Influence of Lead (Pb) and Its Relationship with the pH of Water on the Growth of Creole Maize (Zea mays L.)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site and Plant Matter
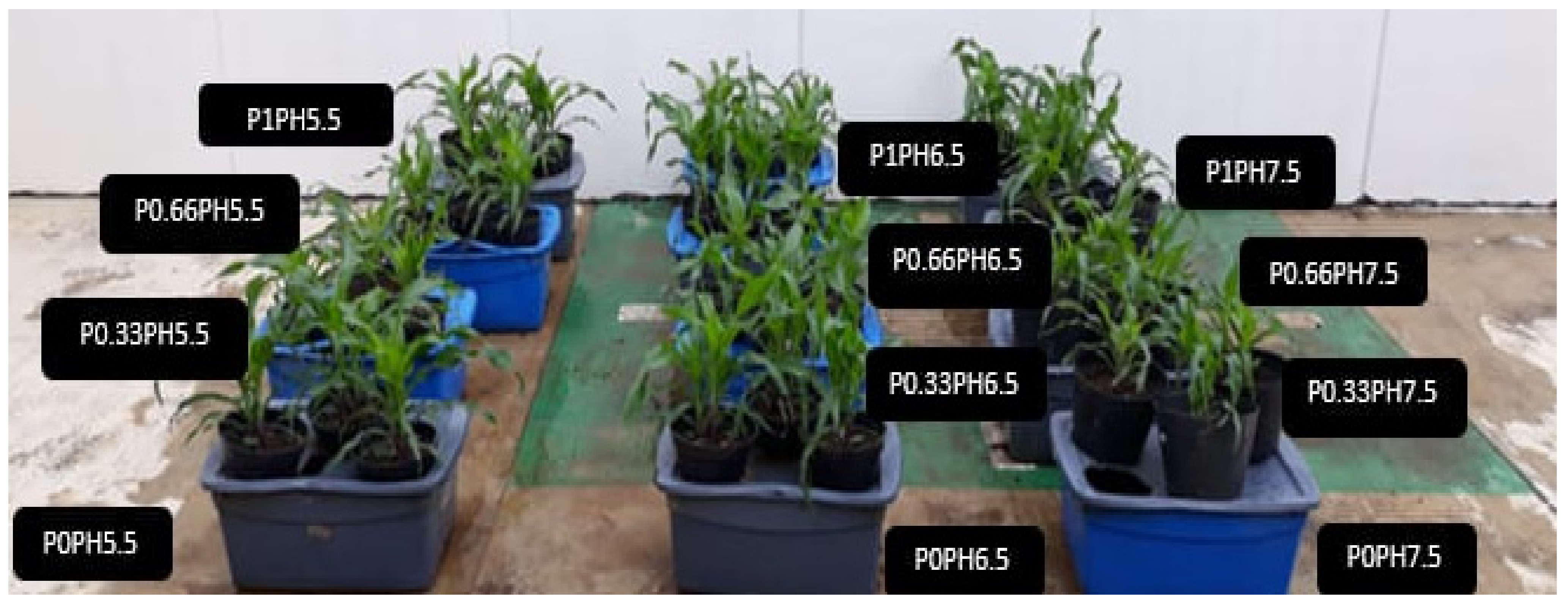
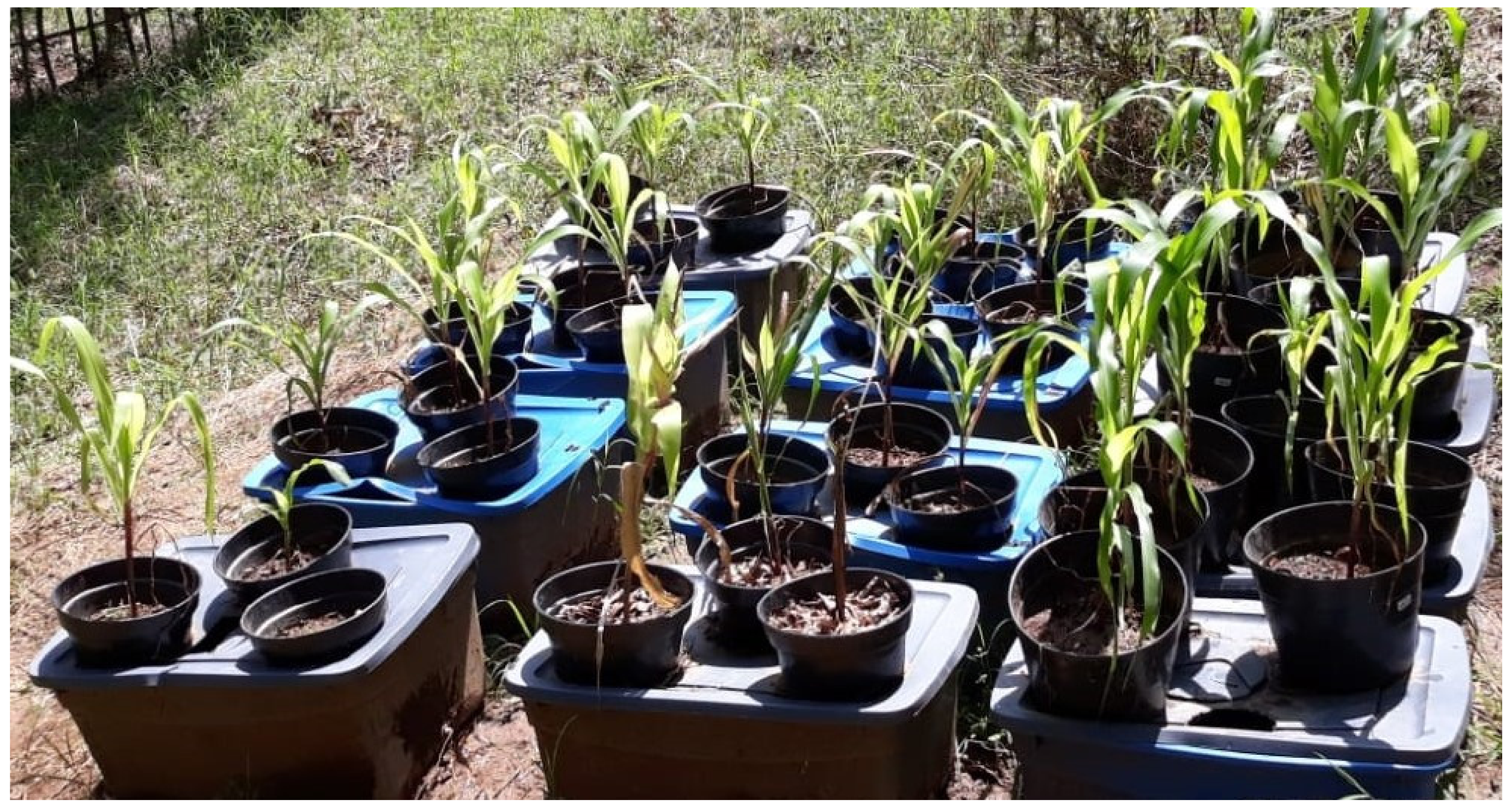
2.2. Experimental Design and Treatment of Maize Plants
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
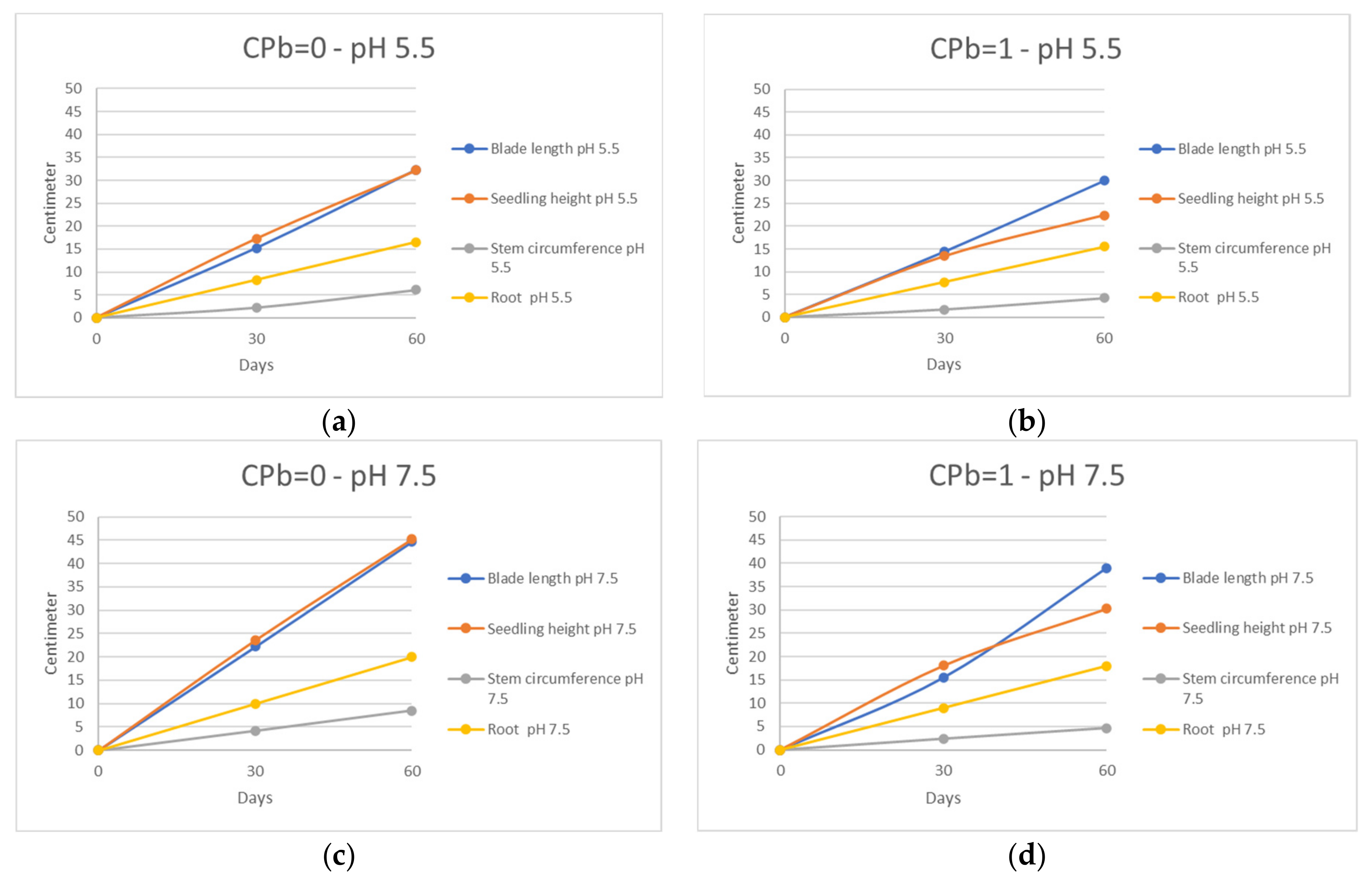
3.1. Leaf Length, Seedling Height, Stem and Root Circumference
3.2. Association of the Results with a Fixed pH as a Function of the Pb Concentration
3.3. Association of Results with Fixed Pb Concentration as a Function of the pH
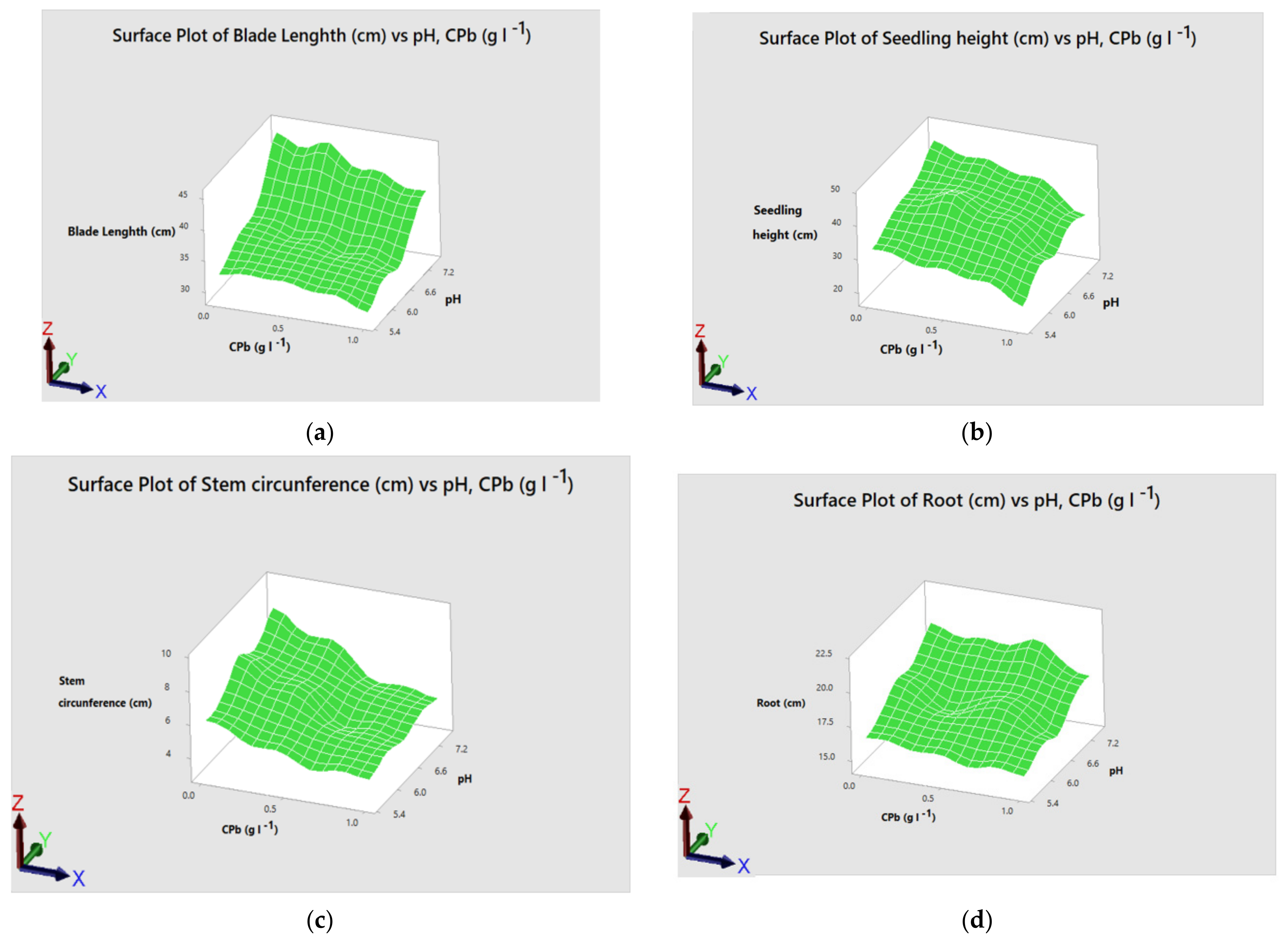
3.4. Association of Results as a Function of the Lead Concentration (CPb) and Potential of Hydrogen (pH)
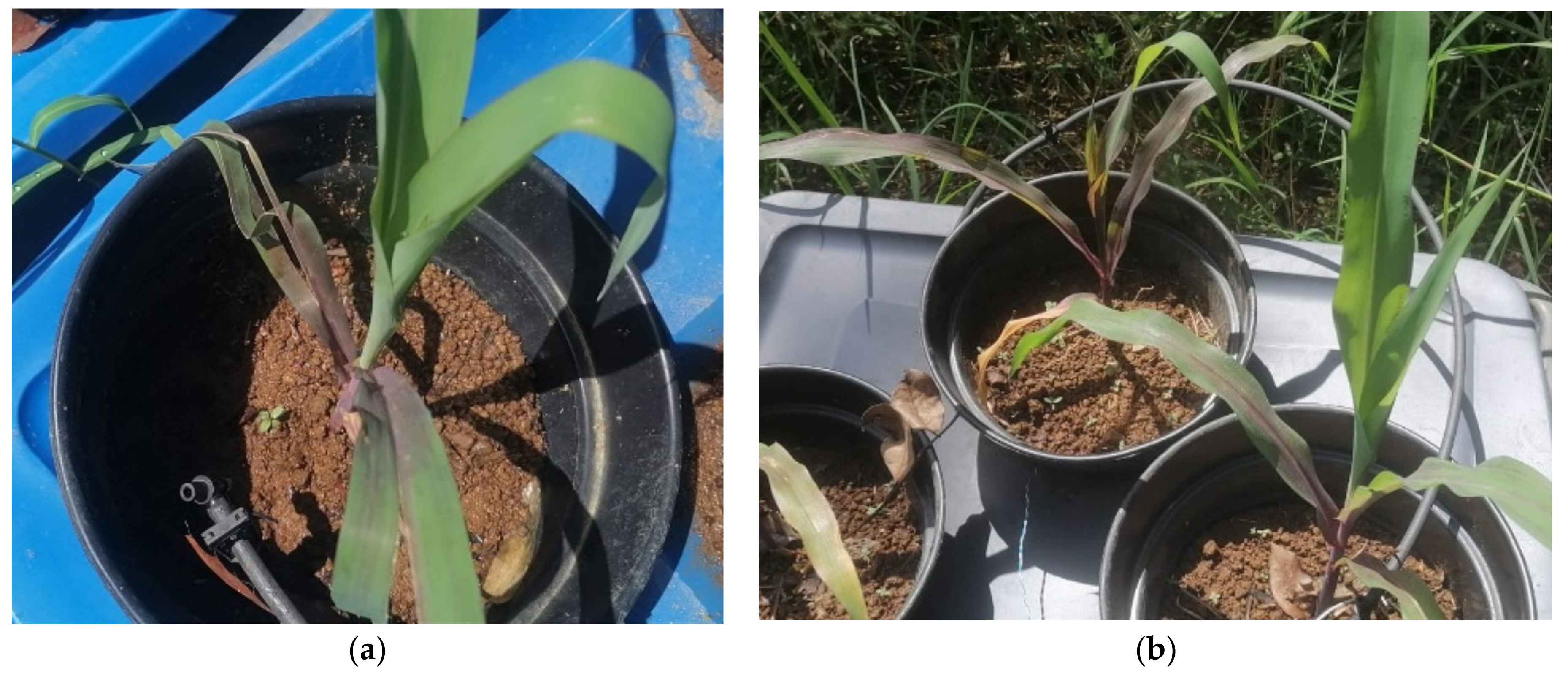
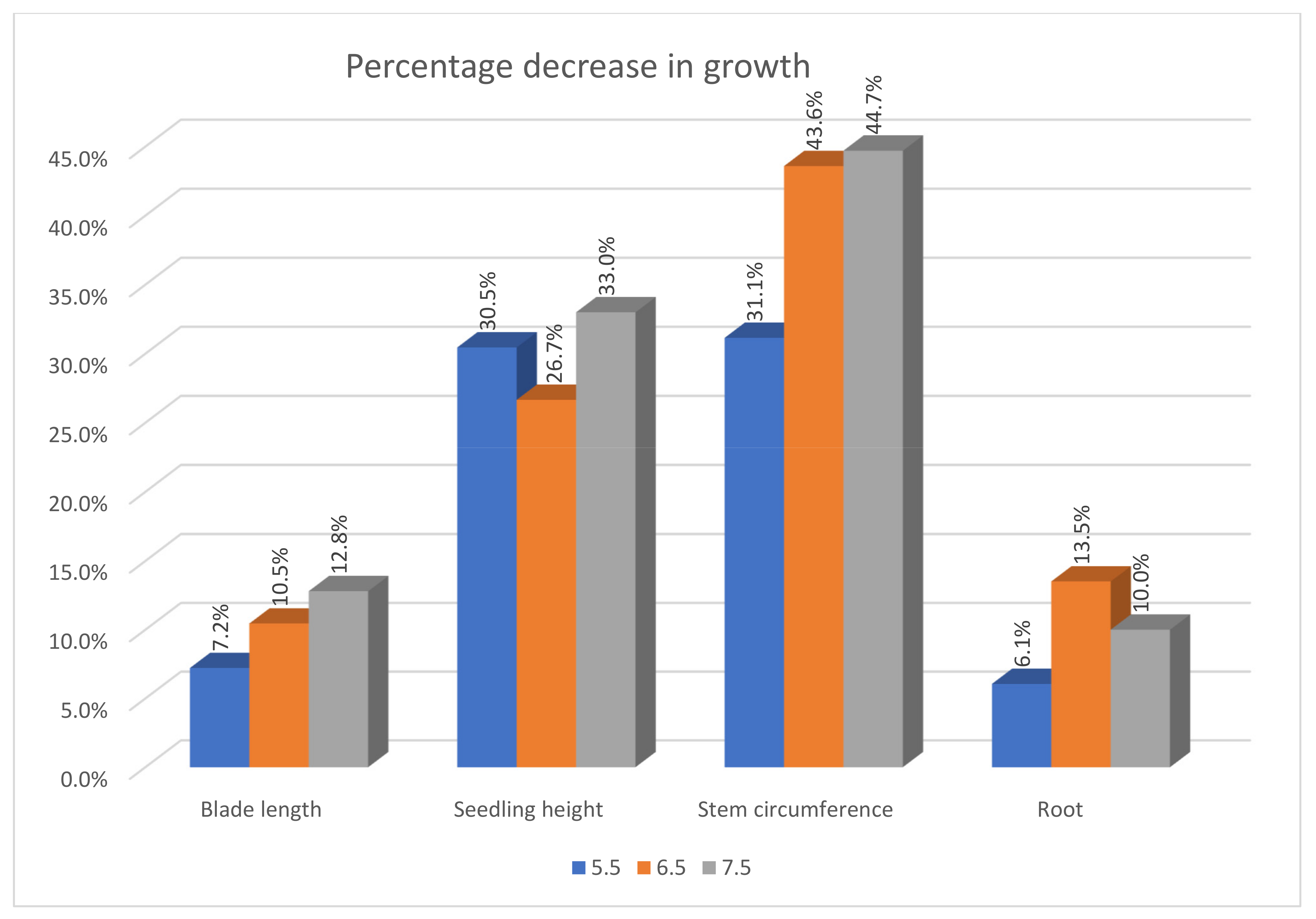
3.5. Comparative Analysis of the Parameters Evaluated without Lead and with the Maximum Lead Concentration (CPb)
4. Discussion
4.1. Leaf Length, Seedling Height, Stem and Root Circumference
4.2. Association of Results with a Fixed pH as a Function of the Pb Concentration
4.3. Association of Results with a Fixed Pb Concentration as a Function of the pH
4.4. Association of the Results as a Function of the Lead Concentration (CPb) and Potential of Hydrogen (pH)
4.5. Comparative Analysis of the Parameters Evaluated without Lead and with the Maximum Lead Concentration (CPb)
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vieira, R.H.; Volesky, B. Biosorption: A solution to pollution? Int. Microbiol. 2000, 3, 17–24. [Google Scholar]
- Tanjung, R.; Fahruddin, F.; Samawi, M. Phytoremediation relationship of lead (Pb) by Eichhornia crassipes on pH, BOD and COD in groundwater. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1341, 022020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahruddin, F.; La Nafie, N.; Asadi, A.; Tuwo, M.; Awaluddin, A.; Management, M.L. Treatment of compost as a source of organic material for bacterial consortium in the removal of sulfate and heavy metal lead (Pb) from acid mine drainage. J. Degrad. 2021, 9, 3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nriagu, J.O. Global metal pollution: Poisoning the biosphere? Environ. Sci. Policy Sustain. Dev. 1990, 32, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, L.A.; Darwish, W.S. Environmental chemical contaminants in food: Review of a global problem. J. Toxicol. 2019, 2019, 2345283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vasilachi, I.C.; Minut, M.; Betianu, C.; Gavrilescu, M. Investigation of the Toxic Effects of Lead on Maize Germination and Growth (Zea mays). In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on e-Health and Bioengineering (EHB), Iasi, Romania, 18–19 November 2021; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Pant, H.; Singh, V.L.R. Lead toxicity in plants and phytoremediation potential of aromatic plants for lead contaminated soils. J. Med. Aromat. Plant Sci. 2020, 42, 205–219. [Google Scholar]
- Han, R.; Zhou, B.; Huang, Y.; Lu, X.; Li, S.; Li, N. Bibliometric overview of research trends on heavy metal health risks and impacts in 1989–2018. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 276, 123249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saletnik, B.; Zaguła, G.; Bajcar, M.; Puchalski, C. Accumulation of cadmium, lead and mercury in seedlings of selected sugar beet varieties as a result of simulated soil contamination. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Food Sci. 2021, 2021, 351–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duffus, J.H. “Heavy metals” a meaningless term?(IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2002, 74, 793–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pourret, O. On the necessity of banning the term “heavy metal” from the scientific literature. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alhogbi, B.G. Potential of coffee husk biomass waste for the adsorption of Pb (II) ion from aqueous solutions. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2017, 6, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukola, D.; Zaid, A.; Olalekan, E.; Falilu, A. Consequences of Anthropogenic Activities on Fish and the Aquatic Environment. Poult Fish Wildl. Sci. 2015, 3, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burri, N.M.; Weatherl, R.; Moeck, C.; Schirmer, M. A review of threats to groundwater quality in the anthropocene. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 684, 136–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonone, S.S.; Jadhav, S.; Sankhla, M.S.; Kumar, R. Water contamination by heavy metals and their toxic effect on aquaculture and human health through food Chain. Lett. Appl. NanoBioScience 2020, 10, 2148–2166. [Google Scholar]
- Vardhan, K.H.; Kumar, P.S.; Panda, R.C. A review on heavy metal pollution, toxicity and remedial measures: Current trends and future perspectives. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 290, 111197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarubbo, L.; Rocha, R., Jr.; Luna, J.; Rufino, R.D.; Santos, V.; Banat, I.M. Some aspects of heavy metals contamination remediation and role of biosurfactants. Chem. Ecol. 2015, 31, 707–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldrian, P. Interactions of heavy metals with white-rot fungi. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2003, 32, 78–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathawara, N.; Parikh, D.; Agarwal, Y. Essential heavy metals in environmental samples from Western India. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2004, 73, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, M.; Salehi, T.; Aminzare, M.; Raeisi, M.; Afshari, A. Contamination of toxic heavy metals in various foods in Iran: A review. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. Eval. 2017, 9, 1692–1697. [Google Scholar]
- Nosalewicz, A.; Kosynets, O.; Nosalewicz, M. Effect of various concentrations of lead and cadmium on early growth of maize. Acta Agrophys 2008, 11, 715–723. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, A.; Wang, Y.; Tan, S.N.; Mohd Yusof, M.L.; Ghosh, S.; Chen, Z. Phytoremediation: A promising approach for revegetation of heavy metal-polluted land. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Buono, D.; Puglia, D.; Bartucca, M.L. Lignin for metal ion remediation in aqueous systems. In Micro and Nanolignin in Aqueous Dispersions and Polymers; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 325–356. [Google Scholar]
- Yantasee, W.; Lin, Y.; Hongsirikarn, K.; Fryxell, G.E.; Addleman, R.; Timchalk, C. Electrochemical sensors for the detection of lead and other toxic heavy metals: The next generation of personal exposure biomonitors. Environ. Health Perspect. 2007, 115, 1683–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sall, M.L.; Diaw, A.K.D.; Gningue-Sall, D.; Efremova Aaron, S.; Aaron, J.-J. Toxic heavy metals: Impact on the environment and human health, and treatment with conducting organic polymers, a review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 29927–29942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaishankar, M.; Tseten, T.; Anbalagan, N.; Mathew, B.B.; Beeregowda, K.N. Toxicity, mechanism and health effects of some heavy metals. Interdiscip. Toxicol. 2014, 7, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tóth, G.; Hermann, T.; Da Silva, M.; Montanarella, L.J.E.I. Heavy metals in agricultural soils of the European Union with implications for food safety. Environ. Int. 2016, 88, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Bravo, F.; Ruz, M.; Morán-Jiménez, M.; Olivares, M.; Rebolledo, A.; Codoceo, J.; Sepúlveda, V.; Jenkin, A.; Santos, J.; Fontanellas, A. Association between aminolevulinate dehydrase genotypes and blood lead levels in children from a lead-contaminated area in Antofagasta, Chile. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2004, 47, 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onalaja, A.O.; Claudio, L. Genetic susceptibility to lead poisoning. Environ. Health Perspect. 2000, 108, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Needleman, H. Lead poisoning. Annu. Rev. Med. 2004, 55, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boldyrev, M. Lead: Properties, history, and applications. Wiki J. Sci. 2018, 1, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, C. The elements. In Handbook of Chemistry and Physics; CRC Press: Cleveland, OH, USA, 2000; p. 81. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh, M.K. Atomic Mass of the Elements. In HPLC Methods on Drug Analysis; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1992; pp. 573–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guruswamy, S. Engineering Properties and Applications of Lead Alloys; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Sobolev, V. Thermophysical properties of lead and lead–bismuth eutectic. J. Nucl. Mater. 2007, 362, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.W.; An, J.; Chua, C.K.; Tran, T. Metallic nanoparticle inks for 3D printing of electronics. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2019, 5, 1800831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.; Khan, E.; Ilahi, I. Environmental chemistry and ecotoxicology of hazardous heavy metals: Environmental persistence, toxicity, and bioaccumulation. J. Chem. 2019, 2019, 6730305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pandey, G.; Madhuri, S. Heavy metals causing toxicity in animals and fishes. Res. J. Anim. Vet. Fish. Sci. 2014, 2, 17–23. [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald, E.; Caffrey, J.; Nesaratnam, S.; McLoughlin, P. Copper and lead concentrations in salt marsh plants on the Suir Estuary, Ireland. Environ. Pollut. 2003, 123, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Gupta, D.; Tian, S.; Yang, X.-e.; Li, T. Lead tolerance and physiological adaptation mechanism in roots of accumulating and non-accumulating ecotypes of Sedum alfredii. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2012, 19, 1640–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamhamdi, M.; Bakrim, A.; Aarab, A.; Lafont, R.; Sayah, F. Lead phytotoxicity on wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) seed germination and seedlings growth. Comptes Rendus Biol. 2011, 334, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, G.; Li, G.; Ma, R.; Kong, Y.; Yuan, J. Selection of sensitive seeds for evaluation of compost maturity with the seed germination index. Waste Manag. 2021, 136, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranal, M.A.; Santana, D.G.D. How and why to measure the germination process? Braz. J. Bot. 2006, 29, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Isaza, G.G. Efecto del plomo sobre la imbibición, germinación y crecimiento de Phaseolus vulgaris L. y Zea mays L. Biotecnol. Veg. 2020, 13, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, P.; Dubey, R.S. Lead toxicity in plants. Braz. J. Plant Physiol. 2005, 17, 35–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Usharani, K.; Roopashree, K.; Naik, D. Role of soil physical, chemical and biological properties for soil health improvement and sustainable agriculture. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 2019, 8, 1256–1267. [Google Scholar]
- Bauder, T.A.; Waskom, R.M.; Sutherland, P.L.; Davis, J.G. Irrigation Water Quality Criteria; Colorado State University Extension: Fort Collins, CO, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, H.; Kim, H.; Jang, T. Irrigation water quality standards for indirect wastewater reuse in agriculture: A contribution toward sustainable wastewater reuse in South Korea. Water Air 2016, 8, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oshunsanya, S.O. Introductory chapter: Relevance of soil pH to agriculture. In Soil pH for Nutrient Availability and Crop Performance; Oshunsanya, S., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, D.; Hao, Z.; Wang, J.; Tao, J. Effects of pH in irrigation water on plant growth and flower quality in herbaceous peony (Paeonia lactiflora Pall.). Sci. Hortic. 2013, 154, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, M.; Delatorre Castillo, J.P.; Sepúlveda, I.; Low, C.; Ruiz, K.B.; Delatorre Herrera, J. Efectos de distintas concentraciones de boro y pH en el crecimiento de Zea mays var. Capia blanco, un maíz ancestral de Chile. Idesia 2021, 39, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayers, R.S.; Westcot, D.W. Water Quality for Agriculture; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Dotor-López, G.; Zúñiga-Cruz, A.; Cruz-Monterrosa, R.; Díaz-Ramírez, M.; Rayas-Amor, A. Quantification of heavy metals in the cultivation of strawberry (Fragaria× ananassa Duch. var. festival) in Tenancingo and Villa Guerrero, Estado de México. Agroproductividad 2017, 10, 29–33. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.; Al Azzawi, T.N.I.; Imran, M.; Hussain, A.; Mun, B.-G.; Pande, A.; Yun, B.-W. Effects of lead (Pb)-induced oxidative stress on morphological and physio-biochemical properties of rice. Biocell 2021, 45, 1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaboudi, K.A.; Ahmed, B.; Brodie, G. Effect of biochar on Pb, Cd and Cr availability and maize growth in artificial contaminated soil. Ann. Agric. Sci. 2019, 64, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salas-Martínez, F.; Valdés-Rodríguez, O.A.; Palacios-Wassenaar, O.M.; Márquez-Grajales, A. Analysis of the Evolution of Drought through SPI and Its Relationship with the Agricultural Sector in the Central Zone of the State of Veracruz, Mexico. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzzon, F.; Arandia Rios, L.W.; Caviedes Cepeda, G.M.; Céspedes Polo, M.; Chavez Cabrera, A.; Muriel Figueroa, J.; Medina Hoyos, A.E.; Jara Calvo, T.W.; Molnar, T.L.; Narro León, L.A. Conservation and use of Latin American maize diversity: Pillar of nutrition security and cultural heritage of humanity. Agronomy 2021, 11, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaramillo Albuja, J.G.; Peña Olvera, B.V.; Hernández Salgado, J.H.; Díaz Ruiz, R.; Espinosa Calderón, A. Caracterización de productores de maíz de temporal en Tierra Blanca, Veracruz. Rev. Mex. Cienc. Agríc. 2018, 9, 911–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gobierno del Estado de Veracruz. Plan Veracruzano de Desarrollo 2019–2024; Gobierno del Estado de Veracruz: Veracruz, México, 2019.
- Mohammed-Ridha, M.J.; Ahmed, A.S.; Raoof, N.N. Investigation of the thermodynamic, kinetic and equilibrium parameters of batch biosorption of Pb (II), Cu (II), and Ni (II) from aqueous phase using low cost biosorbent. Al-Nahrain J. Eng. Sci. 2017, 20, 298–310. [Google Scholar]
- Janmohammadi, M.; Zahed, S.-M.; Ahadnezhad, A.; Yousefzadeh, S.; Sabaghnia, N. Influence of chemical and organic fertilizer on growth, yield and essential oil of dragonhead (Dracocephalum moldavica L.) plant. Acta Agric. Slov. 2015, 103, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, F.; Silberbush, M. Response of maize to foliar vs. soil application of nitrogen–phosphorus–potassium fertilizers. J. Plant Nutr. 2002, 25, 2333–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tridente, A. FIcha técnica Agroquímica; Tridente S.A. de C.V.: Mexico City, Mexico, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Sant, G.; Patapy, C.; Gianocca, C.; Scrivener, K.L. The influence of sodium and potassium hydroxide on alite hydration: Experiments and simulations. Cem. Concr. Res. 2012, 42, 1513–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafitte, H. Identificación de Problemas en la Producción de Maíz Tropical: Guía de Campo; CIMMYT: Mexico City, Mexico, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Snedecor, G.W. Statistical methods: Applied to experiments in agriculture and biology; The Iowa State College Press: Ames, IA, USA, 1956. [Google Scholar]
- Kozak, M.; Krzanowski, W.; Tartanus, M. Use of the correlation coefficient in agricultural sciences: Problems, pitfalls and how to deal with them. An. Acad. Bras. Ciênc. 2012, 84, 1147–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, B.F.; Joiner, B.L.; Cryer, J.D. MINITAB Handbook: Update for Release; Cengage Learning: Boston, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Jariel, D.; Wallace, S.; Jones, U.; Samonte, H. Growth and nutrient composition of maize genotypes in acid nutrient solutions. Agron. J. 1991, 83, 612–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
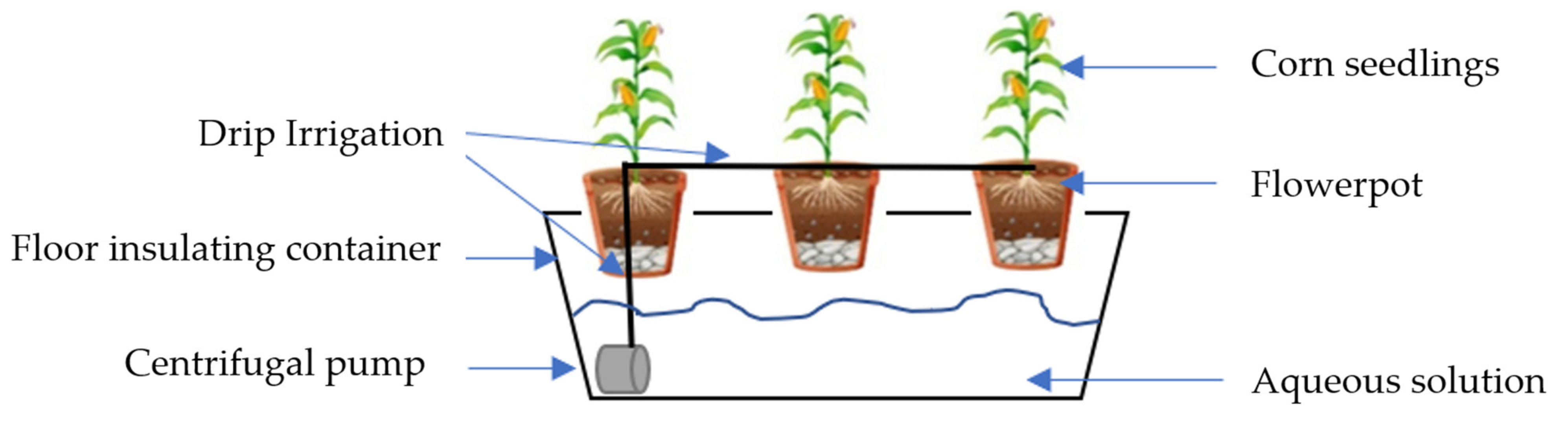





| Parameter | Average | Standard Deviation | Minimum Value | Maximum Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diameter (mm) | 1.48 | 0.27 | 1.0 | 1.9 |
| Weight (g) | 0.4730 | 0.08554 | 0.3547 | 0.6821 |
| Substance | Chemical Symbol | Atomic Mass (g/mol) | Pb/Pb Ratio (NO3)2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lead nitrate | Pb(NO3)2 | 331.2 | |
| Lead | Pb | 207.2 | 1.5985 |
| Concentrations | Pb/L (g L −1) | Pb(NO3)2/L (g) | Pb(NO3)2/20 L (g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| P1 (Control) | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| P2 | 0.333 | 0.532 | 10.646 |
| P3 | 0.666 | 1.065 | 21.291 |
| P4 | 1000 | 1.598 | 31.969 |
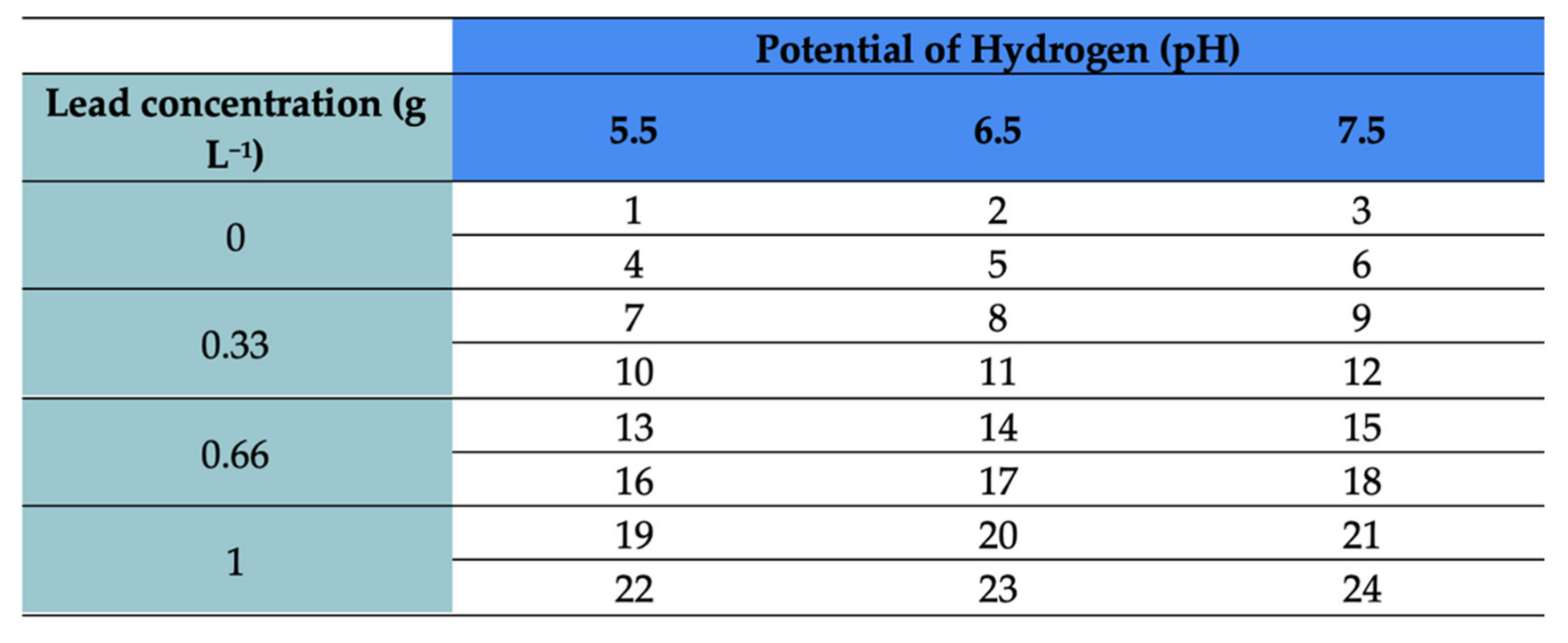
| Double Bottom Irrigation Unit | Lead Concentration (g L−1) | Potential of Hydrogen (pH) |
|---|---|---|
| U1 | 0 | 5.5 |
| U2 | 0 | 6.5 |
| U3 | 0 | 7.5 |
| U4 | 0.33 | 5.5 |
| U5 | 0.33 | 6.5 |
| U6 | 0.33 | 7.5 |
| U7 | 0.66 | 5.5 |
| U8 | 0.66 | 6.5 |
| U9 | 0.66 | 7.5 |
| U10 | 1 | 5.5 |
| U11 | 1 | 6.5 |
| U12 | 1 | 7.5 |
| pH | Equation | R2 | p-Value | Pearson r | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5.5 | Blade Lenghth = 32.962 − 2.36 CPb | 67.06 | 0.000 | −0.819 | 0.181 |
| 6.5 | Blade Lenghth = 35.30 − 3.652 CPb | 99.80 | 0.000 | −0.999 | 0.001 |
| 7.5 | Blade Lenghth = 45.40 − 6.14 CPb | 91.72 | 0.000 | −0.958 | 0.042 |
| 5.5 | Seedling height = 32.526 − 9.29 CPb | 94.38 | 0.001 | −0.971 | 0.029 |
| 6.5 | Seedling Lenghth = 41.17 − 10.62 CPb | 59.85 | 0.009 | −0.774 | 0.226 |
| 7.5 | Seedling Lenght = 46.49 − 14.35 CPb | 90.69 | 0.002 | −0.952 | 0.048 |
| 5.5 | Stem circumference = 5.833 − 1.976 CPb | 94.38 | 0.001 | −0.918 | 0.082 |
| 6.5 | Stem circumference = 7.659 − 3.686 CPb | 90.90 | 0.004 | −0.953 | 0.047 |
| 7.5 | Stem circumference = 8.378 − 4.077 CPb | 93.18 | 0.002 | −0.965 | 0.035 |
| 5.5 | Root = 16.397 − 1.048 CPb | 88.63 | 0.000 | −0.941 | 0.059 |
| 6.5 | Root = 18.149 − 1.81 CPb | 42.65 | 0.003 | −0.653 | 0.347 |
| 7.5 | Root = 20.202 − 1.66 CPb | 56.95 | 0.001 | −0.755 | 0.245 |
| CPb | Equation | R2 | p-Value | Pearson r | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Blade Length = −2.8 + 6.20 pH | 92.31 | 0.849 | 0.961 | 0.179 |
| 0.33 | Blade Length = −0.9 + 5.4 pH | 82.50 | 0.969 | 0.980 | 0.096 |
| 0.66 | Blade Length = 5.4 + 4.61 pH | 82.43 | 0.765 | 0.908 | 0.275 |
| 1 | Blade Length = 4.4 + 4.48 pH | 88.39 | 0.750 | 0.998 | 0.042 |
| 0 | Seedling Length = −3.93 + 6.507 pH | 99.23 | 0.485 | 0.996 | 0.056 |
| 0.33 | Seedling Length = −5.0 + 6.58 pH | 79.54 | 0.856 | 0.892 | 0.299 |
| 0.66 | Seedling Length = −3.4 + 5.85 pH | 92.31 | 0.818 | 0.961 | 0.179 |
| 1 | Seedling Length = 1.10 + 3950 pH | 96.43 | 0.862 | 0.982 | 0.121 |
| 0 | Stem circumference = −0.33 + 1.200 pH | 94.53 | 0.889 | 0.972 | 0.150 |
| 0.33 | Stem circumference = −0.88 + 1.100 pH | 93.56 | 0.722 | 0.967 | 0.163 |
| 0.66 | Stem circumference = 1.608 + 0.4500 pH | 99.59 | 0.075 | 0.998 | 0.041 |
| 1 | Stem circumference = 2.808 + 0.2500 pH | 98.68 | 0.043 | 0.993 | 0.073 |
| 0 | Root = 6.958 + 1.750 pH | 99.32 | 0.086 | 0.997 | 0.052 |
| 0.33 | Root = 5.96 + 1.750 pH | 85.47 | 0.424 | 0.924 | 0.249 |
| 0.66 | Root = 3.208 + 2.250 pH | 99.18 | 0.182 | 0.998 | 0.041 |
| 1 | Root = 8.38 + 1.250 pH | 89.29 | 0.208 | 0.945 | 0.212 |
| Parameter | Double Bottom Irrigation Unit | Difference (cm) | Decrease Percentage (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| U1 | U10 | ||||
| pH 5.5 | Blade length | 32.3 | 30 | 2.3 | 7.2% |
| Seedling height | 32.2 | 22.4 | 9.8 | 30.5% | |
| Stem circumference | 6.1 | 4.2 | 1.9 | 31.1% | |
| Root | 16.5 | 15.5 | 1 | 6.1% | |
| U2 | U11 | ||||
| pH 6.5 | Blade length | 35.4 | 31.7 | 3.7 | 10.5% |
| Seedling height | 37.7 | 27.7 | 10 | 26.7% | |
| Stem circumference | 7.8 | 4.4 | 3.4 | 43.6% | |
| Root | 18.5 | 16 | 2.5 | 13.5% | |
| U3 | U12 | ||||
| pH 7.5 | Blade length | 44.7 | 39 | 5.7 | 12.8% |
| Seedling height | 45.2 | 30.3 | 14.9 | 33.0% | |
| Stem circumference | 8.5 | 4.7 | 3.8 | 44.7% | |
| Root | 20 | 18 | 2 | 10.0% | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hernández-Pitalúa, D.; Hernández-Orduña, M.G.; Martínez-Escalante, G.A.; Lagunes-Gómez, I. Influence of Lead (Pb) and Its Relationship with the pH of Water on the Growth of Creole Maize (Zea mays L.). Agriculture 2022, 12, 749. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12060749
Hernández-Pitalúa D, Hernández-Orduña MG, Martínez-Escalante GA, Lagunes-Gómez I. Influence of Lead (Pb) and Its Relationship with the pH of Water on the Growth of Creole Maize (Zea mays L.). Agriculture. 2022; 12(6):749. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12060749
Chicago/Turabian StyleHernández-Pitalúa, Daniel, María Graciela Hernández-Orduña, Gustavo Alonso Martínez-Escalante, and Isabel Lagunes-Gómez. 2022. "Influence of Lead (Pb) and Its Relationship with the pH of Water on the Growth of Creole Maize (Zea mays L.)" Agriculture 12, no. 6: 749. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12060749
APA StyleHernández-Pitalúa, D., Hernández-Orduña, M. G., Martínez-Escalante, G. A., & Lagunes-Gómez, I. (2022). Influence of Lead (Pb) and Its Relationship with the pH of Water on the Growth of Creole Maize (Zea mays L.). Agriculture, 12(6), 749. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12060749








