Monitoring Soil Enzymes Activity before and after Animal Manure Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection and Preparation of Soil Samples
2.2. Soil Enzymes Analysis
2.3. Chracteristics of Soil Amendments
2.4. Statistical Analysis
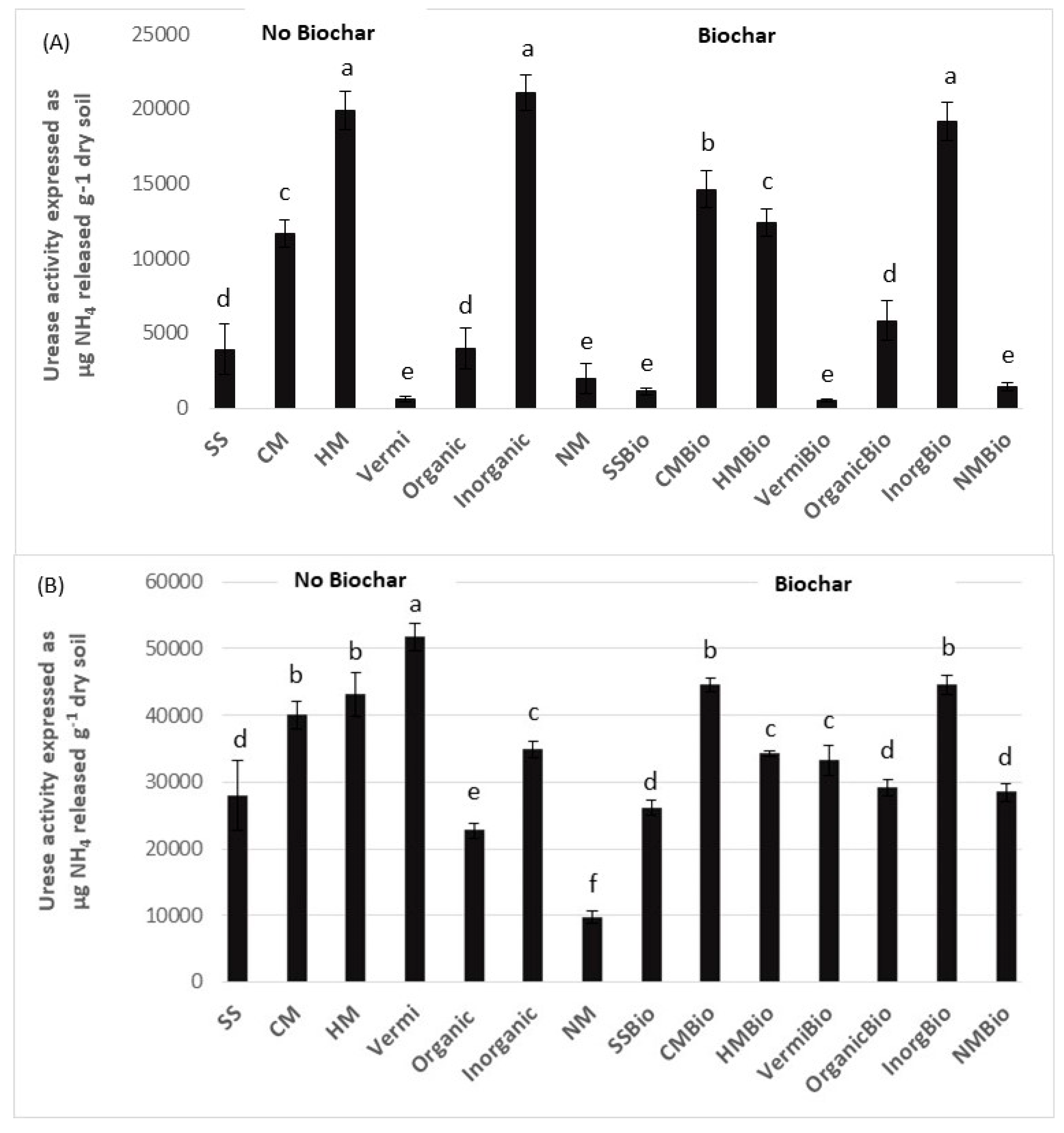
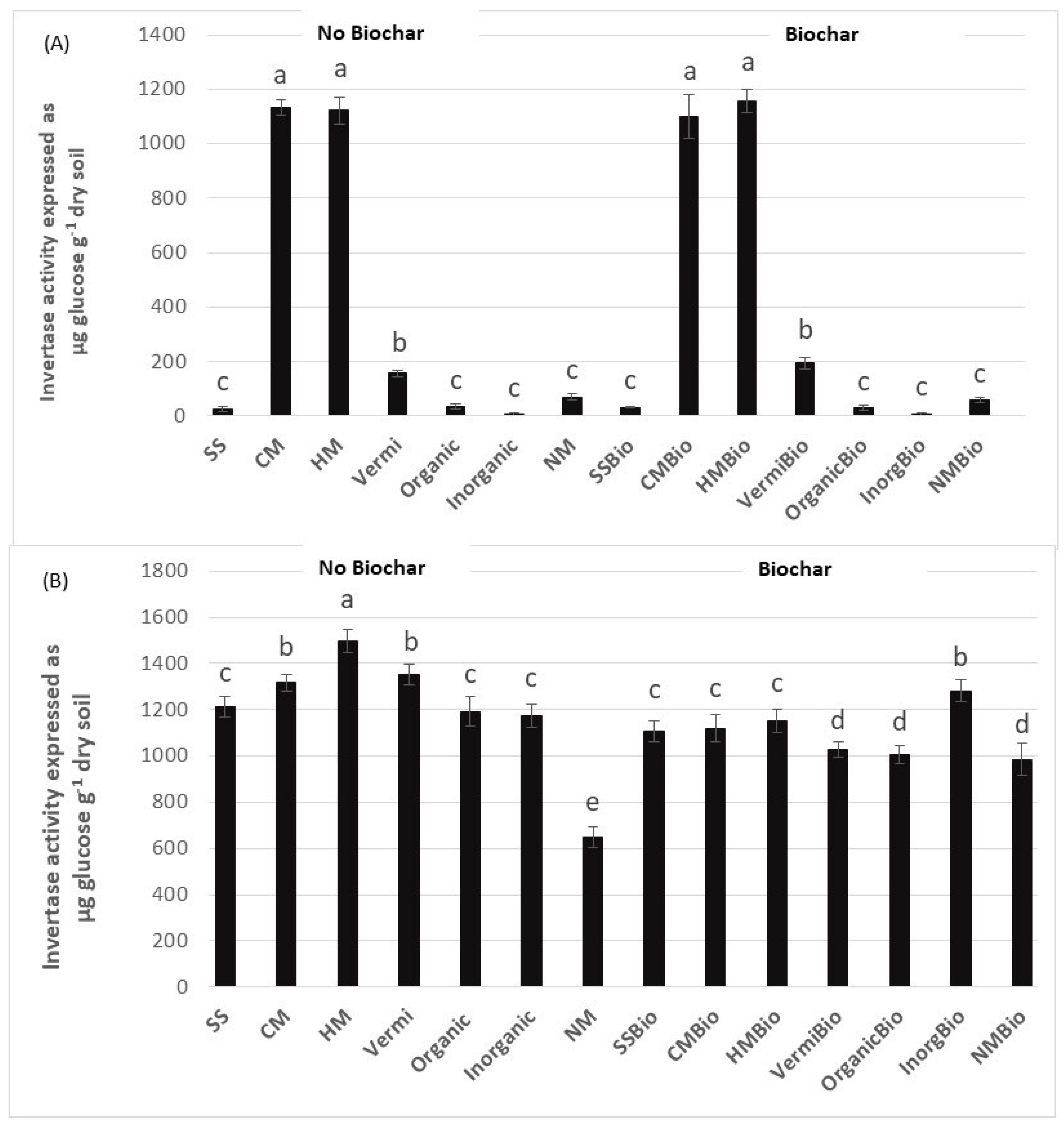
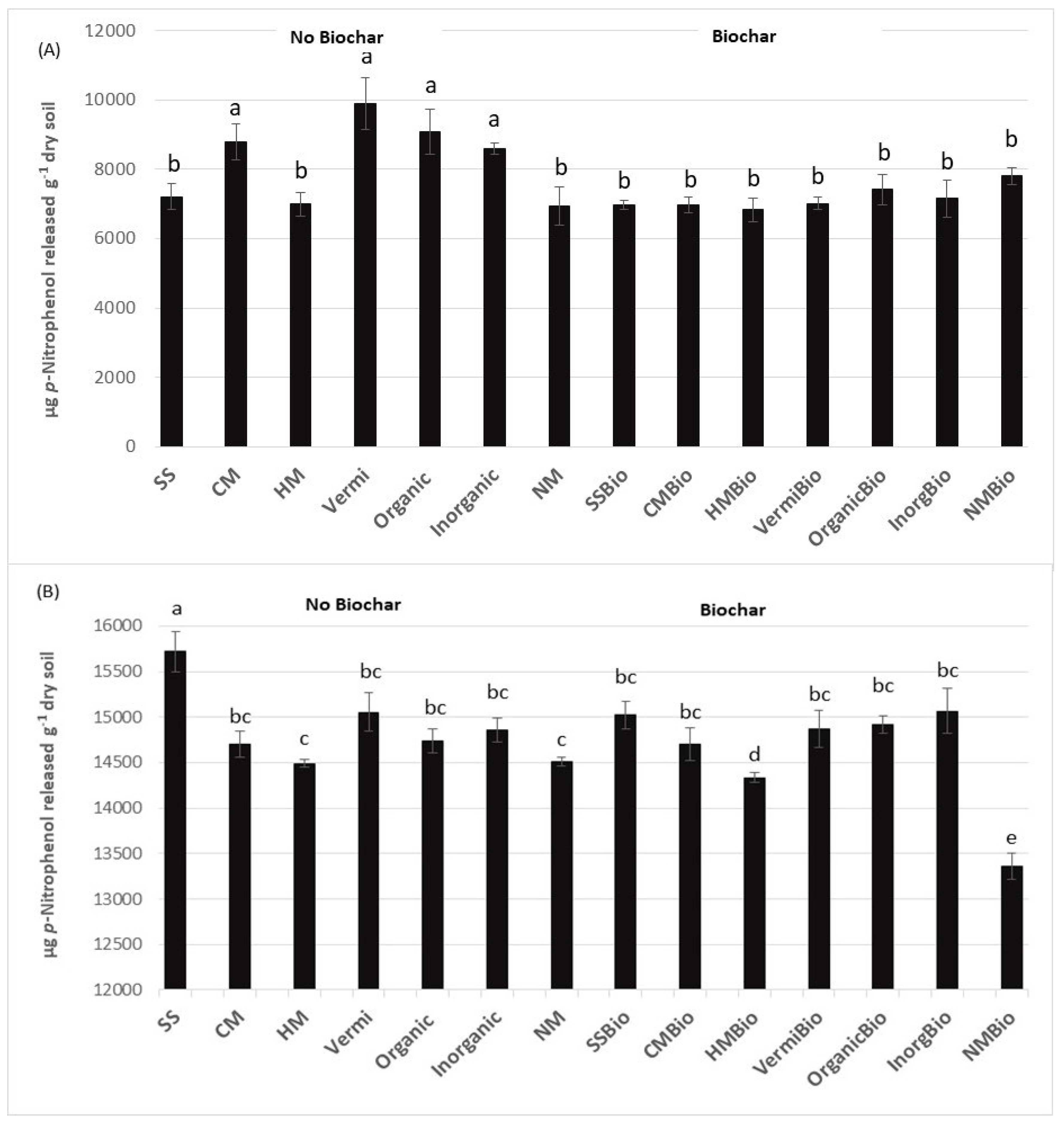
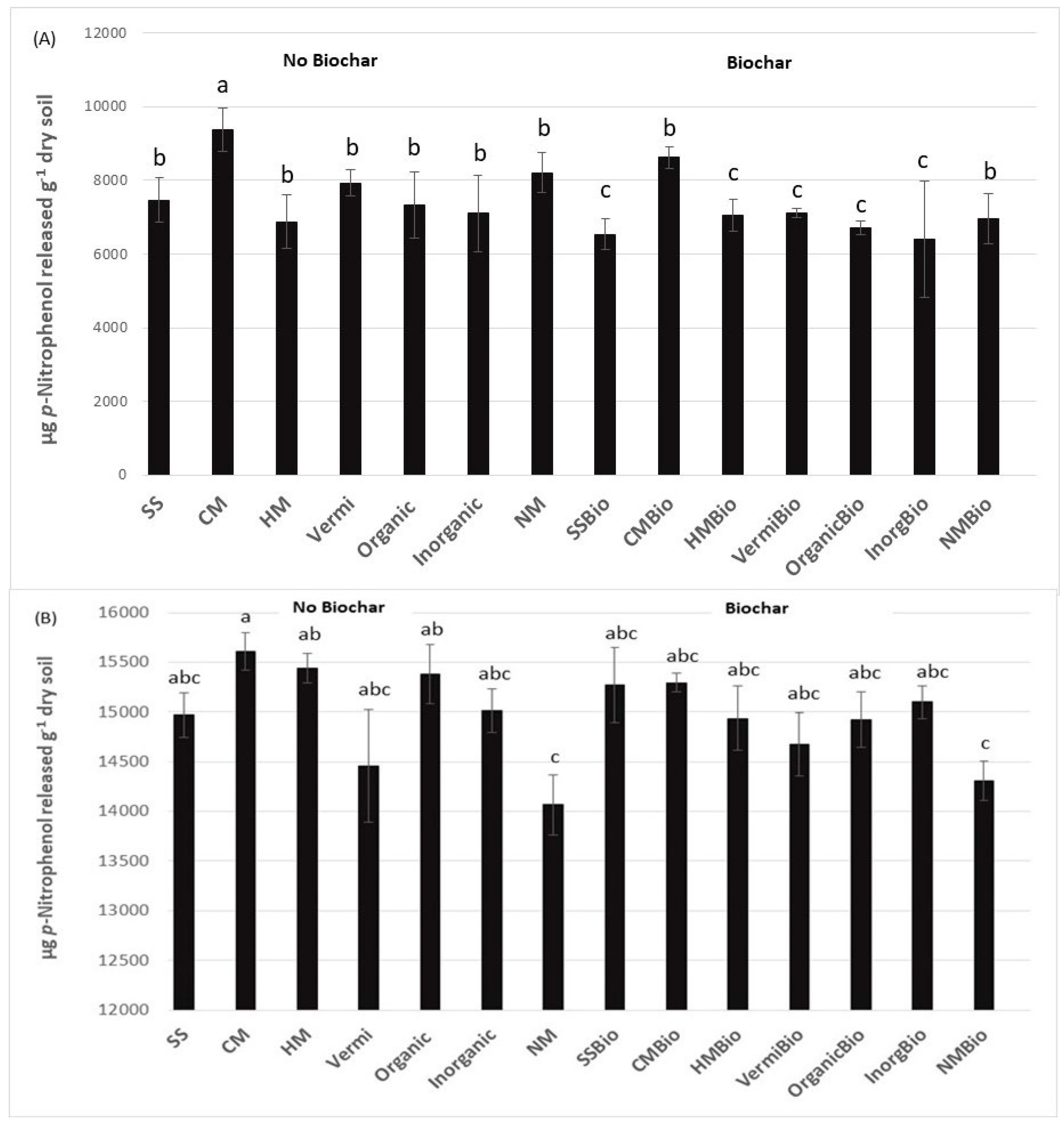
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Antonious, G.F. Biochar and animal manure impact on soil, crop yield and quality. In Agricultural Waste and Residue; Intech- Open Science Books: Rijeka, Croatia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Antonious, G.F. Soil amendments for agricultural production. In Organic Fertilizers: From Basic Concepts to Applied Outcomes; Book Chapter; Larramendy, M.L., Soloneski, S., Eds.; Intech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2016; Chapter 7; pp. 157–187. ISBN 978-953-51-4701-5. [Google Scholar]
- Hinojosa, M.B.; Carreira, J.A.; Rodriguez-Moroto, J.M.; Garcia-Ruiz, R. Effects of pyrite sludge pollution on soil enzyme activities: Ecological dose-response model. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 396, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kizilkaya, R.; As¸kin, T.; Bayraki, B.; Sag˘lam, M. Microbial characteristics of soil contaminated with heavy metals. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2004, 40, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Carballo, E.; González-Barreiro, C.; Scharf, S.; Gans, O. Environmental monitoring study of selected veterinary antibiotics in animal manure and soils in Ausria. Environ. Pollut. 2007, 148, 570–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Effron, D.; de la Hora, A.M.; Defrieri, R.L.; Fontanive, V.; Palma, P.M. Effect of cadmium, copper, and lead on different enzyme activities in a native forest soil. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2004, 35, 1309–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W. Agricultural and Ecological Significance of Soil Enzymes: Soil Carbon Sequestration and Nutrient Cycling. In Soil Enzymology; Shukla, G., Varma, A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; Chapter 3; pp. 43–60. [Google Scholar]
- Andrews, R.K.; Blakeley, R.L.; Zerner, B. Urease: A Ni (II) metalloenzyme. In The Bioinorganic Chemistry of Nickel; Lancaster, J.R., Ed.; VCH: New York, NY, USA, 1989; pp. 141–166. [Google Scholar]
- Simpson, J.R.; Freney, J.R.; Wetselaar, R.; Muirhead, W.A.; Leuning, R.; Denmead, O.T. Transformations and losses of urea nitrogen after application to flooded rice. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 1984, 35, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polacco, J.C. Is nickel a universal component of plant ureases? Plant Sci. Lett. 1977, 10, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobley, H.L.T.; Hausinger, R.P. Microbial urease: Significance, regulation and molecular characterization. Microbiol. Rev. 1989, 53, 85–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lef, L.K.; Nannipieri, P. Methods in Soil Microbiology and Enzyme Activities; Academic Press/Harcourt Brace and Company Publishers: London, UK, 1995; pp. 225–230. [Google Scholar]
- Splading, B.P. Effect of divalent metal cations respiration and extractable enzymes activities of Douglss-fir needle litter. J. Environ. Qual. 1979, 8, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alef, K.; Nannipieri, P.; Trasar-Cepeda, C. Phosphatase activity. In Methods in Applied Soil Microbiology and Biochemistry; Alef, K., Nannipieri, P., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 1995; pp. 335–336. [Google Scholar]
- Araujo, C.L.; Vihko, P.T. Structure of Acid Phosphatases. Methods Mol. Biol. 2013, 1053, 155–166. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia, G.J.M.; Ocampo, J.A.; Garcıa, R.I. Enzymes in the Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Symbiosis. In Enzymes in the Environment: Activity, Ecology, and Applications; Burns, R.G., Dick, R.P., Eds.; Marcel Dekker, Inc.: Basel, Switzerland, 2002; Chapter 5. [Google Scholar]
- Moya, D.; Aldás, C.; López, G.; Kaparaju, P. Municipal solid waste as a valuable renewable energy resource: A worldwide opportunity of energy recovery by using Waste-To-Energy Technologies. Energy Procedia 2017, 134, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonious, G.F. Enzyme activities and heavy metals concentration in soil amended with sewage sludge. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2009, A44, 1019–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, G.J.C.; Plaza, C.; Soler-Rovira, P.; Polo, A. Long-term effects of municipal solid waste compost application on soil enzyme activities and microbial biomass. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2000, 32, 1907–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mierzwa-Hersztek, M.; Gondek, K.; Klimkowicz-Pawlas, A.; Baran, A. Effect of wheat and Miscanthus straw biochars on soil enzymatic activity, ecotoxicity, and plant yield. Int. Agrophys. 2017, 31, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mierzwa-Hersztek1, M.; Klimkowicz-Pawlas, A.; Gondek, K. Influence of poultry litter and poultry litter biochar on soil microbial respiration and nitrifying bacteria activity. Waste Biomass Valor 2018, 9, 379–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mierzwa-Hersztek, M.; Gondek, K.; Klimkowicz-Pawlas, A.; Chmiel, M.J.; Dziedzic, F.; Taras, H. Assessment of soil quality after biochar application based on enzymatic activity and microbial composition. Int. Agrophys. 2019, 33, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Lai, C.; Zeng, G.; Liang, J.; Chen, J.; Xu, J.; Lu, L. The interactions of composting and biochar and their implications for soil amendment and pollution remediation: A review. Cri. Rev. Biotechnol. 2017, 37, 754–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, C.; Verheijen, F.; Puga, J.; Keizer, J.; Ferreira, A. Biochar in vineyards: Impact on soil quality and crop yield four years after the application. In Proceedings of the 19th EGU General Assembly, EGU2017, Vienna, Austria, 23–28 April 2017; p. 1600. [Google Scholar]
- Woolf, D.; Amonette, J.E.; Street-Perrott, A.A.; Lehmann, J.; Joseph, S. Sustainable biochar to mitigate global climate change. Nat. Commun. 2010, 1, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renner, R. Rethinking biochar. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 5932–5933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonious, G.F.; Turley, E.T.; Sikora, F.; Snyder, J.C. Heavy metal mobility in runoff water and absorption by eggplant fruits from sludge treated soil. J. Environ. Sci. Health 2008, 43, 526–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azarmi, R.; Ziveh, P.S.; Satari, M.R. Effect of vermicompost on growth, yield and nutrition status of tomato (Lycopersicum esculentum). Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2008, 11, 1797–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laczi, E.; Apahidean, A.; Luca, E.; Dumitraş, A.; Boancă, P. Headed Chinese cabbage growth and yield influenced by different manure types in organic farming system. Hort. Sci. 2016, 43, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeufer, E.; Bessin, R.; Wright, S.; Strang, J. 2018-19 Vegetable Production Guide for Commercial Growers; University of Kentucky College of Agriculture, Food and Environment Cooperative Extension Service: Lexington, KY, USA; pp. 44–48.
- Tabatabi, M.A.; Bremner, J.M. Assay of urease activity in soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1972, 4, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Public Health Association (APHA). Standard Methods for the Determination of Water and Wastewater, 19th ed.; APHA: Washington, DC, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Antonious, G.F. Impact of soil management and two botanical insecticides on urease and invertase activity. J. Environ. Sci. Health 2003, 38, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balasubramanian, D.; Bagyaraj, D.J.; Rangaswami, G. Studies on the influence of foliar application of chemicals on the microflora and certain enzyme activities in the rhizosphere of Eleusine coracana Gaertn. Plant Soil 1970, 32, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabatabai, M.A.; Bremner, J.M. Use of p-nitrophenol phosphate for assay of soil phosphatase activity. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1969, 1, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EPA Method 6020a: Inductively Coupled Plasma -Mass Spectrometry; USEPA: Washington, DC, USA, 1998.
- SAS Institute Inc. SAS/STAT Guide; Version 6.4; SAS Inc. Campus Drive: Cary, NC, USA, 2016; p. 27513. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Yang, Z.; Wang, X.; Gao, R.; Liu, X. Effects of Cd and Pb pollution on soil enzymatic activities and soil microbiota. Front. Agric. China 2007, 1, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.H.; Lehmann, J.; Thies, J.E.; Burton, S.D.; Engelhard, M.H. Oxidation of black carbon by biotic and abiotic processes. Org. Geochem. 2006, 37, 1477–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, J.; Joseph, S. (Eds.) Biochar for Environmental Management: Science, Technology and Implementation; Routledge: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ameloot, N.; Sleutel, S.; Das, K.C.; Kanagaratnam, J.; De Neve, S. Biochar amendment to soils with contrasting organic matter level: Effects on N mineralization and biological soil properties. Gcb Bioenergy 2015, 7, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alburquerque, J.A.; Calero, J.M.; Barrón, V.; Torrent, J.; del Campillo, M.C.; Gallardo, A.; Villar, R. Effects of biochars produced from different feedstocks on soil properties and sunflower growth. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2014, 177, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyler, G.; Balsberg Pahlsson, A.M.; Bengtsson, G.; Baath, E.; Tranvik, M. Heavy-metal ecology of terrestrial plants, micro-organisms invertebrates. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1989, 47, 189–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berezhetsky, A.L.; Sosovska, O.F.; Durrieu, C.; Chovelon, J.M.; Dzyadevych, S.V.; Tran-Minh, C. Alkaline phosphatase conductometric biosensor for heavy-metal ions determination. IRBM 2008, 29, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonious, G.F.; Turley, E.; Mishra, B.; Heist, Q.; Upadhyaya, Y.; Trivette, T.; Nkuwi, L. Characterization of eggplant grown in animal manure amended soil. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2019, 13, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonious, G.; Turley, E.; Dawood, M. Ascorbic Acid, Sugars, Phenols, and Nitrates Concentrations in Tomato Grown in Animal Manure Amended Soil. Agriculture 2019, 9, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boavida, M.J.; Wetzel, R.G. Inhibition of phosphatase activity by dissolved humic substances and hydrolytic reactivation by natural ultraviolet light. Freshw. Biol. 1998, 40, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Ying, G.; Tao, R.; Zhao, J.L.; Yang, J.; Zhao, L. Effects of six selected antibiotics on plant growth and soil microbial and enzymatic activities. Environmental. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 1636–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renella, G.; Mench, M.; Landi, L.; Nannipieri, P. Microbial activity and hydrolase synthesis in long term Cd-contaminated soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2005, 37, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameloot, N.; Neve, S.D.; Jegajeevagan, K.; Yildiz, G.; Buchan, D.; Funkuin, Y.N.; Prins, W.; Bouckaert, L.; Sleutel, S. Short-term CO2 and N2O emissions and microbial properties of biochar amended sandy loam soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 57, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, M.K.; Lee, K.T. Potential of using organic fertilizer to cultivate Chlorella vulgaris for biodiesel production. Appl. Energy 2012, 94, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Soil Characteristics | Inorganic Fertilizer | CM | Organic Fertilizer | SS | Vermicompost | NM | HM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KCl Soil pH | 5.29 ± 0.11 a | 5.18 ± 0.28 a | 4.88 ± 0.14 b | 4.7633 ± 0.1 b | 4.8 ± 0.15 b | 4.71 ± 0.02 b | 4.72 ± 0.09 b |
| Soil-Water pH | 6.15 ± 0.1 a | 6.057 ± 0.26 a | 5.78 ± 0.13 b | 5.67 ± 0.1 b | 5.71 ± 0.13 b | 5.63 ± 0.02 b | 5.64 ± 0.09 b |
| P, ppm | 121.3 ± 47.9 a | 89.33 ± 6.64 a | 94.83 ± 10.32 a | 100.33 ± 10.69 a | 87.67 ± 9.46 a | 95.83 ± 10.2 a | 116. ± 50 a |
| K, ppm | 533.5 ± 96 ab | 483.8 ± 74.8 ab | 446.83 ± 10.1 bc | 327.5 ± 4.92 d | 557.3 ± 79.8 a | 336.17 ± 12.06 d | 365.5 ± 26.1 cd |
| C, ppm | 1155.3 ± 28.1 bc | 1160.8 ± 51 b | 1112.8 ± 43.9 bcd | 1050 ± 28.2 d | 1230.2 ± 27.9 a | 1091.7 ± 44.9 cd | 1067.2 ± 12.2 d |
| Mg, ppm | 135.33 ± 6.05 c | 139 ± 5.29 c | 130.67 ± 4.51 c | 131.67 ± 3.4 c | 180 ± 11.43 a | 130.33 ± 2.84 c | 150.83 ± 7.8 b |
| Zn, ppm | 5.417 ± 0.36 d | 7.117 ± 0.33 b | 6.217 ± 0.44 c | 7.867 ± 0.34 a | 6.833 ± 0.21 bc | 6.65 ± 0.82 bc | 6.617 ± 0.34 bc |
| Cd, ppm | 0.09 ± 0.01 a | 0.08 ± 0.00 ab | 0.08 ± 0.01 ab | 0.08 ± 0.01 ab | 0.08 ± 0.00 b | 0.07 ± 00 ab | 0.07 ± 0.00 ab |
| Cr, ppm | 0.04 ± 0 a | 0.04 ± 0 a | 0.04 ± 0 a | 0.04 ± 0 a | 0.04 ± 0 a | 0.04 ± 0 a | 0.04 ± 0 a |
| Ni, ppm | 0.54 ± 0.08 a | 0.57 ± 0.14 a | 0.42 ± 0.02 a | 0.54 ± 0.16 a | 0.62 ± 0.15 a | 0.46 ± 0.09 a | 0.52 ± 0.10 a |
| Pb, ppm | 6.22 ± 0.21 d | 8.217 ± 0.7 bc | 7.7 ± 0.325 c | 10.1 ± 0.66 a | 6.23 ± 0.10 d | 9.183 ± 1.17 ab | 7.53 ± 0.73 c |
| Cu, ppm | 2.96 ± 0.17 cd | 3.08 ± 0.08 cd | 3.01 ± 0.1 d | 3.42 ± 0.11 b | 3.927 ± 0.18 a | 3.22 ± 0.1 cb | 3.14 ± 0.15 cd |
| EC, µS cm−1 | 107.37 ± 7.87 ab | 95.83 ± 14.61 b | 112.03 ± 13.23 ab | 106.4 ± 13.67 ab | 122.83 ± 8.59 a | 94.4 ± 13.1 b | 89.03 ± 14.09 b |
| N-NO3, ppm | 79.33 ± 8.39 a | 18.33 ± 9.24 c | 32.67 ± 8.5 bc | 20 ± 3.46 c | 37.33 ± 11.85 b | 20.67 ± 4.51 c | 25.00 ± 6 bc |
| N-NH4, ppm | 50.7 ± 56.6 ab | 66.7 ± 61.4 a | 47 ± 23.5 ab | 29.7 ± 17.9 ab | 3.667 ± 0.58 b | 5.67 ± 3.79 b | 3.33 ± 0.58 b |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Antonious, G.F.; Turley, E.T.; Dawood, M.H. Monitoring Soil Enzymes Activity before and after Animal Manure Application. Agriculture 2020, 10, 166. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture10050166
Antonious GF, Turley ET, Dawood MH. Monitoring Soil Enzymes Activity before and after Animal Manure Application. Agriculture. 2020; 10(5):166. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture10050166
Chicago/Turabian StyleAntonious, George F., Eric T. Turley, and Mohammad H. Dawood. 2020. "Monitoring Soil Enzymes Activity before and after Animal Manure Application" Agriculture 10, no. 5: 166. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture10050166
APA StyleAntonious, G. F., Turley, E. T., & Dawood, M. H. (2020). Monitoring Soil Enzymes Activity before and after Animal Manure Application. Agriculture, 10(5), 166. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture10050166






