flow process, the influencing factors of the working parameters and structural parameters of the planting apparatus were obtained in the seed flow process and the seed suction process so as to design the seed flow device.
- The results of the bench verification test show that when the seed scooping volume is 5.82 mm, the flow angle is 31.08°, the negative pressure at suction hole is 1.7 kPa, the forward speed is 3.82 km·h−1, the qualified index of grain number per hole (Y1) is 93.98%, the qualified index of hole distance (Y2) is 94.27%, and the coefficient of variation of hole distance (Y3) is 4.87%, which is satisfactory for the quinoa planter to sow quinoa seeds.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rubén, V.; Blanca, H.-L. Nutritional and biological value of quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.). Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2017, 14, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, E.; Encina-Zelada, C.; Barros, L.; Gonzales-Barron, U.; Cadavez, V.; Ferreira, I.C. Chemical and nutritional characterization of Chenopodium quinoa Willd (quinoa) grains: A good alternative to nutritious food. Food Chem. 2019, 280, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Zhang, T.; Liu, F.; Li, N.; Li, J. Sunflower Seed Suction Stability Regulation and Seeding Performance Experiments. Agronomy 2023, 13, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.H.; Yi, S.J.; Chen, T.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.F.; Tao, G.X.; Mao, X. Experimental on the Performance of the Combined Type of Seed SowincSeeds with Air Hole and Cell Feed Wheel. J. Agric. Mech. Res. 2023, 45, 180–185. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, S.J.; Chen, T.; Li, Y.F.; Tao, G.X.; Xin, M. Design Test of Millet Hill-drop Seed-metering Device with Combination of Positive-negative Pressure and Hole Wheel. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2021, 52, 83–94, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.S.; Yu, Q.; Wang, L.; Liao, Y.T.; Wang, D.; Liao, Q.X. Design and Experiment of Scoop-type Precision Hole Metering Device for Rapeseed. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2020, 51, 47–54+64. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.R. Hole Group Effect Analysis and Performance Test of Quinoa Air-Suction Precision Seed Metering Device. Master’s Thesis, Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, Hohhot, China, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.P. Discrete Element Analysis and Performance Test of Pneumatic Quinoa Precision Seed Metering Device. Master’s Thesis, Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, Hohhot, China, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Hou, J.; Wu, W.; Han, C.; Wang, X.; Tang, T.; Sun, S. Key Structure Design and Experiment of Air-Suction Vegetable Seed-Metering Device. Agronomy 2022, 12, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wu, J.; Du, J.; Duan, D.; Zhang, T.; Chen, Y. Experimenting and Optimizing Design Parameters for a Pneumatic Hill-Drop Rapeseed Metering Device. Agronomy 2023, 13, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Li, H.; Qi, X.; Nyambura, S.M.; Yin, J.; Ma, Y.; Wang, J. Performance Parameters Optimization of a Three-Row Pneumatic Precision Metering Device for Brassica chinensis. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.H.; Lai, Q.H.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z.G.; Zhao, J.W.; Wang, T.T. Suction force on high-sphericity seeds in an air-suction seed-metering device. Biosyst. Eng. 2021, 211, 125–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.D.; Zhang, D.X.; Jing, H.R.; Yang, L.; Cui, T.; Ding, Y.Q.; Wang, Z.D.; Wang, Y.X.; Zhang, T.L. DEM-CFD coupling simulation and optimization of an inside-filling air-blowing maize precision seed-metering device. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2018, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.T.; Liao, Q.X.; Wang, L.; ZHENG, J.; Gao, P. Investigation on vacuum singulating effect influencing factors of pneumatic precision seed metering device for small particle size of seeds. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2018, 34, 10–17, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Ding, L.; Dou, Y.F.; Wang, W.Z.; Xu, Y.F.; He, X.; Qu, Z. Design and Experiment of Seed Metering Device with Combination Hole and Inner Filling for Cyperus esculentus. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2022, 53, 100–115, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Hu, B.; Cai, Y.Q.; Luo, X.; Mao, Z.B.; Li, J.W.; Guo, M.Y.; Wang, J. Theory and experiment of high-speed seed filling in limited gear-shaped side space based on seeds group stress. J. Jilin Univ. 2023, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, H.M.; Zhou, S.L.; Liu, Y.J.; Zhao, K.D.; Li, Z.W. Design and Test of Directional Vibrating Seed-feeding Device for Flat Solanaceous Vegetable Seeds. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2022, 53, 47–57, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.L.; Wang, Z.M.; Luo, X.W.; Zhang, M.H.; Fang, L.Y.; Liu, S.C.; Xu, P. Design and experiment of wedge churning device for pneumatic cylinder-type seed metering device for hybrid rice. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2019, 35, 1–8, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Du, X.; Liu, C.L.; Jiang, M.; Zhang, F.Y.; Yuan, H.; Yang, H.X. Design and experiment of self-disturbance inner-filling cell wheel maize precision seed-metering device. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2019, 35, 2334, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.D.; Yang, W.C.; Zhang, T.; Wang, W.W.; Zhang, S.; Chen, L.Q. Design and suction performance test of sucking-seed plate combined with groove-tooth structure on high speed precision metering device of rapeseed. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2019, 35, 12–22, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.D.; Yang, W.C.; Wu, Y.Y.; He, S.; Wang, W.W.; Chen, L.Q. Performance analysis and experiments of seed filling assisted by groove-tooth of pneumatic disc precision metering device for rapeseed. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2020, 36, 57–66, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Ding, L.; Yang, L.; Liu, S.R.; Yan, B.X.; He, X.T.; Zhang, D.X. Design of air suction high speed precision maize seed metering device with assistant seed filling plate. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2018, 34, 1–11, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Xie, D.B.; Zang, C.L.; Wu, X.Q.; Wang, W.W.; Liu, L.C.; Chen, L.Q. Design and Test of Garlic Seed Placer with Seed Disturbing Tooth Assisted Air Suction. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2022, 53, 47–57, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Gao, L.P.; Shi, B.B.; Liao, Q.X.; Zhang, B.X.; Zheng, J.; Liao, Y.T. Seeding performance of conical-hole seeding plate of the positive and negative pressure combination precision seed metering device for rapeseed. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2022, 38, 22–33, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Jia, H.L.; Chen, Y.L.; Zhao, J.L.; Wang, J.X.; Guo, M.Z.; Zhuang, J. Design and Experiment of Pneumatic-mechanical Combined Precision Metering Device for Soybean. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2018, 49, 75–86+139, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Shi, S.; Zhou, J.L.; Liu, H.; Fang, H.M.; Cun, S.C.; Zhang, R.F. Design and Experiment of Pneumatic Precision Seed-metering Device with Guided Assistant Seed-filling. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2019, 50, 61–70, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Gaikwad, B.B.; Sirohi, N.S. Design of a low-cost pneumatic seeder for nursery plug trays. Biosyst. Eng. 2008, 99, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.Y.; Ma, X.; Qi, L.; Xing, X.P.; Li, H.W.; Guo, L.J. Theory and Experiment on Vibrating Small-amount Rice Sowing Device. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2018, 49, 119–128+214, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.L.; Wang, C.; Song, J.N.; Du, X.; Zhang, F.Y. Design and Seed-filling Test of Cell-type Precision Seed-metering Device with Vibration Technology. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2018, 49, 108–115, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.L.; Wang, Y.L.; Du, X.; Song, J.N.; Wang, J.C.; Zhang, F.Y. Filling performance analysis and verification of cell-belt rice precision seed-metering based on friction and repeated filling principle. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2019, 35, 29–36, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Level | Factors | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Forward Speed A/(km·h−1) | Negative Pressure B/(kPa) | The Amount of Seed C/(mm) | Flow Angles D/(°) | |
| −1 | 3.5 | 1.5 | 5.5 | 25 |
| 0 | 4 | 1.8 | 6 | 30 |
| 1 | 4.5 | 2.1 | 6.5 | 35 |
| No. | Factors | Index | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | D | Y1 (%) | Y2 (%) | Y3 (%) | |
| 1 | 4.5 | 1.8 | 6 | 35 | 82.56 | 85.6 | 9.53 |
| 2 | 4.5 | 1.5 | 6 | 30 | 79.97 | 86.79 | 6.13 |
| 3 | 3.5 | 1.8 | 6 | 35 | 88.14 | 91.3 | 3.47 |
| 4 | 3.5 | 1.5 | 6 | 30 | 87.36 | 93.17 | 6.35 |
| 5 | 4.5 | 1.8 | 6 | 25 | 81.16 | 84.25 | 7.06 |
| 6 | 4 | 1.5 | 6 | 35 | 88.33 | 91.6 | 3.48 |
| 7 | 4 | 1.8 | 5.5 | 25 | 90.97 | 92.03 | 4.09 |
| 8 | 4 | 2.1 | 5.5 | 30 | 90.03 | 87.05 | 5.11 |
| 9 | 3.5 | 2.1 | 6 | 30 | 85.23 | 83.14 | 5.02 |
| 10 | 4 | 1.5 | 5.5 | 30 | 91.01 | 90.61 | 3.15 |
| 11 | 4.5 | 1.8 | 5.5 | 30 | 84.37 | 85.2 | 9.35 |
| 12 | 4 | 1.8 | 6 | 30 | 93.53 | 93.87 | 4.48 |
| 13 | 4 | 2.1 | 6 | 25 | 85.58 | 83.38 | 4.34 |
| 14 | 4 | 1.8 | 6 | 30 | 94.63 | 94.67 | 5.99 |
| 15 | 4 | 1.8 | 6 | 30 | 94.14 | 94.25 | 4.36 |
| 16 | 4 | 1.5 | 6 | 25 | 86.61 | 90.44 | 5.12 |
| 17 | 4 | 2.1 | 6.5 | 30 | 90.11 | 83.96 | 8.46 |
| 18 | 4 | 1.8 | 6 | 30 | 93.24 | 93.31 | 5.31 |
| 19 | 4 | 1.8 | 6.5 | 25 | 86.88 | 87.66 | 5.24 |
| 20 | 4.5 | 1.8 | 6.5 | 30 | 84.4 | 88.59 | 8.89 |
| 21 | 4 | 1.8 | 6 | 30 | 94.22 | 95.46 | 5.49 |
| 22 | 4 | 1.8 | 5.5 | 35 | 92.36 | 92.14 | 5.67 |
| 23 | 3.5 | 1.8 | 5.5 | 30 | 91.96 | 92.1 | 5.39 |
| 24 | 4 | 1.8 | 6.5 | 35 | 91.43 | 90.21 | 5.13 |
| 25 | 4 | 1.5 | 6.5 | 30 | 87.67 | 91.08 | 3.16 |
| 26 | 3.5 | 1.8 | 6 | 25 | 84.03 | 92.89 | 4.97 |
| 27 | 3.5 | 1.8 | 6.5 | 30 | 86.07 | 89.56 | 4.81 |
| 28 | 4 | 2.1 | 6 | 35 | 90.87 | 87.36 | 6.37 |
| 29 | 4.5 | 2.1 | 6 | 30 | 82.53 | 82.8 | 9.41 |
| No. | Y1/% | Y2/% | Y3/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 93.715 | 93.859 | 3.625 |
| 2 | 93.643 | 92.326 | 4.168 |
| 3 | 92.714 | 94.768 | 5.596 |
| 4 | 95.667 | 94.705 | 4.643 |
| 5 | 94.166 | 95.677 | 6.323 |
| Mean Value | 93.981 | 94.267 | 4.871 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhong, W.; Zhao, X.; Liu, F.; Bai, H.; Dong, W.; Hu, H.; Kong, X. Design and Experiment of Precision Seed Metering Device for Flow Adsorption of Quinoa Seeds. Agriculture 2024, 14, 434. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14030434
Zhong W, Zhao X, Liu F, Bai H, Dong W, Hu H, Kong X. Design and Experiment of Precision Seed Metering Device for Flow Adsorption of Quinoa Seeds. Agriculture. 2024; 14(3):434. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14030434
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhong, Wendong, Xuan Zhao, Fei Liu, Hongbin Bai, Wenxue Dong, Hengtong Hu, and Xiang Kong. 2024. "Design and Experiment of Precision Seed Metering Device for Flow Adsorption of Quinoa Seeds" Agriculture 14, no. 3: 434. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14030434
APA StyleZhong, W., Zhao, X., Liu, F., Bai, H., Dong, W., Hu, H., & Kong, X. (2024). Design and Experiment of Precision Seed Metering Device for Flow Adsorption of Quinoa Seeds. Agriculture, 14(3), 434. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14030434






