Abstract
Salvadora persica is the most used medicinal shrub in the Arab world. This experiment was conducted to evaluate seedling performance at different rates of NPK. Seedlings were treated with N:P:K at 4:2:2 (N:P:K 2:2:2 g + 2 g of nitrogen supplemented as ammonium sulfate), 6:3:3 (N:P:K 3:3:3 g + 3 g of nitrogen supplemented as ammonium sulfate), 2:1:1S (N:P:K 1:1:1 g + 1 g of nitrogen supplemented as ammonium sulfate), 2:1:1U (N:P:K 1:1:1 g + 1 g of nitrogen supplemented as urea), 4:1:1S (N:P:K 1:1:1 g + 3 g of nitrogen supplemented as ammonium sulfate), 4:1:1U (N:P:K 1:1:1 g + 3 g of nitrogen supplemented as urea), 6:1:1S (N:P:K 1:1:1 g + 5 g of nitrogen supplemented as ammonium sulfate), 6:1:1U (N:P:K 1:1:1 g + 5 g of nitrogen supplemented as urea) in addition to the control. The results indicated that NPK application significantly affected the vegetative and root growth parameters and the chemical contents. Among the various treatments of NPK, the application of 6:3:3 rates showed the highest values for aboveground parts, root parameters, and greenness level. Therefore, the present study demonstrates the optimum NPK levels that can enhance seedling growth throughout the nursery period.
1. Introduction
The toothbrush tree (Salvadora persica L.), a member of the Salvadoraceae family, is a special medicinal plant. It is also known as Arak and Miswak in Arabic [1]. S. persica, a facultative halophyte, seems to be a potentially valuable oilseed plant for salt- and alkaline-affected soil [2]. These plants accumulate a high salt level in their cells and tissues and deal with the harmfulness of excessive salt by evolved succulence [3]. They are commonly dispersed in the dry areas of Egypt and frequently in salty soil. It is a small upright evergreen tree or shrub, with a trunk that rarely extends more than 30 inches, with a maximum of 3 m.
Plant reproduction occurs through seeds, layering, and commonly by root suckers. It can be coppiced near to the ground. Seeds are spread by birds and often germinate below other nurse bushes, such as Capparis decidua or Tamarix spp. The growth rate is somewhat slow for the first two to three years after establishing [4].
Sewak is commonly used in Islamic medicine and used by the ancient Arabs to make their teeth white and shiny. The newly flushed leaves are tender and can be eaten in salads and used as a herbal remedy for coughs, asthma, scurvy, rheumatism, and piles [5]. It has been shown to contain many beneficial compounds, i.e., salvadorine, trimethylamine, mustard oil, sulfur, vitamin C, saponins, resins and traces of tannins, sterols, and flavonoids. The WHO advises and supports the routine of chewing S. persica sticks as an effective oral hygiene practice in regions where it is used traditionally. Many researchers have demonstrated the antiperiodontopathic, anticaries, antifungal, and antibacterial effects of the contents S. persica sticks [6,7].
The use of numerous medicinal plants is generally limited to native persons. It is of the greatest significance to preserve this information for later generations; otherwise, it will vanish forever with the loss of native healers and people with ancient health care knowledge.
Around the globe, nutritional supply is key for all plants’ growth, and they must find the main three elements of fertilization, N, P, and K, but nourishment cannot be efficiently applied in a soil–plant system at proportions exceeding 50% [8]. In the growing cycle of each crop, fragmented nutrition supply is an efficient method to decrease fertilizer loss and to increase its usage [8,9,10].
The use of a nitrogen gypsum mixture (gypsum + 9 g of N) during the establishment and early growth stages of S. persica seedlings showed the best outcomes, where it produced an increase of 41% for height and 35% for crown diameter than the control [11]. In another study, all plant characteristics of Salvadora oleoides were enhanced with the application of 100 kg N/ha [12]. The growth of olive trees (cv. Frantoio) was increased significantly when the nitrogen application rate was increased from 250 to 1000 g/tree [13]. The optimum N and K application rates were 750 and 500 g/tree, respectively [13].
NPK fertilizer application produced significant increases in the seedling height, diameter, root length, and fresh and dry weights of the stems, leaves, and roots of Cordia myxa seedlings [14]. Still, using a 3:2:1 ratio of NPK followed by 6:2:1 achieved better results for plant height, stem diameter, fresh weight of leaves, stems, and roots compared to the control (without NPK) Cupressus sempervirens seedlings [15].
Shehata [16] found that the effect of three NPK levels on Poinciana regia seedlings significantly increased stem length, stem diameter, and stem fresh and dry weight using low, medium, or high fertilization rates. To the best of our knowledge, no study has been performed on the effect of NPK application rates on the toothbrush tree’s seedling growth. Thus, an experiment was conducted to find the suitable rate of nutrient application at the seedling stage to produce the best plants to transfer to the open field.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material
Seeds of Salvadora persica L. were purchased from a commercial nursery in the northern Egypt. They were planted in a nursery in plastic trays. Seedlings were transplanted after 45 days, when the seedlings reached 5 cm in height and had 7 leaves, to the experimental conditions.
2.2. Media Preparation
For this experiment, seeds were planted in a media consisting of 3 kg of vermiculite, 2 kg of peatmoss, 20 mg of chelated Fe, and 1 g/L of Rizolex as a fungicide. Trays were filled with mixed media and irrigated, then covered with a plastic sheet. The cover was then removed after 3–5 days; after 10 days, the media were sprayed with 2 kg/200 L of water NPK (19:19:19), then sprayed with NPK every 15–20 days. Seeds were planted in this media and transplanted later to plastic pots (25 × 18 cm) filled with 1:1:1, peat/soil/sand, by volume. The pH of this substrate was 7.6.
2.3. Fertilization Treatments
The experiment started in March and was terminated by the end of October in an open greenhouse in two successive seasons, 2018 and 2019. The average maximum temperature was 28 °C and the average minimum temperature was 15 °C during the experimental period.
NPK fertilizer treatments were used as units per plant divided across 12 weeks as follows:
- Control treatment (without fertilizers) (control);
- N:P:K 4:2:2 (T1) (N:P:K 2:2:2 g + 2 g of nitrogen supplemented as ammonium sulfate);
- N:P:K 6:3:3 (T2) (N:P:K 3:3:3 g + 3 g of nitrogen supplemented as ammonium sulfate);
- N:P:K 2:1:1S (T3) (N:P:K 1:1:1 g + 1 g of nitrogen supplemented as ammonium sulfate);
- N:P:K 2:1:1U (T4) (N:P:K 1:1:1 g + 1 g of nitrogen supplemented as urea);
- N:P:K 4:1:1S (T5) (N:P:K 1:1:1 g + 3 g of nitrogen supplemented as ammonium sulfate);
- N:P:K 4:1:1U (T6) (N:P:K 1:1:1 g + 3 g of nitrogen supplemented as urea);
- N:P:K 6:1:1S (T7) (N:P:K 1:1:1 g + 5 g of nitrogen supplemented as ammonium sulfate);
- N:P:K 6:1:1U (T8) (N:P:K 1:1:1 g + 5 g of nitrogen supplemented as urea).
2.4. Data Records
2.4.1. Vegetative Parameters
Data were collected at the end of the experiment in both seasons. Five plants were collected from each replicate to inspect the effect of the treatments on the vegetative parameters. For each plant, we collected data on shoot height (cm), the number of shoots, the number of leaves, the fresh weight of the green parts (g/plant), and the dry weight of the green parts (g/plant). After the removal of the plants, the roots were cleaned from the soil with tap water and dried with paper tissues, and the length of the roots (cm), the fresh weight of the roots (g/plant), and the dry weight of the roots (g/plant) were measured.
2.4.2. Chemical Analysis
The plants collected were dried at 70 °C for 72 h. For mineral analysis, dried samples (shoots) were digested in sulfuric acid (H2SO4) and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). The total nitrogen content was measured using the micro Kjeldahl method as reported by Pregl [17]. The total phosphorus content was determined using a spectrophotometer as reported by Truog and Meyer [18]. The total potassium content was assessed using a flame photometer, as described by Brown and Lilleland [19]. The greenness level of the leaves was determined using a SPAD 502 Plus Chlorophyll Meter, as described by Lavres et al. [20].
2.5. Statistical Analysis
We used a complete randomized design for the experiment. Each treatment was performed with five replicates. The results are shown as the mean ± standard deviation. Significant differences were established with one-way analysis of variance as described by Snedecor and Cochran [21]. The experimental data were analyzed using SPSS 22. Differences among means were compared using Duncan’s new multiple range tests, with p ≤ 0.05 being considered statistically significant [22].
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Fertilization Treatments on the Aboveground Parameters
Figure 1 shows the effect of the different fertilization rates on the shoot number, the shoot height, and the number of leaves. Figure 2 shows both the fresh and dry weights of the aboveground parts. The N:P:K nutrient supply had a significant effect on young sewak seedlings’ aboveground parts. The number of shoots was significantly increased with the highest level of N in the application rates T2 (6:3:3) and T8 (6:1:1U) when compared to the other treatments in both seasons (Figure 1a). In contrast, the lowest number of shoots was observed when plants were not treated (control) or treated with a low dose of T3 (2:1:1S) and T4 (2:1:1U). Seedling heights were three-times higher using the T8 application rate (6:1:1U) than the control (Figure 1b). Combined increases in P and K did not increase the height compared to the control. The lowest plant heights were observed with the T3 application (2:1:1S) rate. The number of leaves was relatively increased when using the T8 (6:1:1U) application rate than the other treatments and the control in both seasons (Figure 1c). The application rates of T6 (4:1:1U) and T8 (6:1:1U) in both seasons showed a significant increase in the fresh and dry weight of the aboveground parts. The fresh and dry weights of the aboveground parts were increased ten-times more than the control, showing the importance of nutrient supply at the early stages of seedling growth compared to natural situations in arid zones (Figure 2). The use of the T1 (4:2:2) and T2 (6:3:3) application rates with increased P and K doses showed a result closer to the T6 (4:1:1U) and T8 (6:1:1U) application rates. The control had the lowest fresh and dry weight values for the aboveground parts.
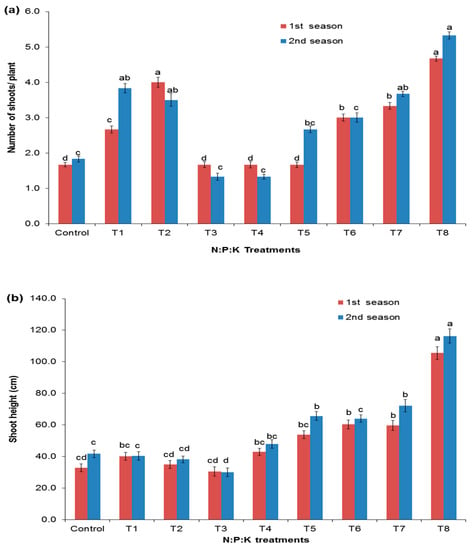
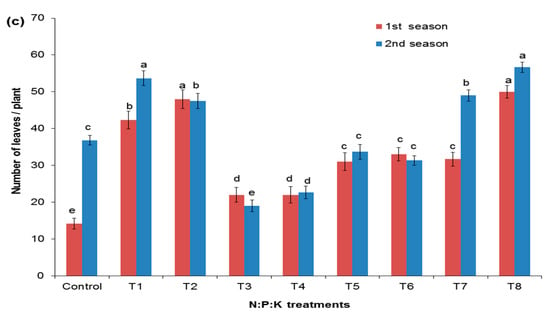
Figure 1.
Effect of NPK treatments on the number of shoots (a), the shoot heights (b), and the number of leaves (c) of Salvadora persica. Dissimilar letters designate the significance among means (p < 0.05) using Duncan’s multiple range test (means ± standard errors (n = 5)) for the different fertilization treatments.
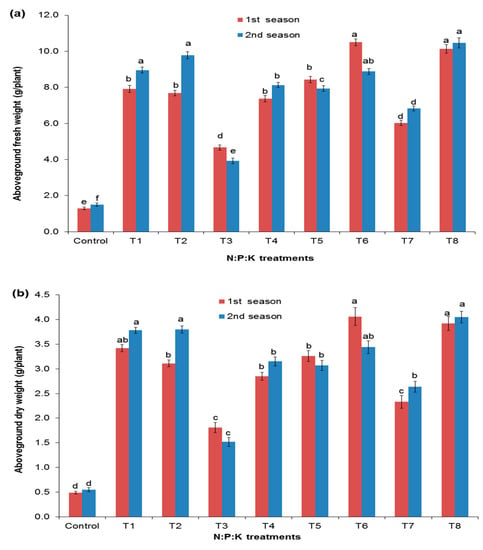
Figure 2.
Effect of NPK treatments on the fresh (a) and dry weight (b) of the aboveground parts of Salvadora persica. Dissimilar letters designate the significance among means (p < 0.05) using Duncan’s multiple range test (means ± standard errors (n = 5)) for the different fertilization treatments.
3.2. Effect of Fertilization Treatments on the Root Parameters
Figure 3 shows that the root length and the root fresh and dry weights were significantly affected by NPK application. Both the root fresh and dry weights demonstrated higher values from the T1 (4:2:2) and T2 (6:3:3) application rates in both seasons (Figure 3a,b). Meanwhile, the control had the lowest root fresh weight and dry weights. The root lengths were significantly increased with the T1 (4:2:2) and T2 (6:3:3), T5 (4:1:1S), and T7 (6:1:1S) application rates in both seasons, respectively (Figure 3c). The control had the lowest root lengths in both seasons.
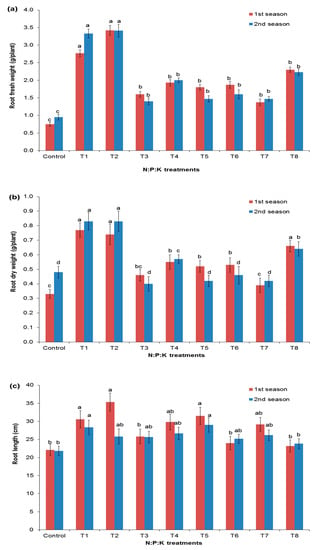
Figure 3.
Effect of NPK doses on the root fresh weights (a), the root dry weights (b), and the root lengths (c) of Salvadora persica. Dissimilar letters designate the significance among means (p < 0.05) using Duncan’s multiple range test (means ± standard errors (n = 5)) for the different fertilization treatments.
3.3. Chemical Contents of the Aboveground Parts
Figure 4 shows that the leaf greenness was significantly affected by NPK doses. The NPK application rates of T1 (4:2:2) and T2 (6:3:3) in the first season (47.3 and 45.0) and in the second season (48.0 and 45.9), respectively, had the highest greenness values. In contrast, the control had the lowest greenness values (27.7 and 28.0 for the first and second seasons, respectively).
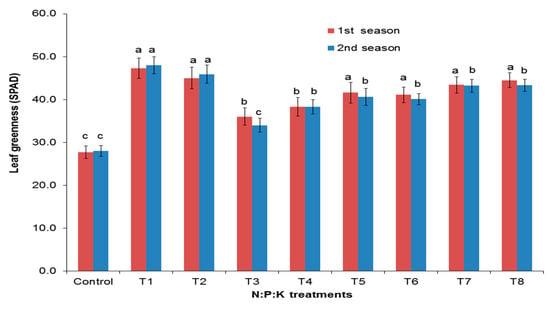
Figure 4.
Effect of NPK doses on Salvadora persica leaf greenness. Dissimilar letters designate the significance among means (p < 0.05) using Duncan’s multiple range test (means ± standard errors (n = 5)) for the different fertilization treatments.
Table 1 shows that the N% in both seasons was affected by NPK application. The T1 (4:2:2) application rate achieved a higher N% (2.07%) than other application rates in the first season. In the second season, the non-treated control achieved a higher N% (2.83%) compared to other NPK application rates. There was no significant difference in the P% among treatments. The NPK application rates affected the K%; the T1 (4:2:2), T4 (2:1:1U), T5 (4:1:1S), and T8 (6:1:1U) application rates had a significant increase in K% compared to the control in the first season, whereas K% in the second season did not show significant differences among NPK application rates and controls.

Table 1.
Effect of NPK doses on the vegetative parameters’ percentage of nitrogen, phosphorous, and potassium contents in Salvadora persica.
4. Discussion
The development level of S. persica is very slow throughout the first two to three years of growth, requiring a significant intervention for its growth during the early stages. The plant reaches maturity after seven to nine years. In contrast, trees raised from root suckers bear fruit earlier, in approximately five to six years [23].
Ponder [24] found that NPK significantly increased the plant height and stem diameter in fertilized seedlings of Eucalyptus saligna and Juglans nigra plants, and NPK fertilizers produced significantly taller seedlings of Eucalyptus tereticornis than the controls. Krohn [25] and Sundralingam [26] demonstrated that the plant height of Tectona grandis responded significantly to NPK treatment compared to the controls. El-Khateeb showed that plant height was significantly increased in the seedlings of Eucalyptus torquate and E. angulosa at an NPK rate of 25:10:15 [27].
Hassan and Dey [28] demonstrated a significant increase in the aboveground parameters of Tectona grandis when NPK was used at 25 g/plant; Alberto [29] showed similar results in Casuarina equisetifolia. Additionally, Habba [30] achieved similar results using a 15:15:10 NPK application rate and Melia azedarach seedlings, and Krishnamurthy and Vijayan [31] using 15 g/seedling of nitrogen and Eucalyptus tereticormis seedlings. At a large scale, Nasr et al. [32] found that the seedlings of Atriplex species and Leucaena leucocephala treated with 30:15:15 kg/4200 m2 had higher plant growth rates [14]. Plants respond according to their needs. Cordia myxa seedlings had better growth with 6:2:1 NKP application rates, whereas, for Cupressus sempervirens seedlings, an application rate of 3:2:1 produced a better performance [15]. Improvements in plant characteristics have also been seen with the application of various fertilization rates in Poinciana regia [16], Casuarina, Eucalyptus [33], Melie azedarach, Acacia cyanophylla, Casuarina glauca, Eucalyptus camaldulensis, and Taxodium distichum [34] seedlings.
In the current research, N application had an encouraging effect on root development, which is in agreement with previous results showing that N has a significant influence on root development, biomass, turn over [35], root development and expansion [36], and greater root-order expansion and branching [37]. The use of N fertilizer can likewise affect the efficiency of water use by manipulating root progress and spreading [38], and an ideal N supply level improves root length and diameter [39], whereas higher or lower N levels have been found to decrease root growth and biomass [40]. Furthermore, N application meaningfully enhanced the diameter of Larix gmelinii root tips [41] and the development, root length, and root diameter of Pongamia pinnata seedlings [42] and Acer mono seedling [38].
Negreiros et al. [43] found a difference in plants’ responses to an increase in soil fertility, where the development factors of Collaea and Calliandra increased with increasing soil richness, while no differences were observed for Mimosa and Chamaecrista. These species are adapted to low fertility, similarly to in S. persica. NPK applications at a higher rate increased the root system’s development, in agreement with Razaq et al. [39]; N and P application can increase seedling strength and growth during the nursery period.
Fernández-Escobar et al. [44] found that the leaf N concentration of olive trees was higher when N fertilization was applied to soil (0–1 kg/tree). Low doses of N should be applied through localized fertilization throughout the year. In agreement with the previous findings, Ahmed and Aly [45] showed that all fertilization treatments significantly increased the height, stem diameter, fresh and dry weights of the leaves, stems, and roots of Acacia saligna seedlings. Diwivedi et al. [46], on Jasminum grandiflorum, found that different N levels of each source significantly increased various vegetative growth traits, such as plant height, stem diameter, leaf area, and the fresh and dry weights of leaves. Azadirachta indica seedling characteristics showed an upward trend with a gradual increase in NPK fertilization rate [47]. The application of N stimulates chlorophyll production by increasing the amount of stromal and thylakoid proteins in leaves [48] and increasing the number of chloroplasts during leaf growth [49]. The greenness of leaves depends on P concentration, since it stabilizes the plant as the environmental conditions change [50]; the biochemical features [51] and biosynthesis of pigment molecules depend on ideal P levels [52].
5. Conclusions
The current work shows that NPK fertilization rates significantly influence the growth and root morphology of S. persica seedlings. The control seedlings showed inferior plant growth, root characteristics, and greenness levels. The optimal seedling values were obtained using the T2 6:3:3 NPK application rate. Therefore, the results of the present study suggest that optimal NPK levels can ensure the production of vigorous and healthy S. persica seedlings. Several gaps and research priorities in medicinal shrub nutrition have been identified, which need to be addressed in the future.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.H., F.F.L., and S.E.H.; methodology, A.H.N., M.H., F.F.L., and E.A.; software, E.A., S.E.H., A.H.N., and A.A.G.; validation, M.H., A.H.N., and A.A.G.; formal analysis, all authors contributed; investigation, M.H., F.F.L., and S.E.H.; resources, F.F.L. and A.A.G.; data curation, E.A., S.E.H., M.H., and A.A.G.; writing—original draft preparation, M.H., F.F.L., and S.E.H.; writing—review and editing, M.H., F.F.L., S.E.H., and E.A.; visualization, M.H., F.F.L., and S.E.H.; funding acquisition, A.A.G. and E.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding for practical work.
Acknowledgments
The authors appreciate and thank Taif University for the financial support via the Taif University Researchers Supporting Project (TURSP-2020/13), Taif University, Taif, Saudi Arabia.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ahmed, S.S.; El-Gengaihi, S.E.E.; Ibrahim, M.E.; Schnug, E. Preliminary phytochemical and propagation trial with Salvadora persica L. Landbauforsch. Volkenrode 2008, 58, 135–138. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, M.P.; Shah, M.T.; Patolia, J.S. Salvadora persica, a potential species for industrial oil production in semiarid saline and alkali soils. Ind. Crops Prod. 2008, 28, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Singh, B.; Tomar, U.K.; Sharma, S. A Manual for Dryland Afforestation and Management; Scientific Publishers: New Delhi, India, 2016; 622p. [Google Scholar]
- Sujata, M. Medicinally potent and highly salt tolerant plant of arid zone-Salvadora persica L. (Meswak): A Review. J. Plant Sci. 2015, 3, 45–49. [Google Scholar]
- Khatak, M.; Khatak, S.; Siddqui, A.A.; Vasudeva, N.; Aggarwal, A.; Aggarwal, P. Salvadora persica. Pharmacogn. Rev. 2010, 4, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Bagieh, N.H.; Idowu, A.; Salako, N.O. Effect of aqueous extract of miswak on the in vitro growth of Candida albicans. Microbios 1994, 80, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chelli-Chentouf, N.; Meddah, A.T.T.; Mullié, C.; Aoues, A.; Meddah, B. In vitro and in vivo antimicrobial activity of Algerian Hoggar Salvadora persica L. extracts against microbial strains from children’s oral cavity. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 144, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbasi, M.K.; Tahir, M.M.; Rahim, N. Effect of N fertilizer source and timing on yield and N use efficiency of rainfed maize (Zea mays L.) in Kashmir–Pakistan. Geoderma 2013, 195, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz Diaz, D.A.; Sawyer, J.E. Plant-available nitrogen from poultry manure as affected by time of application. Agron. J. 2008, 100, 1318–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randall, G.W.; Vetsch, J.A. Corn production on a subsurface-drained mollisol as affected by fall versus spring application of nitrogen and nitrapyrin. Agron. J. 2005, 97, 472–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arya, R.; Chaudhary, K.R.; Lohara, R.R. Effect of nitrogen and gypsum on the establishment and early growth of Salvadora persica (L.) on salt affected soils under hot arid conditions in India. For. Trees Livelihoods 2005, 15, 291–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif, F.; Khan, A.U. Alleviation of salinity tolerance by fertilization in four thorn forest species for the reclamation of salt-affected sites. Pak. J. Bot. 2009, 41, 2901–2915. [Google Scholar]
- Jasrotia, A.; Singh, R.P.; Singh, J.M.; Bhutani, V.P. Response of olive trees to varying levels of N and K fertilization. Acta Hortic. 1999, 474, 337–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, R.A. Seed Germination and Seedlings Growth of Some Ornamental Trees. Master’s Thesis, Minia University, Minia, Egypt, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- El-Tantawy, A.; Shehata, M.S.; Mohamed, S.Y. Effect of chemical fertilization and gibberellin spray on the growth and chemical composition of Cupressus sempervirens var horizontals seedlings. Egypt. J. App. Sci. 1994, 9, 323–344. [Google Scholar]
- Shehata, N.N. Response of Poinciana regia Seedlings to Fertilization in Sandy Soils. Master’s Thesis, Minia University, Minia, Egypt, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Pregl, F. Quantitative Organic Microanalysis, 4th ed.; J. and A. Churchill: London, UK, 1945. [Google Scholar]
- Truog, E.; Meyer, A.H. Improvements in the Deniges Colorimetric method for phosphorous and arsenic. Ind. Eng. Chem. Anal. Ed. 1929, 1, 136–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.D.; Lilleland, O. Rapid determination of potassium and sodium in plant material and soil extracts by flame-photometer. Proc. Am. Soc. Hort. Sci. 1946, 48, 341–346. [Google Scholar]
- Lavres, J., Jr.; Santos, J.D.D.G.D., Jr.; Monteiro, F.A. Nitrate reductase activity and spad readings in leaf tissues of guinea grass submitted to nitrogen and potassium rates. Rev. Bras. Ciência Solo 2010, 34, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snedecor, C.W.; Cochran, W.H. Two-way classification analysis of variance Statistical Methods, 8th ed.; Iowa State University Press: Ames, IA, USA, 1989; pp. 254–268. [Google Scholar]
- Duncan, D.B. Multiple range and multiple (F) test. Biometries 1955, 11, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aumeeruddy, M.Z.; Zengin, G.; Mahomoodally, M.F. A review of the traditional and modern uses of Salvadora persica L. (Miswak): Toothbrush tree of Prophet Muhammad. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 213, 409–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponder, F.J. Fertilization improve black walnut growth on a poorly drained site. Tree Planters Notes 1980, 31, 17–19. [Google Scholar]
- Krohn, T.J. Fertilization of Eucalyptus tereticornis in Southern Guam. Tree Planters Notes 1981, 32, 26–28. [Google Scholar]
- Sundralingam, P. Some preliminary studies on the fertilizer requirements of teak. Malaysian Forest. 1982, 45, 361–366. [Google Scholar]
- El-Khateeb, M.A. Effect of Salinity Irrigation, Chemical Fertilization and Soil Media on Growth, Flowering, Chemical Composition and Essential Oil of Eucalyptus torquata and E. nagulosa. Ph.D. Thesis, Cairo University, Cairo, Egypt, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, M.M.; Dey, H.B. Studies on the nutritional of forest tree optimum NPK doses for teak seedlings. Forest. Abst. 1984, 45, 318. [Google Scholar]
- Alberto, E.B. Growth response of Agoho Casuarina equisetifolia Forst. seedlings to soil treatments, fertilization and root nodule inoculations under nursery conditions. Master’s Thesis, University of the Philippines, Laguna, Philippines, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Habba, E.E. Effect of Some Agricultural Treatments and Growth Regulators on Seed Germination and Seedling Growth of Melia azedarach L. and Peltophorum africanum L. Master’s Thesis, Cairo University, Cairo, Egypt, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Krishnamurthy, R.; Vijayan, C. Response of Eucalyptus “hybrid” (Musore gum) to major nutrient elements. Soils Fertil. 1986, 50, 126–131. [Google Scholar]
- Nasr, M.H.; Hassan, M.T.; El-Sheemy, S.A. Response of different Atriplex species to fertilization in calcareous soil at Nubaria. For. Abst. 1987, 55, 24. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, S.H. Physiological Studies on Seedlings of Some Woody Trees Grown under the New Valley Conditions. Master’s Thesis, Minia University, Minia, Egypt, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- El-Kayal, W.E. Esponse of Seedlings Five Tree Species to Applications of Sewage Sludge and Chemical Fertilizer on Two Soil Types. Master’s Thesis, Alexandria University, Alexandria, Egypt, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Kern, C.C.; Friend, A.L.; Johnson, J.M.F.; Coleman, M.D. Fine root dynamics in a developing Populus deltoides plantation. Tree Physiol. 2004, 24, 651–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Bucio, J.; Cruz-Ramírez, A.; Herrera-Estella, L. The role of nutrient availability in regulating root architecture. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2003, 6, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolfolk, W.T.M.; Friend, A.L. Growth response of cottonwood roots to varied NH4:NO3 ratios in enriched patches. Tree Physiol. 2003, 23, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Q.; Chen, F.; Zhang, F.; Mi, G. Possible involvement of cytokinin in nitrate-mediated root growth in maize. Plant Soil 2005, 277, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razaq, M.; Zhang, P.; Shen, H.L. Influence of nitrogen and phosphorous on the growth and root morphology of Acer mono. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0171321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salih, N.; Ågren, G.I.; Hallbãcken, L. Modeling response of N addition on C and N allocation in Scandinavian Norway spruce stands. Ecosystems 2005, 8, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Gu, J.C.; Zhuang, H.F.; Wang, Z.Q. Effects of ectomycorrhizal colonization and nitrogen fertilization on morphology of root tips in a Larix gmelinii plantation in northeastern China. Ecol. Res. 2010, 25, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaukiyal, S.P.; Mir, R.A.; Pokhriyal, T.C. Effect of nitrogen fertilizer on biomass production and nodulation behavior of Pongamia pinnata Pierre seedlings under nursery conditions. J. For. Res. 2013, 24, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negreiros, D.; Fernandes, G.W.; Silveira, F.A.; Chalub, C. Seedling growth and biomass allocation of endemic and threatened shrubs of rupestrian fields. Acta Oecologica 2009, 35, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Escobar, R.; Beltrán, G.; Sánchez-Zamora, M.A.; García-Novelo, J.; Aguilera, M.P.; Uceda, M. Olive oil quality decreases with nitrogen over-fertilization. HortScience 2006, 41, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, E.T.; Aly, M.K. Response of Acacia saligna seedlings to NPK fertilization and growth regulators. Egypt. J. Appl. Sci. 1998, 13, 290–313. [Google Scholar]
- Diwivedi, R.; Saravanan, S.; Shabi, M.; Kasera, S. Effect of organic and inorganic fertilizer on growth and flower yield of jasmine (Jasminum grandiflorum L.). Pharma Innov. J. 2018, 7, 683–686. [Google Scholar]
- Abd-Elaziz, M.F. Effect of Soil Types and NPK Fertilization Treatments on Azadirachta indica Seedlings. Master’s Thesis, Minia University, Minia, Egypt, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Cooke, J.E.; Martin, T.A.; Davis, J.M. Short-term physiological and developmental responses to nitrogen availability in hybrid poplar. New Phytol. 2005, 167, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Li, M.; Luo, J.; Cao, X.; Qu, L.; Gai, Y.; Jiang, X.; Liu, T.; Bai, H.; Janz, D.; et al. N-fertilization has different effects on the growth, carbon and nitrogen physiology, and wood properties of slow-and fast-growing Populus species. J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 6173–6185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bojović, B.; Stojanović, J. Some wheat leaf characteristics in dependence of fertilization. Kragujevac J. Sci. 2006, 28, 139–146. [Google Scholar]
- Waraich, E.A.; Ahmad, Z.; Ahmad, R.; Saifullah; Ashraf, M.Y. Foliar applied phosphorous enhanced growth, chlorophyll contents, gas exchange attributes and PUE in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). J. Plant Nutr. 2015, 38, 1929–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayal, J.; Goswami, C.L.; Munjal, R. Influence of phosphorus application on water relations, biochemical parameters and gum content in cluster bean under water deficit. Biol. Plant. 2004, 48, 445–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).