Reasonable Nitrogen Regime in the Main Crop Increased Grain Yields in Both Main and Ratoon Rice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site and Materials
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Sampling and Measurements
2.3.1. Root Oxidation Activity (ROA)
2.3.2. Nonstructural Carbohydrate (NSC) Accumulation in the Stem and Leaf
2.3.3. Regenerated Buds
2.3.4. Yield and Its Components
2.3.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Differences in Experimental Factors
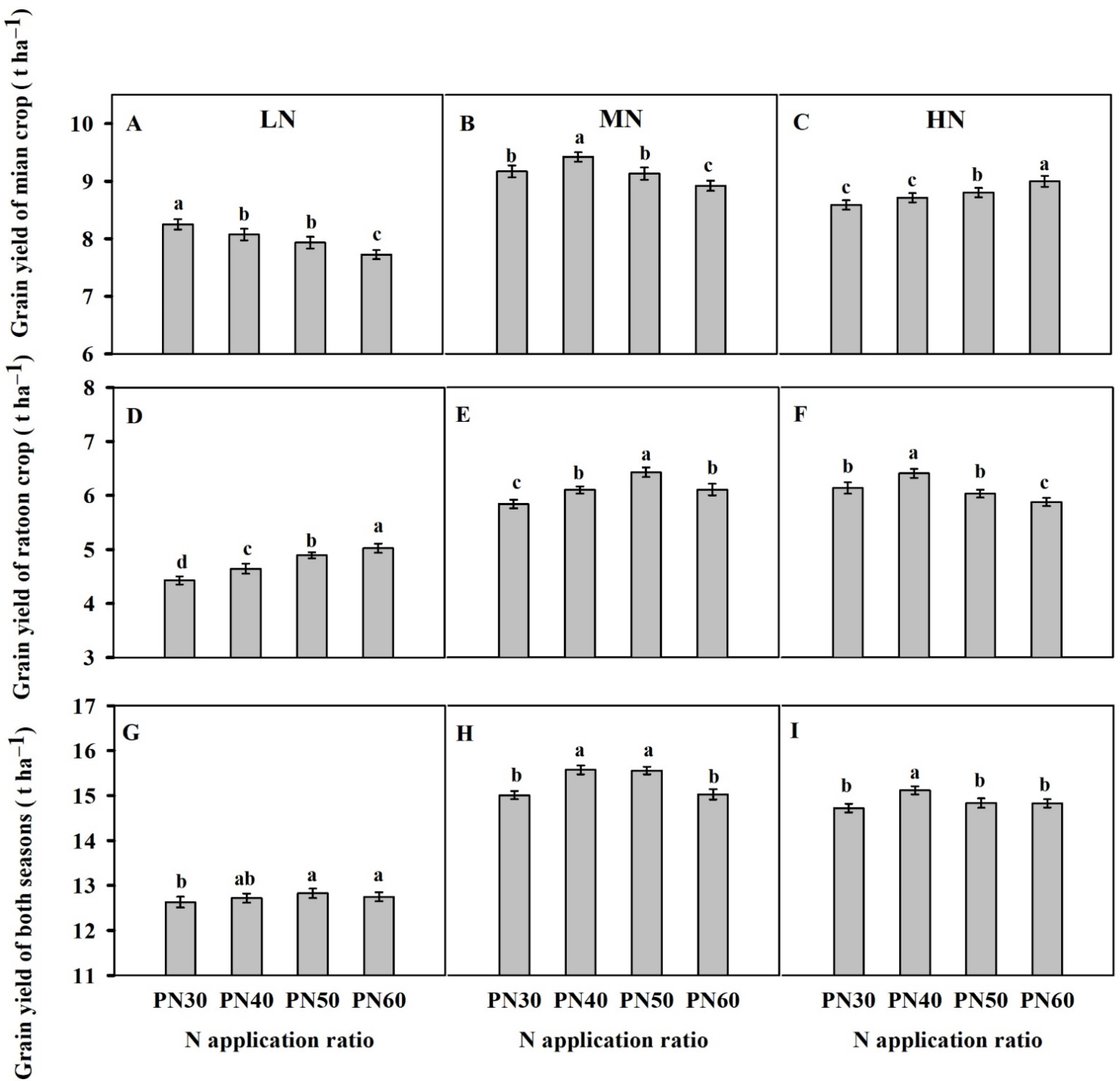
3.2. Yield and Its Components in the Two Seasons
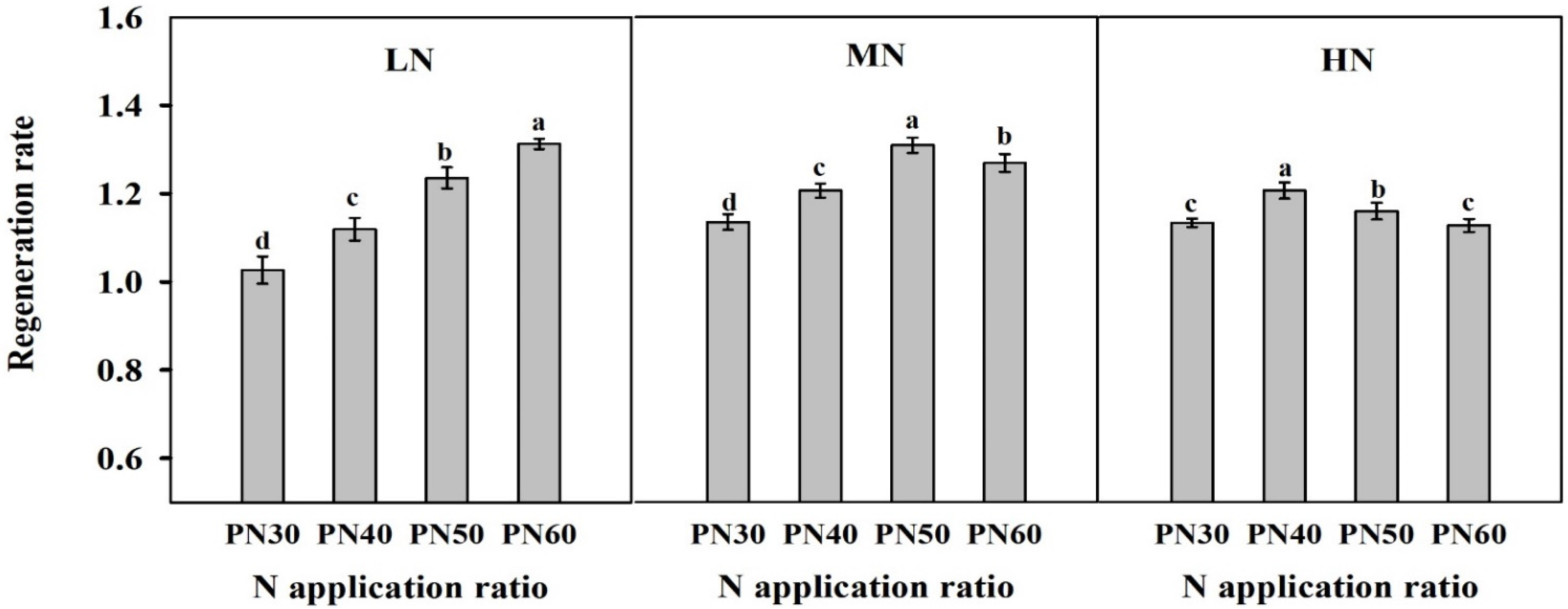
3.3. Regeneration Rate and Its Relationship with Panicle Number and Yield in the Ratoon Crop
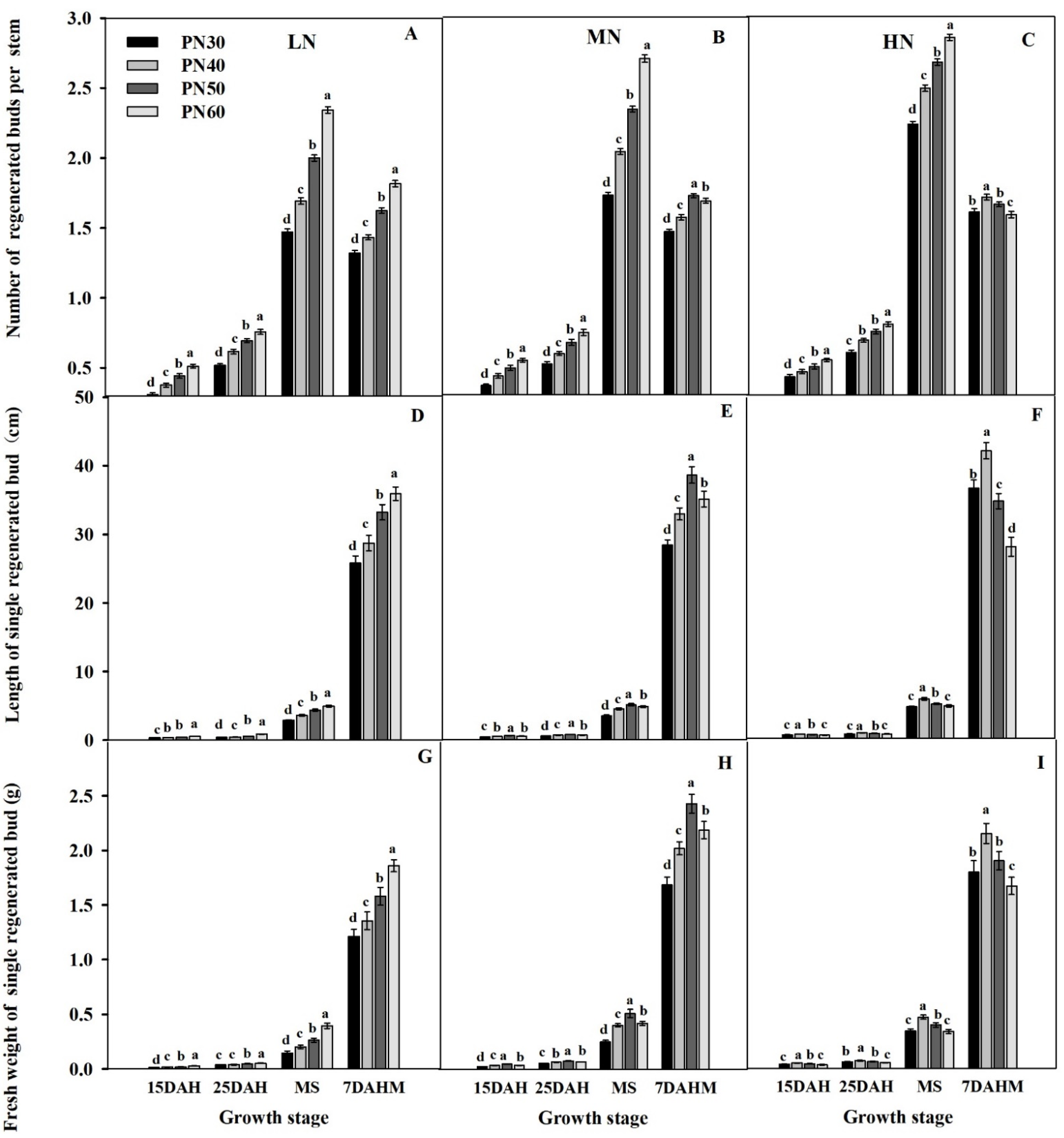
3.4. Regenerated Buds and Its Relationship with Regeneration Rate
3.4.1. Number, Length, and Fresh Weight of Regenerated Buds
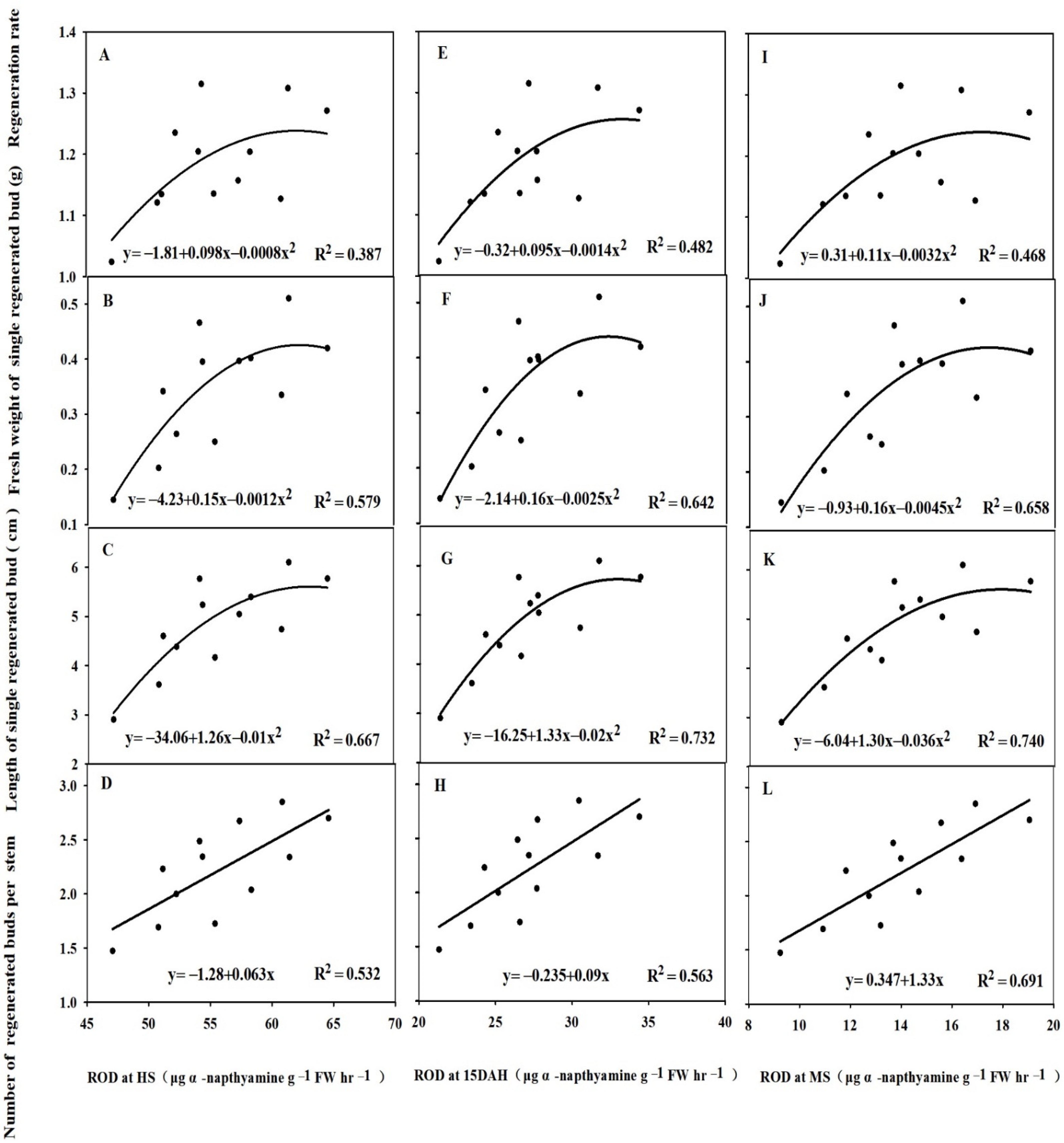
3.4.2. Correlations between the Regeneration Rate and the Length, Fresh Weight, and Number of Regenerated Buds
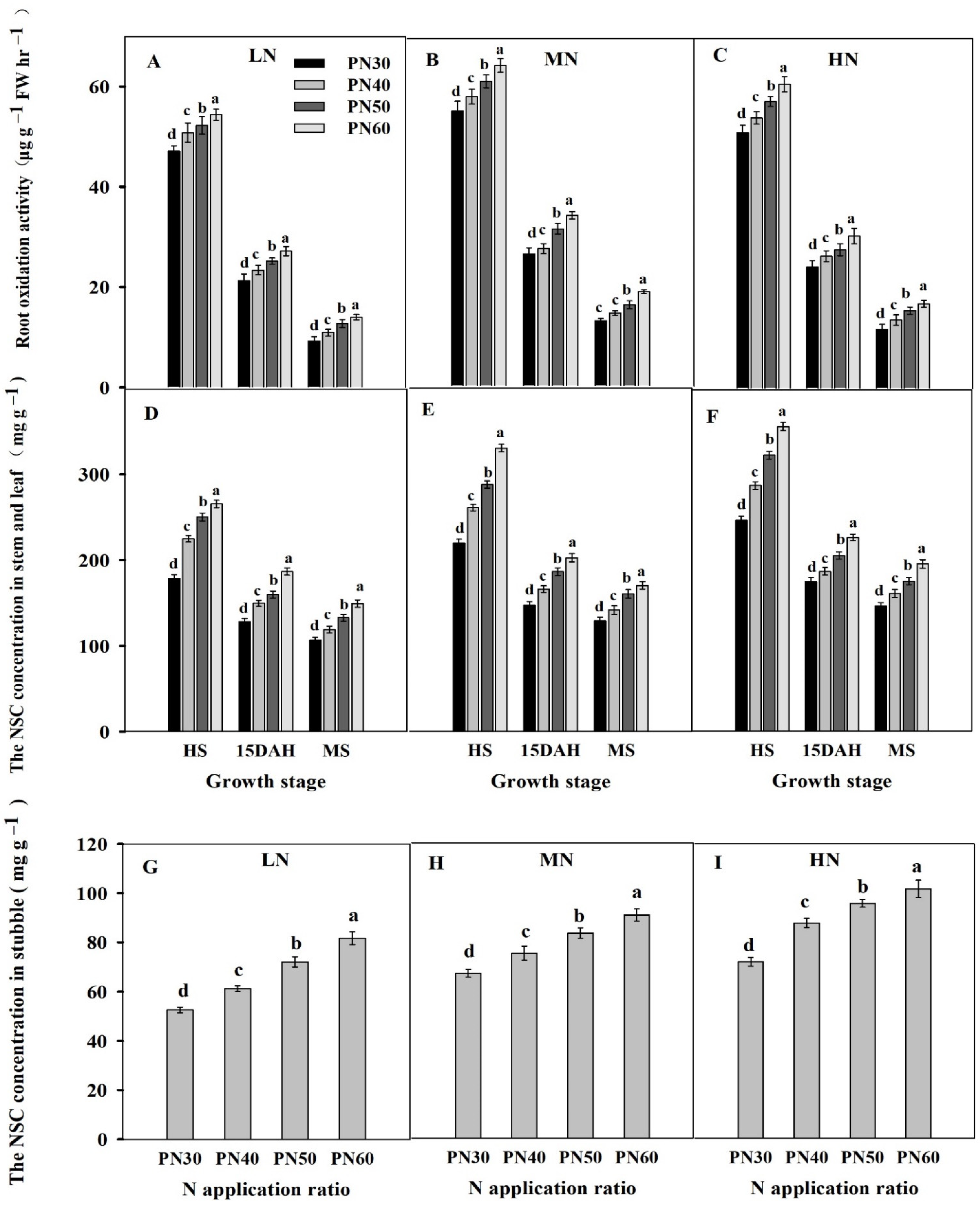
3.5. Effects of N Regime on the ROA and NSC Concentration in the Stem and Leaf of the Main Crop
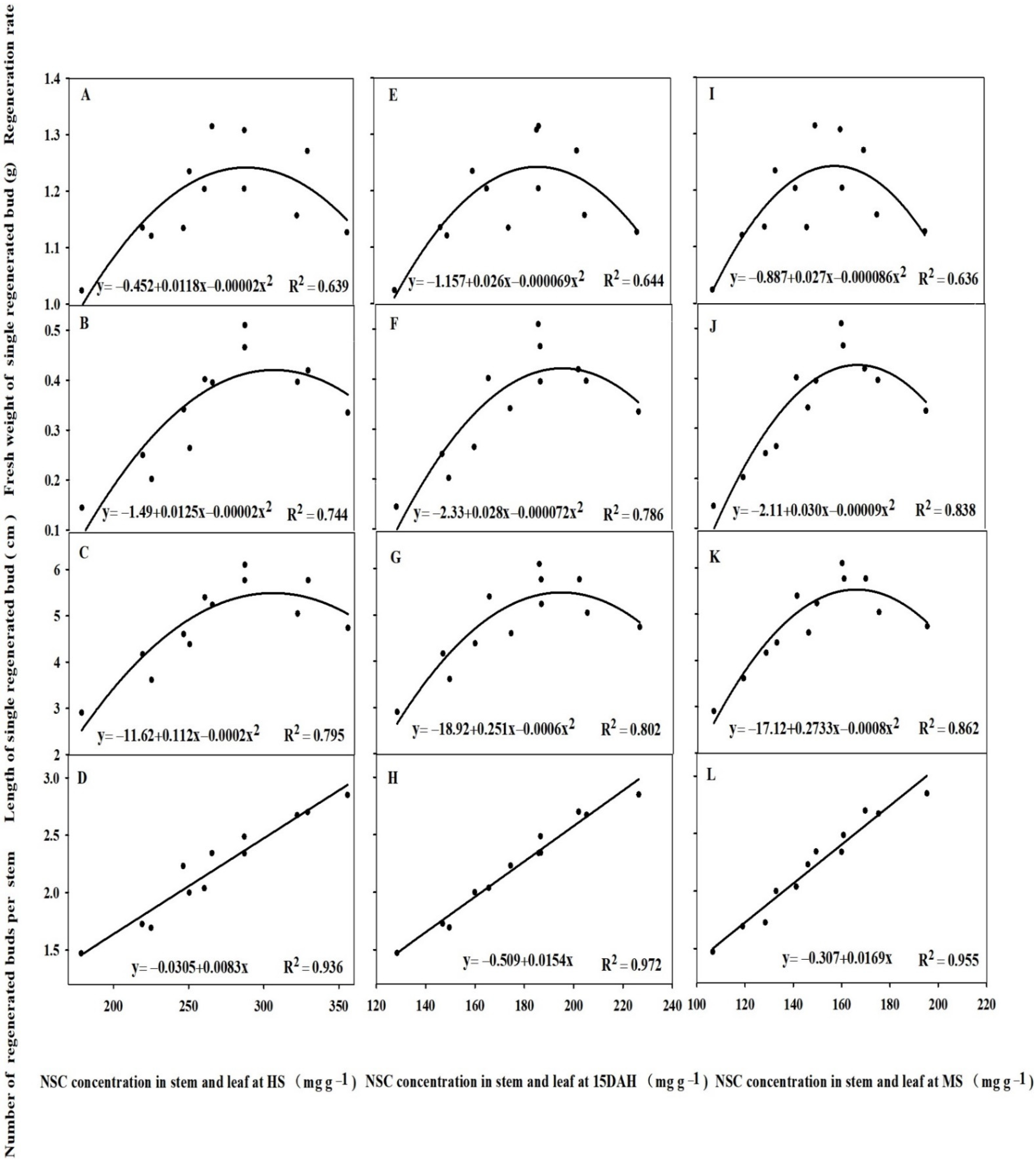
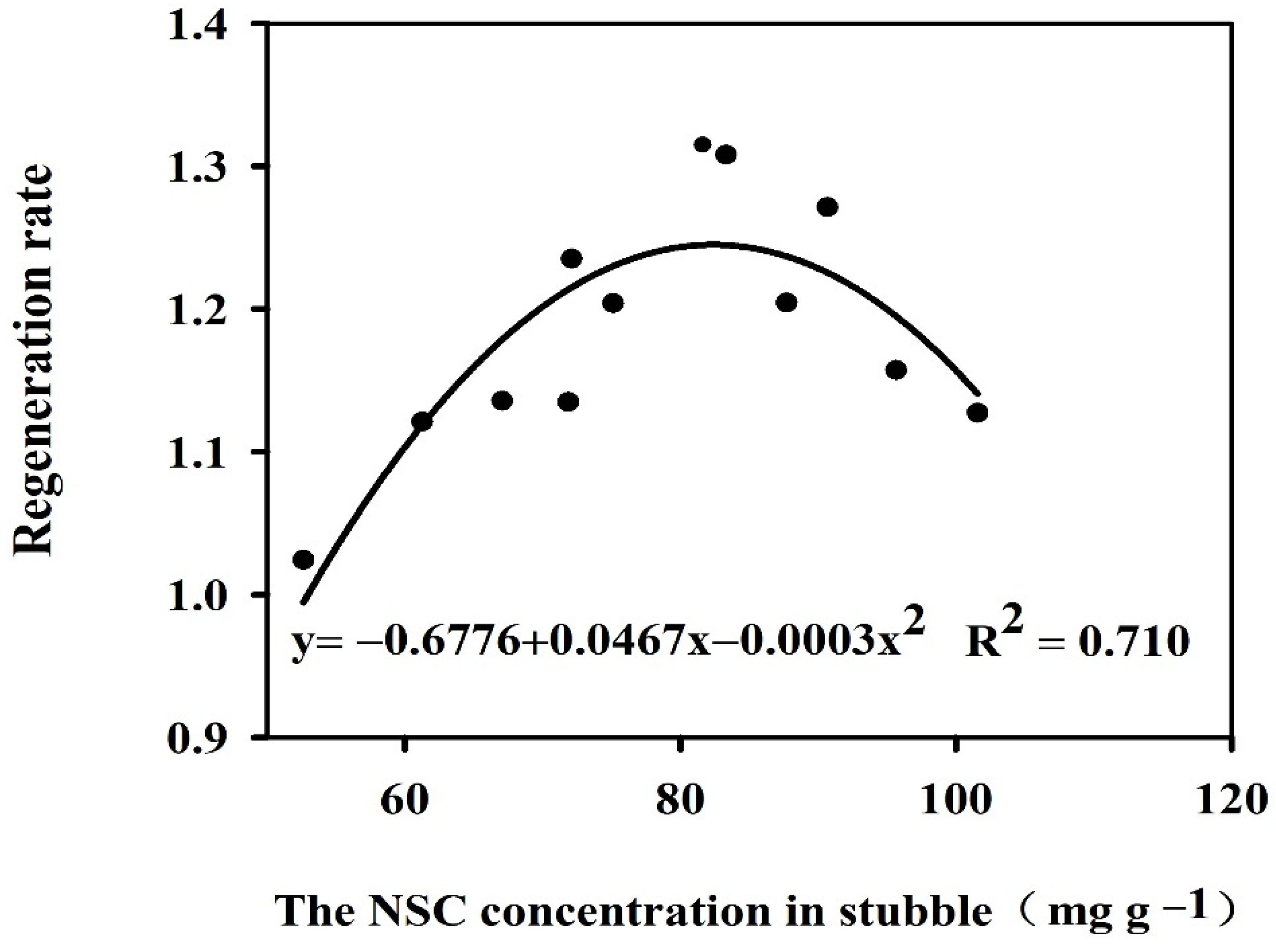
3.6. Relationships between the ROA and NSC Concentration in Stem and Leaf of the Main Crop and Regeneration Rate of the Ratoon Crop
3.7. Effects of N Regime in the Main Crop on the Nitrogen Use Efficiency in Main and Ratoon Corp
4. Discussion
4.1. Reasonable N Regime in the Main Crop Improved the Growth and Development of Regenerated Buds
4.2. Reasonable N Regime in the Main Crop Improved the Regeneration Rate
4.3. Effects of N Regime in the Main Crop on the Yield of the Main and Ratoon Crops
4.4. Effects of the N Regime in the Main Crop on the N Use Efficiency of the Main and Ratoon Crops
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sanderine, N. Global food supply and the impacts of increased use of biofuels. Energy 2011, 37, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.F.; Xu, N.X.; Ding, C.L.; Gu, H.G.; Zhang, W.J.; Sun, L. Developing ratoon rice as forage in subtropical and temperate areas. Field Crops Res. 2020, 245, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.J.; Li, X.X.; Cao, J.; Li, Y.; Huang, J.L.; Peng, S.B. High nitrogen input reduces yield loss from low temperature during the seedling stage in early-season rice. Field Crops Res. 2018, 228, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.M.; Amelia, H.; Nese, S. Rice yield formation under high day and night temperatures—A prerequisite to ensure future food security. Plant Cell Environ. 2020, 43, 1595–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.B. Ratoon rice production in central China: Environmental sustainability and food production. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 764, 142850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, A.B.; Wang, W.Q.; Jiang, G.L.; Sun, H.J.; Jiang, M.; Man, J.G.; Cui, K.H.; Huang, J.L.; Peng, S.B.; Nie, N.X. Source-sink regulation and its effects on the regeneration ability of ratoon rice. Field Crops Res. 2019, 236, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golam, F.; Rosna, T.; Zakaria, P. Rice ratoon crop: A sustainable rice production system for tropical hill agriculture. Sustainability 2014, 6, 5785–5800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, X.C.; Yu, G.L.; Wang, H.; Feng, D.Q.; Zhao, H.Y.; Liu, L.J. Agronomic and physiological characteristics of high-yielding ratoon rice varieties. Agron. J. 2021, 113, 5063–5075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.Q.; He, A.B.; Jiang, G.L.; Sun, H.J.; Jiang, M.; Man, J.G.; Ling, X.X.; Cui, K.H.; Huang, J.L.; Peng, S.B.; et al. Ratoon rice technology: A green and resource-efficient way for rice production. Adv. Agron. 2020, 159, 135–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.W.; Pan, Y.P.; Chen, H.F.; Zhang, Z.X.; Fang, C.X.; Shao, C.H.; Amjad, H.; Lin, W.W.; Lin, W.X. Physiochemical mechanisms involved in the improvement of grain-filling, rice quality mediated by related enzyme activities in the ratoon cultivation system. Field Crops Res. 2020, 258, 107962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dustin, L.H.; Jason, A.B.; Sterling, B. Evaluation of main-crop stubble height on ratoon rice growth and development. Field Crops Res. 2009, 114, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Jiang, P.; Gou, X.Y.; Zhou, X.B.; Zhu, Y.C.; Liu, M.; Xiong, H.; Xu, F.X. Integrated water and nitrogen management practices to enhance yield and environmental goals in rice–ratoon rice systems. Agron. J. 2019, 111, 2821–2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; He, A.B.; Wang, W.Q.; Peng, S.B.; Huang, J.L.; Cui, K.H.; Nie, L.X. Comparisons of regeneration rate and yields performance between inbred and hybrid rice cultivars in a direct seeding rice-ratoon rice system in central China. Field Crops Res. 2018, 223, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.C.; Zheng, C.; Xiao, S.; Sun, Y.T.; Huang, J.L.; Peng, S.B. Agronomic responses of ratoon rice to nitrogen management in central China. Field Crops Res. 2019, 241, 107569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gribaldi, G.; Nurlaili, N.; Firnawati, S.; Nurmala, D.; Ardi, A. Strategy of nitrogen fertilizer application to increase growth and yield of rice in ratoon system at tidal swampland. Aust. J. Crop Sci. 2020, 16, 1004–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jason, A.B.; Patrick, K.B. Ratoon rice response to nitrogen fertilizer. Crop Manag. 2006, 5, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.W.; Wu, J.Y.; Chen, H.F.; Zhang, Z.X.; Fang, C.X.; Shao, C.H.; Lin, W.W.; Weng, P.Y.; Muhammad, U.K.; Lin, W.X. Optimal management of nitrogen fertilizer in the main rice crop and its carrying-over effect on ratoon rice under mechanized cultivation in Southeast China. J. Integr. Agric. 2022, 21, 351–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.W.; Wu, J.Y.; Chen, H.F.; Zhang, Z.X.; Fang, C.X.; Shao, C.H.; Lin, W.W.; Weng, P.Y.; Lin, W.X. Nitrogen fertilizer management for main crop rice and its carrying-over effect on rhizosphere function and yield of ratoon rice. Chin. J. Rice Sci. 2021, 35, 383–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.X.; Zhang, L.; Fan, Q.H.; Xiong, H.; Zhou, X.B.; Zhu, Y.C.; Jiang, P.; Liu, M.; Guo, X.Y.; Xu, F.X. Effects of shift part of nitrogen fertilizer from basal-tillering to panicle initiation on grain yield of mid-season hybrid rice and ratooning rice. Chin. Rice 2014, 20, 48–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.F.; Yang, D.; Liang, Y.Y.; Zhang, Z.X.; Liang, K.J.; Lin, W.X. Effect of nitrogen application strategy in the first cropping rice on dry matter accumulation, grain yield and nitrogen utilization efficiency of the first cropping rice and its ratoon rice crop. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2010, 18, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Q.H. Theory and technology of rice precise and quantitative cultivation. Hybrid Rice 2010, 25, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.S.; Peng, S.B.; Zheng, C.; Xiang, H.S.; Huang, J.L.; Cui, K.H.; Wang, F. Effects of nitrogen fertilization for bud initiation and tiller growth on yield and quality of rice ratoon crop in central China. Field Crops Res. 2021, 272, 108286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramasamy, S.; Berge, H.F.M.; Purushothaman, S. Yield formation in rice in response to drainage and nitrogen application. Field Crops Res. 1997, 51, 65–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.F.; Cui, K.H.; Wei, D.; Huang, J.L.; Xiang, J.; Nie, L.X. Relationships of non-structural carbohydrates accumulation and translocation with yield formation in rice recombinant inbred lines under two nitrogen levels. Physiol. Plant 2011, 141, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, F.X.; Xiong, H.; Hong, S. Relationship between axillary bud growth matter accumulation of stem-sheath after heading of main crop hybrid rice. Chin. J. Rice Sci. 1997, 11, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Xiong, H.; Xu, F.X.; Zhu, Y.C.; Guo, X.Y.; Zhou, X.B.; Liu, M. Relationship between living rate of bud and emergence rate of ratoon rice and characteristics of the first cropping mid-season hybrid rice. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2012, 13, 1873–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.L.; Tu, N.M.; Zhang, S.T. Ratooning properties of axillary buds in hybrid rice. Chin. J. Rice Sci. 2005, 19, 323–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, F.T.; Jund, M.F. Rice ratoon crop yield linked to main crop stem carbohydrates. Crop Sci. 1993, 33, 150–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.S.; Lin, W.; Zhuo, C.Y.; Fang, X.J.; Lin, W.X. The correlation of dry biomass and activity of root system with grain yield in ratoon rice. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2004, 22, 112–115. [Google Scholar]
- Nakano, H.; Tanaka, R.; Wada, H.; Okami, M.; Nakagomi, K.; Hakata, M. Breaking rice yield barrier with the ratooning method under changing climatic conditions: A paradigm shift in rice-cropping systems in southwestern Japan. Agron. J. 2020, 112, 3975–3992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.X.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, X.B.; Guo, X.Y.; Zhu, Y.C.; Liu, M.; Xiong, H. The ratoon rice system with high yield and high efficiency in China: Progress, trend of theory and technology. Field Crops Res. 2021, 272, 108282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Peng, X.L.; Liu, Y.Y.; Zhang, H.; Cheng, L.N. Effects of N application at later stage on absorbability of rice root in cold area. Soils 2011, 43, 548–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Xia, M.; Zhang, H.C.; Cao, L.Q.; Guo, B.W.; Wei, H.Y.; Chen, H.C.; Dai, Q.G.; Huo, Z.Y.; Xu, K.; et al. Effect of nitrogen application regime on yield, nitrogen absorption and utilization of mechanical pot-seedling transplanting rice with good taste quality. Acta Agron. Sin. 2016, 42, 1666–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.D.; Wang, Y.L.; Zhang, Y.P.; Xiang, J.; Zhang, Y.K.; Zhu, D.F.; Chen, H.Z. The nitrogen topdressing mode of indica-japonica and indica hybrid rice are different after side-deep fertilization with machine transplanting. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Wang, Y.T.; Yin, H.Q.; Wang, S.X.; Wang, F.H.; Chen, X.G.; Wang, Y.; Yang, W.B.; Bai, T. Effect of nitrogen application rate on root morphological and physiological characteristics and yield of japonica rice in region along the yellow river. Henan Agric. Sci. 2017, 46, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.X.; Xiong, H.; Zhao, G.L.; Hong, S. A Study on the death mechanism of the axillary buds before harvest of the hybrid midseason rice and its improvement. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2000, 33, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.W.; Zhang, H.C.; Guo, B.W.; Xu, K.; Dai, Q.G.; Wei, H.Y.; Gao, H.; Hu, Y.J.; Cui, P.Y.; Huo, Z.Y. Effects of nitrogen level on yield and quality of japonica soft super rice. J. Integr. Agric. 2017, 16, 1018–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.L.; Gao, S.Y.; Ma, J.X.; Zhang, T.; Wang, T.Y.; Zhang, S.; Wu, Z.X. Effect of nitrogen application rates on the nitrogen utilization, yield and quality of rice. Food Nutr. Sci. 2021, 12, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.; Huang, X.; Chu, G.; Chen, S.; Xu, C.M.; Zhang, X.F.; Wang, D.Y. Effects of postponing topdressing-N on the yield of different types of japonica rice and its relationship with soil fertility. Agronomy 2019, 9, 868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, G.H.; Lin, J.J.; Xue, L.H.; Ding, Y.F.; Wang, S.H.; Yang, L.Z. Fate of basal N under split fertilization in rice with (15)N isotope tracer. Pedosphere 2018, 28, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, H.; Morita, S. Effects of planting time and nitrogen application on dry matter yield of the forage rice cultivar Tachiaoba in southwestern Japan. Plant Prod. Sci. 2009, 12, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.P.; Zhou, W.; Liang, G.Q.; Sun, J.W.; Wang, X.B.; He, P.; Xu, F.S.; Yu, X.C. Effects of nitrogen and density interactions on grain yield and nitrogen use efficiency of double-rice systems. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2015, 21, 763–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Wei, W.W. Effects of different nitrogen supply levels on soil inorganic nitrogen residue, nitrogen balance and yield of rice. J. Shandong Agric. Univ. 2019, 50, 566–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, G.C.; Chen, C.; Yuan, Q.M.; Yang, B.; Zhu, Z.K.; Cao, W.Y.; Zhong, J.; Zhou, J.; Luo, G.; Wang, Y.; et al. The effect of nitrogen fertilizer treatments on root traits and nitrogen use efficiency in indica rice varieties with high nitrogen absorption efficiency. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2016, 36, 642–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassman, K.G.; Peng, S.; Olk, D.C.; Ladha, J.K.; Reichardt, W.; Dobermann, A.; Singh, U. Opportunities for increased nitrogen-use efficiency from improved resource management in irrigated rice systems. Field Crops Res. 1998, 56, 7–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.X.; Xiong, H.; Zhang, L.; Guo, X.Y.; Zhu, Y.C.; Zhou, X.B.; Liu, M. Variation of nitrogen uptake and utilization efficiency of mid-season hybrid rice at different ecological sites under different nitrogen application levels. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2011, 12, 1001–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.Y.; Yu, Z.W. Effects of nitrogen rate on nitrogen fertilizer use of winter wheat and content of soil nitrate-N under different fertility condition. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2006, 26, 815–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.J.; Xu, W.; Tang, C.; Wang, Z.Q.; Yang, J.C. Effect of indigenous nitrogen supply of soil on the grain yield and fertilizer-N use efficiency in rice. Chin. J. Rice Sci. 2005, 12, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.B.; Buresh, R.J.; Huang, J.L.; Yang, J.C.; Zou, Y.B.; Zhong, X.H.; Wang, G.H.; Zhang, F.S. Research strategy in impoving fertilizer-nitrogen use efficiency of irrigated rice in China. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2002, 35, 1095–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| N Rates in Main Crop | Treatment Code | N Rates in Ratoon Crop | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total N Rate | Basal and Tillering Fertilizer | Panicle Fertilizer | Total N Rate | Bud Fertilizer | Seedling Fertilizer | |
| 100 (LN) | 70 (70) | 30 (30) | PN30 | 200 | 50 | 150 |
| 60 (60) | 40 (40) | PN40 | 200 | 50 | 150 | |
| 50 (50) | 50 (50) | PN50 | 200 | 50 | 150 | |
| 40 (40) | 60 (60) | PN60 | 200 | 50 | 150 | |
| 250 (MN) | 175 (70) | 75 (30) | PN30 | 200 | 50 | 150 |
| 150 (60) | 100 (40) | PN40 | 200 | 50 | 150 | |
| 125 (50) | 125 (50) | PN50 | 200 | 50 | 150 | |
| 100 (40) | 150 (60) | PN60 | 200 | 50 | 150 | |
| 400 (HN) | 280 (70) | 120 (30) | PN30 | 200 | 50 | 150 |
| 240 (60) | 160 (40) | PN40 | 200 | 50 | 150 | |
| 200 (50) | 200 (50) | PN50 | 200 | 50 | 150 | |
| 160 (40) | 240 (60) | PN60 | 200 | 50 | 150 | |
| Source of Variation | df | Panicle Number | Spikelet per Panicle | Filled Grain Rate | 1000-Grain Weight | Grain Yield | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main crop | Y | 1 | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS |
| N | 2 | 159.72 ** | 150.20 ** | 131.57 ** | NS | 114.80 ** | |
| R | 3 | 24.62 ** | 24.63 ** | NS | NS | 53.75 ** | |
| Y × N | 2 | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | |
| Y × R | 3 | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | |
| N × R | 6 | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | |
| Y × N × R | 6 | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | |
| Ratoon crop | Y | 1 | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS |
| N | 2 | 359.22 ** | 229.83 ** | NS | NS | 175.72 ** | |
| R | 3 | 42.36 ** | NS | NS | NS | 7.10 ** | |
| Y × N | 2 | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | |
| Y × R | 3 | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | |
| N × R | 6 | 50.04 ** | NS | NS | NS | 7.10 ** | |
| Y × N × R | 6 | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | |
| Source of Variation | df | Indices of Regenerated Bud at MS | ROA at 15DAH | NSC Concentration in Stem and Leaf at 15DAH | NSC Concentration in Stubble | Regeneration Rate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Length | Fresh Weight | Number | ||||||
| Y | 1 | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS |
| N | 2 | 118.4 ** | 40.23 ** | 239.27 ** | 9.93 * | 52.73 ** | 50.12 ** | 13.68 ** |
| R | 3 | 59.29 ** | 29.88 ** | 298.07 ** | 15.61 ** | 53.95 ** | 64.45 ** | 70.91 ** |
| Y × N | 2 | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS |
| Y × R | 3 | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS |
| N × R | 6 | 20.21 ** | 14.33 | 6.44 ** | NS | NS | NS | 29.25 ** |
| Y × N × R | 6 | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS |
| Treatment | Panicles (104 ha−1) | Spikelet per Panicle | Filled Grain Rate (%) | 1000-Grain Weight (g) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LN | PN30 | 296.8 g | 58.2 b | 88.1 a | 29.0 a |
| PN40 | 311.2 f | 57.9 b | 88.3 a | 29.2 a | |
| PN50 | 328.6 e | 58.1 b | 87.7 a | 29.2 a | |
| PN60 | 338.9 d | 57.9 b | 87.8 a | 29.1 a | |
| Mean | 318.8 B | 58.0 B | 88.0 A | 29.1 A | |
| MN | PN30 | 354.4 c | 64.1 a | 88.1 a | 29.2 a |
| PN40 | 371.9 b | 64.1 a | 88.2 a | 29.2 a | |
| PN50 | 389.3 a | 64.2 a | 88.2 a | 29.2 a | |
| PN60 | 368.3 b | 64.3 a | 88.1 a | 29.3 a | |
| Mean | 371.0 A | 64.1 A | 88.1 A | 29.2 A | |
| HN | PN30 | 371.0 b | 65.7 a | 87.8 a | 28.8 a |
| PN40 | 386.2 a | 66.0 a | 87.8 a | 28.6 a | |
| PN50 | 365.9 b | 65.6 a | 87.7 a | 28.7 a | |
| PN60 | 350.1 c | 66.0 a | 87.9 a | 28.9 a | |
| Mean | 368.3 A | 65.8 A | 87.8 A | 28.7 A | |
| Parameters | N Rate | Panicle Number | Yield |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of mother stem | LN | −0.9986 ** | −0.9927 ** |
| MN | −0.4694 | −0.5729 | |
| HN | 0.6810 | 0.5474 | |
| Regeneration rate | LN | 0.9998 ** | 0.9947 ** |
| MN | 0.8707 | 0.9220 * | |
| HN | 0.7989 | 0.8374 |
| Treatment | ANUE in Main Crop | ANUE in Ratoon Crop | ANUE in Both Seasons | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LN | PN30 | 29.7 a | 6.3 f | 14.1 b |
| PN40 | 27.9 b | 7.4 e | 14.2 b | |
| PN50 | 26.6 c | 8.6 d | 14.6 b | |
| PN60 | 24.5 d | 9.3 d | 14.4 b | |
| Mean | 27.2 A | 7.9 B | 14.3 B | |
| MN | PN30 | 15.5 f | 13.4 c | 14.6 b |
| PN40 | 16.6 e | 14.9 b | 15.8 a | |
| PN50 | 15.3 f | 16.4 a | 15.8 a | |
| PN60 | 14.6 g | 14.7 | 14.7 b | |
| Mean | 15.5 B | 14.8 A | 15.2 A | |
| HN | PN30 | 8.3 i | 15.0 b | 10.5 d |
| PN40 | 8.6 i | 16.2 a | 11.1 c | |
| PN50 | 8.8 i | 14.5 b | 10.7 d | |
| PN60 | 9.3 h | 13.6 c | 10.7 d | |
| Mean | 8.7 C | 14.8 A | 10.8 C | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Q.; Liu, X.; Yu, G.; Duan, B.; Wang, H.; Zhao, H.; Feng, D.; Gu, M.; Liu, L. Reasonable Nitrogen Regime in the Main Crop Increased Grain Yields in Both Main and Ratoon Rice. Agriculture 2022, 12, 527. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12040527
Zhang Q, Liu X, Yu G, Duan B, Wang H, Zhao H, Feng D, Gu M, Liu L. Reasonable Nitrogen Regime in the Main Crop Increased Grain Yields in Both Main and Ratoon Rice. Agriculture. 2022; 12(4):527. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12040527
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Qiang, Xiangchen Liu, Guilong Yu, Bin Duan, Hao Wang, Haiying Zhao, Daqing Feng, Mengxuan Gu, and Lijun Liu. 2022. "Reasonable Nitrogen Regime in the Main Crop Increased Grain Yields in Both Main and Ratoon Rice" Agriculture 12, no. 4: 527. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12040527
APA StyleZhang, Q., Liu, X., Yu, G., Duan, B., Wang, H., Zhao, H., Feng, D., Gu, M., & Liu, L. (2022). Reasonable Nitrogen Regime in the Main Crop Increased Grain Yields in Both Main and Ratoon Rice. Agriculture, 12(4), 527. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12040527







