Abstract
We assessed if the commercially reared South American bumblebee Bombus pauloensis forages resources in alfalfa crops by monitoring their colony activity daily. We analyzed the pollen collected by using pollen traps specifically designed for B. pauloensis nests and counted the number of bumblebees in the crop. Consequentially, colony activity was found to be highest during the mornings; 65% of the pollen trap samples analyzed contained alfalfa pollen grains, and 60% of the total pollen loads were identified as alfalfa pollen. Although the honey bee was the predominant pollinator observed in the crop, the high percentage of alfalfa pollen found in the pollen traps of B. pauloensis nests suggests that this species forages resources in alfalfa crops and could be considered a potential managed pollinator.
1. Introduction
Worldwide food production depends heavily on animal pollination [1]. Specifically, around 35% of crop production requires animal pollination [2,3]. The honey bee Apis mellifera is the most widely used managed pollinator in crops, but for certain crops, other bees, like small leaf-cutting bees, stingless bees, bumblebees, and mason bees, are used as managed pollinators [4]. Wild bees can be even more efficient pollinators compared to their managed counterparts [5], which is why integrated management is the recommended practice to have a good pollination service [5,6].
Alfalfa or lucerne (Medicago sativa) is a flowering plant from the legume family Fabaceae native to Asia and introduced around the world as cattle and horse forage. Self-pollination in alfalfa represents around 12% of the total production in a bee-pollinated crop field [7]. The alfalfa flower has five petals, with the two lower ones forming a keel that requires tripping by an insect pollinator to release its pollen [4,8,9,10].
To increase the seed yield of alfalfa crops, both managed bees and wild bees, alone or in combination, are used for pollination [11]. Managed honey bees are used to pollinate alfalfa worldwide, but their efficiency is variable [4,12,13], while managed Megachile rotundata is one of the most effective pollinators of alfalfa [14]; however, it is irrelevant for alfalfa pollination in its native range and is absent in some western European countries [12]. There are many wild bee species in the US, Europe, Australia, South Africa, and China that are effective pollinators [15,16,17,18,19,20,21]. In the US, for example, Nomia melanderi was shown to be just as effective as M. rotundata in tripping alfalfa flowers [9]. Another study conducted in the US by Brunet and Stewart [22] showed that two wild solitary bees (Halictus rubicundus, Andrena asteris), a wild bumblebee (Bombus auricomus) and a managed bumblebee (Bombus impatiens) had a higher tripping rate and a higher number of flowers tripped by raceme than honey bees and M. rotundata. This is not surprising considering that several studies have demonstrated that Bombus spp. (managed or wild) can be effective pollinators for various crops and have thus been commercially reared [1,23,24,25,26,27].
In Argentina, where around 2000 tons of alfalfa seeds are produced each year [28,29], two managed bee species are used for pollination services in this crop: M. rotundata and A. mellifera. The alfalfa leaf-cutting bee was introduced in our country in the 1970s, but its importation has been forbidden since 2011 by the National Secretary of Environment and Sustainable Development [28]. Despite this, around 5% of alfalfa production is supplemented by M. rotundata management in a density of 45,000 females/ha, reaching 1000 kg/ha [28,30]. The more frequently registered and identified wild bee species associated with the production of alfalfa seed are Colletes sp., Megachile sp., Caupolicana lugubris, Xylocopa splendidula, Xylocopa augusti, Bombus bellicosus, and Bombus sp. [31,32]. Studies about wild pollinators of alfalfa are scarce, and few have measured wild pollinator contributions to pollination services [31,33,34,35]. On the other hand, like in other parts of the world with other Bombus species, in Argentina, the native bumblebee Bombus pauloensis is commercially reared for pollination services and used as an alternative pollinator for increasing the production of crops such as strawberry, kiwi, tomato, blueberries, and red clover [27,36,37,38,39]. However, despite observations of Bombus spp. in alfalfa fields in Argentina [40], the study of the behavior and contribution of bumblebees in alfalfa pollination is still pending.
The objective of this study is to assess if the commercially reared bumblebee Bombus pauloensis forages resources in alfalfa crops. Therefore, we first monitored colony activity, measuring the number of bees entering and exiting the nest; secondly, we assessed the density of bees in the alfalfa field; and lastly, with the use of pollen traps, we analyzed the pollen being collected by the bumblebees.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site and Managed Bumblebees
Field studies were performed during the alfalfa flowering season in December 2021 in two plantations supervised by Gentos S.A. and located near Pedro Luro, Villarino (39°32′39.08″ S, 62°38′54.23″ W; 39°33′17.44″ S, 62°39′48.05″ W), province of Buenos Aires, Argentina. Alfalfa cultivars H1 and H2 were grown in plots of 13.6 ha and 9.77 ha, respectively. Cultivars were arranged, due to the combined harvester used to harvest the crops, in sets of 37 rows, each set separated by a narrow street. The two plots were 1.29 km apart, separated by plantations of other crops such as vetches, empty fields, and dirt roads. Irrigation of these plots was done via flooding through aqueducts connected to the Colorado River.
Commercial Bombus pauloensis colonies (100–120 worker strength; n = 20 colonies) provided by Biobest-Brometán Argentina S.R.L. were introduced in the fields during the first day of the experimental period. Twelve colonies were arranged in two groups of six, separated by 198 m in plot 1, whilst in plot 2, eight colonies were arranged in two groups of four, separated by 193 m (Figure S1).
While honey bees were not used for this field assay, the surrounding area had honey bee colonies set up. Plot 1 had three different beehive plots to the west at about 500 m distance. Plot 2 also had three different bee plots to the west nearby, the closest at about 30 m distance and the farthest one at around 500 m (Figure S1).
2.2. Colony Activity
Colony activity was monitored from 17 December 2021 (Day 1) to 20 December 2021 (Day 4) between 8.00 and 16.00 h. We counted the number of bumblebees entering (incoming rate) or exiting (departure rate) at the entrance of the nest as an indicator of colony activity, differentiating between incoming individuals who carried pollen and those who did not. We counted the arrivals/departures for 2 min three times a day: in the morning (8.00–11.00 h), at midday (11.00–13.00 h) and in the afternoon (13.00–16.00 h).
2.3. Pollinator Density
We sampled the density of pollinators on the crop by recording daily the number of individuals foraging on flowers during four consecutive days, between 9.30 and 14.00 h. Following standardized procedures, we counted the total number of pollinators along 50 m transects in both fields [41]. Six transects, separated by 37 rows, were determined around each group of bumblebee colonies (n = 24 transects). Since the colonies were placed in the middle of the fields, three transects were determined on each side of the field, following the rows of the crops. Observers varied to avoid bias.
2.4. Pollen Collection
We designed pollen traps following a device previously developed [42] but specifically made to accommodate Bombus pauloensis (Figure S2). Different filter sizes were evaluated to make sure that pollen loads could be collected while still allowing bumblebees to access the nest. Seven traps were distributed among the colonies in Plot 1, and eight traps in the colonies in Plot 2. These traps can be left on the colonies without the filter that removes the pollen loads from the bumblebees’ hind legs, allowing the bumblebees to go in and out undisturbed. Filters to the traps were placed early in the morning and removed at the end of the day. Pollen traps worked between 4.5 to 6.5 h each day. Pollen loads that were in the catch basin were collected and stored in plastic vials for later analysis at the laboratory. Samples were carefully divided by day and by nest. Alfalfa flowers and those from the surrounding flora were collected in plastic bags and stored in ice for later comparison with pollen obtained from pollen traps.
2.5. Pollen Analysis
Pollen from the pollen traps was first dried in an oven at 100 °C for 30 min. The amount of pollen loads for each sample was separated by color and weighed. Pollen samples were analyzed in two different ways. To analyze the presence of alfalfa pollen in the pollen traps, random pollen loads were selected to be viewed under the microscope (Labomed CX RIII; 1000x; Labomed Inc, Los Angeles, CA, USA). These pollen loads were gently scraped with a toothpick, and the pollen obtained was placed on a microscope slide with a drop of distilled water, covered, and then sealed with nail polish. Each sample was photographed and compared with both the bibliography and samples of alfalfa obtained at the field. Traps that contained alfalfa were marked as 1, and traps that did not contain alfalfa were marked as 0. To analyze the amount of alfalfa pollen loads in the total amount of pollen loads collected, we separated pollen loads by color, as in the previous bibliography, we found the color assigned to the pollen load corresponded to the palynological assessment done with the microscope [43,44]. This analysis gave us an approximated amount of alfalfa pollen loads per trap as opposed to only knowing if alfalfa was present or not.
2.6. Environmental Variables
Measurements of temperature and light intensity were recorded using a HOBO data logger (® Onset Computer Corporation; Onset Computer Corporation, Falmouth, MA, USA) placed in field 1. The flowering percentage during the campaign period was acquired from the field manager, and it was estimated to be between 20 and 40%. These variables were considered for the statistical analysis of colony activity and pollinator density in the field.
2.7. Statistical Analysis
All statistical analysis was performed in R v4.3.1 [45] via RStudio v2023.06.1-524 [46]. To analyze all colony activity (total incoming bees, incoming bees with pollen, departures), we proposed a Poisson model. However, as the models did not fit, we tried a Conway–Maxwell–Poisson distribution model using the glmmTMB package [47] with the variables light intensity, temperature, day (four-level factor corresponding to 1–4 days), shift (three-level factor corresponding to morning, midday and afternoon) and plot (two-level factor corresponding to plots 1 and 2) as fixed effects and nest as random effects. The flowering percentage of the plots was included as an offset variable to account for differences between the two plots. To analyze bee density, we first proposed a Poisson model; as it did not fit, we tried the Conway–Maxwell–Poisson distribution model using the glmmTMB package with the variables: day (four-level factor), plot (two-level factor), temperature and light intensity as fixed effects and row and observer as random effects. To analyze the number of corbiculae gathered in each trap, we proposed a Poisson distribution model using the lme4 package [48]. Day (four-level factor corresponding to 1–4 days) and plot (two-level factor corresponding to plots 1 and 2) were set as fixed effects and nest as random effects. To analyze the total weight of pollen gathered, we proposed a linear fixed effects model using the lme4 package and applied a log transformation on the weight [48]. Day and plot were proposed as fixed effects and nest as random effects. To analyze the corbicular weight, we proposed a linear model using the lme4 package and applied a log transformation to the weight. Day and plot were proposed as fixed effects. To analyze the presence of alfalfa pollen in the pollen traps, we proposed a binomial model with the variables day (four-level factor corresponding to 1–4 days) and plot (two-level factor corresponding to plots 1 and 2) as fixed effects and nest as a random effect. Traps that contained alfalfa were marked as 1, and traps that did not contain alfalfa were marked as 0. To analyze the amount of alfalfa pollen loads in the total amount of pollen loads collected, we considered a linear mixed effects model and proposed the variables day (four-level factor) and plot (two-level factor) as fixed effects and nest as random effects; the working time of traps was considered as an offset variable. The significance of each term was tested by using the drop1 function from the lme4 package, which drops all possible fixed-effect terms from a model [49]. Non-significant terms were removed (p > 0.05). For additional information, refer to the Supplementary Material.
3. Results
3.1. Colony Activity
Regarding the total incoming bees, the time of day and the plot were significant. The number of incoming bees per 2 min was higher during the morning than during midday (Compois, z = −2.416; p = 0.016) and during the afternoon (Compois, z = −4.957; p = 7.15 × 10−7; Figure 1a). There was also a significant difference between the number of incoming bees between both plots, with the number of incoming bees being higher in plot 2 than in plot 1 (Compois, z = 3.035; p = 0.002; Figure 1b; Table S1).
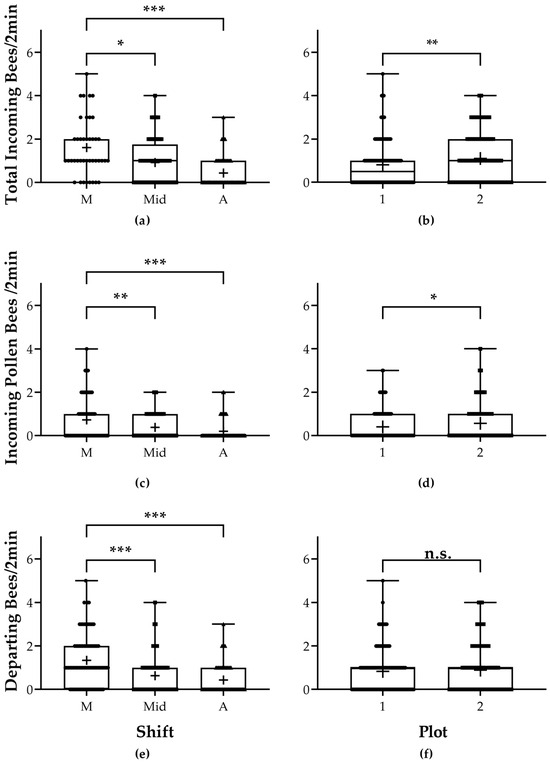
Figure 1.
Colony activity. (a) Number of bumblebees entering the nest in 2 min for each shift. Significant differences were found; the total incoming bumblebees were higher during the morning shift (M) than during midday (Mid) or the afternoon (A). (b) Number of bumblebees entering the nest in 2 min per plot. The total number of incoming bumblebees was higher in plot 2 than in plot 1. (c) Number of bumblebees entering the nest with pollen in 2 min for each shift. Significant differences were found; incoming bumblebees carrying pollen were higher during the morning shift (M) than during midday (Mid) or the afternoon (A). (d) Number of bumblebees entering the nest with pollen in 2 min per plot. The number of incoming bumblebees carrying pollen was higher in plot 2 than in plot 1. (e) Number of bumblebees departing the nest in 2 min for each shift. Significant differences were found; departing bumblebees were higher during the morning shift (M) than during midday (Mid) or the afternoon (A). (f) Number of bumblebees departing the nest in 2 min per plot. No significant differences were found. Whiskers show the max and min for each category, plus signs denote the mean, and points are individual observations. p < 0.001: ‘***’, p < 0.01: ‘**’, and p < 0.05: ‘*’.
When it came to the incoming bees carrying pollen loads, again, both the shift and plot were significant. The number of incoming bees with pollen was different between morning and midday (Compois, z = −2.687, p = 0.007) and between morning and afternoon (Compois, z = −3.982, p = 6.83 × 10−5; Figure 1c); there was also a difference between plot 1 and 2 (Compois, z = 0.223, p = 0.026; Figure 1d; Table S2).
When it came to the number of bees leaving the nest, we only found significant differences for the shift between morning and midday (Compois, z = −4.322, p = 1.55 × 10−5) and between morning and afternoon (Compois, z = −5.229, p = 1.71 × 10−7; Figure 1e; Table S3); no significant differences were found between plots (Compois, z = 1.2, p = 0.229; Figure 1f).
3.2. Pollinator Density
The observed density of bumblebees in the field was extremely low. The maximum number of bumblebees observed collecting resources from alfalfa was only 2 (Figure 2a). In comparison, the maximum number of honey bees observed on the field was 31. Honey bee density was similar between plots (LRT = 2.162, Pr (>Chi) = 0.142; Figure 2b) but varied throughout the blooming period (LRT = 11.445, Pr (>Chi) = 0.01; Figure 2c, Table S4). Unfortunately, due to the small number of bumblebees registered in the field, it was not possible to perform any statistical analysis for them.
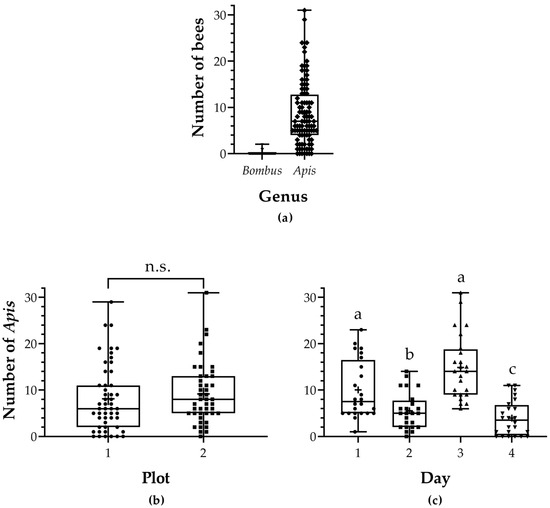
Figure 2.
Pollinator density in the field. (a) Total number of bumblebees (Bombus) and honey bees (Apis) registered. (b) Number of honey bees (Apis) by plot. The density between plots was similar. (c) Number of honey bees (Apis) per day. Significant differences were found between days. Whiskers show max and min, plus signs denote the mean, and dots are individual observations. Different letters denote significant differences, and ‘n.s.’ stands for non-significant differences.
3.3. Pollen Analysis
Regarding the number of pollen loads collected by the bumblebees, we observed that the number of collected pollen baskets increased during the blooming period (LRT = 72.328 p = 1.354 × 10−15). In particular, day 2 was different from day 1 (z = 4.270, Pr(>|z|) < 0.001); day 3 was different from day 1 (z= 6.940, Pr(>|z|) < 0.001); day 4 was different from day 1 (z = 7.998, Pr(>|z|) < 0.001); day 3 was different from day 2 (z = 3.063, Pr(>|z|) = 0.0117); day 4 was different from day 2 (z = 4.349, Pr(>|z|) < 0.001) and there was no difference between day 4 and day 3 (z = 1.359, Pr(>|z|) = 0.5228; Figure 3a, Table S5).
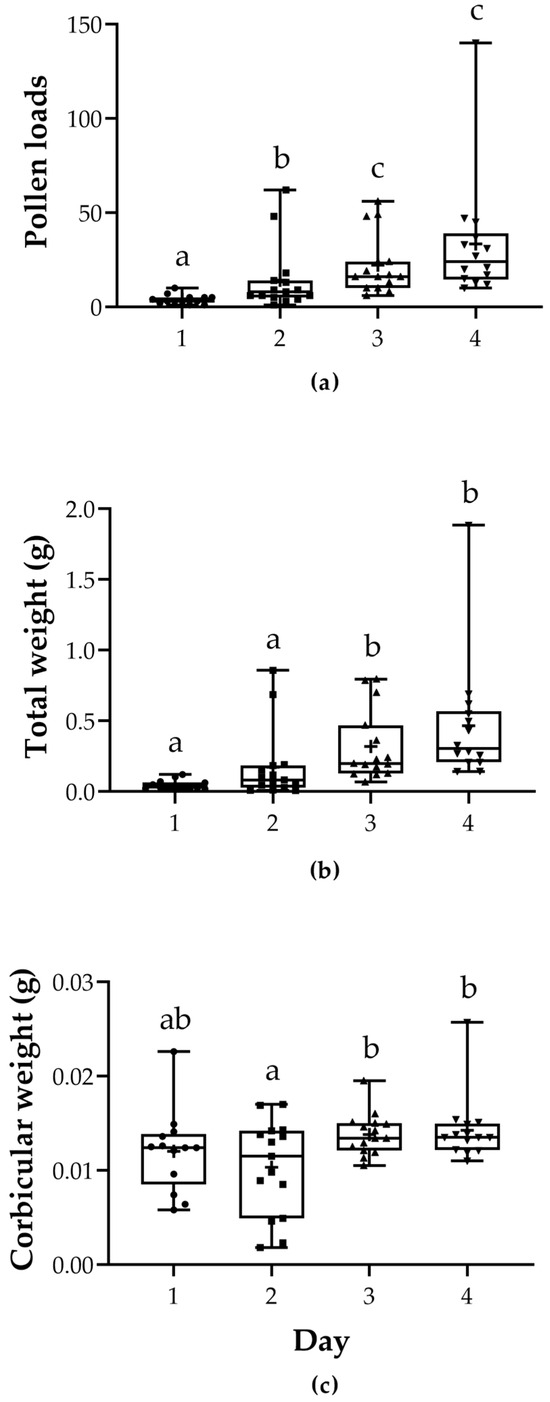
Figure 3.
Pollen load harvest obtained from pollen traps attached to B. pauloensis nests. (a) Total number of pollen loads per day. (b) Total weight (g) of the pollen loads collected per day. (c) Estimated individual weight (g) of pollen loads per day. Whiskers show max and min, plus signs denote the mean, and points are individual observations. Different letters denote significant differences.
The corbiculae were also weighed. There was a significant difference between dates (LRT = 43.526 Pr(Chi) = 1.903 × 10−9). The weight of the collected pollen was not significantly different between day 2 and 1 (z = 2.210, Pr(>|z|) = 0.120) or day 4 and day 3 (z = 1.170, Pr(>|z|) = 0.646), however it was significantly different between days 3 and 1 (z = 6.162, Pr(>|z|) < 0.001), days 4 and 1 (z = 7.160, Pr(>|z|) < 0.001), days 3 and 2 (z = 4.129, Pr(>|z|) < 0.001) and days 4 and 2 (z = 5.214, Pr(>|z|) < 0.001) (Figure 3b, Table S6). The individual weight of each pollen load was estimated by dividing the total weight of pollen loads of the same color by their total number. While the total weight was observed to increase slightly throughout the blooming period, the corbicular weight did not increase. Day 2 was significantly different from day 3 (t = 2.953, Pr(>|t|) = 0.0233) and from day 4 (t = 3.043, Pr(>|t|) = 0.0189), but not from day 1 (t = −1.672, Pr(>|t|) = 0.3485; Figure 3c, Table S7).
When analyzing the presence of alfalfa pollen in the pollen traps, we found that 37 of the 57 samples contained alfalfa pollen grains—around 65% of the samples showed alfalfa pollen grain presence in them. Alfalfa presence was not date dependent (LRT = 1.021, Pr(Chi) = 0.796); however, there was a significant difference between plots (LRT = 4.355, Pr(Chi) = 0.0369). Plot 1 had alfalfa pollen presences in 13 of 27 samples (48%), while plot 2 had alfalfa presence in 24 of 30 (80%) samples (Figure 4a, Table S8). When we analyzed the number of alfalfa pollen loads in the total pollen loads, determined by color and corroborated by palynological analysis [43,44], we obtained that 60% of the total pollen loads corresponded to alfalfa and the remainder corresponded to pollen from other sources. Unlike the previous analysis (presence/absence of alfalfa grains), the proportion of alfalfa corbiculae was not plot dependent (LRT = 1.148, Pr(Chi) = 0.284) but date dependent (LRT = 14.15, Pr(Chi) = 0.0027), the third day having less proportion of alfalfa than days 1 and 2 but not day 4 (Figure 4b, Table S9).
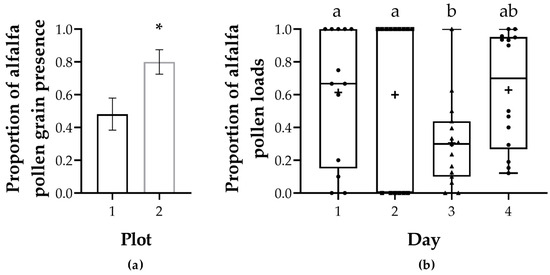
Figure 4.
Alfalfa pollen presence in pollen traps attached to B. pauloensis nests. (a) Proportion of samples indicating the presence of alfalfa pollen grains. The graph shows the average presence of alfalfa pollen in the traps per plot. The error bars represent the standard error of the mean. p < 0.05: ‘*’. (b) Proportions of alfalfa pollen loads per day. Alfalfa pollen loads were determined by color and palynological analysis. Whiskers show max and min, plus signs denote the mean, and points are individual observations. Different letters denote significant differences.
4. Discussion
The results obtained in this study show that the South American bumblebee Bombus pauloensis forages resources in alfalfa crops used for seed production. Bumblebee activity was, as expected [49], higher during the mornings, both for general activity as well as for pollen recollection. Additionally, the pollen collected by bumblebees in terms of units, weights, and sizes increased throughout the crop blooming period. Even though the number of bumblebees observed in the field was almost null, the results obtained from the palynological analysis indicate that bumblebees are able to gather alfalfa pollen and, therefore, trigger the tripping mechanism required for alfalfa pollination. More than half (65%) of the samples analyzed showed alfalfa presence (i.e., alfalfa pollen grains were observed in the sample), and 60% of the pollen loads were identified by color as belonging to alfalfa. The use of pollen traps in this study was crucial since it allowed us to demonstrate that bumblebees forage for pollen in alfalfa flowers and could be considered managed pollinators for pollination services in this crop.
As mentioned in the introduction, the alfalfa flower has its stamens contained inside the keel, and to expose them, an insect must land on it. When it comes to honey bees, pollen foragers are desirable in alfalfa crops for seed production, but not nectar foragers. Bohart and collaborators [8,50] demonstrated that honey bee pollen foragers activate (i.e., expose the stamen by posing on the keel) around 80% of visited flowers, while only 1% is activated by honey bee nectar foragers. Foragers for this species generally avoid activating the keel—in order to avoid getting hit—by inserting their proboscises in between the wing petals and the banner petal [51], whilst to collect pollen, it is necessary for them to pose on the keel, activating the mechanism that exposes the anthers [8,52].
Bohart and collaborators [50], as well as Peck and Bolton [53], suggest using high concentrations of honey bees in alfalfa crop fields reduces the attraction of the crop to other bees, like bumblebees, and recommend utilizing low numbers of honey bee hives to attract wild pollinators. However, other studies suggest that honey bee presence does not affect the presence of other bees [54]. When honey bees are introduced to alfalfa crops, their density increases during the first few days but later on diminishes as they are hit by the activated alfalfa flowers. When colonies are replaced, the same pattern can be observed [54,55]. Other researchers, such as Levin [56,57], observed that honey bees from new colonies visit alfalfa flowers more frequently than honey bees from older colonies, regardless of whether they had previous experience with alfalfa or not. Honey bees from newly introduced colonies visited alfalfa for longer time periods when alfalfa was scarce in comparison to areas where alfalfa was more abundant. These studies suggest that A. mellifera is not the best pollinator for alfalfa crops.
Our results show that the total amount and weight of pollen gathered throughout the blooming period increased. However, the individual weight of the pollen loads did not increase, as observed in other studies [58,59]. The increasing amount of pollen collected throughout the blooming period suggests, as in previous studies, that it takes time for bumblebees to learn the complex motor skills involved in the removal of pollen from different flower morphologies [58,60,61,62]. In this sense, differences observed between plots for the analyzed variables could be given by the two cultivars involved in this study, which could present differences in their floral volatile profile, nectar volume, and concentration, as well as pollen quality. In turn, these could be reflected in the bumblebees’ activity, as observed in other studies [63,64,65].
Considering that Bombus individuals have been reported in alfalfa crops in Argentina [40] and that B. pauloensis is a managed species, it would be possible to introduce commercial B. pauloensis nests during alfalfa flowering season in adequate quantities. At present, there are no studies concerning B. pauloensis nest density necessary for alfalfa seed production. However, a study by Mänd and collaborators [66] suggests that, for B. lucorum in alfalfa, a density between two to seven bumblebees per 10 m2 is needed to achieve 80–90% of alfalfa flower tripping. In this study, bumblebee nest density was below one nest (100–120 workers) per hectare (around 0.1 bumblebees per 10 m2), an insufficient quantity to achieve the observation of bumblebees in the field, and probably insufficient for adequate pollination of the alfalfa crop. Considering that many of the nests were presented with alfalfa pollen in their pollen traps, we can assume that B. pauloensis visited the alfalfa flower and was able to trip the mechanism that exposes the anthers to pollen.
Hence, our preliminary study revealed interesting results that show that this native bumblebee species forage resources in alfalfa crops and could, therefore, be a potential pollinator of alfalfa crops used for hybrid seed production. Future research experiments, including closure and first visit assays, as well as yield measures, are needed to determine this bumblebee’s potential as an alfalfa pollinator. Furthermore, assays that focus on their ability to learn floral odors [67,68] could be considered for the study of targeted pollination, a strategy that has been successful in diverse pollinator-dependent crops with honey bees [69].
5. Conclusions
The South American bumblebee Bombus pauloensis is able to forage resources from the alfalfa flowers, as evidenced by the pollen trap samples analyzed in this study. Even though the overall bumblebee density on the field itself was near zero, probably due to the fact that the number of nests in the field was extremely low (less than one nest per hectare), 60% of the pollen loads were identified as alfalfa pollen. More studies are necessary in order to conclude that this bumblebee species is an effective alfalfa pollinator, but our results represent a first step to gaining a deeper understanding of this insect–plant interaction.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/agriculture14122192/s1; Figure S1: Satellite view of the study site; Figure S2: Pollen trap designed for B. pauloensis; Table S1: Colony Activity: Total incoming bees; Table S2: Colony Activity: Incoming bees with pollen; Table S3: Colony Activity: Departing bees; Table S4: Honey bee density in the field; Table S5: Number of pollen loads collected by the bumblebees; Table S6: Total weight of pollen loads collected by the bumblebees; Table S7: Corbicular weight of pollen loads collected by the bumblebees; Table S8: Presence of alfalfa pollen; Table S9: Proportion of alfalfa pollen; Data Set S1: Alfalfa Data Set; Script S1: Alfalfa Script.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, W.M.F., F.P. and D.N.; methodology, W.M.F., F.P. and D.N.; formal analysis, D.N.; data curation, D.N.; writing—original draft preparation, D.N., F.P. and W.M.F.; writing—review and editing, W.M.F., F.P. and D.N.; supervision, W.M.F. and F.P.; funding acquisition, W.M.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Agencia Nacional de Promoción Científica y Tecnológica (Grant no. PICT 2019 2438), Secretaría de Ciencia y Técnica, Universidad de Buenos Aires (Grant no. UBACYT 2018 20020170100078BA), Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas (Grant no. PIP 112-201501-00633).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available in Supplementary Material.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Gentos S.A. for its support in the agricultural setting. We also thank the CONICET, the University of Buenos Aires, and ANPCYT for financial support. This project received logistical support from Beeflow SAU, and the bumblebee nests were provided by Biobest-Brometán Argentina S.R.L.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Roubik, D.W. (Ed.) The Pollination of Cultivated Plants: A Compendium for Practitioners; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2018; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Klein, A.-M.; Vaissière, B.E.; Cane, J.H.; Steffan-Dewenter, I.; Cunningham, S.A.; Kremen, C.; Tscharntke, T. Importance of Pollinators in Changing Landscapes for World Crops. Proc. R. Soc. B 2007, 274, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potts, S.G.; Biesmeijer, J.C.; Kremen, C.; Neumann, P.; Schweiger, O.; Kunin, W.E. Global Pollinator Declines: Trends, Impacts and Drivers. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2010, 25, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delaplane, K.S.; Mayer, D.F. Crop Pollination by Bees; CABI Publishing: Oxon, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garibaldi, L.A.; Steffan-Dewenter, I.; Winfree, R.; Aizen, M.A.; Bommarco, R.; Cunningham, S.A.; Kremen, C.; Carvalheiro, L.G.; Harder, L.D.; Afik, O.; et al. Wild Pollinators Enhance Fruit Set of Crops Regardless of Honey Bee Abundance. Science 2013, 339, 1608–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaacs, R.; Williams, N.; Ellis, J.; Pitts-Singer, T.L.; Bommarco, R.; Vaughan, M. Integrated Crop Pollination: Combining Strategies to Ensure Stable and Sustainable Yields of Pollination-Dependent Crops. Basic Appl. Ecol. 2017, 22, 44–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riday, H.; Reisen, P.; Raasch, J.A.; Santa-Martinez, E.; Brunet, J. Selfing Rate in an Alfalfa Seed Production Field Pollinated with Leafcutter Bees. Crop Sci. 2015, 55, 1087–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohart, G.E. Pollination of Alfalfa and Red Clover. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1957, 2, 355–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cane, J.H. Pollinating Bees (Hymenoptera: Apiformes) of U.S. Alfalfa Compared for Rates of Pod and Seed Set. J. Econ. Entomol. 2002, 95, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGregor, S.E. Insect Pollination of Cultivated Crop Plants; Agricultural Research Service, US Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1976.
- Wang, X.; Liu, H.; Li, X.; Song, Y.; Chen, L.; Jin, L. Correlations between Environmental Factors and Wild Bee Behavior on Alfalfa (Medicago sativa) in Northwestern China. Environ. Entomol. 2009, 38, 1480–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhardt, J.F. Some Responses of Honey Bees to Alfalfa. Am. Nat. 1952, 86, 257–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansen, C. Honey Bees and Alfalfa Seed Production in Eastern Washington; Washington State University Extension: Pullman, WA, USA, 1966.
- Pitts-Singer, T.L.; Cane, J.H. The Alfalfa Leafcutting Bee, Megachile rotundata: The World’s Most Intensively Managed Solitary Bee. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2011, 56, 221–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linsley, G.E. Insect Pollinators of Alfalfa in California. J. Econ. Entomol. 1946, 39, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohart, G.E. Alfalfa Pollinators with Special Reference to Species Other Than Honey Bees. In Proceedings of the Tenth International Congress of Entomology, Montreal, QC, Canada, 17–25 August 1956; Agricultural Research Service, US Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1958; pp. 929–937. Available online: https://digitalcommons.usu.edu/bee_lab_be/41/ (accessed on 21 October 2024).
- Batra, S.W.T. Comparative Efficiency of Alfalfa Pollination by Nomia melanderi, Megachile rotundata, Anthidium florentinum and Pithitis smaragdula (Hymenoptera: Apoidea). J. Kans. Entomol. Soc. 1976, 49, 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- Tasei, J.N.; Picard, M.; Carre, S. Les Insectes Pollinisateurs De La Luzerne (Medicago sativa L.) en France. Apidologie 1978, 9, 175–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watmough, R.H. The Potential of Megachile gratiosa Cameron, Xylocopa caffra (Linnaeus) (Hymenoptera: Megachilidae and Anthophoridae) and Other Solitary Bees as Pollinators of Alfalfa, Medicago sativa L. (Fabaceae), in the Oudtshoorn District, South Africa. Afr. Entomol. 1999, 7, 312–315. [Google Scholar]
- Cane, J.H. A Native Ground-Nesting Bee (Nomia melanderi) Sustainably Managed to Pollinate Alfalfa across an Intensively Agricultural Landscape. Apidologie 2008, 39, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, H.; Huang, L.; Zhang, S.; Deng, Z.; Li, J.; Jin, L. Biodiversity of Wild Alfalfa Pollinators and Their Temporal Foraging Characters in Hexi Corridor, Northwest China. Entomol. Fenn. 2012, 23, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Brunet, J.; Stewart, C.M. Impact of Bee Species and Plant Density on Alfalfa Pollination and Potential for Gene Flow. Psyche A J. Entomol. 2010, 2010, 201858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velthuis, H.H.W.; Van Doorn, A. A Century of Advances in Bumblebee Domestication and the Economic and Environmental Aspects of Its Commercialization for Pollination. Apidologie 2006, 37, 421–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mader, E.; Spivak, M.; Evans, E. Managing Alternative Pollinators: A Handbook for Beekeepers, Growers, and Conservationists; SARE Handbook 11, NRAES-186; SARE: New York, NY, USA; NRAES: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Riaño, D.; Espinoza, J.P.; Cure, J.R.; Rodriguez, D. Pollination Behavior and Efficiency of Bombus atratus Franklin in Sweet Peppers (Capsicum annum L.) Grown in a Greenhouse Comportamiento y Eficiencia de Polinización de Bombus atratus Franklin En Pimentón (Capsicum annum L.) Sembrado Bajo Invernadero TT. Rev. Colomb. Cienc. Hort. 2015, 9, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, K.T.; Gonzalez, A.; Lechowicz, M.J. Pollination Services Are Mediated by Bee Functional Diversity and Landscape Context. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2015, 200, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estravis-Barcala, M.C.; Palottini, F.; Macri, I.; Nery, D.; Farina, W.M. Managed Honeybees and South American Bumblebees Exhibit Complementary Foraging Patterns in Highbush Blueberry. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renzi, J.P.; Reinoso, O.; Bruna, M.; Crisanti, P.; Rodríguez, G.; Cantamutto, M.A. Producción de Semillas de Alfalfa (Medicago sativa) y Otras Forrajeras En El Valle Bonaerense Del Río Colorado; EEA: Hilario Ascasubi, Argentina, 2018; Volume 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basigalup, D.H. Investigación, Producción e Industrialización de La Alfalfa En Argentina; Basigalup, D.H., Ed.; Ediciones INTA: Buenos Aires, Argentina, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Bosch, J.; Kemp, W.P. Alfalfa Leafcutting Bee Population Dynamics, Flower Availability, and Pollination Rates in Two Oregon Alfalfa Fields. J. Econ. Entomol. 2005, 98, 1077–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moschetti, C.J.; Martínez, E.M.; Echeverría, E.M.; Ávalos, L.M. Producción de Semilla de Alfalfa; Basigalup, D.H., Ed.; Ediciones INTA: Buenos Aires, Argentina, 2007; pp. 405–448. [Google Scholar]
- Haedo, J.P.; Martínez, L.C.; Graffigna, S.; Marrero, H.J.; Torretta, J.P. Managed and Wild Bees Contribute to Alfalfa (Medicago sativa) Pollination. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2022, 324, 107711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochoa, L.H. La Producción de Semilla de Alfalfa En La Provincia de Santiago Del Estero. In Simposio De Producción De Semilla De Alfalfa; IDIA N.° 391–392; INTA: Buenos Aires, Argentina, 1980; pp. 78–87. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez, M.J.; Ves Losada, J.C.; Naab, O.; Baudino, E.M.; Dreussi, L.W. Himenópteros Polinizadores Asociados al Cultivo de Alfalfa En El Area Del Caldenal de La Provincia de La Pampa; INTA: Anguil, Argentina, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Haedo, J.P.; Graffigna, S.; Martínez, L.C.; Torretta, J.P.; Marrero, H.J. Estimación Del Servicio de Polinización En Un Cultivo de Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) Mediante La Cuantificación de Flores Disparadas. Ecol. Austral 2022, 32, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basualdo, M.; Messina, N.; Rodríguez, E.M.; Rivadeneira, M.F.M.F. Bombus atratus (Hymenoptera: Apidae) Como Polinizador de Arándanos (Vaccinium corymbosum L.). Hortic. Argent. 2013, 32, 127. [Google Scholar]
- Basualdo, M.; Rodríguez, E.M. Resultados de La Evaluación de La Actividad de Forrajeo de Bombus pauloensis En Tomate; Convenio Brometán–INTA: Tandil, Argentina, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Cavigliasso, P.; Bello, F.; Rivadeneira, M.F.; Monzon, N.O.; Gennari, G.P.; Basualdo, M. Pollination Efficiency of Managed Bee Species (Apis mellifera and Bombus pauloensis) in Highbush Blueberry (Vaccinium corymbosum) Productivity. J. Hort. Res. 2020, 28, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvarrey, S.; Arbulo, N.; Rossi, C.; Santos, E.; Salvarrey, L.; Invernizzi, C. Use of Native Bumblebees (Bombus atratus Franklin and Bombus bellicosus Smith) to Improve Seed Production of Red Clover (Trifolium pratense)./Utilización de Abejorros Nativos (Bombus atratus Franklin y Bombus bellicosus Smith) Para Mejorar La Producción de Trèbol Rojo (Trifolium pratense). Agrociencia 2017, 21, 95–104. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez, E.M.M. Polinización de Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) Utilización de Abeja Melífera (Apis mellifera L.); INTA Ediciones-Dirección Nacional Asistente de Comunicación Institucional Gerencia de Contenidos Periodísticos y Editoriales: Hilario Ascasubi, Argentina, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Vaissière, B.E.; Freitas, B.B.M.; Gemmill-Herren, B. Protocol to Detect and Assess Pollination Deficits in Crops: A Handbook for Its Use; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United nations (FAO): Rome, Italy, 2011; p. 70. [Google Scholar]
- Judd, H.J.; Huntzinger, C.; Ramirez, R.; Strange, J.P. A 3D Printed Pollen Trap for Bumble Bee (Bombus) Hive Entrances. JoVE 2020, 161, e61500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newstrom-Lloyd, L.; Scheele, F.; Raine, I.; Li, X.; Gonzalez, M.; Roper, T. Pollen Pellet Colour, Purity & Identification. Sustainable Farming Fund—Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry: Wellington, New Zealand, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Conti, I.; Medrzycki, P.; Grillenzoni, F.V.; Corvucci, F.; Tosi, S.; Malagnini, V.; Spinella, M.; Mariotti, M.G. Floral Diversity of Pollen Collected by Honey Bees (Apis mellifera L.)—Validation of the Chromatic Assessment Method. J. Apic. Sci. 2016, 60, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria. Available online: https://www.R-project.org (accessed on 4 July 2024).
- RStudio Team. RStudio: Integrated Development Environment for R. Posit Software; PBC: Boston, MA, USA, 2023; Available online: http://www.rstudio.com/ (accessed on 4 July 2024).
- Brooks, M.; Kristensen, K.; van Benthem, K.; Magnusson, A.; Berg, C.; Nielsen, A.; Skaug, H.; Maechler, M.; Bolker, B. GlmmTMB Balances Speed and Flexibility Among Packages for Zero-Inflated Generalized Linear Mixed Modeling. R J. 2017, 9, 378–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, D.; Mächler, M.; Bolker, B.; Walker, S. Fitting Linear Mixed-Effects Models Using Lme4. J. Stat. Softw. 2015, 67, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinrich, B. Bumblebee Economics; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Bohart, G.E.; Nye, W.P.; Levin, M.D. Growing Alfalfa for Seed; Agricultural Experiment Station—Utah State Agricultural College-United States Department of Agriculture: Logan, UT, USA, 1955; Volume 135. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, H. Die Befruchtung der Blumen durch Insekten und die gegenseitigen Anpassungen beider: Ein Beitrag zur Erkenntniss des ursächlichen Zusammenhanges in der organischen Natur (The Fertilization of Flowers by Insects and the Mutual Adaptations of Both: A Contribution to the Understanding of the Causal Relationships in Organic Nature); Engelmann: Leipzig Germany, 1873. [Google Scholar]
- Helmbold, F. Untersuchungen Tiber Die Befruchtungsverhaltnisse, Tiber Die Bedingungen Und Tiber Die Vererbung Der Samenerzeugung Bei Luzerne (Investigations on Fertilization, on the Conditions and Inheritance of Seed Production in Lucerne (Medicago sativa). Zeitsclzrift Für Pflanzenzilclztung 1929, 14, 113–173. [Google Scholar]
- Peck, O.; Bolton, J.L. Alfalfa Seed Production in Northern Saskatchewan as Affected by Bees, with a Report on Means of Increasing the Populations of Native Bees. Sci. Agric. 1946, 26, 388–418. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, L.G. Increased Production of Alfalfa Seed with Honey-Bees Pollination. In North American Alfalfa Improvement Conference; Aamodt, O.S., Ed.; Lethbridge: Alberta, Canada, 1950; pp. 38–40. [Google Scholar]
- Vansell, G.H. Use of Honey Bees in Alfalfa Seed Production; US Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1951.
- Levin, M.D. A Technique for Estimating the Percentage of Honey Bees Visiting Alfalfa. J. Econ. Entomol. 1955, 48, 484–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, M.D. Distribution Patterns of Young and Experienced Honey Bees Foraging on Alfalfa. J. Econ. Entomol. 1959, 52, 969–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raine, N.E.; Chittka, L. Pollen Foraging: Learning a Complex Motor Skill by Bumblebees (Bombus terrestris). Naturwissenschaften 2007, 94, 459–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz, P.C.; Arenas, A.; Fernández, V.M.; Susic Martin, C.; Basilio, A.M.; Farina, W.M. Honeybee Cognitive Ecology in a Fluctuating Agricultural Setting of Apple and Pear Trees. Behav. Ecol. 2013, 24, 1058–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baur, A.; Strange, J.P.; Koch, J.B. Foraging Economics of the Hunt Bumble Bee, a Viable Pollinator for Commercial Agriculture. Environ. Entomol. 2019, 48, 799–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laverty, T.M.; Plowright, R.C. Flower Handling by Bumblebees: A Comparison of Specialists and Generalists. Anim. Behav. 1988, 36, 733–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodward, G.L.; Laverty, T.M. Recall of Flower Handling Skills by Bumble Bees: A Test of Darwin’s Interference Hypothesis. Anim. Behav. 1992, 44, 1045–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbaneja-Bernat, P.; Cloonan, K.; Zhang, A.; Salazar-Mendoza, P.; Rodriguez-Saona, C. Fruit volatiles mediate differential attraction of Drosophila suzukii to wild and cultivated blueberries. J. Pest Sci. 2021, 94, 1249–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Saona, C.; Parra, L.; Quiroz, A.; Isaacs, R. Variation in highbush blueberry floral volatile profiles as a function of pollination status, cultivar, time of day and flower part: Implications for flower visitation by bees. Ann. Bot. 2011, 107, 1377–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, J.; Shen, J.; Zhao, H.; Ma, W.; Jiang, Y. Differences in EAG Response and Behavioral Choices between Honey Bee and Bumble Bee to Tomato Flower Volatiles. Insects 2022, 13, 987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mänd, M.; Maavara, V.; Martin, A.J.; Mänd, R. The Density of Bombus lucorum (L.) Required to Effect Maximum Pollination of Alfalfa in Estonia. J. Apic. Sci. 1996, 35, 79–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palottini, F.; Estravis-Barcala, M.C.; Farina, W.M. Odor learning in classical conditioning of proboscis extension in the South American native bumblebee Bombus atratus (Hymenoptera: Apidae). Front. Psychol. 2018, 9, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nery, D.; Palottini, F.; Farina, W.M. Classical olfactory conditioning promotes long term memory and improves odor-cued flight orientation in the South American native bumblebee Bombus pauloensis. Curr. Zool. 2020, 67, 561–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farina, W.M.; Arenas, A.; Estravis-Barcala, M.C.; Palottini, F. Targeted crop pollination by training honey bees: Advances and perspectives. Front. Bee Sci. 2023, 1, 1253157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).