An Approach for Rice Bacterial Leaf Streak Disease Segmentation and Disease Severity Estimation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Disease Severity Label
2.3. Model Architecture
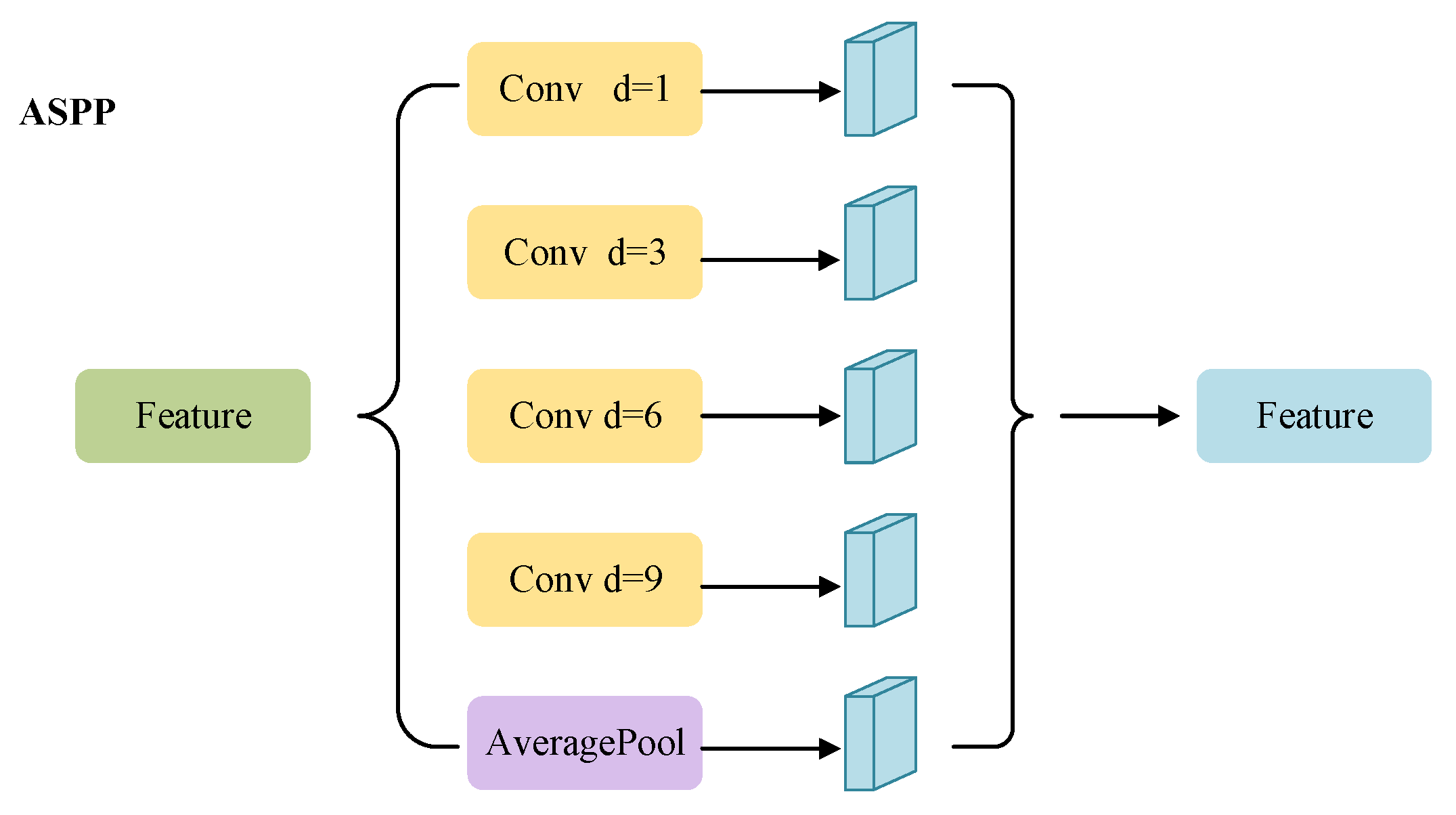
2.3.1. Down-Sample Stage
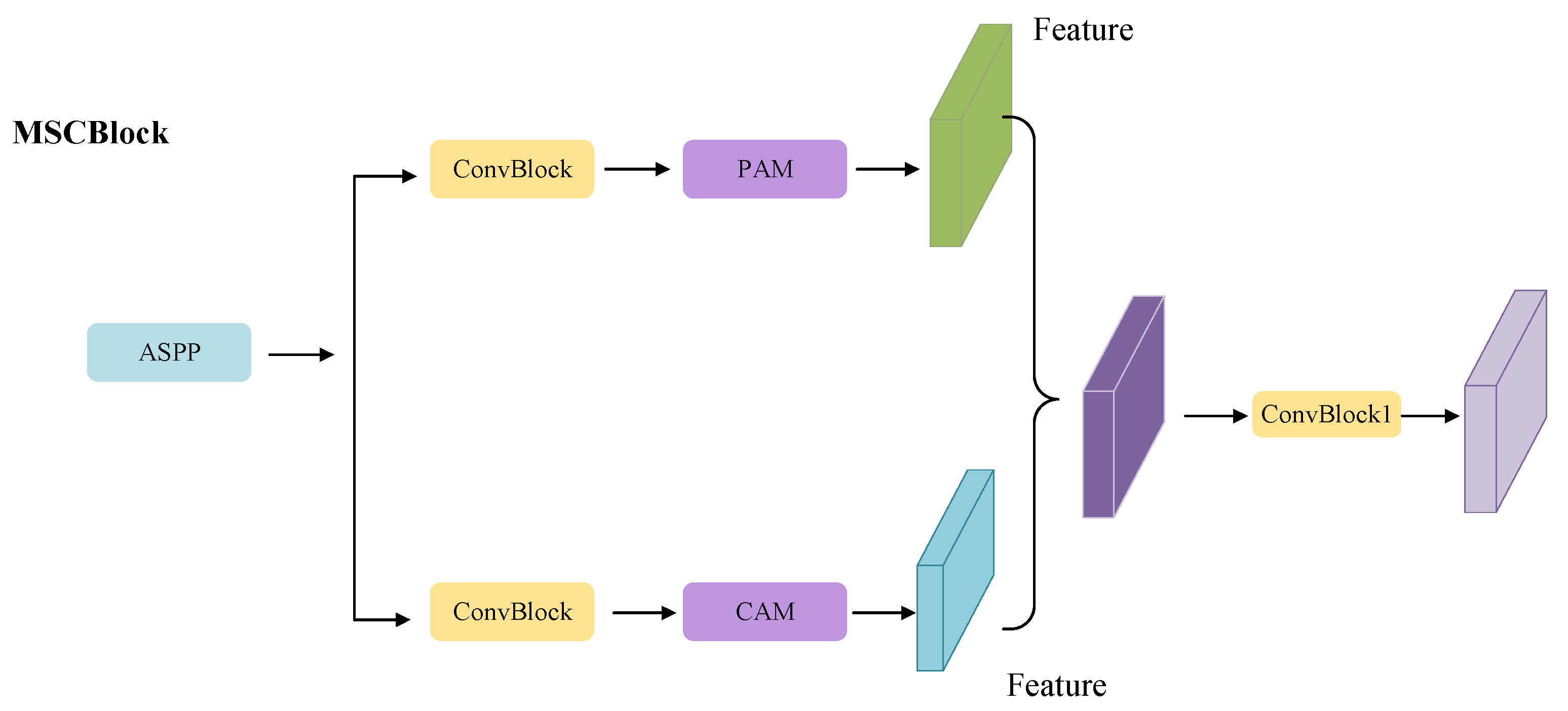
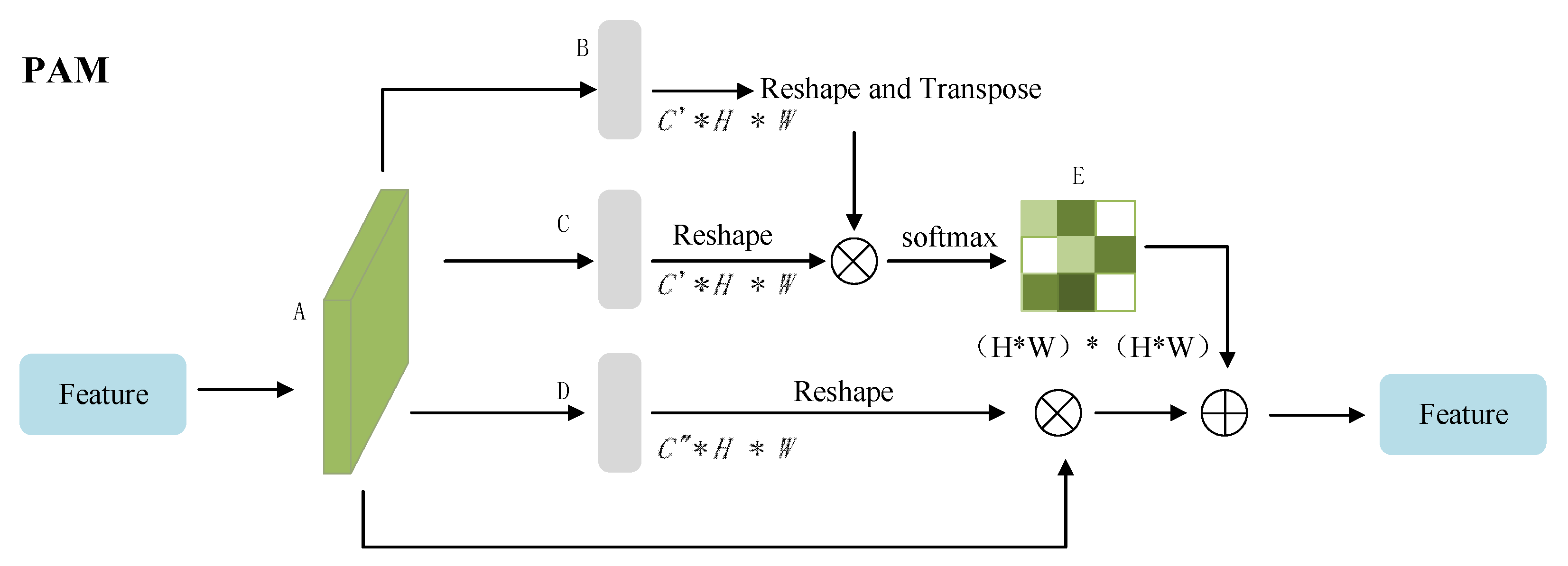
2.3.2. Skip Connection Stage with Attention Block
2.3.3. Up-Sample Stage
2.4. Experimental Process
3. Results
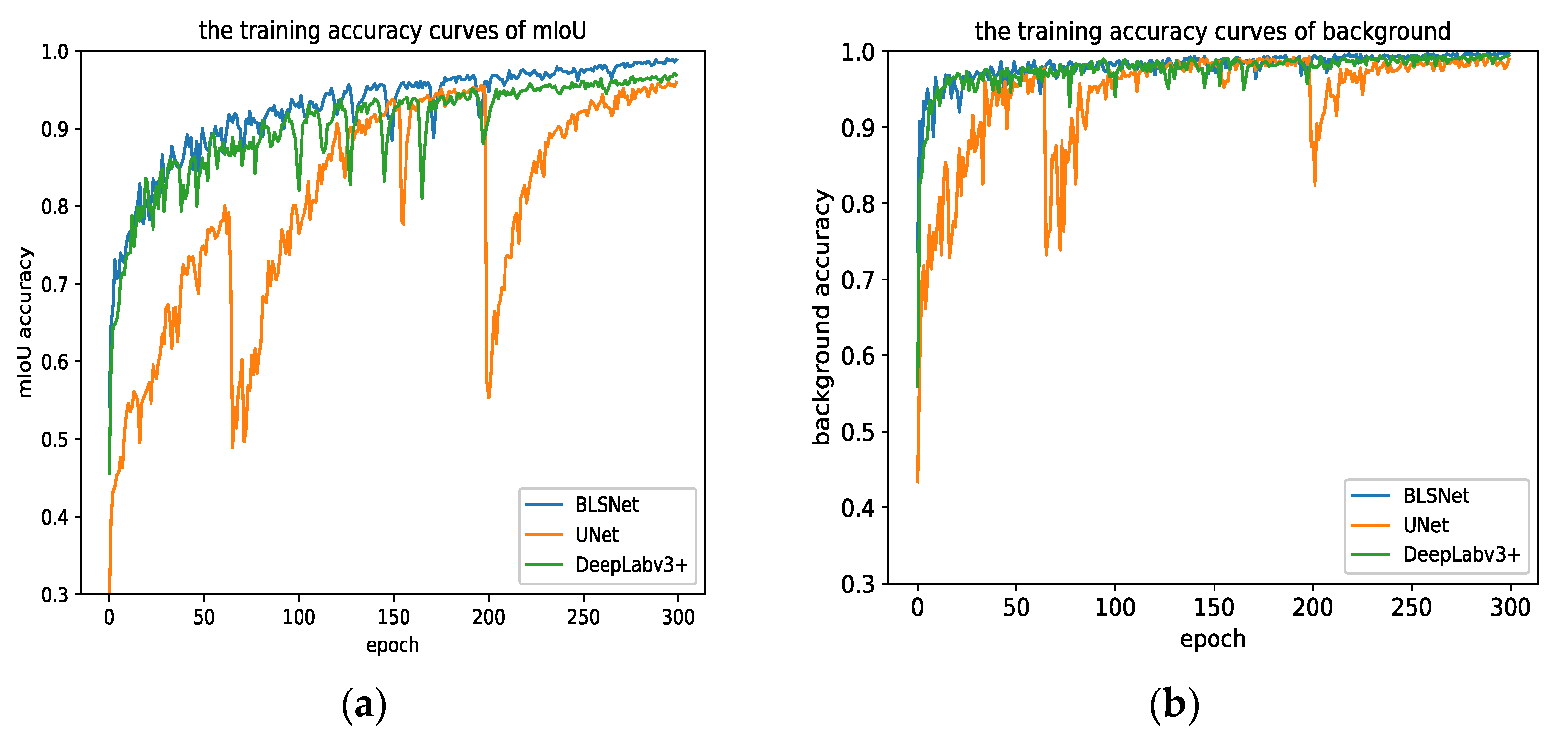
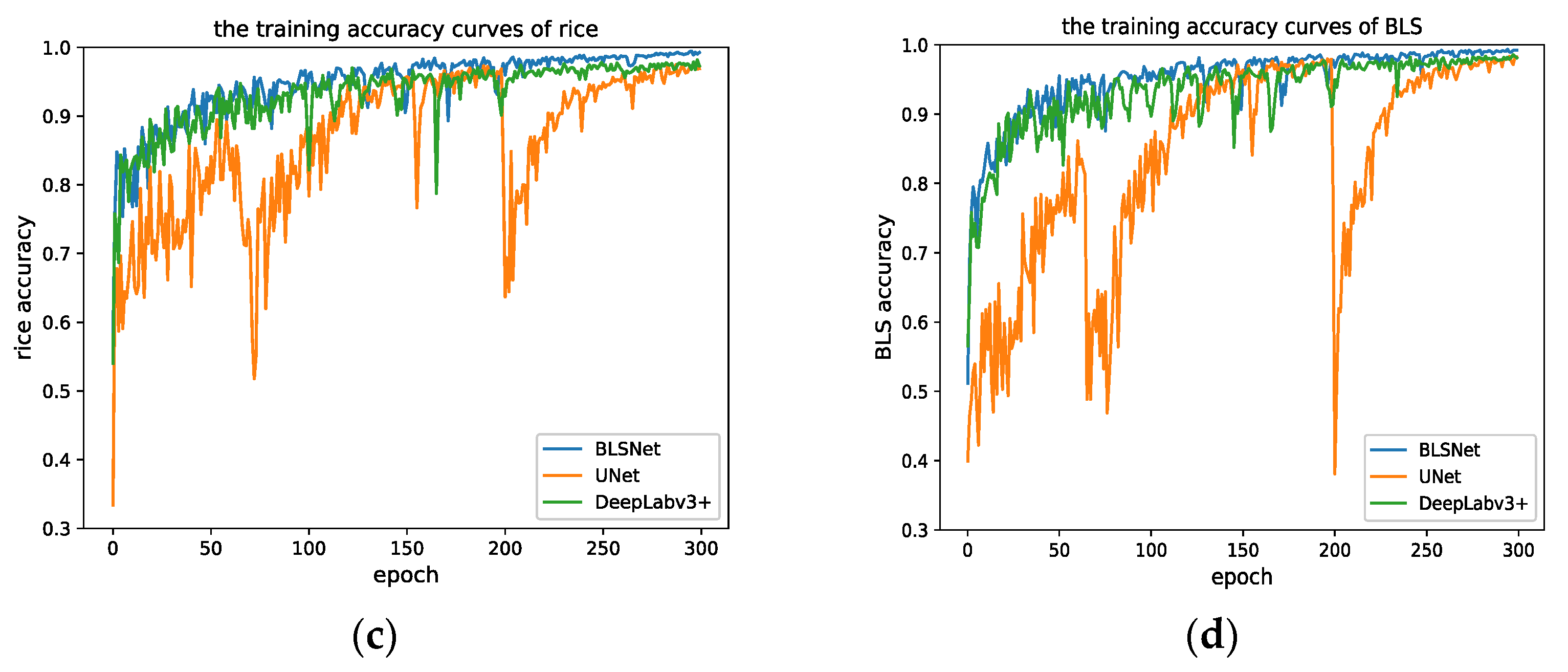
3.1. Training Results
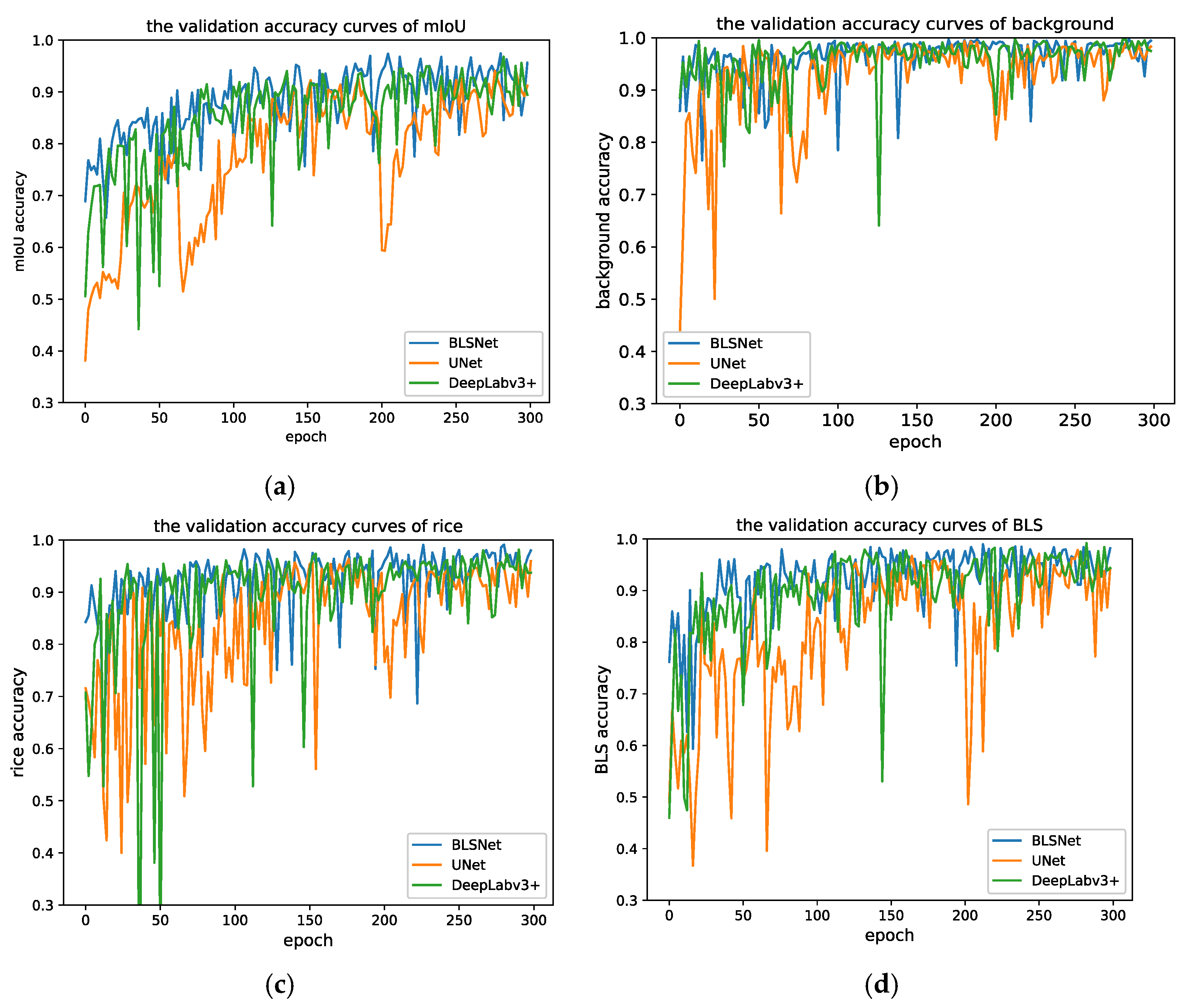
3.2. Validation Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Ablation Study on Attention Block
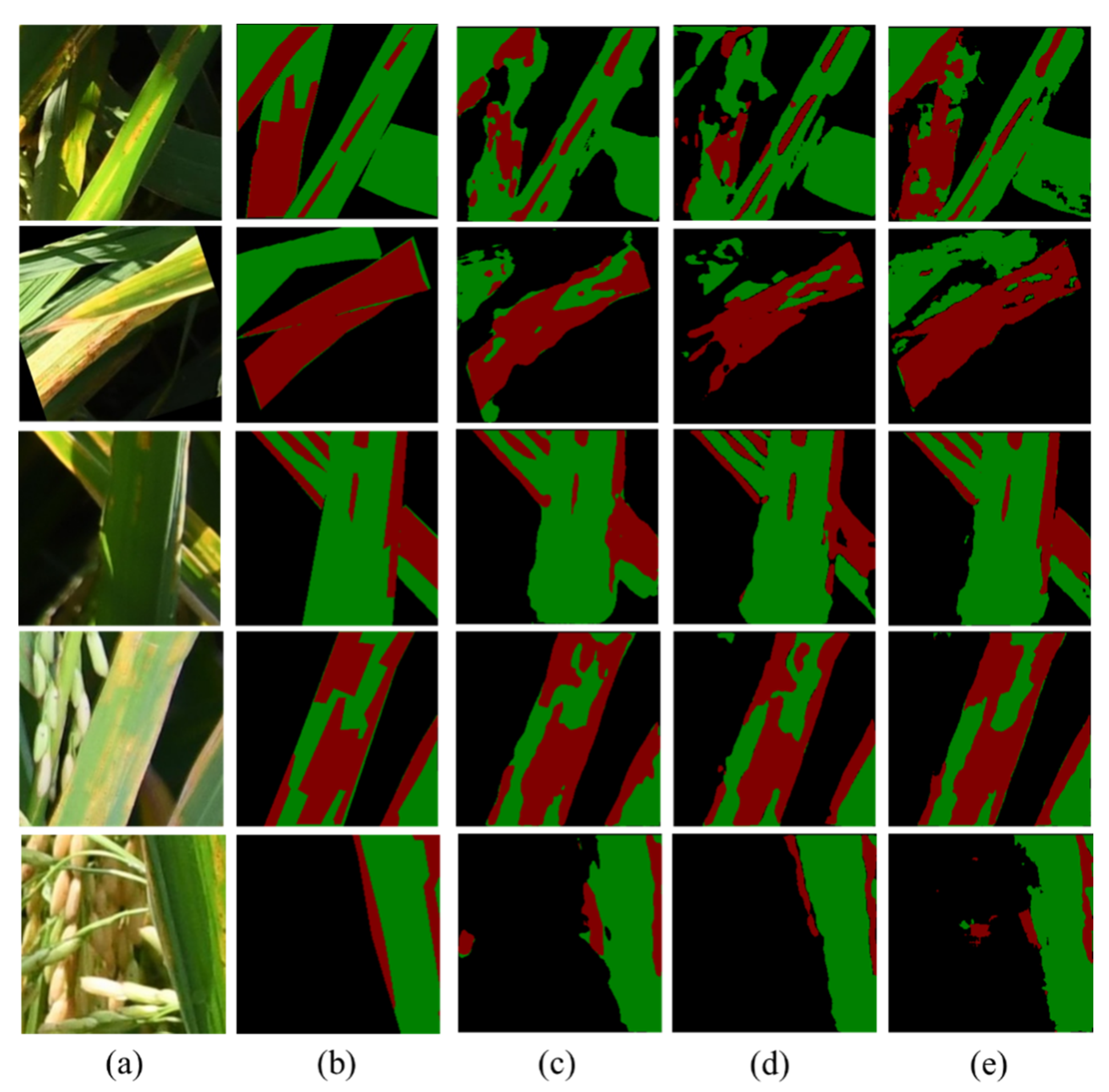
4.2. Prediction Results Comparison
4.3. Comparison of Model Prediction Time
4.4. Disease Severity Estimation Comparison
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- NIÑO-LIU, D.O.; Ronald, P.C.; Bogdanove, A.J. Xanthomonas oryzae pathovars: Model pathogens of a model crop. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2006, 7, 303–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, A.A.; Jadhav, B. Monitoring and controlling rice diseases using image processing techniques. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Computing, Analytics and Security Trends (CAST), Pune, India, 19–21 December 2016; pp. 471–476. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Yang, T.; Tian, Y. Crop disease leaf image segmentation method based on color features. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer and Computing Technologies in Agriculture, Boston, MA, USA, 18–20 October 2008; pp. 713–717. [Google Scholar]
- Revathi, P.; Hemalatha, M. Homogenous segmentation based edge detection techniques for proficient identification of the cotton leaf spot diseases. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2012, 47, 18–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Meng, Q. Automatic citrus canker detection from leaf images captured in field. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2011, 32, 2036–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prajapati, H.B.; Shah, J.P.; Dabhi, V.K. Detection and classifcation of rice plant diseases. Intell. Decis. Technol. 2017, 11, 357–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, R.D.L.; Gonçalves, D.N.; Oruê, J.P.M.; Kanashiro, W.E.S.; Rodrigues, J.F.; Machado, B.B.; Gonçalves, W.N. Local descriptors for soybean disease recognition. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2016, 125, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 3431–3440. [Google Scholar]
- Sethy, P.K.; Barpanda, N.K.; Rath, A.K.; Behera, S.K. Deep feature based rice leaf disease identification using support vector machine. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 175, 105527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, U.P.; Chouhan, S.S.; Jain, S.; Jain, S.; Jain, S. Multilayer convolution neural network for the classification of mango leaves infected by anthracnose disease. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 43721–43729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Gu, Y.H.; Park, C.; Park, J.; Yoo, S.J. Transfer learning-based search model for hot pepper diseases and pests. Agriculture 2020, 10, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Yi, S.; Zeng, N.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Identification of rice diseases using deep convolutional neural networks. Neurocomputing 2017, 267, 378–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barman, U.; Choudhury, R.D.; Sahu, D.; Barman, G.G. Comparison of convolution neural networks for smartphone image based real time classification of citrus leaf disease. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, M.H.; Potgieter, J.; Arif, K.M. Plant disease classification: A comparative evaluation of convolutional neural networks and deep learning optimizers. Plants 2020, 9, 1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabir, M.M.; Ohi, A.Q.; Mridha, M. A Multi-plant disease diagnosis method using convolutional neural network. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2011.05151. [Google Scholar]
- Karlekar, A.; Seal, A. SoyNet: Soybean leaf diseases classification. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 172, 105342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chen, J.; Zhang, D.; Sun, Y.; Nanehkaran, Y.A. Using deep transfer learning for image-based plant disease identification. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 173, 105393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, S.; Beauseroy, P.; Smolarz, A. Unsupervised adversarial deep domain adaptation method for potato defects classification. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 174, 105501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalpana, M.; Karthiba, L.; Kumar, A.V.S. Disease severity diagnosis for rice using fuzzy verdict method. In New Trends in Computational Vision and Bio-Inspired Computing: Selected Works Presented at the ICCVBIC 2018; Coimbatore, I., Smys, S., Iliyasu, A.M., Bestak, R., Shi, F., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 873–880. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Q.; Xiang, S.; Hu, Y.; Coppola, G.; Zhang, D.; Sun, W. PD2SE-Net: Computer-assisted plant disease diagnosis and severity estimation network. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2019, 157, 518–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esgario, J.G.M.; Krohling, R.A.; Ventura, J.A. Deep learning for classification and severity estimation of coffee leaf biotic stress. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 169, 105162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhakar, M.; Purushothaman, R.; Awasthi, D.P. Deep learning based assessment of disease severity for early blight in tomato crop. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2020, 79, 28773–28784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Duan, L.; Liu, L.; Tu, H.; Yang, P.; Wu, D.; Chen, G.; Xiong, L.; Yang, W.; Liu, Q. Panicle-SEG: A robust image segmentation method for rice panicles in the field based on deep learning and superpixel optimization. Plant Methods 2017, 13, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerkech, M.; Hafiane, A.; Canals, R. Vine disease detection in UAV multispectral images using optimized image registration and deep learning segmentation approach. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 174, 105446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.F.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, S.W. Segmenting Crop Disease Leaf Image by Modified Fully-Convolutional Networks. Intell. Comput. Theor. Appl. 2019, 646–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tusubira, J.F.; Akera, B.; Nsumba, S.; Nakatumba-Nabende, J.; Mwebaze, E. Scoring Root Necrosis in Cassava Using Semantic Segmentation. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2005.03367. [Google Scholar]
- Abdalla, A.; Cen, H.; Wan, L.; Rashid, R.; Weng, H.; Zhou, W.; He, Y. Fine-tuning convolutional neural network with transfer learning for semantic segmentation of ground-level oilseed rape images in a field with high weed pressure. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2019, 167, 105091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, S.; Pandey, S.; Goel, S. Plants disease identification and classification through leaf images: A survey. Arch. Comput. Method Eng. 2019, 26, 507–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, M.H.; Potgieter, J.; Arif, K. Plant disease detection and classification by deep learning. Plants 2019, 8, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Chen, Y.; Liu, B.; He, D.; Liang, C. Real-time detection of apple leaf diseases using deep learning approach based on improved convolutional neural networks. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 59069–59080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wiesner-Hanks, T.; Stewart, E.L.; DeChant, C.; Kaczmar, N.; Gore, M.A.; Nelson, R.J.; Lipson, H. Autonomous detection of plant disease symptoms directly from aerial imagery. Plant Phenome J. 2019, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wang, R.; Xie, C.; Liu, L.; Zhang, J.; Li, R.; Wang, F.; Zhou, M.; Liu, W. A recognition method for rice plant diseases and pests video detection based on deep convolutional neural network. Sensors 2020, 20, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Sun, Y.; Wang, J. Automatic image-based plant disease severity estimation using deep learning. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2017, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; Chug, A.; Singh, A.P. Application of convolutional neural networks for evaluation of disease severity in tomato plant. J. Discret. Math. Sci. Cryptogr. 2020, 23, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.; Gong, L.; Huang, Y.; Liu, C.; Pan, J. Deep learning-based segmentation and quantification of cucumber powdery mildew using convolutional neural network. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrivastava, V.K.; Pradhan, M.K.; Minz, S.; Thakur, M.P. Rice plant disease classification using transfer learning of deep convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of the International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing & Spatial Information Sciences, ISPRS-GEOGLAM-ISRS Joint Int. Workshop on “Earth Observations for Agricultural Monitoring”, New Delhi, India, 18–20 February 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, D.; Suzauddola, M.; Nanehkaran, Y.A.; Sun, Y. Identification of plant disease images via a squeeze-and-excitation MobileNet model and twice transfer learning. IET Image Process. 2021, 15, 1115–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Mallick, C.; Dutta, S. Deep Learning-Based Automated Feature Engineering for Rice Leaf Disease Prediction. In Proceedings of the Computational Intelligence in Pattern Recognition, Singapore, 18–19 November 2020; pp. 133–141. [Google Scholar]
- Sethy, P.K.; Barpanda, N.K.; Rath, A.K.; Behera, S.K. Rice false smut detection based on Faster R-CNN. Indones. J. Elect. Eng. Comput. Sci 2020, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhassouny, A.; Smarandache, F. Smart mobile application to recognize tomato leaf diseases using Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference of Computer Science and Renewable Energies (ICCSRE), Agadir, Morocco, 22–24 July 2019; IEEE Computer Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Russell, B.C.; Torralba, A.; Murphy, K.P. LabelMe: A database and web-based tool for image annotation. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2008, 77, 157–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradski, G.; Kaehler, A. Learning OpenCV: Computer Vision with the OpenCV Library; O’Reilly Media, Inc.: California, CA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, A. Pillow (PIL Fork) Documentation, 2015; Release.
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Cham, Switzedland, 5–9 October 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.-C.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Rethinking atrous convolution for semantic image segmentation. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.05587. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition(CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, 18–22 June 2018; IEEE Computer Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]
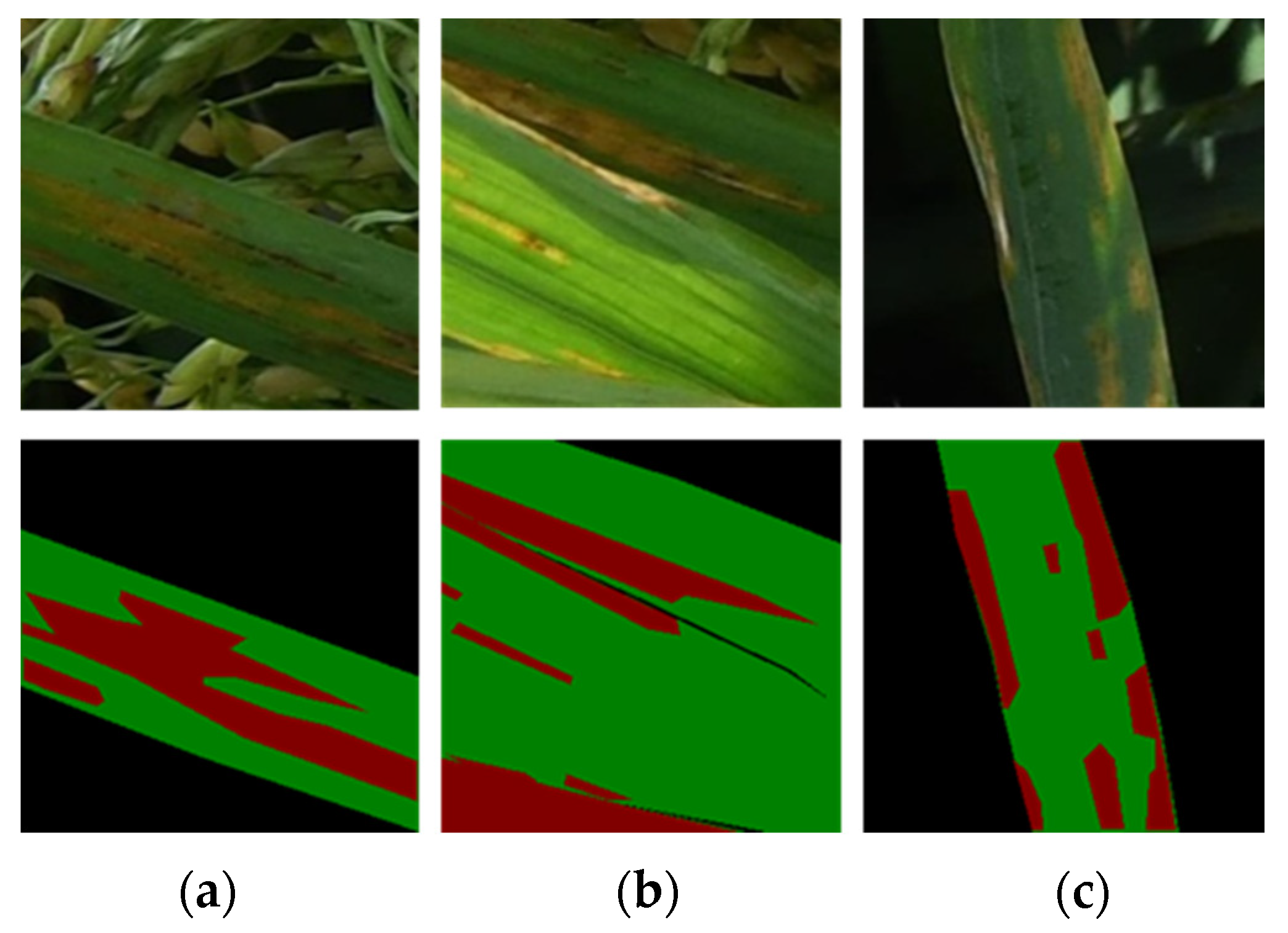








| Disease Severity Level | Training | Validation |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 34 | 11 |
| 2 | 109 | 18 |
| 3 | 351 | 79 |
| 4 | 280 | 78 |
| 5 | 194 | 45 |
| Total | 968 | 231 |
| Indicators | UNet | DeepLabV3+ | BLSNet |
|---|---|---|---|
| mIoU | 0.912 | 0.895 | 0.956 |
| Background | 0.983 | 0.975 | 0.994 |
| BLS | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.982 |
| Rice | 0.959 | 0.938 | 0.980 |
| Indicator | BLSNet | Without1 | Without2 | Without3 | Without4 | Without1–3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mIoU | 0.956 | 0.949 | 0.952 | 0.951 | 0.935 | 0.957 |
| Background | 0.982 | 0.979 | 0.982 | 0.978 | 0.957 | 0.980 |
| BLS | 0.982 | 0.979 | 0.982 | 0.978 | 0.957 | 0.980 |
| Rice | 0.980 | 0.974 | 0.980 | 0.976 | 0.968 | 0.980 |
| Model | UNet | DeepLabV3+ | BLSNet |
|---|---|---|---|
| Prediction Time (s) | 0.020 | 0.028 | 0.021 |
| Severity Level | BLSNet | UNet | DeepLabV3+ |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.91 | 0.91 | 0.91 |
| 2 | 0.89 | 1.00 | 0.89 |
| 3 | 0.92 | 0.85 | 0.87 |
| 4 | 0.95 | 0.91 | 0.91 |
| 5 | 0.95 | 0.89 | 0.93 |
| Average accuracy | 0.94 | 0.89 | 0.90 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, S.; Zhang, K.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, Y.; Ban, W.; Chen, Y.; Zhuang, H.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J.; Yang, T. An Approach for Rice Bacterial Leaf Streak Disease Segmentation and Disease Severity Estimation. Agriculture 2021, 11, 420. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture11050420
Chen S, Zhang K, Zhao Y, Sun Y, Ban W, Chen Y, Zhuang H, Zhang X, Liu J, Yang T. An Approach for Rice Bacterial Leaf Streak Disease Segmentation and Disease Severity Estimation. Agriculture. 2021; 11(5):420. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture11050420
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Shuo, Kefei Zhang, Yindi Zhao, Yaqin Sun, Wei Ban, Yu Chen, Huifu Zhuang, Xuewei Zhang, Jinxiang Liu, and Tao Yang. 2021. "An Approach for Rice Bacterial Leaf Streak Disease Segmentation and Disease Severity Estimation" Agriculture 11, no. 5: 420. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture11050420
APA StyleChen, S., Zhang, K., Zhao, Y., Sun, Y., Ban, W., Chen, Y., Zhuang, H., Zhang, X., Liu, J., & Yang, T. (2021). An Approach for Rice Bacterial Leaf Streak Disease Segmentation and Disease Severity Estimation. Agriculture, 11(5), 420. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture11050420






