Effects of Nitrogen Application Strategy on Nitrogen Enzyme Activities and Protein Content in Spring Wheat Grain
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Test Site Overview
2.2. Experimental Design and Management
2.3. Key Enzyme Activities of Nitrogen Metabolism in Spring Wheat Grain: The Nitrate Reductase (NR), Glutamine Synthetase (GS), and Glutamate-Pyruvate Aminotransferase (GPT) in Spring Wheat Grain
2.4. Protein Content and Its Fraction Content
2.5. Yield and Protein Yield of Spring Wheat Grain
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
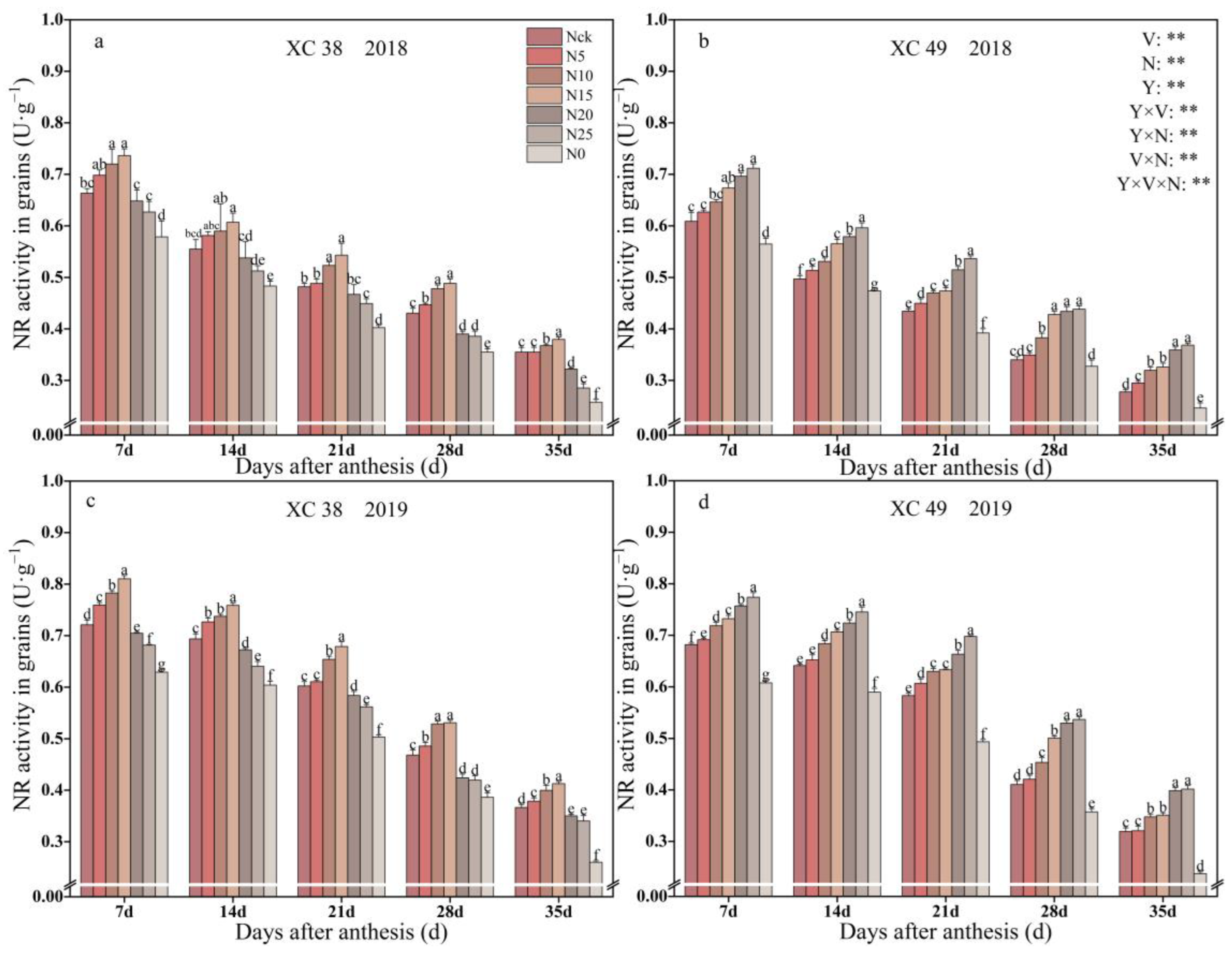
3.1. Nitrate Reductase (NR) Activity of Spring Wheat Grain
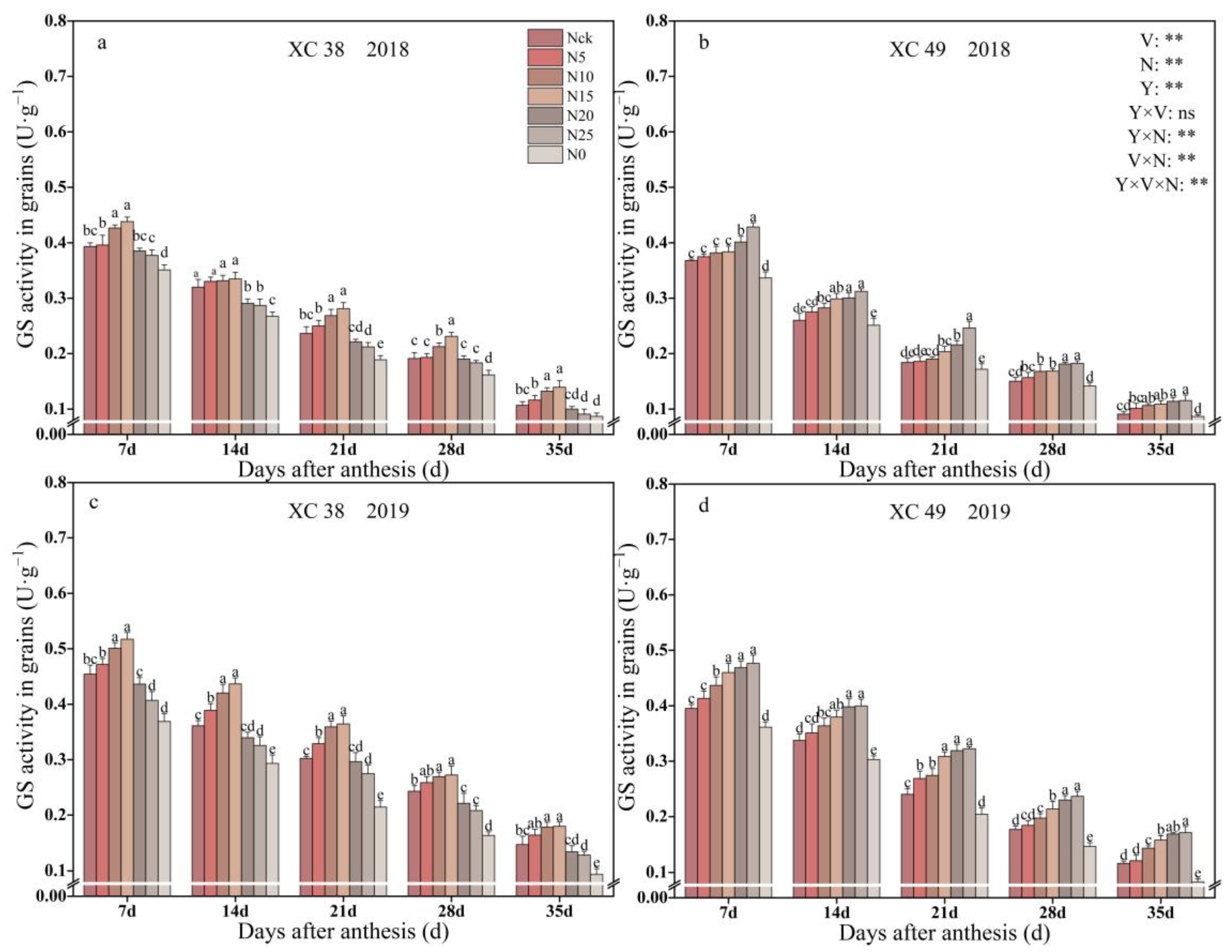
3.2. Glutamine Synthetase (GS) Activity of Spring Wheat Grain
3.3. Glutamate-Pyruvate Aminotransferase (GPT) Activity of Spring Wheat Grain
3.4. Protein Content of Spring Wheat Grain
3.5. Protein Components of Spring Wheat Grain
3.6. Yield, Yield Components, and Protein Yield of Spring Wheat
3.7. Correlation between Grain Indexes of Spring Wheat
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Fertilizer Management on Activities of Key Enzymes for Nitrogen Metabolism in Spring Wheat Grain
4.2. Effects of Fertilizer Management on Protein Content and Protein Components in Spring Wheat Grain
4.3. Effects of Fertilizer Management on Grain Yield and Protein Yield in Spring Wheat Grain
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, R.; Cheng, W.H.; Cui, J.; Liao, J.; Fan, H.; Zheng, Z.; Ma, F.Y. Lateral spacing in drip-irrigated wheat: The effects on soil moisture, yield, and water use efficiency. Field Crops Res. 2015, 179, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.G.; Fan, L.F.; Ma, X.H.; Lin, J.Y.; Zhu, H.R.; Qiu, S.J. Spatial-temporal patterns of Xinjiang’s grain output increase and the contribution factors during 2007–2015. J. Arid Land Resour. Environ. 2018, 32, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kant, S. Understanding nitrate uptake, signaling and remobilisation for improving plant nitrogen use efficiency. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2018, 74, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.L.; Sadras, V.O.; Lu, G.Y.; Zhang, P.X.; Han, Y.; Liu, L.; Xie, J.Y.; Yang, X.Y.; Zhang, S.L. A global meta-analysis of split nitrogen application for improved wheat yield and grain protein content. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 213, 105111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadeem, M.Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Ahmad, S.; Ding, Y.; Li, G. Quantifying the impact of reduced nitrogen rates on grain yield and nitrogen use efficiency in the wheat and rice rotation system of the Yangtze River Region. Agronomy 2022, 12, 920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Li, Y.; Liang, Z.; Guo, H.; Cai, J.; Jiang, D.; Cao, W.; Dai, T. Genetic improvement of nitrogen uptake and utilization of winter wheat in the Yangtze River Basin of China. Field Crop Res. 2016, 196, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Fu, P.H.; Wang, F.; Fahad, S.; Mohaparta, P.K.; Chen, Y.T.; Zhang, C.D.; Peng, S.B.; Cui, K.H.; Nie, L.X.; et al. Optimizing nitrogen management to balance rice yield and environmental risk in the Yangtze River’s middle reaches. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 4901–4912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poffenbarger, H.J.; Sawyer, J.E.; Barker, D.W.; Olk, D.C.; Six, J.; Castellano, M.J. Legacy effects of long-term nitrogen fertilizer application on the fate of nitrogen fertilizer inputs in continuous maize. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 265, 544–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravier, C.; Meynard, J.M.; Cohan, J.P.; Gate, P.; Jeuffroy, M.H. Early nitrogen deficiencies favor high yield, grain protein content and n use efficiency in wheat. Eur. J. Agron. 2017, 89, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Ma, B.L.; Fan, J.J.; Sun, M.; Yi, Y.; Guo, W.S.; Voldeng, H.D. Management of nitrogen fertilization to balance reducing lodging risk and increasing yield and protein content in spring wheat. Field Crops Res. 2019, 241, 107584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossmann, A.; Scherf, K.A.; Rühl, G.; Greef, J.M.; Mühling, K.H. Effects of a late N fertiliser dose on storage protein composition and bread volume of two wheat varieties differing in quality. J. Cereal Sci. 2020, 93, 102944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.H.; Chen, Y.L.; Ding, Y.F.; Geng, C.M.; Li, Q.; Liu, Z.H.; Wang, S.H.; Tang, S. Charactering protein fraction concentrations as influenced by nitrogen application in low-glutelin rice cultivars. J. Integr. Agric. 2016, 15, 537–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossmann, A.; Buchner, P.; Savill, G.P.; Hawkesford, M.J.; Scherf, K.A.; Mühling, K.H. Foliar N application at anthesis alters grain protein composition and enhances baking quality in winter wheat only under a low n fertiliser regimen. Eur. J. Agron. 2019, 109, 125909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.X.; Yang, M.T.; Cai, J.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Q.; Cao, W.X.; Dai, T.B.; Jiang, D. Nitrogen topdressing timing influences the spatial distribution patterns of protein components and quality traits of flours from different pearling fractions of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) grains. Field Crops Res. 2018, 216, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.W.; Ma, D.Y.; Ma, G.; Wang, C.Y.; Xie, X.D.; Kang, G.Z. Responses of glutamine synthetase activity and gene expression to nitrogen levels in winter wheat cultivars with different grain protein content. J. Cereal Sci. 2017, 74, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, W.F.; Xue, X.X.; Li, X.K.; Khan, M.R.; Yan, J.Y.; Ren, T.; Cong, R.H.; Lu, J.W. Interactive effects of nitrogen and potassium on: Grain yield, nitrogen uptake and nitrogen use efficiency of rice in low potassium fertility soil in China. Field Crops Res. 2019, 236, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, E.; Fidalgo, F.; Teixeira, J.; Aguiar, A.A.; Ferreira IM PL, V.O. Influence of the temporal and spatial variation of nitrate reductase, glutamine synthetase and soil composition in the n species content in lettuce (Lactuca sativa). Plant Sci. 2014, 219–220, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Chang, L.Y.; Muhammad, K.; Zhang, J.J.; Huang, D.F. Alleviation of Drought Stress by Nitrogen Application in Brassica campestris ssp. Chinensis L. Agronomy 2018, 8, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Z.Q.; Wang, D.M.; Chang, X.H.; Wang, Y.J.; Yang, Y.S.; Zhao, G.C. Effects of zinc fertilizer and short-term high temperature stress on wheat grain production and wheat flour proteins. J. Integr. Agric. 2018, 17, 1979–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Y.; Xiong, S.P.; Wei, Y.H.; Meng, X.D.; Wang, X.C.; Ma, X.M. The role of glutamine synthetase isozymes in enhancing nitrogen use efficiency of N-efficient winter wheat. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, I.; Dong, Q.; Wang, X.R.; Gui, H.P.; Niu, J.; Li, L.L.; Zhang, H.H.; Pang, N.C.; Zhang, X.L.; Song, M.Z. N-efficient cotton genotype grown under low nitrogen shows relatively large root system, high biomass accumulation and nitrogen metabolism. Agron. J. 2021, 114, 582–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forde, B.G.; Lea, P.J. Glutamate in plants: Metabolism, regulation, and signalling. J. Exp. Bot. 2007, 58, 2339–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zörb, C.; Ludewig, U.; Hawkesford, M.J. Perspective on Wheat Yield and Quality with Reduced Nitrogen Supply. Trends Plant Sci. 2018, 23, 1029–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayadi, S.; Jallouli, S.; Chamekh, Z.; Zouari, I.; Landi, S.; Hammami, Z.; Ben Azaiez, F.E.; Baraket, M.; Esposito, S.; Trifa, Y. Variation of Grain Yield, Grain Protein Content and Nitrogen Use Efficiency Components under Different Nitrogen Rates in Mediterranean Durum Wheat Genotypes. Agriculture 2022, 12, 916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, C.; Bio AF, M.; Domínguez-Valdivia, M.D.; Aparicio-Tejo, P.M.; Lamsfus, C.; Martins-Loução, M.A. How does glutamine synthetase activity determine plant tolerance to ammonium? Planta 2006, 223, 1068–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baars JJ, P.; Op den Camp HJ, M.; Hermans JM, H.; Mikes, V.; van der Drift, C.; Van Griensven LJ, L.D.; Vogels, G.D. Nitrogen assimilating enzymes in the white button mushroom Agaricus bisporus. Microbiology 1994, 140, 1161–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.H.; Cheng, F.M.; Cheng, W.D.; Zhang, G.P. Positional variations in phytic acid and protein content within a panicle of japonica rice. J. Cereal Sci. 2005, 41, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Dugo, V.; Durand, J.L.; Gastal, F. Water deficit and nitrogen nutrition of crops. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2010, 30, 529–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yu, M.; Du, X.Q.; Wang, Z.F.; Wu, W.H.; Quintero, F.J.; Jin, X.H.; Li, H.D.; Wang, Y. NRT1.5/NPF7.3 Functions as a Proton-Coupled H+ /K+ Antiporter for K+ Loading into the Xylem in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Adv. Publ. 2017, 29, 2016–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.Y.; Huang, X.; Hou, J.F.; Han, Q.X.; Hou, G.G.; Wang, C.Y.; Guo, T.C. Quantitative analysis of the grain amyloplast proteome reveals differences in metabolism between two wheat cultivars at two stages of grain development. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.L.; Liu, Y.; Ge, J.F.; Li, R.K.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Huo, Z.Y.; Xu, K.; Wei, H.H.; Dai, Q.G. Improved physiological and morphological traits of root synergistically enhanced salinity tolerance in rice under appropriate nitrogen application rate. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 982637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tikhomirova, E.V. Changes of nitrogen metabolism in millet at elevated temperatures. Field Crops Res. 1985, 11, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giunta, F.; Mefleh, M.; Pruneddu, G.; Motzo, R. Role of Nitrogen Uptake and Grain Number on the Determination of Grain Nitrogen Content in Old Durum Wheat Cultivars. Agronomy 2021, 11, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Effah, Z.; Li, L.L.; Xie, J.H.; Liu, C.; Xu, A.X.; Karikari, B.; Anwar, S.; Zeng, M. Regulation of Nitrogen Metabolism, Photosynthetic Activity, and Yield Attributes of Spring Wheat by Nitrogen Fertilizer in the Semi-arid Loess Plateau Region. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2022, 2022, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.; Liu, W.; Li, S.; Zhang, P.; Wang, C.; Lu, H.; Wang, L.; Xie, Y.; Ma, D.; Kang, G. Determining the Optimal N Input to Improve Grain Yield and Quality in Winter Wheat with Reduced Apparent N Loss in the North China Plain. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, R.A.; Howe, G.N.; Ibrahim, Z. Irrigated spring wheat and timing and amount of nitrogen fertilizer. I. Grain yield and protein content. Field Crops Res. 1993, 33, 37–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.C.; Wang, Z.H.; Huang, M.; Hui, X.L.; Wang, S.; Zhao, Y.; He, H.X.; Zhang, X.; Diao, C.P.; Cao, H.B.; et al. Plastic film mulch increased winter wheat grain yield but reduced its protein content in dryland of northwest China. Field Crops Res. 2018, 218, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.X.; Liu, S.J.; Dong, Y.J.; Liao, Y.C.; Han, J. A nitrogen fertilizer strategy for simultaneously increasing wheat grain yield and protein content: Mixed application of controlled-release urea and normal urea. Field Crops Res. 2022, 277, 108405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godfrey, D.; Hawkesford, M.J.; Powers, S.J.; Millar SShewry, P.R. Effects of crop nutrition on wheat grain composition and end use quality. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 3012–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvat, D.; Simic, G.; Dvojkovic, K.; Ivik, M.; Plavsin, I.; Novoselovic, D. Gluten Protein Compositional Changes in Response to Nitrogen Application Rate. Agronomy 2021, 11, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Dai, X.L.; Jia, D.Y.; Li, H.Y.; Wang, Y.C.; Li, C.X.; Xu, H.C.; He, M.R. Effects of plant density on grain yield, protein size distribution, and breadmaking quality of winter wheat grown under two nitrogen fertilisation rates. Eur. J. Agron. 2016, 73, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, Z.H.; Yu, R.; Li, F.C.; Li, K.Y.; Cao, H.B.; Yang, N.; Li, M.H.; Dai, J.; Zan, Y.L.; et al. Optimal nitrogen input for higher efficiency and lower environmental impacts of winter wheat production in China. Agriculture. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 224, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, A.S.; Bradburne, R.P.; Fish, L.; Snape, J.W. New quantitative trait loci influencing grain texture and protein content in bread wheat. J. Cereal Sci. 2004, 40, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reznick JP, K.; Barth, G.; Kaschuk, G.; Pauletti, V. Nitrogen and cultivars as field strategies to improve the nutritional status of wheat grain and flour. J. Cereal Sci. 2021, 102, 103290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.C.; Chang, X.H.; Yang, Y.S.; Li, S.S.; Feng, M.; Ding, Y.P.; Wang, X.H.; Zhang, T.H. Grain yield and protein components responding to the amount and rate of nitrogen application in winter wheat. J. Triticeae Crops 2009, 29, 294–298, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Johansson, E.; Prieto-Linde, M.L.; Jönsson, J.Ö. Effects of Wheat Cultivar and Nitrogen Application on Storage Protein Composition and Breadmaking Quality. Cereal Chem. J. 2001, 78, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.C.; Hui, X.L.; Wang, Z.H.; Zhang, X.; Xie, Y.H.; Gao, Z.Q.; Chai, S.X.; Lu, Q.L.; Li, T.L.; Sun, M.; et al. Multi-site evaluation of plastic film mulch and nitrogen fertilization for wheat grain yield, protein content and its components in semiarid areas of China. Field Crops Res. 2019, 240, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giunta, F.; Pruneddu, G.; Motzo, R. Grain yield and grain protein of old and modern durum wheat cultivars grown under different cropping systems. Field Crops Res. 2019, 230, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.X.; Yu, H.X.; Ma, W.J.; Sun, J.Q.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, R.C.; Ning, T.Y.; Li, Q.F.; Liu, Q.Q.; Guo, T.T.; et al. A major and stable QTL controlling wheat thousand grain weight: Identification, characterization, and CAPS marker development. Mol. Breed. 2020, 40, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.F.; Long, L.I.; Mao, X.G.; Wang, J.Y.; Jing, R.L. dCAPS markers developed for nitrate transporter genes TaNRT2L12s associating with 1000-grain weight in wheat. J. Integr. Agric. 2020, 19, 1543–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koppensteiner, L.J.; Kaul, H.P.; Piepho, H.P.; Barta, N.; Euteneuer, P.; Bernas, J.; Klimek-Kopyra, A.; Gronauer, A.; Neugschwandtner, R.W. Yield and yield components of facultative wheat are affected by sowing time, nitrogen fertilization and environment. Eur. J. Agron. 2022, 140, 126591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, Y.; Sui, X.; Wang, J.; Duan, Q.; Wu, C.; Ding, C.; Li, T. Effects of Nitrogen Application Rate on Protein Components and Yield of Low-Gluten Rice. Agriculture 2021, 11, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abad, A.; Lloveras, J.; Michelena, A. Nitrogen fertilization and foliar urea effects on durum wheat yield and quality and on residual soil nitrate in irrigated mediterranean conditions. Field Crops Res. 2004, 87, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Treatment | Pure Nitrogen (kg hm−2) | Base Fertilizer (20%) | Top Dressing (80%) | Two-Leaf One-Hearted Period (10%) | Tillering Period (10%) | Jointing Period:5 Leaf Age (40%) | Booting Period (20%) | Flowering Period (15%) | Milk Ripening Period (5%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nck | 300 | 60 | 240 | 24 | 24 | 96 | 48 | 36 | 12 |
| N5 | 285 | 57 | 228 | 22.8 | 22.8 | 91.2 | 45.6 | 34.2 | 11.4 |
| N10 | 270 | 54 | 216 | 21.6 | 21.6 | 86.4 | 43.2 | 32.4 | 10.8 |
| N15 | 255 | 51 | 204 | 20.4 | 20.4 | 81.6 | 40.8 | 30.6 | 10.2 |
| N20 | 240 | 48 | 192 | 19.2 | 19.2 | 76.8 | 38.4 | 28.8 | 9.6 |
| N25 | 225 | 45 | 180 | 18 | 18 | 72 | 36 | 27 | 9 |
| N0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Source of Variation | Dependent Variable | SS | DF | MS | F | Sig. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y | protein | 15.28 | 1 | 15.28 | 12,272.12 | ** |
| NR | 0.15 | 1 | 0.15 | 8700.14 | ** | |
| GS | 0.06 | 1 | 0.06 | 2155.40 | ** | |
| GPT | 0.14 | 1 | 0.14 | 8724.61 | ** | |
| V | protein | 35.87 | 1 | 35.87 | 28,819.49 | ** |
| NR | 0.00 | 1 | 0.00 | 265.28 | ** | |
| GS | 0.01 | 1 | 0.01 | 349.38 | ** | |
| GPT | 0.09 | 1 | 0.09 | 5361.47 | ** | |
| T | protein | 26.25 | 6 | 4.37 | 3513.90 | ** |
| NR | 0.13 | 6 | 0.02 | 1260.98 | ** | |
| GS | 0.05 | 6 | 0.01 | 286.57 | ** | |
| GPT | 0.13 | 6 | 0.02 | 1360.32 | ** | |
| Y × V | protein | 1.00 | 1 | 1.00 | 800.81 | ** |
| NR | 0.00 | 1 | 0.00 | 57.23 | ** | |
| GS | 0.00 | 1 | 0.00 | 1.61 | ns | |
| GPT | 0.01 | 1 | 0.01 | 357.64 | ** | |
| Y × N | protein | 2.57 | 6 | 0.43 | 343.76 | ** |
| NR | 0.00 | 6 | 0.00 | 22.25 | ** | |
| GS | 0.01 | 6 | 0.00 | 31.18 | ** | |
| GPT | 0.01 | 6 | 0.00 | 119.87 | ** | |
| V × N | protein | 13.25 | 6 | 2.21 | 1773.73 | ** |
| NR | 0.07 | 6 | 0.01 | 700.52 | ** | |
| GS | 0.03 | 6 | 0.00 | 157.18 | ** | |
| GPT | 0.09 | 6 | 0.01 | 880.63 | ** | |
| Y × V × N | protein | 1.10 | 6 | 0.18 | 147.07 | ** |
| NR | 0.00 | 6 | 0.00 | 5.45 | ** | |
| GS | 0.00 | 6 | 0.00 | 8.71 | ** | |
| GPT | 0.00 | 6 | 0.00 | 19.58 | ** |
| Year (Y) | Varieties (V) | Treatment (T) | Content of Albumin (%) | Content of Globulin (%) | Content of Gliadin (%) | Content of Glutelin (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | XC 38 | Nck | 2.28 ± 0.12 ab | 1.34 ± 0.07 ab | 2.74 ± 0.06 b | 4.33 ± 0.13 a |
| N5 | 2.29 ± 0.12 ab | 1.35 ± 0.04 ab | 2.75 ± 0.03 ab | 4.34 ± 0.07 a | ||
| N10 | 2.39 ± 0.16 a | 1.42 ± 0.08 a | 2.88 ± 0.04 a | 4.43 ± 0.06 a | ||
| N15 | 2.42 ± 0.11 a | 1.43 ± 0.08 a | 2.89 ± 0.08 a | 4.44 ± 0.09 a | ||
| N20 | 2.24 ± 0.11 ab | 1.31 ± 0.05 bc | 2.71 ± 0.07 bc | 4.32 ± 0.12 a | ||
| N25 | 2.24 ± 0.1 ab | 1.29 ± 0.04 bc | 2.68 ± 0.11 bc | 4.28 ± 0.08 b | ||
| N0 | 2.13 ± 0.14 b | 1.21 ± 0.01 c | 2.59 ± 0.1 c | 4.28 ± 0.1 b | ||
| XC 49 | Nck | 1.83 ± 0.03 b | 1.14 ± 0.03 bc | 2.6 ± 0.02 bc | 3.49 ± 0.11 bc | |
| N5 | 1.86 ± 0.01 b | 1.16 ± 0.09 abc | 2.65 ± 0.04 b | 3.5 ± 0.07 bc | ||
| N10 | 1.87 ± 0.02 b | 1.18 ± 0.03 abc | 2.67 ± 0.02 b | 3.53 ± 0.01 bc | ||
| N15 | 1.88 ± 0.02 b | 1.19 ± 0.1 abc | 2.68 ± 0.02 b | 3.56 ± 0.07 ab | ||
| N20 | 1.98 ± 0.03 a | 1.27 ± 0.02 ab | 2.8 ± 0.09 a | 3.67 ± 0.04 a | ||
| N25 | 1.99 ± 0.03 a | 1.28 ± 0.12 a | 2.81 ± 0.02 a | 3.68 ± 0.02 a | ||
| N0 | 1.78 ± 0.05 c | 1.11 ± 0.03 c | 2.54 ± 0.03 c | 3.41 ± 0.09 c | ||
| 2019 | XC 38 | Nck | 2.54 ± 0.09 bc | 1.53 ± 0.1 b | 3.11 ± 0.13 bc | 4.75 ± 0.03 bc |
| N5 | 2.63 ± 0.07 b | 1.6 ± 0.05 b | 3.18 ± 0.08 bc | 4.86 ± 0.06 b | ||
| N10 | 2.66 ± 0.09 b | 1.64 ± 0.17 b | 3.2 ± 0.1 b | 4.88 ± 0.09 b | ||
| N15 | 2.97 ± 0.11 a | 1.81 ± 0.1 a | 3.54 ± 0.07 a | 5.41 ± 0.03 a | ||
| N20 | 2.43 ± 0.09 cd | 1.46 ± 0.06 bc | 2.99 ± 0.15 cd | 4.61 ± 0.14 c | ||
| N25 | 2.34 ± 0.08 d | 1.33 ± 0.07 cd | 2.84 ± 0.08 d | 4.43 ± 0.09 d | ||
| N0 | 2.17 ± 0.11 e | 1.27 ± 0.08 d | 2.6 ± 0.1 e | 4.22 ± 0.09 e | ||
| XC 49 | Nck | 1.96 ± 0.08 d | 1.22 ± 0.09 bc | 2.75 ± 0.12 cd | 3.6 ± 0.12 cd | |
| N5 | 1.2 ± 0.07 cd | 1.27 ± 0.11 bc | 2.95 ± 0.13 bc | 3.76 ± 0.09 bc | ||
| N10 | 2.12 ± 0.14 bc | 1.34 ± 0.13 b | 3.05 ± 0.1 b | 3.9 ± 0.14 b | ||
| N15 | 2.18 ± 0.13 b | 1.36 ± 0.07 b | 3.06 ± 0.12 b | 3.93 ± 0.13 b | ||
| N20 | 2.2 ± 0.13 b | 1.37 ± 0.11 b | 3.12 ± 0.11 b | 3.94 ± 0.06 b | ||
| N25 | 2.52 ± 0.11 a | 1.56 ± 0.05 a | 3.38 ± 0.11 a | 4.52 ± 0.08 a | ||
| N0 | 1.82 ± 0.06 e | 1.14 ± 0.06 c | 2.57 ± 0.10 d | 3.46 ± 0.09 d | ||
| F | Y | ** | ** | ** | ** | |
| V | ** | ** | ** | ** | ||
| T | ** | ** | ** | ** | ||
| Y × V | ** | ns | ns | ns | ||
| Y × N | ** | ns | ** | ** | ||
| V × N | ** | ** | ** | ** | ||
| Y × V × N | ** | ns | ** | ** | ||
| Year (Y) | Variety (V) | Nitrogen (N) | 1000-Grain Weight (g) | Spike Number (×104·hm−2) | Grain Number per Spike | Actual Yield (kg·hm−2) | Protein Yield (kg·hm−2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | XC 38 | Nck | 42.51 ± 0.87 bc | 437.28 ± 9.87 bc | 39.15 ± 0.93 a | 6915.10 ± 9.52 d | 729.78 ± 1.00 d |
| N5 | 42.81 ± 1.33 abc | 444.61 ± 13.47 ab | 39.34 ± 2.29 a | 7035.70 ± 5.08 c | 742.51 ± 0.54 c | ||
| N10 | 44.15 ± 0.69 ab | 455.13 ± 10.47 a | 40.41 ± 1.12 a | 7108.20 ± 8.05 b | 750.16 ± 0.85 b | ||
| N15 | 45.36 ± 1.42 a | 455.85 ± 3.07 a | 40.33 ± 0.58 a | 7355.70 ± 15.24 a | 776.28 ± 1.61 a | ||
| N20 | 41.51 ± 1.9 bc | 432.18 ± 7.03 bc | 38.98 ± 1.51 a | 6892.40 ± 14.31 e | 727.39 ± 1.51 e | ||
| N25 | 41.32 ± 1.82 c | 431.98 ± 5.74 bc | 38.09 ± 2.13 a | 6862.50 ± 5.29 f | 724.23 ± 0.56 f | ||
| N0 | 40.65 ± 1.56 c | 426.42 ± 1.81 c | 37.61 ± 1.00 a | 4047.40 ± 5.55 g | 427.14 ± 0.59 g | ||
| XC 49 | Nck | 37.03 ± 1.5 bc | 386.12 ± 12.26 ab | 36.14 ± 1.12 ab | 6537.90 ± 7.12 e | 689.98 ± 0.75 e | |
| N5 | 37.23 ± 0.49 bc | 386.85 ± 6.05 ab | 37.06 ± 2.4 ab | 6587.50 ± 17.69 d | 695.21 ± 1.87 d | ||
| N10 | 37.32 ± 0.92 bc | 387.45 ± 11.87 ab | 37.57 ± 1.14 ab | 6678.20 ± 13.24 c | 704.78 ± 1.40 c | ||
| N15 | 37.51 ± 0.87 bc | 397.86 ± 6.60 a | 38.14 ± 2.35 ab | 6787.80 ± 12.96 b | 716.35 ± 1.37 b | ||
| N20 | 39.02 ± 1.76 ab | 398.25 ± 10.59 a | 39.54 ± 2.22 a | 6795.10 ± 10.21 b | 717.12 ± 1.08 b | ||
| N25 | 39.94 ± 1.41 a | 398.54 ± 8.14 a | 39.12 ± 2.31 ab | 6822.60 ± 8.32 a | 720.02 ± 0.88 a | ||
| N0 | 36.57 ± 1.03 c | 375.65 ± 8.61 b | 35.56 ± 1.13 b | 3984.20 ± 18.40 f | 420.47 ± 1.94 f | ||
| 2019 | XC 38 | Nck | 42.39 ± 0.61 ab | 422.10 ± 8.38 abc | 37.39 ± 2.85 a | 6999.71 ± 13.48 d | 912.88 ± 1.76 b |
| N5 | 42.77 ± 2.01 ab | 423.75 ± 3.42 abc | 37.88 ± 2.67 a | 7147.39 ± 7.32 c | 932.14 ± 0.96 b | ||
| N10 | 44.39 ± 0.88 ab | 432.52 ± 4.66 ab | 39.46 ± 4.01 a | 7216.03 ± 6.72 b | 941.09 ± 0.88 a | ||
| N15 | 45.22 ± 1.69 a | 437.90 ± 3.77 a | 39.11 ± 3.78 a | 7397.39 ± 8.03 a | 964.74 ± 1.05 a | ||
| N20 | 42.05 ± 2.84 ab | 420.78 ± 3.57 abc | 37.25 ± 1.33 a | 6931.4 ± 8.65 e | 903.97 ± 1.13 c | ||
| N25 | 41.56 ± 2.22 b | 420.39 ± 15.79 bc | 36.83 ± 1.55 a | 6882.17 ± 6.49 f | 897.55 ± 0.85 c | ||
| N0 | 38.24 ± 1.31 c | 414.93 ± 13.33 c | 35.21 ± 0.93 a | 4083.30 ± 19.74 g | 532.53 ± 2.57 d | ||
| XC 49 | Nck | 40.13 ± 2.07 ab | 399.26 ± 10.67 a | 36.62 ± 1.74 ab | 6567.50 ± 4.97 d | 856.51 ± 0.65 d | |
| N5 | 40.54 ± 2.18 ab | 399.46 ± 10.26 a | 37.24 ± 0.86 ab | 6724.60 ± 8.31 c | 877.00 ± 1.08 c | ||
| N10 | 40.94 ± 2.41 ab | 401.94 ± 10.66 a | 37.27 ± 2.29 ab | 6755.50 ± 4.28 b | 881.03 ± 0.56 b | ||
| N15 | 41.13 ± 1.58 ab | 403.78 ± 5.40 a | 37.48 ± 2.85 ab | 6778.87 ± 16.13 a | 884.08 ± 2.10 a | ||
| N20 | 42.48 ± 2.99 ab | 409.54 ± 6.84 a | 38.79 ± 0.69 a | 6821.09 ± 13.36 e | 889.58 ± 1.74 e | ||
| N25 | 43.73 ± 2.97 a | 414.68 ± 10.68 a | 38.09 ± 1.77 ab | 6844.40 ± 8.86 f | 892.62 ± 1.15 f | ||
| N0 | 37.44 ± 3.61 b | 397.29 ± 15.19 a | 34.82 ± 1.46 b | 3994.50 ± 10.47 g | 520.95 ± 1.37 g | ||
| F | Y | ** | ns | * | ** | ** | |
| V | ** | ** | * | ** | ** | ||
| T | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ||
| Y × V | ** | ** | ns | ** | ** | ||
| Y × N | ns | ns | ns | ** | ** | ||
| V × N | ** | ** | ns | ** | ** | ||
| Y × V × N | ns | ns | ns | ** | ** | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, R.; Wang, H.; Jiang, G.; Yin, H.; Che, Z. Effects of Nitrogen Application Strategy on Nitrogen Enzyme Activities and Protein Content in Spring Wheat Grain. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1891. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12111891
Wang R, Wang H, Jiang G, Yin H, Che Z. Effects of Nitrogen Application Strategy on Nitrogen Enzyme Activities and Protein Content in Spring Wheat Grain. Agriculture. 2022; 12(11):1891. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12111891
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Rongrong, Haiqi Wang, Guiying Jiang, Haojie Yin, and Ziqiang Che. 2022. "Effects of Nitrogen Application Strategy on Nitrogen Enzyme Activities and Protein Content in Spring Wheat Grain" Agriculture 12, no. 11: 1891. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12111891
APA StyleWang, R., Wang, H., Jiang, G., Yin, H., & Che, Z. (2022). Effects of Nitrogen Application Strategy on Nitrogen Enzyme Activities and Protein Content in Spring Wheat Grain. Agriculture, 12(11), 1891. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12111891




