The Influence of Shallow Groundwater on the Physicochemical Properties of Field Soil, Crop Yield, and Groundwater
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Volumetric Lysimeter System
2.3. Experiment Design
2.4. Sampling Methods and Data Collection
2.4.1. Daily Evaporation and Leakage Replenishment
2.4.2. Meteorological Data
2.4.3. Determination of Groundwater and Its Chemical Indicators
2.4.4. Determination of Soil and Its Chemical Indicators
2.4.5. Maize Dry Matter Accumulation
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
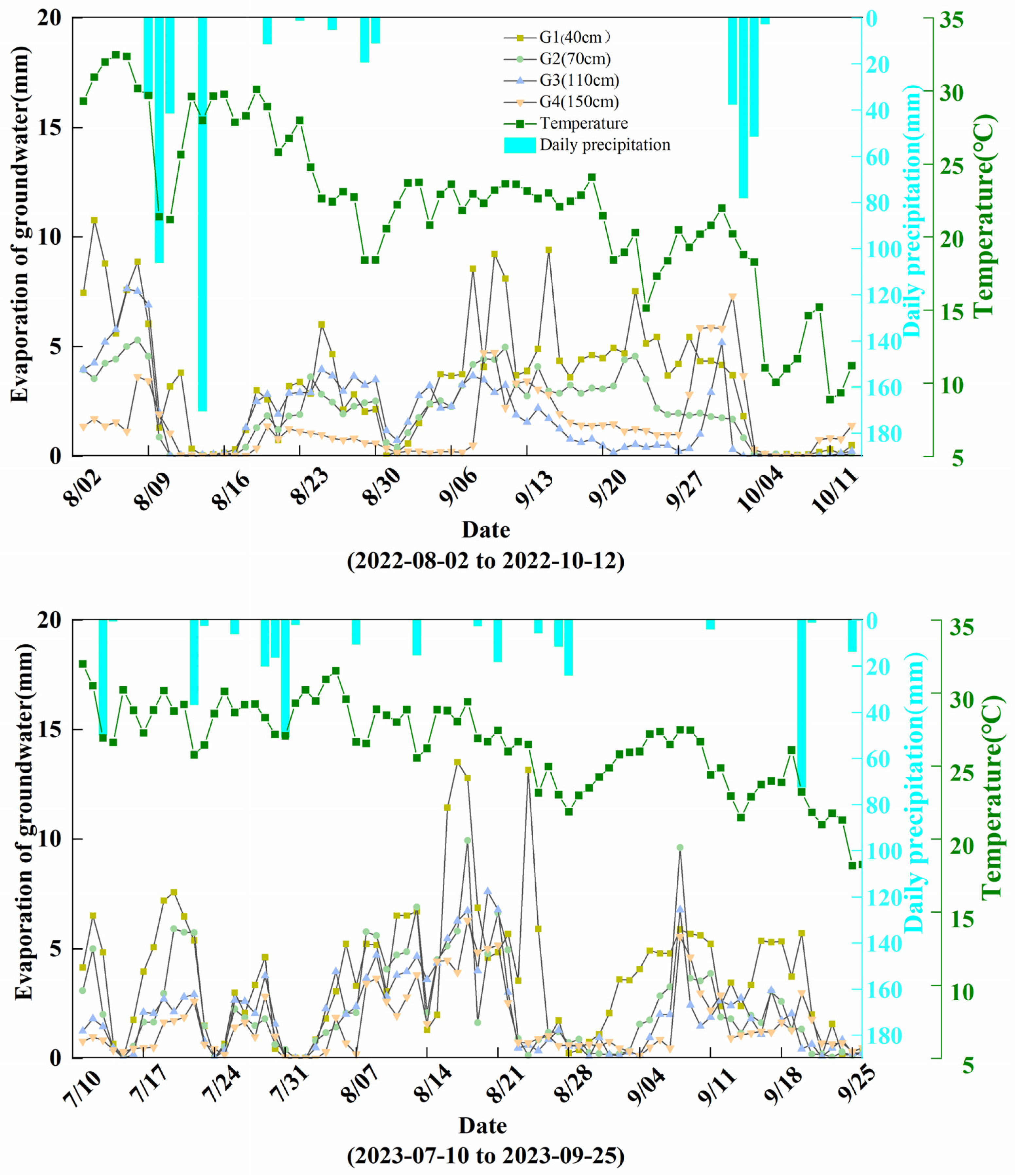
3.1. Meteorology and Groundwater Evaporation during the Maize Growth Season
3.2. Impact of Shallow Groundwater Depth on Soil Physicochemical Properties
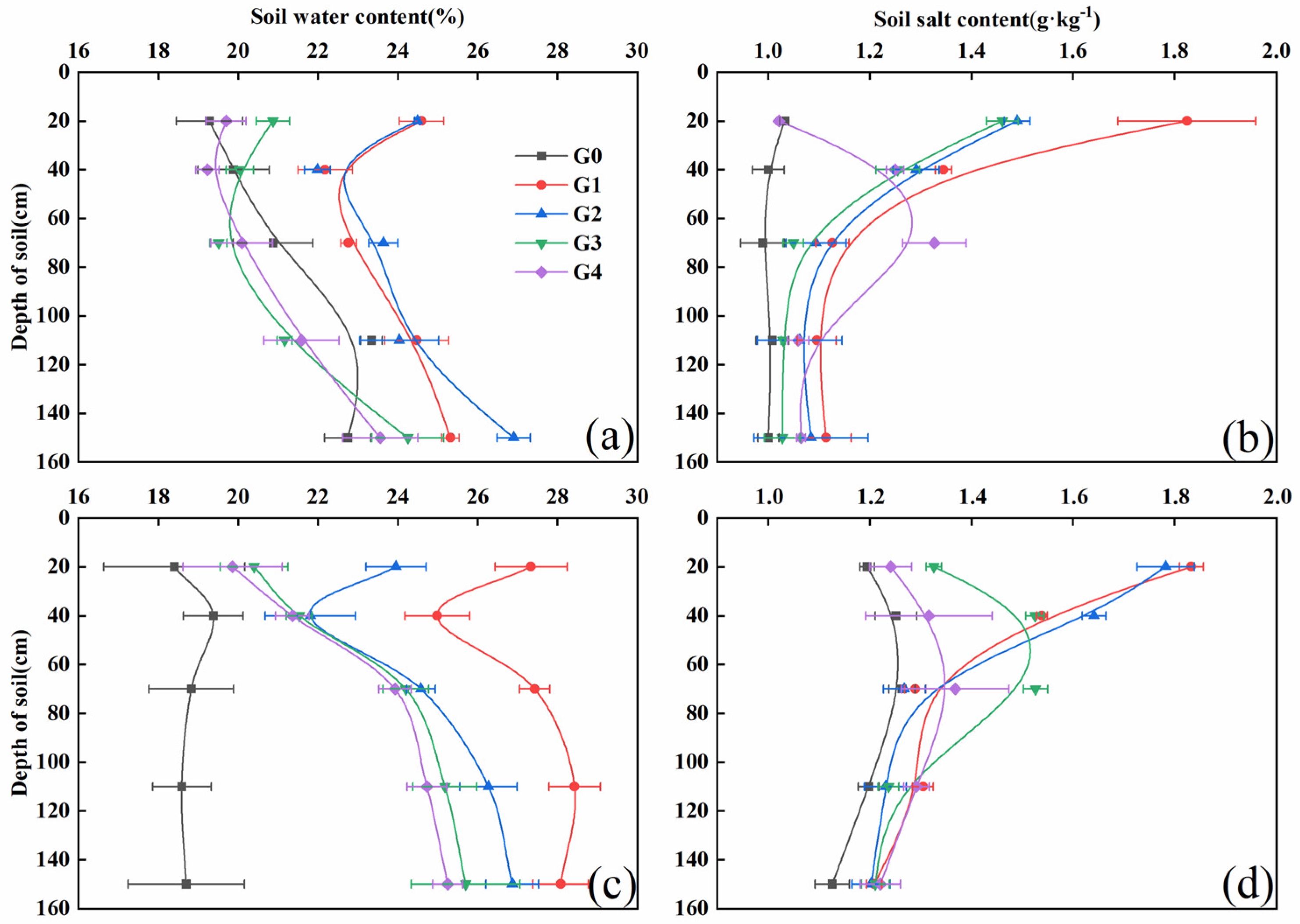
3.2.1. The Influence of Shallow Groundwater Depth on Soil Moisture and Salt Content
3.2.2. Influence of Shallow Groundwater Depth on Soil Nutrient Content
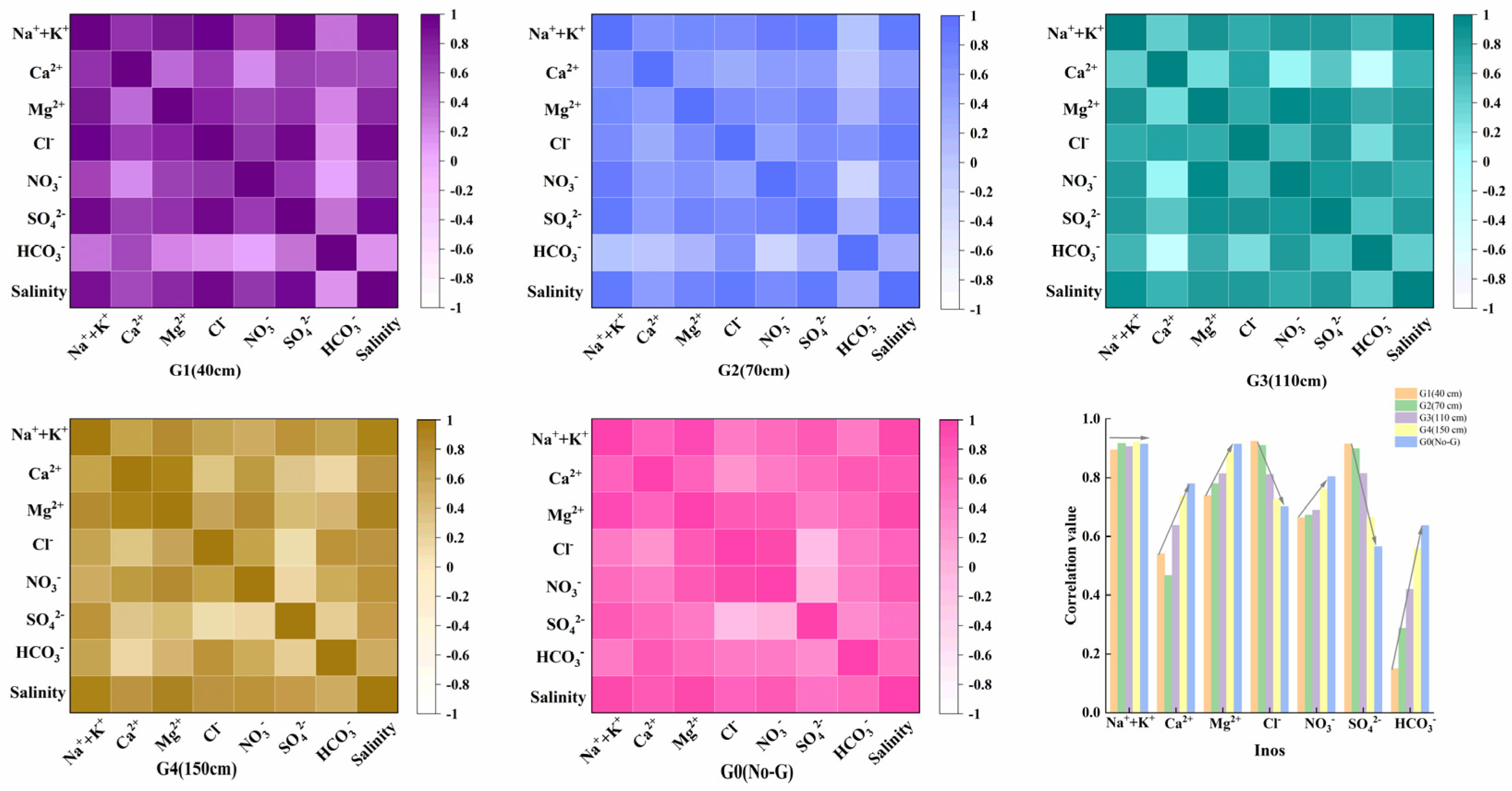
3.2.3. Ionic Characteristics of Soil Salinity
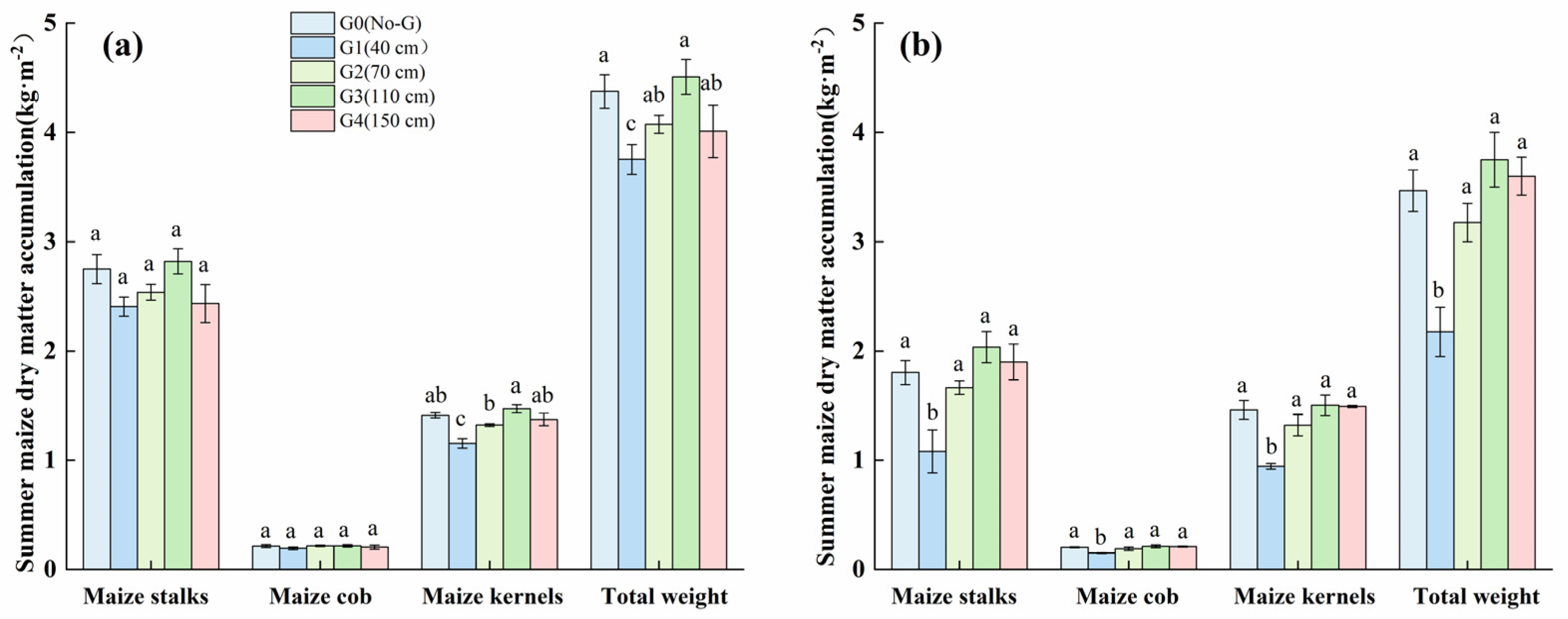
3.3. Shallow Groundwater Depth Affects Crop Dry Matter Accumulation
3.4. Relationship between Groundwater Depth, Surface Soil Physicochemical Properties, and Summer Maize Yield
3.5. Ion Variations in Shallow Groundwater
3.5.1. Time Variation of Ion Content in Shallow Groundwater with Different Burial Depths
3.5.2. Changes in Ion Types in Groundwater
4. Discussion
4.1. The Response of Soil Physicochemical Properties and Crop Yield to Groundwater Depth
4.2. The Relationship between Surface Salinity and Groundwater
4.3. The Enhancement of the Environmental Quality of Soil through the Regulation of Groundwater Depth
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fan, Y.; Li, H.; Miguez-Macho, G. Global Patterns of Groundwater Table Depth. Science 2013, 339, 940–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, B.; Dong, S.; Liu, P.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, J. Ridge tillage improves plant growth and grain yield of waterlogged summer maize. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 177, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghobadi, M.E.; Ghobadi, M.; Zebarjadi, A. Effect of waterlogging at different growth stages on some morphological traits of wheat varieties. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2017, 61, 635–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahrawat, K.L. Organic matter accumulation in submerged soils. Adv. Agron. 2003, 81, 169–201. [Google Scholar]
- Abliz, A.; Tiyip, T.; Ghulam, A.; Halik, Ü.; Ding, J.-L.; Sawut, M.; Zhang, F.; Nurmemet, I.; Abliz, A. Effects of shallow groundwater table and salinity on soil salt dynamics in the Keriya Oasis, Northwestern China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 260–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhu, J.; Zhou, X.; Li, F. Effects of shallow groundwater table and fertilization level on soil physico-chemical properties, enzyme activities, and winter wheat yield. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 208, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trillo, N.; Fernández, R.J. Wheat Plant Hydraulic Properties Under Prolonged Experimental Drought: Stronger Decline in Root-system Conductance than in Leaf Area. Plant Soil 2005, 277, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Paredes, P.; Shi, H.; Ramos, T.B.; Dou, X.; Dai, L.; Pereira, L.S. Impacts of a shallow saline water table on maize evapotranspiration and groundwater contribution using static water table lysimeters and the dual Kc water balance model SIMDualKc. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 273, 107887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Wu, J.; Yang, Y.; Peng, X.; Li, C.; Zhao, Q. A method to determine optimum ecological groundwater table depth in semi-arid areas. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 139, 108915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Qiao, J. Modelling the response of vegetation restoration to changes in groundwater level, based on ecologically suitable groundwater depth. Hydrogeol. J. 2018, 26, 2189–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahlown, M.A.; Ashraf, M.; Zia-ul, H. Effect of shallow groundwater table on crop water requirements and crop yields. Agric. Water Manag. 2005, 76, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Meng, Y.-L.; Cao, N.; Li, D.-S.; Zhou, Z.-G.; Chen, B.-L.; Dou, F.-G. The effects of soil moisture and salinity as functions of groundwater depth on wheat growth and yield in coastal saline soils. J. Integr. Agric. 2019, 18, 2472–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, F.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, R. Evaluating the Effect of Groundwater Table on Summer Maize Growth Using the AquaCrop Model. Environ. Model. Assess. 2019, 25, 343–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florio, E.L.; Mercau, J.L.; Jobbágy, E.G.; Nosetto, M.D. Interactive effects of water-table depth, rainfall variation, and sowing date on maize production in the Western Pampas. Agric. Water Manag. 2014, 146, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadioglu, H.; Hatterman-Valenti, H.; Jia, X.; Chu, X.; Aslan, H.; Simsek, H. Groundwater Table Effects on the Yield, Growth, and Water Use of Canola (Brassica napus L.) Plant. Water 2019, 11, 1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.L.; Carberry, P.; Wang, G.Y.; Lü, R.H.; Lü, H.Z.; Xia, A.P. Quantifying the yield gap in wheat–maize cropping systems of the Hebei Plain, China. Field Crops Res. 2011, 124, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno Méndez, E. An Argument for Weakly Magnetized, Slowly Rotating Progenitors of Long Gamma-Ray Bursts. Astrophys. J. 2013, 781, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhu, X.; Li, Y.; Li, M.; Pan, Y.; Shi, P. Agricultural irrigation in China. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2013, 68, 147A–154A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Graaf, I.E.M.; Gleeson, T.; Rens van Beek, L.P.H.; Sutanudjaja, E.H.; Bierkens, M.F.P. Environmental flow limits to global groundwater pumping. Nature 2019, 574, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Duan, Q.; Yeh, P.J.-F.; Pan, Y.; Gong, H.; Moradkhani, H.; Gong, W.; Lei, X.; Liao, W.; Xu, L.; et al. Sub-regional groundwater storage recovery in North China Plain after the South-to-North water diversion project. J. Hydrol. 2021, 597, 126156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Chen, H.; Fu, S.; Li, F.; Wu, Z.; Xu, D. Analysis of exploitation control in typical groundwater over-exploited area in North China Plain. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2021, 66, 851–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaopricha, N.T.; Marín-Spiotta, E. Soil burial contributes to deep soil organic carbon storage. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 69, 251–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Li, G.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, X.; Lu, C. Effects of water table and fertilization management on nitrogen loading to groundwater. Agric. Water Manag. 2006, 82, 86–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venterink, H.O.; Davidsson, T.E.; Kiehl, K.; Leonardson, L.J.P. Impact of drying and re-wetting on N, P and K dynamics in a wetland soil. Plant Soil 2002, 243, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeboonruang, U. Relationship between groundwater properties and soil salinity at the Lower Nam Kam River Basin in Thailand. Environ. Earth Sci. 2012, 69, 1803–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimov, A.K.; Šimůnek, J.; Hanjra, M.A.; Avliyakulov, M.; Forkutsa, I. Effects of the shallow water table on water use of winter wheat and ecosystem health: Implications for unlocking the potential of groundwater in the Fergana Valley (Central Asia). Agric. Water Manag. 2014, 131, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, C.; Huo, Z. Optimizing irrigation and drainage by considering agricultural hydrological process in arid farmland with shallow groundwater. J. Hydrol. 2020, 585, 124785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C. Simulation soil water–salt dynamics in saline wasteland of Yongji Irrigation Area in Hetao Irrigation District of China. Water Supply 2021, 21, 2681–2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, G.; Yuan, J.; Xu, X.; Zhao, S.; Peng, C.; Wu, J.; Zhou, Z. Effects of an integrated rice-crayfish farming system on soil organic carbon, enzyme activity, and microbial diversity in waterlogged paddy soil. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2018, 38, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Qiao, Y.; Leng, P.; Zhang, Q.; Du, K.; Tian, C.; Li, X.; Chen, G.; Li, F. Influence of the shallow groundwater table on the groundwater N(2)O and direct N(2)O emissions in summer maize field in the North China Plain. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 799, 149495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Jin, H.; Yuan, Z.; Yang, C. Synergetic variations of active layer soil water and salt in a permafrost-affected meadow in the headwater area of the Yellow River, northeastern Qinghai–Tibet plateau. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2022, 10, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Wang, S.; Liu, X.; Sun, H. Evaluating soil water and salt transport in response to varied rainfall events and hydrological years under brackish water irrigation in the North China Plain. Geoderma 2022, 422, 115954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xia, J.; Zhao, X.; Chen, Y. Effects of planting Tamarix chinensis on shallow soil water and salt content under different groundwater depths in the Yellow River Delta. Geoderma 2019, 335, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, D.A.; Konukcu, F.; Gowing, J.W. Effect of watertable depth on evaporation and salt accumulation from saline groundwater. Soil Res. 2005, 43, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Xia, J.; Chen, W.; Chen, Y.P. Effect of groundwater depth on the distribution of water and salinity in the soil-Tamarix chinensis system under evaporation conditions. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2017, 37, 6074–6080. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Chang, S.X.; Salifu, K.F. Soil texture and layering effects on water and salt dynamics in the presence of a water table: A review. Environ. Rev. 2014, 22, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Sun, H.; Zhang, P.; Wu, F.; Qiao, J.; Li, T.; Wang, Y.; An, S. Review of Managing Soil Organic C Sequestration from Vegetation Restoration on the Loess Plateau. Forests 2023, 14, 1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, M.; Six, J. Soil structure and microbiome functions in agroecosystems. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2023, 4, 4–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhang, Z.H.E.; Wan, S. Predominant role of water in regulating soil and microbial respiration and their responses to climate change in a semiarid grassland. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2009, 15, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, L.; Pang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, J.; Lu, C.; Li, Y. Buried straw layer plus plastic mulching improves soil organic carbon fractions in an arid saline soil from Northwest China. Soil Tillage Res. 2017, 165, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Bai, J.; Wang, W.; Zhang, G.; Jia, J.; Cui, B.; Liu, X. Effects of soil moisture on carbon mineralization in floodplain wetlands with different flooding frequencies. J. Hydrol. 2019, 574, 1074–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, T.Y.; Jia, B.Y.; Hu, Y.L.; Yang, Q.; Mao, W. Effects of groundwater depth on soil environmental factors and root biomass of typical plant communities in sandy grassland. Pratacult. Sci. 2021, 38, 1694–1705. [Google Scholar]
- Anuradha, M.; Sivaraju, K.; Krishnamurthy, V. Effect of waterlogging on physiological characteristics, yield and quality of flue-cured tobacco. Indian J. Plant Physiol. 2013, 18, 67–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Pal, M.; Joshi, R.; Sairam, R.K. Yield, growth and physiological responses of mung bean [Vigna radiata (L.) Wilczek] genotypes to waterlogging at vegetative stage. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants 2012, 19, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz, A.C.; Jin, L. Chemical and hydrological controls on salt accumulation in irrigated soils of southwestern U.S. Geoderma 2021, 391, 114976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Qian, H.; Xu, P.; Li, W.; Feng, W.; Liu, R. Effect of hydrogeological conditions on groundwater nitrate pollution and human health risk assessment of nitrate in Jiaokou Irrigation District. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 298, 126783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Qian, H.; Wu, J. Conjunctive use of groundwater and surface water to reduce soil salinization in the Yinchuan Plain, North-West China. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2018, 34, 337–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Qian, H.; Zheng, L.; Feng, W.; Wang, H.; Gao, Y. Alterations to groundwater chemistry due to modern water transfer for irrigation over decades. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 717, 137170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimojimaa, E.; Yoshioka, R.; Tamagawa, I. Salinization owing to evaporation from bare-soil surfaces and its influences on the evaporation. J. Hydrol. 1996, 178, 109–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, F.; Ren, S.; Zou, T.; Yang, P. Effects of infiltration and evaporation with treated wastewater and salt solutions on soil moisture and salinize-alkalization. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2013, 29, 120–129. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.X. Study on Law and Effect of Soil Evaporation in Bare soil under the Influence of Temperature and Humidity; Chang’an University: Xi’an, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Cuevas, J.; Daliakopoulos, I.N.; del Moral, F.; Hueso, J.J.; Tsanis, I.K. A Review of Soil-Improving Cropping Systems for Soil Salinization. Agronomy 2019, 9, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minhas, P.S.; Ramos, T.B.; Ben-Gal, A.; Pereira, L.S. Coping with salinity in irrigated agriculture: Crop evapotranspiration and water management issues. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 227, 105832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, X.; Brown, L.C.; Qu, X. Current status and prospects of agricultural drainage in China. Irrig. Drain. 2007, 56, S47–S58. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Pu, L.; Han, M.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, R.; Xiang, Y. Soil salinization research in China: Advances and prospects. J. Geogr. Sci. 2014, 24, 943–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, R.; Wang, X.; Han, X.; Yan, Y.; Huang, S.; Huang, J.; Shen, T.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J. Effects of Combined Main Ditch and Field Ditch Control Measures on Crop Yield and Drainage Discharge in the Northern Huaihe River Plain, Anhui Province, China. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, R.; Yang, J.; Zhang, T.; Hong, L.; Wang, M.; Yu, S.; Wang, X. Studies on soil water and salt balances and scenarios simulation using SaltMod in a coastal reclaimed farming area of eastern China. Agric. Water Manag. 2014, 131, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Li, P.; Qian, H.; Fang, Y. Assessment of soil salinization based on a low-cost method and its influencing factors in a semi-arid agricultural area, northwest China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 71, 3465–3475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heng, T.; Liao, R.; Wang, Z.; Wu, W.; Li, W.; Zhang, J. Effects of combined drip irrigation and sub-surface pipe drainage on water and salt transport of saline-alkali soil in Xinjiang, China. J. Arid Land 2018, 10, 932–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heng, T.; He, X.-L.; Yang, L.-L.; Xu, X.; Feng, Y. Mechanism of Saline–Alkali land improvement using subsurface pipe and vertical well drainage measures and its response to agricultural soil ecosystem. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 293, 118583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, H.; Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Huang, Q.; Liu, Y. Influence of reservoir seepage prevention measures and drainage ditch behind dam on groundwater depth of surrounding farmland. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2017, 33, 98–107. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Huang, G.; Sun, C.; Pereira, L.S.; Ramos, T.B.; Huang, Q.; Hao, Y. Assessing the effects of water table depth on water use, soil salinity and wheat yield: Searching for a target depth for irrigated areas in the upper Yellow River basin. Agric. Water Manag. 2013, 125, 46–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M. Drought and Flood in Huaibei Plain Area Groundwater Equilibrium Governance Deep Study on Appropriate; Yangzhou University: Yangzhou, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]





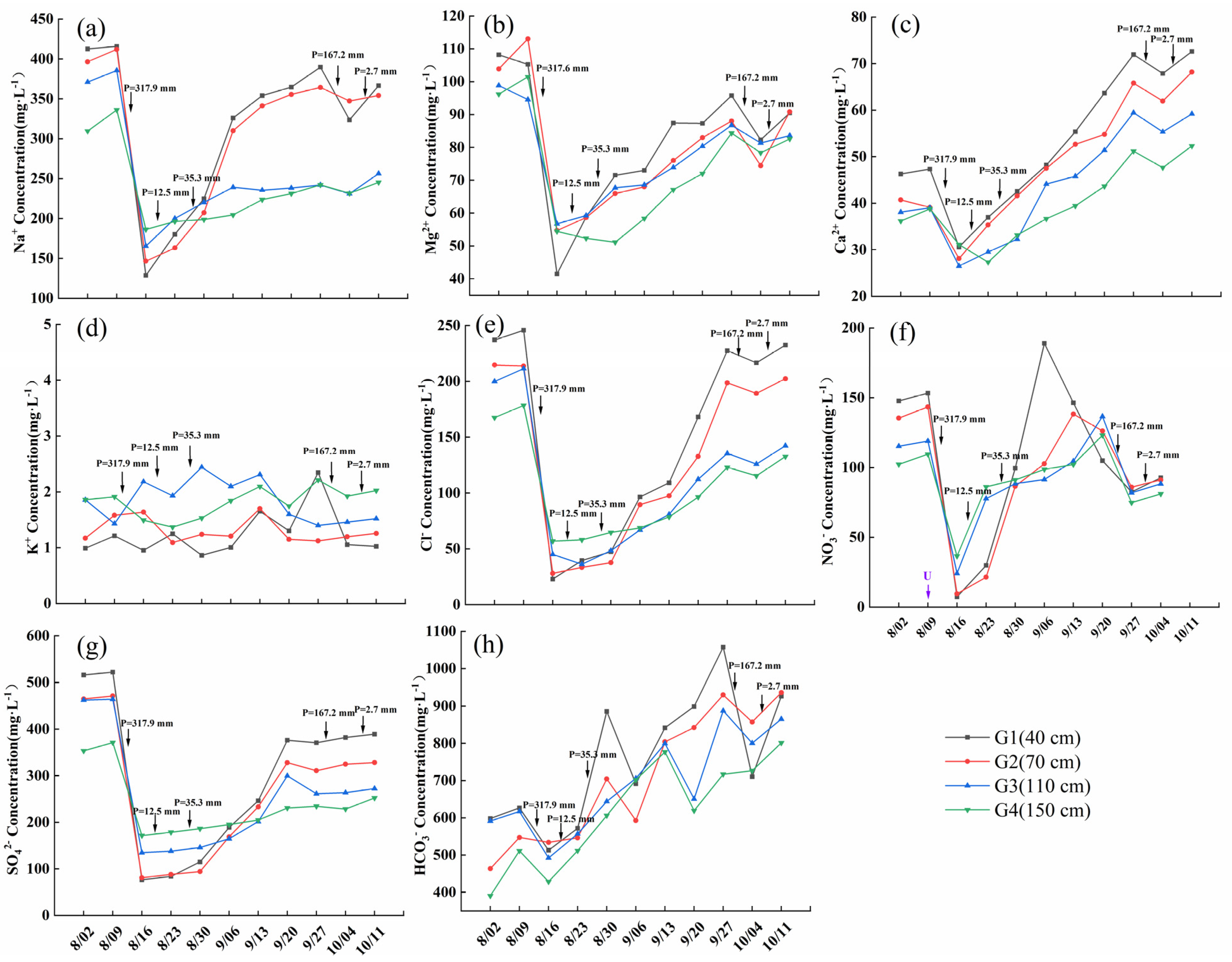
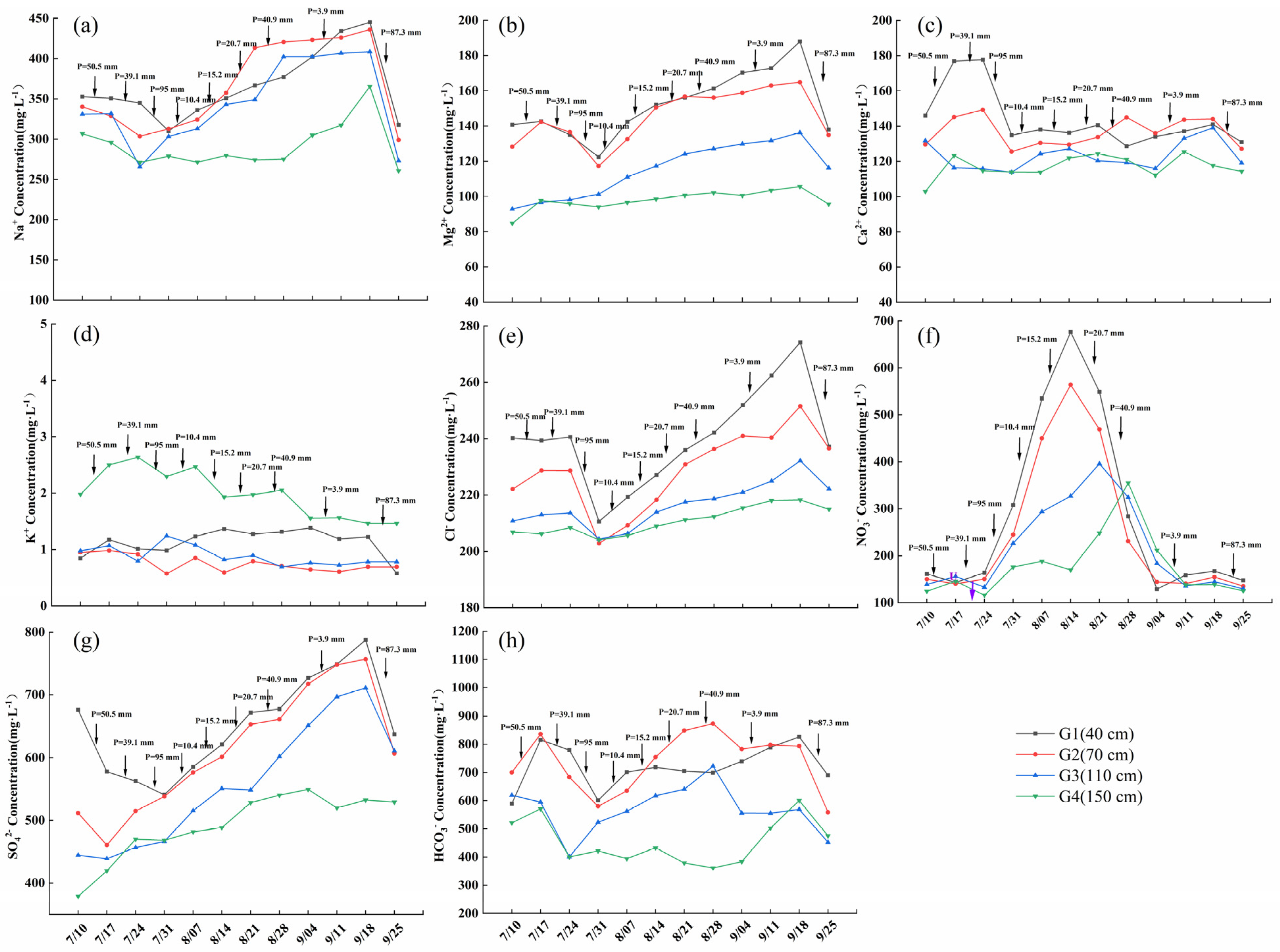
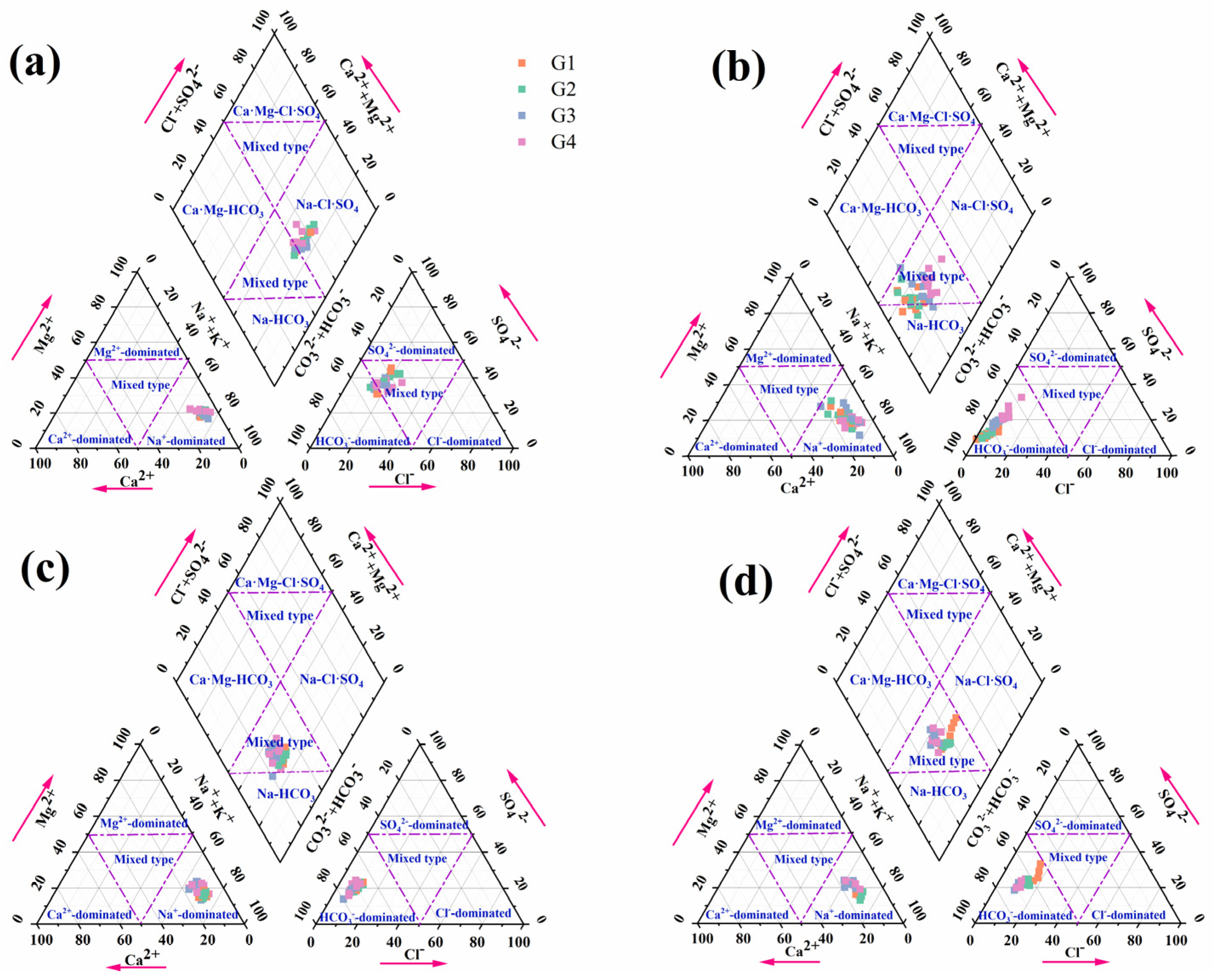


| Venue | Research Objects | Groundwater Level (Burial Depth)/m | Best Depth/m | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shuguang Experimental Station, Hetao plain, Inner Mongolia, China | Summer maize | 0.85~2.25 | 1.75 | [8] |
| The Yellow River Basin | Poplar trees | 0.5~3.0 | 1.87 | [9] |
| The plain of Tianjin | Shrubland and grassland | <2~15 | Shrubland: 3~5 Grassland: 1~3 | [10] |
| Lahore, Pakistan | Wheat, maize, sugarcane, sunflower, berseem, and sorghum | 0.5~3 | Wheat, maize, sunflower, berseem, and sorghum: 1.5~2 Sugarcane: >2 | [11] |
| Seed Stock Station of Dafeng, Jiangsu Province, China | Wheat | 1.0~3.0 | 1.8 | [12] |
| The Hebei Province, China | Summer wheat | 1.0~3.0 | 1.5 | [13] |
| The south of the town of Vicuna Mackenna in Córdoba, Argentina | Wheat | <1.5~>3.8 | 1.5~2.5 | [14] |
| North Dakota, USA | Canola | 0.3~0.9 | 0.9 | [15] |
| Na+ | K+ | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | Cl− | NO3− | SO42− | HCO3− | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ion concentration (mg·L−1) | 308.7 | 2.0 | 37.2 | 107.8 | 203.5 | 0.071 | 356.1 | 299.3 |
| Groundwater Depth | Na+ + K+ mg/kg | Ca2+ mg/kg | Mg2+ mg/kg | Cl− mg/kg | NO3− mg/kg | SO42− mg/kg | HCO3− mg/kg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cG1 | 246.17 | 148.54 | 38.95 | 37.85 | 47.22 | 253.24 | 851.35 |
| cG2 | 197.25 | 138.82 | 35.75 | 36.18 | 31.55 | 190.84 | 798.21 |
| cG3 | 182.21 | 132.49 | 38.25 | 24.93 | 36.69 | 165.33 | 789.83 |
| cG4 | 155.45 | 126.48 | 36.47 | 22.37 | 34.32 | 140.15 | 733.59 |
| cG0 | 140.27 | 131.67 | 39.77 | 24.38 | 16.48 | 164.14 | 713.75 |
| ΔG1−G0 | 105.9 | 16.87 | - | 13.47 | 30.74 | 89.07 | 137.6 |
| 2022 | P (mm) | PIGS | 2023 | P (mm) | PIGS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8/08 | 34.8 | Heavy rainfall | 7/12 | 49.9 | Heavy rainfall |
| 8/09 | 106.1 | Heavy rainstorm | 7/13 | 0.6 | Light rainfall |
| 8/10 | 41.4 | Heavy rainfall | 7/21 | 36.8 | Heavy rainfall |
| 8/13 | 170.4 | Heavy rainstorm | 7/22 | 2.3 | Light rainfall |
| 8/19 | 11.3 | Medium rainfall | 7/25 | 6 | Light rainfall |
| 8/22 | 1.2 | Light rainfall | 7/28 | 20 | Medium rainfall |
| 8/25 | 5 | Light rainfall | 7/29 | 16.2 | Medium rainfall |
| 8/28 | 19.3 | Medium rainfall | 7/30 | 50.9 | Rainstorm |
| 8/29 | 11 | Medium rainfall | 7/31 | 1.9 | Light rainfall |
| 10/01 | 37.6 | Heavy rainfall | 8/06 | 10.4 | Medium rainfall |
| 10/02 | 78.2 | Rainstorm | 8/12 | 15.2 | Medium rainfall |
| 10/03 | 51.4 | Rainstorm | 8/18 | 2.5 | Light rainfall |
| 10/04 | 2.7 | Light rainfall | 8/20 | 18.2 | Medium rainfall |
| 8/24 | 5.6 | Light rainfall | |||
| 8/26 | 11.4 | Medium rainfall | |||
| 8/27 | 23.9 | Medium rainfall | |||
| 9/10 | 3.9 | Light rainfall | |||
| 9/19 | 72.6 | Rainstorm | |||
| 9/20 | 1 | Light rainfall | |||
| 9/24 | 13.7 | Medium rainfall |
| 2022 | |||||
| Precipitation greater than evaporation period I | Evaporation greater than precipitation period | Precipitation greater than evaporation period II | |||
| Cumulative rainfall/mm | Groundwater evaporation/mm | Cumulative rainfall/mm | Groundwater evaporation/mm | Cumulative rainfall/mm | Groundwater evaporation/mm |
| P = 400.5 | EG1 = 101.26 | P = 0 | EG1 = 139.39 | P = 169.9 | EG1 = 19.96 |
| EG2 = 59.48 | EG2 = 83.58 | EG2 = 8.58 | |||
| EG3 = 83.16 | EG3 = 43.72 | EG3 = 9.80 | |||
| EG4 = 28.40 | EG4 = 44.70 | EG4 = 32.77 | |||
| 2023 | |||||
| Precipitation greater than evaporation period I | Evaporation greater than precipitation period | Precipitation greater than evaporation period II | |||
| Cumulative rainfall/mm | Groundwater evaporation/mm | Cumulative rainfall/mm | Groundwater evaporation/mm | Cumulative rainfall/mm | Groundwater evaporation/mm |
| P = 184.6 | EG1 = 69.35 | P = 0 | EG1 = 219.94 | P = 87.3 | EG1 = 10.05 |
| EG2 = 45.32 | EG2 = 137.55 | EG2 = 2.45 | |||
| EG3 = 33.69 | EG3 = 124.11 | EG3 = 2.90 | |||
| EG4 = 21.69 | EG4 = 95.92 | EG4 = 7.59 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Li, Z.; Fu, W.; Li, F. The Influence of Shallow Groundwater on the Physicochemical Properties of Field Soil, Crop Yield, and Groundwater. Agriculture 2024, 14, 341. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14030341
Li X, Li Z, Fu W, Li F. The Influence of Shallow Groundwater on the Physicochemical Properties of Field Soil, Crop Yield, and Groundwater. Agriculture. 2024; 14(3):341. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14030341
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xurun, Zhao Li, Weizhang Fu, and Fadong Li. 2024. "The Influence of Shallow Groundwater on the Physicochemical Properties of Field Soil, Crop Yield, and Groundwater" Agriculture 14, no. 3: 341. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14030341
APA StyleLi, X., Li, Z., Fu, W., & Li, F. (2024). The Influence of Shallow Groundwater on the Physicochemical Properties of Field Soil, Crop Yield, and Groundwater. Agriculture, 14(3), 341. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14030341







