The In-Silico Development of DNA Markers for Breeding of Spring Barley Varieties That Are Resistant to Spot Blotch in Russia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material and Genotyping Data
2.2. Pathogen Isolates and Culture Conditions
2.3. Resistance to Spot Blotch
- Experimental design
- Disease evaluation
2.4. Resistance to Root Rot
- Experimental design
- Disease evaluation
2.5. Association Analysis
2.6. Conversion to KASP Markers
3. Results
3.1. Phenotyping
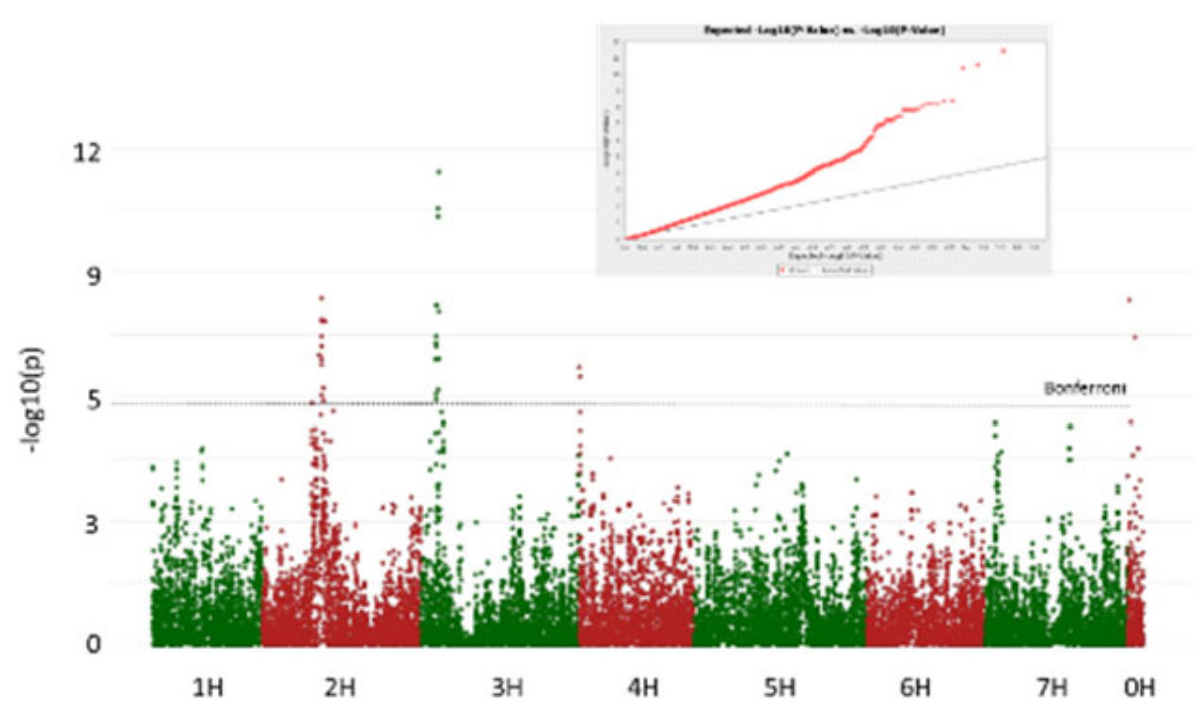
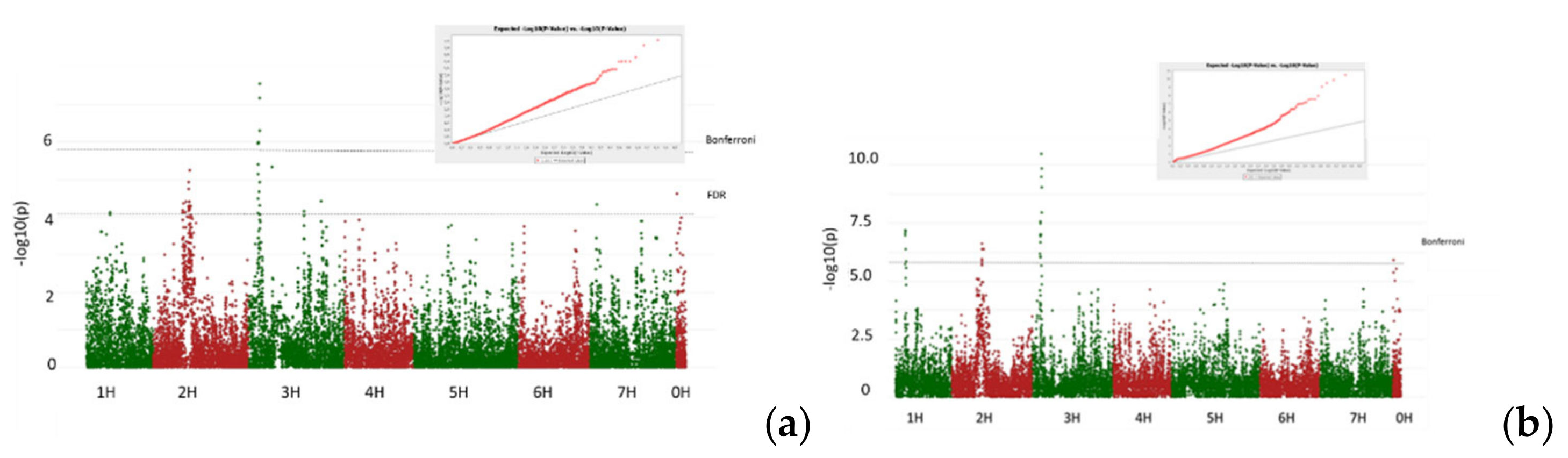
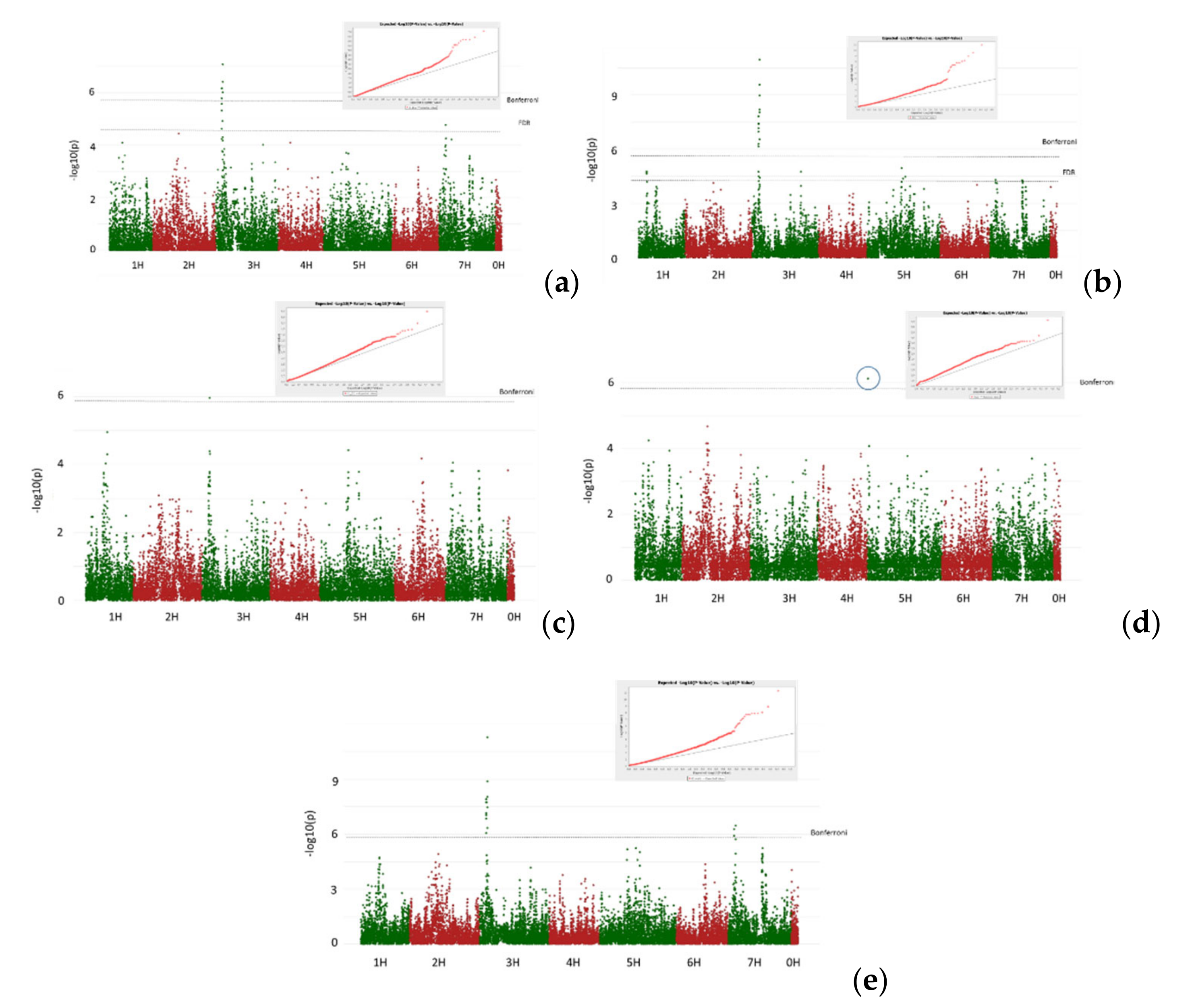
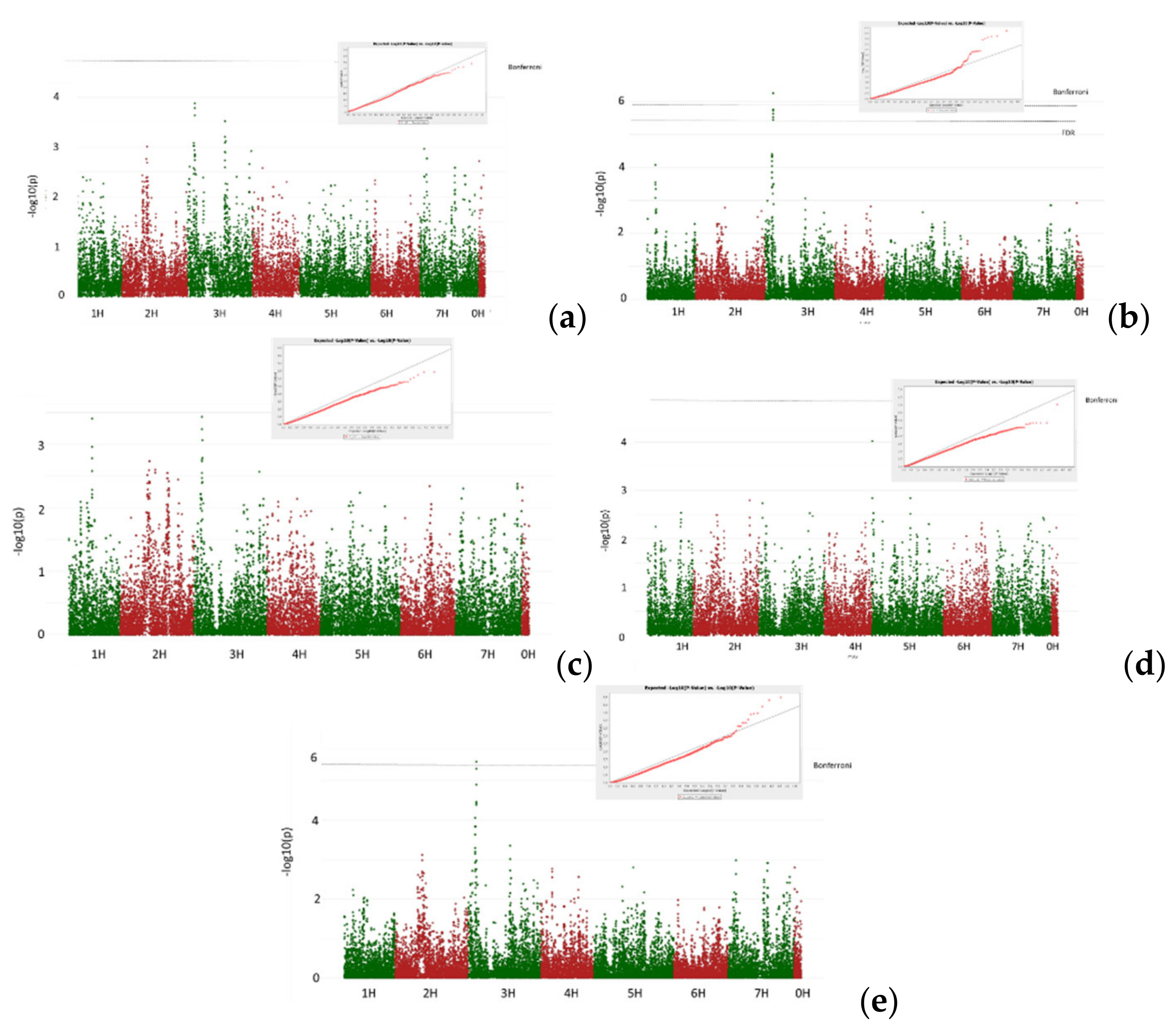
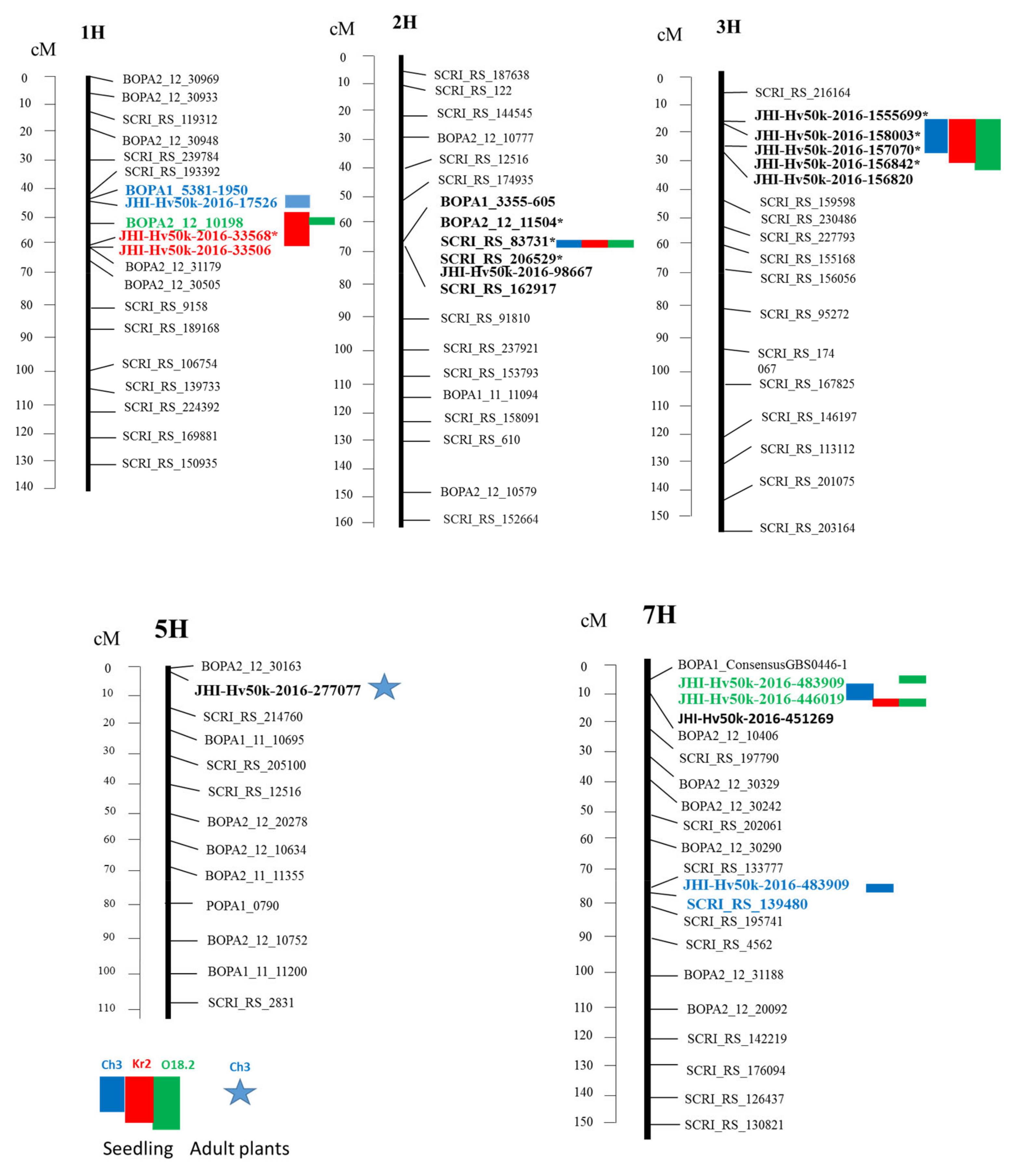
3.2. GWAS Analysis
- Isolate O18.2. Seedling resistance
- Isolate Ch3. Adult resistance
- Common root rot
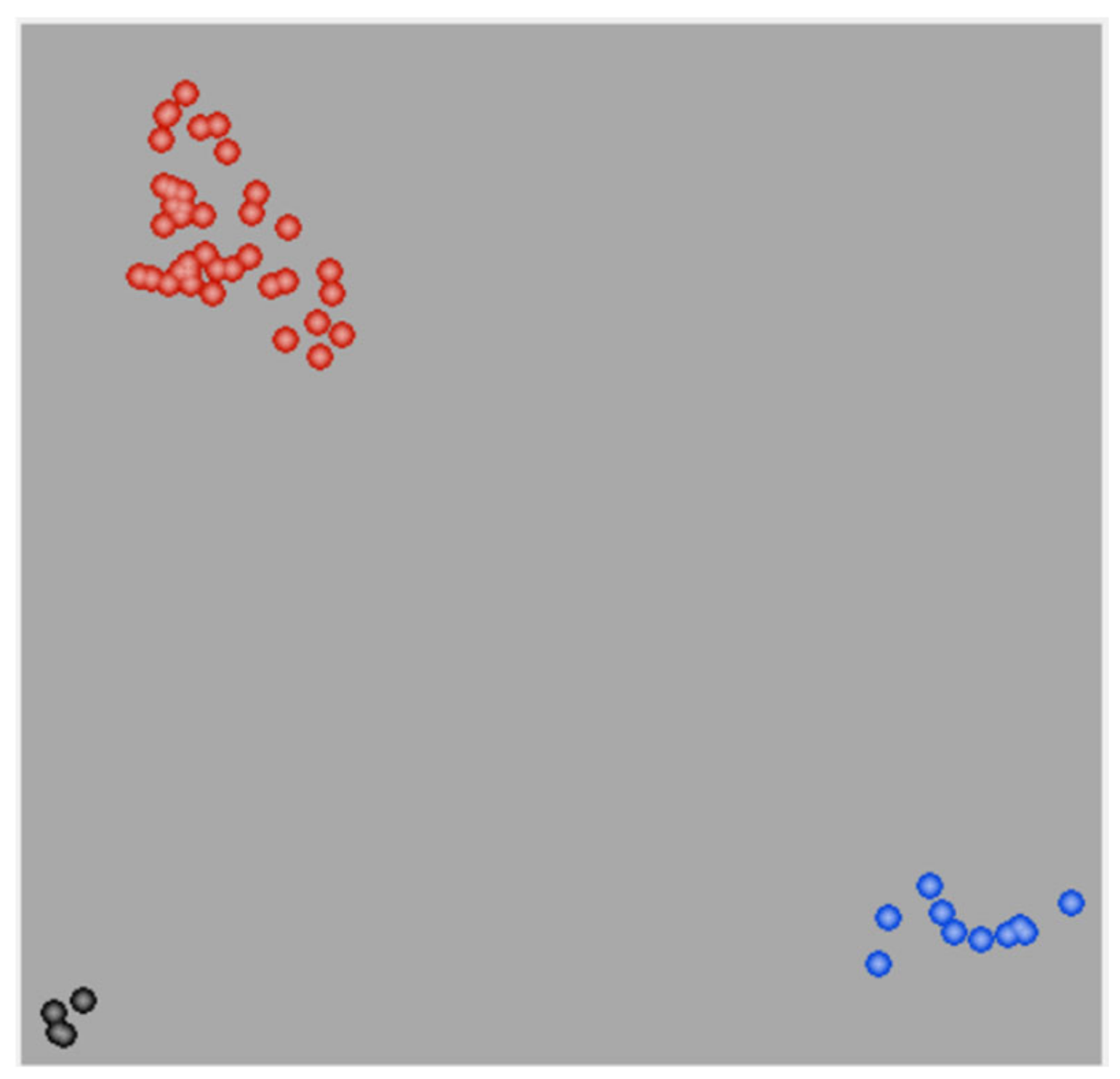
3.3. PCA
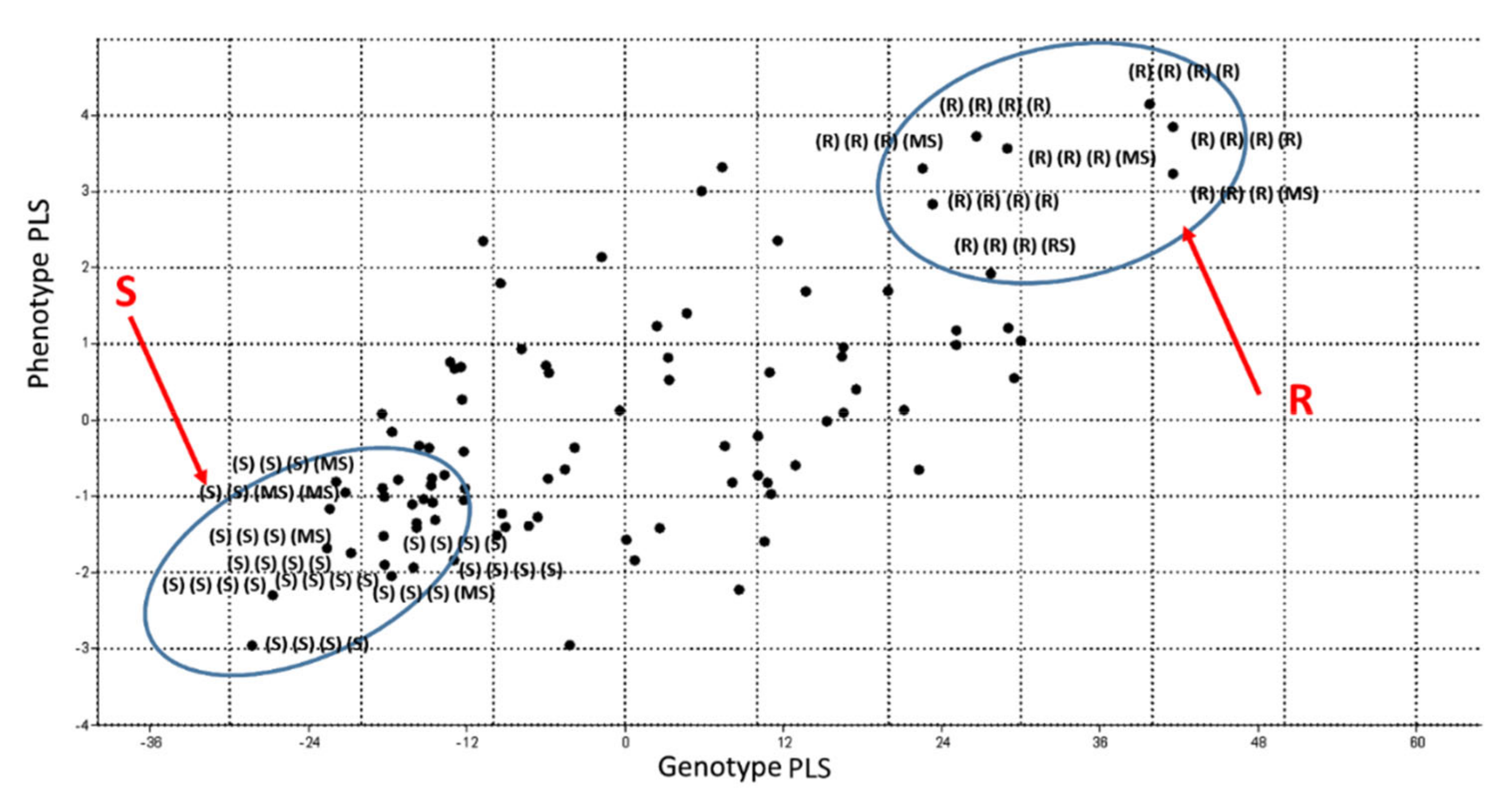
3.4. PLS Analysis
3.5. KASP Genotyping Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

References
- Arabi, M.I.E.; Al-Daoude, A.; Jawhar, M. Interrelationship between spot blotch and common root rot in barley. Australas. Plant Pathol. 2006, 35, 477–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pua, E.C.; Pelletier, R.L.; Klinck, H.R. Seedling blight, spot blotch, and common root rot in Quebec and their effect on grain yield in barley. Can. J. Plant Pathol. 1985, 7, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutcher, H.R.; Bailey, K.L.; Rossnagel, B.G.; Legge, W.G. Heritability of common root rot and spot blotch resistance in barley. Can. J. Plant Pathol. 1994, 16, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novakazi, F.; Afanasenko, O.; Lashina, N.; Platz, G.J.; Snowdon, R.; Loskutov, I.; Ordon, F. Genome-wide association studies in a barley (Hordeum vulgare) diversity set reveal a limited number of loci for resistance to spot blotch (Bipolaris sorokiniana). Plant Breed. 2019, 139, 521–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, R.V. Yield losses in barley cultivars caused by spot blotch. Can. J. Plant Pathol. 1979, 1, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonman, J.M.; Bockelman, H.E.; Jackson, L.F.; Steffenson, B.J. Disease and insect resistance in cultivated barley accessions from the USDA National Small Grains Collection. Crop Sci. 2005, 45, 1271–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afanasenko, O.S. Plant genetic protection: Problems and prospects. Zaschita I Karantin Rastenij 2016, 1, 13–16. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Wilcoxson, R.D.; Rasmusson, D.C.; Miles, M.R. Development of barley resistant to spot blotch and genetics of resistance. Plant Dis. 1990, 74, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, J.K.; Smith, K.P.; Muehlbauer, G.J.; Chao, S.; Close, T.J.; Steffenson, B.J. Association mapping of spot blotch resistance in wild barley. Mol. Breed 2010, 26, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, Y.; Wang, R.; Ali, S.; Zhao, M.; Zhong, S. Sources and genetics of spot blotch resistance to a new pathotype of Cochliobolus sativus in the USDA national small grains collection. Plant Dis. 2016, 100, 1988–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bykova, I.; Lashina, N.; Efimov, V.; Afanasenko, O.; Khlestkina, E. Identification of 50K Illumina-chip SNPs associated with resistance to spot blotch in barley. BMC Plant Biol. 2017, 17, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radyukevich, T.N.; Bondareva, L.; Kartasheva, L. Assessment of new collection samples of barley accoding to commercially valuable traits in the conditions of north-west of Russia. Perm Agrar. J. 2018, 4, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapina, V.V.; Smolin, N.V.; Zhemchuzhina, N.S.; Ovchinnikov, A.P. Etiology of root rot and blights of barley in the southern part of the cental non-chernozam region. Bull. Altai State Agrar. Univ. 2014, 3, 34–39. [Google Scholar]
- Sheshegova, T.; Shchekleina, L.; Shchennikova, I.; Mart’yanova, A. Dependence of fungal infection development of seasonal dynamics of climate factors. Dostizheniya Nauk. I Tekh. APK 2017, 31, 58–61. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Piening, L.J.; Orr, D. Effects of crop rotation on common root rot of barley. Can. J. Plant Pathol. 1988, 10, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorobej, I. Annual feed crop disease and their phytosanitary control in the forest-steppe of Western Siberia. Ph.D. Thesis, Novosibirsk State University, Novosibirsk, Russia, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Almgren, I.; Gustafsson, M.; Fält, A.S.; Lindgren, H.; Liljeroth, E. Interaction between root and leaf disease development in barley cultivars after inoculation with different isolates of Bipolaris sorokiniana. J. Phytopathol. 1999, 147, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffenson, B.; Hayes, P.; Kleinhofs, A. Genetics of seedling and adult plant resistance to net blotch (Pyrenophora teres f. teres) and spot blotch (Cochliobolus sativus) in barley. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1996, 92, 552–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, G.L.; Liu, S.; Hall, M.D.; Brooks, W.S.; Chao, S.; Muehlbauer, G.J.; Baik, B.K.; Steffenson, B.; Griffey, C.A. Marker-trait associations in Virginia Tech winter barley identified using genome-wide mapping. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2013, 126, 693–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Steffenson, B.J. Association Mapping of Septoria Speckled Leaf Blotch Resistance in U.S. Phytopathology 2013, 103, 600–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, L.; Germán, S.; Pereyra, S.; Hayes, P.M.; Pérez, C.A.; Capettini, F.; Locatelli, A.; Berberian, N.M.; Falconi, E.E.; Estrada, R.; et al. Multi-environment multi-QTL association mapping identifies disease resistance QTL in barley germplasm from Latin America. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2015, 128, 501–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Leng, Y.; Ali, S.; Wang, M.; Zhong, S. Genome-wide association mapping of spot blotch resistance to three different pathotypes of Cochliobolus sativus in the USDA barley core collection. Mol. Breed. 2017, 37, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyawali, S.; Chao, S.; Vaish, S.S.; Singh, S.P.; Rehman, S.; Vishwakarma, S.R.; Verma, R.P. Genome wide association studies (GWAS) of spot blotch resistance at the seedling and the adult plant stages in a collection of spring barley. Mol. Breed. 2018, 38, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, Y.; Zhao, M.; Wang, R.; Steffenson, B.J.; Brueggeman, R.S.; Zhong, S. The gene conferring susceptibility to spot blotch caused by Cochliobolus sativus is located at the Mla locus in barley cultivar Bowman. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2018, 131, 1531–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visioni, A.; Rehman, S.; Viash, S.S.; Singh, S.P.; Vishwakarma, R.; Gyawali, S.; Al-Abdallat, A.M.; Verma, R.P.S. Genome Wide Association Mapping of Spot Blotch Resistance at Seedling and Adult Plant Stages in Barley. Front. Plant Sci. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haas, M.; Menke, J.; Chao, S.; Steffenson, B.J. Mapping quantitative trait loci conferring resistance to a widely virulent isolate of Cochliobolus sativus in wild barley accession PI 466423. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2016, 129, 1831–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arabi, M.I.E.; Jawhar, M. Molecular and pathogenic variation identified among isolates of Cochliobolus sativus. Aust. Plant Pathol. 2007, 36, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutcher, H.R.; Bailey, K.L.; Rossnagel, B.G.; Legge, W.G. Identification of RAPD markers for common root rot and spot blotch (Cochliobolus sativus) resistance in barley. Genome 1996, 39, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, S.; Steffenson, B.J. Identification and characterization of DNA markers associated with a locus conferring virulence on barley in the plant pathogenic fungus Cochliobolus sativus. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2002, 104, 1049–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantalapiedra, C.P.; Boudiar, R.; Casas, A.M.; Igartua, E.; Contreras-Moreira, B. BARLEYMAP: Physical and genetic mapping of nucleotide sequences and annotation of surrounding loci in barley. Mol. Breed. 2015, 35, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fetch, T.G.; Steffenson, B.J. Special Report Rating Scales for Assessing Infection Responses of Barley Infected with Cochliobolus sativus. Plant Dis. 1999, 83, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradbury, P.J.; Zhang, Z.; Kroon, D.E.; Casstevens, T.M.; Ramdoss, Y.; Buckler, E.S. TASSEL: Software for association mapping of complex traits in diverse samples. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2633–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gower, J.C. Some distance properties of latent root and vector methods used in multivariate analysis. Biometrika 1966, 53, 325–338. [Google Scholar]
- Polunin, D.A.; Shtaiger, I.A.; Efimov, V.M. Development of the JACOBI 4 software package for multidimensional analysis of microchip data. Vestnik NGU 2014, 12, 90–98. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Gutiérrez, L.; Berberian, N.; Capettini, F.; Falcioni, E.; Fros, D.; Germán, S.; Hayes, P.M.; Huerta-Espino, J.; Herrera, S.; Pereyra, S.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Mapping Identifies Disease-Resistance QTLs in Barley Germplasm from Latin America. In Advance in Barley Sciences; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 209–215. [Google Scholar]
- Afanasenko, O.S.; Koziakov, A.V.; Hedlay, P.E.; Lashina, N.M.; Anisimova, A.V.; Manninen, O.; Jalli, M.; Potokina, E.K. Mapping of the Loci Controlling the Resistance to Pyrenophora teres f. teres and Cochliobolus sativus in two Double Haploid Barley Populations. Russ. J. Genet. Appl. Res. 2015, 5, 242–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grewal, T.S.; Rossnagel, B.G.; Scoles, G.J. Mapping quantitative trait loci associated with spot blotch and net blotch resistance in a doubled-haploid barley population. Mol. Breed. 2012, 30, 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bovill, J.; Lehmensiek, A.; Sutherland, M.W.; Platz, G.J.; Usher, T.; Franckowiak, J.; Mace, E. Mapping spot blotch resistance genes in four barley populations. Mol. Breed. 2010, 26, 653–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilgic, H.; Steffenson, B.J.; Hayes, P.M. Comprehensive genetic analyses reveal differential expression of spot blotch resistance in four populations of barle. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2005, 111, 1238–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| p-Value | Spot Blotch (Kr2) Seedling | Spot Blotch (Ch3) Seedling | Spot Blotch (O18.2) Seedling | Spot Blotch (Ch3) Adult | Root Rot (O18.2) Seedling | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Correlation | ||||||
| Spot blotch (Kr2) seedling | - | 8.83 × 10−11 | 2.82 × 10−14 | 1.50 × 10−3 | 8.88 × 10−3 | |
| Spot blotch (Ch3) seedling | 0.61 | - | 2.27 × 10−16 | 9.80 × 10−09 | 5.71 × 10−3 | |
| Spot blotch (O18.2) Seedling | 0.69 | 0.73 | - | 1.57 × 10−4 | 4.86 × 10−3 | |
| Spot blotch (Ch3) Adult | 0.34 | 0.57 | 0.43 | - | 5.55 × 10−4 | |
| Root rot (O18.2) Seedling | 0.23 | 0.25 | 0.22 | 0.28 | - | |
| Trait | 1 Phen | 1 Gen | 2 Phen | 2 Gen | 3 Phen | 3 Gen |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spot blotch (Kr2) seedling | 0.814 | 0.545 | −0.161 | −0.151 | 0.243 | 0.25 |
| Spot blotch (Ch3) seedling | 0.896 | 0.582 | 0.222 | 0.082 | −0.101 | −0.105 |
| Spot blotch (O18.2) seedling | 0.894 | 0.639 | −0.103 | −0.121 | −0.032 | 0.034 |
| Spot blotch (Ch3) Adult | 0.646 | 0.359 | 0.7 | 0.328 | −0.237 | −0.229 |
| Name of SNP | Chr | Position | Interval (cM) | The Sequence Structure Containing SNP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JHI-Hv50k-2016-33568 | 1 | 446893297 | 50–61.2 | ATTACATTGGATTACTAATTCAGGCCTCGTTCGTTCGACAGGGATTTAGA[A/C]GGGGTTTGGCAGGGATTGAGGTGGATATAATTCCCTACAAGTCATATTCC |
| JHI-Hv50k-2016-156842 | 3 | 17559189 | 18.72–26.18 | CGTGGTTGCAACAATACTGCTTATCTACGGGAGAGCTTCACGGACAAATC[A/G]CTCCTGGATAGGCTTCATTGTTTCAATGCATTTCCTTTGGGTGGCACTGA |
| JHI-Hv50k-2016-157070 | 3 | 17888495 | GTTCGATTTGATTCTTTGGGTCGGGTTAATACATATGATTGAAATGTGTT[C/G]GTGCTGACGCTTGTCCTGATCATGTCCATGCAGGTTCATCAACCTGCGGC | |
| JHI-Hv50k-2016-156820 | 3 | 17557023 | TCCACTGTCATCTTTGACAATGCCAGCCTCTCGAGTACCACCTGTAAACC[C/T]CATTCAACGGAATACATGTCAAATGAATGGTCGTCTGGACGGAGAGGATT | |
| JHI-Hv50k-2016-157182 | 3 | 17954351 | TGGACTTTTTTTTGCTTGTGGTTTGGGTGGACAGAATCTGCACAAACAAA[A/T]GTTTTGTCATTTATCATGTATAAAATTTTGTGAGTGTTCTGGTCAACGGG | |
| JHI-Hv50k-2016-156833 | 3 | 17558292 | TTGCTCTTGCAATGGAGGCCATCACTCACCAACAACCTTGACACAAACAA[A/T]AGCAGCCCGGTGCATTTCACCGCATCCGACGGCGACTGCTCGATCATCGA | |
| JHI-Hv50k-2016-155569 | 3 | 15256329 | 18.72 | TCTTCCTGTGTTTACGATCACTGTCGCTCTCTGATTCACTATCAGATTCC[A/G]AGGAAGAATAGCTTCGCCTCCTGTGCTTTCTTGACTTGAGCTTCTTCTCC |
| JHI-Hv50k-2016-277077 | 5 | 546242 | 1.12–1.22 | GCTGCCAACTCTTCTTTTTGTGCATTCCTTTTGTCCGCGTCCTATTAAC[G/A]AGTGGTTTGATGTGCAGATGTTGGCCAAGAAAGTCGACACTTTAACAAAG |
| JHI-Hv50k-2016-446766** | 7 | 10867101 | 7.52–15.44 | TATTCGCTGAAACCTGCTTTCATGAAGATGTCGCTCCAGTCCTTTTCATC[A/C]CGCTGGCGGCCTCTCGTCATCACCAGCTTCAACATATCAACCAGGTGATG |
| JHI-Hv50k-2016-448898 | 7 | 13541902 | AAGAACCAGTTCACTGCCGAGTAAGTTCCCAATACCCCGAATATTCTGCG[T/C]GGGCCAATAAGTCCCCATATGACGGACGCATCGTAGAACACATGATCAGT | |
| JHI-Hv50k-2016-451269 | 7 | 16899719 | GAAAAAAAGTTCATTGCATGATAAAGAACGGCCAGGAACCAGTAATTAGG[A/T]CTCCTTGGTCAAGAATTATCATACCTTGGCGCCCTCACCTCCTATGAAGA |
| SNP Names | Chromosome | Alleles | Resistant Varieties | Nucleotide Prediction Percentage in Resistant Varieties | Susceptible Varieties | Nucleotide Prediction Percentage in Susceptible Varieties |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JHI-Hv50k-2016-33568 | 1H | CC | 6 | 55% | 5 | 55% |
| AA | 5 | 6 | ||||
| CA | - | - | ||||
| JHI-Hv50k-2016-156842 | 3H | GG | 3 | 73% | 11 | 100% |
| AA | 8 | 0 | ||||
| GA | - | - | ||||
| JHI-Hv50k-2016-157070 | 3H | GG | 5 | 45% | 11 | 100% |
| CC | 4 | 0 | ||||
| GC | - | - | ||||
| JHI-Hv50k-2016-156820 | 3H | TT | 7 | 67% | 2 | 72% |
| AA | 3 | 8 | ||||
| TA | - | 1 | ||||
| JHI-Hv50k-2016-157182 | 3H | TT | 7 | 67% | 2 | 72% |
| AA | 3 | 8 | ||||
| TA | - | 1 | ||||
| JHI-Hv50k-2016-156833 | 3H | TT | 9 | 87% | 4 | 55% |
| AA | 2 | 6 | ||||
| TA | - | - | ||||
| JHI-Hv50k-2016-155569 | 3H | GG | 5 | 45% | 10 | 100% |
| AA | 4 | 0 | ||||
| GA | 2 | 1 | ||||
| JHI-Hv50k-2016-277077 | 5H | AA | 0 | 0% | 0 | 100% |
| GG | 10 | 11 | ||||
| AG | - | - | ||||
| JHI-Hv50k-2016-448898 | 7H | TT | 8 | 27% | 11 | 100% |
| CC | 3 | 0 | ||||
| TC | - | - | ||||
| JHI-Hv50k-2016-451269 | 7H | AA | 6 | 36% | 8 | 73% |
| TT | 4 | 3 | ||||
| TA | 1 | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
V. Rozanova, I.; M. Lashina, N.; M. Efimov, V.; S. Afanasenko, O.; K. Khlestkina, E. The In-Silico Development of DNA Markers for Breeding of Spring Barley Varieties That Are Resistant to Spot Blotch in Russia. Agriculture 2020, 10, 505. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture10110505
V. Rozanova I, M. Lashina N, M. Efimov V, S. Afanasenko O, K. Khlestkina E. The In-Silico Development of DNA Markers for Breeding of Spring Barley Varieties That Are Resistant to Spot Blotch in Russia. Agriculture. 2020; 10(11):505. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture10110505
Chicago/Turabian StyleV. Rozanova, Irina, Nina M. Lashina, Vadim M. Efimov, Olga S. Afanasenko, and Elena K. Khlestkina. 2020. "The In-Silico Development of DNA Markers for Breeding of Spring Barley Varieties That Are Resistant to Spot Blotch in Russia" Agriculture 10, no. 11: 505. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture10110505
APA StyleV. Rozanova, I., M. Lashina, N., M. Efimov, V., S. Afanasenko, O., & K. Khlestkina, E. (2020). The In-Silico Development of DNA Markers for Breeding of Spring Barley Varieties That Are Resistant to Spot Blotch in Russia. Agriculture, 10(11), 505. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture10110505







