Epileptiform Discharge and Electrographic Seizures during the Hypothermia Phase as Predictors of Rewarming Seizures in Children after Resuscitation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Population
2.2. Cooling Methods and Continuous EEG Monitoring Protocol
2.3. EEG Data Interpretation
2.4. Data Collection
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
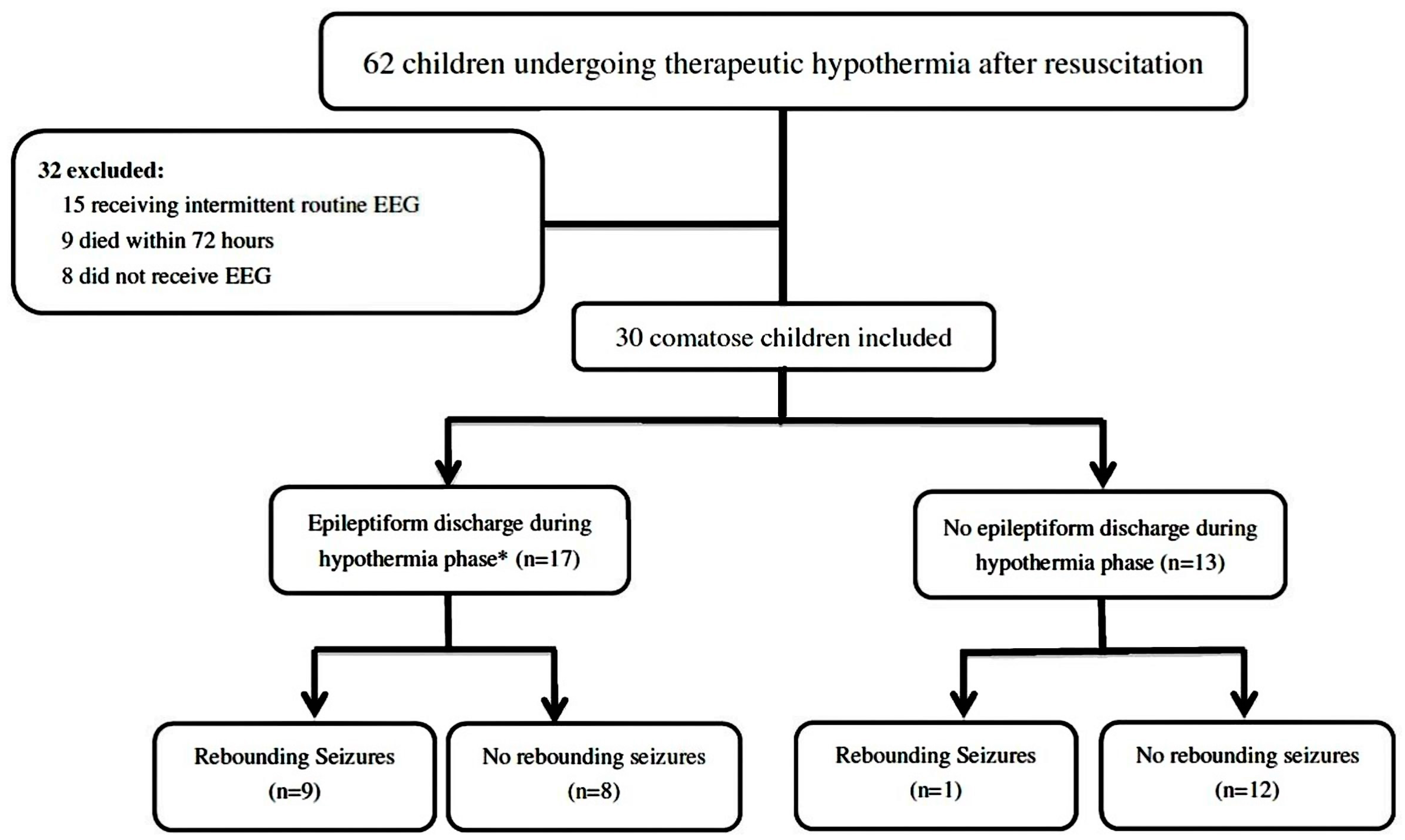
3.1. Patients
3.2. Variables during and after Resuscitation
3.3. Survival Rate and Functional Outcomes
3.4. EEG Recording during Therapeutic Hypothermia and Rewarming Seizures
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Topjian, A.A.; de Caen, A.; Wainwright, M.S.; Abella, B.S.; Abend, N.S.; Atkins, D.L.; Bembea, M.M.; Fink, E.L.; Guerguerian, A.M.; Haskell, S.E.; et al. Pediatric Post-Cardiac Arrest Care: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2019, 140, e194–e233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rittenberger, J.C.; Popescu, A.; Brenner, R.P.; Guyette, F.X.; Callaway, C.W. Frequency and timing of nonconvulsive status epilepticus in comatose post-cardiac arrest subjects treated with hypothermia. Neurocrit Care 2012, 16, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mani, R.; Schmitt, S.E.; Mazer, M.; Putt, M.E.; Gaieski, D.F. The frequency and timing of epileptiform activity on continuous electroencephalogram in comatose post-cardiac arrest syndrome patients treated with therapeutic hypothermia. Resuscitation 2012, 83, 840–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knight, W.A.; Hart, K.W.; Adeoye, O.M.; Bonomo, J.B.; Keegan, S.P.; Ficker, D.M.; Szaflarski, J.P.; Privitera, M.D.; Lindsell, C.J. The incidence of seizures in patients undergoing therapeutic hypothermia after resuscitation from cardiac arrest. Epilepsy Res. 2013, 106, 396–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abend, N.S.; Topjian, A.; Ichord, R.; Herman, S.T.; Helfaer, M.; Donnelly, M.; Nadkarni, V.; Dlugos, D.J.; Clancy, R.R. Electroencephalographic monitoring during hypothermia after pediatric cardiac arrest. Neurology 2009, 72, 1931–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topjian, A.A.; Sánchez, S.M.; Shults, J.; Berg, R.A.; Dlugos, D.J.; Abend, N.S. Early Electroencephalographic Background Features Predict Outcomes in Children Resuscitated From Cardiac Arrest. Pediatr. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 17, 547–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostendorf, A.P.; Hartman, M.E.; Friess, S.H. Early Electroencephalographic Findings Correlate With Neurologic Outcome in Children Following Cardiac Arrest. Pediatr. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 17, 667–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lybeck, A.; Friberg, H.; Aneman, A.; Hassager, C.; Horn, J.; Kjærgaard, J.; Kuiper, M.; Nielsen, N.; Ullén, S.; Wise, M.P.; et al. TTM-trial Investigators. Prognostic significance of clinical seizures after cardiac arrest and target temperature management. Resuscitation 2017, 114, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, G.B.; Jordan, K.G.; Doig, G.S. An assessment of nonconvulsive seizures in the intensive care unit using continuous EEG monitoring: An investigation of variables associated with mortality. Neurology 1996, 47, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossetti, A.O.; Oddo, M.; Liaudet, L.; Kaplan, P.W. Predictors of awakening from postanoxic status epilepticus after therapeutic hypothermia. Neurology 2009, 72, 744–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abend, N.S.; Wusthoff, C.J.; Goldberg, E.M.; Dlugos, D.J. Electrographic seizures and status epilepticus in critically ill children and neonates with encephalopathy. Lancet. Neurol. 2013, 12, 1170–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundgren, J.; Smith, M.L.; Blennow, G.; Siesjö, B.K. Hyperthermia aggravates and hypothermia ameliorates epileptic brain damage. Exp. Brain Res. 1994, 99, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakashima, K.; Todd, M.M. Effects of hypothermia on the rate of excitatory amino acid release after ischemic depolarization. Stroke 1996, 27, 913–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polderman, K.H. Mechanism of action, physiological effects, and complications of hypothermia. Crit. Care Med. 2009, 37, S186–S202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battin, M.; Bennet, L.; Gunn, A.J. Rebound seizures during rewarming. Pediatrics 2004, 114, 1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerrits, L.C.; Battin, M.R.; Bennet, L.; Gonzalez, H.; Gunn, A.J. Epileptiform activity during rewarming from moderate cerebral hypothermia in the near-term fetal sheep. Pediatr. Res. 2005, 57, 342–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Herman, S.T.; Abend, N.S.; Bleck, T.P.; Chapman, K.E.; Drislane, F.W.; Emerson, R.G.; Gerard, E.E.; Hahn, C.D.; Husain, A.M.; Kaplan, P.W.; et al. Consensus statement on continuous EEG in critically ill adults and children, part I: Indications. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2015, 32, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, S.T.; Abend, N.S.; Bleck, T.P.; Chapman, K.E.; Drislane, F.W.; Emerson, R.G.; Gerard, E.E.; Hahn, C.D.; Husain, A.M.; Kaplan, P.W.; et al. Consensus statement on continuous EEG in critically ill adults and children, part II: Personnel, technical specifications, and clinical practice. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2015, 32, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.J.; Hsia, S.H.; Wang, H.S.; Chiang, M.C.; Lin, K.L. Therapeutic hypothermia associated with increased survival after resuscitation in children. Pediatr. Neurol. 2013, 48, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.J.; Hsia, S.H.; Wang, H.S.; Chiang, M.C.; Lin, K.L. Transcranial Doppler ultrasound in therapeutic hypothermia for children after resuscitation. Resuscitation 2015, 89, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.J.; Lin, C.Y.; Hsia, S.H.; Wang, H.S.; Chiang, M.C.; Lin, K.L.; iCNS Group. 72-H therapeutic hypothermia improves neurological outcomes in paediatric asphyxial out-of-hospital cardiac arrest: An exploratory investigation. Resuscitation 2018, 133, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.J.; Lin, Y.J.; Hsia, S.H.; Kuo, H.C.; Wang, H.S.; Hsu, M.H.; Chiang, M.C.; Lin, C.Y.; Lin, K.L. Early clinical predictors of neurological outcome in children with asphyxial out-of-hospital cardiac arrest treated with therapeutic hypothermia. Front. Pediatr. 2020, 7, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirsch, L.J.; LaRoche, S.M.; Gaspard, N.; Gerard, E.; Svoronos, A.; Herman, S.T.; Mani, R.; Arif, H.; Jette, N.; Minazad, Y.; et al. American Clinical Neurophysiology Society’s Standardized Critical Care EEG Terminology: 2012 version. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2013, 30, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leitinger, M.; Beniczky, S.; Rohracher, A.; Gardella, E.; Kalss, G.; Qerama, E.; Höfler, J.; Hess Lindberg-Larsen, A.; Kuchukhidze, G.; Dobesberger, J.; et al. Salzburg Consensus Criteria for Non-Convulsive Status Epilepticus—Approach to clinical application. Epilepsy Behav. 2015, 49, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topjian, A.A.; French, B.; Sutton, R.M.; Conlon, T.; Nadkarni, V.M.; Moler, F.W.; Dean, J.M.; Berg, R.A. Early post resuscitation hypotension is associated with increased mortality following pediatric cardiac arrest. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 42, 1518–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crepeau, A.Z.; Britton, J.W.; Fugate, J.E.; Rabinstein, A.A.; Wijdicks, E.F. Electroencephalography in survivors of cardiac arrest: Comparing pre- and post-therapeutic hypothermia eras. Neurocrit. Care 2015, 22, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, S.M.; Carpenter, J.; Chapman, K.E.; Dlugos, D.J.; Gallentine, W.B.; Giza, C.C.; Goldstein, J.L.; Hahn, C.D.; Kessler, S.K.; Loddenkemper, T.; et al. Pediatric ICU EEG monitoring: Current resources and practice in the United States and Canada. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2013, 30, 156–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristic | Rewarming Seizures (n = 10) | Non-Rewarming Seizures (n = 20) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | 1.000 | ||
| Female | 3 (30%) | 5 (25%) | |
| Male | 7 (70%) | 15 (75%) | |
| Age | 0.842 | ||
| 1–11 months | 3 (30%) | 8 (45%) | |
| 1–4 years | 3 (30%) | 7 (30%) | |
| 5–8 years | 2 (20%) | 3 (15%) | |
| 9–18 years | 2 (20%) | 2 (10%) | |
| Chronic pre-existing illness | 0.992 | ||
| No | 6 (60%) | 11 (55%) | |
| Respiratory | 1 (10%) | 2 (10%) | |
| Neurologic | 2 (20%) | 5 (25%) | |
| Other | 1 (10%) | 2 (10%) | |
| Cardiac arrest location | 0.372 | ||
| OHCA | 7 (70%) | 17 (85%) | |
| IHCA | 3 (30%) | 3 (15%) | |
| Bystander-witnessed cardiac arrest | 4 (40%) | 13 (65%) | 0.255 |
| Bystander-performed CPR | 3 (30%) | 12 (60%) | 0.245 |
| Initial rhythm | 0.284 | ||
| Asystole | 9 (90%) | 19 (95%) | |
| Bradycardia/PEA | 0 | 1 (5%) | |
| VT/Vf | 1 (10%) | 0 | |
| Seizures before therapeutic hypothermia | 2 (20%) | 7 (35%) | 0.675 |
| Characteristics | Rewarming Seizures (n = 10) | Non-Rewarming Seizures (n = 20) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristics during resuscitation | |||
| Interval from CPR to ROSC (min) | 28.20 ± 15.55 | 22.90 ± 14.84 | 0.342 |
| Serum pH | 7.21 ± 0.18 | 7.10 ± 0.21 | 0.171 |
| Initial glucose (mg/dL) | 293.60 ± 128.64 | 334.00 ± 204.24 | 0.576 |
| Initial lactate (mmol/L) | 83.66 ± 41.53 | 87.29 ± 42.37 | 0.840 |
| Post-cardiac arrest GCS | 3.70 ± 1.15 | 3.70 ± 1.55 | 1.000 |
| PRISM score | 34.70 ± 5.61 | 38.60 ± 8.89 | 0.218 |
| PLODS | 38.60 ± 11.77 | 35.95 ± 8.39 | 0.536 |
| Outcome | |||
| Hospital length of stay (days) | 53.80 ± 30.75 | 50.20 ± 39.94 | 0.805 |
| 1-month mortality | 2 (20%) | 4 (20%) | 1.000 |
| 6-month neurologic outcome (n = 24) | 0.362 | ||
| Good prognosis (PCPC score ≤ 2) | 3 (37.5%) | 3 (18.7%) | |
| Poor prognosis (PCPC score ≥ 3) | 5 (62.5%) | 13 (81.3%) |
| Age (y)/Sex/Cardiac Arrest Location | Seizure before TH | Hypothermia Phase | Rewarming Phase | LOS (Days) | 6-Month PCPC | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EEG BG # | ED | ES | EEG BG # | ES | Seizure Onset (h) * | |||||
| Rewarming Seizures Group | ||||||||||
| Any ED or ES during the Hypothermia Phase | ||||||||||
| 1 | 6.49/M/OHCA | Y | 3 | GED | CSE | 3 | CSE | 6 | 105 | 3 |
| 2 | 3.17/M/OHCA | Y | 3 | N | CSE | 3 | NCS | 65 | 27 | -a |
| 3 | 4.33/M/OHCA | N | 3 | GED | CSE | 3 | CSE | 37 | 50 | 3 |
| 4 | 4.39/M/IHCA | N | 3 | GED | NCS | 3 | NCS | 14 | 48 | 1 |
| 5 | 0.80/M/OHCA | N | 3 | PLED | NCS | 3 | NCS | 62 | 47 | 3 |
| 6 | 0.21/M/IHCA | N | 3 | FED | NCS | 3 | NCS | 22 | 50 | 3 |
| 7 | 7.22/M/OHCA | N | 2 | PLED | NCS | 2 | NCS | 15 | 18 | -a |
| 8 | 0.53/F/OHCA | N | 2 | PLED | NCS | 3 | NCS | 53.5 | 66 | 3 |
| 9 | 16.52/F/OHCA | N | 2 | FED | N | 2 | NCS | 46.5 | 22 | 1 |
| No ED or ES during the Hypothermia Phase | ||||||||||
| 10 | 13.04/F/IHCA | N | 3 | N | N | 3 | NCS | 52 | 105 | 2 |
| Non-rewarming seizures group | ||||||||||
| Any ED or ES during the Hypothermia Phase | ||||||||||
| 11 | 3.48/M/OHCA | Y | 3 | GED | N | 4 | N | - | 11 | -a |
| 12 | 7.26/M/OHCA | Y | 3 | N | NCSE | 4 | N | - | 12 | -a |
| 13 | 3.78/M/OHCA | Y | 3 | N | ECS | 4 | N | - | 9 | -a |
| 14 | 1.16/M/OHCA | Y | 2 | PLED | NCS | 2 | N | - | 37 | 3 |
| 15 | 10.75/F/IHCA | Y | 2 | PLED | ECS | 2 | N | - | 39 | 3 |
| 16 | 4.11/F/OHCA | N | 3 | GED | NCSE | 3 | N | - | 110 | 4 |
| 17 | 1.79/M/OHCA | N | 3 | GED | NCS | 3 | N | - | 24 | 2 |
| 18 | 0.47/M/OHCA | N | 2 | PLED | N | 3 | N | - | 72 | 5 |
| No ED or ES during the Hypothermia Phase | ||||||||||
| 19 | 0.02/F/OHCA | Y | 3 | N | N | 4 | N | - | 34 | 3 |
| 20 | 1.04/M/OHCA | Y | 2 | N | N | 2 | N | - | 14 | 1 |
| 21 | 0.45/M/OHCA | Y | 2 | N | N | 2 | N | - | 28 | 3 |
| 22 | 0.16/M/OHCA | N | 4 | N | N | 4 | N | - | 67 | 3 |
| 23 | 0.54/M/OHCA | N | 4 | N | N | 4 | N | - | 138 | 4 |
| 24 | 0.41/M/OHCA | N | 4 | N | N | 4 | N | - | 43 | 3 |
| 25 | 0.18/M/OHCA | N | 4 | N | N | 4 | N | - | 42 | 5 |
| 26 | 0.23/M/OHCA | N | 4 | N | N | 4 | N | - | 23 | -a |
| 27 | 4.59/F/IHCA | N | 3 | N | N | 3 | N | - | 68 | 5 |
| 28 | 15.4/M/OHCA | N | 3 | N | N | 3 | N | - | 53 | 3 |
| 29 | 5.87/M/OHCA | N | 2 | N | N | 2 | N | - | 41 | 3 |
| 30 | 8.47/F/IHCA | N | 1 | N | N | 1 | N | - | 15 | 1 |
| Characteristics | Rewarming Seizures (n = 10) | Non-Rewarming Seizures (n = 20) | Odds Ratio | 95% CI | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Duration of EEG Monitoring (hours) | 181.17 ± 17.33 | 153.66 ± 13.15 | - | - | <0.001 * |
| Background during the Hypothermia Phase | 0.76 | 0.275–2.125 | 0.606 | ||
| Normal | 0 | 1 (5%) | |||
| Slow–disorganized | 3 (30%) | 6 (30%) | |||
| Discontinuous or burst suppression | 7 (70%) | 8 (40%) | |||
| Attenuated–featureless | 0 | 5 (25%) | |||
| Epileptiform Discharge (Interictal, Ictal or both) during the Hypothermia Phase | 13.50 | 1.42–128.25 | 0.023 * | ||
| Yes | 9 (90%) | 8 (45%) | |||
| No | 1 (10%) | 12 (55%) | |||
| Epileptiform Discharge (Interictal) | 9.33 | 1.51–57.65 | 0.016 * | ||
| Yes | 8 (80%) | 6 (40%) | |||
| No | 2 (20%) | 14 (60%) | |||
| Electrographic Seizures | 9.33 | 1.51–57.65 | 0.016 * | ||
| Yes | 8 (80%) | 6 (20%) | |||
| No | 2 (30%) | 14 (80%) | |||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, J.-J.; Hsu, M.-H.; Hsia, S.-H.; Lin, Y.-J.; Wang, H.-S.; Kuo, H.-C.; Chiang, M.-C.; Chan, O.-W.; Lee, E.-P.; Lin, K.-L.; et al. Epileptiform Discharge and Electrographic Seizures during the Hypothermia Phase as Predictors of Rewarming Seizures in Children after Resuscitation. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2151. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9072151
Lin J-J, Hsu M-H, Hsia S-H, Lin Y-J, Wang H-S, Kuo H-C, Chiang M-C, Chan O-W, Lee E-P, Lin K-L, et al. Epileptiform Discharge and Electrographic Seizures during the Hypothermia Phase as Predictors of Rewarming Seizures in Children after Resuscitation. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(7):2151. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9072151
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Jainn-Jim, Mei-Hsin Hsu, Shao-Hsuan Hsia, Ying-Jui Lin, Huei-Shyong Wang, Hsuan-Chang Kuo, Ming-Chou Chiang, Oi-Wa Chan, En-Pei Lee, Kuang-Lin Lin, and et al. 2020. "Epileptiform Discharge and Electrographic Seizures during the Hypothermia Phase as Predictors of Rewarming Seizures in Children after Resuscitation" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 7: 2151. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9072151
APA StyleLin, J.-J., Hsu, M.-H., Hsia, S.-H., Lin, Y.-J., Wang, H.-S., Kuo, H.-C., Chiang, M.-C., Chan, O.-W., Lee, E.-P., Lin, K.-L., & the iCNS Group. (2020). Epileptiform Discharge and Electrographic Seizures during the Hypothermia Phase as Predictors of Rewarming Seizures in Children after Resuscitation. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(7), 2151. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9072151





