Insight in miRNome of Long-Term Non-Progressors and Elite Controllers Exposes Potential RNAi Role in Restraining HIV-1 Infection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Samples
2.2. Small RNA Extraction
2.3. Next-Generation Sequencing
2.4. Analysis of miRNA
2.5. miRNA Alignment
2.6. Differential Expression Analysis
2.7. Target Genes Identification and Functional Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Next-Generation Sequencing Quality Assessment
3.3. miRNA Mapping
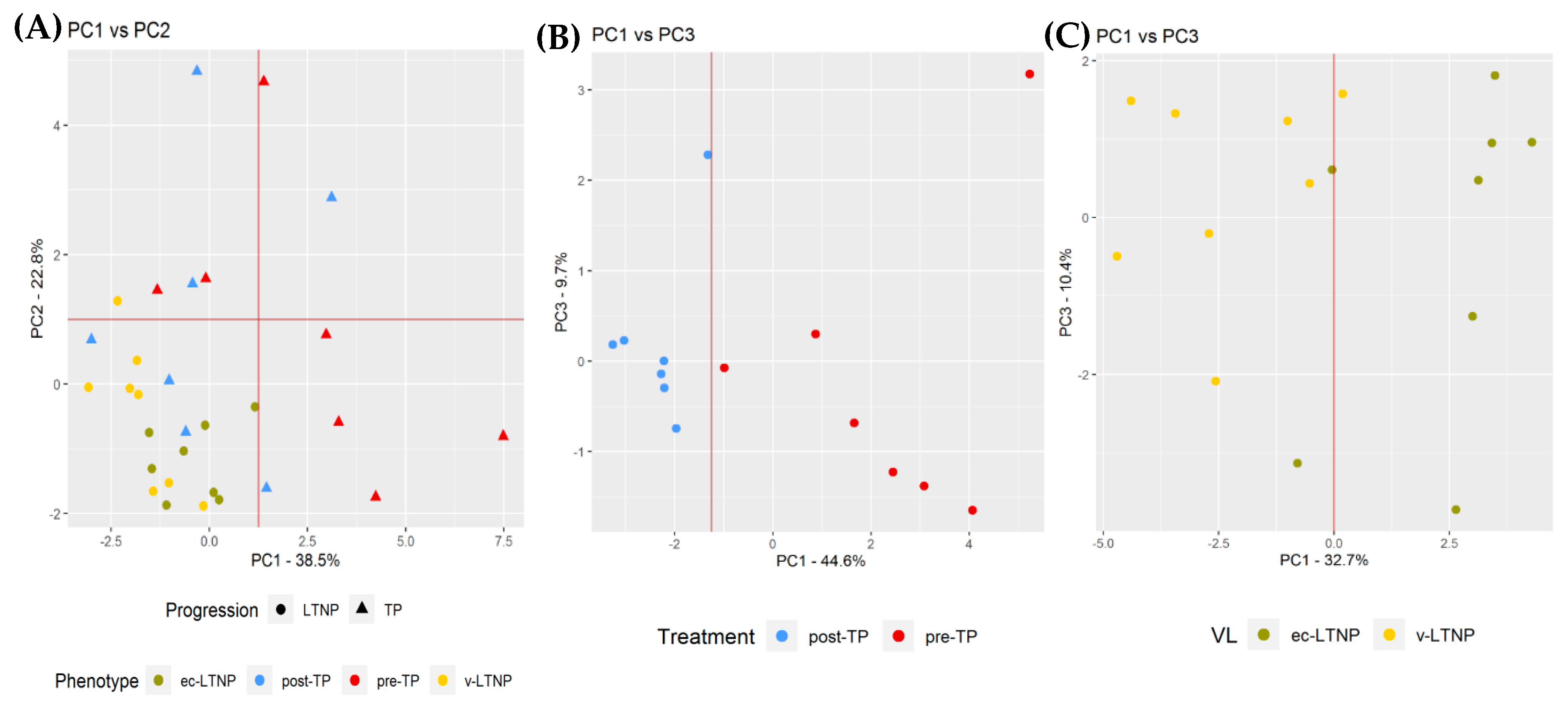
3.4. Global Comparison
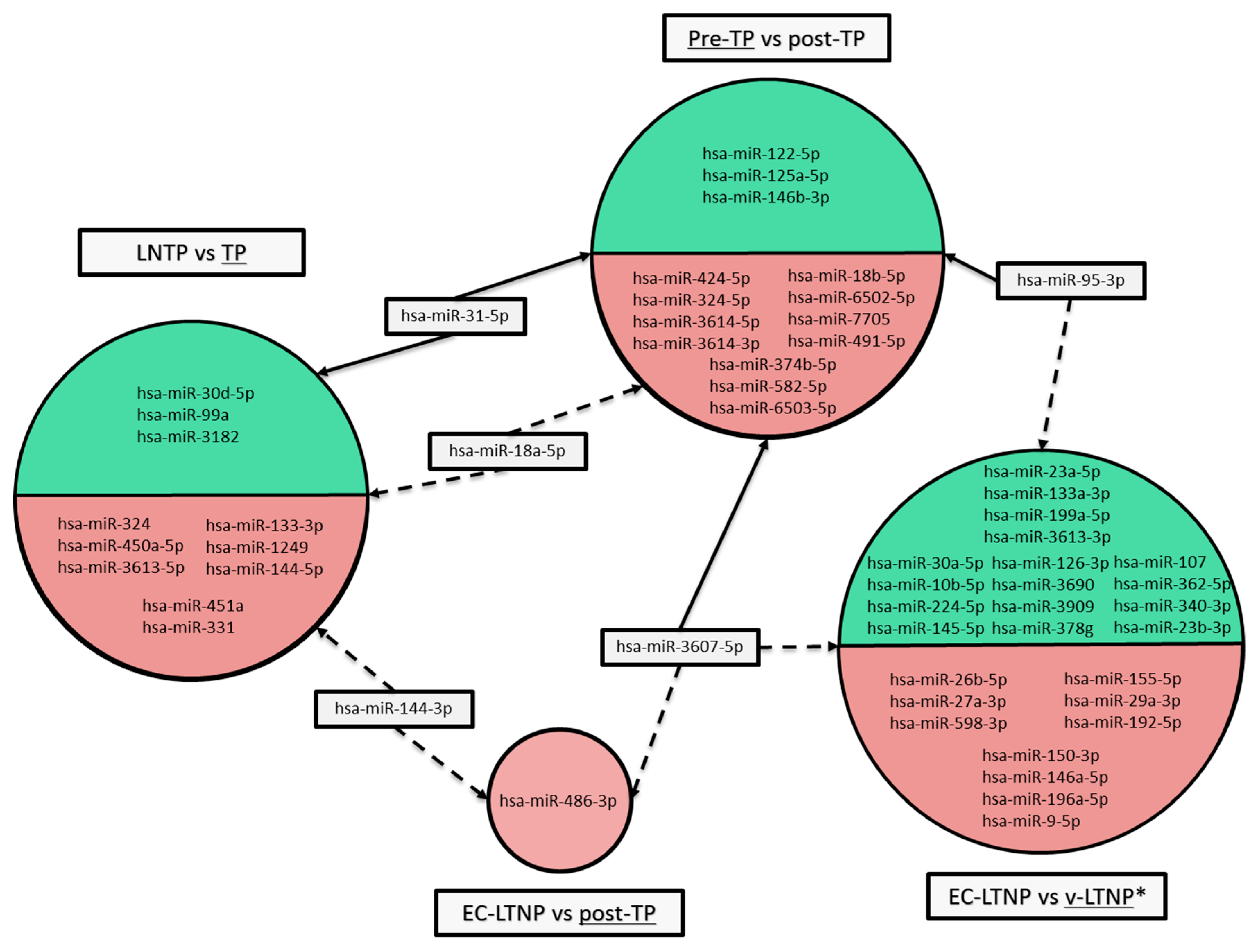
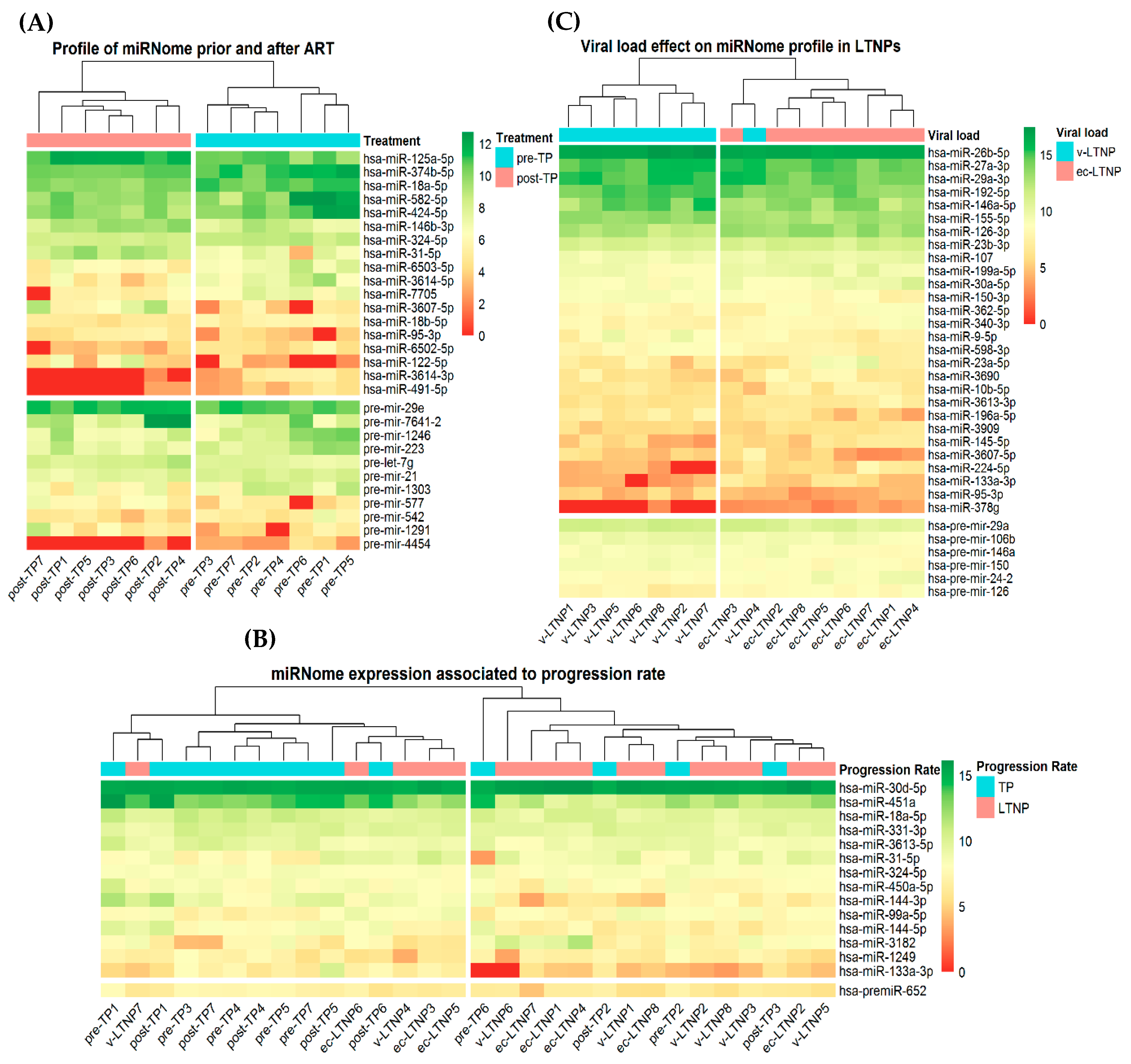
3.5. Differences in miRNA Expression Associated with Viral Replication
3.6. Differences in miRNA Expression Associated with Disease Progression
3.7. Differences of miRNA Expression Associated with EC-LTNP Phenotype
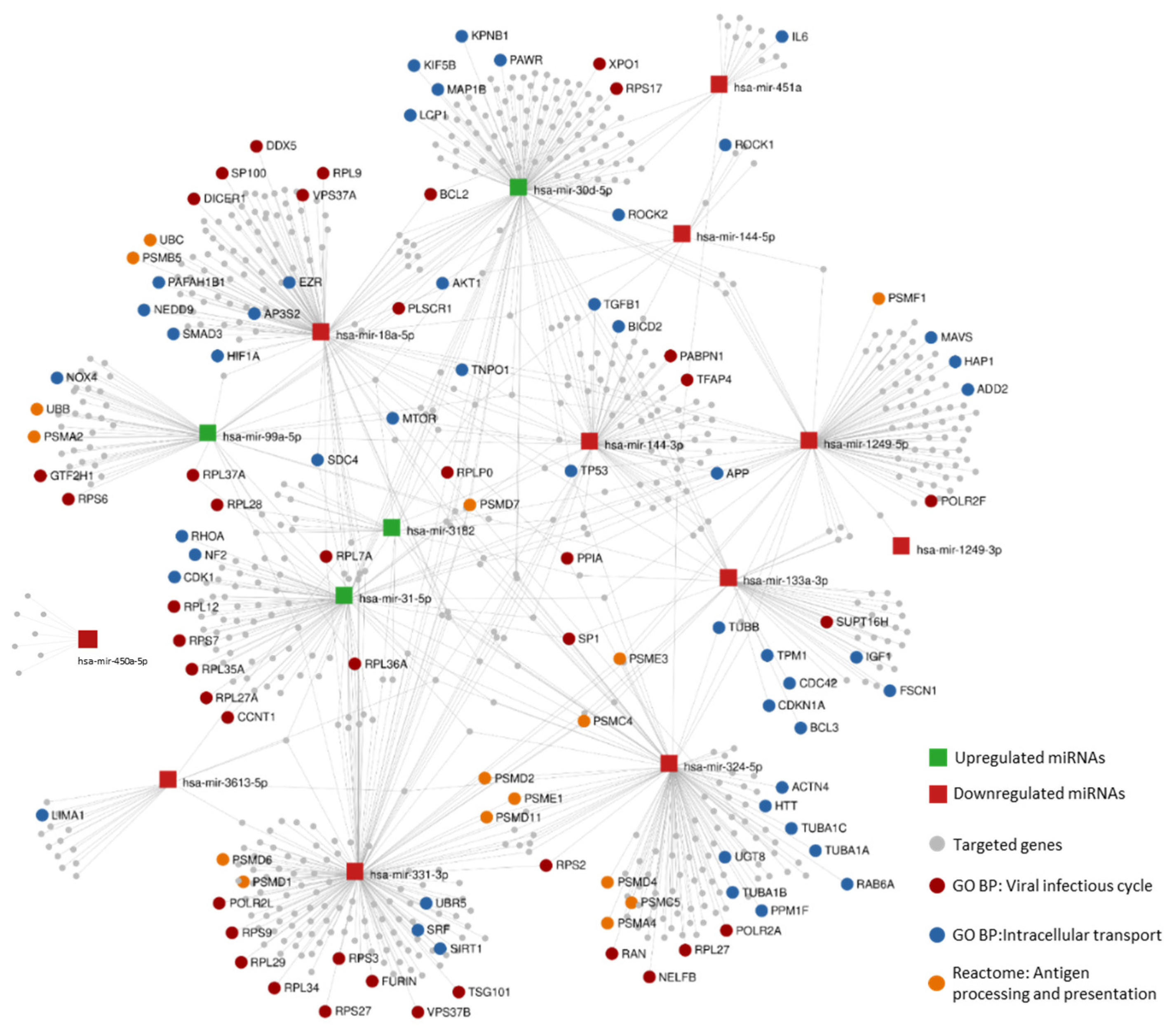
3.8. Potentially Altered Pathways Regulated by DE miRNA Associated with Disease Progression
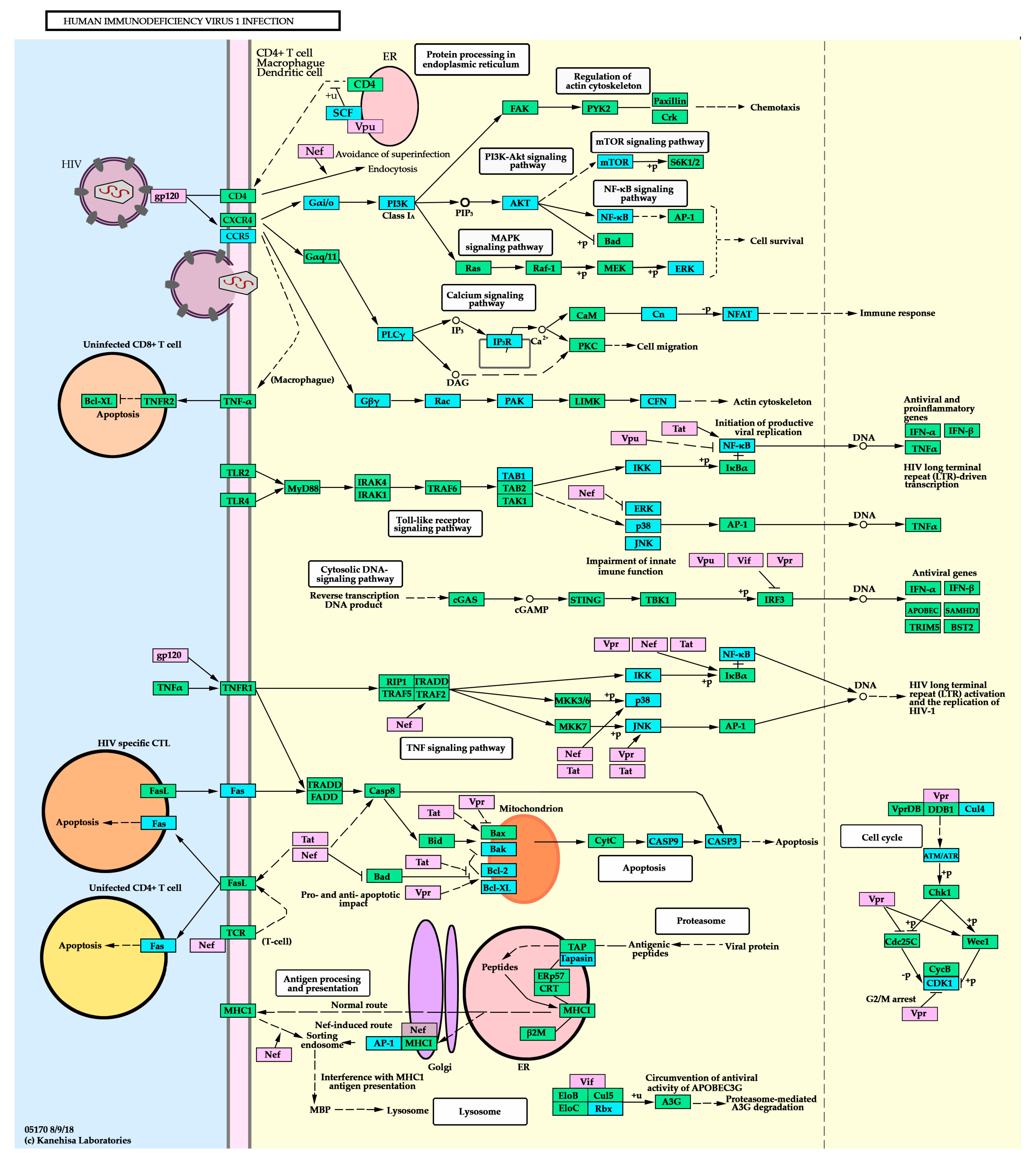
3.8.1. DE miRNA Predictably Targets Various Genes Involved in the KEGG HIV-1 Infection Pathway
3.8.2. Enrichment Analysis of Likely Altered Pathways Based on HIV-1 Human Interaction Database
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Garcia, F.; Plana, M.; Vidal, C.; Cruceta, A.; O’Brien, W.A.; Pantaleo, G.; Pumarola, T.; Gallart, T.; Miró, J.M.; Gatell, J.M. Dynamics of viral load rebound and immunological changes after stopping effective antiretroviral therapy. AIDS 1999, 13, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurdasani, D.; Iles, L.; Dillon, D.G.; Young, E.H.; Olson, A.D.; Naranbhai, V.; Fidler, S.; Gkrania-Klotsas, E.; Post, F.A.; Kellam, P.; et al. A systematic review of definitions of extreme phenotypes of HIV control and progression. AIDS 2014, 28, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paolucci, S.; Gulminetti, R.; Maserati, R.; Dossena, L.; Baldanti, F. Accumulation of defective HIV-1 variants in a patient with slow disease progression. Curr. HIV Res. 2011, 9, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casado, C.; Pernas, M.; Sandonis, V.; Alvaro-Cifuentes, T.; Olivares, I.; Fuentes, R.; Martínez-Prats, L.; Grau, E.; Ruiz, L.; Delgado, R.; et al. Identification of a cluster of HIV-1 controllers infected with low replicating viruses. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e77663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz, N.V.G.; Amorim, R.; Oliveira, F.E.; Speranza, F.A.C.; Costa, L.J. Mutations in the nef and vif genes associated with progression to AIDS in elite controller and slow-progressor patients. J. Med. Virol. 2013, 85, 563–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blankson, J.N.; Bailey, J.R.; Thayil, S.; Yang, H.-C.; Lassen, K.; Lai, J.; Gandhi, S.K.; Siliciano, J.D.; Williams, T.M.; Siliciano, R.F. Isolation and characterization of replication-competent human immunodeficiency virus type 1 from a subset of elite suppressors. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 2508–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereyra, F.; Jia, X.; McLaren, P.J.; Telenti, A.; De Bakker, P.I.W.; Walker, B.D. The major genetic determinants of HIV-1 control affect HLA class I peptide presentation. Science 2010, 330, 1551–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díez-Fuertes, F.; De La Torre-Tarazona, H.E.; Calonge, E.; Pernas, M.; Bermejo, M.; García-Pérez, J.; Álvarez, A.; Capa, L.; García-García, F.; Saumoy, M.; et al. Association of a single nucleotide polymorphism in the ubxn6 gene with long-term non-progression phenotype in HIV-positive individuals. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2019, 26, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hütter, G.; Nowak, D.; Mossner, M.; Ganepola, S.; Müßig, A.; Allers, K.; Schneider, T.; Hofmann, J.; Kücherer, C.; Blau, O.; et al. Long-Term Control of HIV by CCR5 Delta32/Delta32 Stem-Cell Transplantation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 692–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poropatich, K.; Sullivan, D.J. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 long-term non-progressors: The viral, genetic and immunological basis for disease non-progression. J. Gen. Virol. 2011, 92, 247–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imami, N.; Westrop, S.J.; Grageda, N.; Herasimtschuk, A.A. Long-Term Non-Progression and Broad HIV-1-Specific Proliferative T-Cell Responses. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betts, M.R.; Nason, M.C.; West, S.M.; De Rosa, S.C.; Migueles, S.A.; Abraham, J.; Lederman, M.M.; Benito, J.M.; Goepfert, P.A.; Connors, M.; et al. HIV nonprogressors preferentially maintain highly functional HIV-specific CD8+ T cells. Blood 2006, 107, 4781–4789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díez-Fuertes, F.; De La Torre-Tarazona, H.E.; Calonge, E.; Pernas, M.; del Mar Alonso-Socas, M.; Capa, L.; García-Pérez, J.; Sakuntabhai, A.; Alcamí, J. Transcriptome Sequencing of Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells from Elite Controller-Long Term Non Progressors. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luque, M.C.; Santos, C.C.; Mairena, E.C.; Wilkinson, P.; Boucher, G.; Segurado, A.C.; Fonseca, L.A.; Sabino, E.; Kalil, J.E.; Cunha-Neto, E. Gene expression profile in long-term non progressor HIV infected patients: In search of potential resistance factors. Mol. Immunol. 2014, 62, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.L.; Zhang, Z.N.; Wu, X.; Jiang, Y.J.; Fu, Y.J.; Shang, H. Transcriptomic meta-analysis identifies gene expression characteristics in various samples of HIV-infected patients with nonprogressive disease. J. Transl. Med. 2017, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craig, C.M.; Darryl, C.J. Revealing the world of RNA interference. Nature 2004, 431, 338–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaminathan, G.; Martin-Garcia, J.; Navas-Martin, S. RNA viruses and microRNAs: Challenging discoveries for the 21st century. Physiol. Genom. 2013, 45, 1035–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, M.; Kim, V.N. Regulation of microRNA biogenesis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 509–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klase, Z.; Houzet, L.; Jeang, K.-T. MicroRNAs and HIV-1: Complex Interactions. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 40884–40890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, B.; Fu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wu, H.; Ma, P.; Zeng, W.; Zhang, T.; Lian, S.; Wu, H. Potential Application of MicroRNA Profiling to the Diagnosis and Prognosis of HIV-1 Infection. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojha, R.; Nandani, R.; Pandey, R.K.; Mishra, A.; Prajapati, V.K. Emerging role of circulating microRNA in the diagnosis of human infectious diseases. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 1030–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghalehnoei, H.; Bagheri, A.; Fakhar, M.; Mishan, M.A. Circulatory microRNAs: Promising non-invasive prognostic and diagnostic biomarkers for parasitic infections. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2019, 39, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brochado-Kith, Ó.; Gómez Sanz, A.; Real, L.M.; Crespo García, J.; Ryan Murúa, P.; Macías, J.; Cabezas González, J.; Troya, J.; Pineda, J.A.; Arias Loste, M.T.; et al. MicroRNA Profile of HCV Spontaneous Clarified Individuals, Denotes Previous HCV Infection. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobrino-Vegas, P.; Gutiérrez, F.; Berenguer, J.; Labarga, P.; García, F.; Alejos-Ferreras, B.; Muñoz, M.A.; Moreno, S.; Del Amo, J. La cohorte de la red española de investigación en sida y su biobanco: Organización, principales resultados y pérdidas al seguimiento. Enferm. Infecc. Microbiol. Clin. 2011, 29, 645–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Consuegra, I.; Rodríguez-Aierbe, C.; Santiuste, I.; Bosch, A.; Martínez-Marín, R.; Fortuto, M.A.; Díaz, T.; Martí, S.; Muñoz-Fernández, M.Á. Isolation Methods of Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells in Spanish Biobanks: An Overview. Biopreserv. Biobank. 2017, 15, 305–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozomara, A.; Griffiths-Jones, S. miRBase: Annotating high confidence microRNAs using deep sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D68–D73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackenberg, M.; Rodríguez-Ezpeleta, N.; Aransay, A.M. miRanalyzer: An update on the detection and analysis of microRNAs in high-throughput sequencing experiments. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, W132–W138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S.; Lönnstedt, I.; Speed, T.; Robinson, M.; Smyth, G.; McCarthy, D.; Chen, Y.; Smyth, G.; et al. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, V.; Bell, G.W.; Nam, J.-W.; Bartel, D.P. Predicting effective microRNA target sites in mammalian mRNAs. Elife 2015, 4, e05005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KEGG PATHWAY: Hsa05170. Available online: https://www.genome.jp/dbget-bin/www_bget?pathway+hsa05170 (accessed on 28 February 2020).
- HIV-1 Interactions Database. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genome/viruses/retroviruses/hiv-1/interactions/ (accessed on 29 March 2020).
- Pinney, J.W.; Dickerson, J.E.; Fu, W.; Sanders-Beer, B.E.; Ptak, R.G.; Robertson, D.L. HIV-host interactions: A map of viral perturbation of the host system. AIDS 2009, 23, 549–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ptak, R.G.; Fu, W.; Sanders-Beer, B.E.; Dickerson, J.E.; Pinney, J.W.; Robertson, D.L.; Rozanov, M.N.; Katz, K.S.; Maglott, D.R.; Pruitt, K.D.; et al. Cataloguing the HIV type 1 human protein interaction network. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2008, 24, 1497–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, W.; Sanders-Beer, B.E.; Katz, K.S.; Maglott, D.R.; Pruitt, K.D.; Ptak, R.G. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1, human protein interaction database at NCBI. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, D417–D422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ako-Adjei, D.; Fu, W.; Wallin, C.; Katz, K.S.; Song, G.; Darji, D.; Brister, J.R.; Ptak, R.G.; Pruitt, K.D. HIV-1, Human Interaction database: Current status and new features. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D566–D570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleazard, T.; Lamb, J.A.; Griffiths-Jones, S. Bias in microRNA functional enrichment analysis. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1592–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.-Y.; Jiang, S.-S.; Hsiao, J.-R.; Hsiao, M.; Hsu, Y.-M.; Wu, G.-H.; Chang, W.-M.; Chang, J.-Y.; Jin, S.-L.C.; Shiah, S.-G. IL-8 induces miR-424-5p expression and modulates SOCS2/STAT5 signaling pathway in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Mol. Oncol. 2016, 10, 895–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.M.; Li, J.C.B.; Lin, S.S.; Lee, D.C.W.; Liu, L.; Chen, Z.; Lau, A.S.Y. HIV-1 transactivator protein induction of suppressor of cytokine signaling-2 contributes to dysregulation of IFNγ signaling. Blood 2009, 113, 5192–5201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Luo, C.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, J. MicroRNA-18b inhibits the growth of malignant melanoma via inhibition of HIF-1α-mediated glycolysis. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 36, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmane, S.L.; Amini, S.; Sen, S.; Khalili, K.; Sawaya, B.E. Regulation of the HIV-1 promoter by HIF-1α and Vpr proteins. Virol. J. 2011, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, D.; Chen, K.; Deng, H.; Rao, H.; Huang, H.; Liao, Y.; Sun, X.; Lu, S.; Yuan, Z.; Xie, D.; et al. MicroRNA-374b suppresses proliferation and promotes apoptosis in T-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma by repressing AKT1 and Wnt-16. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 4881–4891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Xu, M.; Huang, Q.; Gates, A.T.; Zhang, X.D.; Castle, J.C.; Stec, E.; Ferrer, M.; Strulovici, B.; Hazuda, D.J.; et al. Genome-Scale RNAi Screen for Host Factors Required for HIV Replication. Cell Host Microbe 2008, 4, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.; Tan, Y.S.; Cheng, W.-C.; Kingsbury, T.J.; Heimfeld, S.; Civin, C.I. MIR144 and MIR451 regulate human erythropoiesis via RAB14. Br. J. Haematol. 2015, 168, 583–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, M.; Williams, J.A.; Chu, H.; Chen, X.; Wang, J.-J.J.; Ding, L.; Akhirome, E.; Wen, X.; Lapierre, L.A.; Goldenring, J.R.; et al. Rab11-FIP1C and Rab14 Direct Plasma Membrane Sorting and Particle Incorporation of the HIV-1 Envelope Glycoprotein Complex. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Yu, B.; Zhang, F.; Guo, Z.; Li, L. microRNA-18a Promotes Cell Migration and Invasion Through Inhibiting Dicer l Expression in Hepatocellular Carcinoma In Vitro. Chin. Med. Sci. J. 2017, 32, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Triboulet, R.; Mari, B.; Lin, Y.-L.; Chable-Bessia, C.; Bennasser, Y.; Lebrigand, K.; Cardinaud, B.; Maurin, T.; Barbry, P.; Baillat, V.; et al. Suppression of MicroRNA-Silencing Pathway by HIV-1 During Virus Replication. Science 2007, 315, 1579–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Chen, J.; Wang, D.; Peng, H.; Tan, X.; Xiong, D.; Huang, A.; Tang, H. Upregulated in Hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma cells, miR-331-3p promotes proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by targeting ING5. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 38093–38106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, R.; Liu, Z.; Yu, Y.; Lu, H. ING5 is a Tip60 cofactor that acetylates p53 in response to DNA damage. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 3749–3760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, C.-H.; Kim, S.-Y.; Byeon, S.E.; Jeong, Y.; Lee, J.; Kim, K.P.; Park, J.; Bae, Y.-S. p53-derived host restriction of HIV-1 replication by protein kinase R-mediated Tat phosphorylation and inactivation. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 4262–4280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.; Rai, P.; Plagov, A.; Lan, X.; Mathieson, P.W.; Saleem, M.A.; Husain, M.; Malhotra, A.; Singhal, P.C. Rapamycin-induced modulation of miRNA expression is associated with amelioration of HIV-associated nephropathy (HIVAN). Exp. Cell Res. 2013, 319, 2073–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Heredia, A.; Le, N.; Gartenhaus, R.B.; Sausville, E.; Medina-Moreno, S.; Zapata, J.C.; Davis, C.; Gallo, R.C.; Redfield, R.R. Targeting of mTOR catalytic site inhibits multiple steps of the HIV-1 lifecycle and suppresses HIV-1 viremia in humanized mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 9412–9417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Z.; Wang, D.; Zhao, W.; Song, M.; You, F.; Yang, L.; Chen, L. microRNA-450a targets DNA methyltransferase 3a in hepatocellular carcinoma. Exp. Ther. Med. 2011, 2, 951–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luzzi, A.; Morettini, F.; Gazaneo, S.; Mundo, L.; Onnis, A.; Mannucci, S.; Rogena, E.A.; Bellan, C.; Leoncini, L.; De Falco, G. HIV-1 Tat induces DNMT over-expression through microRNA dysregulation in HIV-related non Hodgkin lymphomas. Infect. Agent. Cancer 2014, 9, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.K.; McCormick, T.S.; Eapen, B.L.; Yohannes, E.; Chance, M.R.; Weinberg, A. Comparison of epigenetic profiles of human oral epithelial cells from HIV positive (on HAART) and HIV-negative subjects. Epigenetics 2013, 8, 703–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taganov, K.D.; Boldin, M.P.; Chang, K.-J.; Baltimore, D. NF-kappaB-dependent induction of microRNA miR-146, an inhibitor targeted to signaling proteins of innate immune responses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 12481–12486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quaranta, M.T.; Olivetta, E.; Sanchez, M.; Spinello, I.; Paolillo, R.; Arenaccio, C.; Federico, M.; Labbaye, C. miR-146a controls CXCR4 expression in a pathway that involves PLZF and can be used to inhibit HIV-1 infection of CD4+ T lymphocytes. Virology 2015, 478, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Y.; Luo, M.; Yu, T.; Chen, L.; Huang, Q.; Chen, S.; Xie, L.; Zeng, Y.; Luo, F.; Xiong, H.; et al. CRISPR/Cas9-mediated deletion of miR-146a enhances antiviral response in HIV-1 infected cells. Genes Immun. 2019, 20, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, S.-F.; Chen, H.; Song, J.-X. MiR-106b-5p Inhibits Tumor Necrosis Factor-α-induced Apoptosis by Targeting Phosphatase and Tensin Homolog Deleted on Chromosome 10 in Vascular Endothelial Cells. Chin. Med. J. (Engl.) 2016, 129, 1406–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Hollenbaugh, J.A.; Kim, D.-H.; Kim, B. Novel PI3K/Akt inhibitors screened by the cytoprotective function of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Tat. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e21781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Zhou, J.; Wang, T.; Han, J.; Ma, L.; Yu, H.; Geng, D.; Fan, H.; Zhang, Q.; Hua, F.; et al. MiR-30a inhibits Th17 differentiation and demyelination of EAE mice by targeting the IL-21R. Brain. Behav. Immun. 2016, 57, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannello, A.; Boulassel, M.-R.; Samarani, S.; Debbeche, O.; Tremblay, C.; Toma, E.; Routy, J.-P.; Ahmad, A. Dynamics and Consequences of IL-21 Production in HIV-Infected Individuals: A Longitudinal and Cross-Sectional Study. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witwer, K.W.; Watson, A.K.; Blankson, J.N.; Clements, J.E. Relationships of PBMC microRNA expression, plasma viral load, and CD4+ T-cell count in HIV-1-infected elite suppressors and viremic patients. Retrovirology 2012, 9, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egaña-Gorroño, L.; Escribà, T.; Boulanger, N.; Guardo, A.C.; León, A.; Bargalló, M.E.; Garcia, F.; Gatell, J.M.; Plana, M.; Arnedo, M.; et al. Differential MicroRNA Expression Profile between Stimulated PBMCs from HIV-1 Infected Elite Controllers and Viremic Progressors. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duskova, K.; Nagilla, P.; Le, H.-S.; Iyer, P.; Thalamuthu, A.; Martinson, J.; Bar-Joseph, Z.; Buchanan, W.; Rinaldo, C.; Ayyavoo, V. MicroRNA regulation and its effects on cellular transcriptome in Human Immunodeficiency Virus-1 (HIV-1) infected individuals with distinct viral load and CD4 cell counts. BMC Infect. Dis. 2013, 13, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynoso, R.; Laufer, N.; Hackl, M.; Skalicky, S.; Monteforte, R.; Turk, G.; Carobene, M.; Quarleri, J.; Cahn, P.; Werner, R.; et al. MicroRNAs differentially present in the plasma of HIV elite controllers reduce HIV infection in vitro. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pimentel, F.; Bonilla, P.; Ravishankar, Y.G.; Contag, A.; Gopal, N.; LaCour, S.; Lee, T.; Niemz, A. Technology in MicroRNA Profiling: Circulating MicroRNAs as Noninvasive Cancer Biomarkers in Breast Cancer. J. Lab. Autom. 2015, 20, 574–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Del Cojo, M.; López-Huertas, M.R.; Díez-Fuertes, F.; Rodríguez-Mora, S.; Bermejo, M.; López-Campos, G.; Mateos, E.; Jiménez-Tormo, L.; Gómez-Esquer, F.; Díaz-Gil, G.; et al. Changes in the cellular microRNA profile by the intracellular expression of HIV-1 Tat regulator: A potential mechanism for resistance to apoptosis and impaired proliferation in HIV-1 infected CD4+ T cells. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0185677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennasser, Y.; Le, S.Y.; Benkirane, M.; Jeang, K.T. Evidence that HIV-1 encodes an siRNA and a suppressor of RNA silencing. Immunity 2005, 22, 607–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casey Klockow, L.; Sharifi, H.J.; Wen, X.; Flagg, M.; Furuya, A.K.M.; Nekorchuk, M.; De Noronha, C.M.C. The HIV-1 protein Vpr targets the endoribonuclease Dicer for proteasomal degradation to boost macrophage infection. Virology 2013, 444, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connell, R.M.; Rao, D.S.; Baltimore, D. microRNA Regulation of Inflammatory Responses. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 30, 295–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.-N.; Xu, J.-J.; Fu, Y.-J.; Liu, J.; Jiang, Y.-J.; Cui, H.-L.; Zhao, B.; Sun, H.; He, Y.-W.; Li, Q.-J.; et al. Transcriptomic Analysis of Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells in Rapid Progressors in Early HIV Infection Identifies a Signature Closely Correlated with Disease Progression. Clin. Chem. 2013, 59, 1175–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Wu, D.; Li, P.; Xu, B.; Lu, Q.; Zhang, W. microRNA-18a, a member of the oncogenic miR-17-92 cluster, targets Dicer and suppresses cell proliferation in bladder cancer T24 cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2012, 5, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dueck, A.; Meister, G. MicroRNA processing without Dicer. Genome Biol. 2010, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yahyaei, S.; Biasin, M.; Saulle, I.; Gnudi, F.; De Luca, M.; Tasca, K.I.; Trabattoni, D.; Lo Caputo, S.; Mazzotta, F.; Clerici, M. Identification of a Specific miRNA Profile in HIV-Exposed Seronegative Individuals. JAIDS J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2016, 73, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Lin, Y.; Luo, T.; Xiao, Z.; Zhou, Q. A dual PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling inhibitor miR-99a suppresses endometrial carcinoma. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2016, 8, 719–731. [Google Scholar]
- Akbay, B.; Shmakova, A.; Vassetzky, Y.; Dokudovskaya, S. Modulation of mTORC1 Signaling Pathway by HIV-1. Cells 2020, 9, 1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahluwalia, J.K.; Khan, S.Z.; Soni, K.; Rawat, P.; Gupta, A.; Hariharan, M.; Scaria, V.; Lalwani, M.; Pillai, B.; Mitra, D.; et al. Human cellular microRNA hsa-miR-29a interferes with viral nef protein expression and HIV-1 replication. Retrovirology 2008, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, P.; Ansari, M.Y.; Bapat, S.; Thakar, M.; Gangakhedkar, R.; Jameel, S. The microRNA miR-29a is associated with human immunodeficiency virus latency. Retrovirology 2014, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Li, H.; Wu, X.; Covarrubias, M.; Scherer, L.; Meinking, K.; Luk, B.; Chomchan, P.; Alluin, J.; Gombart, A.F.; et al. Interplay between HIV-1 infection and host microRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 2181–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ott, M.; Geyer, M.; Zhou, Q. The control of HIV transcription: Keeping RNA polymerase II on track. Cell Host Microbe 2011, 10, 426–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, K.; Sung, T.-L.; Rice, A.P. Regulation of Cyclin T1 and HIV-1 Replication by MicroRNAs in Resting CD4+ T Lymphocytes. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 3244–3252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, R.; Soni, K.; Saravanan, S.; Balakrishnan, P.; Kumar, V.; Boobalan, J.; Solomon, S.S.; Scaria, V.; Solomon, S.; Brahmachari, S.K.; et al. Anti-HIV microRNA expression in a novel Indian cohort. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swaminathan, G.; Rossi, F.; Sierra, L.J.; Gupta, A.; Navas-Martín, S.; Martín-García, J. A Role for microRNA-155 Modulation in the Anti-HIV-1 Effects of Toll-Like Receptor 3 Stimulation in Macrophages. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Mora, S.; De Wit, F.; García-Perez, J.; Bermejo, M.; López-Huertas, M.R.; Mateos, E.; Martí, P.; Rocha, S.; Vigón, L.; Christ, F.; et al. The mutation of Transportin 3 gene that causes limb girdle muscular dystrophy 1F induces protection against HIV-1 infection. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, P.; Liu, B.; Wu, J.Q.; Soriano, V.; Vispo, E.; Carroll, A.P.; Goldie, B.J.; Cairns, M.J.; Saksena, N.K. Genome-wide mRNA and miRNA analysis of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) reveals different miRNAs regulating HIV/HCV co-infection. Virology 2014, 450–451, 336–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fowler, L.; Conceicao, V.; Perera, S.S.; Gupta, P.; Beng Chew, C.; Dyer, W.B.; Saksena, N.K. First Evidence for the Disease-Stage, Cell-Type, and Virus Specificity of microRNAs during Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type-1 Infection. Med. Sci. 2016, 4, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.; Kukkonen, S.; Gupta, S.; Aldovini, A. Association of Tat with promoters of PTEN and PP2A subunits is key to transcriptional activation of apoptotic pathways in HIV-infected CD4+ T cells. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1001103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Grevenynghe, J.; Procopio, F.A.; He, Z.; Chomont, N.; Riou, C.; Zhang, Y.; Gimmig, S.; Boucher, G.; Wilkinson, P.; Shi, Y.; et al. Transcription factor FOXO3a controls the persistence of memory CD4 + T cells during HIV infection. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houzet, L.; Klase, Z.; Yeung, M.L.; Wu, A.; Le, S.Y.; Quiñones, M.; Jeang, K.T. The extent of sequence complementarity correlates with the potency of cellular miRNA-mediated restriction of HIV-1. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 11684–11696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Group | Patient ID | Sex | Origin | CD4+ T Cell Count (Cell/mm3) | Via of Infection | HCV Co-Infection |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EC-LTNP | EC-LTNP-1 | M | European | 635 | IDU | Yes |
| EC-LTNP-2 | M | European | 555 | IDU | Yes | |
| EC-LTNP-3 | F | European | 596 | IDU | Yes | |
| EC-LTNP-4 | F | European | 1081 | SEX | No | |
| EC-LTNP-5 | F | European | 603 | SEX | Yes | |
| EC-LTNP-6 | M | European | 640 | IDU | Yes | |
| EC-LTNP-7 | M | European | 514 | IDU | Yes | |
| EC-LTNP-8 | M | European | 708 | IDU | Yes | |
| vLTNP | vLTNP-1 | M | European | 625 | SEX | No |
| vLTNP-2 | M | European | 590 | IDU | Yes | |
| vLTNP-3 | M | European | 1049 | IDU | Yes | |
| vLTNP-4 | M | European | 593 | IDU | Yes | |
| vLTNP-5 | F | European | 492 | IDU | Yes | |
| vLTNP-6 | M | European | NA | SEX | No | |
| vLTNP-7 | M | European | 889 | IDU | No | |
| vLTNP-8 | M | European | 929 | IDU | Yes | |
| pre-TP | pre-TP-1 | M | European | 290 | IDU | Yes |
| pre-TP-2 | M | European | 332 | SEX | No | |
| pre-TP-3 | M | European | 397 | SEX | No | |
| pre-TP-4 | F | European | 270 | SEX | No | |
| pre-TP-5 | M | European | 624 | SEX | No | |
| pre-TP-6 | M | European | 157 | SEX | No | |
| pre-TP-7 | M | European | 47 | SEX | No | |
| post-TP | post-TP-1 | M | European | 720 | IDU | Yes |
| post-TP-2 | M | European | 525 | SEX | No | |
| post-TP-3 | M | European | 550 | SEX | No | |
| post-TP-4 | F | European | 650 | SEX | No | |
| post-TP-5 | M | European | 439 | SEX | No | |
| post-TP-6 | M | European | 415 | SEX | No | |
| post-TP-7 | M | European | 578 | SEX | No |
| Group | Gene | miRNA | Expression Change | 3′ UTR Predicted Site | Canonical Site Types 1 | References 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pre-TP vs. post-TP | SOCS2 | miR-424-5p | ↓ | 2253–2259 | 7mer-1A | [38,39] |
| HIF1A | miR-18b-5p | ↓ | 409–415 | 7mer-m8 | [40,41] | |
| AKT1 | miR-374b-5p | ↓ | 2434–2440 | 7mer-1A | [42,43] | |
| WNT16 | miR-374b-5p | ↓ | 1262–1269 | 8mer | ||
| LTNP vs. TP | RAB14 | miR-144-5p | ↓ | 361–367 | 7mer-m8 | [44,45] |
| miR-144-3p | ↓ | 1052–1058 | 7mer-1A | |||
| miR-451a | ↓ | 3207–3213 | 7mer-m8 | |||
| DICER1 | miR-18a-5p | ↓ | 1201–1208 | 7mer-m8 | [46,47] | |
| ↓ | 4300–4307 | 8mer | ||||
| ING5 | miR-331-3p | ↓ | 4147–4154 | 8mer | [48,49,50] | |
| MTORC1 | miR-99a-5p | ↑ | 295–301 | 7mer-m8 | [51,52] | |
| DNMT3 | miR-450a-5p | ↓ | 649–655 | 7mer-1A | [53,54,55] | |
| EC-LTNP vs. vLTNP | TRAF6 | miR-146a-5p | ↓ | 40–47 | 8mer | [56,57,58] |
| IRAK1 | 473–480 | 8mer | ||||
| PTEN | miR-1063 | ↓ | 272–278 | 7mer-m8 | [59,60] | |
| IL21R | miR-30a-5p | ↑ | 125–132 | 8mer | [61,62] |
| miRNA | log2(FC) | p-Value | q-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| miR-3607-5p | −1.6073 | 0.00001 | 0.0064 |
| miR-486-3p | −1.0910 | 0.00002 | 0.0071 |
| miR-144-3p | −1.2943 | 0.0003 | 0.0892 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ayala-Suárez, R.; Díez-Fuertes, F.; Calonge, E.; De La Torre Tarazona, H.E.; Gracia-Ruíz de Alda, M.; Capa, L.; Alcamí, J. Insight in miRNome of Long-Term Non-Progressors and Elite Controllers Exposes Potential RNAi Role in Restraining HIV-1 Infection. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2452. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9082452
Ayala-Suárez R, Díez-Fuertes F, Calonge E, De La Torre Tarazona HE, Gracia-Ruíz de Alda M, Capa L, Alcamí J. Insight in miRNome of Long-Term Non-Progressors and Elite Controllers Exposes Potential RNAi Role in Restraining HIV-1 Infection. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(8):2452. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9082452
Chicago/Turabian StyleAyala-Suárez, Rubén, Francisco Díez-Fuertes, Esther Calonge, Humberto Erick De La Torre Tarazona, María Gracia-Ruíz de Alda, Laura Capa, and José Alcamí. 2020. "Insight in miRNome of Long-Term Non-Progressors and Elite Controllers Exposes Potential RNAi Role in Restraining HIV-1 Infection" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 8: 2452. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9082452
APA StyleAyala-Suárez, R., Díez-Fuertes, F., Calonge, E., De La Torre Tarazona, H. E., Gracia-Ruíz de Alda, M., Capa, L., & Alcamí, J. (2020). Insight in miRNome of Long-Term Non-Progressors and Elite Controllers Exposes Potential RNAi Role in Restraining HIV-1 Infection. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(8), 2452. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9082452





