Low Concentrations of Eucalyptus Essential Oil Induce Age, Sex, and Mating Status-Dependent Stimulatory Responses in Drosophila suzukii
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Drosophila suzukii Rearing
2.2. Eucalyptus Essential Oil
2.3. Toxicity Assessment of Eucalyptus EO against Drosophila suzukii
2.4. Exposure of Old Mated Adults to Eucalyptus EO Low Concentrations
2.5. Exposure of Newly Emerged Virgin Adults to Eucalyptus EO Low concentrations
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Toxicity Bioassays
3.2. Effects of Low Concentrations of Eucalyptus EO on the Biological and Reproductive Traits of Old Mated Flies
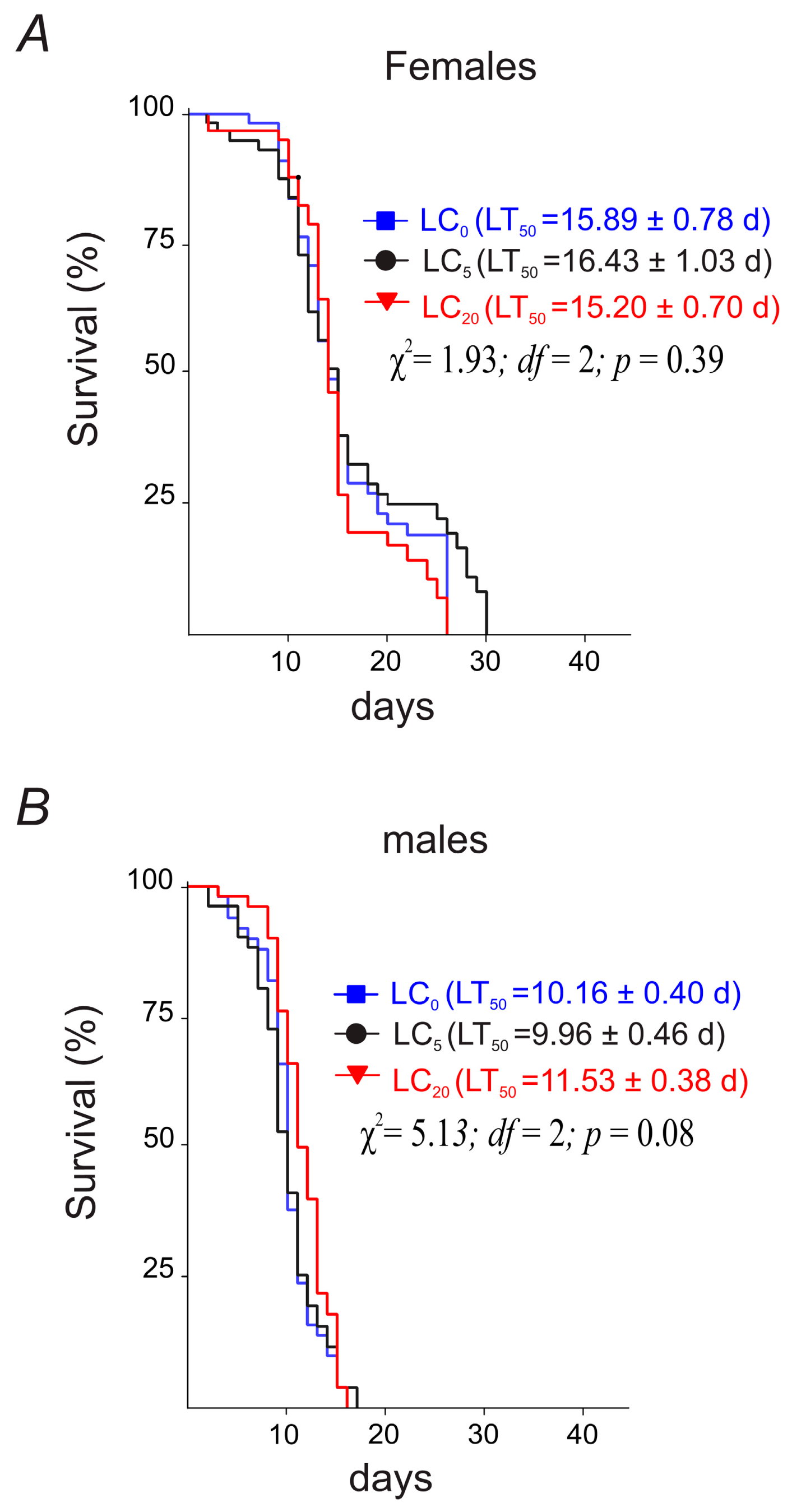
3.2.1. Parental Flies’ Longevity
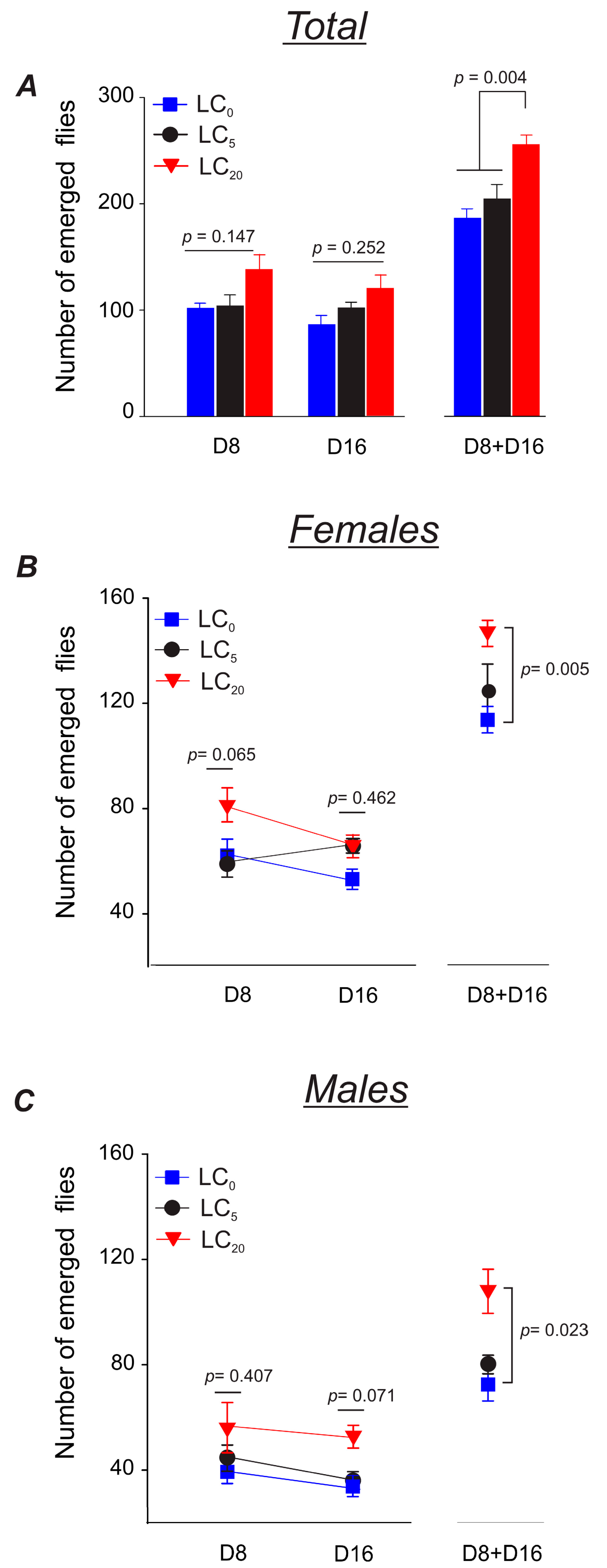
3.2.2. Parental Flies’ Fertility
3.2.3. Progeny Pupal and Flies’ Body Mass
3.3. Effects of Low Concentration of Eucalyptus EO on the Biological and Reproductive Traits of Newly Emerged Virgin Adults
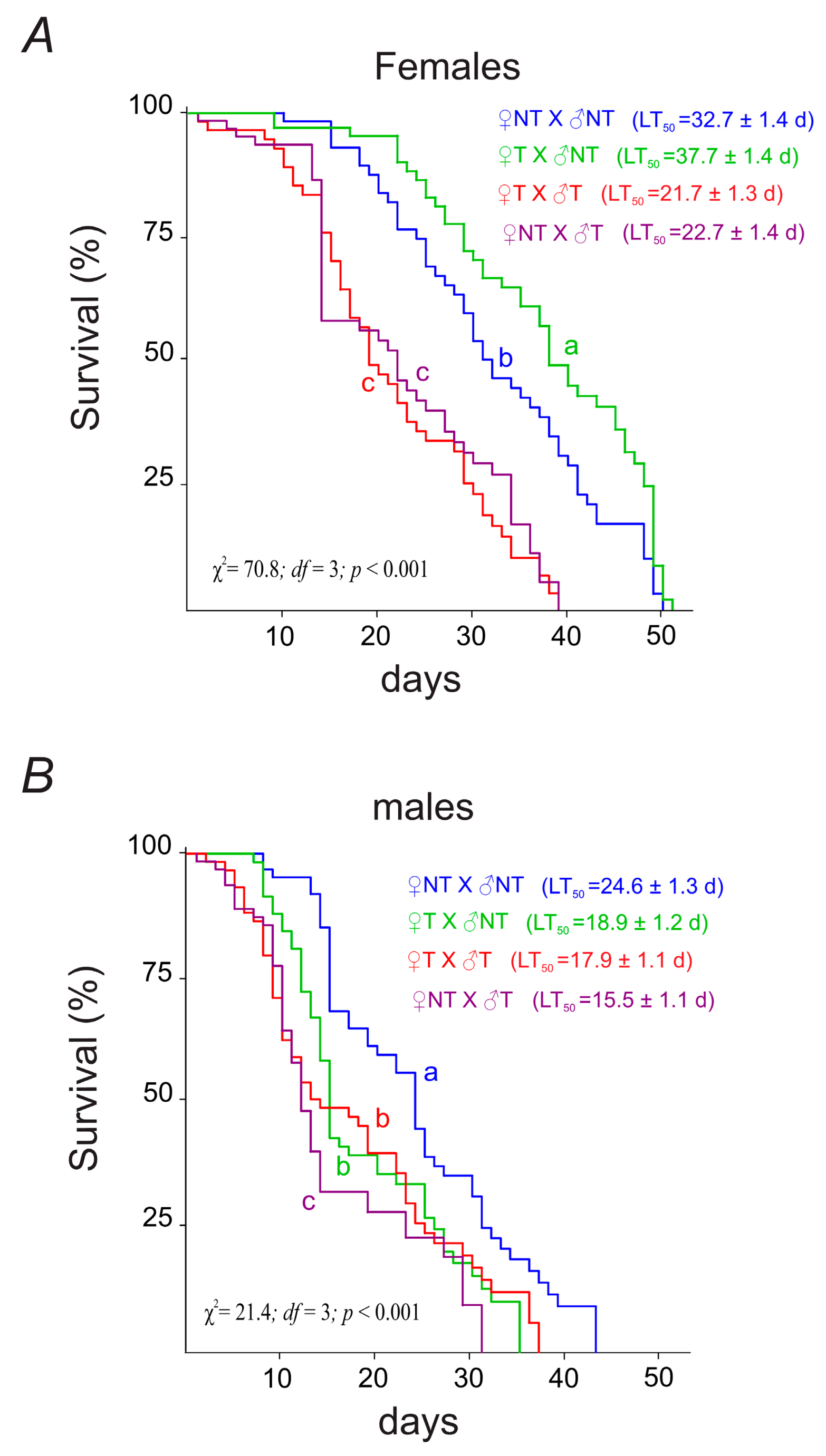
3.3.1. Parental Flies’ Longevity
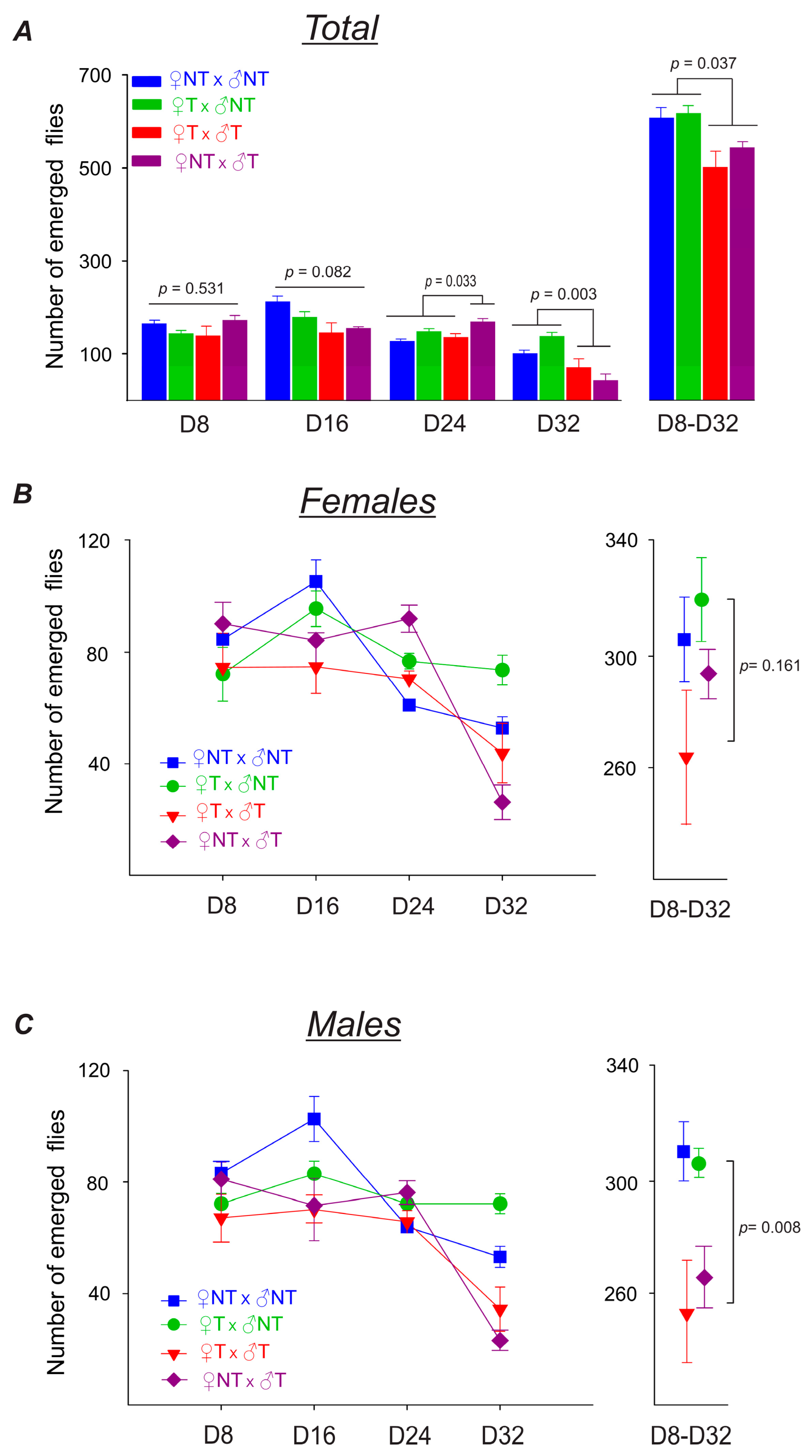
3.3.2. Parental Flies’ Fertility
3.3.3. Progeny Flies’ Body Mass
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Benelli, G.; Rizzo, R.; Zeni, V.; Govigli, A.; Samková, A.; Sinacori, M.; Lo Verde, G.; Pavela, R.; Cappellacci, L.; Petrelli, R.; et al. Carlina acaulis and Trachyspermum ammi Essential Oils Formulated in Protein Baits Are Highly Toxic and Reduce Aggressiveness in the Medfly, Ceratitis Capitata. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 161, 113191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddi, K.; Turchen, L.M.; Viteri Jumbo, L.O.; Guedes, R.N.; Pereira, E.J.; Aguiar, R.W.; Oliveira, E.E. Rethinking Biorational Insecticides for Pest Management: Unintended Effects and Consequences. Pest Manag. Sci. 2020, 76, 2286–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isman, M.B. Commercial Development of Plant Essential Oils and Their Constituents as Active Ingredients in Bioinsecticides. Phytochem. Rev. 2020, 19, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, T.P.; Haddi, K.; Corrêa, R.F.T.; Zapata, V.L.B.; Piau, T.B.; Souza, L.F.N.; Santos, S.-M.G.; Oliveira, E.E.; Jumbo, L.O.V.; Ribeiro, B.M.; et al. Prolonged Mosquitocidal Activity of Siparuna guianensis Essential Oil Encapsulated in Chitosan Nanoparticles. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rix, R.R.; Guedes, R.N.C.; Christopher Cutler, G. Hormesis Dose-Response Contaminant-Induced Hormesis in Animals. Curr. Opin. Toxicol. 2022, 30, 100336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutler, G.C.; Amichot, M.; Benelli, G.; Guedes, R.N.C.; Qu, Y.; Rix, R.R.; Ullah, F.; Desneux, N. Hormesis and Insects: Effects and Interactions in Agroecosystems. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 825, 153899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedes, R.N.C.; Rix, R.R.; Cutler, G.C. Pesticide-Induced Hormesis in Arthropods: Towards Biological Systems. Curr. Opin. Toxicol. 2022, 29, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddi, K.; Oliveira, E.E.; Faroni, L.R.A.; Guedes, D.C.; Miranda, N.N.S. Sublethal Exposure to Clove and Cinnamon Essential Oils Induces Hormetic-Like Responses and Disturbs Behavioral and Respiratory Responses in Sitophilus zeamais (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2015, 108, 2815–2822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonov, A.; Arlia-Ciommo, A.; Piano, A.; Svistkova, V.; Lutchman, V.; Medkour, Y.; Titorenko, V. Longevity Extension by Phytochemicals. Molecules 2015, 20, 6544–6572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerofotis, C.D.; Ioannou, C.S.; Nakas, C.T.; Papadopoulos, N.T. The Odor of a Plant Metabolite Affects Life History Traits in Dietary Restricted Adult Olive Flies. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papanastasiou, S.A.; Bali, E.-M.D.; Ioannou, C.S.; Papachristos, D.P.; Zarpas, K.D.; Papadopoulos, N.T. Toxic and Hormetic-like Effects of Three Components of Citrus Essential Oils on Adult Mediterranean Fruit Flies (Ceratitis capitata). PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asplen, M.K.G.; Anfora, A.; Biondi, D.S.; Choi, D.; Chu, K.M.; Daane, P.; Gilbert, A.P.; Gutierrez, K.A.; Hoelmer, W.D.; Hutchison, R.; et al. Invasion Biology of Spotted Wing Drosophila (Drosophila suzukii): A Global Perspective and Future Priorities. J. Pest Sci. 2015, 88, 469–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.C.; Bruck, D.J.; Dreves, A.J.; Ioriatti, C.; Vogt, H.; Baufeld, P. In Focus: Spotted Wing Drosophila, Drosophila suzukii, across Perspectives. Pest Manag. Sci. 2011, 67, 1349–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamby, K.A.; Bellamy, D.E.; Chiu, J.C.; Lee, J.C.; Walton, V.M.; Wiman, N.G.; York, R.M.; Biondi, A. Biotic and Abiotic Factors Impacting Development, Behavior, Phenology, and Reproductive Biology of Drosophila suzukii. J. Pest Sci. 2016, 89, 605–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deprá, M.; Poppe, J.L.; Schmitz, H.J.; De Toni, D.C.; Valente, V.L.S. The First Records of the Invasive Pest Drosophila Suzukii in the South American Continent. J. Pest Sci. 2014, 87, 379–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreazza, F.; Haddi, K.; Oliveira, E.E.; Ferreira, J.A.M. Drosophila suzukii (Diptera: Drosophilidae) Arrives at Minas Gerais State, a Main Strawberry Production Region in Brazil. Florida Entomol. 2016, 99, 796–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahenzli, F.; Strack, T.; Daniel, C. Screening of 25 Different Natural Crop Protection Products against Drosophila suzukii. J. Appl. Entomol. 2018, 142, 563–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dam, D.; Molitor, D.; Beyer, M. Natural Compounds for Controlling Drosophila suzukii. A Review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2019, 39, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eben, A.; Sporer, F.; Vogt, H.; Wetterauer, P.; Wink, M. Search for Alternative Control Strategies of Drosophila suzukii (Diptera: Drosophilidae): Laboratory Assays Using Volatile Natural Plant Compounds. Insects 2020, 11, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gullickson, M.; Flavin Hodge, C.; Hegeman, A.; Rogers, M. Deterrent Effects of Essential Oils on Spotted-Wing Drosophila (Drosophila suzukii): Implications for Organic Management in Berry Crops. Insects 2020, 11, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, L.; Cardoso, M.d.G.; Konig, I.F.M.; Ferreira, V.R.F.; Caetano, A.R.S.; Campolina, G.A.; Haddi, K. Toxicity, Histopathological Alterations and Acetylcholinesterase Inhibition of Illicium verum Essential Oil in Drosophila Suzukii. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finetti, L.; Civolani, S.; Mirandola, D.; Benetti, L.; Francati, S.; Albanese, F.; Menicucci, F.; Michelozzi, M.; Bellardi, M.G.; Dindo, M.L.; et al. Monarda Didyma Hydrolate Affects the Survival and the Behaviour of Drosophila suzukii. Insects 2022, 13, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caetano, A.R.S.; Cardoso, M.d.G.; Haddi, K.; Campolina, G.A.; Souza, B.M.; Lunguinho, A.; Souza, L.; Nelson, D.L.; Oliveira, J.E. Rosmarinus Officinalis Essential Oil Incorporated into Nanoparticles as an Efficient Insecticide against Drosophila suzukii (Diptera: Drosophilidae). Austral Entomol. 2022, 61, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batish, D.R.; Singh, H.P.; Kohli, R.K.; Kaur, S. Eucalyptus Essential Oil as a Natural Pesticide. For. Ecol. Manag. 2008, 256, 2166–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakad, A.K.; Pandey, V.V.; Beg, S.; Rawat, J.M.; Singh, A. Biological, Medicinal and Toxicological Significance of Eucalyptus Leaf Essential Oil: A Review. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 833–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, B.; Sharifi-Rad, J.; Quispe, C.; Llaique, H.; Villalobos, M.; Smeriglio, A.; Trombetta, D.; Ezzat, S.M.; Salem, M.A.; Zayed, A.; et al. Insights into Eucalyptus Genus Chemical Constituents, Biological Activities and Health-Promoting Effects. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 91, 609–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreazza, F.; Bernardi, D.; Marangon, R.B.; Botton, M.; Nava, D.E. Técnica de Criação de Drosophila suzukii (Matsumura, 1931) (Diptera: Drosophilidae) em Dieta Artificial; Boletim Pesquisa e Desenvolvimento/Embrapa Clima Temperado: Pelotas, Brazil, 2016; 23p. [Google Scholar]
- Mendonça, L.d.P.; Oliveira, E.E.; Andreazza, F.; Rezende, S.M.; Faroni, L.R.D.; Guedes, R.N.C.; Haddi, K. Host Potential and Adaptive Responses of Drosophila suzukii (Diptera: Drosophilidae) to Barbados Cherries. J. Econ. Entomol. 2019, 112, 3002–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WFN. Óleos Essenciais. Available online: https://www.wnf.com.br/ (accessed on 1 December 2021).
- Yeom, H.-J.; Kang, J.; Kim, S.-W.; Park, I.-K. Fumigant and Contact Toxicity of Myrtaceae Plant Essential Oils and Blends of Their Constituents against Adults of German Cockroach (Blattella germanica) and Their Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitory Activity. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2013, 107, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erland, L.A.E.; Rheault, M.R.; Mahmoud, S.S. Insecticidal and Oviposition Deterrent Effects of Essential Oils and Their Constituents against the Invasive Pest Drosophila suzukii (Matsumura) (Diptera: Drosophilidae). Crop Prot. 2015, 78, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, M.; Kim, J.; Yoon, K.A.; Lee, S.H.; Park, C.G. Biological Activity of Myrtaceae Plant Essential Oils and Their Major Components against Drosophila suzukii (Diptera: Drosophilidae). Pest Manag. Sci. 2017, 73, 404–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Jang, M.; Shin, E.; Kim, J.; Lee, S.H.; Park, C.G. Fumigant and Contact Toxicity of 22 Wooden Essential Oils and Their Major Components against Drosophila suzukii (Diptera: Drosophilidae). Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2016, 133, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedini, S.; Cosci, F.; Tani, C.; Pierattini, E.C.; Venturi, F.; Lucchi, A.; Ioriatti, C.; Ascrizzi, R.; Flamini, G.; Ferroni, G.; et al. Essential Oils as Post-Harvest Crop Protectants against the Fruit Fly Drosophila suzukii: Bioactivity and Organoleptic Profile. Insects 2020, 11, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Bedmar, Z.; Anter, J.; de La Cruz-Ares, S.; Muñoz-Serrano, A.; Alonso-Moraga, Á.; Pérez-Guisado, J. Role of Citrus Juices and Distinctive Components in the Modulation of Degenerative Processes: Genotoxicity, Antigenotoxicity, Cytotoxicity, and Longevity in Drosophila. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part A 2011, 74, 1052–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioannou, C.S.; Papadopoulos, N.T.; Kouloussis, N.A.; Tananaki, C.I.; Katsoyannos, B.I. Essential Oils of Citrus Fruit Stimulate Oviposition in the Mediterranean Fruit Fly Ceratitis capitata (Diptera: Tephritidae). Physiol. Entomol. 2012, 37, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, S.M.; Haddi, K.; Viteri Jumbo, L.O.; Oliveira, E.E. Progeny of the Maize Weevil, Sitophilus zeamais, Is Affected by Parental Exposure to Clove and Cinnamon Essential Oils. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2017, 163, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vayndorf, E.M.; Lee, S.S.; Liu, R.H. Whole Apple Extracts Increase Lifespan, Healthspan and Resistance to Stress in Caenorhabditis elegans. J. Funct. Foods 2013, 5, 1235–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Deng, N.; Wang, H.; Li, T.; Chen, L.; Zheng, B.; Liu, R.H. Effects of Orange Extracts on Longevity, Healthspan, and Stress Resistance in Caenorhabditis elegans. Molecules 2020, 25, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, C.; Wakita, Y.; Inoue, T.; Hiramitsu, M.; Okada, M.; Mitani, Y.; Segawa, S.; Tsuchiya, Y.; Nabeshima, T. Effects of Lifelong Intake of Lemon Polyphenols on Aging and Intestinal Microbiome in the Senescence-Accelerated Mouse Prone 1 (SAMP1). Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedes, R.N.C.; Walse, S.S.; Throne, J.E. Sublethal Exposure, Insecticide Resistance, and Community Stress. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2017, 21, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedes, R.N.C.; Cutler, G.C. Insecticide-Induced Hormesis and Arthropod Pest Management. Pest Manag. Sci. 2014, 70, 690–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, S.; Carey, J.R.; Liedo, P.; Ingram, D.K.; Müller, H.-G.; Wang, J.-L.; Yao, F.; Yu, B.; Zhou, A. The Prolongevity Effect of Resveratrol Depends on Dietary Composition and Calorie Intake in a Tephritid Fruit Fly. Exp. Gerontol. 2009, 44, 472–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.-S.; Lee, B.-S.; Semnani, S.; Avanesian, A.; Um, C.-Y.; Jeon, H.-J.; Seong, K.-M.; Yu, K.; Min, K.-J.; Jafari, M. Curcumin Extends Life Span, Improves Health Span, and Modulates the Expression of Age-Associated Aging Genes in Drosophila melanogaster. Rejuvenation Res. 2010, 13, 561–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, A.; Bandani, A.R. Does Timing of Post-Stressor Exposure Mating Matter for Parental Effect? J. Stored Prod. Res. 2022, 99, 102021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmon, A.B.; Marx, D.B.; Harshman, L.G. A Cost of Reproduction in Drosophila melanogaster: Stress Susceptibility. Evolution 2001, 55, 1600–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddi, K.; Mendes, M.V.; Barcellos, M.S.; Lino-Neto, J.; Freitas, H.L.; Guedes, R.N.C.; Oliveira, E.E. Sexual Success after Stress? Imidacloprid-Induced Hormesis in Males of the Neotropical Stink Bug Euschistus heros. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0156616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blouquy, L.; Mottet, C.; Olivares, J.; Plantamp, C.; Siegwart, M.; Barrès, B. How Varying Parameters Impact Insecticide Resistance Bioassay: An Example on the Worldwide Invasive Pest Drosophila suzukii. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0247756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddi, K.; Viteri Jumbo, L.O.; Costa, M.S.; Santos, M.F.; Faroni, L.R.A.; Serrão, J.E.; Oliveira, E.E. Changes in the Insecticide Susceptibility and Physiological Trade-Offs Associated with a Host Change in the Bean Weevil Acanthoscelides obtectus. J. Pest Sci. 2018, 91, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flatt, T.; Kawecki, T.J. Juvenile Hormone as a Regulator of the Trade-off between Reproduction and Life Span in Drosophila melanogaster. Evolution 2007, 61, 1980–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jager, T.; Barsi, A.; Ducrot, V. Hormesis on Life-History Traits: Is There Such Thing as a Free Lunch? Ecotoxicology 2013, 22, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrese, E.J.; Kozumbo, W.J. The Hormetic Dose-Response Mechanism: NRF2 Activation. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 167, 105526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Ru, X.; Wen, T. Nrf2, a Transcription Factor for Stress Response and Beyond. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottino-Rojas, V.; Talyuli, O.A.C.; Carrara, L.; Martins, A.J.; James, A.A.; Oliveira, P.L.; Paiva-Silva, G.O. The Redox-Sensing Gene Nrf2 Affects Intestinal Homeostasis, Insecticide Resistance, and Zika Virus Susceptibility in the Mosquito Aedes Aegypti. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 9053–9063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Lethal Concentrations | No. of Insects | EO Concentrations (μL·mL−1) | Fiducial Interval (95%) | χ2 | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 805 | 1.10 | 0.98 | |||
| LC5 | 0.22 | 0.17–0.26 | |||
| LC20 | 0.38 | 0.32–0.43 | |||
| LC50 | 0.67 | 0.61–0.71 | |||
| LC90 | 1.57 | 1.40–1.83 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pineda, M.; Alves, E.L.d.A.; Antunes, J.A.; Carvalho, V.d.C.; Haddi, K. Low Concentrations of Eucalyptus Essential Oil Induce Age, Sex, and Mating Status-Dependent Stimulatory Responses in Drosophila suzukii. Agriculture 2023, 13, 404. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13020404
Pineda M, Alves ELdA, Antunes JA, Carvalho VdC, Haddi K. Low Concentrations of Eucalyptus Essential Oil Induce Age, Sex, and Mating Status-Dependent Stimulatory Responses in Drosophila suzukii. Agriculture. 2023; 13(2):404. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13020404
Chicago/Turabian StylePineda, Maria, Emanuel Lucas de Andrade Alves, Julia Almeida Antunes, Vinícius de Castro Carvalho, and Khalid Haddi. 2023. "Low Concentrations of Eucalyptus Essential Oil Induce Age, Sex, and Mating Status-Dependent Stimulatory Responses in Drosophila suzukii" Agriculture 13, no. 2: 404. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13020404
APA StylePineda, M., Alves, E. L. d. A., Antunes, J. A., Carvalho, V. d. C., & Haddi, K. (2023). Low Concentrations of Eucalyptus Essential Oil Induce Age, Sex, and Mating Status-Dependent Stimulatory Responses in Drosophila suzukii. Agriculture, 13(2), 404. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13020404






