An Experimental Analysis of the Seed-Filling Mechanism of Maize-Precision Hole-Planter Clamping
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Structure and Working Principle of the Hole Seeder
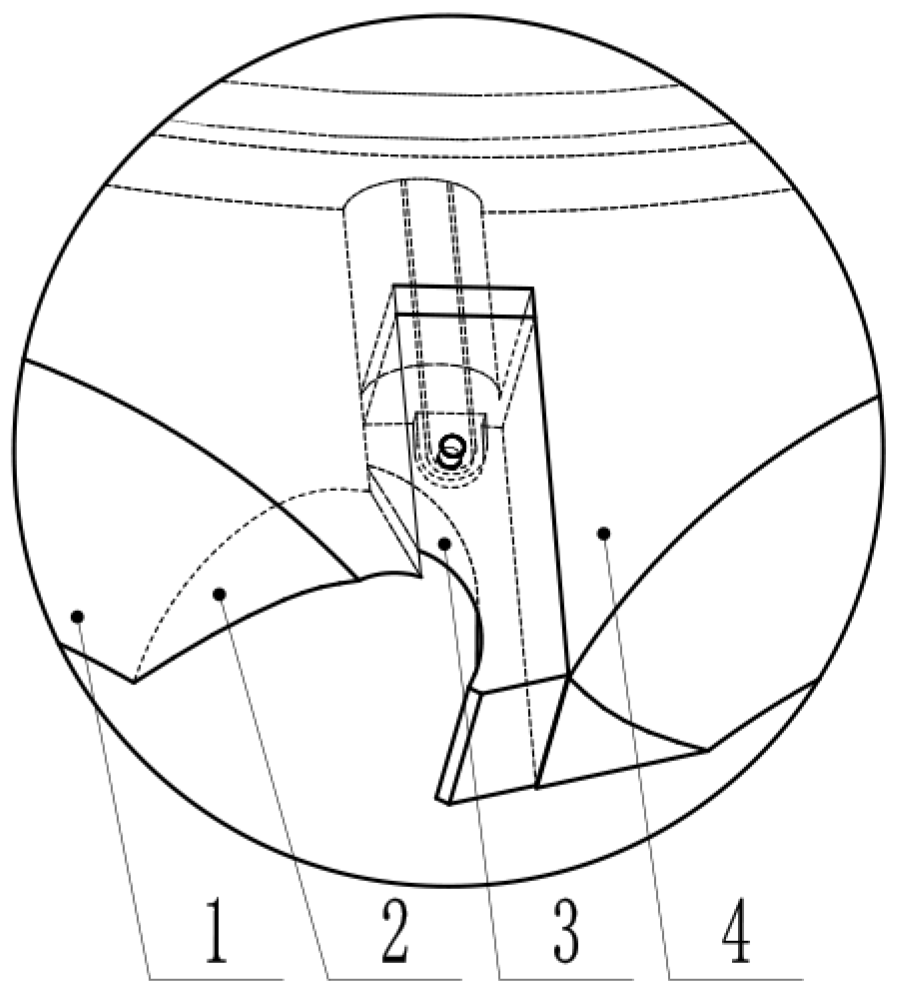
2.1. Overall Structure of the Hole Seeder
2.2. Operation Principle of the Hole Seeder
3. Parameter Design of Combined-Type Holes
3.1. Geometric Parameters of Maize Seeds
3.2. Combined-Type Hole Design
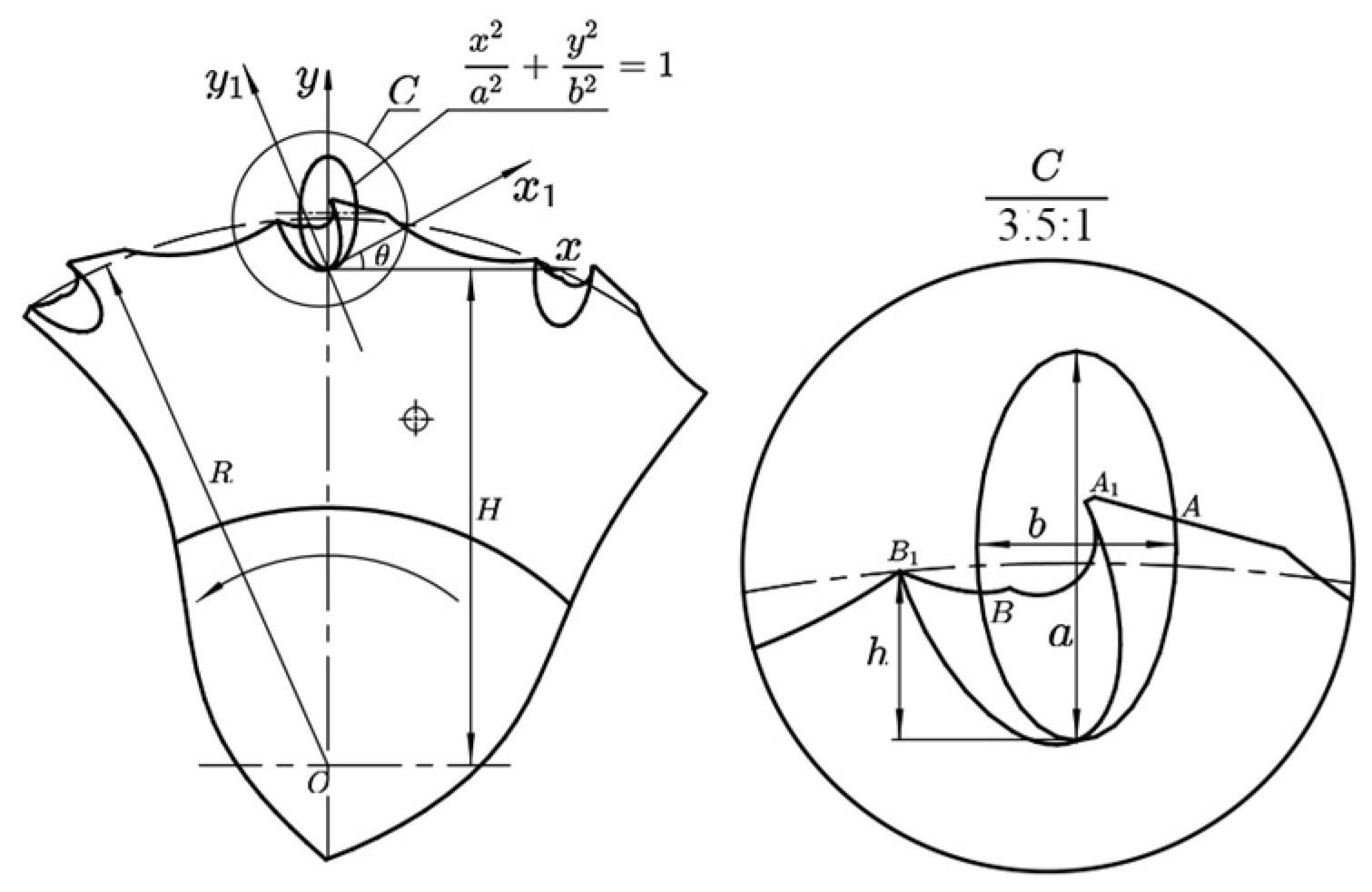
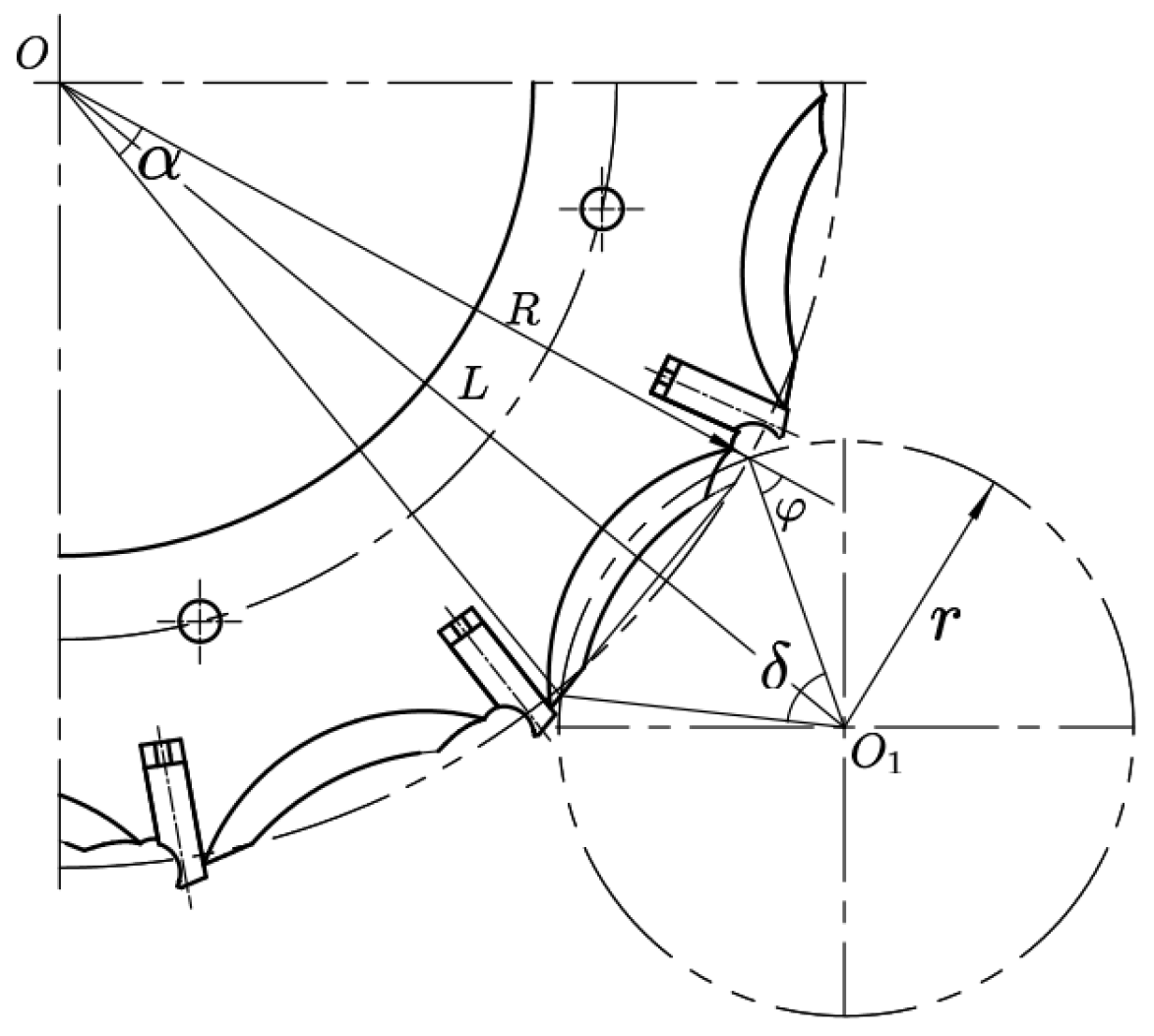
3.2.1. Determination of the Number of Combined-Type Holes
3.2.2. Determination of the Geometric Parameters of the Combined-Type Holes
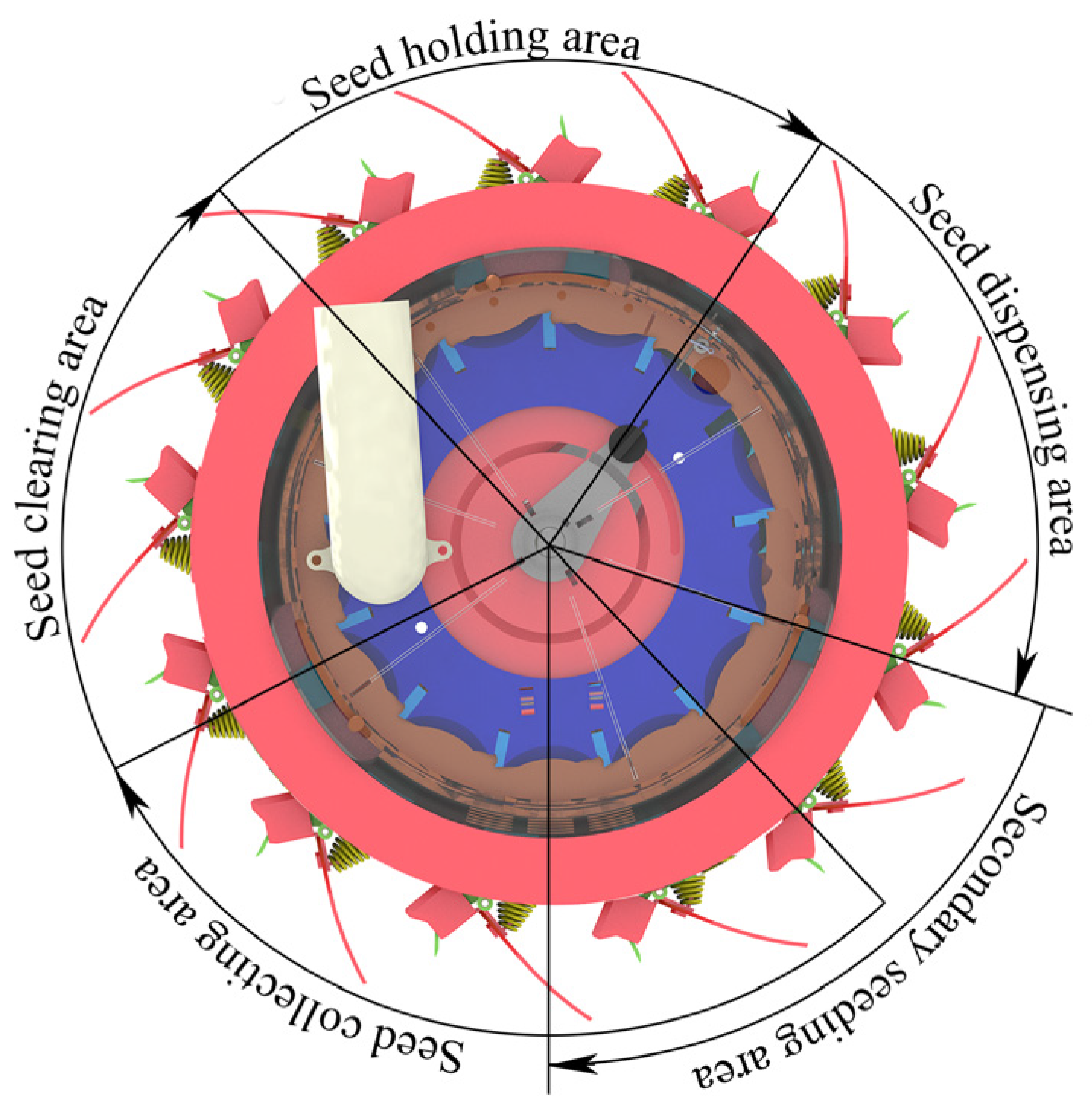
4. Analysis of the Working Process of the Seed Picker Disc Assembly
4.1. Seed Pick-Up Slider Motion Design
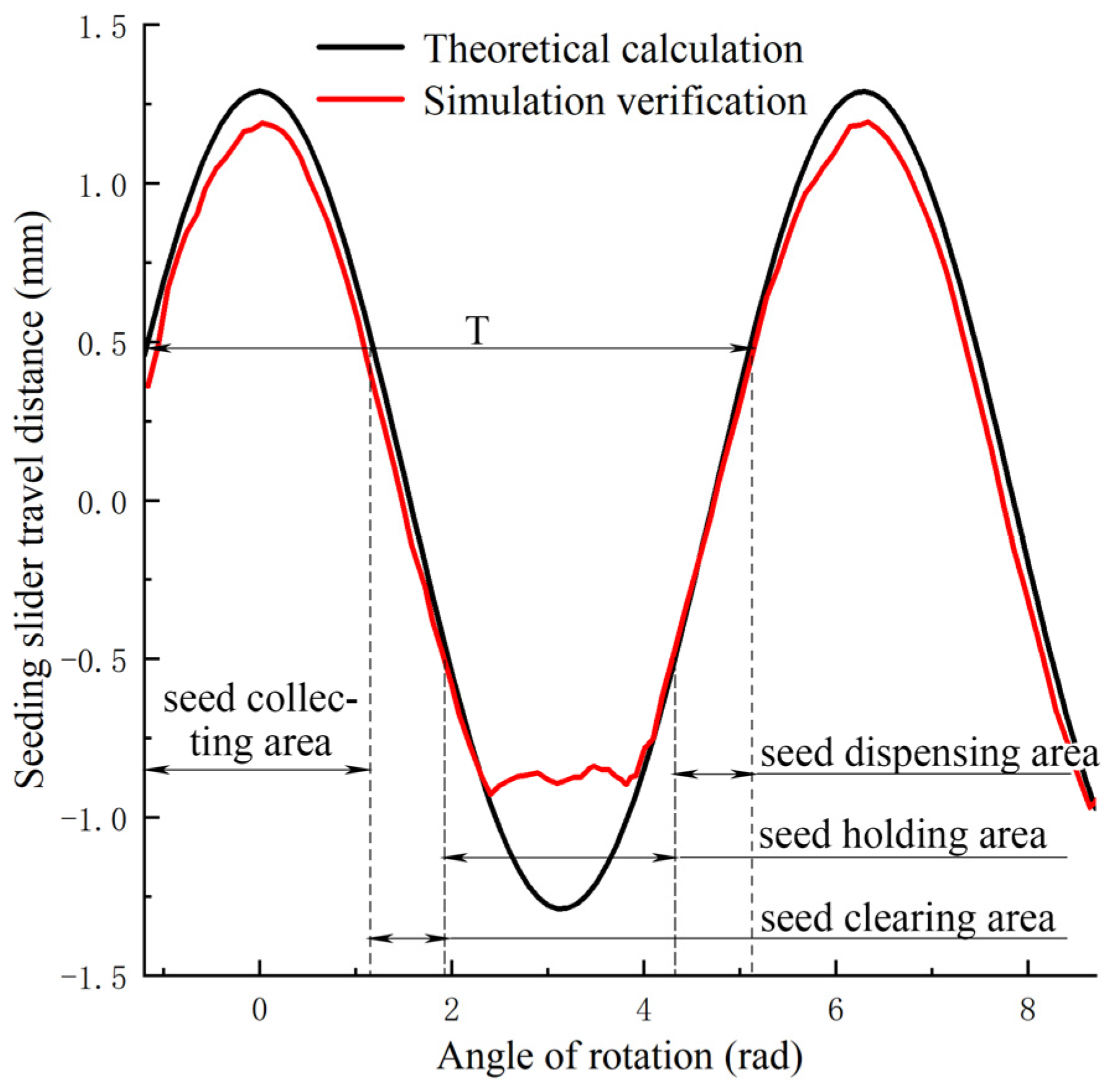
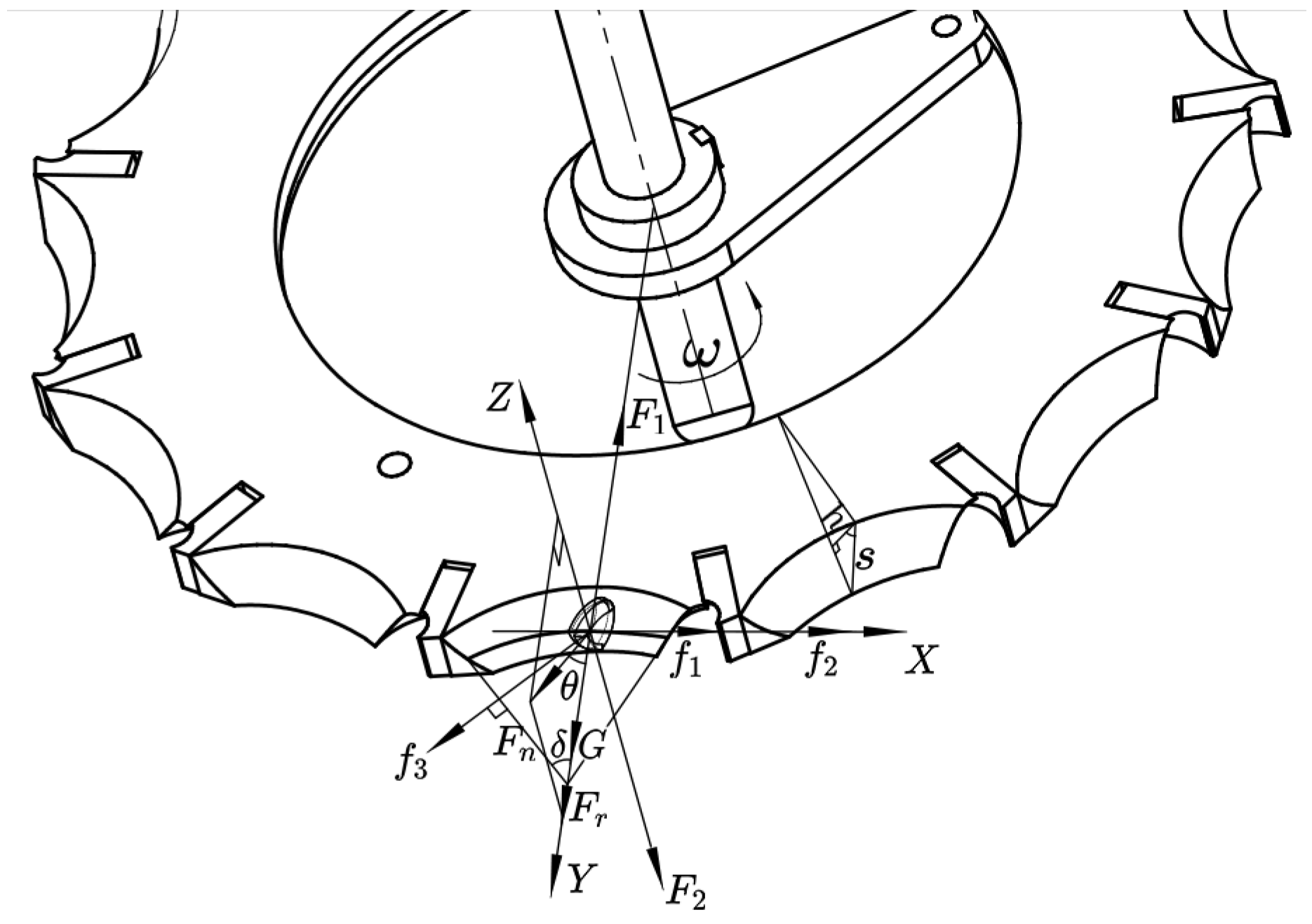
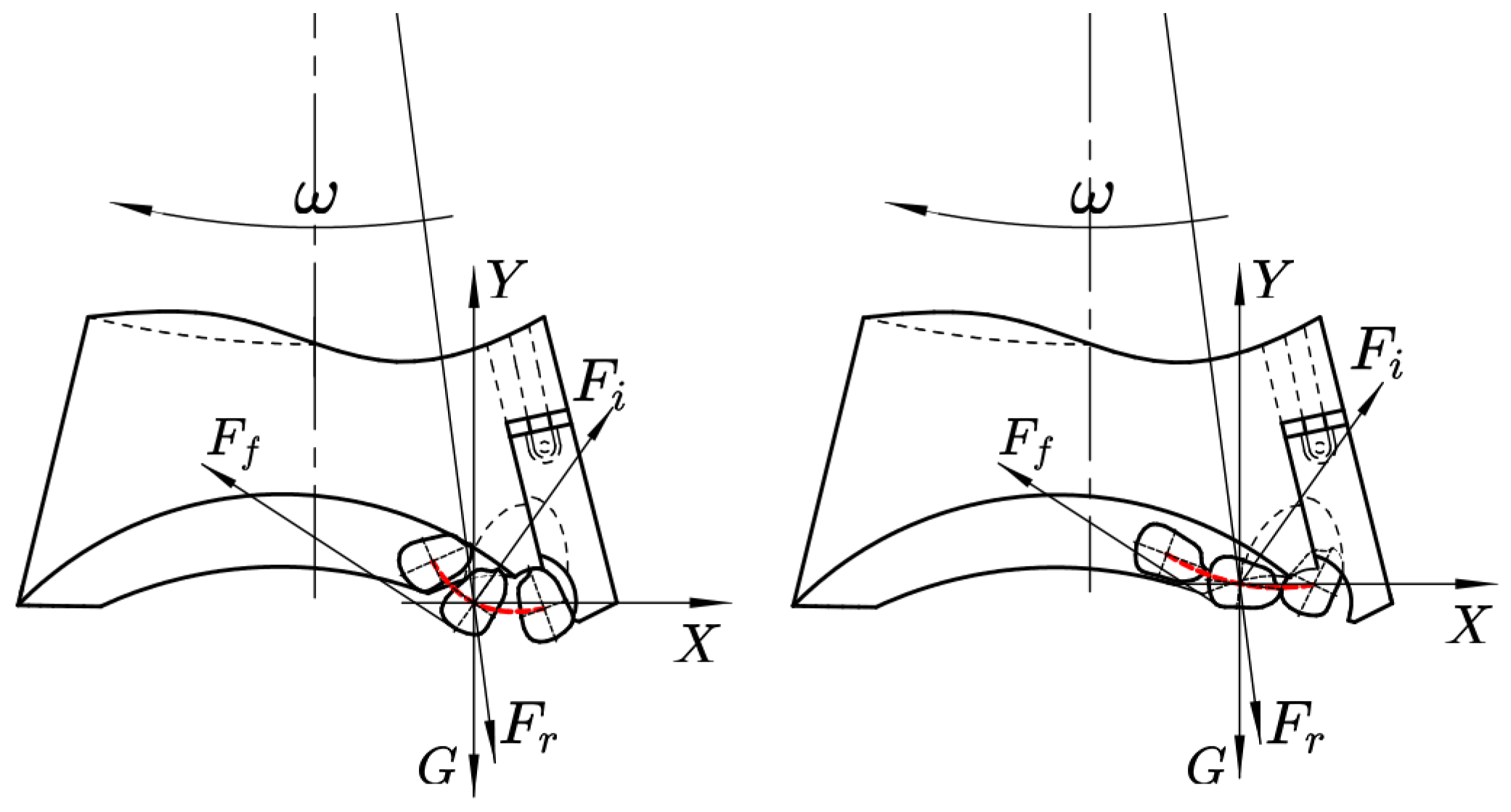
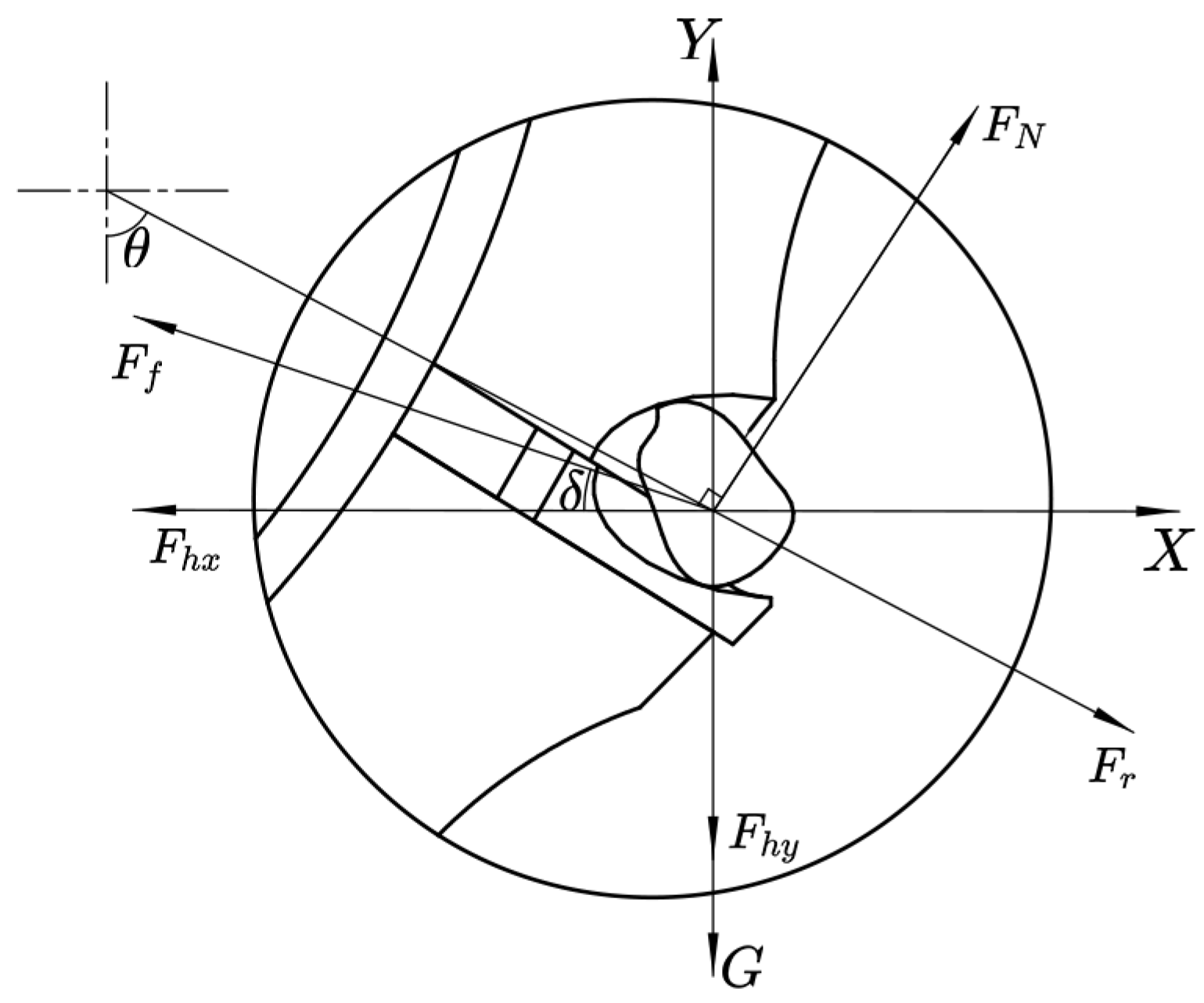
4.1.1. Mechanical Static Modeling
4.1.2. Kinematic Simulation and Verification of Seed Pick-Up Slider
4.2. Kinematic Analysis of the Seed Transfer Process
4.3. Kinematic Analysis of the Seed Extraction Process
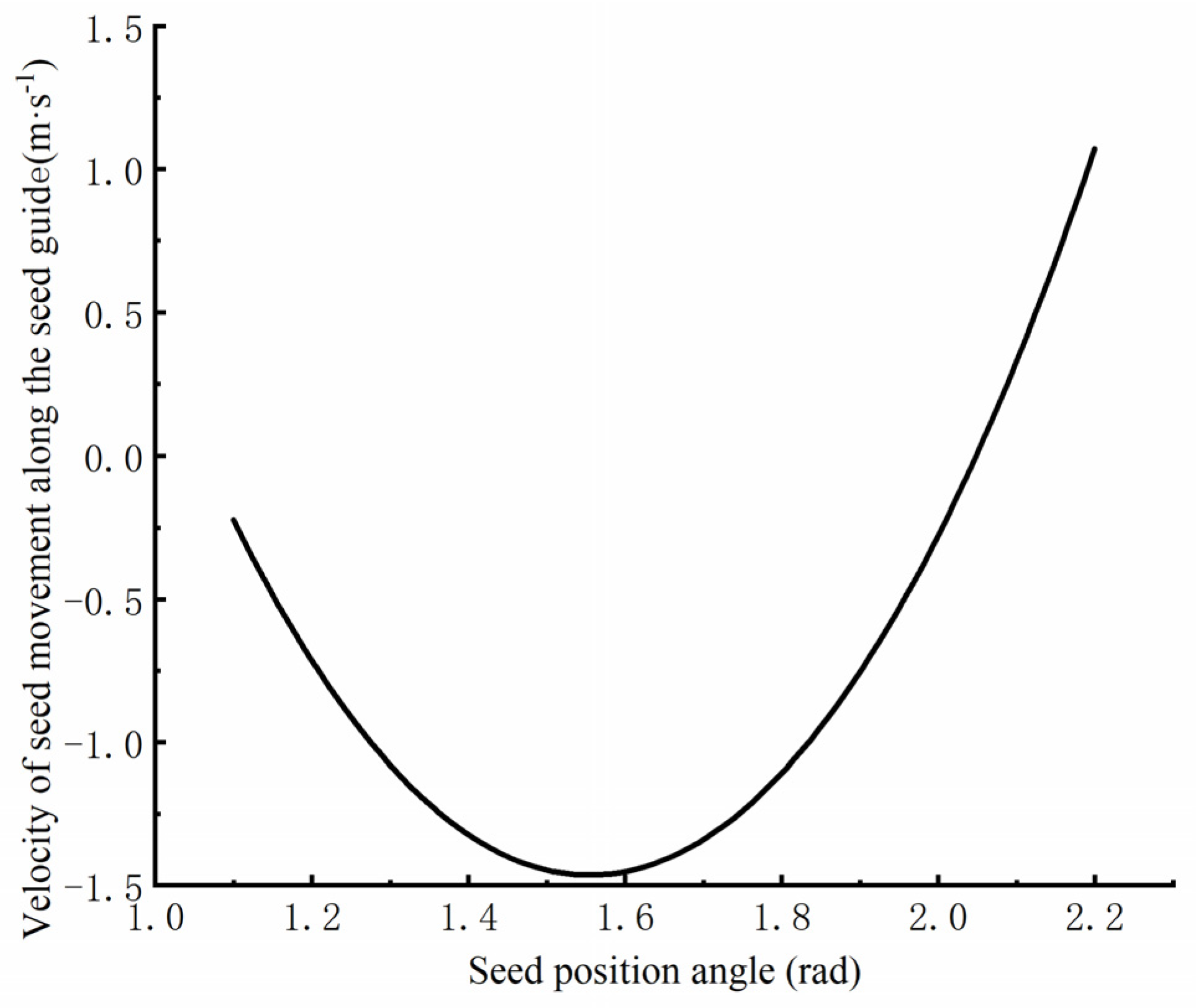
4.4. Analysis of the Limiting Speed of the Seed Extraction Disc
5. Simulation and Analysis of Seed-Picking Process in Hole Seeding
5.1. Simulation Modeling
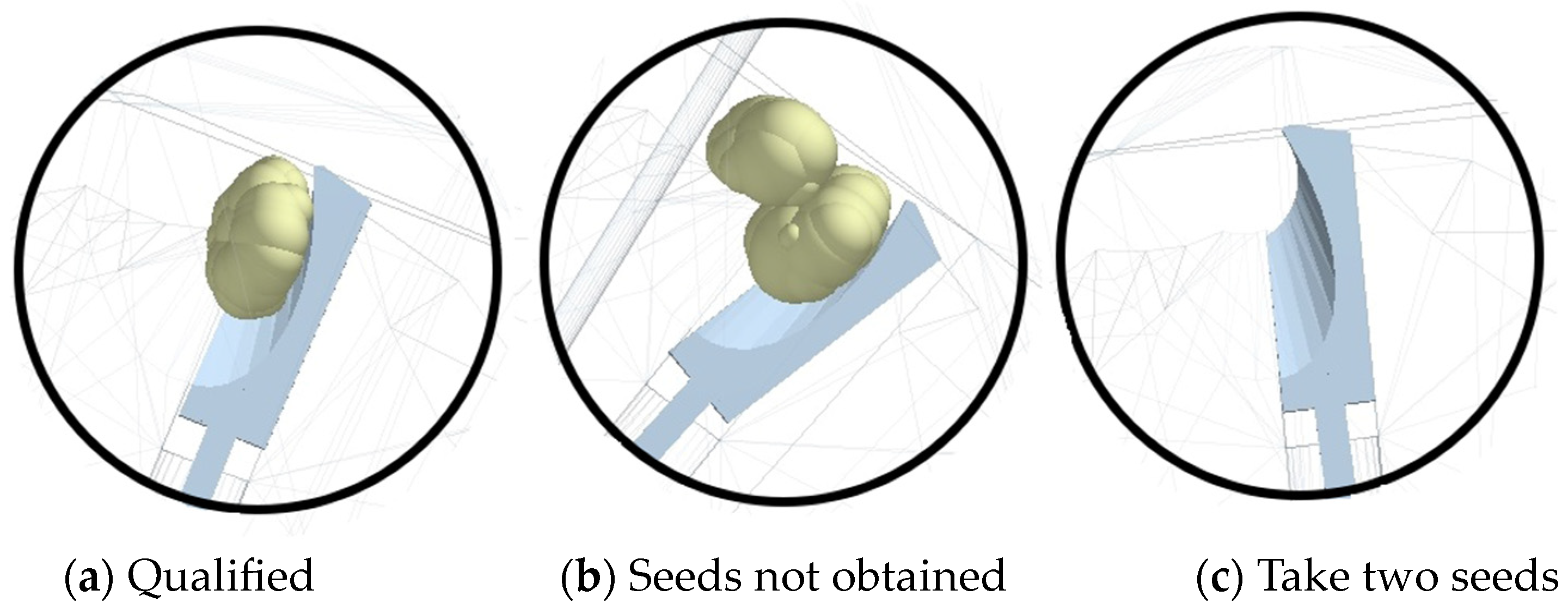
5.2. Seeding Performance and Testing
6. Seeding Performance Simulation Test
6.1. Test Program
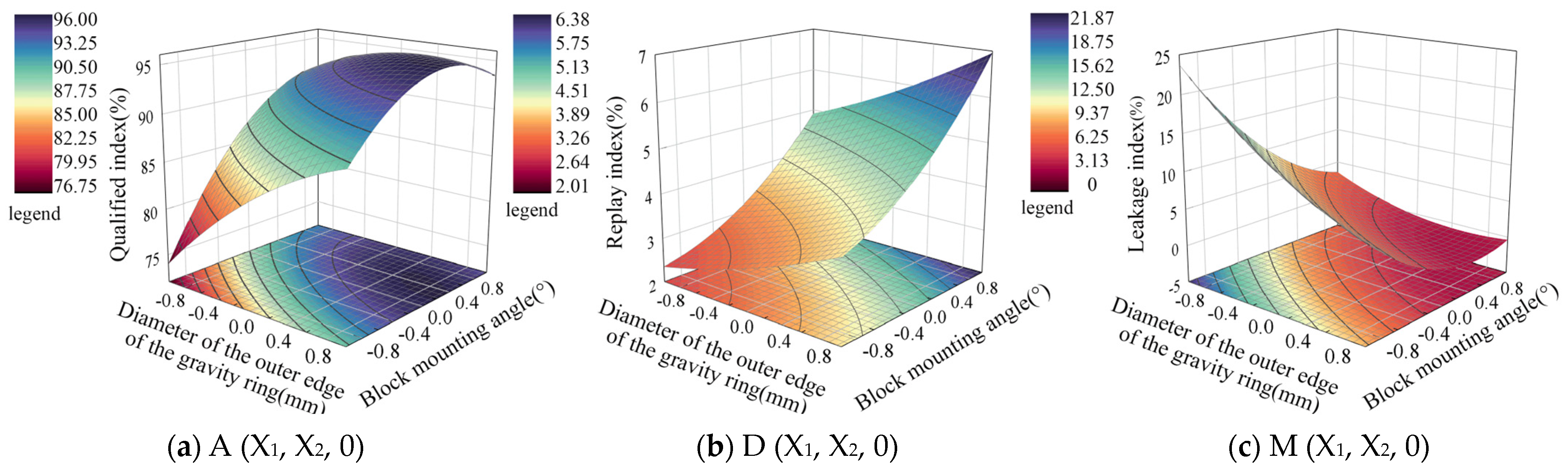
6.2. Analysis of Sowing Performance Test Results
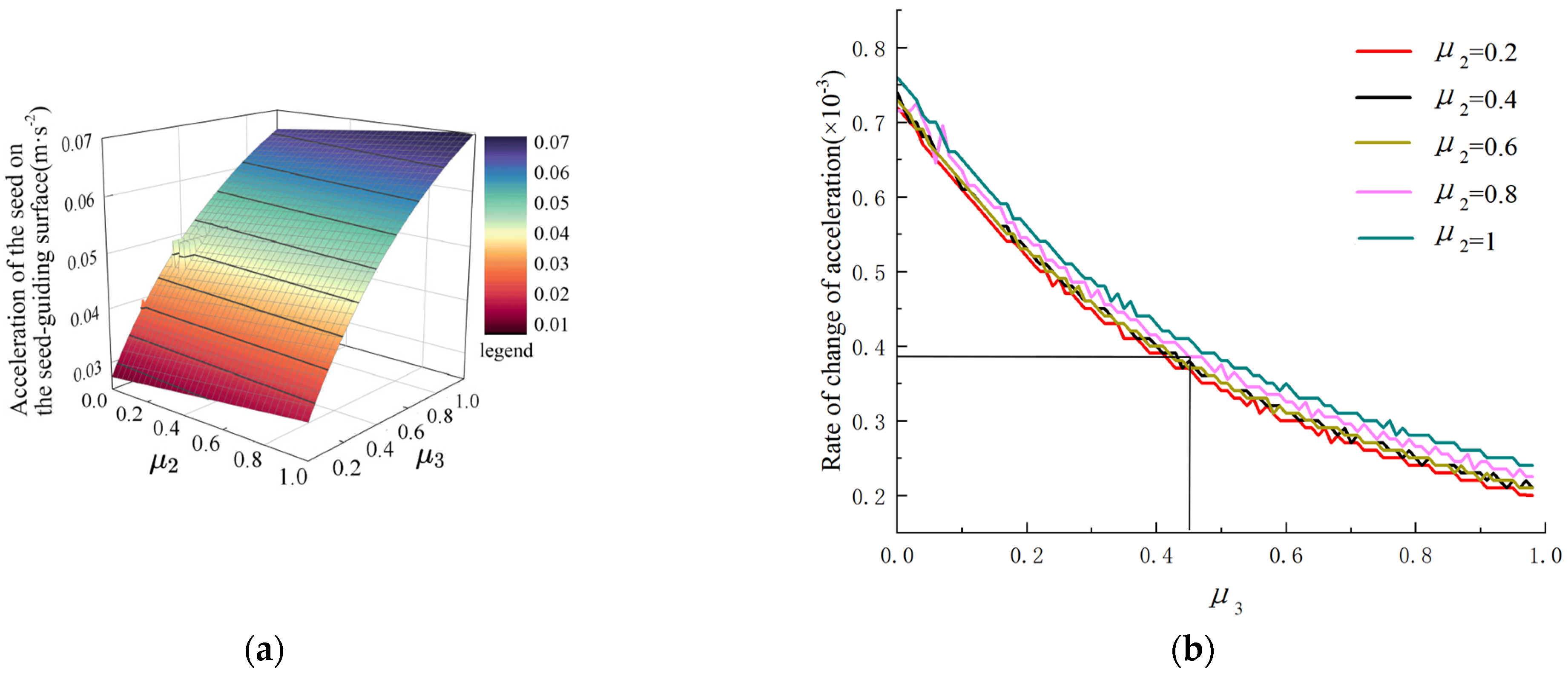
6.3. Parameter Optimization
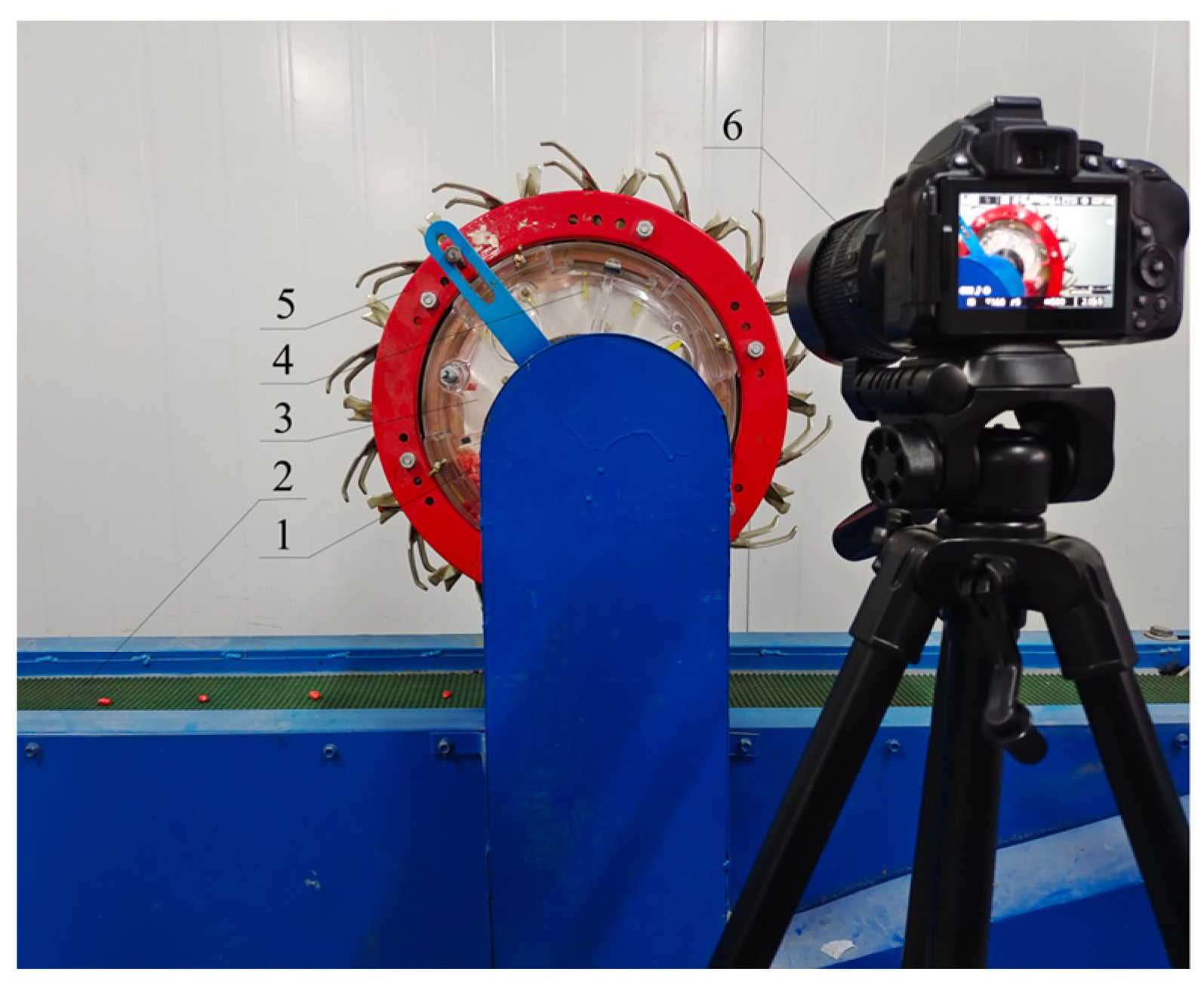
7. Bench Test Validation
8. Discussions
9. Conclusions
- (1)
- This study clarified the adjustment range of the hole and its influencing factors and revealed the force state of the seed in the process of seed guiding, filling, and carrying by analyzing the mechanics of the seed-taking process of the seed-taking disc.
- (2)
- With the help of the simulation platform for the seed extraction process, we found that the seeds near the edge of the seed tray in the rising zone had the most similar speed to the seed tray, which is an important factor for successful seed extraction. The main cause of leakage was the “hitching arch” of the seed, and a targeted solution to break the arch by oscillating the seed pick-up slider was proposed.
- (3)
- A three-factor, three-level Box–Behnken central combination simulation test was conducted and the results were optimized. The optimum combination of parameters was obtained as follows: diameter of the outer edge of the gravity ring, 174.3 mm; installation angle of the block, 131.9°; and speed of the hole seeder, 85.2 rpm. The optimal combination of parameters was rounded off, and a test rig was built for validation. The test results show that, under the optimal parameter combination, the active clamped hole seeder had a seeding qualification index of 93.29%, re-seeding index of 1.06%, and leakage index of 5.65%, meeting the requirements for precision seeding.
10. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, L.; Yan, B.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, T.; Wang, Y.; Cui, T. Research Progress on Precision Planting Technology of Maize. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2016, 47, 38–48. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.Y.; Xia, J.F.; Liu, G.Y.; Cheng, J.; Wei, Y.S.; Xie, D.Y. Design and Analysis of a Pneumatic Automatic Compensation System for Miss-Seeding Based on Speed Synchronization. Agriculture 2023, 13, 1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.H.; Zhang, D.X.; Yang, L.; Cui, T.; Song, W.; He, X.T.; Dong, J.Q. Optimal design and experiment of critical components of hand-pushing corn plot precision planter. Agriculture 2022, 12, 2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Cheng, J.; Shi, Z.; Wang, M.; Fu, H.; Wu, H. Simulation and Experiment of Seed Taking Performance of Swing-clamp Type Maize Precision Seed-metering Divice. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2023, 54, 38–50. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, J.; Gao, X.; Zhang, S.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, C. Design and Test of Guiding Seed Throwing Mechanism for Maize Posture Control and Driving Metering Device. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2023, 54, 25–34. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, D.; Zhang, M.; He, K.; Li, Y.; Xie, C. Design and Experiment of Declined Disc Plate with Double Ring Corn Metering Device. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2018, 49, 68–76. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Tang, H.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; Huang, H. Optimization design and experiment on ripple surface type pickup finger of precision maize seed metering device. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2017, 10, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Yan, B.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, T.; Cui, T. Research progress on precision planting technology of maize. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery. 2016, 10, 801. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Zheng, Z.; Yu, Y.; Liu, T.; Zhang, Z. Determination of the energetic coefficient of restitution of maize grain based on laboratory experiments and dem simulations. Powder Technol. 2020, 362, 645–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liang, Z.; Liu, L. Impact Mechanical Characteristics Analysis of Rice Grain. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2013, 44, 88–92. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.; Yang, Y.; Memon, M.S.; Tan, C.; Wang, L.; Tang, P. Design and simulation for seeding performance of high-speed inclined corn metering device based on discrete element method (dem). Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 19415. [Google Scholar]
- Horabik, J.; Parafiniuk, P.; Wiacek, J.; Kobylka, R.; Molenda, M.; Stasiak, M. Dem modelling of the influence of initial stress state on the discharge rate of spherical particles from a model silo. Powder Technol. Int. J. Sci. Technol. Wet Dry Part. Syst. 2022, 403, 117402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Zhang, X.; Shi, Z.; Cheng, J.; Wu, H.; Wang, M.; Yu, Y. Design and test of maize precision seeder with seed-disturbance and side-filling slotted disk. J. Huazhong Agric. Univ. 2023, 42, 229–239. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, B.; Cai, Y.; Luo, X.; Mao, Z.; Li, J.; Guo, M.; Wang, J. Theory and experiment of high-speed seed filling in limited gear-shaped side space based on seeds group stress. J. Jilin Univ. (Eng. Technol. Ed.) 2022, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahul, K.; Raheman, H.; Paradkar, V. Design and development of a 5r 2dof parallel robot arm for handling paper pot seedlings in a vegetable transplanter. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2019, 166, 105014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, J.; Wang, J.; Guo, M.; Zhuang, J. Design and Experiment of Pneumatic-mechanical Combined Precision Metering Device for Soybean. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2018, 49, 75–86. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Y.Q.; Luo, X.; Hu, B.; Mao, Z.B.; Li, J.W.; Guo, M.Y.; Wang, J. Theoretical and experimental analyses of high-speed seed filling in limited gear-shaped side space of cotton precision dibbler. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 200, 107202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Q.; Zhang, G.; Zheng, K.; Liu, H.; Tang, N.; Liu, W.; Ji, C. Design and experiment of the spoon clip type seed metering device for Allium chinense. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2023, 39, 15–25. [Google Scholar]
- Vazquez, G.H.; Arf, O.; Sargi, B.A.; Pessoa, A.C.O. Corn seed size and shape influence on plant growth and grain yield. Biosci. J. 2012, 28, 16–24. [Google Scholar]
- Horabik, J.; Molenda, M. Parameters and contact models for DEM simulations of agricultural granular materials: A review. Biosyst. Eng. 2016, 147, 206–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wassgren, C.; Veikle, E.; Ambrose, K. Determination of material and interaction properties of maize and wheat kernels for DEM simulation. Biosyst. Eng. 2020, 195, 208–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markauskas, D.; Ramírez-Gómez, Á.; Kačianauskas, R.; Zdancevičius, E. Maize grain shape approaches for DEM modelling. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2015, 118, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Xiang, W.; Luo, K.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Qin, K. Design and Experiment of Radix Peucedani Weeding Machine Separating Weeds and Soil with Combination of Throwing and Pushing. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2023, 54, 106–114. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, C.; Ding, W.; Liu, Z.; An, M.; Zhang, X.; Qin, K. Design and Experiment of Seed Disperser for Ning-guo Radix peucedani Based on Rocky Dem. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2023, 54, 53–64. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, C.; Liu, Z.; Ding, W.; Wu, M.; Zhang, X. Design and Experiment of Ning-guo Radix Peucedani Bionic Digging Shovel. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2023, 54, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, L.; Zhao, W.; Yang, X. Effects of typical corn kernel shapes on the forming of repose angle by DEM simulation. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2022, 15, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T1593-2015; Agricultural Wheeled Tractor—Rear-Mounted Three-Point Linkage—Categories 0, 1N, 1, 2N, 2, 3N, 3, 4N and 4. China Standard Press: Beijing, China, 2015.
- JB/T 10293-2001; Specifications of Single Seed Drill (Precision Drill). Institute of Mechanical Science: Beijing, China, 2001.
- Ma, C.; Yi, S.; Tao, G.; Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, G.; Gao, F. Research on Receiving Seeds Performance of Belt-Type High-Speed Corn Seed Guiding Device Based on Discrete Element Method. Agriculture 2023, 13, 1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Zhao, W.; Hua, C.; Rao, G.; Guo, J.; Wang, Z. Study on the Intercropping Mechanism and Seeding Improvement of the Cavity Planter with Vertical Insertion Using DEM-MBD Coupling Method. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Liu, L.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X. Numerical simulation of seed-movement characteristics in new maize delivery device. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

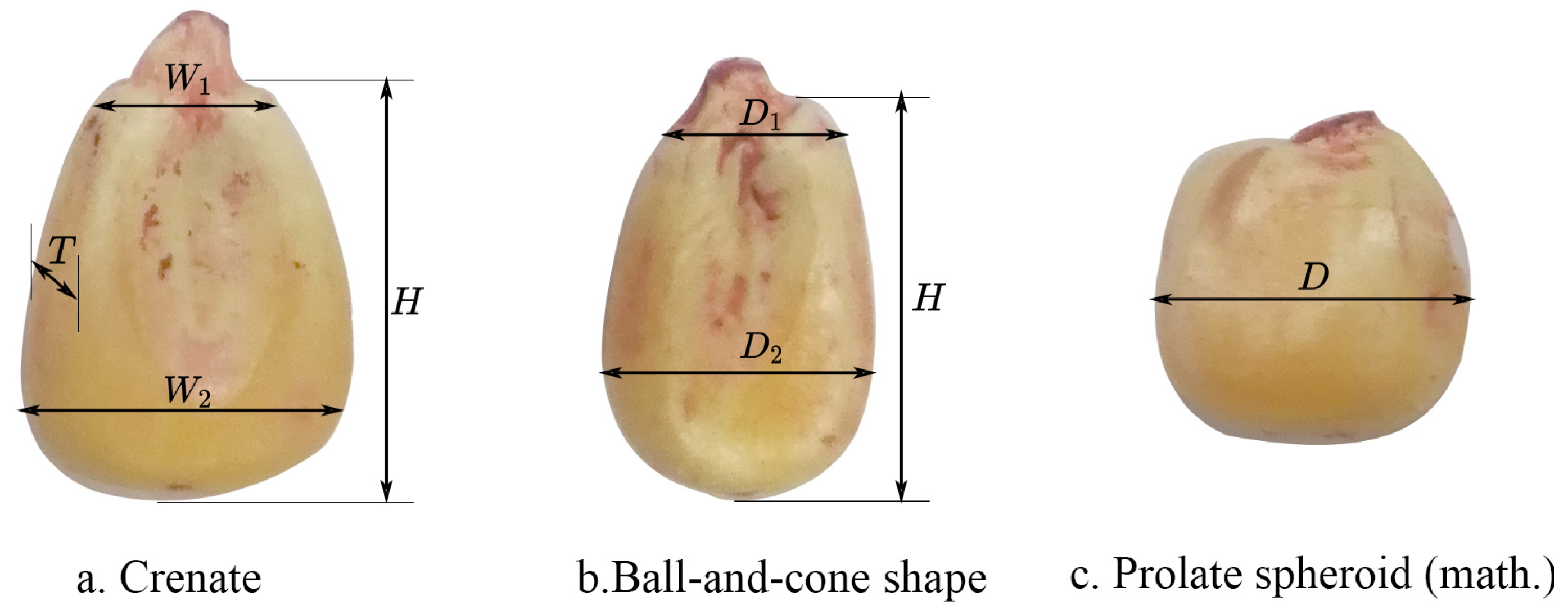



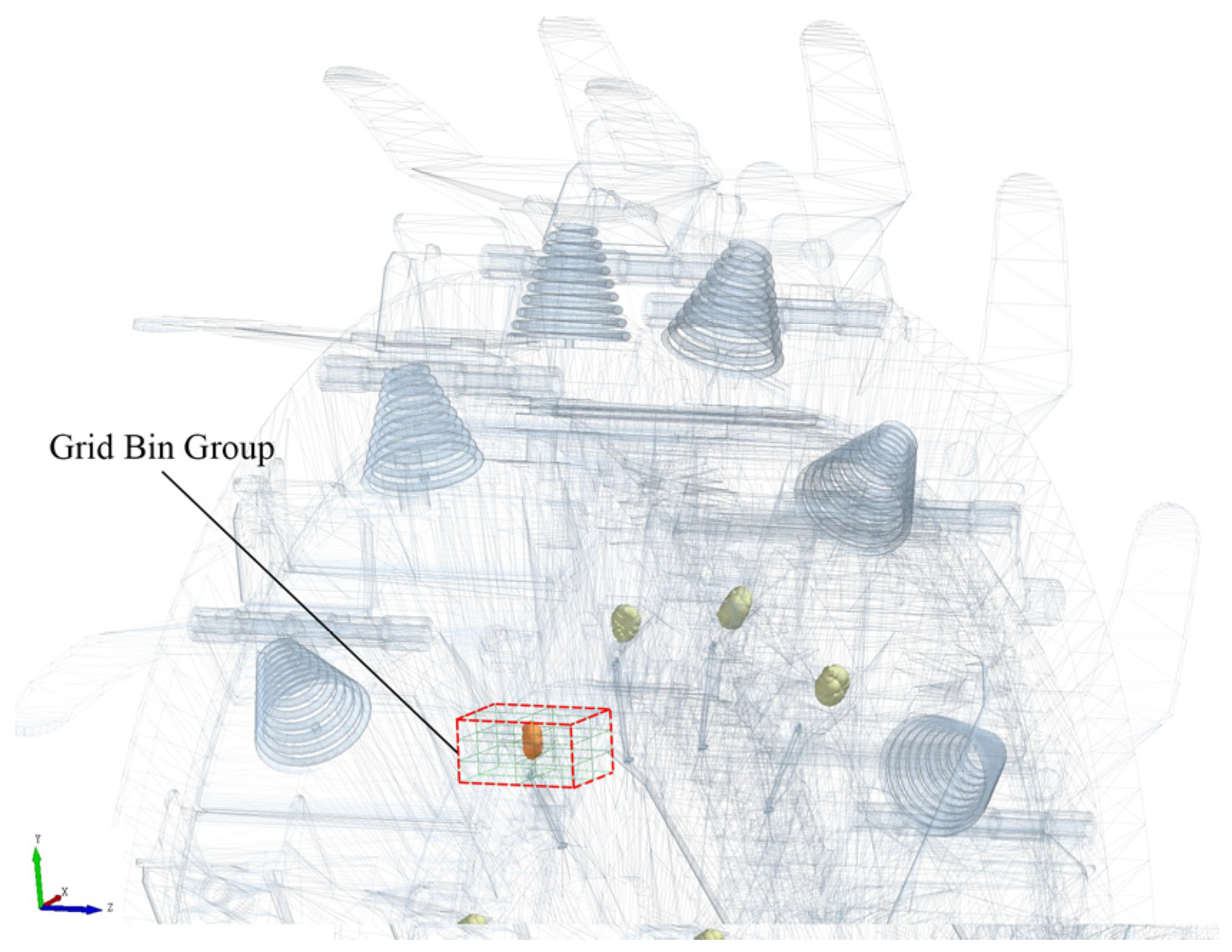

| Type | Relevant Parameters (mm) | Percentage | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | Overall width (W1) | Lower width (W2) | Above average (H) | Thicker (T) | |
| 7.15 | 8.92 | 11.57 | 4.43 | 47.6% | |
| b | Overall diameter (D1) | Lower diameter (D2) | Above average (H) | ||
| 6.27 | 8 | 11.14 | 23.8% | ||
| c | Caliber (D) | ||||
| 5.5 | 28.6% | ||||
| Corn | Poisson’s ratio Young’s modulus/MPa Serrated particle density/kg·m−3 Spherical and conical particle density/kg·m−3 Quasi-spherical particle density/kg·m−3 Collision recovery coefficient Static friction coefficient | 0.4 26 1213 1194 1234 0.37 0.2 | [20] [20] Determine Determine Determine [21] [22] |
| PLA | Poisson’s ratio Shear modulus/Pa Density/kg·m−3 | 0.35 3 × 109 1240 | [23] [24] [25] |
| Steel | Poisson’s ratio Shear modulus/Pa Density/kg·m−3 | 0.3 7.9 × 1010 7800 | EDEM self-contained materials EDEM self-contained materials EDEM self-contained materials |
| Corn and PLA | Collision recovery coefficient Static friction coefficient Coefficient of rolling friction | 0.45 0.85 0.05 | Determine Determine Determine |
| Corn and Steel | Collision-recovery coefficient Static friction coefficient Coefficient of rolling friction | 0.5 0.32 0.01 | [26] Determine [26] |
| Levels | Factors | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| The Diameter of the Outer Edge of the Gravity Ring X1/mm | The Angle of the Block Installation X2/° | The Speed of the Hole Planter X3/rpm | |
| −1 | 172 | 125 | 60 |
| 0 | 174 | 135 | 84 |
| 1 | 176 | 145 | 108 |
| Experiment Factors | Experiment Indexes | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | The Diameter of the Outer Edge of the Gravity Ring X1/mm | The Angle of the Block Installation X2/° | The Speed of the Hole Planter X3/rpm | Qualified Index A | Replay Index D | Leakage Index M |
| 1 | 172 | 93.6 | 60 | 91.15 | 3.85 | 5 |
| 2 | 176 | 93.6 | 60 | 94.36 | 5.64 | 0 |
| 3 | 172 | 117 | 60 | 79.1 | 2.82 | 18.08 |
| 4 | 176 | 117 | 60 | 92.69 | 4.75 | 2.56 |
| 5 | 172 | 105.3 | 45 | 74.49 | 2.31 | 23.2 |
| 6 | 176 | 105.3 | 45 | 89.11 | 3.72 | 7.17 |
| 7 | 172 | 105.3 | 75 | 91.28 | 5 | 3.72 |
| 8 | 176 | 105.3 | 75 | 92.84 | 7.05 | 0.11 |
| 9 | 174 | 93.6 | 45 | 85.64 | 3.46 | 10.9 |
| 10 | 174 | 117 | 45 | 76.41 | 3.07 | 20.52 |
| 11 | 174 | 93.6 | 75 | 93.46 | 6.4 | 0.14 |
| 12 | 174 | 117 | 75 | 92.95 | 5.39 | 1.66 |
| 13 | 174 | 105.3 | 60 | 92.44 | 3.72 | 3.84 |
| 14 | 174 | 105.3 | 60 | 91.93 | 3.85 | 4.22 |
| 15 | 174 | 105.3 | 60 | 93.72 | 3.97 | 2.31 |
| 16 | 174 | 105.3 | 60 | 94.61 | 3.98 | 1.41 |
| 17 | 174 | 105.3 | 60 | 92.3 | 3.72 | 3.98 |
| Source | Qualified Index A (%) | Leakage Index D (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sum of Squares | df | F-Value | p-Value | Sum of Squares | df | F-Value | p-Value | |
| Module | 646.72 | 9 | 52.71 | <0.0001 ** | 26.98 | 9 | 88.44 | <0.0001 ** |
| X1 | 130.98 | 1 | 95.09 | <0.0001 ** | 7.41 | 1 | 218.67 | <0.0001 ** |
| X2 | 74.12 | 1 | 53.81 | 0.0002 ** | 0.845 | 1 | 24.93 | 0.0016 ** |
| X3 | 249.98 | 1 | 181.50 | <0.0001 ** | 16.36 | 1 | 482.67 | <0.0001 ** |
| X1×2 | 20.52 | 1 | 14.90 | 0.0062 ** | 0.5929 | 1 | 17.49 | 0.0041 ** |
| X1X3 | 42.45 | 1 | 30.82 | 0.0009 ** | 0.09 | 1 | 2.66 | 0.1472 |
| X2X3 | 18.71 | 1 | 13.58 | 0.0078 ** | 0.0784 | 1 | 2.31 | 0.1721 |
| X12 | 18.62 | 1 | 13.52 | 0.0079 ** | 0.3789 | 1 | 11.18 | 0.0124 * |
| X22 | 15.65 | 1 | 11.36 | 0.0119 * | 0.6906 | 1 | 20.38 | 0.0028 ** |
| X32 | 65.71 | 1 | 47.1 | 0.0002 ** | 0.3664 | 1 | 10.81 | 0.0133 * |
| Residual | 9.64 | 7 | 0.0339 | 7 | ||||
| Lack of fit | 4.74 | 3 | 1.29 | 0.3928 | 0.1659 | 3 | 3.1 | 0.1517 |
| Pure error | 4.90 | 4 | 0.0714 | 4 | ||||
| Cor total | 656.36 | 16 | 27.21 | 16 | ||||
| Source | Replay index M (%) | |||||||
| Sum of squares | df | F-value | p-value | |||||
| Module | 856.01 | 9 | 68.8 | <0.0001 ** | ||||
| X1 | 200.7 | 1 | 145.18 | <0.0001 ** | ||||
| X2 | 90.79 | 1 | 65.67 | <0.0001 ** | ||||
| X3 | 394.24 | 1 | 285.19 | <0.0001 ** | ||||
| X1X2 | 28.09 | 1 | 20.32 | 0.0028 ** | ||||
| X1X3 | 38.63 | 1 | 27.94 | 0.0011 ** | ||||
| X2X3 | 16.36 | 1 | 11.84 | 0.0108 * | ||||
| X12 | 13.69 | 1 | 9.9 | 0.0162 * | ||||
| X22 | 9.77 | 1 | 7.06 | 0.0326 * | ||||
| X32 | 56.26 | 1 | 40.7 | 0.0004 ** | ||||
| Residual | 9.68 | 7 | ||||||
| Lack of fit | 3.92 | 3 | 0.9092 | 0.5116 | ||||
| Pure error | 5.75 | 4 | ||||||
| Cor total | 27.21 | 16 | ||||||
| Test Number | Qualified Index (%) | Replay Index (%) | Leakage Index (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 93.62 | 5.65 | 0.37 |
| 2 | 92.89 | 6.12 | 0.99 |
| 3 | 93.36 | 5.20 | 1.44 |
| Average value | 93.29 | 5.65 | 1.06 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, J.; Sun, S.; Wang, J.; Hu, B.; Luo, X.; Xu, X. An Experimental Analysis of the Seed-Filling Mechanism of Maize-Precision Hole-Planter Clamping. Agriculture 2024, 14, 398. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14030398
Ma J, Sun S, Wang J, Hu B, Luo X, Xu X. An Experimental Analysis of the Seed-Filling Mechanism of Maize-Precision Hole-Planter Clamping. Agriculture. 2024; 14(3):398. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14030398
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Jinhu, Sheng Sun, Jian Wang, Bin Hu, Xin Luo, and Xiaoyun Xu. 2024. "An Experimental Analysis of the Seed-Filling Mechanism of Maize-Precision Hole-Planter Clamping" Agriculture 14, no. 3: 398. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14030398
APA StyleMa, J., Sun, S., Wang, J., Hu, B., Luo, X., & Xu, X. (2024). An Experimental Analysis of the Seed-Filling Mechanism of Maize-Precision Hole-Planter Clamping. Agriculture, 14(3), 398. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14030398






