Biochemical Indicators and Mortality in Honey Bee (Apis mellifera) Workers after Oral Exposure to Plant Protection Products and Their Mixtures
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Honey Bee Workers Rearing
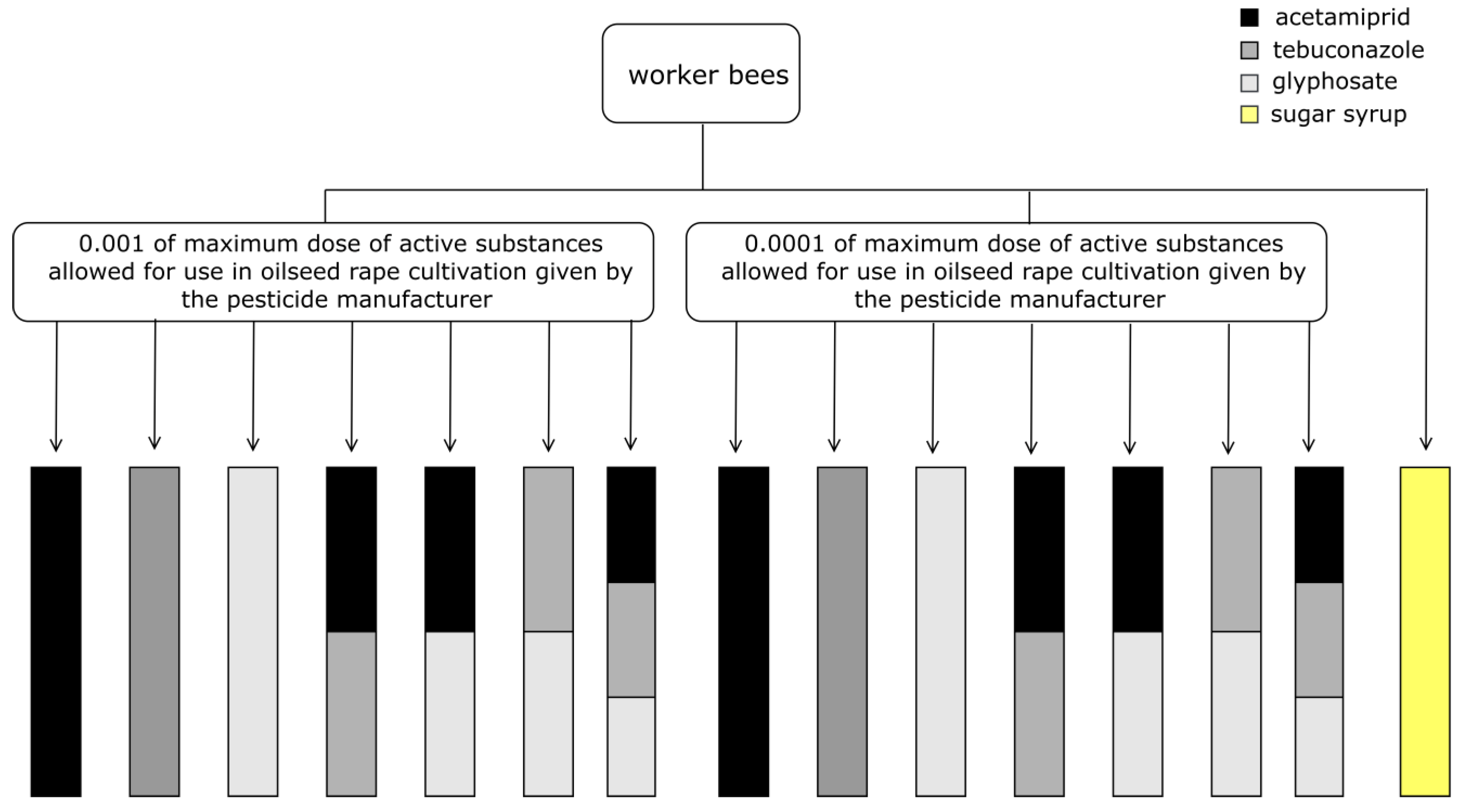
2.2. Pesticide Exposure
- acetamiprid: 250 or 25 ppb
- tebuconazole: 1612.5 or 161.25 ppb
- glyphosate: 7200 or 720 ppb
- acetamiprid: 125 or 12.5 ppb
- tebuconazole: 806.25 or 80.625 ppb
- glyphosate: 3600 or 360 ppb
- acetamiprid: 83.33 or 8.33 ppb
- tebuconazole: 537.5 or 53.75 ppb
- glyphosate: 2400 or 240 ppb
2.3. Food Intake and Mortality
2.4. Hemolymph Collection and Analysis
2.5. Biochemical Analysis
2.6. Biochemical Analysis—Enzymes
- Alanine aminotransferase (ALT)
- ALT = alanine aminotransferase,
- LDH = lactate dehydrogenase
- Aspartate aminotransferase (AST)
- AST = aspartate aminotransferase
- MDH = malate dehydrogenase
- Alkaline phosphatase (ALP)
- ALP = alkaline phosphatase
- Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase (GGTP)
2.7. Biochemical Analysis—Non-Enzymatic Antioxidant
2.7.1. Albumin
2.7.2. Creatinine
2.7.3. Urea
2.7.4. Uric Acid
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Food Intake and Mortality
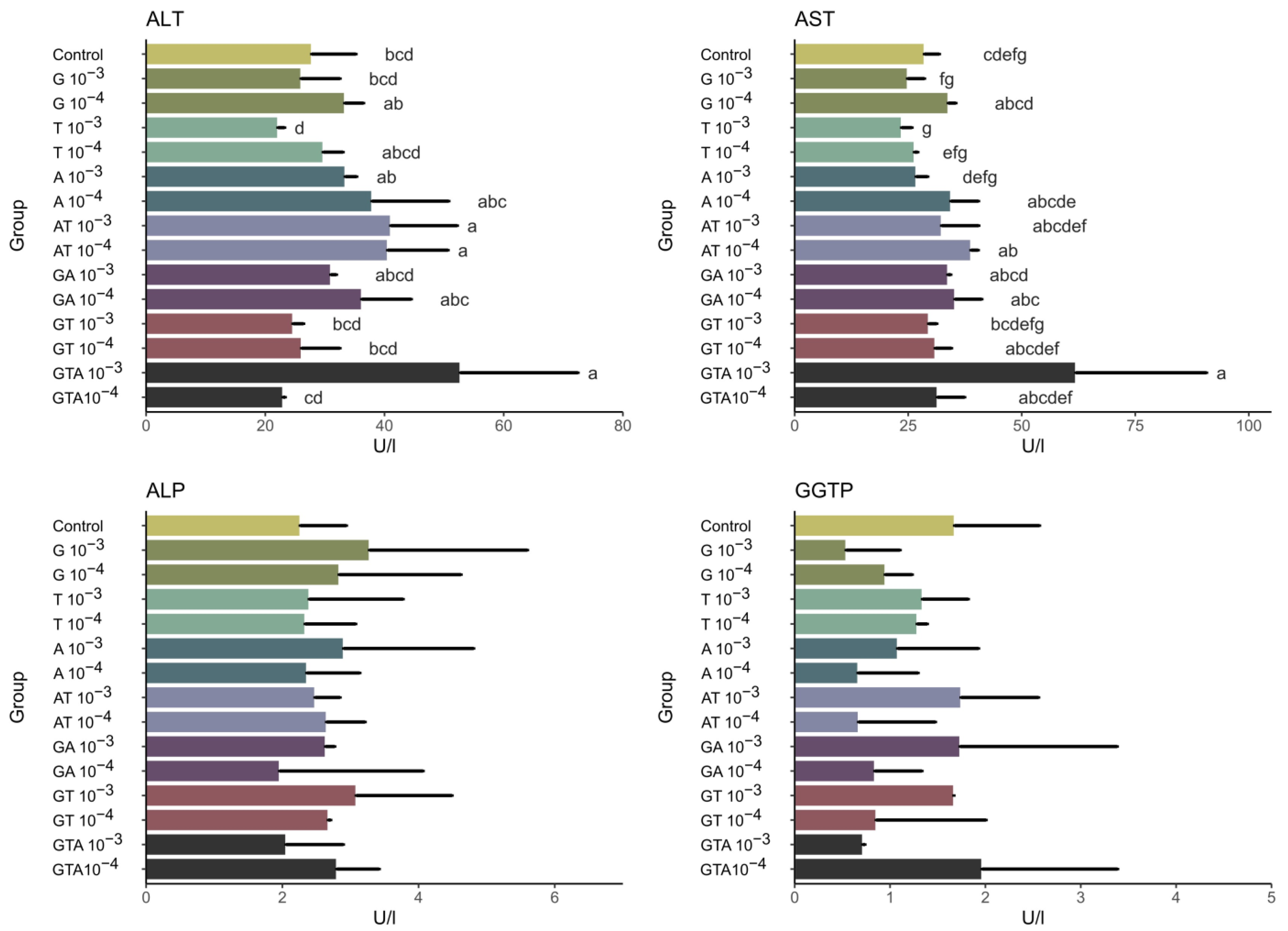
3.2. Biochemical Analysis—Enzymes
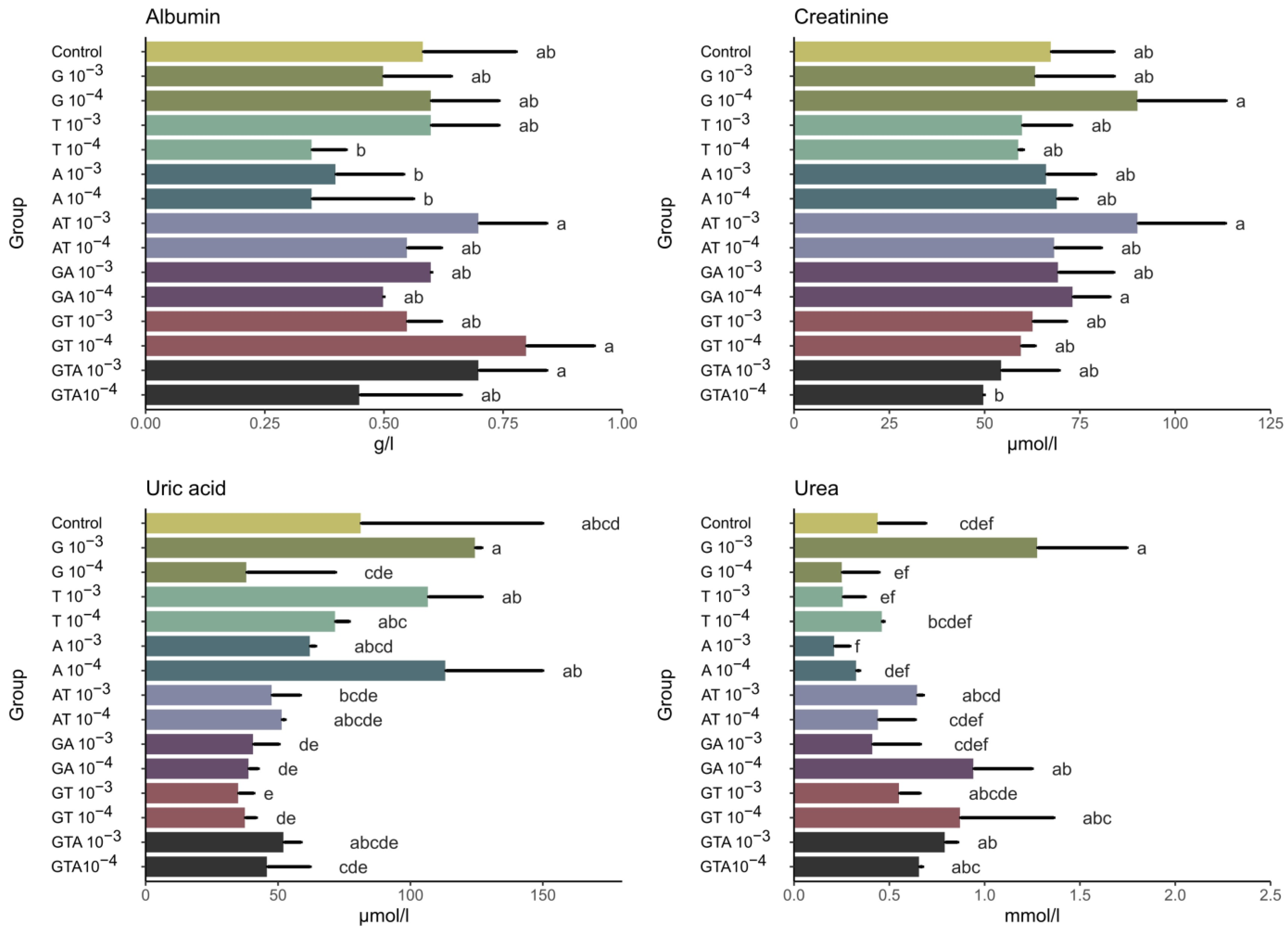
3.3. Biochemical Analysis—Non-Enzymatic Antioxidants
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carvalho, F.P. Pesticides, Environment, and Food Safety. Food Energy Secur 2017, 6, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, I.; Devi, N. Pesticides Classification and Its Impact on Human and Environment. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2017, 6, 140–158. [Google Scholar]
- Popp, J.; Pető, K.; Nagy, J. Pesticide Productivity and Food Security. A Review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2013, 33, 243–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geiger, F.; Bengtsson, J.; Berendse, F.; Weisser, W.W.; Emmerson, M.; Morales, M.B.; Ceryngier, P.; Liira, J.; Tscharntke, T.; Winqvist, C.; et al. Erratum to “Persistent Negative Effects of Pesticides on Biodiversity and Biological Control Potential on European Farmland” [Basic Appl. Ecol. 11 (2010) 97-105]. Basic Appl. Ecol. 2011, 12, 386–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlile. Pesticide Selectivity, Health and the Environment; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Calatayud-Vernich, P.; Calatayud, F.; Simó, E.; Picó, Y. Pesticide Residues in Honey Bees, Pollen and Beeswax: Assessing Beehive Exposure. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 241, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genersch, E. Honey Bee Pathology: Current Threats to Honey Bees and Beekeeping. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 87, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allsopp, M.H.; de Lange, W.J.; Veldtman, R. Valuing Insect Pollination Services with Cost of Replacement. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almasri, H.; Tavares, D.A.; Pioz, M.; Sené, D.; Tchamitchian, S.; Cousin, M.; Brunet, J.-L.; Belzunces, L.P. Mixtures of an Insecticide, a Fungicide and a Herbicide Induce High Toxicities and Systemic Physiological Disturbances in Winter Apis Mellifera Honey Bees. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 203, 111013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paleolog, J.; Wilde, J.; Miszczak, A.; Gancarz, M.; Strachecka, A. Antioxidation Defenses of Apis Mellifera Queens and Workers Respond to Imidacloprid in Different Age-Dependent Ways: Old Queens Are Resistant, Foragers Are Not. Animals 2021, 11, 1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paleolog, J.; Wilde, J.; Siuda, M.; Bąk, B.; Wójcik, Ł.; Strachecka, A. Imidacloprid Markedly Affects Hemolymph Proteolysis, Biomarkers, DNA Global Methylation, and the Cuticle Proteolytic Layer in Western Honeybees. Apidologie 2020, 51, 620–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.C.; Yao, J.; Adamczyk, J.; Luttrell, R. Synergistic Toxicity and Physiological Impact of Imidacloprid Alone and Binary Mixtures with Seven Representative Pesticides on Honey Bee (Apis mellifera). PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renzi, M.T.; Amichot, M.; Pauron, D.; Tchamitchian, S.; Brunet, J.-L.; Kretzschmar, A.; Maini, S.; Belzunces, L.P. Chronic Toxicity and Physiological Changes Induced in the Honey Bee by the Exposure to Fipronil and Bacillus Thuringiensis Spores Alone or Combined. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 127, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migdał, P.; Roman, A.; Strachecka, A.; Murawska, A.; Bieńkowski, P. Changes of Selected Biochemical Parameters of the Honeybee under the Influence of an Electric Field at 50 Hz and Variable Intensities. Apidologie 2020, 51, 956–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanbergen, A.J. Threats to an Ecosystem Service: Pressures on Pollinators. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2013, 11, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De la Rúa, P.; Jaffé, R.; Dall’Olio, R.; Muñoz, I.; Serrano, J. Biodiversity, Conservation and Current Threats to European Honeybees. Apidologie 2009, 40, 263–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łoś, A.; Strachecka, A. Fast and Cost-Effective Biochemical Spectrophotometric Analysis of Solution of Insect “Blood” and Body Surface Elution. Sensors 2018, 18, 1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaki, J.M.; Hogendoorn, K. Non-Insecticide Pesticide Impacts on Bees: A Review of Methods and Reported Outcomes. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 314, 107423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Ma, S.; Liu, F.; Wang, Q.; Wang, X.; Hou, C.; Wu, Y.; Gao, J.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.; et al. Acute and Chronic Toxicity of Acetamiprid, Carbaryl, Cypermethrin and Deltamethrin to Apis mellifera Larvae Reared In Vitro. Pest Manag. Sci. 2020, 76, 978–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medrzycki, P.; Giffard, H.; Aupinel, P.; Belzunces, L.P.; Chauzat, M.P.; Claßen, C.; Colin, M.E.; Dupont, T.; Girolami, V.; Johnson, R.; et al. Standard Methods for Toxicology Research in Apis Mellifera. J. Apic. Res. 2013, 52, 1–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battisti, L.; Potrich, M.; Sampaio, A.R.; de Castilhos Ghisi, N.; Costa-Maia, F.M.; Abati, R.; dos Reis Martinez, C.B.; Sofia, S.H. Is Glyphosate Toxic to Bees? A Meta-Analytical Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 767, 145397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.H.M.; Lenzen, M.; McBratney, A.; Maggi, F. Risk of Pesticide Pollution at the Global Scale. Nat. Geosci. 2021, 14, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gierer, F.; Vaughan, S.; Slater, M.; Thompson, H.M.; Elmore, J.S.; Girling, R.D. A Review of the Factors That Influence Pesticide Residues in Pollen and Nectar: Future Research Requirements for Optimising the Estimation of Pollinator Exposure. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 249, 236–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vargas-Valero, A.; Reyes-Carrillo, J.; Moreno-Reséndez, A.; Véliz-Deras, F.; Gaspar-Ramírez, O.; Rodríguez-Martínez, R. Residuos de Plaguicidas En Miel y Cera de Colonias de Abejas de La Comarca Lagunera. Abanico Vet. 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Ma, C.; Sun, M.; Wang, Y.; Xue, X.; Chen, J.; Song, W.; Li-Byarlay, H.; Luo, S. Pesticide Residues in the Pollen and Nectar of Oilseed Rape (Brassica napus L.) and Their Potential Risks to Honey Bees. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 786, 147443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zioga, E.; Kelly, R.; White, B.; Stout, J.C. Plant Protection Product Residues in Plant Pollen and Nectar: A Review of Current Knowledge. Environ. Res. 2020, 189, 109873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berg, C.J.; King, H.P.; Delenstarr, G.; Kumar, R.; Rubio, F.; Glaze, T. Glyphosate Residue Concentrations in Honey Attributed through Geospatial Analysis to Proximity of Large-Scale Agriculture and Transfer off-Site by Bees. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0198876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Nahhal, Y. Pesticide Residues in Honey and Their Potential Reproductive Toxicity. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 741, 139953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raimets, R.; Naudi, S.; Mänd, M.; Bartkevičs, V.; Smagghe, G.; Karise, R. Translocation of Tebuconazole between Bee Matrices and Its Potential Threat on Honey Bee (Apis mellifera Linnaeus) Queens. Insects 2021, 13, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karise, R.; Raimets, R.; Bartkevics, V.; Pugajeva, I.; Pihlik, P.; Keres, I.; Williams, I.H.; Viinalass, H.; Mänd, M. Are Pesticide Residues in Honey Related to Oilseed Rape Treatments? Chemosphere 2017, 188, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migdał, P.; Murawska, A.; Roman, A. A Modified Standardized Method to Extract and Store Insect Hemolymph with Use of a Glass Capillary. J. Apic. Sci. 2020, 64, 165–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonmatin, J.M.; Moineau, I.; Charvet, R.; Fleche, C.; Colin, M.E.; Bengsch, E.R. A LC/APCI-MS/MS Method for Analysis of Imidacloprid in Soils, in Plants, and in Pollens. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 2027–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmuck, R.; Stadler, T.; Schmidt, H.-W. Field Relevance of a Synergistic Effect Observed in the Laboratory between an EBI Fungicide and a Chloronicotinyl Insecticide in the Honeybee ( Apis mellifera L., Hymenoptera). Pest Manag. Sci. 2003, 59, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decourtye, A.; Devillers, J. Ecotoxicity of Neonicotinoid Insecticides to Bees. In Insect Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 85–95. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, R.; Mavi, G.K.; Raghav, S.; Khan, I. Pesticides Classification and Its Impact on Environment. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2019, 8, 1889–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhu, Y.C.; Li, W. Interaction Patterns and Combined Toxic Effects of Acetamiprid in Combination with Seven Pesticides on Honey Bee (Apis mellifera L.). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 190, 110100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R.M.; Dahlgren, L.; Siegfried, B.D.; Ellis, M.D. Acaricide, Fungicide and Drug Interactions in Honey Bees (Apis mellifera). PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilling, E.D.; Jepson, P.C. Synergism between EBI Fungicides and a Pyrethroid Insecticide in the Honeybee Apis Mellifera. Pestic. Sci. 1993, 39, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, T.S.; van den Heever, J.P.; Limanowka, R.E. Determination of Glyphosate, AMPA, and Glufosinate in Honey by Online Solid-Phase Extraction-Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2019, 36, 434–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Zhu, Y.C.; Adamczyk, J. Responses of Honey Bees to Lethal and Sublethal Doses of Formulated Clothianidin Alone and Mixtures. J. Econ. Entomol. 2018, 111, 1517–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christen, V. Different Effects of Pesticides on Transcripts of the Endocrine Regulation and Energy Metabolism in Honeybee Foragers from Different Colonies. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wade, A.; Lin, C.H.; Kurkul, C.; Regan, E.R.; Johnson, R.M. Combined Toxicity of Insecticides and Fungicides Applied to California Almond Orchards to Honey Bee Larvae and Adults. Insects 2019, 10, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessler, S.C.; Tiedeken, E.J.; Simcock, K.L.; Derveau, S.; Mitchell, J.; Softley, S.; Radcliffe, A.; Stout, J.C.; Wright, G.A. Bees Prefer Foods Containing Neonicotinoid Pesticides. Nature 2015, 521, 74–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, W.; Schmehl, D.R.; Mullin, C.A.; Frazier, J.L. Four Common Pesticides, Their Mixtures and a Formulation Solvent in the Hive Environment Have High Oral Toxicity to Honey Bee Larvae. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e77547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Migdal, P.; Murawska, A.; Berbeć, E.; Plotnik, M.; Skorus, A.; Latarowski, K. Selected Biochemical Markers Change after Oral Administration of Pesticide Mixtures in Honey Bees. Toxics 2022, 10, 590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badawy, M.E.I.; Nasr, H.M.; Rabea, E.I. Toxicity and Biochemical Changes in the Honey Bee Apis Mellifera Exposed to Four Insecticides under Laboratory Conditions. Apidologie 2015, 46, 177–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faita, M.R.; Cardozo, M.M.; Amandio, D.T.T.; Orth, A.I.; Nodari, R.O. Glyphosate-Based Herbicides and Nosema Sp. Microsporidia Reduce Honey Bee (Apis mellifera L.) Survivability under Laboratory Conditions. J. Apic. Res. 2020, 59, 332–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomé, H.V.V.; Schmehl, D.R.; Wedde, A.E.; Godoy, R.S.M.; Ravaiano, S.V.; Guedes, R.N.C.; Martins, G.F.; Ellis, J.D. Frequently Encountered Pesticides Can Cause Multiple Disorders in Developing Worker Honey Bees. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 256, 113420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vázquez, D.E.; Ilina, N.; Pagano, E.A.; Zavala, J.A.; Farina, W.M. Glyphosate Affects the Larval Development of Honey Bees Depending on the Susceptibility of Colonies. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0205074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez, D.E.; Latorre-Estivalis, J.M.; Ons, S.; Farina, W.M. Chronic Exposure to Glyphosate Induces Transcriptional Changes in Honey Bee Larva: A Toxicogenomic Study. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 261, 114148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajda, M.; Łoś, A.; Merska, M. Effect of Amphotericin B on the Biochemical markers in the Haemolymph of Honey Bees. Med. Weter 2014, 70, 766–769. [Google Scholar]
- Strachecka, A.; Olszewski, K.; Paleolog, J. Varroa Treatment with Bromfenvinphos Markedly Suppresses Honeybee Biochemical Defence Levels. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2016, 160, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migdał, P.; Murawska, A.; Bieńkowski, P.; Strachecka, A.; Roman, A. Effect of the Electric Field at 50 Hz and Variable Intensities on Biochemical Markers in the Honey Bee’s Hemolymph. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0252858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Şapcaliu, A.; Pavel, C.; Savu, V.; Căuia, E.; Matei, M.; Rădoi, I. Biochemical and Cytological Investigations on Haemolymph of Apis Mellifera Carpathica Bee in Stressful Conditions. Bull. UASVM Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2010, 67, 313–320. [Google Scholar]
- Strachecka, A.; Olszewski, K.; Paleolog, J. Curcumin Stimulates Biochemical Mechanisms of Apis Mellifera Resistance and Extends the Apian Life-Span. J. Apic. Sci. 2015, 59, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strachecka, A.; Olszewski, K.; Paleolog, J.; Borsuk, G.; Bajda, M.; Krauze, M.; Merska, M.; Chobotow, J. Coenzyme Q10 Treatments Influence the Lifespan and Key Biochemical Resistance Systems in the Honeybee Apis Mellifera. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2014, 86, 165–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strachecka, A.; Krauze, M.; Olszewski, K.; Borsuk, G.; Paleolog, J.; Merska, M.; Chobotow, J.; Bajda, M.; Grzywnowicz, K. Unexpectedly Strong Effect of Caffeine on the Vitality of Western Honeybees (Apis mellifera). Biochemistry 2014, 79, 1192–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugeçti Serkan, K.B. Effects of Oxfendazole on Metabolic Enzymes in Hemolymph of Galleria mellonella L.(Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) Larvae Reared on Artificial Diet. Karaelmas Sci. Eng. J. 2018, 8, 129–137. [Google Scholar]
- Shemesh, O.; Golbetz, H.; Kriss, J.P.; Myers, B.D. Limitations of Creatinine as a Filtration Marker in Glomerulopathic Patients. Kidney Int. 1985, 28, 830–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bursell, E. The Excretion of Nitrogen in Insects. Adv. Insect Physiol. 1967, 4, 33–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Migdał, P.; Murawska, A.; Berbeć, E.; Zarębski, K.; Ratajczak, N.; Roman, A.; Latarowski, K. Biochemical Indicators and Mortality in Honey Bee (Apis mellifera) Workers after Oral Exposure to Plant Protection Products and Their Mixtures. Agriculture 2024, 14, 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14010005
Migdał P, Murawska A, Berbeć E, Zarębski K, Ratajczak N, Roman A, Latarowski K. Biochemical Indicators and Mortality in Honey Bee (Apis mellifera) Workers after Oral Exposure to Plant Protection Products and Their Mixtures. Agriculture. 2024; 14(1):5. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14010005
Chicago/Turabian StyleMigdał, Paweł, Agnieszka Murawska, Ewelina Berbeć, Karol Zarębski, Natalia Ratajczak, Adam Roman, and Krzysztof Latarowski. 2024. "Biochemical Indicators and Mortality in Honey Bee (Apis mellifera) Workers after Oral Exposure to Plant Protection Products and Their Mixtures" Agriculture 14, no. 1: 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14010005
APA StyleMigdał, P., Murawska, A., Berbeć, E., Zarębski, K., Ratajczak, N., Roman, A., & Latarowski, K. (2024). Biochemical Indicators and Mortality in Honey Bee (Apis mellifera) Workers after Oral Exposure to Plant Protection Products and Their Mixtures. Agriculture, 14(1), 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14010005





