Combined Surgical and Orthodontic Treatments in Children with OSA: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Protocol and Registration
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
- Population: children diagnosed with OSA by polysomnography (PSG) or by a home sleep study.
- Intervention: subjects who underwent surgery such as AT and orthodontic treatment (i.e., RME, MA). RME and MA were searched for individually since the focus was on orthodontic treatment (either RME or MA or both together with surgery (tonsillectomy or adenoidectomy)).
- Comparison: a combination of clinical assessments to evaluate the efficiency of surgery and orthodontic treatment to resolve OSA.
- Outcomes: three main outcomes were evaluated: severity of OSA, oxygen saturation and recurrence of OSA after treatment.
- Study design: randomized, non-randomized trials, cohort and case-control studies, case series and case reports were included.
2.3. Information Sources
2.4. Search Strategy
2.5. Study Selection
2.6. Data Collection Process
2.7. Data Items
2.8. Risk of Bias in Individual Studies
2.9. Summary Measures
3. Results
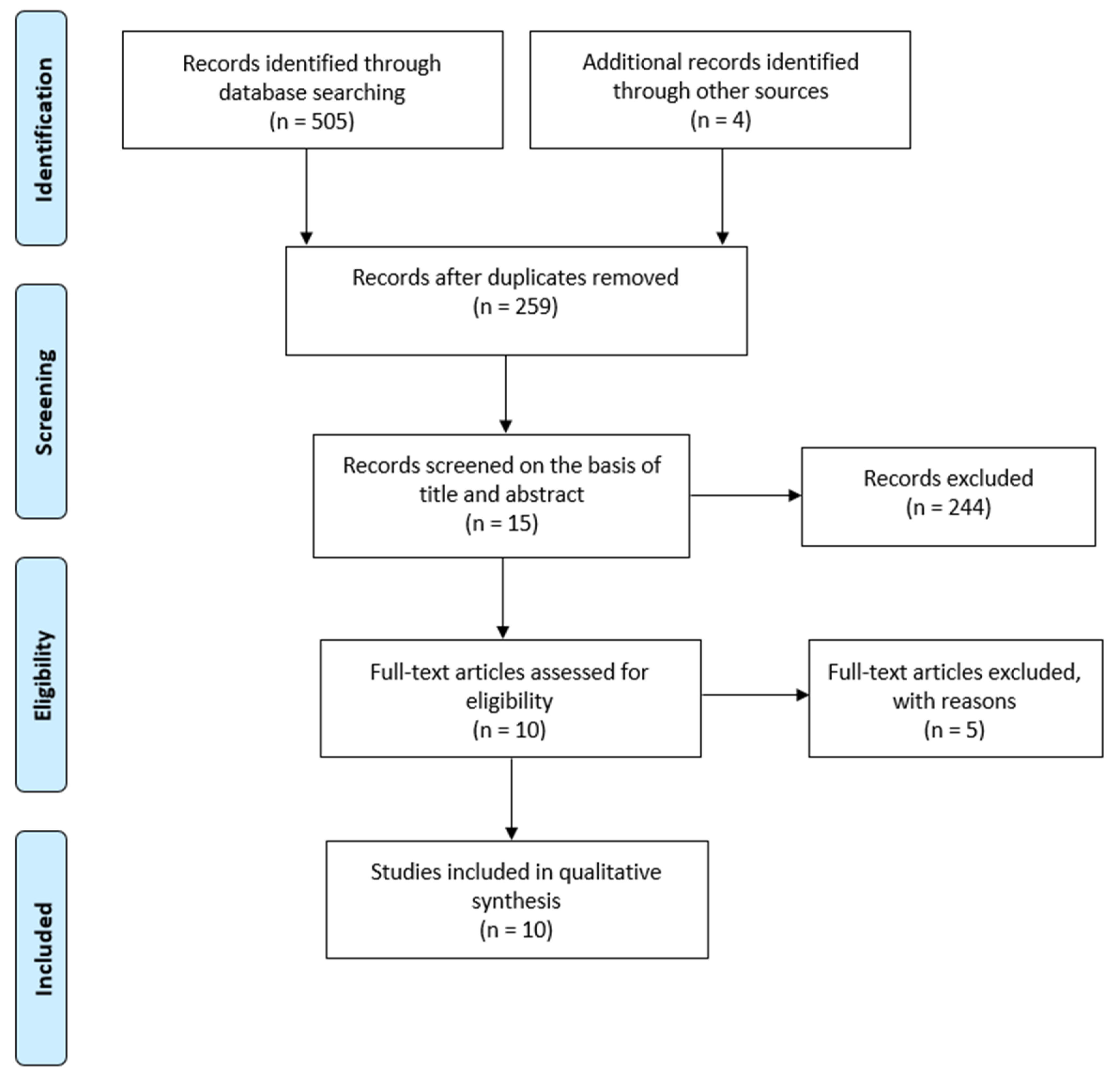
3.1. Selection of Studies
3.2. Study Characteristics
3.3. Risk of Bias Within Studies
3.4. Results of Individual Studies
3.4.1. Severity of OSA
3.4.2. Oxygen Saturation
3.4.3. Recurrence
4. Discussion
4.1. Summary of Evidence
4.1.1. Severity of OSA
4.1.2. Oxygen Saturation
4.1.3. Recurrence
4.2. Importance of Pediatric Treatment
4.2.1. Multidisciplinary Approaches
4.2.2. Optimal Age
4.3. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AHI | Apnea hypoapnea index |
| AT | Adenotonsillectomy |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| HST | Home sleep study |
| MA | Mandibular advancement |
| MT | Myofunctional therapy |
| NRCT | Non-randomized controlled trial |
| ODI | Oxygen desaturation index |
| OSA | Obstructive sleep apnea |
| PSG | Polysomnography |
| RCT | Randomized controlled trial |
| RDI | Respiratory disturbance index |
| RME | Rapid maxillary expansion |
| PTH | Post-tonsillectomy hemorrhage |
Appendix A
| MedLine (N = 129) (Ovid) http://ovidsp.tx.ovid.com | Database: Ovid MEDLINE(R) ALL <1946 to 1 April 2020> | |||
| Search Strategy: | ||||
| -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ||||
| 1) apnea.mp. or exp Apnea/ | 55,675 | |||
| 2) expansion.mp. | 167,509 | |||
| 3) extraction.mp. | 275,062 | |||
| 4) orthodon *.mp. | 57,238 | |||
| 5) 2 or 3 or 4 | 491,026 | |||
| 6) tonsil *.mp. | 36,364 | |||
| 7) adenoid *.mp. | 17,236 | |||
| 8) 6 or 7 | 47,732 | |||
| 9) 1 and 5 and 8 | 129 | |||
| Embase (N = 194) (Ovid) http://ovidsp.tx.ovid.com | Database: Embase <1974 to 1 April 2020> | |||
| Search Strategy: | ||||
| -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ||||
| 1) exp apnea/or apnea.mp. | 92,729 | |||
| 2) expansion.mp. | 215,648 | |||
| 3) exp extraction/or extraction.mp. | 443,345 | |||
| 4) orthodon *.mp. | 54,485 | |||
| 5) 2 or 3 or 4 (704,171) | 704,171 | |||
| 6) tonsil *.mp. (42,139) | −42,139 | |||
| 7) adenoid *.mp. | 18,653 | |||
| 8) 6 or 7 | 55,708 | |||
| 9) 1 and 5 and 8 | 194 | |||
| PubMed (N = 136) http://www.ncbi.nln.nih.gov/pubmed | #12 | Add | Search (#1 and #6 and #10) Filters: Humans | 136 |
| #11 | Add | Search (#1 and #6 and #10) | 156 | |
| #10 | Add | Search (#8 or #9) | 47,643 | |
| #9 | Add | Search adenoid * | 17,210 | |
| #8 | Add | Search tonsil * | 36,293 | |
| #6 | Add | Search (#2 or #3 or #5) | 504,872 | |
| #5 | Add | Search orthodon * | 73,679 | |
| #3 | Add | Search extraction | 274,317 | |
| #2 | Add | Search expansion | 166,756 | |
| #1 | Add | Search apnea | 58,662 | |
| Cochrane (N = 38) | ID | Search | Hits | |
| #1 | apnea | 9046 | ||
| #2 | Expansion | 5534 | ||
| #3 | Extraction | 21,029 | ||
| #4 | Orthodon * | 4587 | ||
| #5 | #2 or #3 or #4 | 29,693 | ||
| #6 | Tonsil * | 3659 | ||
| #7 | Adenoid * | 1189 | ||
| #8 | #6 or #7 | 4129 | ||
| #9 | #1 and #5 and #8 | 38 | ||
| LILACS (N = 8) | Apnea, orthodon *, extraction, expansion, tonsil *, adenoid * | |||
| 2014 Villa et al. [22] | 2013 Guilleminault et al. [24] | 2013 Guilleminault et al. [25] | 2012 Pirelli al. [26] | 2011 Guilleminault et al. [27] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Question 1 | 0 no, 1 yes | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| Question 2 | 0 no, 1 yes | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Question 3 | 0 no, 1 yes | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Question 4 | 0 no, 1 yes | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Question 5 | 0 no, 1 partially, 2 yes | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 |
| Question 6 | 0 no, 1 yes | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Question 7 | 0 no, 1 yes | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Question 8 | 0 no, 1 yes | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Question 9 | 0 no, 1 yes | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Question 10 | 0 no, 1 yes | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Question 11 | 0 no, 1 yes | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Question 12 | 0 no, 1 yes | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Question 13 | 0 no, 1 yes | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Question 14 | 0 no, 1 yes | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Question 15 | 0 no, 1 yes | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Question 16 | 0 no, 1 yes | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Question 17 | 0 no, 1 yes | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Question 18 | 0 no, 1 yes | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Question 19 | 0 no, 1 yes | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| Question 20 | 0 no, 1 yes | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Question 21 | 0 no, 1 yes | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Question 22 | 0 no, 1 yes | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Question 23 | 0 no, 1 yes | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Question 24 | 0 no, 1 yes | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Question 25 | 0 no, 1 yes | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Question 26 | 0 no, 1 yes | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Question 27 | 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Total score | 14 | 15 | 20 | 13 | 20 | |
| Quality | Poor | Fair | Good | Poor | Good | |
| Topic | Item | 2014 Kim et al. [23] | 2019 Alexander et al. [18] | 2019 Bignotti et al. [19] | 2019 Nauert et al. [20] | 2018 Gracco et al. [21] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Key Words | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Abstract | 3a | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 3b | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| 3c | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| 3d | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| Introduction | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Patient Information | 5a | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 5b | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| 5c | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| 5d | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| Clinical Findings | 6 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Timeline | 7 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Diagnostic Assessment | 8a | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 8b | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 8c | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | |
| 8d | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Therapeutic Intervention | 9a | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 9b | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| 9c | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| Follow-up and Outcomes | 10a | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 10b | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | |
| 10c | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| 10d | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Discussion | 11a | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 11b | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | |
| 11c | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | |
| 11d | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | |
| Patient Perspective | 12 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Informed Consent | 13 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Total | 18 | 19 | 20 | 16 | 23 |
References
- Loughlin, G.M.; Brouillette, R.T.; Brooke, L.J.; Carroll, J.L.; Chipps, B.E.; England, S.J.; Ferber, P.; Ferraro, N.F.; Gaultier, C.; Givan, D.C.; et al. Standards and indications for cardiopulmonary sleep studies in children. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1996, 153, 866–878. [Google Scholar]
- Marcus, C.L.; Annett, R.D.; Brooks, L.J.; Brouillette, R.T.; Carroll, J.L.; Givan, D.; Gozal, D.; Kiley, J.; Redline, S.; Rosen, C.L.; et al. Cardiorespiratory sleep studies in children. Establishment of normative data and polysomnographic predictors of morbidity. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1999, 160, 1381–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abtahi, S.; Witmans, M.; Alsufyani, N.A.; Major, M.P.; Major, P.W. Pediatric sleep-disordered breathing in the orthodontic population: Prevalence of positive risk and associations. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2020, 157, 466–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcus, C.L.; Brooks, L.J.; Draper, K.A.; Gozal, D.; Halbower, A.C.; Jones, J.; Schechter, M.S.; Sheldon, S.H.; Spruyt, K.; Ward, S.D.; et al. Diagnosis and management of childhood obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Pediatrics 2012, 130, 576–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcus, C.L.; McColley, S.A.; Carroll, J.L.; Loughlin, G.M.; Smith, P.L.; Schwartz, A.R. Upper airway collapsibility in children with obstructive sleep-apnea syndrome. J. Appl. Physiol. 1994, 77, 918–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arens, R.; Marcus, C.L. Pathophysiology of upper airway obstruction: A developmental perspective. Sleep 2004, 27, 997–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redline, S.; Amin, R.; Beebe, D.; Chervin, R.D.; Garetz, S.L.; Giordani, B.; Marcus, C.L.; Moore, R.H.; Rosen, C.L.; Arens, R.; et al. The childhood adenotonsillectomy trial (CHAT): Rationale, design, and challenges of a randomized controlled trial evaluating a standard surgical procedure in a pediatric population. Sleep 2011, 34, 1509–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schechter, M.S. Technical report: Diagnosis and management of childhood obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Pediatrics 2002, 109, e69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcus, C.L.; Moore, R.H.; Rosen, C.L.; Giordani, B.; Garetz, S.L.; Taylor, H.G.; Mitchell, R.B.; Amin, R.; Katz, E.S.; Arens, R.; et al. A randomized trial of adenotonsillectomy for childhood sleep apnea. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 2366–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.L.; Kheirandish-Gozal, L.; Gozal, D. Obstructive sleep apnea in children: Update on the recognition, treatment and management of persistent disease. Expert. Rev. Respir. Med. 2016, 10, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirilä-Parkkinen, K.; Pirttiniemi, P.; Nieminen, P.; Tolonen, U.; Pelttari, U.; Löppönen, H. Dental arch morphology in children with sleep-disordered breathing. Eur. J. Orthod. 2009, 31, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guilleminault, C.; Partinen, M.; Praud, J.P.; Quera-Ssalva, M.A.; Powell, N.; Riley, R. Morphometric facial changes and obstructive sleep-apnea in adolescents. J. Pediatr. 1989, 114, 997–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilleminault, C.; Li, K.K.; Khramtsov, A.; Pelayo, R.; Martinez, S. Sleep disordered breathing: Surgical outcomes in prepubertal children. Laryngoscope 2004, 114, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tasker, C.; Crosby, J.H.; Stradling, J.R. Evidence for persistence of upper airway narrowing during sleep, 12 years after adenotonsillectomy. Arch. Dis. Child. 2002, 86, 34–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, R.B.; Kelly, J. Outcome of adenotonsillectomy for severe obstructive sleep apnea in children. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2004, 68, 1375–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souki, B.Q.; Pimenta, G.B.; Souki, M.Q.; Franco, L.P.; Becker, H.M.G.; Pinto, J.A. Prevalence of malocclusion among mouth breathing children: Do expectations meet reality? Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2009, 73, 767–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, N.; Boota, A.; Hooks, K.; White, J.R. Rapid maxillary expansion and adenotonsillectomy in 9-year-old twins with pediatric obstructive sleep apnea syndrome: An interdisciplinary effort. J. Am. Osteopath. Assoc. 2019, 119, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bignotti, D.; De Stefani, A.; Mezzofranco, L.; Bruno, G.; Gracco, A. Multidisciplinary approach in a 12-year-old patient affected by severe obstructive sleep apnea: A case-report. Sleep Med. Res. 2019, 10, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauert, K. Kieferorthopädische Behandlung der obstruktiven Schlafapnoe im Kindesalter—Ein Fallbericht. Atemwegs Lungenkrankh. 2019, 45, 46–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gracco, A.; Bruno, G.; de Stefani, A.; Ragona, R.M.; Mazzoleni, S.; Stellini, E. Combined orthodontic and surgical treatment in a 8-years-old patient affected by severe obstructive sleep apnea: A case-report. J. Clin. Pediatr. Dent. 2018, 42, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villa, M.P.; Castaldo, R.; Miano, S.; Paolini, M.C.; Vitelli, O.; Tabarrini, A.; Mazzotta, A.R.; Cecili, M.; Barreto, M. Adenotonsillectomy and orthodontic therapy in pediatric obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep Breath 2014, 18, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M. Orthodontic treatment with rapid maxillary expansion for treating a boy with severe obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep Med. Res. 2014, 5, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilleminault, C.; Huang, Y.S.; Monteyrol, P.J.; Sato, R.; Quo, S.; Lin, C.H. Critical role of myofascial reeducation in pediatric sleep-disordered breathing. Sleep Med. 2013, 14, 518–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilleminault, C.; Huang, Y.-S.; Quo, S.; Monteyrol, P.-J.; Lin, C.-H.; , C-H. Teenage sleep-disordered breathing: Recurrence of syndrome. Sleep Med. 2013, 14, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirelli, P.; Saponara, M.; Guilleminault, C. Rapid maxillary expansion before and after adenotonsillectomy in children with obstructive sleep apnea. Somnologie Schlafforschung Schlafmed. 2012, 16, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilleminault, C.; Monteyrol, P.-J.; Huynh, N.T.; Pirelli, P.; Quo, S.; Li, K. Adeno-tonsillectomy and rapid maxillary distraction in pre-pubertal children, a pilot study. Sleep Breath 2011, 15, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downs, S.H.; Black, N. The feasibility of creating a checklist for the assessment of the methodological quality both of randomised and non-randomised studies of health care interventions. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 1998, 52, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, D.S.; Barber, M.S.; Kienle, G.S.; Aronson, J.K.; von Schoen-Angerer, T.; Tugwell, P.; Kiene, H.; Helfand, M.; Altman, D.G.; Sox, H.; et al. CARE guidelines for case reports: Explanation and elaboration document. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2017, 89, 218–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, M.; Johnson, J. Obstructive sleep apnea diagnosis and management. Mo. Med. 2017, 114, 120–124. [Google Scholar]
- Landsberg, R.; Friedman, M.; Ascher-Landsberg, J. Treatment of hypoxemia in obstructive sleep apnea. Am. J. Rhinol. 2001, 15, 311–313. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Torre, C.; Camacho, M.; Liu, S.Y.; Huon, L.K.; Capasso, R. Epiglottis collapse in adult obstructive sleep apnea: A systematic review. Laryngoscope 2016, 126, 515–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camacho, M.; Dunn, B.; Torre, C.; Sasaki, J.; Gonzales, R.; Liu, S.-C.; Chan, D.K.; Certal, V.; Cable, B.B. Supraglottoplasty for laryngomalacia with obstructive sleep apnea: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Laryngoscope 2016, 126, 1246–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villa, M.P.; Brasili, L.; Ferretti, A.; Vitelli, O.; Rabasco, J.; Mazzotta, A.R.; Pietropaoli, N.; Martella, S. Oropharyngeal exercises to reduce symptoms of OSA after AT. Sleep Breath 2015, 19, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luz Alonso-Álvarez, M.; Canet, T.; Cubell-Alarco, M.; Estivill, E.; Fernández-Julián, E.; Gozal, D.; Jurado-Luque, M.J.; Lluch-Roselló, M.A.; Martínez-Pérez, F.; Merino-Andreu, M.; et al. Consensus document on sleep apnea-hypopnea syndrome in children (full version). Sociedad Española de Sueño. El Área de Sueño de la Sociedad Española de Neumología y Cirugía Torácica(SEPAR). Arch. Bronconeumol. 2011, 47, 2–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrents, R.G.; Shelgikar, A.V.; Conley, R.S.; Flores-Mir, C.; Hans, M.; Levine, M.; McNamara, J.A.; Palomo, J.M.; Pliska, B.; Stockstill, J.W.; et al. Obstructive sleep apnea and orthodontics: An American Association of Orthodontists White Paper. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2019, 156, 13–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, S.R.A.; Weckx, L.L.M.; Ortolani, C.L.F.; Bakor, S.F. Estudo das alterações craniofaciais e da importância da expansão rápida da maxila após adenotonsilectomia. Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2012, 78, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, R.B.; Archer, S.M.; Ishman, S.L.; Rosenfeld, R.M.; Coles, S.; Finestone, S.A.; Friedman, N.R.; Giordano, T.; Hildrew, D.M.; Kim, T.W.; et al. Clinical Practice Guideline: Tonsillectomy in Children (Update)-Executive Summary. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2019, 160, 187–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belyea, J.; Chang, Y.; Rigby, M.H.; Corsten, G.; Hong, P. Post-tonsillectomy complications in children less than three years of age: A case-control study. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2014, 78, 871–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindquist, N.R.; Feng, Z.; Patro, A.; Mukerji, S.S. Age-related causes of emergency department visits after pediatric adenotonsillectomy at a tertiary pediatric referral center. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2019, 127, 109668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haas, A.J. Long-term posttreatment evaluation of rapid palatal expansion. Angle Orthod. 1980, 50, 189–217. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Melsen, B.; Melsen, F. The postnatal development of the palatomaxillary region studied on human autopsy material. Am. J. Orthod. 1982, 82, 329–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baccetti, T.; Franchi, L.; Stahl, F. Comparison of 2 comprehensive Class II treatment protocols including the bonded Herbst and headgear appliances: A double-blind study of consecutively treated patients at puberty. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2009, 135, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baccetti, T.; Franchi, L.; Toth, L.R.; McNamara, J.A., Jr. Treatment timing for Twin-block therapy. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2000, 118, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martina, R.; Cioffi, I.; Galeotti, A.; Tagliaferri, R.; Cimino, R.; Michelotti, A.; Valletta, R.; Farella, M.; Paduano, S. Efficacy of the Sander bite-jumping appliance in growing patients with mandibular retrusion: A randomized controlled trial. Orthod. Craniofac. Res. 2013, 16, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, K.; Wright, J.; Conboy, F.; Sanjie, Y.; Mandall, N.; Chadwick, S.; Connolly, I.; Cook, P.; Birnie, D.; Hammond, M.; et al. Effectiveness of early orthodontic treatment with the Twin-block appliance: A multicenter, randomized, controlled trial. Part 1: Dental and skeletal effects. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2003, 124, 234–243. [Google Scholar]
- Baccetti, T. El tiempo: La cuarta dimensión en el plan de tratamiento de la maloclusión de Clase II. Rev. Esp. Ortod. 2011, 41, 199–204. [Google Scholar]
- Narang, I.; Mathew, J.L. Childhood obesity and obstructive sleep apnea. J. Nutr. Metab. 2012, 2012, 134202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, R.B.; Boss, E.F. Pediatric obstructive sleep apnea in obese and normal-weight children: Impact of adenotonsillectomy on quality-of-life and behavior. Dev. Neuropsychol. 2009, 34, 650–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Year—Principal Author | Type of Study | Type of Treatment | Type of Screening | Sample Size | Age of Participants (Year) Mean + SD | Sex | BMI (kg/m2) Mean + SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 Alexander et al. [18] | Case report | RME followed by AT | HST | 2 | 9 | F | / |
| 2019 Bignotti et al. [19] | Case report | AT followed by twin block | PSG | 1 | 12 | M | 22.2 |
| 2019 Nauert [20] | Case report | AT followed by Bionator | PSG | 1 | 3 | F | / |
| 2018 Gracco et al. [21] | Case report | At the same time: RME + epiglottoplasty + reduction of the tongue base | PSG | 1 | 8 | F | / |
| 2014 Villa et al. [22] | NRCT | Group 1: AT: 25 Group 2: RME: 22 Group 3: AT + RME: 5 | PSG | 52 | Group 1: 3.7 ± 0.92 * Group 2: 6.58 ± 1.83 * Group 3: 4.6 ± 3.2 | Group 1 and 2: 34M/13F Group 3: 3M/2F | Group 1: 15.75 ± 1.82 * Group 2: 18.82 ± 3.44 * Group 3: 16.65 ± 3.65 |
| 2014 Kim [23] | Case report | AT followed by RME F: Final treatment FU: Follow-up 2–5 years after treatment | PSG | 1 | 11 | M | 22.4 |
| 2013 Guilleminault et al. [24] | Case—Control | AT followed by RME, Follow-up: MT or WMT | PSG | 24 †: Group MT: 11 Group WMT: 13 | I: 5.5 ± 1.2 F: 7.3 ± 1.5 FU: 11.6 ± 1.2 | 14M/10F | / |
| 2013 Guilleminault et al. [25] | Case—Control | Follow-up study of OSA in teenagers after AT + RME treated in their childhood | PSG | 29 | I: 7.6 ± 1.7 F: 8.6 ± 2.8 FU: 14.4 ± 0.9 | 20M/9F | NR: 15.9 ± 1.9 R: 15.7 ± 2.1 |
| 2012 Pirelli et al. [26] | NRCT | Group 1: RME: 40 Group 2: AT: 40 Group 3: Residual OSA: RME + AT and AT + RME: 42 | HST | Group 1 and 2: 80 Group 3: 42 | 7.3 | 43M/37F | <24 |
| 2011 Guilleminault et al. [27] | RCT | Group 1: AT followed by RME, Group 2: RME followed by AT | PSG | 31: Group 1: 16 Group 2: 15 † | 6.5 ± 0.2 | 14M/17F | / |
| Year—Principal Author | Type of Treatment | AHI Initial (Events/h) Mean + SD | AHI Intermediate (Events/h) Mean + SD | AHI Final (Events/h) Mean + SD | RDI Initial (Events/h) Mean + SD | RDI Intermediate (Events/h) Mean + SD | RDI Final (Events/h) Mean + SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 Alexander et al. [18] | RME followed by AT | Patient A: 74 Patient B: 16 | Post RME: Patient A: 11 Patient B: 4 | Patient A: 0.9 Patient B: 1.6 | / | / | / |
| 2019 Bignotti et al. [19] | AT followed by twin block | 25.5 | Post AT: 3.4 | 0.7 | / | / | / |
| 2019 Nauert [20] | AT followed by Bionator | / | Post AT: 10.2 | 5-year follow-up: normal cognitive development and any evidence of OSA | / | / | / |
| 2018 Gracco et al. [21] | At the same time: RME + epiglottoplasty + reduction of the tongue base | 21.8 | / | 0.6 | / | / | / |
| 2014 Villa et al. [22] | Group 1: AT: 25 Group 2: RME: 22 Group 3: AT + RME: 5 | Group 1: 17.25 ± 13.94 * Group 2: 5.81 ± 6.05 * Group 3: 10.14 ± 7.25 | / | Group 1: 1.79 ± 1.82 * Group 2: 2.64 ± 3.11 * Group 3: 0.88 ± 0.95 | / | / | / |
| 2014 Kim et al. [23] | AT followed by RME F: Final treatment FU: Follow-up 2–5 years after treatment | / | 18.9 | F: 4.4 FU: 1 | / | 19.8 | F and FU: 5.9 |
| 2013 Guilleminault et al. [24] | AT followed by RME, Follow-up: MT or WMT | 10.5 ± 2.6 | Post AT†: 4.3 ± 1.6 | F: 0.4 ± 0.3 MT: 0.5 ± 0.4 * WMT: 5.3 ± 1.5 | / | / | / |
| 2013 Guilleminault et al. [25] | Follow-up study of OSA in teenagers after AT + RME treated in their childhood | 9 ± 5 | Post AT: 3 ± 4 | F: 0.4 ± 0.4 NR: 0.5 ± 0.2 * R: 3.1 ± 1 * | 15 ± 6.4 | Post AT: 7 ± 6 | F: 0.6 ± 0.5 NR: 1.5 ± 1.2 * R: 7 ± 1.2 |
| 2012 Pirelli et al. [26] | Group 1: RME: 40; Group 2: AT: 40; Group 3: Residual OSA: RME + AT and AT + RME: 42 | Group 1 and 2: 12.8 | Group 3: RME + AT: 13 ± 3.5 AT + RME: 15 ± 2.9 | Group 1 (6/40) and G2 (15/40): 6.5 ±3.1 Group 3: 39/42 patients were cured | / | / | / |
| 2011 Guilleminault et al. [27] | Group 1: AT followed by RME, Group 2: RME followed by AT | Group 1: 12.5 ± 0.8 Group 2: 11.1 ± 0.7 | Group 1: 4.9 ± 0.6 Group 2: 5.4 ± 0.6 | Group 1: 0.9 ± 0.3 Group 2: 0.9 ± 0.3 | Group 1: 21.3 ± 1.0 Group 2: 19.5 ± 1.0 | Group 1: 8.0 ± 0.7 Group 2: 7.9 ± 0.5 | Group 1: 1.6 ± 0.6 Group 2: 1.7 ± 0.8 |
| Year—Principal Author | Lowest SaO2 Initial (%) Mean + SD | Lowest SaO2 Intermediate (%) Mean + SD | Lowest SaO2 Final (%) Mean + SD | Average Sa02 Initial (%) Mean + SD | Average SaO2 Intermediate (%) Mean + SD | Average SaO2 Final (%) Mean + SD | ODI Initial (Events/Hour) | ODI Intermediate (Events/h) | ODI Final (Events/h) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 Alexander et al. [18] | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / |
| 2019 Bignotti et al. [19] | Nadir: 89 | Nadir: 93 | Nadir: 50 | 97.3 | 96.0 | 96.0 | 22.0 | 0.7 | 3.2 |
| 2019 Nauert [20] | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / |
| 2018 Gracco et al. [21] | / | / | / | 96.5% | / | 98.1 | 23.4 | / | 1 |
| 2014 Villa et al. [22] | / | / | / | Group 1: 96.11 ± 2.7 * Group 2: 96.56 ± 1.47 * Group 3: 97.85± 1.28 | / | Group 1: 97.50 ± 1.14 * Group 2: 97.42 ± 1.84 * Group 3: 97.42 ± 2.06 | / | / | / |
| 2014 Kim e al. [23] | / | Nadir: 60 | Nadir FT: 85 Nadir: FU: 94 | / | / | / | / | / | / |
| 2013 Guilleminault et al. [24] | 90 ±1.5 | Post AT†: 92 ± 1 | F: 95 ± 1 MT: 96 ± 1 * WMT: 91 ± 1.8 | / | / | / | / | / | / |
| 2013 Guilleminault et al. [25] | 91 ± 2.5 | Post AT: 94 ± 3 | F: 98 ± 1.5 NR: 97 ± 1 * R: 92.5 ± 1.5 * | / | / | / | / | / | / |
| 2012 Pirelli et al. [26] | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / |
| 2011 Guilleminault et al. [27] | Group 1: 92.1 ± 0.5 Group 2: 92.5 ± 0.4 | Group 1: 95.2 ± 0.3 Group 2: 95.9 ± 0.3 | Group 1: 98.0 ± 0.2 * Group 2: 97.6 ± 0.3 * | / | / | / | / | / | / |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Templier, L.; Rossi, C.; Miguez, M.; Pérez, J.D.l.C.; Curto, A.; Albaladejo, A.; Vich, M.L. Combined Surgical and Orthodontic Treatments in Children with OSA: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2387. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9082387
Templier L, Rossi C, Miguez M, Pérez JDlC, Curto A, Albaladejo A, Vich ML. Combined Surgical and Orthodontic Treatments in Children with OSA: A Systematic Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(8):2387. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9082387
Chicago/Turabian StyleTemplier, Laura, Cecilia Rossi, Manuel Miguez, Javier De la Cruz Pérez, Adrián Curto, Alberto Albaladejo, and Manuel Lagravère Vich. 2020. "Combined Surgical and Orthodontic Treatments in Children with OSA: A Systematic Review" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 8: 2387. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9082387
APA StyleTemplier, L., Rossi, C., Miguez, M., Pérez, J. D. l. C., Curto, A., Albaladejo, A., & Vich, M. L. (2020). Combined Surgical and Orthodontic Treatments in Children with OSA: A Systematic Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(8), 2387. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9082387






