The Role of Interventional Radiology for the Treatment of Hepatic Metastases from Neuroendocrine Tumor: An Updated Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Transarterial Embolization and Transarterial Chemoembolization
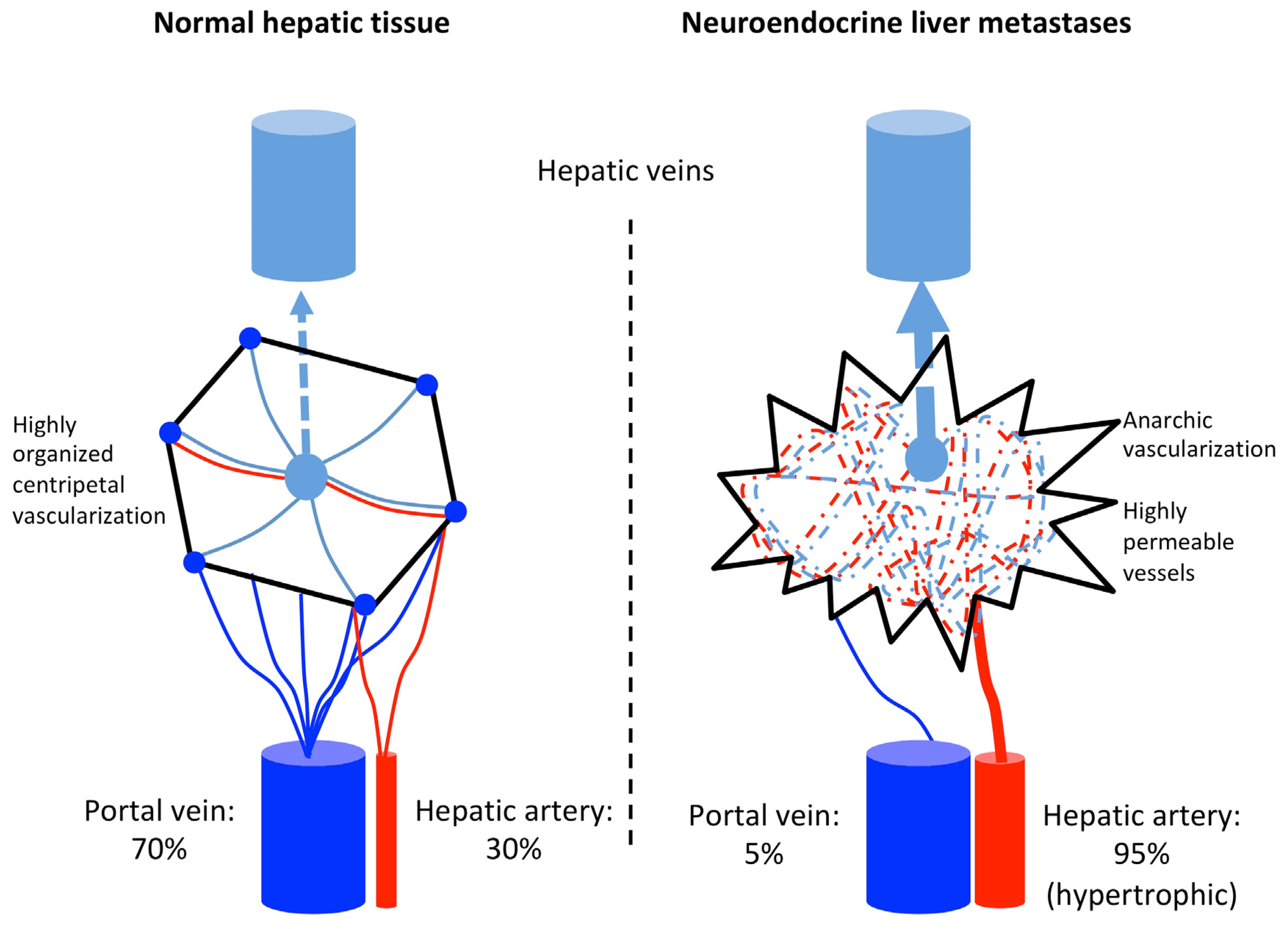
2.1. Rational of Transarterial Therapies
2.2. TAE or TACE?
2.3. Materials for Embolization
2.4. How to Perform TACE?
2.5. Tolerance and Side-Effects
2.5.1. Liver Ischemia
2.5.2. Non-Targeted Embolization
2.5.3. Other Complications
2.5.4. Mortality Related with TAE and TACE in NELMs
2.6. Contraindications
2.7. Therapeutic Response to TAE and TACE in NELMs
2.8. Prognostic Factors
2.8.1. Clinical Parameters
2.8.2. Procedure Parameters
2.8.3. Biological Prognostic Factors
2.8.4. Pre- and Post-Treatment Imaging Prognostic Factors
2.9. Patients Selection: Role of Interventional Radiologist
3. Selective Internal Radiation Therapy (SIRT)
3.1. Principles and Rationale for SIRT
3.2. How to Perform a SIRT
3.3. Complications of SIRT
3.4. Contraindication of SIRT
3.5. Expected Therapeutic Response of SIRT for NELM
3.5.1. Overall Survival
3.5.2. Disease Control and Radiological Response
3.5.3. Biological Control
3.5.4. Symptoms and Quality of Life
3.6. Prognosis Factors
3.6.1. SIRT Parameters
3.6.2. Post-Therapeutic Imaging Prognosis Factors
3.6.3. Clinical and Pathological Prognosis Factors
3.6.4. Biological Prognosis Factors
4. Comparison of TAE, TACE, and SIRT for the Treatment of NELM
5. Specificity of NELMs Compared to Other Hepatic Metastases
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dasari, A.; Shen, C.; Halperin, D.; Zhao, B.; Zhou, S.; Xu, Y.; Shih, T.; Yao, J.C. Trends in the incidence, prevalence, and survival outcomes in patients with neuroendocrine tumors in the united states. JAMA Oncol. 2017, 3, 1335–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallet, J.; Law, C.H.; Cukier, M.; Saskin, R.; Liu, N.; Singh, S. Exploring the rising incidence of neuroendocrine tumors: A population-based analysis of epidemiology, metastatic presentation, and outcomes. Cancer 2015, 121, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, J.C.; Hassan, M.; Phan, A.; Dagohoy, C.; Leary, C.; Mares, J.E.; Abdalla, E.K.; Fleming, J.B.; Vauthey, J.N.; Rashid, A.; et al. One hundred years after “carcinoid”: Epidemiology of and prognostic factors for neuroendocrine tumors in 35,825 cases in the united states. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 3063–3072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riihimaki, M.; Hemminki, A.; Sundquist, K.; Sundquist, J.; Hemminki, K. The epidemiology of metastases in neuroendocrine tumors. Int. J. Cancer 2016, 139, 2679–2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudreaux, J.P.; Klimstra, D.S.; Hassan, M.M.; Woltering, E.A.; Jensen, R.T.; Goldsmith, S.J.; Nutting, C.; Bushnell, D.L.; Caplin, M.E.; Yao, J.C.; et al. The nanets consensus guideline for the diagnosis and management of neuroendocrine tumors: Well-differentiated neuroendocrine tumors of the jejunum, ileum, appendix, and cecum. Pancreas 2010, 39, 753–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavel, M.; Baudin, E.; Couvelard, A.; Krenning, E.; Oberg, K.; Steinmuller, T.; Anlauf, M.; Wiedenmann, B.; Salazar, R.; Barcelona Consensus Conference Participants, p. Enets consensus guidelines for the management of patients with liver and other distant metastases from neuroendocrine neoplasms of foregut, midgut, hindgut, and unknown primary. Neuroendocrinology 2012, 95, 157–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fohlen, A.; Tasu, J.P.; Kobeiter, H.; Bartoli, J.M.; Pelage, J.P.; Guiu, B. Transarterial chemoembolization (tace) in the management of hepatocellular carcinoma: Results of a French national survey on current practices. Diagn. Interv. Imaging 2018, 99, 527–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clouse, M.E.; Perry, L.; Stuart, K.; Stokes, K.R. Hepatic arterial chemoembolization for metastatic neuroendocrine tumors. Digestion 1994, 55 (Suppl. S3), 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobin, A.; Mansson, B.; Lunderquist, A. Evaluation of temporary liver dearterialization and embolization in patients with metastatic carcinoid tumour. Acta Oncol. 1989, 28, 419–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folkman, J. What is the evidence that tumors are angiogenesis dependent? J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1990, 82, 4–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armbruster, M.; Zech, C.J.; Sourbron, S.; Ceelen, F.; Auernhammer, C.J.; Rist, C.; Haug, A.; Singnurkar, A.; Reiser, M.F.; Sommer, W.H. Diagnostic accuracy of dynamic gadoxetic-acid-enhanced MRI and PET/CT compared in patients with liver metastases from neuroendocrine neoplasms. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2014, 40, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorffel, Y.; Wermke, W. Neuroendocrine tumors: Characterization with contrast-enhanced ultrasonography. Ultraschall Med. Eur. J. Ultrasound 2008, 29, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronot, M.; Cuccioli, F.; Dioguardi Burgio, M.; Vullierme, M.P.; Hentic, O.; Ruszniewski, P.; d’Assignies, G.; Vilgrain, V. Neuroendocrine liver metastases: Vascular patterns on triple-phase MDCT are indicative of primary tumour location. Eur. J. Radiol. 2017, 89, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biolato, M.; Marrone, G.; Racco, S.; Di Stasi, C.; Miele, L.; Gasbarrini, G.; Landolfi, R.; Grieco, A. Transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) for unresectable HCC: A new life begins? Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2010, 14, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pericleous, M.; Caplin, M.E.; Tsochatzis, E.; Yu, D.; Morgan-Rowe, L.; Toumpanakis, C. Hepatic artery embolization in advanced neuroendocrine tumors: Efficacy and long-term outcomes. Asia. Pac. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 12, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitt, S.C.; Knuth, J.; Keily, J.M.; McDermott, J.C.; Weber, S.M.; Chen, H.; Rilling, W.S.; Quebbeman, E.J.; Agarwal, D.M.; Pitt, H.A. Hepatic neuroendocrine metastases: Chemo-or bland embolization? J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2008, 12, 1951–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiore, F.; Del Prete, M.; Franco, R.; Marotta, V.; Ramundo, V.; Marciello, F.; Di Sarno, A.; Carratu, A.C.; De Luca di Roseto, C.; Colao, A.; et al. Transarterial embolization (TAE) is equally effective and slightly safer than transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) to manage liver metastases in neuroendocrine tumors. Endocrine 2014, 47, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruutiainen, A.T.; Soulen, M.C.; Tuite, C.M.; Clark, T.W.; Mondschein, J.I.; Stavropoulos, S.W.; Trerotola, S.O. Chemoembolization and bland embolization of neuroendocrine tumor metastases to the liver. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2007, 18, 847–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Johnson, M.M.; Murthy, R.; Ahrar, K.; Wallace, M.J.; Madoff, D.C.; McRae, S.E.; Hicks, M.E.; Rao, S.; Vauthey, J.N.; et al. Hepatic arterial embolization and chemoembolization for the treatment of patients with metastatic neuroendocrine tumors: Variables affecting response rates and survival. Cancer 2005, 104, 1590–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maire, F.; Lombard-Bohas, C.; O’Toole, D.; Vullierme, M.P.; Rebours, V.; Couvelard, A.; Pelletier, A.L.; Zappa, M.; Pilleul, F.; Hentic, O.; et al. Hepatic arterial embolization versus chemoembolization in the treatment of liver metastases from well-differentiated midgut endocrine tumors: A prospective randomized study. Neuroendocrinology 2012, 96, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.X.; Wileyto, E.P.; Soulen, M.C. Randomized embolization trial for neuroendocrine tumor metastases to the liver (retnet): Study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials 2018, 19, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engelman, E.S.; Leon-Ferre, R.; Naraev, B.G.; Sharma, N.; Sun, S.; O’Dorisio, T.M.; Howe, J.; Button, A.; Zamba, G.; Halfdanarson, T.R. Comparison of transarterial liver-directed therapies for low-grade metastatic neuroendocrine tumors in a single institution. Pancreas 2014, 43, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloomston, M.; Al-Saif, O.; Klemanski, D.; Pinzone, J.J.; Martin, E.W.; Palmer, B.; Guy, G.; Khabiri, H.; Ellison, E.C.; Shah, M.H. Hepatic artery chemoembolization in 122 patients with metastatic carcinoid tumor: Lessons learned. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2007, 11, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, X.D.; Carr, B.I. Hepatic artery chemoembolization for the treatment of liver metastases from neuroendocrine tumors: A long-term follow-up in 123 patients. Med. Oncol. 2011, 28 (Suppl. 1), 286–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allison, D.J.; Modlin, I.M.; Jenkins, W.J. Treatment of carcinoid liver metastases by hepatic-artery embolisation. Lancet 1977, 2, 1323–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martensson, H.; Nobin, A.; Bengmark, S.; Lunderquist, A.; Owman, T.; Sanden, G. Embolization of the liver in the management of metastatic carcinoid tumors. J. Surg. Oncol. 1984, 27, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stokes, K.R.; Stuart, K.; Clouse, M.E. Hepatic arterial chemoembolization for metastatic endocrine tumors. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 1993, 4, 341–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poujade, O.; Ceccaldi, P.F.; Davitian, C.; Amate, P.; Chatel, P.; Khater, C.; Aflak, N.; Vilgrain, V.; Luton, D. Uterine necrosis following pelvic arterial embolization for post-partum hemorrhage: Review of the literature. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2013, 170, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco, C.H.; Charnsangavej, C.; Ajani, J.; Samaan, N.A.; Richli, W.; Wallace, S. The carcinoid syndrome: Palliation by hepatic artery embolization. Am. J. Roentgenol. 1986, 147, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zener, R.; Yoon, H.; Ziv, E.; Covey, A.; Brown, K.T.; Sofocleous, C.T.; Thornton, R.H.; Boas, F.E. Outcomes after transarterial embolization of neuroendocrine tumor liver metastases using spherical particles of different sizes. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2019, 42, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkelbauer, F.W.; Niederle, B.; Pietschmann, F.; Thurnher, S.; Wildling, R.; Prokesch, R.; Lammer, J. Hepatic artery embolotherapy of hepatic metastases from carcinoid tumors: Value of using a mixture of cyanoacrylate and ethiodized oil. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 1995, 165, 323–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loewe, C.; Schindl, M.; Cejna, M.; Niederle, B.; Lammer, J.; Thurnher, S. Permanent transarterial embolization of neuroendocrine metastases of the liver using cyanoacrylate and Lipiodol: Assessment of mid- and long-term results. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2003, 180, 1379–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozpar, R.; Nas, O.F.; Hacikurt, K.; Taskapilioglu, M.O.; Kocaeli, H.; Hakyemez, B. Endovascular treatment of intracranial arteriovenous malformations using detachable-tip microcatheters and Onyx 18((r)). Diagn. Interv. Imaging 2019, 100, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelage, J.P.; Fohlen, A.; Mitry, E.; Lagrange, C.; Beauchet, A.; Rougier, P. Chemoembolization of neuroendocrine liver metastases using streptozocin and tris-acryl microspheres: Embozar (embosphere + zanosar) study. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2017, 40, 394–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grote, R.; Schmoll, E.; Dohring, W.; Rosenthal, H.; Reimer, P.; Dralle, H. Chemical embolization of carcinoid metastases in the liver. RöFo-Fortschr. Geb. Röntgenstrahlen Bildgeb. Verfahr. 1990, 153, 595–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.H.; Ajani, J.A.; Carrasco, C.H.; Dumas, P.; Richli, W.; Lawrence, D.; Chuang, V.; Wallace, S. Selective hepatic arterial chemoembolization for liver metastases in patients with carcinoid tumor or islet cell carcinoma. Cancer Investig. 1999, 17, 474–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Yao, J.C.; Ahrar, K.; Wallace, M.J.; Morello, F.A.; Madoff, D.C.; Murthy, R.; Hicks, M.E.; Ajani, J.A. Hepatic artery embolization and chemoembolization for treatment of patients with metastatic carcinoid tumors: The M.D. Anderson experience. Cancer J. 2003, 9, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogl, T.J.; Gruber, T.; Naguib, N.N.; Hammerstingl, R.; Nour-Eldin, N.E. Liver metastases of neuroendocrine tumors: Treatment with hepatic transarterial chemotherapy using two therapeutic protocols. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2009, 193, 941–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- De Baere, T.; Deschamps, F.; Teriitheau, C.; Rao, P.; Conengrapht, K.; Schlumberger, M.; Leboulleux, S.; Baudin, E.; Hechellhammer, L. Transarterial chemoembolization of liver metastases from well differentiated gastroenteropancreatic endocrine tumors with doxorubicin-eluting beads: Preliminary results. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2008, 19, 855–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaur, S.K.; Friese, J.L.; Sadow, C.A.; Ayyagari, R.; Binkert, C.A.; Schenker, M.P.; Kulke, M.; Baum, R. Hepatic arterial chemoembolization using drug-eluting beads in gastrointestinal neuroendocrine tumor metastatic to the liver. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2011, 34, 566–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guiu, B.; Deschamps, F.; Aho, S.; Munck, F.; Dromain, C.; Boige, V.; Malka, D.; Leboulleux, S.; Ducreux, M.; Schlumberger, M.; et al. Liver/biliary injuries following chemoembolisation of endocrine tumours and hepatocellular carcinoma: Lipiodol vs. Drug-eluting beads. J. Hepatol. 2012, 56, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joskin, J.; de Baere, T.; Auperin, A.; Tselikas, L.; Guiu, B.; Farouil, G.; Boige, V.; Malka, D.; Leboulleux, S.; Ducreux, M.; et al. Predisposing factors of liver necrosis after transcatheter arterial chemoembolization in liver metastases from neuroendocrine tumor. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2015, 38, 372–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhagat, N.; Reyes, D.K.; Lin, M.; Kamel, I.; Pawlik, T.M.; Frangakis, C.; Geschwind, J.F. Phase ii study of chemoembolization with drug-eluting beads in patients with hepatic neuroendocrine metastases: High incidence of biliary injury. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2013, 36, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitano, M.; Davidson, G.W.; Shirley, L.A.; Schmidt, C.R.; Guy, G.E.; Khabiri, H.; Dowell, J.D.; Shah, M.H.; Bloomston, M. Transarterial chemoembolization for metastatic neuroendocrine tumors with massive hepatic tumor burden: Is the benefit worth the risk? Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2016, 23, 4008–4015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plante, A.; Baudin, E.; Do Cao, C.; Hentic, O.; Dubreuil, O.; Terrebonne, E.; Granger, V.; Smith, D.; Lombard-Bohas, C.; Walter, T. Patient-reported tolerance in treatments approved in neuroendocrine tumors: A national survey from the french group of endocrine tumors. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 2018, 42, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhlman, J.E.; Fishman, E.K. Acute abdomen in AIDS: CT diagnosis and triage. Radiographics 1990, 10, 621–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofocleous, C.T.; Petre, E.N.; Gonen, M.; Reidy-Lagunes, D.; Ip, I.K.; Alago, W.; Covey, A.M.; Erinjeri, J.P.; Brody, L.A.; Maybody, M.; et al. Factors affecting periprocedural morbidity and mortality and long-term patient survival after arterial embolization of hepatic neuroendocrine metastases. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2014, 25, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez, S.; Denys, A.; Madeira, I.; Hammel, P.; Vilgrain, V.; Menu, Y.; Bernades, P.; Ruszniewski, P. Hepatic arterial chemoembolization with streptozotocin in patients with metastatic digestive endocrine tumours. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2000, 12, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartnell, G.G.; Gates, J.; Stuart, K.; Underhill, J.; Brophy, D.P. Hepatic chemoembolization: Effect of intraarterial lidocaine on pain and postprocedure recovery. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 1999, 22, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornelis, F.H.; Monard, E.; Moulin, M.A.; Vignaud, E.; Laveissiere, F.; Ben Ammar, M.; Nouri-Neuville, M.; Barral, M.; Lombart, B. Sedation and analgesia in interventional radiology: Where do we stand, where are we heading and why does it matter? Diagn. Interv. Imaging 2019, 100, 753–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolmannskog, F.; Kolbenstvedt, A.N.; Schrumpf, E.; Hanssen, L.E. Side effects and complications after hepatic artery embolization in the carcinoid syndrome. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 1991, 26, 557–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granberg, D.; Eriksson, L.G.; Welin, S.; Kindmark, H.; Janson, E.T.; Skogseid, B.; Oberg, K.; Eriksson, B.; Nyman, R. Liver embolization with trisacryl gelatin microspheres (Embosphere) in patients with neuroendocrine tumors. Acta Radiol. 2007, 48, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, D.H.; Paciorek, A.; Mulvey, C.K.; Chan, H.; Fidelman, N.; Meng, L.; Nakakura, E.K.; Zhang, L.; Bergsland, E.K.; Van Loon, K. Periprocedural management of patients undergoing liver resection or embolotherapy for neuroendocrine tumor metastases. Pancreas 2019, 48, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strosberg, J.R.; Choi, J.; Cantor, A.B.; Kvols, L.K. Selective hepatic artery embolization for treatment of patients with metastatic carcinoid and pancreatic endocrine tumors. Cancer Control. 2006, 13, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strosberg, J.R.; Weber, J.M.; Choi, J.; Campos, T.L.; Valone, T.L.; Han, G.; Schell, M.J.; Kvols, L.K. A phase ii clinical trial of sunitinib following hepatic transarterial embolization for metastatic neuroendocrine tumors. Ann. Oncol. 2012, 23, 2335–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirley, L.A.; McNally, M.; Chokshi, R.; Jones, N.; Tassone, P.; Guy, G.; Khabiri, H.; Schmidt, C.; Shah, M.; Bloomston, M. Transarterial chemoembolization is ineffective for neuroendocrine tumors metastatic to the caudate lobe: A single institution review. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2015, 13, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.; Clark, T.W.; Baum, R.A.; Soulen, M.C. Risk factors for liver abscess formation after hepatic chemoembolization. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2001, 12, 965–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaco, D.S.; Hajarizadeh, H.; Mueller, C.R.; Fletcher, W.S.; Pommier, R.F.; Woltering, E.A. Treatment of metastatic carcinoid tumors using multimodality therapy of octreotide acetate, intra-arterial chemotherapy, and hepatic arterial chemoembolization. Am. J. Surg. 1995, 169, 523–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newgard, B.J.; Getrajdman, G.I.; Erinjeri, J.P.; Covey, A.M.; Brody, L.A.; Sofocleous, C.T.; Brown, K.T. Incidence and consequence of nontarget embolization following bland hepatic arterial embolization. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2019, 42, 1135–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.X.; Rose, S.; White, S.B.; El-Haddad, G.; Fidelman, N.; Yarmohammadi, H.; Hwang, W.; Sze, D.Y.; Kothary, N.; Stashek, K.; et al. Embolotherapy for neuroendocrine tumor liver metastases: Prognostic factors for hepatic progression-free survival and overall survival. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2017, 40, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Therasse, E.; Breittmayer, F.; Roche, A.; De Baere, T.; Indushekar, S.; Ducreux, M.; Lasser, P.; Elias, D.; Rougier, P. Transcatheter chemoembolization of progressive carcinoid liver metastasis. Radiology 1993, 189, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sward, C.; Johanson, V.; Nieveen van Dijkum, E.; Jansson, S.; Nilsson, O.; Wangberg, B.; Ahlman, H.; Kolby, L. Prolonged survival after hepatic artery embolization in patients with midgut carcinoid syndrome. Br. J. Surg. 2009, 96, 517–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, K.T.; Koh, B.Y.; Brody, L.A.; Getrajdman, G.I.; Susman, J.; Fong, Y.; Blumgart, L.H. Particle embolization of hepatic neuroendocrine metastases for control of pain and hormonal symptoms. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 1999, 10, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chey, V.; Chopin-laly, X.; Micol, C.; Lepiliez, V.; Forestier, J.; Lombard-bohas, C.; Walter, T. Acute pancreatitis after transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for liver metastases of carcinoid tumors. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 2011, 35, 583–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seto, A.H.; Abu-Fadel, M.S.; Sparling, J.M.; Zacharias, S.J.; Daly, T.S.; Harrison, A.T.; Suh, W.M.; Vera, J.A.; Aston, C.E.; Winters, R.J.; et al. Real-time ultrasound guidance facilitates femoral arterial access and reduces vascular complications: FAUST (femoral arterial access with ultrasound trial). JACC Cardiovasc. Interv. 2010, 3, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kress, O.; Wagner, H.J.; Wied, M.; Klose, K.J.; Arnold, R.; Alfke, H. Transarterial chemoembolization of advanced liver metastases of neuroendocrine tumors—A retrospective single-center analysis. Digestion 2003, 68, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarmohammadi, H.; Erinjeri, J.P.; Brown, K.T. Embolization of metastatic neuroendocrine tumor resulting in clinical manifestations of syndrome of inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2015, 26, 533–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ramirez, M.; Ravichandran, S.; Ronald, L.; Pabon-Ramos, W.M.; Smith, T.P.; Kim, C.Y.; Ronald, J. Recognition and management of dermatologic complications from interventional radiology procedures. Diagn. Interv. Imaging 2019, 100, 659–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christante, D.; Pommier, S.; Givi, B.; Pommier, R. Hepatic artery chemoinfusion with chemoembolization for neuroendocrine cancer with progressive hepatic metastases despite octreotide therapy. Surgery 2008, 144, 885–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamat, P.P.; Gupta, S.; Ensor, J.E.; Murthy, R.; Ahrar, K.; Madoff, D.C.; Wallace, M.J.; Hicks, M.E. Hepatic arterial embolization and chemoembolization in the management of patients with large-volume liver metastases. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2008, 31, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, R.; Rempp, H.; Schmidt, D.; Pereira, P.L.; Claussen, C.D.; Clasen, S. Prolonged antibiotic prophylaxis in patients with bilioenteric anastomosis undergoing percutaneous radiofrequency ablation. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2012, 23, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osborne, D.A.; Zervos, E.E.; Strosberg, J.; Boe, B.A.; Malafa, M.; Rosemurgy, A.S.; Yeatman, T.J.; Carey, L.; Duhaine, L.; Kvols, L.K. Improved outcome with cytoreduction versus embolization for symptomatic hepatic metastases of carcinoid and neuroendocrine tumors. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2006, 13, 572–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisenhauer, E.A.; Therasse, P.; Bogaerts, J.; Schwartz, L.H.; Sargent, D.; Ford, R.; Dancey, J.; Arbuck, S.; Gwyther, S.; Mooney, M.; et al. New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: Revised recist guideline (version 1.1). Eur. J. Cancer 2009, 45, 228–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lencioni, R.; de Baere, T.; Soulen, M.C.; Rilling, W.S.; Geschwind, J.F. Lipiodol transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review of efficacy and safety data. Hepatology 2016, 64, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Do Minh, D.; Chapiro, J.; Gorodetski, B.; Huang, Q.; Liu, C.; Smolka, S.; Savic, L.J.; Wainstejn, D.; Lin, M.; Schlachter, T.; et al. Intra-arterial therapy of neuroendocrine tumour liver metastases: Comparing conventional tace, drug-eluting beads tace and yttrium-90 radioembolisation as treatment options using a propensity score analysis model. Eur. Radiol. 2017, 27, 4995–5005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuyama, H.; Ikeda, M.; Takahashi, H.; Ohno, I.; Hashimoto, Y.; Mitsunaga, S.; Sakamoto, Y.; Kondo, S.; Morizane, C.; Ueno, H.; et al. Transarterial (chemo)embolization for liver metastases in patients with neuroendocrine tumors. Oncology 2017, 92, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korse, C.M.; Bonfrer, J.M.; Prevoo, W.; Baas, P.; Taal, B.G. Increase of angiogenic growth factors after hepatic artery embolization in patients with neuroendocrine tumours. Tumour Biol. 2011, 32, 647–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hur, S.; Chung, J.W.; Kim, H.C.; Oh, D.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Bang, Y.J.; Kim, W.H. Survival outcomes and prognostic factors of transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for hepatic neuroendocrine metastases. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2013, 24, 947–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahu, S.; Schernthaner, R.; Ardon, R.; Chapiro, J.; Zhao, Y.; Sohn, J.H.; Fleckenstein, F.; Lin, M.; Geschwind, J.F.; Duran, R. Imaging biomarkers of tumor response in neuroendocrine liver metastases treated with transarterial chemoembolization: Can enhancing tumor burden of the whole liver help predict patient survival? Radiology 2017, 283, 883–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.; Ni, J.; Weng, L.; Ma, F.; Li, S.; Wang, W.; Sang, X.; Lu, X.; Zhong, S.; Mao, Y. Aggressive locoregional treatment improves the outcome of liver metastases from grade 3 gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Medicine 2015, 94, e1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roche, A.; Girish, B.V.; de Baere, T.; Ducreux, M.; Elias, D.; Laplanche, A.; Boige, V.; Schlumberger, M.; Ruffle, P.; Baudin, E. Prognostic factors for chemoembolization in liver metastasis from endocrine tumors. Hepatogastroenterology 2004, 51, 1751–1756. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Arrese, D.; McNally, M.E.; Chokshi, R.; Feria-Arias, E.; Schmidt, C.; Klemanski, D.; Gregory, G.; Khabiri, H.; Shah, M.; Bloomston, M. Extrahepatic disease should not preclude transarterial chemoembolization for metastatic neuroendocrine carcinoma. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2013, 20, 1114–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erinjeri, J.P.; Deodhar, A.; Thornton, R.H.; Allen, P.J.; Getrajdman, G.I.; Brown, K.T.; Sofocleous, C.T.; Reidy, D.L. Resolution of hepatic encephalopathy following hepatic artery embolization in a patient with well-differentiated neuroendocrine tumor metastatic to the liver. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2010, 33, 610–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schell, S.R.; Camp, E.R.; Caridi, J.G.; Hawkins, I.F., Jr. Hepatic artery embolization for control of symptoms, octreotide requirements, and tumor progression in metastatic carcinoid tumors. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2002, 6, 664–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrache, F.; Vullierme, M.P.; Roy, C.; El Assoued, Y.; Couvelard, A.; O’Toole, D.; Mitry, E.; Hentic, O.; Hammel, P.; Levy, P.; et al. Arterial phase enhancement and body mass index are predictors of response to chemoembolisation for liver metastases of endocrine tumours. Br. J. Cancer 2007, 96, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onesti, J.K.; Shirley, L.A.; Saunders, N.D.; Davidson, G.W.; Dillhoff, M.E.; Khabiri, H.; Guy, G.E.; Dowell, J.D.; Schmidt, C.R.; Shah, M.H.; et al. Elevated alkaline phosphatase prior to transarterial chemoembolization for neuroendocrine tumors predicts worse outcomes. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2016, 20, 580–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Pandey, A.; Ghasabeh, M.A.; Pandey, P.; Varzaneh, F.N.; Zarghampour, M.; Khoshpouri, P.; Ameli, S.; Li, Z.; Hu, D.; et al. Prognostic value of baseline volumetric multiparametric MR imaging in neuroendocrine liver metastases treated with transarterial chemoembolization. Eur. Radiol. 2019, 29, 5160–5171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Mestier, L.; Lepage, C.; Baudin, E.; Coriat, R.; Courbon, F.; Couvelard, A.; Do Cao, C.; Frampas, E.; Gaujoux, S.; Gincul, R.; et al. Digestive neuroendocrine neoplasms (NEN): French intergroup clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up (SNFGE, GTE, Renaten, Tenpath, FFCD, Gercor, Unicancer, SFCD, SFED, SFRO, SFR). Dig. Liver Dis 2020, 59, 473–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, J.C.; Walker, S.C.; Ackermann, R.J.; Cotton, L.A.; Ensminger, W.D.; Shapiro, B. Hepatic radioembolization with yttrium-90 containing glass microspheres: Preliminary results and clinical follow-up. J. Nucl. Med. 1994, 35, 1637–1644. [Google Scholar]
- Nijsen, J.F.; Zonnenberg, B.A.; Woittiez, J.R.; Rook, D.W.; Swildens-van Woudenberg, I.A.; van Rijk, P.P.; van het Schip, A.D. Holmium-166 poly lactic acid microspheres applicable for intra-arterial radionuclide therapy of hepatic malignancies: Effects of preparation and neutron activation techniques. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. 1999, 26, 699–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Maat, G.H.; Seevinck, P.R.; Bos, C.; Bakker, C.J. Quantification of holmium-166 loaded microspheres: Estimating high local concentrations using a conventional multiple gradient echo sequence with s(0)-fitting. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2012, 35, 1453–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumper, R.J.; Ryo, U.Y.; Jay, M. Neutron-activated holmium-166-poly (l-lactic acid) microspheres: A potential agent for the internal radiation therapy of hepatic tumors. J. Nucl. Med. 1991, 32, 2139–2143. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Frilling, A.; Clift, A.K.; Braat, A.; Alsafi, A.; Wasan, H.S.; Al-Nahhas, A.; Thomas, R.; Drymousis, P.; Habib, N.; Tait, P.N. Radioembolisation with 90y microspheres for neuroendocrine liver metastases: An institutional case series, systematic review and meta-analysis. HPB 2019, 21, 773–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomozawa, Y.; Jahangiri, Y.; Pathak, P.; Kolbeck, K.J.; Schenning, R.C.; Kaufman, J.A.; Farsad, K. Long-term toxicity after transarterial radioembolization with yttrium-90 using resin microspheres for neuroendocrine tumor liver metastases. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2018, 29, 858–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paprottka, P.M.; Hoffmann, R.T.; Haug, A.; Sommer, W.H.; Raessler, F.; Trumm, C.G.; Schmidt, G.P.; Ashoori, N.; Reiser, M.F.; Jakobs, T.F. Radioembolization of symptomatic, unresectable neuroendocrine hepatic metastases using yttrium-90 microspheres. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2012, 35, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daghir, A.A.; Gungor, H.; Haydar, A.A.; Wasan, H.S.; Tait, N.P. Embolisation of the gastroduodenal artery is not necessary in the presence of reversed flow before yttrium-90 radioembolisation. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2012, 35, 839–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chansanti, O.; Jahangiri, Y.; Matsui, Y.; Adachi, A.; Geeratikun, Y.; Kaufman, J.A.; Kolbeck, K.J.; Stevens, J.S.; Farsad, K. Tumor dose response in yttrium-90 resin microsphere embolization for neuroendocrine liver metastases: A tumor-specific analysis with dose estimation using SPECT-CT. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2017, 28, 1528–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, A.S.; Dezarn, W.A.; McNeillie, P.; Coldwell, D.; Nutting, C.; Carter, D.; Murthy, R.; Rose, S.; Warner, R.R.; Liu, D.; et al. Radioembolization for unresectable neuroendocrine hepatic metastases using resin 90y-microspheres: Early results in 148 patients. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 31, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grober, O.S.; Nultsch, M.; Laatz, K.; Ulrich, G.; Seidensticker, R.; Pethe, A.; Dudeck, O.; Pech, M.; Knoop, B.O.; Ricke, J.; et al. Radioembolization with (90)y-labeled microspheres: Post-therapeutic therapy validation with bremsstrahlung-spect. Z. Med. Phys. 2011, 21, 274–280. [Google Scholar]
- Sangro, B.; Martinez-Urbistondo, D.; Bester, L.; Bilbao, J.I.; Coldwell, D.M.; Flamen, P.; Kennedy, A.; Ricke, J.; Sharma, R.A. Prevention and treatment of complications of selective internal radiation therapy: Expert guidance and systematic review. Hepatology 2017, 66, 969–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braat, M.N.; van Erpecum, K.J.; Zonnenberg, B.A.; van den Bosch, M.A.; Lam, M.G. Radioembolization-induced liver disease: A systematic review. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 29, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Currie, B.M.; Hoteit, M.A.; Ben-Josef, E.; Nadolski, G.J.; Soulen, M.C. Radioembolization-induced chronic hepatotoxicity: A single-center cohort analysis. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2019, 30, 1915–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangro, B.; Gil-Alzugaray, B.; Rodriguez, J.; Sola, I.; Martinez-Cuesta, A.; Viudez, A.; Chopitea, A.; Inarrairaegui, M.; Arbizu, J.; Bilbao, J.I. Liver disease induced by radioembolization of liver tumors: Description and possible risk factors. Cancer 2008, 112, 1538–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, J.Y.; Rhee, T.K.; Atassi, B.; Gates, V.L.; Kulik, L.; Mulcahy, M.F.; Larson, A.C.; Ryu, R.K.; Sato, K.T.; Lewandowski, R.J.; et al. Radiation dose limits and liver toxicities resulting from multiple yttrium-90 radioembolization treatments for hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2007, 18, 1375–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil-Alzugaray, B.; Chopitea, A.; Inarrairaegui, M.; Bilbao, J.I.; Rodriguez-Fraile, M.; Rodriguez, J.; Benito, A.; Dominguez, I.; D’Avola, D.; Herrero, J.I.; et al. Prognostic factors and prevention of radioembolization-induced liver disease. Hepatology 2013, 57, 1078–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuckerman, D.A.; Kennard, R.F.; Roy, A.; Parikh, P.J.; Weiner, A.A. Outcomes and toxicity following yttrium-90 radioembolization for hepatic metastases from neuroendocrine tumors-a single-institution experience. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2019, 10, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.K.; Mackey, R.V.; Riaz, A.; Gates, V.L.; Benson, A.B., 3rd; Miller, F.H.; Yaghmai, V.; Gabr, A.; Salem, R.; Lewandowski, R.J. Long-term hepatotoxicity of yttrium-90 radioembolization as treatment of metastatic neuroendocrine tumor to the liver. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2017, 28, 1520–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elf, A.K.; Andersson, M.; Henrikson, O.; Jalnefjord, O.; Ljungberg, M.; Svensson, J.; Wangberg, B.; Johanson, V. Radioembolization versus bland embolization for hepatic metastases from small intestinal neuroendocrine tumors: Short-term results of a randomized clinical trial. World J. Surg. 2018, 42, 506–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delicque, J.; Hermida, M.; Piron, L.; Allimant, C.; Belgour, A.; Pageaux, G.P.; Ben Bouallegue, F.; Assenat, E.; Mariano-Goulart, D.; Guiu, B.; et al. Intra arterial treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: Comparison of MELD score variations between radio-embolization and chemo-embolization. Diagn. Interv. Imaging 2019, 100, 689–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braat, A.; Kappadath, S.C.; Ahmadzadehfar, H.; Stothers, C.L.; Frilling, A.; Deroose, C.M.; Flamen, P.; Brown, D.B.; Sze, D.Y.; Mahvash, A.; et al. Radioembolization with (90)y resin microspheres of neuroendocrine liver metastases: International multicenter study on efficacy and toxicity. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2019, 42, 413–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Wang, W. Yttrium-90 radioembolization for unresectable metastatic neuroendocrine liver tumor: A systematic review. Eur. J. Radiol. 2018, 100, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bester, L.; Meteling, B.; Pocock, N.; Saxena, A.; Chua, T.C.; Morris, D.L. Radioembolisation with yttrium-90 microspheres: An effective treatment modality for unresectable liver metastases. J. Med. Imaging Radiat. Oncol. 2013, 57, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cholapranee, A.; van Houten, D.; Deitrick, G.; Dagli, M.; Sudheendra, D.; Mondschein, J.I.; Soulen, M.C. Risk of liver abscess formation in patients with prior biliary intervention following yttrium-90 radioembolization. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2015, 38, 397–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbier, C.E.; Garske-Roman, U.; Sandstrom, M.; Nyman, R.; Granberg, D. Selective internal radiation therapy in patients with progressive neuroendocrine liver metastases. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2016, 43, 1425–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devcic, Z.; Rosenberg, J.; Braat, A.J.; Techasith, T.; Banerjee, A.; Sze, D.Y.; Lam, M.G. The efficacy of hepatic 90y resin radioembolization for metastatic neuroendocrine tumors: A meta-analysis. J. Nucl. Med. 2014, 55, 1404–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fan, K.Y.; Wild, A.T.; Halappa, V.G.; Kumar, R.; Ellsworth, S.; Ziegler, M.; Garg, T.; Rosati, L.M.; Su, Z.; Hacker-Prietz, A.; et al. Neuroendocrine tumor liver metastases treated with yttrium-90 radioembolization. Contemp. Clin. Trials 2016, 50, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peker, A.; Cicek, O.; Soydal, C.; Kucuk, N.O.; Bilgic, S. Radioembolization with yttrium-90 resin microspheres for neuroendocrine tumor liver metastases. Diagn. Interv. Radiol. 2015, 21, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memon, K.; Lewandowski, R.J.; Mulcahy, M.F.; Riaz, A.; Ryu, R.K.; Sato, K.T.; Gupta, R.; Nikolaidis, P.; Miller, F.H.; Yaghmai, V.; et al. Radioembolization for neuroendocrine liver metastases: Safety, imaging, and long-term outcomes. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2012, 83, 887–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, J.; Quinn, R.; Glenn, D.M.; Janssen, J.; Tong, D.; Liaw, W.; Morris, D.L. Radioembolization with selective internal radiation microspheres for neuroendocrine liver metastases. Cancer 2008, 113, 921–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinowski, M.; Dressler, M.; Konig, A.; El-Sheik, M.; Rinke, A.; Hoffken, H.; Gress, T.M.; Arnold, R.; Klose, K.J.; Wagner, H.J. Selective internal radiotherapy with yttrium-90 microspheres for hepatic metastatic neuroendocrine tumors: A prospective single center study. Digestion 2009, 79, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cramer, B.; Xing, M.; Kim, H.S. Prospective longitudinal quality of life assessment in patients with neuroendocrine tumor liver metastases treated with 90y radioembolization. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2016, 41, e493–e497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braat, A.; Ahmadzadehfar, H.; Kappadath, S.C.; Stothers, C.L.; Frilling, A.; Deroose, C.M.; Flamen, P.; Brown, D.B.; Sze, D.Y.; Mahvash, A.; et al. Radioembolization with (90)y resin microspheres of neuroendocrine liver metastases after initial peptide receptor radionuclide therapy. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2020, 43, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceelen, F.; Theisen, D.; de Albeniz, X.G.; Auernhammer, C.J.; Haug, A.R.; D’Anastasi, M.; Paprottka, P.M.; Rist, C.; Reiser, M.F.; Sommer, W.H. Towards new response criteria in neuroendocrine tumors: Which changes in MRI parameters are associated with longer progression-free survival after radioembolization of liver metastases? J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2015, 41, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sommer, W.H.; Ceelen, F.; Garcia-Albeniz, X.; Paprottka, P.M.; Auernhammer, C.J.; Armbruster, M.; Nikolaou, K.; Haug, A.R.; Reiser, M.F.; Theisen, D. Defining predictors for long progression-free survival after radioembolisation of hepatic metastases of neuroendocrine origin. Eur. Radiol. 2013, 23, 3094–3103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filippi, L.; Scopinaro, F.; Pelle, G.; Cianni, R.; Salvatori, R.; Schillaci, O.; Bagni, O. Molecular response assessed by (68)GA-DOTANOC and survival after (90)y microsphere therapy in patients with liver metastases from neuroendocrine tumours. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2016, 43, 432–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saxena, A.; Chua, T.C.; Zhao, J.; Morris, D.L. Liver-directed therapy for neuroendocrine neoplasm hepatic metastasis prolongs survival following progression after initial surgery. J. Surg. Oncol. 2012, 105, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paprottka, K.J.; Schoeppe, F.; Ingrisch, M.; Rubenthaler, J.; Sommer, N.N.; De Toni, E.; Ilhan, H.; Zacherl, M.; Todica, A.; Paprottka, P.M. Pre-therapeutic factors for predicting survival after radioembolization: A single-center experience in 389 patients. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2017, 44, 1185–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egger, M.E.; Armstrong, E.; Martin, R.C., 2nd; Scoggins, C.R.; Philips, P.; Shah, M.; Konda, B.; Dillhoff, M.; Pawlik, T.M.; Cloyd, J.M. Transarterial chemoembolization vs radioembolization for neuroendocrine liver metastases: A multi-institutional analysis. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2020, 230, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singla, S.; LeVea, C.M.; Pokuri, V.K.; Attwood, K.M.; Wach, M.M.; Tomaszewski, G.M.; Kuvshinoff, B.; Iyer, R. Ki67 score as a potential predictor in the selection of liver-directed therapies for metastatic neuroendocrine tumors: A single institutional experience. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2016, 7, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitney, R.; Valek, V.; Fages, J.F.; Garcia, A.; Narayanan, G.; Tatum, C.; Hahl, M.; Martin, R.C., 2nd. Transarterial chemoembolization and selective internal radiation for the treatment of patients with metastatic neuroendocrine tumors: A comparison of efficacy and cost. Oncologist 2011, 16, 594–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorentini, G.; Sarti, D.; Nani, R.; Aliberti, C.; Fiorentini, C.; Guadani, S. Updates of colorectal cancer liver metastases therapy: Review on DERIBI. Hepat. Oncol. 2020, 7, HEP16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barat, M.; Cottereau, A.-S.; Kedra, A.; Dermine, S.; Palmieri, L.-J.; Coriat, R.; Dautry, R.; Tselikas, L.; Soyer, P.; Dohan, A. The Role of Interventional Radiology for the Treatment of Hepatic Metastases from Neuroendocrine Tumor: An Updated Review. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2302. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9072302
Barat M, Cottereau A-S, Kedra A, Dermine S, Palmieri L-J, Coriat R, Dautry R, Tselikas L, Soyer P, Dohan A. The Role of Interventional Radiology for the Treatment of Hepatic Metastases from Neuroendocrine Tumor: An Updated Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(7):2302. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9072302
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarat, Maxime, Anne-Ségolène Cottereau, Alice Kedra, Solène Dermine, Lola-Jade Palmieri, Romain Coriat, Raphael Dautry, Lambros Tselikas, Philippe Soyer, and Anthony Dohan. 2020. "The Role of Interventional Radiology for the Treatment of Hepatic Metastases from Neuroendocrine Tumor: An Updated Review" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 7: 2302. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9072302
APA StyleBarat, M., Cottereau, A.-S., Kedra, A., Dermine, S., Palmieri, L.-J., Coriat, R., Dautry, R., Tselikas, L., Soyer, P., & Dohan, A. (2020). The Role of Interventional Radiology for the Treatment of Hepatic Metastases from Neuroendocrine Tumor: An Updated Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(7), 2302. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9072302





