Ecological Risk Assessment of Soil Heavy Metals and Pesticide Residues in Tea Plantations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
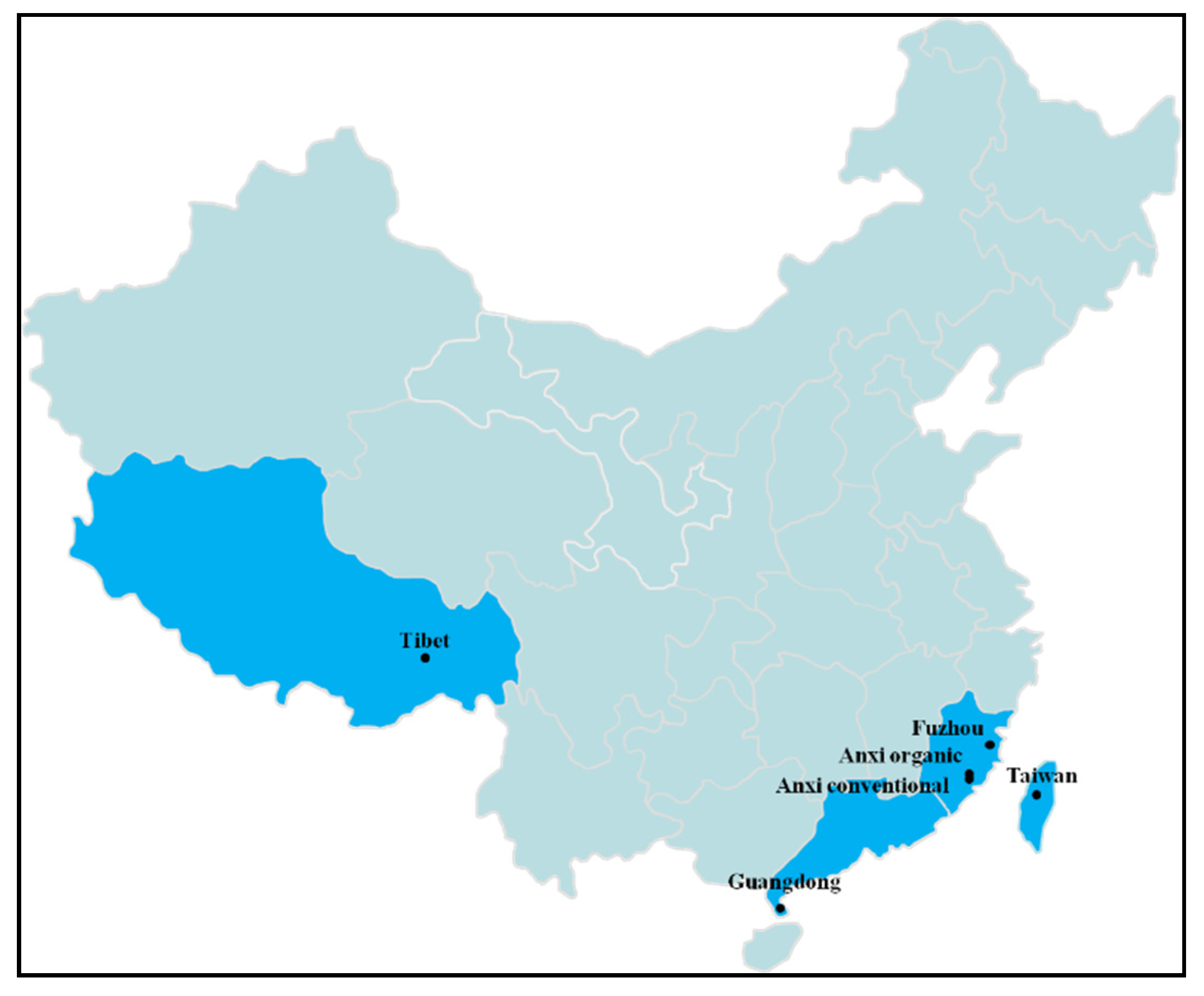
2.1. Sample Collection and Pretreatment
2.2. Analytical Methods for Heavy Metals
2.3. Ecological Risk Assessment
2.4. Analytical Methods for Pesticide Residues in Soil
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Heavy Metals in Soil of Tea Plantations
3.2. Pesticide Residue Contents and Pollution Index in Tea Garden Soils
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Karak, T.; Bhagat, R.M. Trace elements in tea leaves, made tea and tea infusion: a review. Food Res. Int. 2010, 43, 2234–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Liu, X. Discussion on the present status and corresponding measurement of China tea safe and quality. J. Tea 2006, 2, 66–69. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Zhao, Z.Z.; Wang, J.G.; Zhang, Z.W.; Lu, S.F. Hazard assessment on heavy metal pollution in surface soil from tea gardens of Wuzhishan. Agric. Sci. Tech. Hunan. 2011, 12, 426–465. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Zhang, Z.; Li, P.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Ding, X. Determination for major chemical contaminants in tea (Camellia sinensis) matrices: A review. Food Res. Int. 2013, 53, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.Z.; Zhou, D.M.; Huang, D.Q.; Long, C.; Zhang, H.L.; Hui, W. Heavy metal transfer from soil to vegetable in southern Jiangsu Province, China. Pedosphere 2009, 19, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.K.; Agrawal, M.; Marshall, F.M. Heavy metals in vegetables collected from production and market sites of a tropical urban area of India. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2009, 47, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Liu, X.; Bai, J.; Shih, K.; Zeng, E.Y.; Cheng, H. Assessing heavy metal pollution in the surface soils of a region that had undergone three decades of intense industrialization and urbanization. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 6150–6159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, A.; Alansi, S.; Altufail, M. Determination of lead in Saudi Arabian imported green tea by ICP-MS. J. Chem. 2012, 9, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sharma, R.K.; Agrawal, M.; Marshall, F.M. Heavy metal contamination of soil and vegetables in suburban areas of Varanasi, India. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2007, 66, 258–266. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, G.; Huang, J.; Yang, J. The impacts of food safety standards on China’s tea exports. China Econ. Rev. 2012, 23, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissmannová, H.D.; Mihocová, S.; Chovanec, P.; Pavlovský, J. Potential ecological risk and human health risk assessment of heavy metal pollution in industrial affected soils by coal mining and metallurgy in Ostrava, Czech Republic. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Lu, W.X.; Zhao, H.Q.; Yang, Q.C.; Yang, Z.P. Potential ecological risk assessment and prediction of soil heavy-metal pollution around coal gangue dump. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 14, 1599–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, N.F.; Nasr, S.M.; Okbah, M.A. Potential ecological risk of heavy metals in sediments from the Mediterranean coast, Egypt. J. Environ. Health Sci. Engin. 2015, 13, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowalska, J.B.; Mazurek, R.; Gasiorek, M.; Zaleski, T. Pollution indices as useful tools for the comprehensive evaluation of the degree of soil contamination–A review. Environ. Geochem. Health 2018, 40, 2395–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hui, Z.; Caiqiu, W.; Jiping, J.; Xuyin, Y.; Qiao, W.; Wenming, P.; Tao, L.; Jie, Q.; Hanpei, Z. Assessment of heavy metal contamination in roadside soils along the Shenyang-Dalian Highway in Liaoning Province, China. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2017, 26, 1539–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Feng, M.; Hao, X. Application of Nemerow index method and integrated water quality index method in water quality assessment of Zhangze Reservoir. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 128, 012160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Yu, R.; Hu, G.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X. Bioavailability of heavy metals in soil of the Tieguanyin tea garden, southeastern China. Acta Geochem. 2017, 36, 519–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, B.; Li, L.; Duan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, J.; Xia, M.; Wang, Y.; Frang, W.; Zhu, X. Zn, Ni, Mn, Cr, Pb and Cu in soil-tea ecosystem: The concentrations, spatial relationship and potential control. Chemosphere 2018, 204, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wali, A.; Colinet, G.; Ksibi, M. Speciation of heavy metals by modified bcr sequential extraction in soils contaminated by phosphogypsum in Sfax, Tunisia. Environ. Res. Engin. Manag. 2015, 70, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, M.; Kiran, B.; Rani, S.; Rani, A.; Kaur, B.; Mittal, N. Heavy metal accumulation in vegetables irrigated with water from different sources. Food Chem. 2008, 111, 811–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakanson, L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, F.; Ding, Y.J.; Gao, J.R.; Chen, J.; Yan, H.Q.; Shao, W. Heavy metal pollution and assessment in the tidal flat sediments of Haizhou Bay, China. Mar. Poll. Bull. 2013, 74, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.J.; Chen, C.X.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Y.Q.; Yang, S.K.; Lu, C.Y. Study on soil environmental background values in Fujian province. Environ. Sci. 1992, 4, 70–75. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Kong, M.; Peng, F.Q.; Zhang, Y.M.; Yin, H.B.; Liu, Z.; Chao, J.Y. Occurrence characteristic and potential risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of Circum-Chaohu Basin. China Environ. Sci. 2015, 35, 1863–1871. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Yan, T.Z. Application of Nemerow index method in the evaluation of soil heavy metal pollution. J. Henan Inst. Educ. 2012, 2, 35–39. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.T.; Sun, H. Differences of nemerow index method and fuzzy comprehensive evaluation method in evaluation heavy metal pollution in soil. Admin. Techn. Environ. Monit. 2016, 4, 27–31. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Z.; Li, S.; Wand, L. Assessment of soil heavy metals for eco-environment and human health in a rapidly urbanization area of the upper Yangtze Basin. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolan, N.S.; Duraisamy, V.P. Role of inorganic and organic soil amendments on immobilisation and phytoavailability of heavy metals: A review involving specific case studies. Soil Res. 2003, 41, 533–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuy, P.T.; Van Geluwe, S.; Nguyen, V.A.; Van der Bruggen, B. Current pesticide practices and environmental issues in Vietnam: management challenges for sustainable use of pesticides for tropical crops in (South-East) Asia to avoid environmental pollution. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2012, 14, 379–387. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, Z.; Guo, P.; Zheng, L.; Huang, X.; Bi, J. Distribution of HCHs and DDTs in the soil–plant system in tea gardens in Fujian, a major tea-producing province in China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2013, 171, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockstad, E. European Union expands ban of three neonicotinoid pesticides. Sciencemag 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, R.; Das, S.J.; Das, A.C. Effect of synthetic pyrethroid insecticides on N2-fixation and its mineralization in tea soil. Europ. J. Soil Biol. 2016, 74, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moeder, M.; Bauer, C.; Popp, P.; van Pinxteren, M.; Reemtsma, T. Determination of pesticide residues in wine by membrane-assisted solvent extraction and high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 403, 1731–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Eir Grade | Pollution Grade | RI Grade | Comprehensive Ecological Risk Grade |
|---|---|---|---|
| Eir < 40 | Slight (Low) | RI < 135 | Slight (Low) |
| 40 ≤ Eir < 80 | Mid (Medium) | 135 ≤ RI < 265 | Mid (Medium) |
| 80 ≤ Eir < 160 | Strong (Heavy) | 265 ≤ RI < 525 | Strong (Heavy) |
| 160 ≤ Eir < 320 | Stronger (Heavier) | 525 ≤ RI | Stronger (Serious) |
| 320 ≤ Eir | Strongest (Serious) |
| Variable | Sites | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Taiwan | Tibet | Guangdong | Fuzhou | Anxi Organic | Anxi Conven | F Value | p | |
| Cd | 0.037 a (0.014) | 0.076 a (0.062) | 0.084 a (0.003) | 0.158 b (0.010) | 0.037 a (0.016) | 0.015 a (0.006) | 36.89 | <0.001 |
| Cr1 | 75.0 c (4.2) | 51.4 bc (29.9) | 216.7 d (15.1) | 31.7 ab (1.7) | 15.8 a (2.0) | 15.7 a (0.7) | 35.95 | <0.001 |
| Pb | 33.2 b (4.6) | 30.6 b (14.0) | 11.0 a (7.0) | 73.5 c (4.1) | 49.2 b (4.4) | 35.3 b (3.5) | 25.09 | <0.001 |
| Cu1 | 20 b (1.9) | 17.1 b (5.9) | 70.7 c (3.6) | 86.0 c (9.1) | 15.7 b (2.0) | 5.7 a (1.0) | 100.24 | <0.001 |
| Ni1 | 21.9 b (4.8) | 21.5 b (10.4) | 106 c (5.0) | 17.8 b (0.4) | 6.5 a (1.3) | 5.8 a (0.4) | 51.38 | <0.001 |
| Zn1 | 66.7 b (4.8) | 76.3 bc (13.5) | 89.9 c (0.6 | 151.3 d (2.6) | 76.9 bc (1.2) | 40.4 a (1.3) | 53.67 | <0.001 |
| Hg | 0.06 (0.01) | 0.07 (0.05) | 0.074 (0.007) | 0.073 (0.009) | 0.069 (0.003) | 0.054 (0.004) | 0.351 | 0.872 |
| As | 8.1 (0.6) | 14.1 (10.3) | 10.6 (0.3) | 5.66 (0.340) | 3.99 (0.05) | 4.01 (0.63) | 2.71 | 0.073 |
| pH | 4.01 b (0.08) | 5.56 d (0.30) | 5.15 c (0.08) | 6.82 e (0.05) | 3.33 a (0.05) | 3.63 a (0.19) | 223.94 | <0.001 |
| Methamidophos | 93.4 (16.4) | 94.9 (41.8) | 64.3 (14.4) | 60.5 (30.3) | 91.1 (33.3) | 111.4 (29.3) | 1.358 | 0.306 |
| Imidacloprid | 32.0 a (10.1) | 41.8a (34.3) | 101.6 b (49.6) | 14.1a (1.6) | 22.5a (17.8) | 6.5a (1.5) | 5.208 | 0.009 |
| HCHs | - | 1.1 (1.1) | - | - | - | 0.4 (0.4) | - | |
| Bifenthrin | 3.3 (1.0) | - | - | 1.0 (1.8) | - | 0.3 (0.5) | - | |
| Permethrin | 18.7 (14.9) | - | 76.0 (131.6) | 10.1 (17.4) | - | - | - | |
| Sampling Site | Eir | RI | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd | Cr | Pb | Cu | Ni | Zn | Hg | As | ||
| Tibet | 28.17 | 1.34 | 5.25 | 3.90 | 3.34 | 1.03 | 118.89 | 7.16 | 169.08 |
| Guangdong | 25.32 | 7.06 | 0.94 | 19.37 | 23.86 | 1.25 | 54.81 | 9.85 | 142.48 |
| Fuzhou | 87.59 | 1.53 | 10.53 | 19.92 | 6.60 | 1.83 | 35.88 | 9.80 | 173.69 |
| Anxi organic | 20.28 | 0.76 | 7.05 | 3.63 | 2.40 | 0.93 | 34.07 | 6.91 | 76.03 |
| Anxi conventional | 8.28 | 0.76 | 5.05 | 1.32 | 2.13 | 0.49 | 26.83 | 6.94 | 51.80 |
| Cd | Cr | Pb | Cu | Ni | Zn | Hg | As | pH | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd | 1 | ||||||||
| Cr | 0.16 | 1 | |||||||
| Pb | 0.493 | −0.706 | 1 | ||||||
| Cu | 0.885 * | 0.482 | 0.258 | 1 | |||||
| Ni | 0.236 | 0.987 ** | −0.649 | 0.553 | 1 | ||||
| Zn | 0.962 ** | 0.077 | 0.62 | 0.876 * | 0.15 | 1 | |||
| Hg | 0.74 | 0.429 | 0.098 | 0.693 | 0.496 | 0.734 | 1 | ||
| As | 0.208 | 0.512 | −0.55 | 0.086 | 0.477 | 0.014 | 0.453 | 1 | |
| pH | 0.952 ** | 0.193 | 0.338 | 0.787 | 0.255 | 0.837 * | 0.658 | 0.417 | 1 |
| Sampling Site | Single Pollution Index Pi | Comprehensive Pollution Index P | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HCHs | Bifenthrin | Methamidophos | Imidacloprid | Permethrin | ||
| Taiwan | - | 0.007 | 1.87 | 0.06 | 0.0009 | 1.375 |
| Tibet | 0.02 | - | 1.90 | 0.08 | - | 1.399 |
| Guangdong | - | - | 1.29 | 0.20 | 0.0038 | 0.943 |
| Fuzhou | - | 0.002 | 1.21 | 0.03 | 0.0005 | 0.877 |
| Anxi organic | - | - | 1.82 | 0.04 | - | 1.334 |
| Anxi conventional | 0.01 | 0.001 | 2.23 | 0.01 | - | 1.647 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, H.; Shi, L.; Yang, G.; You, M.; Vasseur, L. Ecological Risk Assessment of Soil Heavy Metals and Pesticide Residues in Tea Plantations. Agriculture 2020, 10, 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture10020047
He H, Shi L, Yang G, You M, Vasseur L. Ecological Risk Assessment of Soil Heavy Metals and Pesticide Residues in Tea Plantations. Agriculture. 2020; 10(2):47. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture10020047
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Haifang, Longqing Shi, Guang Yang, Minsheng You, and Liette Vasseur. 2020. "Ecological Risk Assessment of Soil Heavy Metals and Pesticide Residues in Tea Plantations" Agriculture 10, no. 2: 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture10020047
APA StyleHe, H., Shi, L., Yang, G., You, M., & Vasseur, L. (2020). Ecological Risk Assessment of Soil Heavy Metals and Pesticide Residues in Tea Plantations. Agriculture, 10(2), 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture10020047





