Abstract
Soil salinization processes have increased over the years and affect large parts of agricultural fields. The purpose of this review was to highlight the most important aspects regarding the potential effects of soil salinity on plants. In the current context of climate change, extreme weather and increased drought periods can lead to plant metabolic dysfunctionalities and accumulation of salt ions because of the increasing need for irrigation. The most important limiting factor, salinity, has a highly negative impact on plant growth independent of the appearance of either natural or anthropic status. The negative aspects include decreased leaf development rate, a low water level in all parts of the plant, reduced cell division and elongation, and low-intensity photosynthetic rate. Other negative aspects are directly related to stomata closure, reduced transpiration, low CO2 level, and limitations on seed germination. However, there are also some positive aspects to the presence of salinity in soil. The field offers unlimited possibilities of research in order to activate pathways that help plants become resistant to salt stress. Several physiological parameters can benefit from low salt concentration (halopriming), such as germination, vigor, rapid seedling growth, and increased stomata number. Further studies should focus on both the positive and negative aspects of the increase in soil salinity.
1. Introduction
Soil salinization is the process of excessive salt accumulation that leads to an increase in the concentration of different soluble salt types [1]. It has become a more common phenomenon due to climate change and especially severe droughts, which has resulted in increased need for irrigation [2]. Salinization causes major constraints and reduces crop yield because of limitations on different crops [3]. Soil alkalization or sodification results in an increase in the adsorbed sodium concentration in the soil solution. This process leads to variations in soil pH towards lower values [4]. If they occur simultaneously, salinization and alkalization can lead to the formation of the soil salinization process [5]. Soil degradation, in general, can have several causes, including global climate change [6], improper use of agricultural techniques [7], increased and uncontrolled irrigation [8,9], and excessive use of chemical fertilizers [10,11]. In the current context, the soil salinization process represents a real threat because it negatively affects substrates by changing their physical, chemical, and biological properties. Salinization is caused by soil erosion and is a consequence of cation and anion accumulation in the soil [12]. Cations are represented by Na+, Ca2+, Mg2+, while anions include NO3−, CO32−, SO42−, and Cl− [12,13]. All these minerals and their compounds produce an imbalance in the soil ionic solution. Thus, the soil solution becomes unavailable for plants, leading to negative effects on physiological processes [14]. Chemical reactions in the soil solution can also increase the level of plant osmotic pressure [15]. Another negative effect produced by excess salt in the soil is a reduction in the water potential values, which results in the unavailability of nutrients for plant germination, growth, and development [16]. Although salinity stress is generally considered harmful to plants, there are some potential positive aspects of salinity stress that may be observed in certain plant species or under certain conditions [17,18,19,20,21]. Salinity stress can increase the uptake of certain nutrients, such as potassium and calcium, which are important for plant growth and development under normal conditions [22,23,24]. Some plants can adjust their osmotic potential in response to salinity stress, which can help them maintain their water balance and survive in saline soils [25] as well as increase their resistance to drought periods. Salinity stress can promote the biosynthesis of antioxidants in plants in order to restrain increased levels of reactive oxygen species [26], which can protect plants from oxidative damage and other types of stress.
Soil salinization is a real threat to agriculture as it reduces suitable arable land area for the majority of crops. Moreover, by the year 2050, more than 50% of arable land will be susceptible to salinization [27]. Soil salinity is a global problem, with every continent having multiple affected areas [28,29,30], although there are large variations between different countries [31]. In Europe, soil salinization requires immediate attention. Romania is included in the short list of countries that are most affected by soil salinization [32], and it is known to have three problematic areas that are susceptible to salinization. The main areas with soils affected by salinization are located along the Danube floodplain in the south and southeast of the country and on the perimeter of the Tisa River Basin in the western part of the country [33]. The soil–plant system is strongly affected in these areas because of salinization and alkalization processes, and the agroecological potential is reduced [34]. All these factors represent a socioeconomic risk for sustainable development of the region and require special attention, research, and adaptive measures.
The methodology used in this study was based on three concurrent searches on the Web of Science Core Collection (last accessed on 9 February 2023), as shown in Figure 1. The first search with the keywords “physiological changes” × “plant under salinity stress” yielded 1134 results. The second search was performed based on “salinization stress” × “plant organisms” and yielded 22 articles. The third search was carried out with the keywords “general aspects” × “plants under salinity stress” and resulted in 12 publications. All three combinations of keywords were set on the basis of holistic research in the field of salinity with the ultimate goal of extracting the most relevant information to establish a complex experimental design. Another aspect to the choice of keywords was the diversity of words used to analyze the same “salinity” phenomenon, with the different combinations chosen based on their potential to expand the search area. Thus, a dual perspective was created on this topic: the first one represented multiple standalone experiments that have analyzed specific plant physiological response, while the second one permitted an ecophysiological vision over multiple results that can be assembled in a holistic overview. The refined criterion was performed by quick filters, and only open-access articles were considered. The open-access filter was selected according to international trends and recommendations for scientific information that are easy to consult. The following filter refined the search on a more granular level (mesolevel) and only included publications from “Crop Science” and “Crop Protection”. The reason for this second refined database filter was to ensure that only information relevant to food security and sustainable development of agriculture was included. In total, 327 publications were compiled from the first search, of which 38 were review papers. From the second search, four publications were obtained, of which one was a review. From the third search, two publications were obtained, of which one was a review. The keywords from all publications were analyzed to obtain a general overview of salinity stress from the plant physiology perspective.
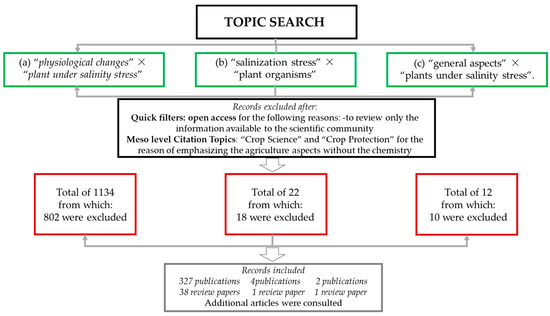
Figure 1.
Prisma diagram summarizing the research methodology.
With the help of the filtered data, the aim was to highlight the most important general aspects that need to be explored to determine the effects of salinity stress on plant growth and development. The most important topics related to salinity were explored, with the research relevance and perspective of each one being highlighted. Soil salinity was treated as a phenomenon that occurs in agricultural fields, followed by the assessment of its potential impact. The presence of salinity is a stress that leads to multiple physiological changes in plants, with different responses in terms of resistance and tolerance. Wheat was used as a case study to emphasize the response to salinity stress. The choice of this species was due to its agronomic importance and its tolerance level, which would allow us to assemble multiple studies into a complex one. The final objective was to propose multiple perspective steps in the holistic study of salinity stress.
2. The Phenomenon of Soil Salinization
Soil salinization represents a phenomenon caused by the accumulation of several ions and cations [35]. Soil salinization has both natural and anthropogenic causes [36]. The natural accumulation of salts in the soil can occur through a series of factors, such as the presence of salt deposits [36], sea depositions [36], and water salinization of the low water table [37]. All these processes can be increased by the nature of the parental rock [38]. Soil fossil salts can be altered in time, thus increasing the local salinity level [5]. Here, the porosity and permeability characteristics of the soil is changed, thus creating major restrictions for associated areas that are susceptible to salinity to different degrees [2]. On the other hand, agricultural techniques and technologies that are inadequately managed and performed, the use of chemical fertilizers, irrigation on a massive scale, improper household water discharges, and use of salt to prevent water freezing in the roads in winter are anthropogenic promoters of excess salt accumulation in the soil [36,39]. In agricultural soils, this phenomenon is usually caused by evapotranspiration [40].
In the literature, these two classes of soil salinization are also classified as primary and secondary regarding their consequences [41]. The term “primary” refers to natural soil salinization and usually occurs in regions characterized by an arid or semiarid climate. Here, soluble salts accumulate because of an intensive soil evaporation index and as a consequence of insufficient precipitation to leach excess salts from natural rocks in the downward soil profile. These salts accumulate in the upper soil profile layers. The “salt cycle” has also been found to be responsible for excess salt in the soil. Here, the ocean salts carried by wind and clouds are delivered by rain into the soils [42]. The term “secondary” refers to changes induced as a consequence of anthropic activities originating from agricultural activity or different industries [41]. Irrigation with salt-rich water changes the water solution balance and leads to a decline of perennial crops, which is detrimental to annual intensive cropping systems. Beyond the known causes, accidental salt release from wastewater represents an important source of soil salinity caused by humans.
Climate change has negative impacts on soil salinity levels. Many regions around the world are increasingly characterized by aridity, mainly due to unusually extreme events and increased annual temperatures [43]. Therefore, irrigation systems in agricultural fields are necessary to obtain high agricultural yields [44]. The use of water in irrigation systems is closely connected with increased salinization processes in the soil. Two years ago, it was declared that salinity-affected areas will increase annually by 10% worldwide [45]. Some 20% of the total cropped fields are already affected by salinity, along with 33% of the total agricultural fields with irrigation systems [45]. Furthermore, this susceptibility is expected to increase with time due to salinization caused by increasing extreme thermal temperatures [42]. It is therefore important to determine the best research direction to deal with this issue. The amount of surfaces affected by salinity represents a real threat, which is why studying the effects of this abiotic stress on plant growth and development requires special attention. Soil salinity is most often expressed by the electrical conductivity of the soil solution or by the form of osmotic potential [46]. The electrical conductivity of the soil solution is derived from the same parameter of irrigation water and precipitation [47]. The most important aspect is the physiological suitability of the crop and yield production in the presence of salinity [48,49]. Without sufficient quantities of biomass, it is difficult to test the chemistry or molecular characteristics [50]. With no biomass at all due to crops suffering under salinity stress and thus becoming dry and dying in the early phenological stages, these tests are impossible to carry out and become irrelevant.
Under saline stress conditions, plants exhibit multiple physiological changes (Figure 2a), which are mostly visible in the rate of photosynthesis and the different physiological parameters [51,52]. Smaller plant leaves present higher chlorophyll content per area but have a reduced amount of photosynthesis rate. Both water consumption and intake are visible by the osmotic stress and the increase in proline levels [53,54].
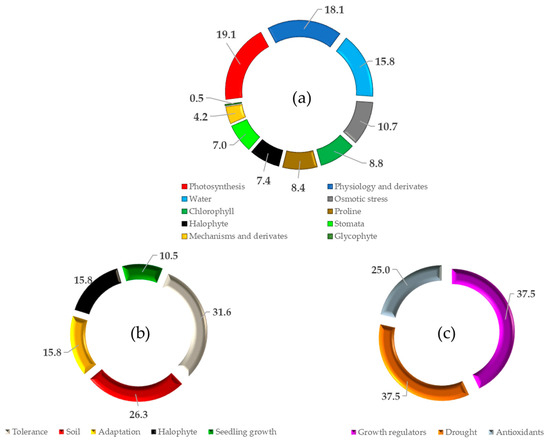
Figure 2.
The results obtained by selected keywords of three searches in the Web of Science (a) “physiological changes” × “plant under salinity stress”; (b) “salinization stress” × “plant organisms”; (c) “general aspects” × “plants under salinity stress”.
A restrictive search yielded studies focused on plant tolerance and adaptation capacity in the context of soil salinization stresses (Figure 2b). In early growth stages, plants are more sensitive to salinity [55,56]. The presence of salinity stress overlapping drought periods is one of the most important research topics in the current context of climate change (Figure 2c) [57,58]. Growth regulators can overcome and mitigate salinity stress, which is visible in higher or lower antioxidants found in plants in a species-dependent manner [59,60]. Due to increased salinity levels, it is imperative to observe and monitor vegetation coverage because deep rooting species can prosper and replace [61,62,63,64] plants with superficial root systems over time.
3. The Impact of High Salinity Levels on Plant Growth and Development
Salinity is the most serious threat to agriculture as it is a limiting factor for crop growth and development and thus crop yield [65]. The consequences that can occur as a result of soil salinization are varied. A high level of salt in the soil influences the osmotic pressure of the solution, which becomes unavailable to the cultivated plant, thus causing water deficit [66]. Therefore, plants cannot grow and develop optimally by benefitting from the extraction of substrate water. Through alkalization, salinization causes an increase in soil pH. However, the soil solution can become acidic when the cation exchange between Na+ and H+ leads to increased H+ concentration in the soil solution, thus lowering the pH. Soils with a more acidic pH can negatively influence plants and have toxic effects [5].
Crop salt tolerance can be influenced by a series of environmental and edaphic factors. The most important climatic factors with a direct influence on plant response to salinity are temperature, air pollution, and relative humidity [67].
The excess accumulation of salts originating from Na+, Ca2+, and Mg2+ cations and Cl−, CO3−, and NO3− anions have negative effects on plant growth and development (Figure 3), with changes especially seen in the plant size.
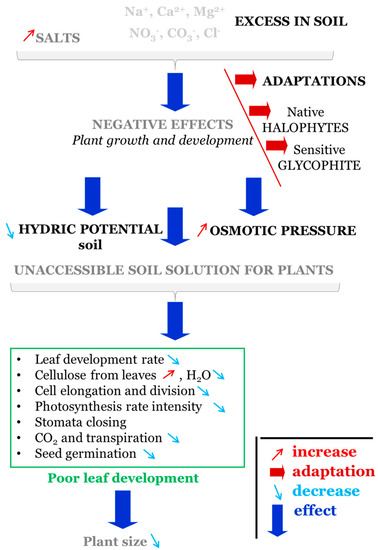
Figure 3.
Scheme of the principal impact of salinity stress.
Plant organisms can be divided into two large categories depending on how they are affected by salinity (Figure 3): the adapted ones, called native halophytes, and the sensitive ones, called glycophytes [68]. The highly tolerant species can possess a halophytic mechanism and translocate salts collected by roots directly to some salt glands with the attribute of onward excretion [69]. Excess salt in the soil has negative consequences on plants through two processes: decreasing the water potential and increasing the osmotic pressure [70]. Disturbance of these parameters makes the soil solution inaccessible to plants, which has negative effects on various factors and processes. A decrease in the photosynthesis intensity rate, a decrease in the leaf development rate, and stomata closure are other negative effects of soil salinization. Soil salinity influences cell elongation and division, affects seed germination, lowers water levels, and increases the cellulose content of leaves. These phenomena lead to the poor development of leaves and eventually cause a decrease in the plant height [71]. On the other hand, native salt-resistant species exhibit multiple mechanism of growth and development, even at higher salinity levels [72,73]. These plants tolerate changes in the external concentration of salts while maintaining the internal osmotic potential at low values [74]. Germination rates are maintained or decrease in value under different saline conditions, with a higher sensitivity in the early growth stages than in the vegetative ones [75]. A crop rotation system that alternate nonhalophytes (conventional species) and halophytes may reduce the salinity and help maintain yield [76].
4. Salinity Stress as a Driver in Plant Physiological and Biochemical Process
Increased soil salinity can cause unbalanced physiological and biochemical processes due to nutritional imbalance, osmotic stress, water deficit, and oxidative stress [52]. The primary biochemical defense reaction of plants to salinity is represented by the modification of the adaptation mechanism to osmotic stress [77]. This results in the accumulation of proline, proteins, and soluble carbohydrates but also a decrease in the phenolic content of the plants [78]. The low level of phenols results in a reduction of the antioxidant potential of plants [78]. Salt stress produces various reactions in the plant metabolic system by increasing the level of soluble organic compounds inside the cell, also called compatible solutes [79]. Moreover, the disturbance of the metabolism at the cellular level leads to damage of the antioxidant capacity of plant organisms sensitive to salinity due to the decreasing level of anthocyanins [80]. On the contrary, in halophyte species, the anthocyanins level is increased by the stimulation of metabolism induced by saline stress [81]. The increasing cell wall lignin content and restraining root growth are processes that plants use to adapt against saline stress [82]. The exposure of plants to salt stress facilitates the biosynthesis of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Ethylene, which is a plant stress hormone, and ROS function as signal markers that intervene in the remediation of numerous processes in different plant organs, including the resistance to salinity as an abiotic stress [83]. Pectin content and composition are other biochemical parameters that are increased and modified under saline conditions. Being an important constituent of the cell wall matrix, its content variation can affect root growth and dry biomass [84].
In addition, metabolic changes induced by high salinity levels impact other organic compounds in the cellular level, known as osmoprotectants [85]. These compounds, such as oligosaccharides and amino acids, of which proline [86] is especially dominant, act as one of the signaling markers for the presence of environmental stress [81]. Glycine betaine is also an osmolyte involved in plant metabolism, similar to proline, whose presence is correlated with exposure to high levels of salinity [87]. Synthesized under the effect of already installed hydric stress, glycine betaine is involved in maintaining the resistance of cell membrane and its components and provides osmotic adjustments [88]. Substances such as RFO, known as Raffinose family oligosaccharides, are synthesized from sucrose and represent another group of compatible solutes or osmolytes that can adapt plant mechanisms in order to cope with the changes produced by salt stress [89].
Germination is a physiological process strongly influenced by salt accumulation in the substrate [90]. Previous studies have shown that low concentrations of salts can also improve the germination of some species, such as Capsicum annum and Solanum lycopersicum, Brasica oleracea [91]. For Lolium rigidum and Triticum aestivum, there can be both positive and negative effects [92].
Plant emergence represents one of the most critical growth stages when a stable root system is developing close to the soil surface, usually where salts accumulate. Depending on their genetics, agricultural crop species can be susceptible to specific salts or particular management practices, such as irrigation. Therefore, when irrigation water contains salts, plant leaves can suffer injuries. When these conditions appear, the best solution is to select salinity-resistant crop varieties or rootstocks to maximize the use of zones representative of saline water [93].
Other physiological parameters that are modified by salt stress are the water content at the root and stem levels of plants and the relative water content at the foliar level [94]. Previous studies on Lactuca sativa as a test plant have shown that at low salt concentrations (up to 50 mM NaCl), root and stem water content and relative leaf water content do not vary significantly but are significantly affected by higher salt concentrations (100–200 mM NaCl) [95]. Salinity has a direct effect on the plant–water relationship, transpiration, and transpiration use efficiency [96]. Plant turgor decreases when stress is present, and it can influence stomatal opening and cell division and expansion [97]. Other turgor pressure from plants can have no influence on water transport because of osmotic adjustment, which is the change in osmotic potential by alteration of salt concentration, thus resulting in reduction of the potential pressure. The effects of salinity on ions can be highlighted by an increase in organic solutes compatible with high salinity levels [96]. These compatible solutes, such as proline and glycine betaine, are responsible for water balance from the cytoplasm because of the decrease in water potential from the vacuole due to ion accumulation [98].
The effects of salinity on photosynthesis is represented by a reduction of it. Salinity induces a reduction in plant leaves with higher number of chloroplast density per leaf area unit [99]. The impact of salinity on limitations occurring in the fundamental process of photosynthesis is determined by membrane dehydration, which leads to a decrease in cell permeability for carbon dioxide. A high soil osmotic potential has negative effects on the water potential of plants and decreases the osmotic potential of membranes. Therefore, photosynthetic electron transport is negatively influenced. Normally, in a vegetal cell, the salt concentration is around 1.5%. An increased soil salt concentration can also block access to water in the root cells by disturbing the osmosis mechanism [100].
The effects of salinity on plant senescence can be calculated with imaging analysis of salt-induced senescence areas [96]. At the seedling stage, plants can be classified as follows: normal growth and no leaf symptoms; nearly normal growth with some leaves and tips being whitish and rolled; growth severely retarded with most leaves rolled and only a few elongated; complete growth arrest with most of the leaves dried and some plants dead and almost all plants dead or dying [101].
The morphological parameters of interest are root length, stem length, leaf length, total plant mass, dry mass, and plant fresh mass. They vary according to the concentration of the applied saline treatment, which has significant effects in the case of high salt concentrations [102]. The most visible symptom of the effect of salinity on plants is a yellowing of leaves due to leaf senescence, then brown color at death [96]. Leaf shedding was the first symptom when purslane (Portulaca oleracea L.) was subjected to saline stress [103], followed by lower fresh and dry biomass weights and reduced number of flowers. Principally, the shoots suffer from Na accumulation. This aspect is most visible in older leaves because they accumulate Na for longer. The photosynthetic rate and leaf greenness are species dependent, with some plants being able to maintain these parameters for a longer time in the presence of salt stress than others [96].
5. Tolerance as a Plant Salinity Stress Response
Soil salinity is most often expressed by the electrical conductivity of the soil solution or by the form of osmotic potential [104]. The electrical conductivity of the soil solution derives from the same parameter of irrigation water and precipitation [105]. The soil solution is the result of the interaction between water and salts from the soil. Depending on the electrical conductivity of the soil solution, the soil can be divided into several categories that more or less limit the growth and development of plants [106]. A soil with electrical conductivity between 0 and 2 (mS/cm) is considered to be nonsaline and has a negligible effect on plants [107]. Electrical conductivity within values of 2 and 4 mS/cm integrates the soil into the weak salinization class and results in yield reduction of some sensitive plants. Medium salinization includes soils with an electrical conductivity between 4 and 8 mS/cm, which can result in a reduction in yield for the majority of plants. Electrical conductivity between 8 and 12 mS/cm characterizes the class of soils with very high salinity, where only the growth and development of salt-tolerant plants are possible [107]. The extreme salinization class includes soils that have an electrical conductivity higher than 16 mS/cm, and it can only produce reasonable harvest for very salt-tolerant plants [107]. The most common vegetables and fruit crops can be classified into the following classes: salinity sensitive, moderately sensitive, moderately tolerant, and tolerant plants [67,108,109] (Table 1). Based on the selected literature, 20 plants were classified in the four classes. The sensitive ones were found to be pea and bean, while the moderately sensitive ones included clover, alfalfa, sunflower, cabbage, potato, and spinach. Maize was declared as both moderately sensitive [67,109] and moderately tolerant [108]. Soybean followed the same pattern as maize and was framed as MS [108] and MT [67,109]. The third crop with opposite classification was cowpea with MS [109] and MT [67] qualities. The moderately tolerant species included wheat, forage barley, rape, sorghum, and forage rye, while the tolerant class included durum wheat, barley for grain, and sugar beet.

Table 1.
The degree of salt tolerance level for different crops.
In addition to the ones presented in Figure 3, other salinity-sensitive plants include strawberry Fragaria x Ananassa, Angola pea Cajanus cajan, parsnip Pastinaca sativa, onion bulb Allium cepa, mung bean Phaseolus mungo, and fennel Foeniculum vulgare [26]. Plants that are moderately sensitive to salinity also include watermelon Citrullus lanatus, tomatoes Lycopersicon lycopersicum, sweet potato Ipomea batatas, spinach Spinacia oleracea, radish Raphnus sativus, potato Solanum tuberosum, pepper Capsicum annuum, peas Pisum sativum, onion seeds Allium cepa, lettuce Lactuca sativa, kale Brassica oleracea, garlic Allium sativum, eggplant Solanum melongena variety esculentum, cucumber Cucumis sativus Brussels sprouts Brassica oleracea, cauliflower Brassica oleracea, and sweet corn Zea mays [26]. Plants that are moderately tolerant to salinity include Psophocarpus tetragomolobus winged bean, Cucurbita pepo pumpkin, Portulaca oleracea fat grass, Vigna unguiculata black-eyed bean, Apium graveolens var. sweet, broccoli Brassica oleracea, beetroot Beta vulgaris, lima bean Phaseolus lunatus, and artichoke Cynara scolymus [26]. Plants tolerant to salinity include asparagus Asparagus officinalis and chard Beta vulgaris subs. Cicla [26].
6. The Case Study of Wheat, a Major Cereal Crop, with Regard to Salinity Tolerance
Wheat is a major crop that is present in almost all crop rotations in agricultural ecosystems worldwide [157,158,159]. In the literature, there is evidence that different varieties of the same cereal species react differently to salinity stress [160,161]. Therefore, future research should focus on finding the most tolerant genotypes from international and national varieties. Wheat varieties with increased salinity tolerance can also be bred, with chlorophyll content, yield, and harvest quality among the important factors [161]. To improve wheat growth, different methods have been tested, such as water regime by applying optimal irrigation or soil reclamation. Both measures are expensive or time-consuming and provide very short-term solutions to counter the negative effects of salinity [162]. Experiments in field conditions are recommended to establish the degree of resistance to salinity of wheat genotypes because other environmental factors, such as soil properties, climatic regime, and spatial heterogeneity, can have an impact, especially on the generative stages [161]. Experiments in controlled conditions, where the influence of abiotic factors is missing compared to the field conditions, can produce faster results but may contain increased biases. The biases can appear because all the set conditions for optimal growth and development can produce good salinity responses in the vegetative stages but with no corresponding effect in practice in the field [161,163]. Under saline environments, plant characteristics can differ greatly depending on their tolerance class. In this case, a measure of interactions between seed yield and yield biomass can give a better indication of wheat genotype resistance [164].
As a starting measure before setting up a crop in saline field conditions, different seed priming methods, such as halopriming [165], can be used. This can result in improved values for above- and belowground fresh and dry biomass or shoot and root length [166]. Furthermore, some specific morphophysiological parameters can highlight salt tolerance and stress. This is an easy assessment method for quantifying the phenotypic response of plants and organogenesis features [167] because of their adaptive mechanism to salinity [165,168]. In saline conditions, using seed priming methods, remarkable variations were observed in the period from start of germination to physiological maturity [166]. The principal reason for weak aboveground development of wheat can be explained by water deficiency, ionic toxicity, and unavailable photosynthates [169]. Wheat reaction varies with different salinity values, which is visible in yield reduction of 6 to 8 dS m−1 [170]. However, some varieties succeed in alleviating excess salinity by activating the mechanisms of osmoregulation, sodium exclusion, or potassium retention [171]. The most commonly affected physiological mechanisms include water absorption depending on the amount of sodium and chloride ions, homeostasis, and the osmotic potential, which can be negatively impacted by enzymatic activity and hormonal disorders [172]. Stress tolerance is genetically inherited by descendants through a key stress gene locus (QTL) [173], a research area that needs attention in the future, especially for ensuring a comparable yield [174]. High concentrations of salts directly affect the leaves of different ages by accumulating a high level of ions [175]. Plants can also activate specific mechanisms to restrict ions from the xylem through the Casparian strip, thus protecting the shoots and leaves [176]. Another mechanism that restricts the Na+ ions in root cell vacuoles [174] was studied in an ancestral germplasm wheat, which acts as protection from Na+ in aboveground tissues [171,177].
7. Ecophysiological Perspectives in Salinity Stress
The entire salinity issue should be viewed through a holistic perspective, both by integrating the knowledge with the newest advances in agronomy, soil science, and climatology and by creating new indicators relevant for the current challenges in this field [178,179,180]. The first step is to create a strong connection between already developed climatic scenarios and salinity scenarios that still need to be developed. This approach uses both mathematical models and satellite or drone surveys to constantly update information regarding the models. It offers a survey area around the world, with the most important points displayed at a high resolution.
A second step that is critical for the correct understanding of salinity stress related to crops is the proposal and validation of new ecophysiological indices that will increase knowledge of this phenomenon and will be very useful in breeding programs [181,182,183,184]. The indices need to be easy to use and cheap enough to be replicated in the field, even by individuals with low to medium level of training. Additionally, new studies on plant physiology with detailed analysis of each phenological stage should be carried out. This type of research represents a vital point in the understanding of sensitivity related to salinity at the phenological stage, which will lead to more detailed knowledge on the entire growth and development period. By identifying the most sensitive phenological stages, new agronomic techniques can be proposed to mitigate salinity stress.
Another step is to externalize studies from laboratories and controlled experiments, where the results are limited to model plants or variables proposed and observed by the researchers [185,186,187,188,189,190]. A system of farm networks can be identified for areas where salinity is currently a problem or will present a problem in the near future. Involving farmers along with scientists will increase the amount of data collected from the field, the modeling and forecasting potential, and the overall speed of studies on agronomic issues related to salinity stress. This approach will also increase knowledge of farmers themselves, and most importantly, all the observations will be recorded in a similar manner that will reduce the time necessary for synchronizing the data. Both plants and the soil where they are cultivated need to be constantly monitored, which will ensure a large database with a diverse gradient of salinity that will allow realistic comparison.
Furthermore, both rhizosphere and phyllosphere microbiomes should be studied in the search for microorganisms adapted or tolerant to salinity [191,192,193,194,195,196,197]. This research will respond to current requirements of microbial specificity for crops, with microbial communities acting as a support for plants during the entire growth and development period. The use of microbial consortia to reduce salinity level is a good biological approach during cropping. An important focus of microbiome research should be the fallow periods, where cover crops can be directed to increase microbial activity, resulting in reduction of salinity values.
The final step in this holistic, complex process is to synchronize all the information and to create new scales for the assessment of crop status during the vegetation period. New scenarios based on integrative models will respond faster and better to the requirements and the constant increase in this phenomenon.
8. Conclusions
The salinity phenomenon represents a hot topic for researchers given the current challenges posed by climate change. Ambitious targets should be set to observe plant growth in the entire growth period, especially highlighting the key phenological developmental stages. Within an interconnection analysis between different morphological and physiological parameters, some crop associations can be proposed to form sustainable cropping systems under saline soil conditions. This measure represents a heterogeneous system based on soil analysis.
In order to mitigate this abiotic stress, it is important to understand the effects of soil salinity on plant growth and development and the consequent changes in physiological parameters. By understanding the effects of different levels of salinity on plants, adjustments to agricultural practices can be made, such as implementing crop rotation systems that alternate nonhalophytes and halophytes in order to reduce soil salinity and maintain yield. Plants adapt to salinity by modifying their mechanisms, which can result in decreased phenolic content and antioxidant potential. Water content, turgor, and photosynthesis are also affected and lead to decreased plant growth and development. Future research should focus on finding the most tolerant genotypes, and field experiments are recommended to establish the degree of resistance to salinity. Seed priming methods, especially halopriming, have shown potential in improving growth and development in saline environments.
Soil salinity could offer the opportunity to carry out new studies aimed at implementing new agronomic practices and strategies. All the mechanisms that restrict the effects of salinity outside the aboveground biomass need to be intensively studied. Another perspective is a research focused on ancient germplasm collections, which may lead to the identification of alternative survival mechanisms and genetic resources that can be used in breeding programs. Agricultural production worldwide is significantly limited by soil salinity, and studies should be oriented to mitigate its effect and to even create new varieties of plants adapted to saline soils conditions.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.T., V.S., V.A.S. and S.V.; methodology, M.T., V.S. and V.A.S.; validation, R.V., C.B., M.H. and A.V.; resources, M.T., Ș.G. and A.V.; data curation, V.S. and C.B.; writing—original draft preparation, M.T., V.A.S., V.S., S.V. and R.V.; writing—review and editing, M.T., V.A.S., V.S., S.V. and R.V.; supervision, V.A.S. and S.V.; funding acquisition, M.T. and S.V. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Research Development Projects to finance excellence (PFE)—14/20022–2024 granted by the Romanian Ministry of Research and Innovation.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The information used to compile this review can be found on the Web of Science and Google Scholar following the keyword combinations proposed at the end of Section 1. All the titles consulted are given in the reference list.
Acknowledgments
This paper is part of a PhD study in the thematic area of Ecophysiological Changes in Plant Reactions to Salt Stress in the Context of Climate Change, conducted by the first author M.T. under the coordination of Sorin Vâtcă (S.V.).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Gupta, R.K.; Abrol, I.P.; Finkl, C.W.; Kirkham, M.B.; Arbestain, M.C.; Macías, F.; Chesworth, W.; Germida, J.J.; Loeppert, R.H.; Cook, M.G.; et al. Soil Salinity and Salinization. In Encyclopedia of Soil Science; Chesworth, W., Ed.; Encyclopedia of Earth Sciences Series; Springer Netherlands: Dordrecht, The Netherland, 2008; pp. 699–704. ISBN 978-1-4020-3995-9. [Google Scholar]
- Okur, B.; Örçen, N. Soil Salinization and Climate Change. In Climate Change and Soil Interactions; Elsevier: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 331–350. [Google Scholar]
- Modiga, B.A.; Covașă, M.; Slabu, C.; Marta, A.E.; Jităreanu, C.D. Determination of Productivity and Chlorine Concentration in Some Bean Cultivation, from the Region of Moldova, under Salt Stress. Sci. Pap. -Ser. B Hortic. 2019, 63, 169–175. [Google Scholar]
- Bui, E.N. Causes of Soil Salinization, Sodification, and Alkalinization. In Oxford Research Encyclopedia of Environmental Science; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- ICPA. 2009. Available online: https://www.icpa.ro/documente/diagnoza.pdf (accessed on 20 February 2023).
- Smith, P.; Calvin, K.; Nkem, J.; Campbell, D.; Cherubini, F.; Grassi, G.; Korotkov, V.; Le Hoang, A.; Lwasa, S.; McElwee, P. Which Practices Co-Deliver Food Security, Climate Change Mitigation and Adaptation, and Combat Land Degradation and Desertification? Glob. Change Biol. 2020, 26, 1532–1575. [Google Scholar]
- Pacheco, F.A.L.; Fernandes, L.F.S.; Junior, R.F.V.; Valera, C.A.; Pissarra, T.C.T. Land Degradation: Multiple Environmental Consequences and Routes to Neutrality. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2018, 5, 79–86. [Google Scholar]
- Besser, H.; Dhaouadi, L.; Hadji, R.; Hamed, Y.; Jemmali, H. Ecologic and Economic Perspectives for Sustainable Irrigated Agriculture under Arid Climate Conditions: An Analysis Based on Environmental Indicators for Southern Tunisia. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2021, 177, 104134. [Google Scholar]
- Scherr, S.J. The Future Food Security and Economic Consequences of Soil Degradation in the Developing World. In Response to Land Degradation; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019; pp. 155–170. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, G.S. Land Degradation and Challenges of Food Security. Rev. Eur. Stud. 2019, 11, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liliane, T.N.; Charles, M.S. Factors Affecting Yield of Crops. In Agronomy-Climate Change & Food Security; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020; p. 9. [Google Scholar]
- Qadir, M.; Qureshi, A.S.; Cheraghi, S.A.M. Extent and Characterisation of Salt-Affected Soils in Iran and Strategies for Their Amelioration and Management. Land Degrad. Dev. 2008, 19, 214–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; An, F.; Ma, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, X.; Liu, Z. Variations on Soil Salinity and Sodicity and Its Driving Factors Analysis under Microtopography in Different Hydrological Conditions. Water 2016, 8, 227. [Google Scholar]
- Naidu, R.; Rengasamy, P. Ion Interactions and Constraints to Plant Nutrition in Australian Sodic Soils. Soil Res. 1993, 31, 801–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pessarakli, M.; Szabolcs, I. Soil Salinity and Sodicity as Particular Plant/Crop Stress Factors. In Handbook of Plant and Crop Stress, 4th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019; pp. 3–21. [Google Scholar]
- Jouyban, Z. The Effects of Salt Stress on Plant Growth. Tech. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2012, 2, 7–10. [Google Scholar]
- Maryum, Z.; Luqman, T.; Nadeem, S.; Khan, S.M.U.D.; Wang, B.; Ditta, A.; Khan, M.K.R. An Overview of Salinity Stress, Mechanism of Salinity Tolerance and Strategies for Its Management in Cotton. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 907937. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Carillo, P.; Annunziata, M.G.; Pontecorvo, G.; Fuggi, A.; Woodrow, P. Salinity Stress and Salt Tolerance. Abiotic Stress Plants-Mech. Adapt. 2011, 1, 21–38. [Google Scholar]
- Van Zandt, P.A.; Tobler, M.A.; Mouton, E.; Hasenstein, K.H.; Mopper, S. Positive and Negative Consequences of Salinity Stress for the Growth and Reproduction of the Clonal Plant, Iris Hexagona. J. Ecol. 2003, 91, 837–846. [Google Scholar]
- Ontoria, Y.; Webster, C.; Said, N.; Ruiz, J.M.; Pérez, M.; Romero, J.; McMahon, K. Positive Effects of High Salinity Can Buffer the Negative Effects of Experimental Warming on Functional Traits of the Seagrass Halophila ovalis. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 158, 111404. [Google Scholar]
- Isayenkov, S.V.; Maathuis, F.J. Plant Salinity Stress: Many Unanswered Questions Remain. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 80. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Larbi, A.; Kchaou, H.; Gaaliche, B.; Gargouri, K.; Boulal, H.; Morales, F. Supplementary Potassium and Calcium Improves Salt Tolerance in Olive Plants. Sci. Hortic. 2020, 260, 108912. [Google Scholar]
- Kumari, S.; Chhillar, H.; Chopra, P.; Khanna, R.R.; Khan, M.I.R. Potassium: A Track to Develop Salinity Tolerant Plants. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 167, 1011–1023. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, M.; Zhou, H.; Ma, C.; Wang, P. Regulation of Plant Responses to Salt Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Jiang, J.-G. Osmotic Adjustment and Plant Adaptation to Environmental Changes Related to Drought and Salinity. Environ. Rev. 2010, 18, 309–319. [Google Scholar]
- Grieve, C.M.; Grattan, S.R.; Maas, E.V. Plant Salt Tolerance. ASCE Man. Rep. Eng. Pract. 2012, 71, 405–459. [Google Scholar]
- Mustafa, G.; Akhtar, M.S.; Abdullah, R. Global Concern for Salinity on Various Agro-Ecosystems. In Salt Stress, Microbes, and Plant Interactions: Causes and Solution: Volume 1; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Prăvălie, R.; Patriche, C.; Borrelli, P.; Panagos, P.; Roșca, B.; Dumitraşcu, M.; Nita, I.-A.; Săvulescu, I.; Birsan, M.-V.; Bandoc, G. Arable Lands under the Pressure of Multiple Land Degradation Processes. A Global Perspective. Environ. Res. 2021, 194, 110697. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Negacz, K.; Malek, Ž.; de Vos, A.; Vellinga, P. Saline Soils Worldwide: Identifying the Most Promising Areas for Saline Agriculture. J. Arid. Environ. 2022, 203, 104775. [Google Scholar]
- Pavuluri, S. Kinetic Approach for Modeling Salt Precipitation in Porous-Media; GRIN Verlag: Munich, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hassani, A.; Azapagic, A.; Shokri, N. Global Predictions of Primary Soil Salinization under Changing Climate in the 21st Century. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6663. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Daliakopoulos, I.N.; Tsanis, I.K.; Koutroulis, A.; Kourgialas, N.N.; Varouchakis, A.E.; Karatzas, G.P.; Ritsema, C.J. The Threat of Soil Salinity: A European Scale Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 573, 727–739. [Google Scholar]
- Prăvălie, R.; Patriche, C.; Săvulescu, I.; Sîrodoev, I.; Bandoc, G.; Sfîcă, L. Spatial Assessment of Land Sensitivity to Degradation across Romania. A Quantitative Approach Based on the Modified MEDALUS Methodology. Catena 2020, 187, 104407. [Google Scholar]
- Várallyay, G. Climate Change, Soil Salinity and Alkalinity. In Proceedings of the Soil Responses to Climate Change; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1994; pp. 39–54. [Google Scholar]
- Rengasamy, P.; de Lacerda, C.F.; Gheyi, H.R. Salinity, Sodicity and Alkalinity. In Subsoil Constraints for Crop Production; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 83–107. [Google Scholar]
- Litalien, A.; Zeeb, B. Curing the Earth: A Review of Anthropogenic Soil Salinization and Plant-Based Strategies for Sustainable Mitigation. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 698, 134235. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Metternicht, G.I.; Zinck, J.A. Remote Sensing of Soil Salinity: Potentials and Constraints. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 85, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Arora, S. Diagnostic Properties and Constraints of Salt-Affected Soils. In Bioremediation of Salt Affected Soils: An Indian Perspective; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 41–52. [Google Scholar]
- Mohanavelu, A.; Naganna, S.R.; Al-Ansari, N. Irrigation Induced Salinity and Sodicity Hazards on Soil and Groundwater: An Overview of Its Causes, Impacts and Mitigation Strategies. Agriculture 2021, 11, 983. [Google Scholar]
- Dimitriadou, S.; Nikolakopoulos, K.G. Evapotranspiration Trends and Interactions in Light of the Anthropogenic Footprint and the Climate Crisis: A Review. Hydrology 2021, 8, 163. [Google Scholar]
- Dehaan, R.L.; Taylor, G.R. Field-Derived Spectra of Salinized Soils and Vegetation as Indicators of Irrigation-Induced Soil Salinization. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 80, 406–417. [Google Scholar]
- Kordrostami, M.; Rabiei, B. Salinity Stress Tolerance in Plants: Physiological, Molecular, and Biotechnological Approaches. In Plant Abiotic Stress Tolerance: Agronomic, Molecular and Biotechnological Approaches; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 101–127. [Google Scholar]
- Sidău, M.R.; Croitoru, A.-E.; Alexandru, D.-E. Comparative Analysis between Daily Extreme Temperature and Precipitation Values Derived from Observations and Gridded Datasets in North-Western Romania. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodkhe, U.; Tanwar, S.; Bhattacharya, P.; Kumar, N. Blockchain for Precision Irrigation: Opportunities and Challenges. Trans. Emerg. Telecommun. Technol. 2022, 33, e4059. [Google Scholar]
- Hnilickova, H.; Kraus, K.; Vachova, P.; Hnilicka, F. Salinity Stress Affects Photosynthesis, Malondialdehyde Formation, and Proline Content in Portulaca oleracea L. Plants 2021, 10, 845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corwin, D.L.; Yemoto, K. Salinity: Electrical Conductivity and Total Dissolved Solids. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2020, 84, 1442–1461. [Google Scholar]
- Mau, Y.; Porporato, A. A Dynamical System Approach to Soil Salinity and Sodicity. Adv. Water Resour. 2015, 83, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munns, R.; Day, D.A.; Fricke, W.; Watt, M.; Arsova, B.; Barkla, B.J.; Bose, J.; Byrt, C.S.; Chen, Z.-H.; Foster, K.J. Energy Costs of Salt Tolerance in Crop Plants. New Phytol. 2020, 225, 1072–1090. [Google Scholar]
- Flagella, Z.; Cantore, V.; Giuliani, M.M.; Tarantino, E.; De Caro, A. Crop Salt Tollerance: Physiological, Yield and Quality Aspects. In Recent Research Developments in Plant Biology; Transworld Research Signpost: Trivandrum, India, 2002; Volume 2, pp. 155–186. [Google Scholar]
- Vâtcă, S.; Vidican, R.; Ștefania, G.; Horvat, M.; Vâtcă, A.; Stoian, V.A.; Stoian, V. Blackcurrant Variety Specific Growth and Yield Formation as a Response to Foliar Fertilizers. Agronomy 2020, 10, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, B.; Huang, B. Mechanism of Salinity Tolerance in Plants: Physiological, Biochemical, and Molecular Characterization. Int. J. Genom. 2014, 2014, 701596. [Google Scholar]
- Farrant, J.M.; Costa, M.-C.D. Molecular Mechanisms and Genetics of Plant Resistance to Abiotic Stress; MDPI: Basel, Switzerland, 2020; ISBN 978-3-03928-122-0. [Google Scholar]
- Dos Santos, T.B.; Ribas, A.F.; de Souza, S.G.H.; Budzinski, I.G.F.; Domingues, D.S. Physiological Responses to Drought, Salinity, and Heat Stress in Plants: A Review. Stresses 2022, 2, 113–135. [Google Scholar]
- Hayat, S.; Hayat, Q.; Alyemeni, M.N.; Wani, A.S.; Pichtel, J.; Ahmad, A. Role of Proline under Changing Environments: A Review. Plant Signal. Behav. 2012, 7, 1456–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.; Cao, X.; Zhong, C.; Zhu, L.; Khaskheli, M.A.; Fiaz, S.; Zhang, J.; Jin, Q. Sodium Chloride Stress during Early Growth Stages Altered Physiological and Growth Characteristics of Rice. Chil. J. Agric. Res. 2018, 78, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uçarlı, C. Effects of Salinity on Seed Germination and Early Seedling Stage. In Abiotic Stress in Plants; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020; p. 211. [Google Scholar]
- Angon, P.B.; Tahjib-Ul-Arif, M.; Samin, S.I.; Habiba, U.; Hossain, M.A.; Brestic, M. How Do Plants Respond to Combined Drought and Salinity Stress?—A Systematic Review. Plants 2022, 11, 2884. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Corwin, D.L. Climate Change Impacts on Soil Salinity in Agricultural Areas. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2021, 72, 842–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ondrasek, G.; Rathod, S.; Manohara, K.K.; Gireesh, C.; Anantha, M.S.; Sakhare, A.S.; Parmar, B.; Yadav, B.K.; Bandumula, N.; Raihan, F. Salt Stress in Plants and Mitigation Approaches. Plants 2022, 11, 717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quamruzzaman, M.; Manik, S.N.; Shabala, S.; Zhou, M. Improving Performance of Salt-Grown Crops by Exogenous Application of Plant Growth Regulators. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 788. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tan, J.; Ben-Gal, A.; Shtein, I.; Bustan, A.; Dag, A.; Erel, R. Root Structural Plasticity Enhances Salt Tolerance in Mature Olives. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2020, 179, 104224. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Liang, L.; Liu, S.; An, T.; Fang, Y.; Xu, B.; Zhang, S.; Deng, X.; Palta, J.A.; Siddique, K.H. Maize Genotypes with Deep Root Systems Tolerate Salt Stress Better than Those with Shallow Root Systems during Early Growth. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2020, 206, 711–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arif, M.R.; Islam, M.T.; Robin, A.H.K. Salinity Stress Alters Root Morphology and Root Hair Traits in Brassica napus. Plants 2019, 8, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Testerink, C. Root Dynamic Growth Strategies in Response to Salinity. Plant Cell Environ. 2022, 45, 695–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Huo, Z.; Wang, H. Simulation for Response of Crop Yield to Soil Moisture and Salinity with Artificial Neural Network. Field Crops Res. 2011, 121, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munns, R. Comparative Physiology of Salt and Water Stress. Plant Cell Environ. 2002, 25, 239–250. [Google Scholar]
- Christie, B.R. CRC Handbook of Plant Science in Agriculture; Christie, B.R., Ed.; CRC Series in Agriculture; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, S.; Irfan, M.; Ahmad, A.; Hayat, S. Causes of Salinity and Plant Manifestations to Salt Stress: A Review. J. Environ. Biol. 2011, 32, 667. [Google Scholar]
- Öztürk, M.; Waisel, Y.; Khan, M.A.; Görk, G. Biosaline Agriculture and Salinity Tolerance in Plants; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, S.; Modi, P.; Dave, A.; Vijapura, A.; Patel, D.; Patel, M. Effect of Abiotic Stress on Crops. In Sustainable Crop Production; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020; p. 3. [Google Scholar]
- Cakir, R. Effect of Water Stress at Different Development Stages on Vegetative and Reproductive Growth of Corn. Field Crops Res. 2004, 89, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, N.; Hasnain, M.; Roessner, U.; Abideen, Z. Strategies in Improving Plant Salinity Resistance and Use of Salinity Resistant Plants for Economic Sustainability. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 52, 2150–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Feng, G.; Zhang, F. Salinity and Temperature Effects on Germination for Three Salt-Resistant Euhalophytes, Halostachys caspica, Kalidium foliatum and Halocnemum strobilaceum. Plant Soil 2006, 279, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flowers, T.J. Physiology of Halophytes. In Biosalinity in Action: Bioproduction with Saline Water; Pasternak, D., San Pietro, A., Eds.; Developments in Plant and Soil Sciences; Springer Netherlands: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1985; pp. 41–56. ISBN 978-94-009-5111-2. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, F.; Guo, J.; Shabala, S.; Wang, B. Reproductive Physiology of Halophytes: Current Standing. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 9, 1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shabala, S. Learning from Halophytes: Physiological Basis and Strategies to Improve Abiotic Stress Tolerance in Crops. Ann. Bot. 2013, 112, 1209–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, J.A. Salinity Tolerance in Plants: Trends and Perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Hassan, M.; FUERTES, M.M.; SÁNCHEZ, F.J.R.; Vicente, O.; Boscaiu, M. Effects of Salt and Water Stress on Plant Growth and on Accumulation of Osmolytes and Antioxidant Compounds in Cherry Tomato. Not. Bot. Horti Agrobot. 2015, 43, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohnert, H.J.; Nelson, D.E.; Jensen, R.G. Adaptations to Environmental Stresses. Plant Cell 1995, 7, 1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daneshmand, F.; Arvin, M.J.; Kalantari, K.M. Physiological Responses to NaCl Stress in Three Wild Species of Potato in Vitro. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2010, 32, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sytar, O.; Mbarki, S.; Zivcak, M.; Brestic, M. The Involvement of Different Secondary Metabolites in Salinity Tolerance of Crops. In Salinity Responses and Tolerance in Plants, Volume 2: Exploring RNAi, Genome Editing and Systems Biology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 21–48. [Google Scholar]
- Gall, H.L.; Philippe, F.; Domon, J.-M.; Gillet, F.; Pelloux, J.; Rayon, C. Cell Wall Metabolism in Response to Abiotic Stress. Plants 2015, 4, 112–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Smith, J.A.C.; Harberd, N.P.; Jiang, C. The Regulatory Roles of Ethylene and Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) in Plant Salt Stress Responses. Plant Mol. Biol. 2016, 91, 651–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Otie, V.; Matsuura, A.; Junichi, K.; Irshad, M.; Zheng, Y.; Fujimaki, H.; An, P. Pectin Characteristics Affect Root Growth in Spinach under Salinity. Plants 2022, 11, 3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amudha, J.; Balasubramani, G. Recent Molecular Advances to Combat Abiotic Stress Tolerance in Crop Plants. Biotechnol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2011, 6, 31–58. [Google Scholar]
- Hare, P.D.; Cress, W.A.; Van Staden, J. Dissecting the Roles of Osmolyte Accumulation during Stress. Plant Cell Environ. 1998, 21, 535–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo-Domènech, L.L.; Tifrea, A.; Grigore, M.N.; Boscaiu, M.; Vicente, O. Proline and Glycine Betaine Accumulation in Two Succulent Halophytes under Natural and Experimental Conditions. Plant Biosyst. Int. J. Deal. All Asp. Plant Biol. 2016, 150, 904–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Martino, C.; Delfine, S.; Pizzuto, R.; Loreto, F.; Fuggi, A. Free Amino Acids and Glycine Betaine in Leaf Osmoregulation of Spinach Responding to Increasing Salt Stress. New Phytol. 2003, 158, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wu, X.; Sun, W.; Yu, X.; Demura, T.; Li, D.; Zhuge, Q. Galactinol Synthase Confers Salt-Stress Tolerance by Regulating the Synthesis of Galactinol and Raffinose Family Oligosaccharides in Poplar. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 165, 113432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saberali, S.F.; Moradi, M. Effect of Salinity on Germination and Seedling Growth of Trigonella foenum-graecum, Dracocephalum moldavica, Satureja hortensis and Anethum graveolens. J. Saudi Soc. Agric. Sci. 2019, 18, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojović, B.; \DJelić, G.; Topuzović, M.; Stanković, M. Effects of NaCl on Seed Germination in Some Species from Families Brassicaceae and Solanaceae. Kragujev. J. Sci. 2010, 32, 83–87. [Google Scholar]
- Ashraf, M.; Foolad, M.R. Pre-Sowing Seed Treatment—A Shotgun Approach to Improve Germination, Plant Growth, and Crop Yield under Saline and Non-Saline Conditions. Adv. Agron. 2005, 88, 223–271. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson: EIP-AGRI Focus Group Soil Salinisation. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/eip/agriculture/sites/default/files/eip-agri_fg_soil_salinisation_final_report_2020_en.pdf (accessed on 26 February 2023).
- Taffouo, V.D.; Nouck, A.E.; Nyemene, K.P.; Tonfack, B.; Meguekam, T.L.; Youmbi, E. Effects of Salt Stress on Plant Growth, Nutrient Partitioning, Chlorophyll Content, Leaf Relative Water Content, Accumulation of Osmolytes and Antioxidant Compounds in Pepper (Capsicum Annuum L.) Cultivars. Not. Bot. Horti Agrobot. 2017, 45, 481–490. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, F.; Kamal, A.; Singh, A.; Ashfaque, F.; Alamri, S.; Siddiqui, M.H.; Khan, M.I.R. Seed Priming with Gibberellic Acid Induces High Salinity Tolerance in Pisum Sativum through Antioxidants, Secondary Metabolites and up-Regulation of Antiporter Genes. Plant Biol. 2021, 23, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negrão, S.; Schmöckel, S.M.; Tester, M. Evaluating Physiological Responses of Plants to Salinity Stress. Ann. Bot. 2017, 119, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsiao, T.C.; Xu, L.-K. Sensitivity of Growth of Roots versus Leaves to Water Stress: Biophysical Analysis and Relation to Water Transport. J. Exp. Bot. 2000, 51, 1595–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Reis, S.P.; Lima, A.M.; De Souza, C.R.B. Recent Molecular Advances on Downstream Plant Responses to Abiotic Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 8628–8647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munns, R.; Tester, M. Mechanisms of Salinity Tolerance. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2008, 59, 651–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yildiz, M.; Poyraz, İ.; Çavdar, A.; Özgen, Y.; Beyaz, R. Plant Responses to Salt Stress. In Plant Breeding-Current and Future Views; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Gregoria, G.B.; Senadhira, D.; Mendoza, R.D. Screening Rice for Salinity Tolerance. International Rice Research Institute: Manila, Philippines, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Maskri, A.; Al-Kharusi, L.; Al-Miqbali, H.; Khan, M.M. Effects of Salinity Stress on Growth of Lettuce (Lactuca sativa) under Closed-Recycle Nutrient Film Technique. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2010, 12, 377–380. [Google Scholar]
- Alam, M.; Juraimi, A.S.; Rafii, M.Y.; Hamid, A.A.; Aslani, F.; Hakim, M.A. Salinity-Induced Changes in the Morphology and Major Mineral Nutrient Composition of Purslane (Portulaca oleracea L.) Accessions. Biol. Res. 2016, 49, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Todd, J.L.; Luo, H. Turfgrass Salinity Stress and Tolerance—A Review. Plants 2023, 12, 925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walczak, A. The Use of World Water Resources in the Irrigation of Field Cultivations. J. Ecol. Eng. 2021, 22, 186–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safdar, H.; Amin, A.; Shafiq, Y.; Ali, A.; Yasin, R.; Shoukat, A.; Hussan, M.U.; Sarwar, M.I. A Review: Impact of Salinity on Plant Growth. Nat. Sci. 2019, 17, 34–40. [Google Scholar]
- Katerji, N.; Van Hoorn, J.W.; Hamdy, A.; Mastrorilli, M. Salinity Effect on Crop Development and Yield, Analysis of Salt Tolerance According to Several Classification Methods. Agric. Water Manag. 2003, 62, 37–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Saline Soil and Their Management. 2022. Available online: https://www.fao.org/3/x5871e/x5871e04.htm (accessed on 22 February 2023).
- Downton, W.J.S.; Läuchli, A. Salt Tolerance of Food Crops: Prospectives for Improvements. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 1984, 1, 183–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EL Sabagh, A.; Islam, M.S.; Skalicky, M.; Ali Raza, M.; Singh, K.; Anwar Hossain, M.; Hossain, A.; Mahboob, W.; Iqbal, M.A.; Ratnasekera, D. Salinity Stress in Wheat (Triticum Aestivum L.) in the Changing Climate: Adaptation and Management Strategies. Front. Agron. 2021, 3, 661932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saddiq, M.S.; Iqbal, S.; Hafeez, M.B.; Ibrahim, A.M.; Raza, A.; Fatima, E.M.; Baloch, H.; Woodrow, P.; Ciarmiello, L.F. Effect of Salinity Stress on Physiological Changes in Winter and Spring Wheat. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moustafa, E.S.; Ali, M.M.; Kamara, M.M.; Awad, M.F.; Hassanin, A.A.; Mansour, E. Field Screening of Wheat Advanced Lines for Salinity Tolerance. Agronomy 2021, 11, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabagh, A.E.; Çiğ, F.; Seydoşoğlu, S.; Battaglia, M.L.; Javed, T.; Iqbal, M.A.; Awad, M. Salinity Stress in Maize: Effects of Stress and Recent Developments of Tolerance for Improvement. Cereal Grains 2021, 1, 213. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, F.H.; Goes, G.F.; Almeida, M.d.S.; Magalhães, C.L.; Sousa, J.; Sousa, G.G. Maize Crop Yield in Function of Salinity and Mulch. Rev. Bras. Eng. Agrícola Ambient. 2021, 25, 840–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Wang, J.; Shangguan, T.; Wu, R.; Li, S.; Chen, G.; Xu, S. SMXLs Regulate Seed Germination under Salinity and Drought Stress in Soybean. Plant Growth Regul. 2022, 96, 397–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Sahile, A.A.; Jan, R.; Asaf, S.; Hamayun, M.; Imran, M.; Adhikari, A.; Kang, S.-M.; Kim, K.-M.; Lee, I.-J. Halotolerant Bacteria Mitigate the Effects of Salinity Stress on Soybean Growth by Regulating Secondary Metabolites and Molecular Responses. BMC Plant Biol. 2021, 21, 176. [Google Scholar]
- Abulfaraj, A.A.; Jalal, R.S. Use of Plant Growth-Promoting Bacteria to Enhance Salinity Stress in Soybean (Glycine Max L.) Plants. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 3823–3834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dell’Aversana, E.; Hessini, K.; Ferchichi, S.; Fusco, G.M.; Woodrow, P.; Ciarmiello, L.F.; Abdelly, C.; Carillo, P. Salinity Duration Differently Modulates Physiological Parameters and Metabolites Profile in Roots of Two Contrasting Barley Genotypes. Plants 2021, 10, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhter, M.S.; Noreen, S.; Mahmood, S.; Ashraf, M.; Alsahli, A.A.; Ahmad, P. Influence of Salinity Stress on PSII in Barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) Genotypes, Probed by Chlorophyll-a Fluorescence. J. King Saud Univ. -Sci. 2021, 33, 101239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouertani, R.N.; Jardak, R.; Ben Chikha, M.; Ben Yaala, W.; Abid, G.; Karmous, C.; Hamdi, Z.; Mejri, S.; Jansen, R.K.; Ghorbel, A. Genotype-Specific Patterns of Physiological and Antioxidative Responses in Barley under Salinity Stress. Cereal Res. Commun. 2022, 50, 851–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, E.; Moustafa, E.S.; Abdul-Hamid, M.I.; Ash-shormillesy, S.M.; Merwad, A.-R.M.; Wafa, H.A.; Igartua, E. Field Responses of Barley Genotypes across a Salinity Gradient in an Arid Mediterranean Environment. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 258, 107206. [Google Scholar]
- Bimurzayev, N.; Sari, H.; Kurunc, A.; Doganay, K.H.; Asmamaw, M. Effects of Different Salt Sources and Salinity Levels on Emergence and Seedling Growth of Faba Bean Genotypes. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 18198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, H.I.; El-Sayed, A.A.; Rady, M.M.; Caruso, G.; Sekara, A.; Abdelhamid, M.T. Coupling Effects of Phosphorus Fertilization Source and Rate on Growth and Ion Accumulation of Common Bean under Salinity Stress. PeerJ 2021, 9, e11463. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Afzal, M.; Alghamdi, S.S.; Migdadi, H.H.; El-Harty, E.; Al-Faifi, S.A. Agronomical and Physiological Responses of Faba Bean Genotypes to Salt Stress. Agriculture 2022, 12, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aly, T.A.; Mustapha, A.T.; Zhang, L.; Yu, X.; Yagoub, A.E.A.; Ma, H.; Chen, L.; Zhou, C. Interaction Effects of Salinity and Ultrasound Pretreatment on the Phytochemical Compounds of Clover Sprouts. Acta Sci. Nutr. Health 2021, 5, 90–101. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelrazek, S.A.; Fayed, R.I.M.; El Naka, A. Salinity Effects of Irrigation Water and Cultivation of Egyptian Clover (Trifolium alexandrinum, L.) on Physicochemical Properties of Calcareous Soil. Alex. Sci. Exch. J. 2022, 43, 555–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirkol, G. PopW Improves Salt Stress Tolerance of Red Clover (Trifolium pratense L.) via Activating Phytohormones and Salinity Related Genes. Biologia 2023, 78, 979–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.; Wang, G.; Yu, X.; Li, L.; Li, C.; Song, Y.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Guan, C. Assessing Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) Tolerance to Salinity at Seedling Stage and Screening of the Salinity Tolerance Traits. Plant Biol. 2021, 23, 664–674. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Y.; Fan, Y.; Chen, Y.; Hao, X.; Li, S.; Kang, S. Response of Dry Matter and Water Use Efficiency of Alfalfa to Water and Salinity Stress in Arid and Semiarid Regions of Northwest China. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 254, 106934. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, C.; Li, X.; Tian, D.; Xu, B.; Zhang, C.; Ren, J.; Chen, N. Evaluation of the Effects of Water and Salinity Stress on the Growth and Biochemistry of Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) at the Branching Stage. Sustainability 2022, 14, 10262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Mageed, T.A.A.; Mekdad, A.A.; Rady, M.O.; Abdelbaky, A.S.; Saudy, H.S.; Shaaban, A. Physio-Biochemical and Agronomic Changes of Two Sugar Beet Cultivars Grown in Saline Soil as Influenced by Potassium Fertilizer. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2022, 22, 3636–3654. [Google Scholar]
- Bouras, H.; Bouaziz, A.; Bouazzama, B.; Hirich, A.; Choukr-Allah, R. How Phosphorus Fertilization Alleviates the Effect of Salinity on Sugar Beet (Beta vulgaris L.) Productivity and Quality. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alotaibi, F.; Bamagoos, A.A.; Ismaeil, F.M.; Zhang, W.; Abou-Elwafa, S.F. Application of Beet Sugar Byproducts Improves Sugar Beet Biofortification in Saline Soils and Reduces Sugar Losses in Beet Sugar Processing. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 30303–30311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayawardhane, J.; Goyali, J.C.; Zafari, S.; Igamberdiev, A.U. The Response of Cowpea (Vigna unguiculata) Plants to Three Abiotic Stresses Applied with Increasing Intensity: Hypoxia, Salinity, and Water Deficit. Metabolites 2022, 12, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maamallan, S.; Prakash, M.; Sathiyanarayanan, G.; Rameshkumar, S. Effect of Seed Hardening and Pelleting on Germination and Seedling Attributes of Cowpea under Saline Condition. Legume Res. -Int. J. 2021, 44, 723–729. [Google Scholar]
- Praxedes, S.S.C.; Ferreira Neto, M.; Loiola, A.T.; Santos, F.J.Q.; Umbelino, B.F.; Silva, L.d.A.; Moreira, R.C.L.; de Melo, A.S.; de Lacerda, C.F.; Fernandes, P.D. Photosynthetic Responses, Growth, Production, and Tolerance of Traditional Varieties of Cowpea under Salt Stress. Plants 2022, 11, 1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Chen, K.; He, P.; Dai, Y.; Yin, Y.; Peng, S.; Ding, J.; Yu, S.; Huang, J. Sunflower Photosynthetic Characteristics, Nitrogen Uptake, and Nitrogen Use Efficiency under Different Soil Salinity and Nitrogen Applications. Water 2022, 14, 982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Zeng, W.; Lei, G.; Wu, J.; Huang, J. Predicting the Rooting Depth, Dynamic Root Distribution and the Yield of Sunflower under Different Soil Salinity and Nitrogen Applications. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 170, 113749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveed, M.; Aslam, M.K.; Ahmad, Z.; Abbas, T.; Al-Huqail, A.A.; Siddiqui, M.H.; Ali, H.M.; Ashraf, I.; Mustafa, A. Growth Responses, Physiological Alterations and Alleviation of Salinity Stress in Sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) Amended with Gypsum and Composted Cow Dung. Sustainability 2021, 13, 6792. [Google Scholar]
- Swiontek Brzezinska, M.; Świątczak, J.; Wojciechowska, A.; Burkowska-But, A.; Kalwasińska, A. Consortium of Plant Growth-Promoting Rhizobacteria Enhances Oilseed Rape (Brassica napus L.) Growth under Normal and Saline Conditions. Arch. Microbiol. 2022, 204, 393. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Yu, X.; Yang, H.; Wang, J.; Li, Z.; Bai, C.; Wang, J.; Wang, B.; Zhou, G.; Kuai, J. Physiological Response Mechanism of Oilseed Rape to Abiotic Stress and the Stress-Resistant Cultivation Regulation. In Sustainable Crop Productivity and Quality Under Climate Change; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 207–234. [Google Scholar]
- Mansour, M.M.F.; Emam, M.M.; Salama, K.H.A.; Morsy, A.A. Sorghum under Saline Conditions: Responses, Tolerance Mechanisms, and Management Strategies. Planta 2021, 254, 24. [Google Scholar]
- Punia, H.; Tokas, J.; Malik, A.; Singh, S.; Phogat, D.S.; Bhuker, A.; Mor, V.S.; Rani, A.; Sheokand, R.N. Discerning Morpho-Physiological and Quality Traits Contributing to Salinity Tolerance Acquisition in Sorghum [Sorghum Bicolor (L.) Moench]. South Afr. J. Bot. 2021, 140, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dourado, P.R.M.; de Souza, E.R.; dos Santos, M.A.; Lins, C.M.T.; Monteiro, D.R.; Paulino, M.K.S.S.; Schaffer, B. Stomatal Regulation and Osmotic Adjustment in Sorghum in Response to Salinity. Agriculture 2022, 12, 658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šamec, D.; Linić, I.; Salopek-Sondi, B. Salinity Stress as an Elicitor for Phytochemicals and Minerals Accumulation in Selected Leafy Vegetables of Brassicaceae. Agronomy 2021, 11, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seymen, M.; Yavuz, D.; Eroğlu, S.; Arı, B.Ç.; Tanrıverdi, Ö.B.; Atakul, Z.; Issı, N. Effects of Different Levels of Water Salinity on Plant Growth, Biochemical Content, and Photosynthetic Activity in Cabbage Seedling Under Water-Deficit Conditions. Gesunde Pflanz. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeiner, M.; Juranović Cindrić, I.; Nemet, I.; Franjković, K.; Salopek Sondi, B. Influence of Soil Salinity on Selected Element Contents in Different Brassica Species. Molecules 2022, 27, 1878. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chourasia, K.N.; Lal, M.K.; Tiwari, R.K.; Dev, D.; Kardile, H.B.; Patil, V.U.; Kumar, A.; Vanishree, G.; Kumar, D.; Bhardwaj, V. Salinity Stress in Potato: Understanding Physiological, Biochemical and Molecular Responses. Life 2021, 11, 545. [Google Scholar]
- Sanwal, S.K.; Kumar, P.; Kesh, H.; Gupta, V.K.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, A.; Meena, B.L.; Colla, G.; Cardarelli, M.; Kumar, P. Salinity Stress Tolerance in Potato Cultivars: Evidence from Physiological and Biochemical Traits. Plants 2022, 11, 1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaki, H.E.; Radwan, K.S. The Use of Osmoregulators and Antioxidants to Mitigate the Adverse Impacts of Salinity Stress in Diploid and Tetraploid Potato Genotypes (Solanum Spp.). Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2022, 9, 19. [Google Scholar]
- Yavuz, D.; Kılıç, E.; Seymen, M.; Dal, Y.; Kayak, N.; Kal, Ü.; Yavuz, N. The Effect of Irrigation Water Salinity on the Morph-Physiological and Biochemical Properties of Spinach under Deficit Irrigation Conditions. Sci. Hortic. 2022, 304, 111272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bali, K.M.; Eltarabily, M.G.; Berndtsson, R.; Selim, T. Nutrient and Salinity Management for Spinach Production under Sprinkler Irrigation in the Low Desert Region of California. Irrig. Sci. 2021, 39, 735–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tareq, F.S.; Kotha, R.R.; Ferreira, J.F.; Sandhu, D.; Luthria, D.L. Influence of Moderate to High Salinity on the Phytochemical Profiles of Two Salinity-Tolerant Spinach Genotypes. ACS Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 1, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.H.; Baset Mia, M.A.; Quddus, M.A.; Sarker, K.K.; Rahman, M.; Skalicky, M.; Brestic, M.; Gaber, A.; Alsuhaibani, A.M.; Hossain, A. Salinity-Induced Physiological Changes in Pea (Pisum Sativum L.): Germination Rate, Biomass Accumulation, Relative Water Content, Seedling Vigor and Salt Tolerance Index. Plants 2022, 11, 3493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Roychoudhury, A. Omics Tools to Understand Abiotic Stress Response and Adaptation in Rye, Oat and Barley. In Omics Approach to Manage Abiotic Stress in Cereals; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 513–529. [Google Scholar]
- Rakoczy-Trojanowska, M.; Bolibok-Brągoszewska, H.; Myśków, B.; Dzięgielewska, M.; Stoja\lowski, S.; Grądzielewska, A.; Boczkowska, M.; Moskal, K. Genetics and Genomics of Stress Tolerance. In The Rye Genome; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 213–236. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Steenhuis, T.S.; Davis, K.F.; van der Werf, W.; Ritsema, C.J.; Pacenka, S.; Zhang, F.; Siddique, K.H.M.; Du, T. Diversified Crop Rotations Enhance Groundwater and Economic Sustainability of Food Production. Food Energy Secur. 2021, 10, e311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giraldo, P.; Benavente, E.; Manzano-Agugliaro, F.; Gimenez, E. Worldwide Research Trends on Wheat and Barley: A Bibliometric Comparative Analysis. Agronomy 2019, 9, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, J.; Braun, H.J.; Kosina, P.; Crouch, J.H. Wheat Facts and Futures 2009; CIMMYT: Veracruz, Mexico, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Katerji, N.; Van Hoorn, J.W.; Hamdy, A.; Mastrorilli, M.; Fares, C.; Ceccarelli, S.; Grando, S.; Oweis, T. Classification and Salt Tolerance Analysis of Barley Varieties. Agric. Water Manag. 2006, 85, 184–192. [Google Scholar]
- Gholizadeh, A.; Dehghania, H.; Dvorakb, J. Determination of the Most Effective Traits on Wheat Yield under Saline Stress. Agric. Adv. 2014, 3, 103–110. [Google Scholar]
- Shannon, M.C. Adaptation of Plants to Salinity. Adv. Agron. 1997, 60, 75–120. [Google Scholar]
- Munns, R.; James, R.A. Screening Methods for Salinity Tolerance: A Case Study with Tetraploid Wheat. Plant Soil 2003, 253, 201–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghani, H.; Dvorak, J.; Sabaghnia, N. Graphic Analysis of Biomass and Seed Yield of Beard Wheat in Salt Stress Condition. Ann. Biol. Res 2012, 3, 4246–4253. [Google Scholar]
- Afzal, I.; Rauf, S.; Basra, S.M.A.; Murtaza, G. Halopriming Improves Vigor, Metabolism of Reserves and Ionic Contents in Wheat Seedlings under Salt Stress. Plant Soil Environ. 2008, 54, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Shafi, M.; Bakht, J.; Khan, M.O.; Anwar, S. Response of Wheat Varieties to Salinity Stress as Ameliorated by Seed Priming. Pak. J. Bot. 2019, 51, 1969–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvaiz, A.; Satyawati, S. Salt Stress and Phyto-Biochemical Responses of Plants-a Review. Plant Soil Environ. 2008, 54, 89. [Google Scholar]
- Nasim, M.; Qureshi, R.H.; Aziz, T.; Saqib, M.; Nawaz, S.; Sahi, S.T.; Pervaiz, S. Screening Trees for Salinity Tolerance: A Case-Study with Ten Eucalyptus Species. Pak. J. Agric. Sci. 2007, 44, 385–396. [Google Scholar]
- Shafi, M.; Zhang, G.; Bakht, J.; Khan, M.A.; Islam, U.E.; Khan, M.D.; Raziuddin, G.Z. Effect of Cadmium and Salinity Stresses on Root Morphology of Wheat. Pak. J. Bot. 2010, 42, 2747–2754. [Google Scholar]
- Royo, A.; Abió, D. Salt Tolerance in Durum Wheat Cultivars. Span. J. Agric. Res. 2003, 1, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miransari, M.; Smith, D. Sustainable Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Production in Saline Fields: A Review. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2019, 39, 999–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz De León, J.L.; Escoppinichi, R.; Geraldo, N.; Castellanos, T.; Mujeeb-Kazi, A.; Röder, M.S. Quantitative Trait Loci Associated with Salinity Tolerance in Field Grown Bread Wheat. Euphytica 2011, 181, 371–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanuzzaman, M.; Nahar, K.; Rahman, A.; Anee, T.I.; Alam, M.U.; Bhuiyan, T.F.; Oku, H.; Fujita, M. Approaches to Enhance Salt Stress Tolerance in Wheat. In Wheat Improvement, Management and Utilization; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2017; pp. 151–187. [Google Scholar]
- Genc, Y.; Oldach, K.; Gogel, B.; Wallwork, H.; McDonald, G.K.; Smith, A.B. Quantitative Trait Loci for Agronomic and Physiological Traits for a Bread Wheat Population Grown in Environments with a Range of Salinity Levels. Mol. Breed. 2013, 32, 39–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puniran-Hartley, N.; Hartley, J.; Shabala, L.; Shabala, S. Salinity-Induced Accumulation of Organic Osmolytes in Barley and Wheat Leaves Correlates with Increased Oxidative Stress Tolerance: In Planta Evidence for Cross-Tolerance. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2014, 83, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truşcă, M.; Gâdea, Ş.; Stoian, V.; Vâtcă, A.; Vâtcă, S. Plants Physiology in Response to the Saline Stress Interconnected Effects. Not. Bot. Horti Agrobot. 2022, 50, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munns, R.; James, R.A.; Xu, B.; Athman, A.; Conn, S.J.; Jordans, C.; Byrt, C.S.; Hare, R.A.; Tyerman, S.D.; Tester, M. Wheat Grain Yield on Saline Soils Is Improved by an Ancestral Na+ Transporter Gene. Nat. Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 360–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaman, M.; Shahid, S.A.; Heng, L.; Shahid, S.A.; Zaman, M.; Heng, L. Soil Salinity: Historical Perspectives and a World Overview of the Problem. In Guideline for Salinity Assessment, Mitigation and Adaptation Using Nuclear and Related Techniques; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 43–53. [Google Scholar]
- Dagar, J.C.; Yadav, R.K.; Singh, A.; Singh, N.T. Historical Perspectives and Dynamics of Nature, Extent, Classification and Management of Salt-Affected Soils and Waters. In Research Developments in Saline Agriculture; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 3–52. [Google Scholar]
- Shahid, S.A.; Abdelfattah, M.A.; Taha, F.K. Developments in Soil Salinity Assessment and Reclamation: Innovative Thinking and Use of Marginal Soil and Water Resources in Irrigated Agriculture; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Rakshit, A.; Singh, H.B.; Singh, A.K.; Singh, U.S.; Fraceto, L. New Frontiers in Stress Management for Durable Agriculture; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Lambers, H.; Chapin, F.S.; Pons, T.L. Plant Physiological Ecology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Hasanuzzaman, M. Plant Ecophysiology and Adaptation under Climate Change: Mechanisms and Perspectives II: Mechanisms of Adaptation and Stress Amelioration; Springer Nature: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Moreiras, A.M.; Pacenza, M.; Araniti, F.; Bruno, L. Confocal and Transmission Electron Microscopy for Plant Studies. In Advances in Plant Ecophysiology Techniques; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 253–271. [Google Scholar]
- Cominelli, E.; Conti, L.; Tonelli, C.; Galbiati, M. Challenges and Perspectives to Improve Crop Drought and Salinity Tolerance. New Biotechnol. 2013, 30, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkharabsheh, H.M.; Seleiman, M.F.; Hewedy, O.A.; Battaglia, M.L.; Jalal, R.S.; Alhammad, B.A.; Schillaci, C.; Ali, N.; Al-Doss, A. Field Crop Responses and Management Strategies to Mitigate Soil Salinity in Modern Agriculture: A Review. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopmans, J.W.; Qureshi, A.S.; Kisekka, I.; Munns, R.; Grattan, S.R.; Rengasamy, P.; Ben-Gal, A.; Assouline, S.; Javaux, M.; Minhas, P.S. Critical Knowledge Gaps and Research Priorities in Global Soil Salinity. Adv. Agron. 2021, 169, 1–191. [Google Scholar]
- Yeo, A. Predicting the Interaction between the Effects of Salinity and Climate Change on Crop Plants. Sci. Hortic. 1998, 78, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitman, M.G.; Läuchli, A. Global Impact of Salinity and Agricultural Ecosystems. In Salinity: Environment-Plants-Molecules; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2002; pp. 3–20. [Google Scholar]
- Valenzuela, F.J.; Reineke, D.; Leventini, D.; Chen, C.C.L.; Barrett-Lennard, E.G.; Colmer, T.D.; Dodd, I.C.; Shabala, S.; Brown, P.; Bazihizina, N. Plant Responses to Heterogeneous Salinity: Agronomic Relevance and Research Priorities. Ann. Bot. 2022, 129, 499–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arun, K.D.; Sabarinathan, K.G.; Gomathy, M.; Kannan, R.; Balachandar, D. Mitigation of Drought Stress in Rice Crop with Plant Growth-Promoting Abiotic Stress-Tolerant Rice Phyllosphere Bacteria. J. Basic Microbiol. 2020, 60, 768–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.N. Beneficial Plant-Microbe Interactions for Agricultural Sustainability. J. Appl. Biol. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, i–iv. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parasuraman, P.; Pattnaik, S.; Busi, S. Phyllosphere Microbiome: Functional Importance in Sustainable Agriculture. In New and Future Developments in Microbial Biotechnology and Bioengineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 135–148. [Google Scholar]
- Mukhtar, S.; Malik, K.A.; Mehnaz, S. Microbiome of Halophytes: Diversity and Importance for Plant Health and Productivity. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Lett. 2019, 47, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xun, W.; Chen, L.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, N.; Feng, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, R. Rhizosphere Microbes Enhance Plant Salt Tolerance: Toward Crop Production in Saline Soil. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2022, 20, 6543–6551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, D.; Lade, H. Plant-Growth-Promoting Rhizobacteria to Improve Crop Growth in Saline Soils: A Review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2014, 34, 737–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, S.S.; Rask, K.A.; Vestergård, M.; Johansen, J.L.; Priemé, A.; Frøslev, T.G.; Ekelund, F. Specialized microbiomes facilitate natural rhizosphere microbiome interactions counteracting high salinity stress in plants. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2021, 186, 104430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).



