Influence of Sieve Surface Attitude on Sieving Performance of Granular Materials with Non-Uniform Feeding Conditions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
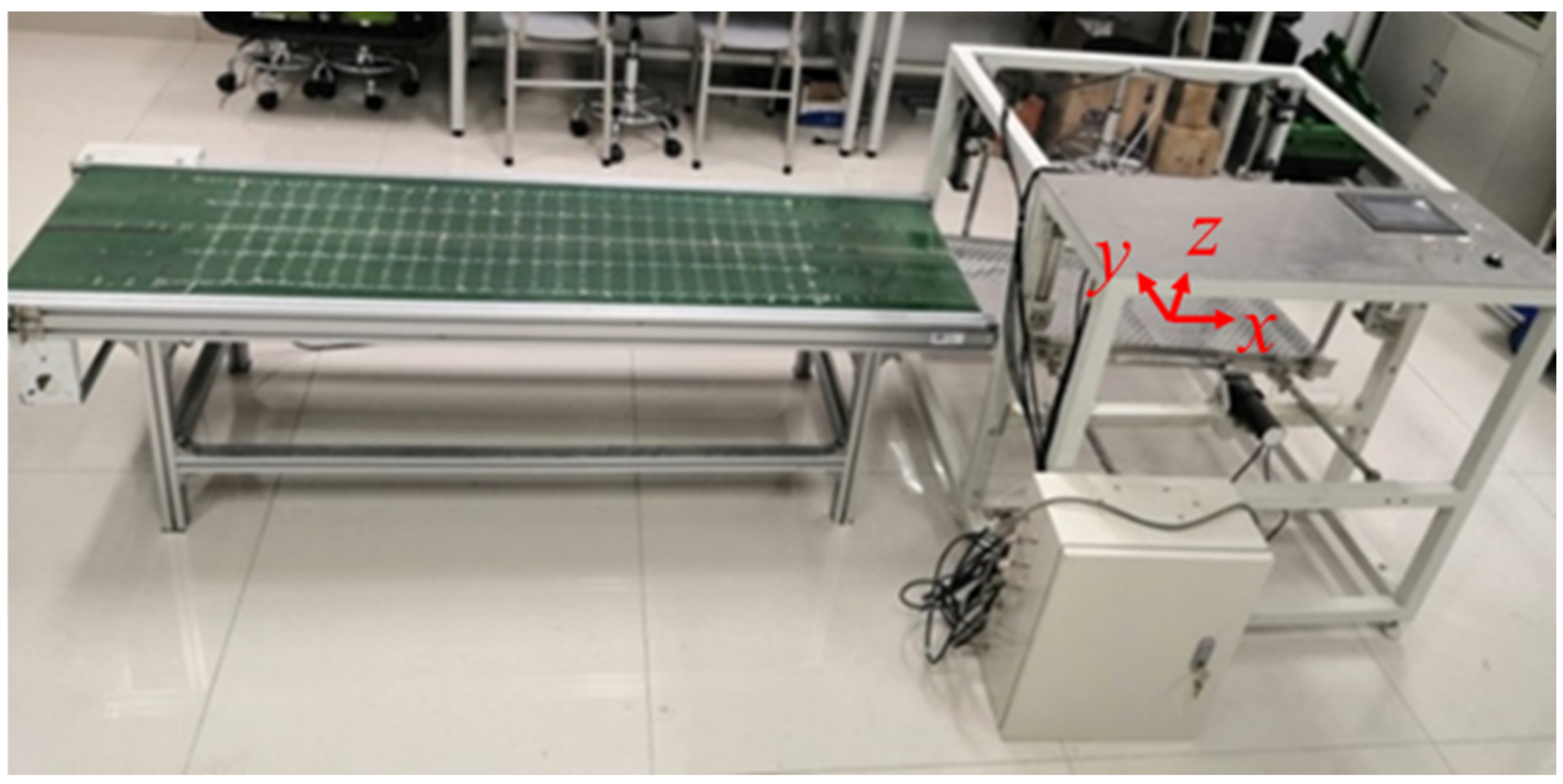
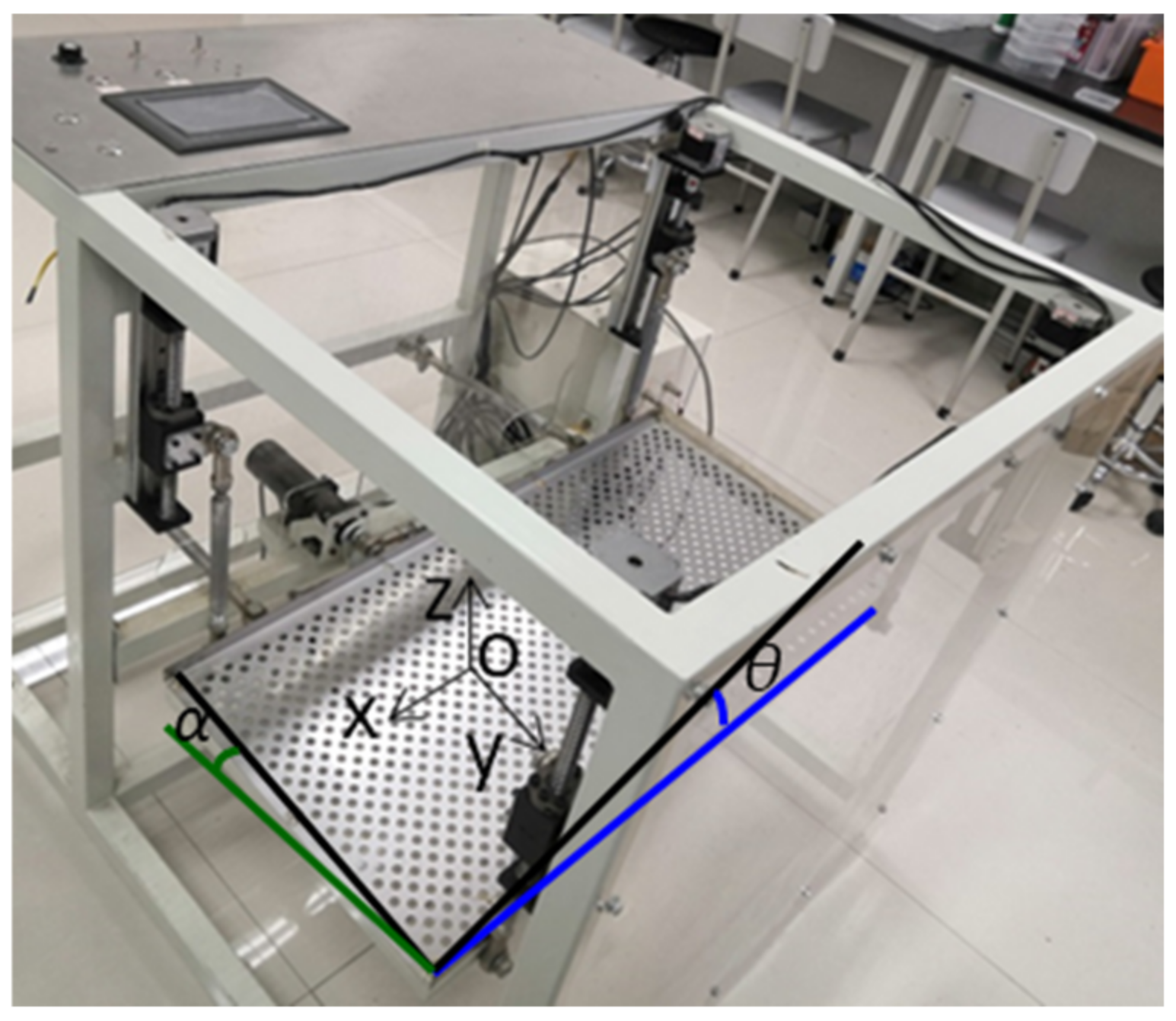
2.1. Multi-DOF Hybrid Vibrating Screen
2.2. Discrete Element Method
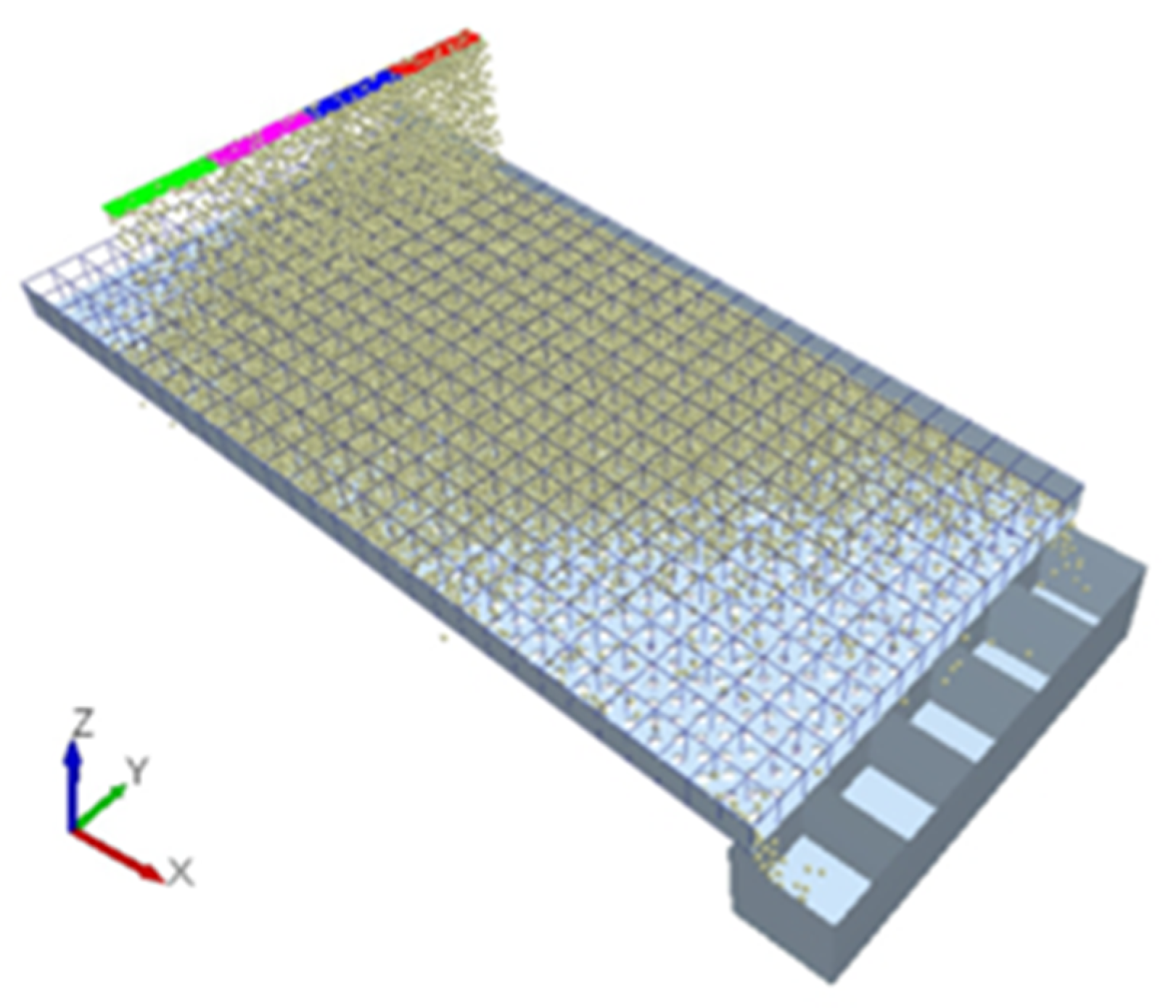
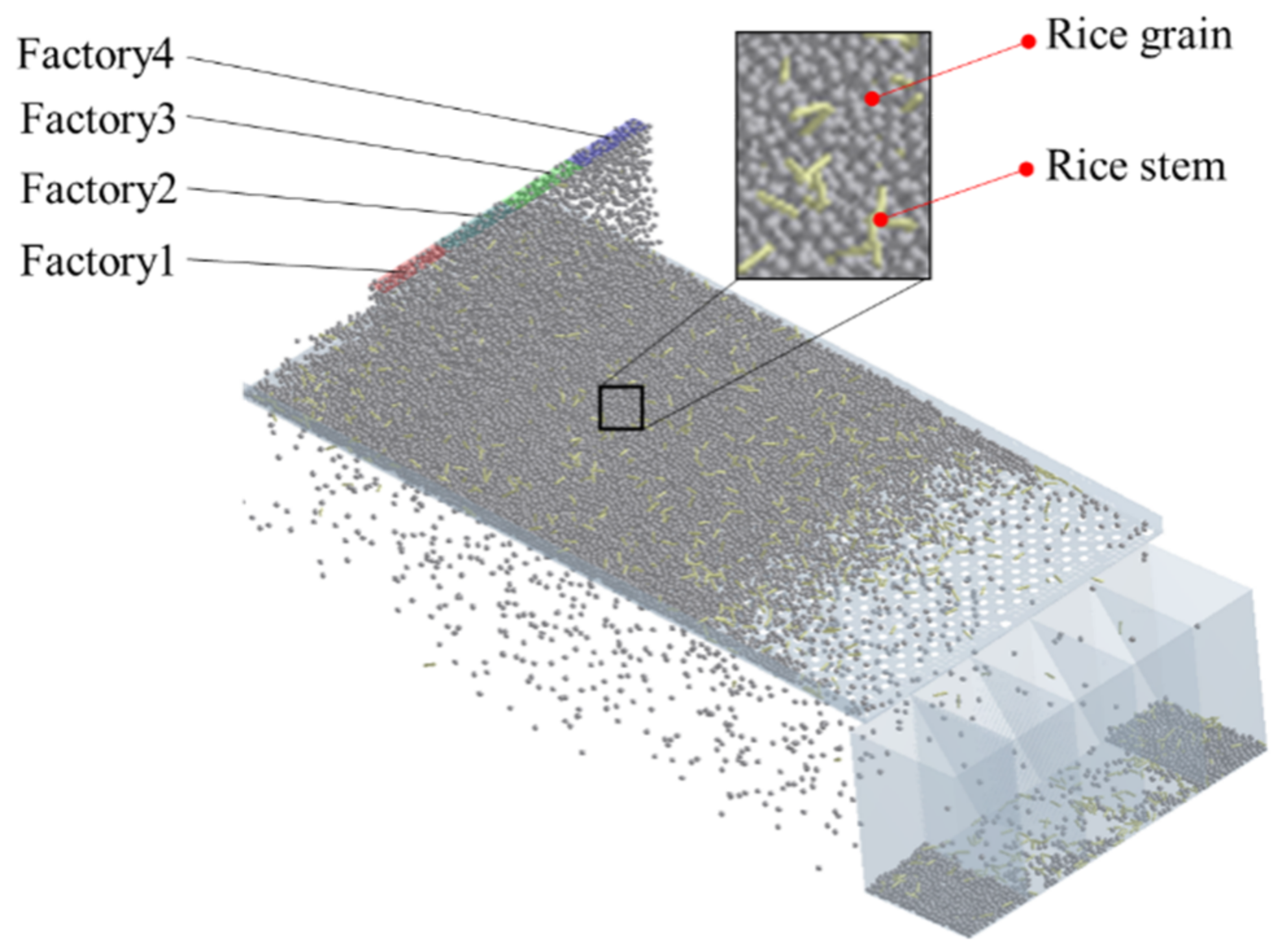
2.3. DEM Simulation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Grain Distribution on Sieve Surface
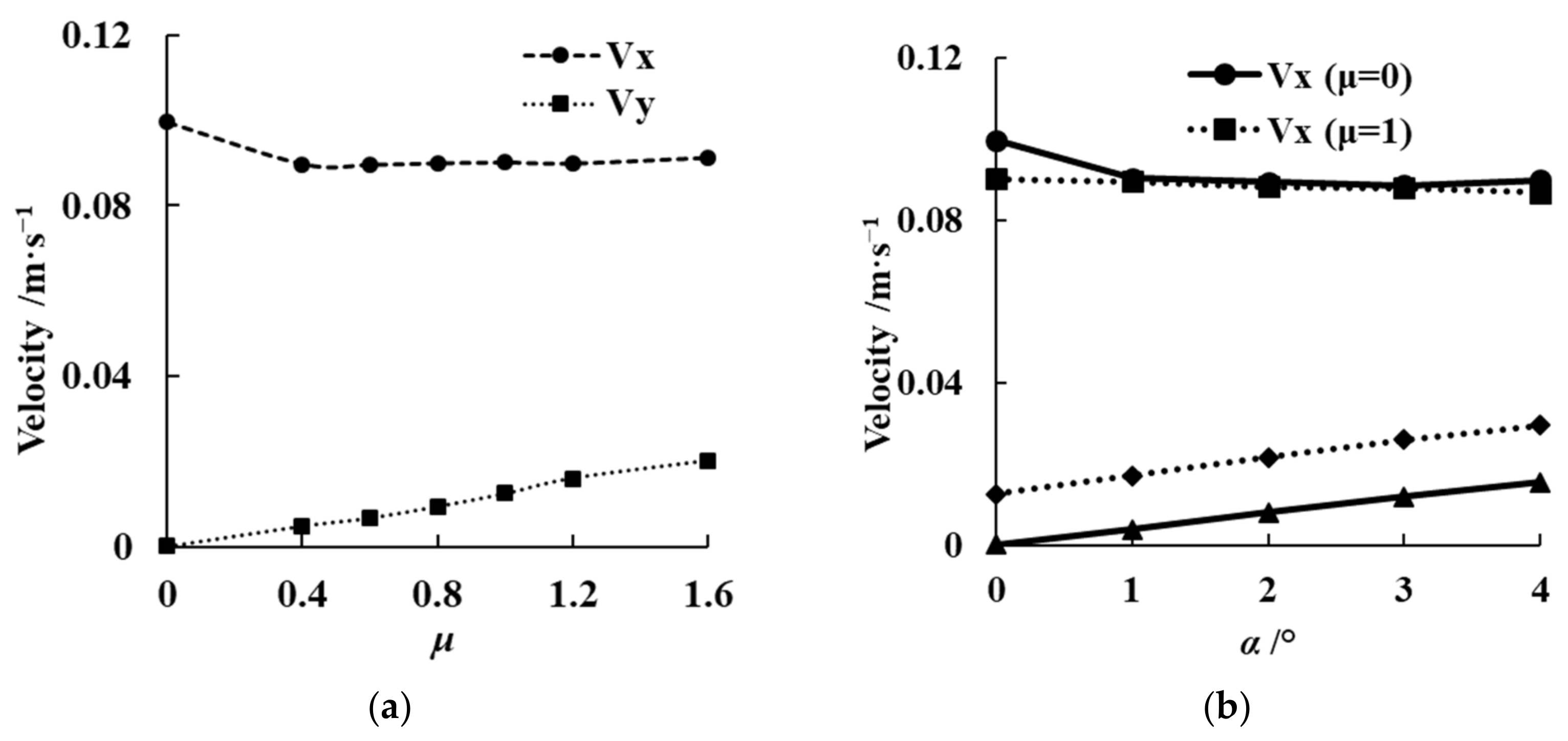
3.2. Effects of Non-Uniformity Feeding and Attitude Angle on Screening Performance
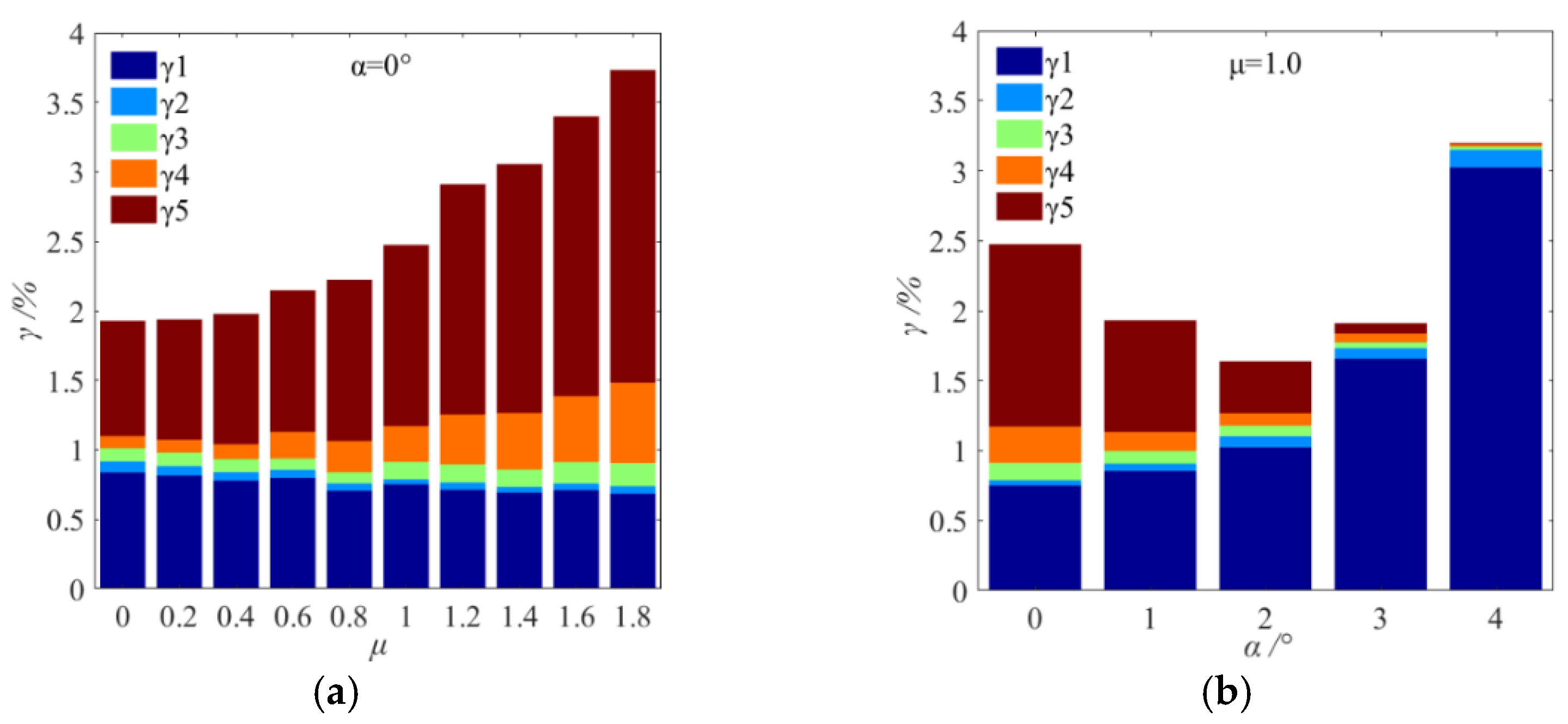
3.3. Distribution of Lost Grains
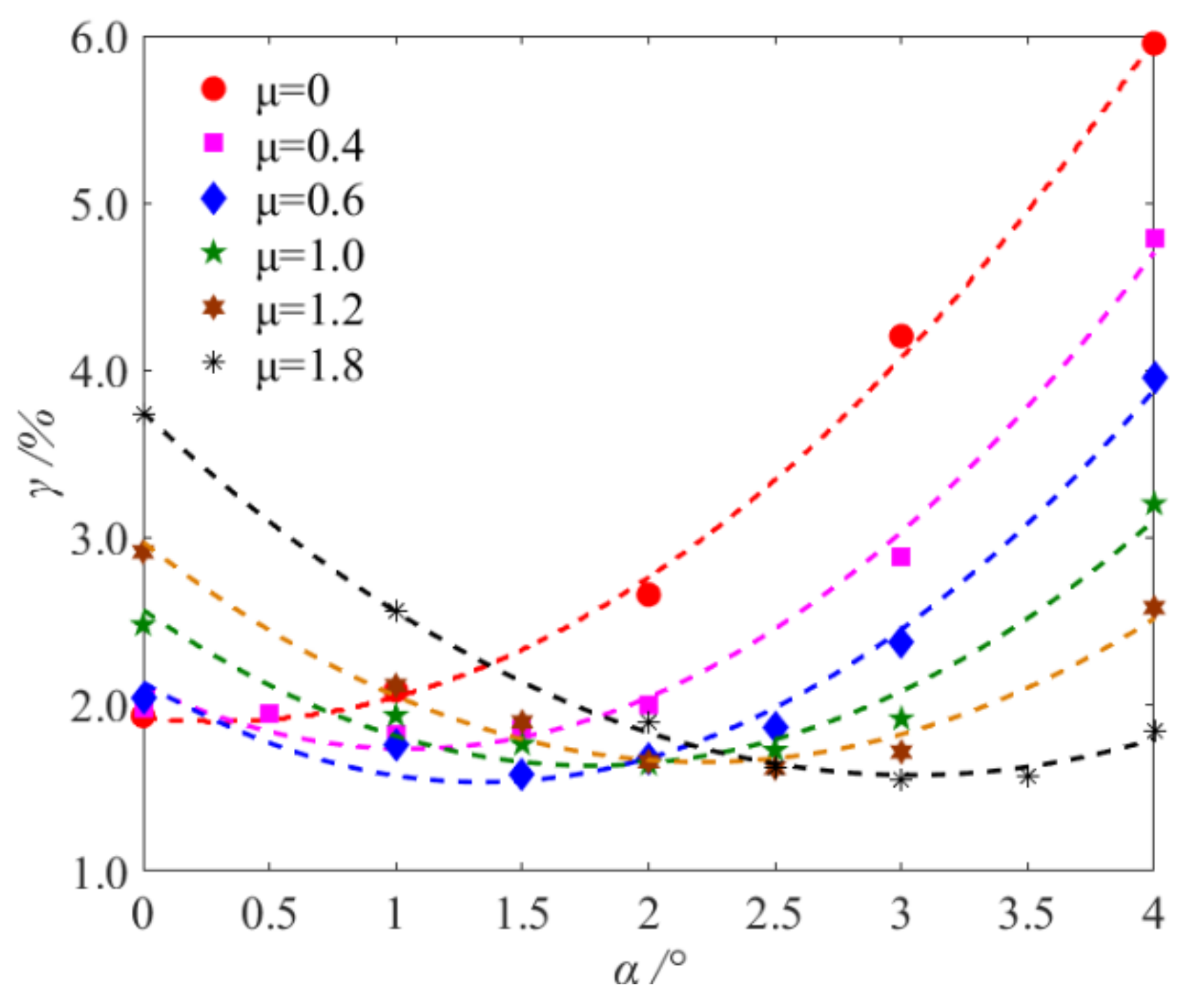
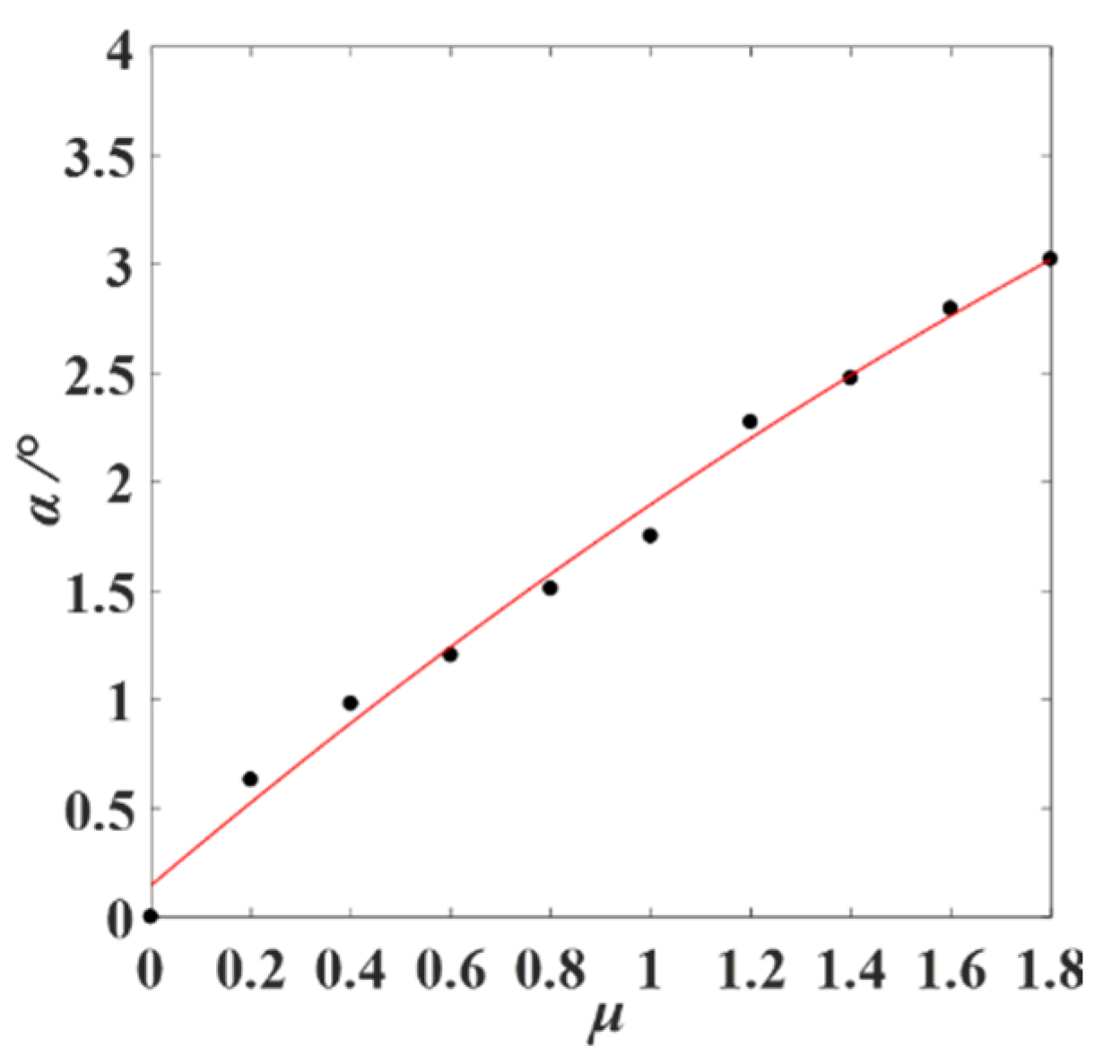
3.4. Optimization of Attitude Angle
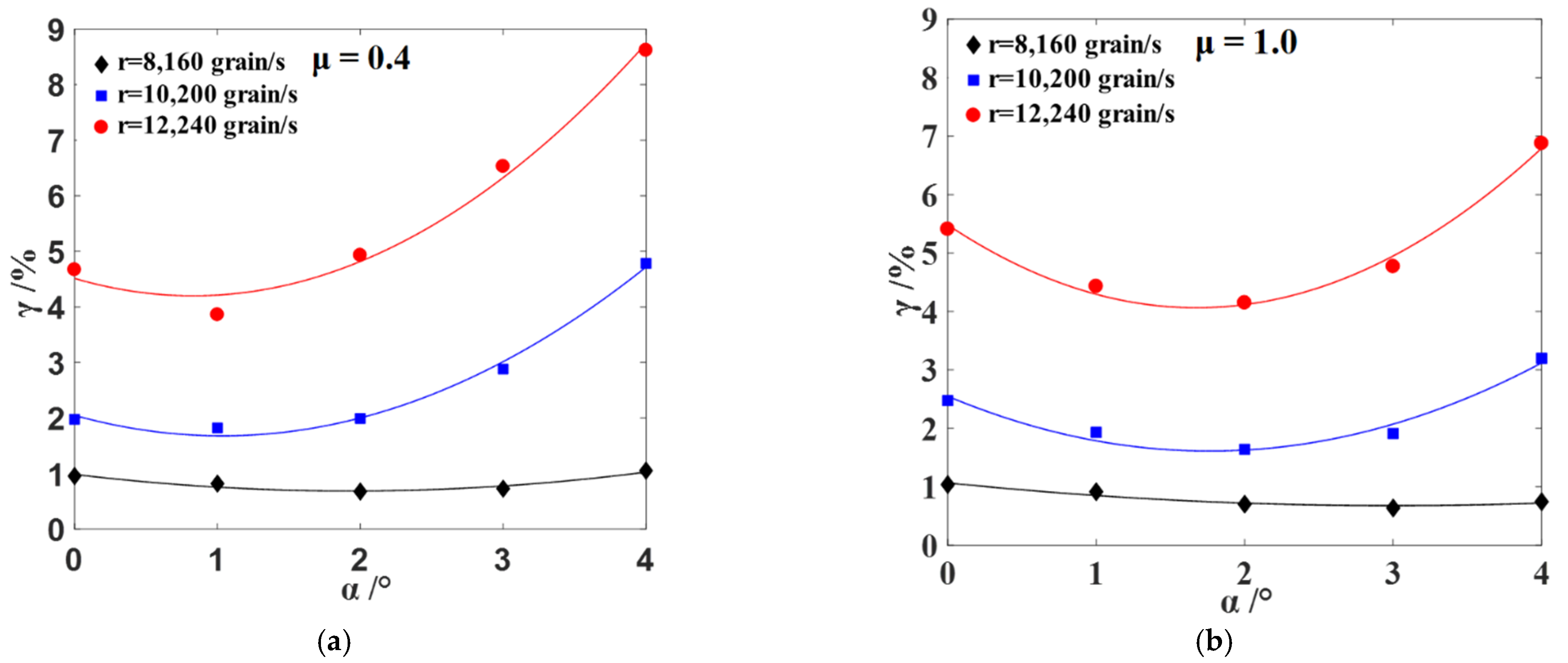
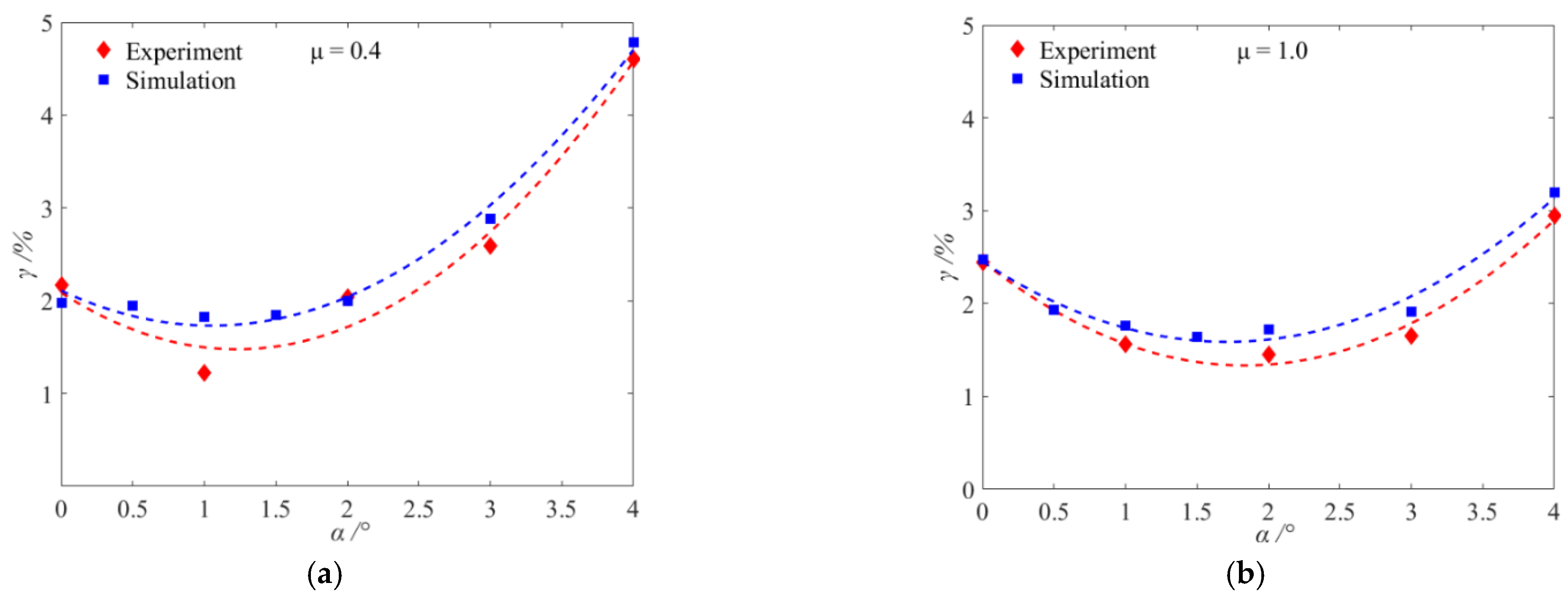
3.5. Verification of DEM Simulations
3.6. Grain Sieving Tests
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Simulation results showed that the non-uniform feeding would lead to the uneven distribution of grains along the y-axis. The attitude angle was closely related to the grain feeding non-uniformity coefficient. A reasonable attitude angle could ensure the uniform distribution of particles on the vibrating screen and increase the particle acceleration in the y-axis of the screen surface, which could improve screening performance.
- (2)
- The total loss rate presented a monotonous increasing tendency with an increasing feeding non-uniformity coefficient (μ). The loss first decreased and then increased with the increase in attitude angle. The optimization of the attitude angle was an effective way to reduce the loss rate when the grains were non-uniformly fed onto the vibrating sieve surface.
- (3)
- According to the relationship between the optional attitude angle (αo) and the minimum loss rate (γmin) under different non-uniformity coefficients (μ), an optimum model for attitude angle was established. The feasibility and stability of the model were verified by simulations and experiments under different total feeding rates.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, J.; Webb, C.; Pandiella, S.S.; Campbell, G.M. Discrete particle motion on sieves—A numerical study using the DEM simulation. Powder Technol. 2003, 133, 190–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tijskens, E.; Ramon, H.; Baerdemaeker, J.D. Discrete element modelling for process simulation in agriculture. J. Sound Vib. 2003, 266, 493–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, K.J.; Yu, A.B. Numerical simulation of the particle flow and sieving behaviour on sieve bend/low head screen combination. Miner. Eng. 2019, 31, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trumic, M.; Magdalinovic, N. New model of screening kinetics. Miner. Eng. 2011, 24, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawinska, K.; Wodzinski, P.; Modrzewski, R. Verification of the mathematical model of the screen blocking process. Powder technol. 2014, 256, 506–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, S.P.; Oberst, S.; Wang, X.W. An experimentally validated rubber shear spring model for vibrating flip-flow screens. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2020, 139, 106619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, J.W.; Cleary, P.W.; Sinnott, M.D.; Morrison, R.D. Using SPH one-way coupled to DEM to model wet industrial banana screens. Miner. Eng. 2011, 24, 741–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.Z.; Tong, X. Characteristics and efficiency of a new vibrating screen with a swing trace. Particuology 2013, 11, 601–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.S.; Qiao, J.P.; Zhou, Z.G.; Zhao, Y.M.; Yang, Y.Z.; Duan, C.L.; Luo, Z.F.; Cai, L.F.; Wang, S.; Pan, M. Time evolution of kinematic characteristics of variable-amplitude equal-thickness screen and material distribution during screening process. Powder Technol. 2018, 336, 350–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Webb, C.; Pandiella, S.S.; Campbell, G.M. A numerical simulation of separation of crop seeds by screening—Effect of particle bed depth. Food Bioprod. Process. 2002, 80, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotich, N.; Tuunila, R.; Elkamel, A.; Louhi-Kultanen, M. Dynamic and perturbative system analysis of granular material in a vibrating screen. Adv. Powder Technol. 2017, 28, 3257–3264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.L.; Su, J.H.; Zhao, X.Q.; Chen, H.; Liu, C.; Liu, S.Q.; Wu, T.X. The study of vibrating screen efficiency based on discrete element method. J. Northeast Norm. Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2018, 50, 78–83. [Google Scholar]
- Shanmugam, B.K.; Vardhan, H.; Raj, M.G.; Kaza, M.; Sah, R. Evaluation of a new vibrating screen for dry screening fine coal with different moisture contents. Int. J. Coal Prep. Util. 2022, 42, 752–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.D.; Zhao, L.L.; Li, H.X.; Liu, C.S.; Hu, E.Y.; Li, Y.W.; Hou, Q.F. DEM study of particles flow on an industrial-scale roller screen. Adv. Powder Technol. 2020, 31, 4445–4456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, J.P.; Duan, C.L.; Jiang, H.S.; Zhao, Y.M.; Chen, J.W.; Huang, L.; Wen, P.F.; Wu, J.D. Research on screening mechanism and parameters optimization of equal thickness screen with variable amplitude based on DEM simulation. Powder Technol. 2018, 331, 296–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.J.; Zhang, T.Y.; Li, L.; Chen, J.Y.; Meng, X.R. Study on screening efficiency of moist raw coal particles on 3-DOF hybrid vibrating screen. Chin. J. Eng. Des. 2016, 23, 264–270. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.J.; Cui, Y.Q.; Zheng, Z.H.; Feng, X.; Shen, B.S.; Li, Y.B. Effect of Different Motion Forms of Vibrating Screen on Screening of Particle Group. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2019, 50, 119–129. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.K.; Wang, C.J.; Yan, C.; Li, H. Design and Dynamic Analysis of a Four-Degree-of-Freedom Chaotic Vibrating Screen. Shock Vib. 2021, 2021, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.S. Research of wheat vibrating screen based on two degrees of freedom. Diploma Thesis, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- He, B.X.; Shen, H.P.; Xue, G.X.; Chu, K.B. Experomental Research on the Screening characteristic of Parallel Vibration Sieve. J. Mech. Transm. 2011, 35, 52–54. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, H.P.; Zhang, J.T.; He, B.X.; Liu, Y.X.; Yang, T.L. Sifter efficiency and experimental study on a new type of vibrating sifter based on PKM. J. Mach. Des. 2011, 28, 83–86. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, J.; Zhang, X.Q.; Wang, C.J. Tea Sieving Based on Three Translation Parallel Machanism. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2012, 43, 101–104. [Google Scholar]
- Cocolo, G.; Curnis, S.; Hjorth, M.; Provolo, G. Effect of different technologies and animal manures on solid-liquid separation efficiencies. J. Agric. Eng. 2012, 43, e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayuga, F. Present and future of the numerical methods in buildings and infrastructures areas of biosystems engineering. J. Agric. Eng. 2015, 46, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, Y.; Xu, B.; Liu, Y.; Ye, S.B.; Li, L.H.; Kong, L.D.; Zheng, D.C. Design optimization and experimental evaluation of a reciprocating grain vibrating screen based on ADAMS system. J. Shanxi Agric. Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2019, 39, 98–104. [Google Scholar]
- Wills, B.A.; Finch, J.A. Chapter 8—Industrial screening. In Wills’ Mineral Processing Technology, 8th ed.; Wills, B.A., Finch, J.A., Eds.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2016; pp. 181–197. [Google Scholar]
- Folami, A.A.; Obioha, E.N.; Adewole, A.A.; Ibiyemi, K.S. Performance evaluation of a developed rice-processing machine. J. Agric. Eng. 2016, 47, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, L.L.; Li, Y.W.; Yang, X.D.; Jiao, Y.; Hou, Q.F. DEM study of size segregation of wet particles under vertical vibration. Adv. Powder Technol. 2019, 30, 1386–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.B.; Xu, Y.; Cui, T.; Zhang, D.X.; Fan, H.F.; Gao, X.J.; Su, Y.; Qiao, M.M.; Song, Z.S. Improving particle dispersion characteristics with a novel cleaning screen: Parameter design and numerical simulation. Powder Technol. 2022, 397, 116987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modrzewski, R.; Obraniak, A.; Rylski, A.; Siczek, K. A Study on the Dynamic Behavior of a Sieve in an Industrial Sifter. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 8590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gursky, V.; Kuzio, I.; Krot, P.; Zimroz, R. Energy-saving inertial drive for dual-frequency excitation of vibrating machines. Energies 2021, 14, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahani, M.; Farzanegan, A.; Noaparast, M. Investigation of screening performance of banana screens using LIGGGHTS DEM solver. Powder Technol. 2015, 283, 32–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, A.; Nezhad, V.S. Employing DEM to study the impact of different parameters on the screening efficiency and mesh wear. Powder Technol. 2016, 297, 126–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleary, P.W.; Wilson, P.; Sinnott, M.D. Effect of particle cohesion on flow and separation in industrial vibrating screens. Miner. Eng. 2018, 119, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raji, A.O.; Favier, J.F. Model for the deformation in agricultural and food particulate materials under bulk compressive loading using discrete element method. I: Theory, model development and validation. J. Food Eng. 2004, 64, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Li, Y.M.; Liang, Z.W.; Gong, Z.Q. DEM simulation and physical testing of rice seed impact against a grain loss sensor. Biosyst. Eng. 2013, 116, 410–419. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.; Jin, M.Z.; Qin, F.; Yang, S.X. A novel neural network approach to modeling particles distribution on vibrating screen. Powder Technol. 2021, 382, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delaney, G.W.; Cleary, P.W.; Hilden, M.; Morrison, R.D. Testing the validity of the spherical DEM model in simulating real granular screening processes. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2012, 68, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

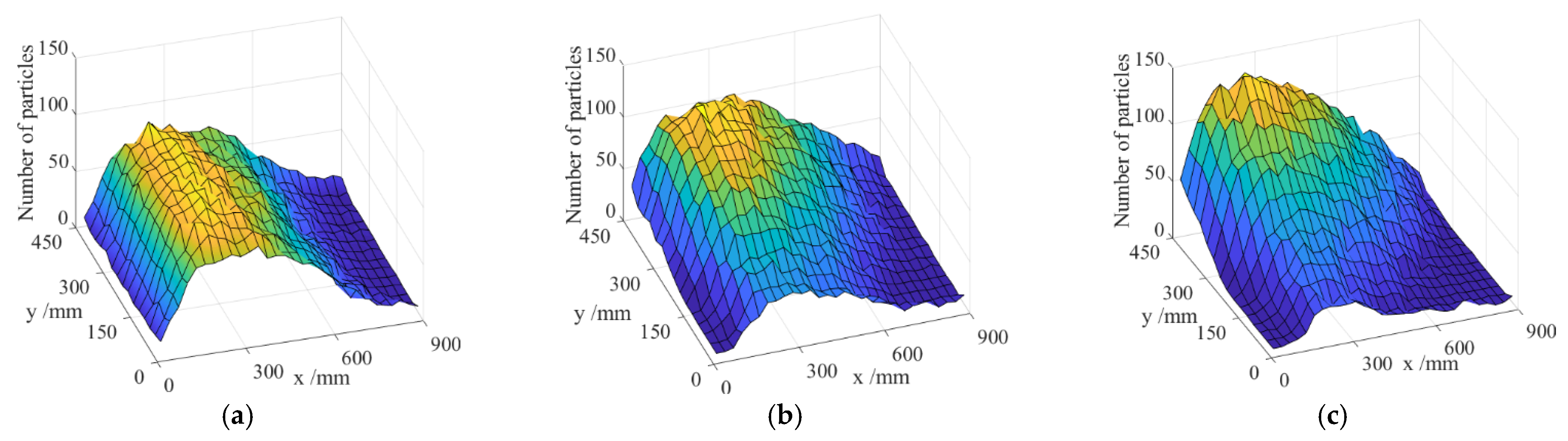
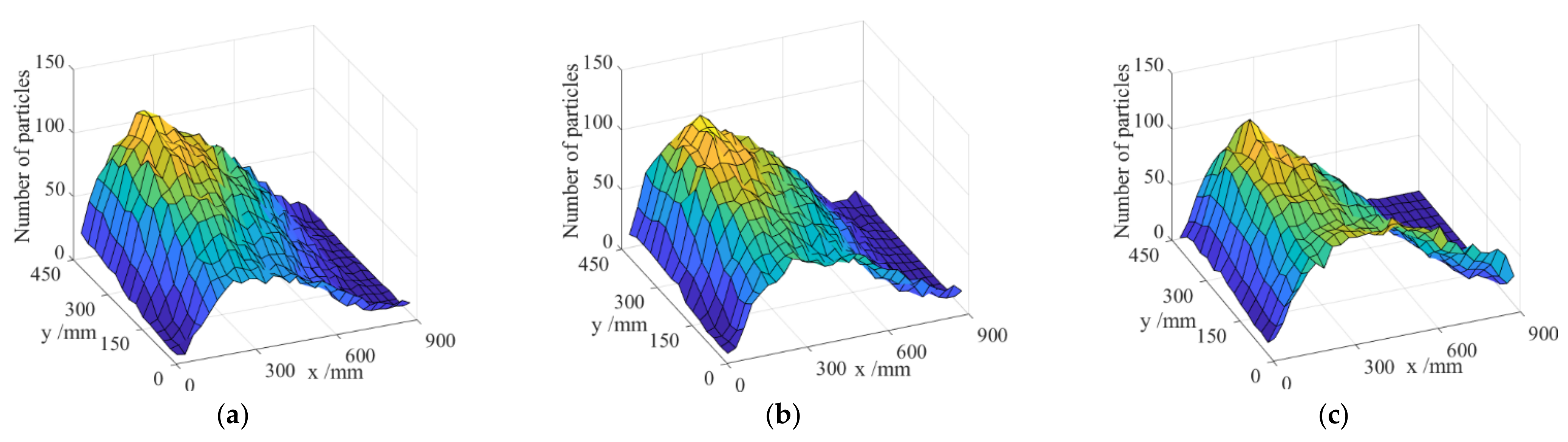

| Parameter | Rice Grain | Stem | Sieve | Grain–Grain | Grain–Sieve | Grain–Stem | Stem–Sieve | Stem–Stem |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Density (kg/m3) | 1150 | 100 | 2800 | |||||
| Yang’s modulus (MPa) | 11.5 | 1 | 72,000 | |||||
| Poisson’s ratio | 0.25 | 0.4 | 0.33 | |||||
| Restitution coefficient | 0.42 | 0.48 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | |||
| Static friction coefficient | 0.56 | 0.35 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 | |||
| Rolling coefficient of friction | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| State Number | Ratio of Feeding Rates, r1:r2:r3:r4 | Non-Uniformity Coefficient (µ) |
|---|---|---|
| S1 | 1:1:1:1 | 0 |
| S2 | 2:3:2:3 | 0.2 |
| S3 | 2:2:3:3 | 0.4 |
| S4 | 2:2:2:4 | 0.6 |
| S5 | 1:2:4:3 | 0.8 |
| S6 | 1:2:3:4 | 1.0 |
| S7 | 1:1:4:4 | 1.2 |
| S8 | 1:1:3:5 | 1.4 |
| S9 | 1:1:2:6 | 1.6 |
| S10 | 1:1:1:7 | 1.8 |
| Square Sum | Mean Square | F | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| 11.503 | 2.876 | 3.319 | 0.031 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, L.; Chen, S.; Zhao, Z.; Ding, H.; Zhu, Y. Influence of Sieve Surface Attitude on Sieving Performance of Granular Materials with Non-Uniform Feeding Conditions. Agriculture 2022, 12, 2023. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12122023
Zhu L, Chen S, Zhao Z, Ding H, Zhu Y. Influence of Sieve Surface Attitude on Sieving Performance of Granular Materials with Non-Uniform Feeding Conditions. Agriculture. 2022; 12(12):2023. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12122023
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Li, Shuren Chen, Zhan Zhao, Hantao Ding, and Yongle Zhu. 2022. "Influence of Sieve Surface Attitude on Sieving Performance of Granular Materials with Non-Uniform Feeding Conditions" Agriculture 12, no. 12: 2023. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12122023
APA StyleZhu, L., Chen, S., Zhao, Z., Ding, H., & Zhu, Y. (2022). Influence of Sieve Surface Attitude on Sieving Performance of Granular Materials with Non-Uniform Feeding Conditions. Agriculture, 12(12), 2023. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12122023






