Straw Return Decomposition Characteristics and Effects on Soil Nutrients and Maize Yield
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Straw Decomposition and Nutrient Release Rate Measurement
2.4. Soil Nutrient Measurement
2.5. Maize Yield Measurement
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Straw Decomposition Rate
3.2. Straw Nutrient Release Rate
3.3. Soil Nutrient Content
3.4. Soil Microbial Quantity
3.5. Maize Yield
3.6. Correlation Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Different Effects of Straw Return Modes on Different Investigation Items
4.2. Relationship between Decomposition Rate, Nutrient Release Rate, and Soil Nutrient Content
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jin, Z.; Shah, T.; Zhang, L.; Liu, H.; Peng, S.; Nie, L. Effect of straw returning on soil organic carbon in rice–wheat rotation system: A review. Food Energy Secur. 2020, 9, e200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Xiong, Y.; Li, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Huang, G. Effects of organic amendment incorporation on maize (Zea mays L.) growth, yield and water-fertilizer productivity under arid conditions. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 269, 107663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhang, X.; Shao, L.; Sun, H.; Niu, J.; Liu, X. Effects of straw and manure management on soil and crop performance in North China Plain. Catena 2020, 187, 104359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Sun, B.; Wu, S.; Feng, H.; Gao, M.; Zhang, B.; Liu, Y. After-effects of straw and straw-derived biochar application on crop growth, yield, and soil properties in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.)-maize (Zea mays L.) rotations: A four-year field experiment. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 780, 146560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Jia, Z.; Liang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, B.; Ding, R.; Wang, J.; Nie, J. Changes in soil characteristics and maize yield under straw returning system in dryland farming. Field Crops Res. 2018, 218, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zheng, M.-J.; Pang, D.-W.; Yin, Y.-P.; Han, M.-M.; Li, Y.-X.; Luo, Y.-L.; Xu, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.-L. Straw return and appropriate tillage method improve grain yield and nitrogen efficiency of winter wheat. J. Integr. Agric. 2017, 16, 1708–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunrat, N.; Sereenonchai, S.; Sansupa, C.; Kongsurakan, P.; Hatano, R. Effect of Rice Straw and Stubble Burning on Soil Physicochemical Properties and Bacterial Communities in Central Thailand. Biology 2023, 12, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunrat, N.; Kongsurakan, P.; Sereenonchai, S.; Hatano, R.J.A. Soil organic carbon in sandy paddy fields of Northeast Thailand: A review. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mochizuki, A.; Homma, K.; Horie, T.; Shiraiwa, T.; Watatsu, E.; Supapoj, N.; Thongthai, C.J.F.C.R. Increased productivity of rainfed lowland rice by incorporation of pond sediments in Northeast Thailand. Field Crops Res. 2006, 96, 422–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Sun, S.; Yao, B.; Peng, Y.; Gao, C.; Qin, T.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, C.; Quan, W. Effects of straw return and straw biochar on soil properties and crop growth: A review. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, B.; Hu, H.; Zhao, Y.; Mu, X.; Liu, K.; Li, C. Effects of Deep Tillage and Straw Returning on Soil Microorganism and Enzyme Activities. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 451493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, L.L.; Wang, H.H.; Lu, C.Y.; Jin, M.J.; Zhu, X.L.; Shen, Y.; Shen, M.X. Effects of straw returning amount and type on soil nitrogen and its composition. J. Appl. Ecol. 2019, 30, 1143–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yu, K.; Feng, H. Effects of straw mulching and plastic film mulching on improving soil organic carbon and nitrogen fractions, crop yield and water use efficiency in the Loess Plateau, China. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 201, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Hu, W.; Xu, Z.; Xue, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Liao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, T.; Cong, R.; et al. Seasonal Temporal Characteristics of In Situ Straw Decomposition in Different Types and Returning Methods. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2022, 22, 4228–4240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guebel, D.; Nudel, B.; Giulietti, A. A simple and rapid micro-Kjeldahl method for total nitrogen analysis. Biotechnol. Tech. 1991, 5, 427–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latta, M.; Eskin, M. A simple and rapid colorimetric method for phytate determination. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1980, 28, 1313–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, R.B.; Richardson, D.; Berry, J.W.; Hood, R.L. Flame photometry a rapid analytical procedure. Ind. Eng. Chem. Anal. Ed. 1945, 17, 605–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soest, P.J.V. Use of detergents in the analysis of fibrous feeds. II. A rapid method for the determination of fiber and lignin. J. Assoc. Off. Agric. Chem. 1963, 46, 829–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schollenberger, C. A rapid approximate method for determining soil organic matter. Soil Sci. 1927, 24, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schofield, R.; Taylor, A.W. The measurement of soil pH. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1955, 19, 164–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, N.; Sutherland, M.L. The accuracy of the plating method for estimating the numbers of soil bacteria, actinomyces, and fungi in the dilution plated. Can. J. Res. 1939, 17, 72–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, X.; Zhuang, J.; Cong, Y.; Lu, Y.; Guo, M. Fine-crush straw returning enhances dry matter accumulation rate of maize seedlings in Northeast China. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejada, M.; Benítez, C. Effects of crushed maize straw residues on soil biological properties and soil restoration. Land Degrad. Dev. 2014, 25, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Li, Y.; Zhai, S.; Fang, C.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Q. Long term ditch-buried straw return affects soil fungal community structure and carbon-degrading enzymatic activities in a rice-wheat rotation system. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2020, 155, 103660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, S.B.; Classen, A.T.; Kardol, P.; Yermakov, Z.; Mille, R.M. Multiple climate change factors interact to alter soil microbial community structure in an old-field ecosystem. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2011, 75, 2217–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yu, S.; Zhou, L.; Fu, S. Soil microbial characteristics and the influencing factors in subtropical forests. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2016, 36, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, K.; Han, Y.; Liu, Z.; Yang, F.; Wang, S.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, C. A crop variety yield prediction system based on variety yield data compensation. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 203, 107460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Liu, H.; Zhang, J.; Liu, P.; Dong, S. Factors affecting summer maize yield under climate change in Shandong Province in the Huanghuaihai Region of China. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2012, 56, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, E.; Chi, F.; Su, Q.; Zhang, J.; Gao, Z. Decomposition regularity of organic materials in Sanjiang Plain region. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2010, 18, 736–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, P.; Jiang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Ma, Z.; Sui, P.; Mei, N.; Qi, H. Effect of straw return methods on maize straw decomposition and soil nutrients contents. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2019, 27, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, X.; Wei, J. Decomposition of rice straw and corn straw under aerobic and anaerobic conditions. J. Agric. Resour. Environ. 2017, 34, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarafdar, J.C.; Meena, S.C.; Kathju, S. Influence of straw size on activity and biomass of soil microorganisms during decomposition. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2001, 37, 157–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Yan, S.; Jia, T.; Dong, S.; Ma, C.; Gong, Z. Decomposition characteristics of rice straw returned to the soil in northeast China. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2019, 114, 211–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Hu, M.; Shi, J.; Tian, X. Improving long-term crop productivity and soil quality through integrated straw-return and tillage strategies. Agron. J. 2022, 114, 1500–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Wei, L.; Turner, N.C.; Ma, S.; Yang, M.; Wang, T. Improved straw management practices promote in situ straw decomposition and nutrient release, and increase crop production. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 250, 119514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, Z.; Cai, C.; Yang, W.; Ma, R.; Zhang, G. Effects of stability, transport distance and two hydraulic parameters on aggregate abrasion of Ultisols in overland flow. Soil Tillage Res. 2013, 126, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quansah, C.; Safo, E.; Ampontuah, E.; Amankwah, A. Soil fertility erosion and the associated cost of NPK removed under different soil and residue management in Ghana. Ghana J. Agric. Sci. 2000, 33, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Qi, J.; Liu, B.; Kan, Z.; Zhao, X.; Xiao, X.; Zhang, H. Strategic tillage effects on soil properties and agricultural productivity in the paddies of Southern China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2020, 31, 1277–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
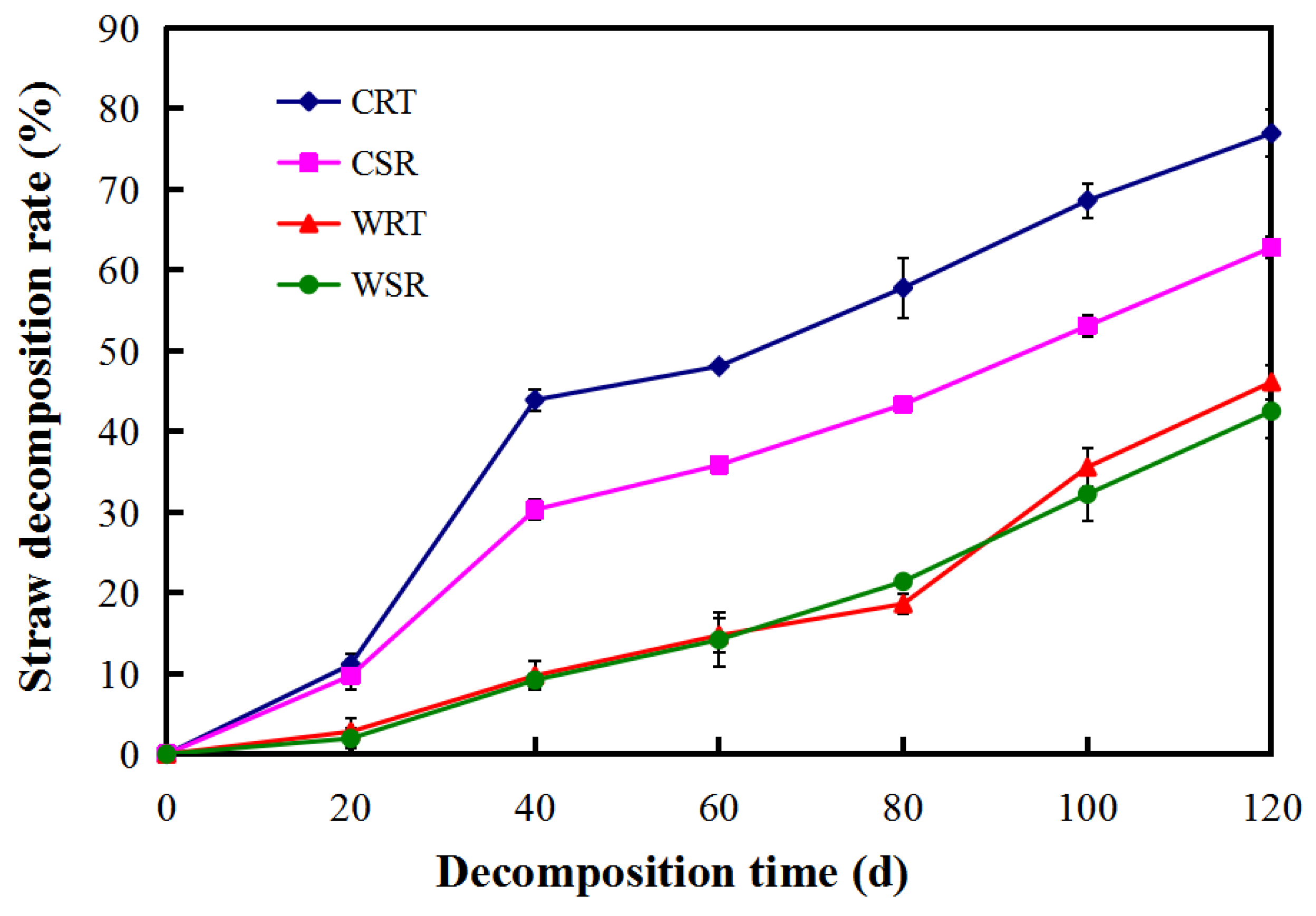


| Straw Return Modes | Straw Decomposition Rates (%) at Different Time Points | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 d | 20 d | 40 d | 60 d | 80 d | 100 d | 120 d | |
| CRT | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | 11.11 ± 1.27 a | 43.89 ± 1.27 a | 48.06 ± 0.48 a | 57.78 ± 3.76 a | 68.61 ± 2.10 a | 76.94 ± 2.93 a |
| CSR | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | 9.72 ± 1.73 a | 30.27 ± 1.27 b | 35.83 ± 0.83 b | 43.33 ± 0.83 b | 53.06 ± 1.27 b | 62.78 ± 1.27 b |
| WRT | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | 2.78 ± 1.73 b | 9.72 ± 1.73 c | 14.72 ± 2.10 c | 18.61 ± 1.27 c | 35.56 ± 2.41 c | 46.11 ± 2.10 c |
| WSR | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | 1.94 ± 1.27 b | 9.17 ± 0.83 c | 14.17 ± 3.33 c | 21.39 ± 0.48 c | 32.22 ± 3.37 c | 42.50 ± 3.33 c |
| Straw Return Modes | Total Nitrogen | Total Phosphorus | Total Potassium | Cellulose | Hemicellulose | Lignin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CRT | 75.16 ± 0.55 a | 73.51 ± 0.21 a | 64.08 ± 1.28 a | 76.39 ± 0.34 a | 75.43 ± 1.75 a | 71.18 ± 1.54 a |
| CSR | 49.39 ± 0.71 b | 61.76 ± 1.10 b | 63.03 ± 1.07 a | 59.95 ± 0.69 b | 65.71 ± 1.03 b | 55.98 ± 0.93 b |
| WRT | 22.25 ± 0.77 d | 39.94 ± 0.07 d | 48.29 ± 1.27 c | 49.22 ± 0.78 c | 55.71 ± 1.03 c | 28.89 ± 1.25 c |
| WSR | 33.18 ± 0.85 c | 54.23 ± 2.20 c | 56.50 ± 0.18 b | 27.36 ± 2.31 d | 31.01 ± 0.12 d | 23.56 ± 0.52 d |
| Treatments | pH | Organic Matter (g/kg) | Total Nitrogen Content (g/kg) | Total Phosphorus Content (g/kg) | Total Potassium Content (g/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 8.53 ± 0.02 a | 11.59 ± 0.46 b | 0.88 ± 0.03 c | 0.62 ± 0.03 c | 16.01 ± 0.71 c |
| RT | 8.39 ± 0.02 b | 13.46 ± 0.53 b | 0.80 ± 0.02 d | 0.53 ± 0.04 d | 16.95 ± 0.55 bc |
| CRT | 8.30 ± 0.02 d | 15.61 ± 0.48 a | 1.01 ± 0.04 a | 0.76 ± 0.04 a | 18.76 ± 0.23 a |
| CSR | 8.32 ± 0.02 d | 15.39 ± 0.29 a | 0.93 ± 0.02 b | 0.76 ± 0.03 a | 18.87 ± 0.38 a |
| WRT | 8.37 ± 0.02 bc | 15.00 ± 0.12 a | 0.91 ± 0.04 bc | 0.64 ± 0.05 bc | 17.76 ± 0.34 b |
| WSR | 8.32 ± 0.03 cd | 15.04 ± 0.34 a | 0.91 ± 0.03 bc | 0.71 ± 0.03 b | 17.84 ± 0.30 b |
| Straw Return Modes | Bacteria (107 CFU/g) | Fungi (104 CFU/g) | Actinomycetes (106 CFU/g) | Total (107 CFU/g) | Maize Grain Yield (t/ha) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RT | 0.97 ± 0.03 c | 6.23 ± 0.06 c | 6.17 ± 0.19 b | 1.59 ± 0.33 c | 6.62 ± 0.12 b |
| CRT | 1.36 ± 0.11 a | 7.38 ± 0.06 a | 6.59 ± 0.12 a | 2.03 ± 0.12 a | 7.06 ± 0.10 a |
| CSR | 1.39 ± 0.07 a | 7.79 ± 0.46 a | 6.80 ± 0.03 a | 2.08 ± 0.08 a | 6.92 ± 0.15 ab |
| WRT | 1.16 ± 0.11 b | 6.85 ± 0.15 b | 5.82 ± 0.12 c | 1.75 ± 0.06 b | 6.79 ± 0.05 ab |
| WSR | 1.28 ± 0.08 ab | 7.44 ± 0.17 a | 6.75 ± 0.10 a | 1.96 ± 0.07 a | 6.76 ± 0.27 ab |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Y.; Long, Y.; Li, S.; Liu, X. Straw Return Decomposition Characteristics and Effects on Soil Nutrients and Maize Yield. Agriculture 2023, 13, 1570. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13081570
Yang Y, Long Y, Li S, Liu X. Straw Return Decomposition Characteristics and Effects on Soil Nutrients and Maize Yield. Agriculture. 2023; 13(8):1570. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13081570
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Yun, Yun Long, Shiwei Li, and Xiaohong Liu. 2023. "Straw Return Decomposition Characteristics and Effects on Soil Nutrients and Maize Yield" Agriculture 13, no. 8: 1570. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13081570
APA StyleYang, Y., Long, Y., Li, S., & Liu, X. (2023). Straw Return Decomposition Characteristics and Effects on Soil Nutrients and Maize Yield. Agriculture, 13(8), 1570. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13081570







